A New Encoding Architecture Based on Shift Multilayer Perceptron and Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation
Highlights
- A novel medical image segmentation framework integrating a Shift Multilayer Perceptron and a Transformer encoder is proposed, effectively capturing both low-level and long-range contextual dependencies.
- The incorporation of Senet Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SASPP) and the channel Feature Aggregation Attention Module (FAAM) enhances feature representation, achieving consistent improvements in Dice coefficients (87.01% on ACDC and 79.35% on Synapse) over state-of-the-art baselines.
- The proposed Multilayer Perceptron–Transformer (MPT) framework improves accuracy and generalization in multi-organ medical image segmentation, providing a robust foundation for clinical diagnosis and surgical planning.
- By optimizing feature fusion and mitigating information loss in U-shaped architectures, this work contributes to the evolution of Transformer–MLP hybrid models for efficient and precise medical image analysis.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A new Multilayer Perceptron Transformer framework is proposed to alleviate low-level feature degradation in U-shaped architectures, achieving a more balanced integration of local detail and global context through direction-aware channel shifting;
- (2)
- A novel skip connection and FAAM-based fusion mechanism is introduced to improve cross-scale feature alignment and enhance the representation of complex spatial–channel relationships;
- (3)
- Extensive experiments conducted on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed MPT framework outperforms several state-of-the-art segmentation methods in both accuracy and robustness.
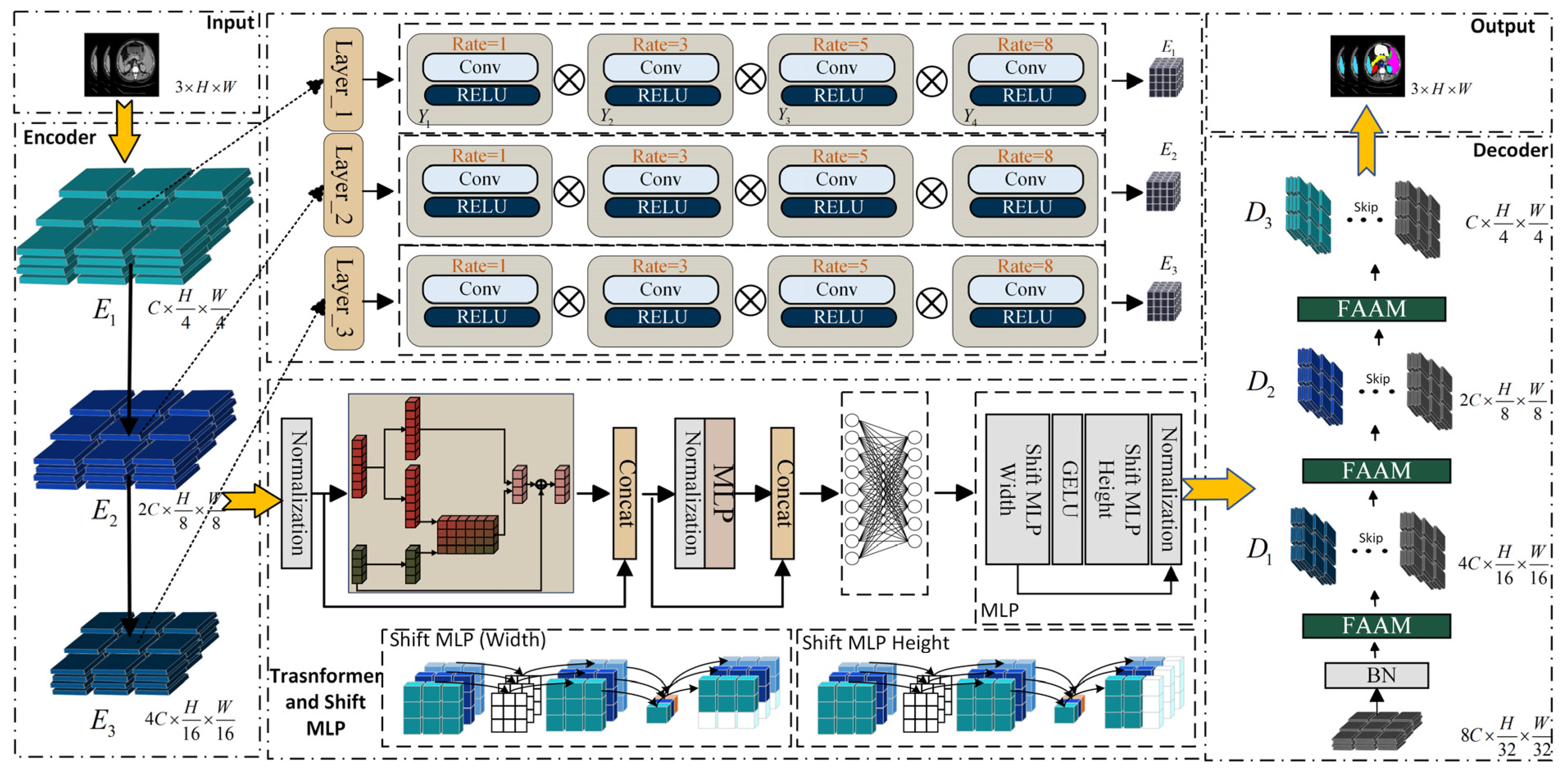
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Senet Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling
| Algorithm 1: Senet Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| encoder layer Output Y |
2.2. Shift Multilayer Perceptron
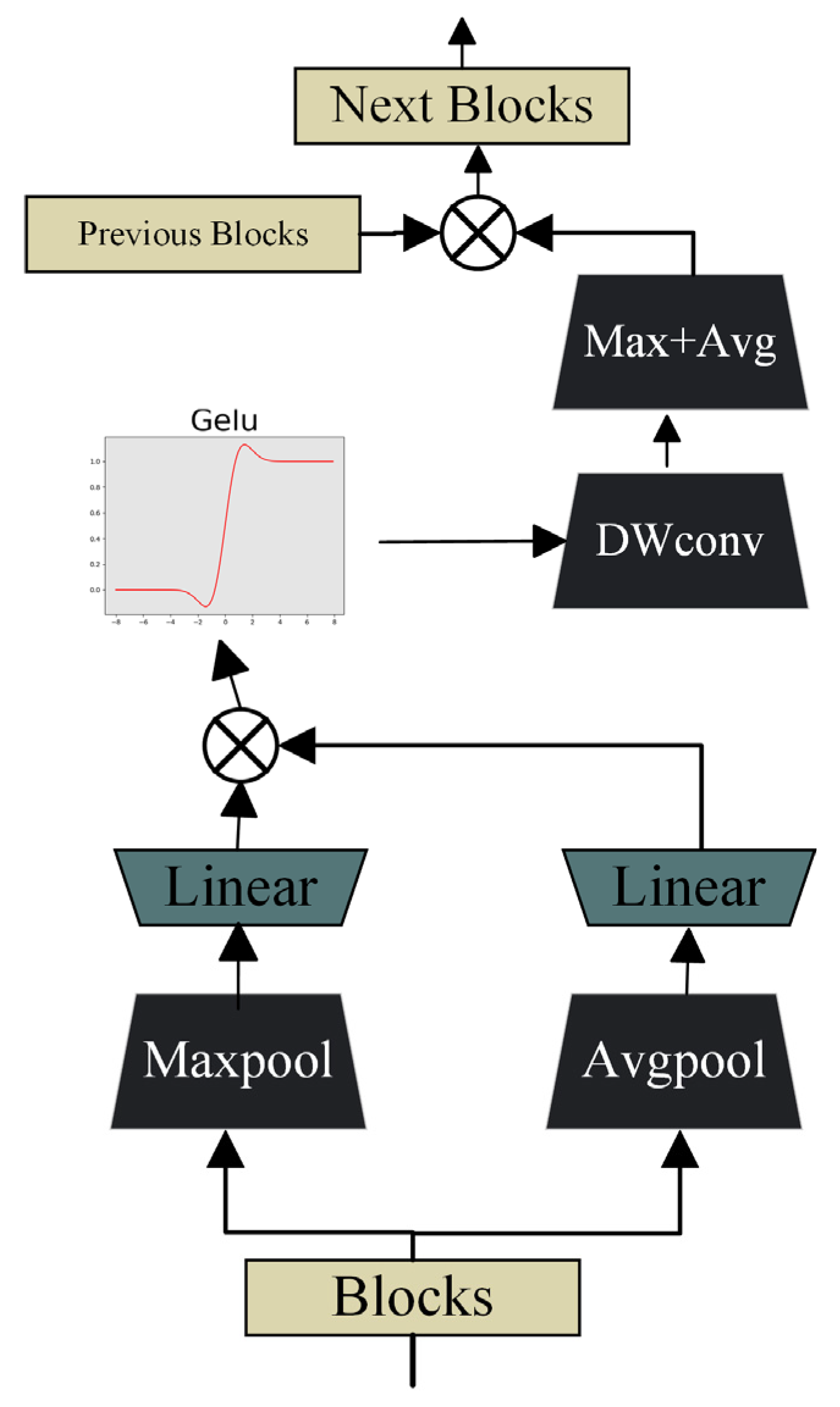
2.3. Feature Aggregation Attention Module (FAAM)
| Algorithm 2: Feature Aggregation Attention Module |
2.4. Spatial and Channel Skip
| Algorithm 3: Spatial and Channel Skip |
3. Results
3.1. Data Introduction
3.2. Evaluation Indicators
- (1)
- Construct a distance matrix for and ;
- (2)
- Calculate the distance from each point to all points in ;
- (3)
- Store these distances in a matrix DA→B;
- (4)
- Similarly, for each point , calculate its distance to all points in and store these distances in a matrix DB→A;
- (5)
- Sort all values from the distance matrices DA→B and DB→A in ascending order;
- (6)
- Find the 95th percentile value and denote it as HD95
3.3. Implementation Details
3.4. Loss Function
3.5. Experimental Results
3.5.1. Comparative Experiments Analysis
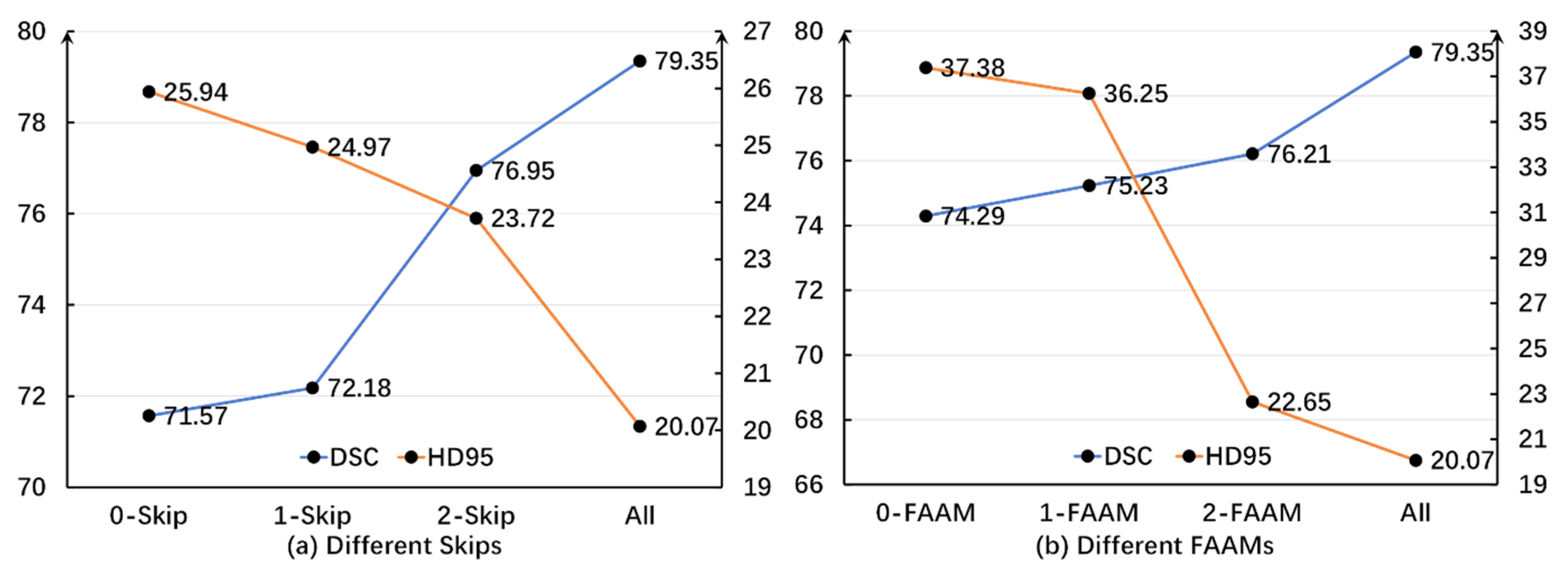
3.5.2. Ablation Experiment Analysis
3.5.3. Statistical Significance Analysis
3.5.4. Experimental Efficiency Analysis
3.5.5. Robustness Analysis Under Imaging Perturbations
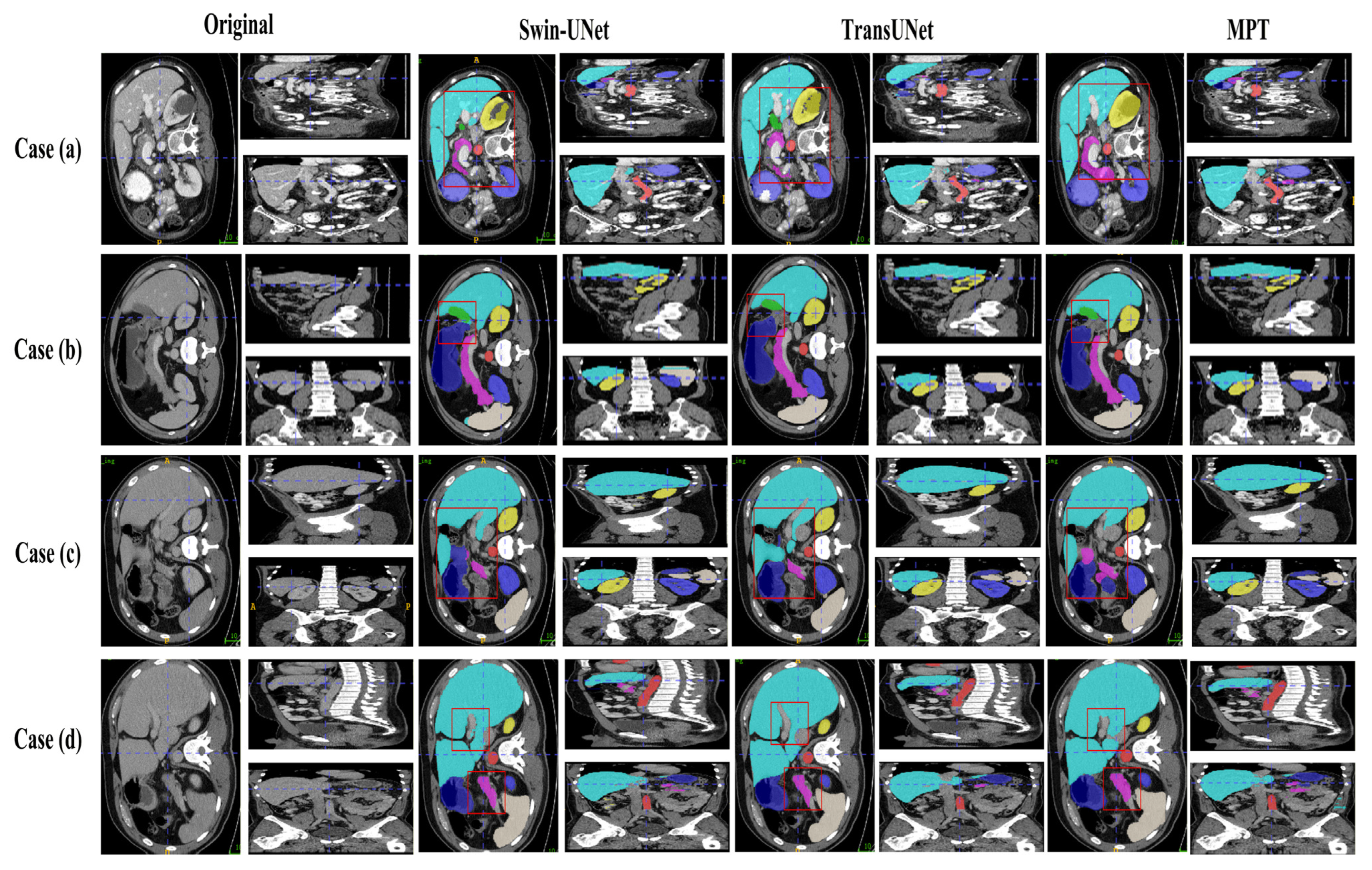
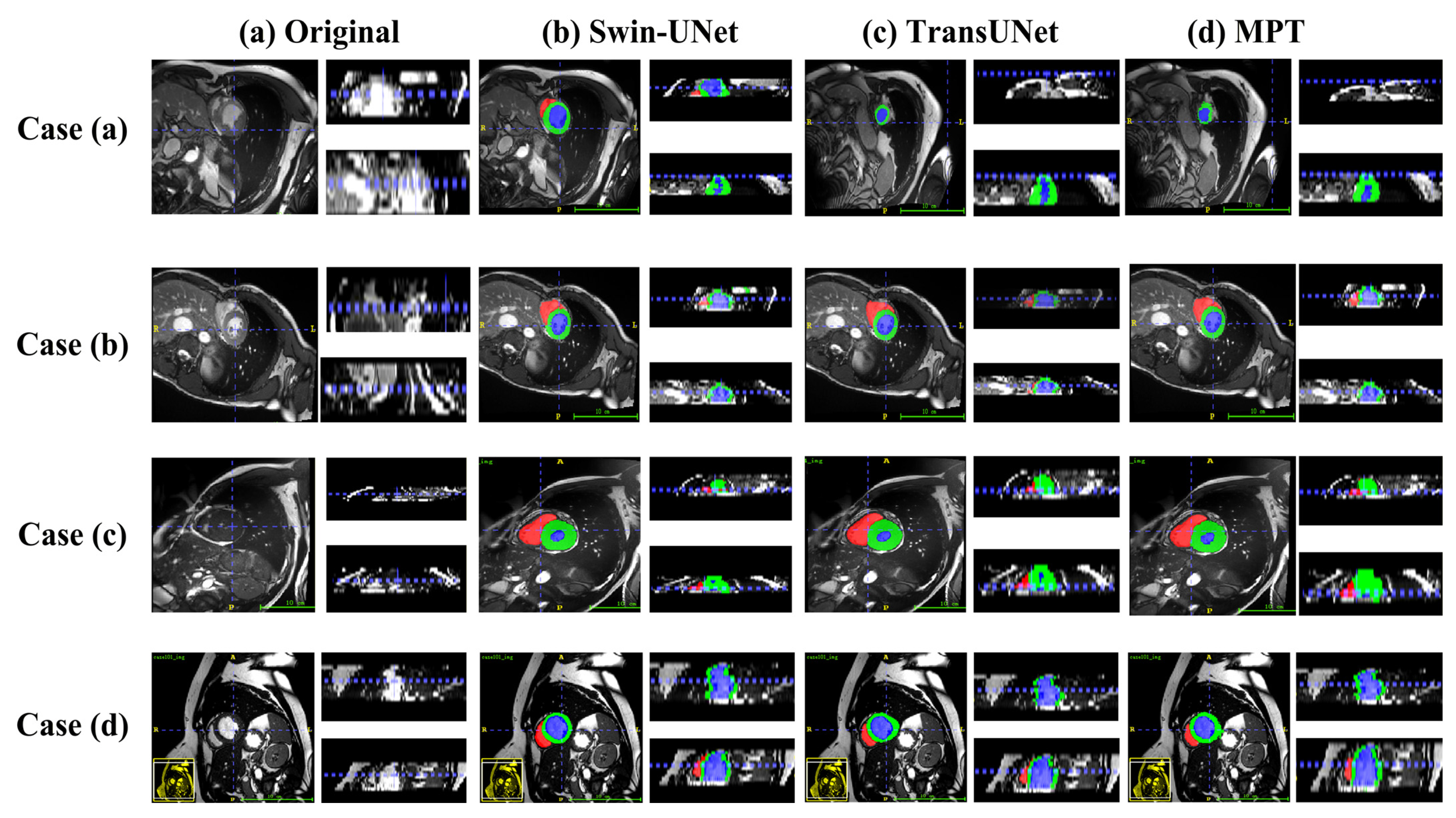
3.6. Visualization of Image Segmentation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPT | Multilayer Perceptron Transformer |
| SASPP | Senet Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| FAAM | Feature Aggregation Attention Module |
| DWConv | Depthwise Convolution |
| DSC | Dice Similarity Coefficient |
| HD95 | 95% Hausdorff Distance |
| ACDC | Automatic Cardiac Diagnostic Challenge (Dataset) |
| CE | Cross Entropy |
| ASPP | Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| DARR | Domain Adaptive Relational Reasoning Network |
| CBAM | Convolutional Block Attention Module |
| DSPNet | Dual-Scale Perception Network |
References
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Ye, Z.; Shang, W.L.; Qiao, S.; Lyu, Z. Label-Conditioned Multi-GAN Fusion: A Robust Data Augmentation Strategy for Medical Image Segmentation. Inf. Fusion 2026, 127, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, W.; Yu, J.; Liang, P.; Kong, D. Mtanet: Multi-Task Attention Network for Automatic Medical Image Segmentation and Classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 43, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, H.; Belaid, A.; Salem, D.B.; Conze, P.H. Cross-Dimensional Transfer Learning in Medical Image Segmentation with Deep Learning. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Tian, S.; Kang, X.; Li, M. CT-Net: Asymmetric Compound Branch Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Neural Netw. 2024, 170, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missaoui, R.; Hechkel, W.; Saadaoui, W.; Helali, A.; Leo, M. Advanced Deep Learning and Machine Learning Techniques for MRI Brain Tumor Analysis: A Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, H.; Geng, S.; Ju, H.; Huang, J.; Fu, F.; Ding, W. F2CAU-Net: A Dual Fuzzy Medical Image Segmentation Cascade Method Based on Fuzzy Feature Learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 184, 113692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Qiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T. SEMI-PLC: A Framework for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Pseudo Label Correction. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 271, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chaddad, A.; Daqqaq, T.; Kateb, R. Enhancing Dual Network Based Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Uncertainty-Guided Pseudo-Labeling. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 330, 114454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, F.; Dong, P.; Li, C. Multiscale TransUNet++: Dense Hybrid U-Net with Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, N.; Isensee, F.; Maier-Hein, K.H.; Hou, X.; Xie, C.; Li, F.; Nan, Y.; Mu, G.; Lin, Z.; Han, M.; et al. The State of the Art in Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation in Contrast-Enhanced CT Imaging: Results of the KiTS19 Challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ren, S.; Guo, K.; Hu, H.; Liang, J. High-Resolution Swin Transformer for Automatic Medical Image Segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Dong, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Jin, Z.; Wang, H. FCT-Net: Efficient Bridge Fusion Incorporating CNN-Transformer Network for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2025, 9, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, D.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Shen, D. Scribformer: Transformer Makes CNN Work Better for Scribble-Based Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 43, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jin, Z.; Guan, C.; Ji, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J. KACNet: Enhancing CNN Feature Representation with Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks for Medical Image Segmentation and Classification. Inf. Sci. 2026, 726, 122760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Z.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, K.; Wu, X. KAC-UNet: A Medical Image Segmentation with the Adaptive Group Strategy and Kolmogorov–Arnold Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 5015413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Du, A.; Orgun, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Yu, Z. Beyond CNNs: Exploiting Further Inherent Symmetries in Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 6776–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Liang, P.; Chang, Q. H-VMUNet: High-Order Vision Mamba U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2025, 624, 129447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention Gated Networks: Learning to Leverage Salient Regions in Medical Images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS Foundation: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, F.; Yuan, R.Y. CSWin-UNet: Transformer UNet with Cross-Shaped Windows for Medical Image Segmentation. Inf. Fusion 2025, 113, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Khan, A. Multi-Axis Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 158, 111251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, W.; Lin, X. EH-Former: Regional Easy-Hard-Aware Transformer for Breast Lesion Segmentation in Ultrasound Images. Inf. Fusion 2024, 109, 102430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yuan, F.; Wang, C. An Effective Multi-Scale Interactive Fusion Network with Hybrid Transformer and CNN for Smoke Image Segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 159, 111177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduvaitov, A.; Buriboev, A.S.; Sultanov, D.; Buriboev, S.; Yusupov, O.; Jasur, K.; Choi, A.J. Enhancing Medical Image Segmentation and Classification Using a Fuzzy-Driven Method. Sensors 2025, 25, 5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiao, L.; Shang, R.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Xu, L. EPT-Net: Edge Perception Transformer for 3D Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 3229–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, X. SSCFormer: Revisiting ConvNet–Transformer Hybrid Framework from Scale-Wise and Spatial–Channel–Aware Perspectives for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 4830–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neha, F.; Bhati, D.; Shukla, D.K.; Dalvi, S.M.; Mantzou, N.; Shubbar, S. U-Net in Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Its Applications Across Modalities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.02242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Byeon, K.; Song, B.; Kim, K.; Kwak, J.T. DIOR-ViT: Differential ordinal learning Vision Transformer for cancer classification in pathology images. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 105, 103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qu, C.; Chen, X.; Bassi, P.R.; Shi, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yu, Q.; Xue, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. AbdomenAtlas: A Large-Scale, Detailed-Annotated, and Multi-Center Dataset for Efficient Transfer Learning and Open Algorithmic Benchmarking. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Abdani, S.R. Spatial Pyramid Pooling with Atrous Convolutional for MobileNet. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Batu Pahat, Malaysia, 27–29 September 2020; pp. 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Ye, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y. Asymmetric Adaptive Heterogeneous Network for Multi-Modality Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, F. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 37, p. 448. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, D.; Yu, Z.; Sun, X.; Gao, S. AS-MLP: An Axial Shifted MLP Architecture for Vision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08391. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xie, E.; Ge, C.; Chen, R.; Liang, D.; Luo, P. CycleMLP: A MLP-like Architecture for Dense Prediction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X. MISFormer: An effective medical image segmentation transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.07162. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z. DME-DeepLabV3+: A Lightweight Model for Diabetic Macular Edema Extraction Based on DeepLabV3+ Architecture. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1150295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Fishman, E.; Yuille, A. Domain Adaptive Relational Reasoning for 3D Multi-Organ Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Yan, S.; Qi, X.; Gao, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X. Few-shot medical image segmentation with high-fidelity prototypes. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 100, 103412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Pan, Y.; Kong, W.; Xu, Z.; Ma, J.; Racharak, T.; Nguyen, L.M.; Xin, J. DA-TransUNet: Integrating spatial and channel dual attention with transformer U-net for medical image segmentation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1398237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Xiang, S. VM-UNet: Vision Mamba UNet for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Z. CTC-Net: A Novel Coupled Feature-Enhanced Transformer and Inverted Convolution Network for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Kitakyushu, Japan, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 273–283. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset | Name | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Train | Synapse | 2212 slices |
| ACDC | 1930 slices | |
| Val | Synapse | 1567 slices |
| ACDC | 551 slices |
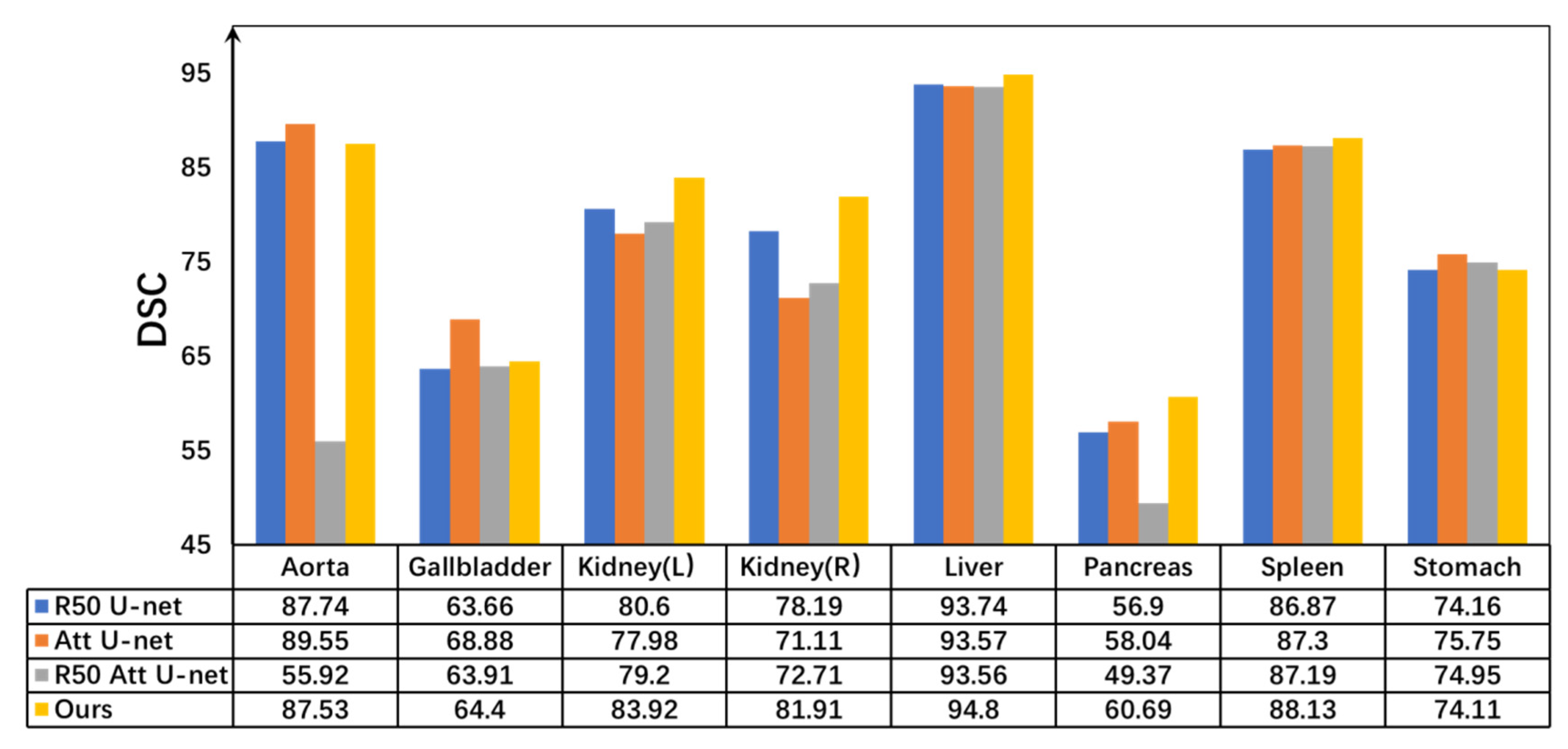
| Methods | Aorta | Gallbladder | Kidney (L) | Kidney (R) | Liver | Pancreas | Spleen | Stomach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-Net [41] | 75.34 | 51.87 | 77.1 | 80.75 | 87.84 | 40.05 | 80.56 | 56.98 |
| U-Net [16] | 87.07 | 68.72 | 77.77 | 68.6 | 93.43 | 53.98 | 86.67 | 75.58 |
| Swin-UNet [24] | 85.47 | 66.53 | 83.28 | 79.61 | 94.29 | 56.58 | 90.66 | 76.6 |
| Deeplabv3+ [42] | 88.04 | 66.51 | 82.76 | 74.21 | 91.23 | 58.32 | 87.43 | 73.53 |
| DARR [43] | 74.74 | 53.77 | 72.31 | 73.24 | 94.08 | 54.18 | 89.90 | 45.96 |
| TransUNet [9] | 87.23 | 63.13 | 81.87 | 77.02 | 94.08 | 55.86 | 85.08 | 75.62 |
| DSPNet [44] | 87.78 | 62.22 | 78.01 | 74.54 | 69.32 | 57.76 | 69.31 | 72.06 |
| DA-TransUNet [45] | 86.54 | 65.2 | 81.70 | 80.45 | 94.5 | 61.62 | 88.53 | 79.73 |
| VM-UNet [46] | 86.40 | 69.4 | 86.16 | 82.76 | 94.1 | 58.80 | 89.51 | 81.40 |
| CTC-Net [47] | 86.46 | 63.53 | 83.71 | 80.79 | 93.7 | 59.73 | 86.87 | 72.39 |
| The proposed | 87.53 | 64.4 | 83.92 | 81.19 | 94.8 | 60.69 | 88.13 | 74.11 |
| Methods | V-Net [41] | U-Net [16] | Swin-UNet [24] | Deeplabv3+ [42] | DARR [43] | TransUNet [9] | The Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | 68.81 | 69.77 | 79.13 | 77.63 | 69.77 | 77.48 | 79.35 |
| HD95 | 36.5 | 39.7 | 21.55 | 39.95 | 23.4 | 31.69 | 20.07 |
| Recall | 64.87 | 73.46 | 77.72 | 91.22 | 86.24 | 76.64 | 94.85 |
| Precision | 79.29 | 82.83 | 93.20 | 91.02 | 95.87 | 85.39 | 96.13 |
| Sensitivity | 75.12 | 75.44 | 87.32 | 8641 | 91.33 | 77.01 | 89.63 |
| Specificity | 93.39 | 94.28 | 94.48 | 95.66 | 96.05 | 95.90 | 96.64 |
| IOU | 74.42 | 66.09 | 68.15 | 63.66 | 81.13 | 77.49 | 73.49 |
| Methods | Average | Aorta | Gallbladder | Kidney (L) | Kidney (R) | Liver | Pancreas | Spleen | Stomach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (TransUNet) | 77.48 | 87.23 | 63.13 | 81.87 | 77.02 | 94.08 | 55.86 | 85.08 | 75.62 |
| +Shift-MLP | 75.60 | 85.73 | 62.07 | 80.88 | 74.03 | 93.34 | 53.13 | 83.52 | 72.10 |
| +FAAM | 77.14 | 87.33 | 63.95 | 78.30 | 73.63 | 93.83 | 61.15 | 87.70 | 70.86 |
| +Spatial–Channel Skip | 68.87 | 74.98 | 40.52 | 69.25 | 66.40 | 92.90 | 51.95 | 83.35 | 71.63 |
| +SASPP | 78.41 | 87.92 | 63.20 | 78.62 | 76.25 | 94.02 | 64.16 | 89.94 | 73.14 |
| +CBAM (instead of FAAM) | 76.23 | 83.44 | 60.12 | 75.79 | 74.98 | 91.33 | 61.74 | 88.71 | 70.49 |
| +ASPP (instead of SASPP) | 77.15 | 85.33 | 61.45 | 77.22 | 75.08 | 92.11 | 63.02 | 88.47 | 72.03 |
| +FAAM + Skip | 77.14 | 86.23 | 62.07 | 80.88 | 74.03 | 93.38 | 53.13 | 83.52 | 72.10 |
| +SASPP + Skip | 74.29 | 87.28 | 60.47 | 75.52 | 74.60 | 93.00 | 52.57 | 83.40 | 67.53 |
| +SASPP + FAAM | 75.90 | 85.73 | 62.06 | 80.87 | 72.12 | 93.21 | 57.79 | 83.32 | 72.10 |
| Proposed MPT | 79.35 | 87.53 | 64.40 | 83.92 | 81.19 | 94.80 | 60.69 | 88.13 | 74.11 |
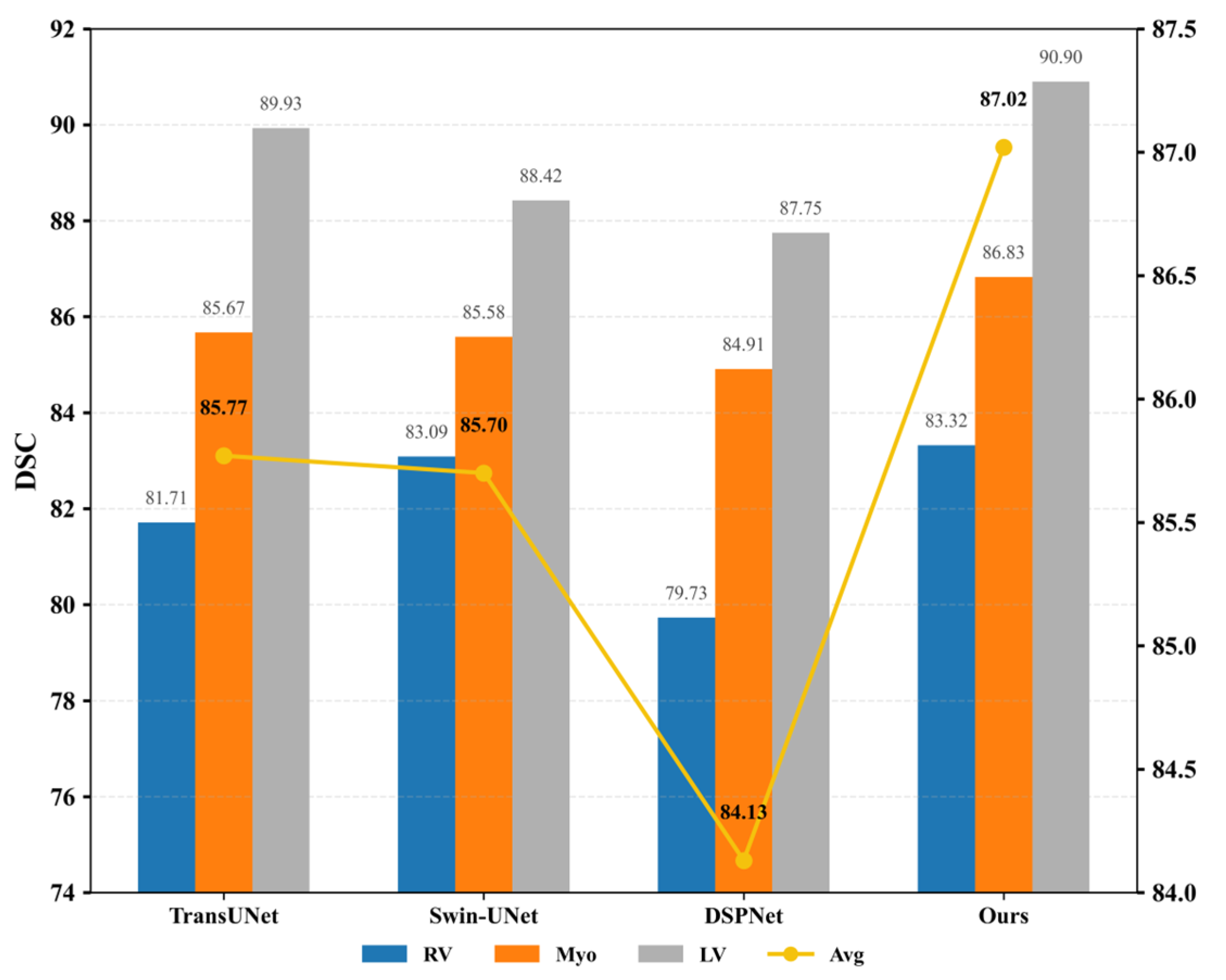
| Methods | Average | RV | MYO | LV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 85.77 | 81.71 | 85.67 | 89.93 |
| +Shift-MLP | 85.85 | 81.5 | 85.51 | 90.55 |
| +Shift-MLP + Skip | 85.97 | 81.64 | 86.03 | 90.24 |
| +Shift-MLP + Skip + FAAM | 86.27 | 82.2 | 86.28 | 90.34 |
| +Shift-MLP + Skip + SASPP | 86.47 | 83.08 | 86.12 | 90.21 |
| Proposed MPT | 87.01 | 83.32 | 86.83 | 90.90 |
| Dataset | Compared Method | Baseline Mean ± SD | MPT (Ours) Mean ± SD | t | p | 95% CI (Mean Diff.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synapse | V-Net | 76.8 ± 0.7 | 78.8 ± 0.5 | 3.01 | 0.016 | [+0.42, +3.68] |
| DARR | 77.7 ± 0.8 | 78.8 ± 0.5 | 2.02 | 0.078 | [−0.18, +2.18] | |
| TransUNet | 78.2 ± 0.6 | 78.8 ± 0.5 | 1.46 | 0.183 | [−0.33, +1.47] | |
| DSPNet | 78.1 ± 0.8 | 78.8 ± 0.5 | 1.38 | 0.205 | [−0.38, +1.68] | |
| ACDC | U-Net | 84.6 ± 0.8 | 86.5 ± 0.6 | 2.87 | 0.020 | [+0.32, +3.28] |
| Attention-UNet | 85.4 ± 0.7 | 86.5 ± 0.6 | 2.06 | 0.073 | [−0.15, +2.25] | |
| Swin-UNet | 86.1 ± 0.6 | 86.5 ± 0.6 | 1.22 | 0.256 | [−0.44, +1.24] | |
| TransUNet | 85.9 ± 0.7 | 86.5 ± 0.6 | 1.46 | 0.181 | [−0.34, +1.54] |
| Model | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) (per 512 × 512 Slice) | Inference Time (ms/Slice) (FP32/AMP) | Peak VRAM (GB) (FP32/AMP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TransUNet | 105.2 | ≈680 | 290/230 | 7.4/4.6 |
| Swin-UNet | 62.1 | ≈500 | 230/185 | 6.3/4.1 |
| MPT (ours) | 51.0 | ≈325 | 200/160 | 5.2/3.6 |
| Perturbation Type | Perturbation Level | Dice (%) | HD95 (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | – | 79.35 | 20.07 |
| Gaussian Noise | σ = 0.01 | 78.87 | 20.56 |
| Gaussian Noise | σ = 0.03 | 78.05 | 21.22 |
| Gaussian Noise | σ = 0.05 | 77.01 | 22.41 |
| Spacing Perturbation | ±5% | 78.63 | 20.84 |
| Spacing Perturbation | ±10% | 78.02 | 21.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhong, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yi, J. A New Encoding Architecture Based on Shift Multilayer Perceptron and Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Sensors 2026, 26, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26020449
Zhong H, Yang J, Wu Y, Yi J. A New Encoding Architecture Based on Shift Multilayer Perceptron and Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Sensors. 2026; 26(2):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26020449
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Hepeng, Jieqiong Yang, Yingfei Wu, and Jizheng Yi. 2026. "A New Encoding Architecture Based on Shift Multilayer Perceptron and Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation" Sensors 26, no. 2: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26020449
APA StyleZhong, H., Yang, J., Wu, Y., & Yi, J. (2026). A New Encoding Architecture Based on Shift Multilayer Perceptron and Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Sensors, 26(2), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/s26020449






