A Review of High-Sensitivity SERS-Active Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensors for Chemical and Biological Detection
Abstract
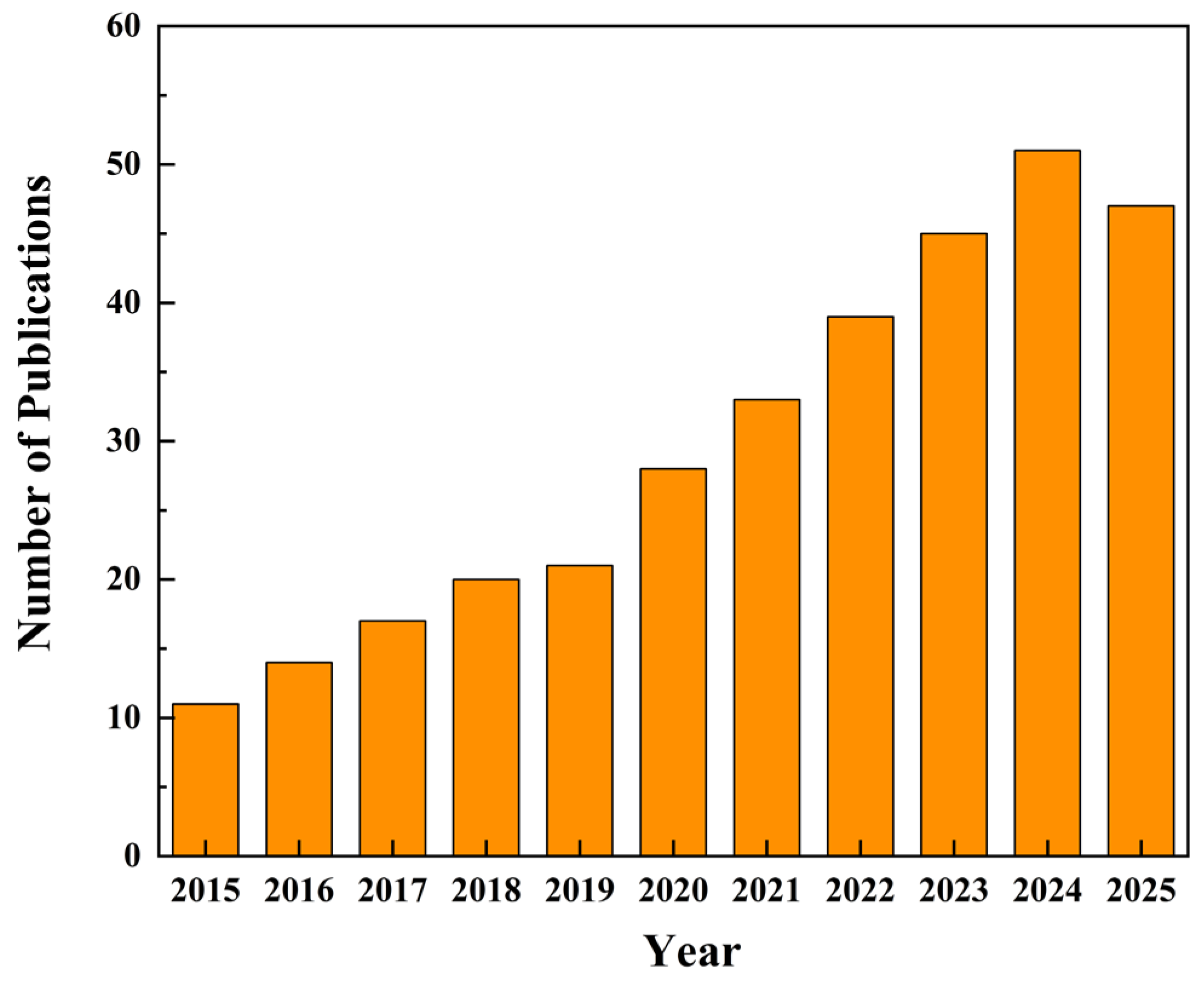
1. Introduction
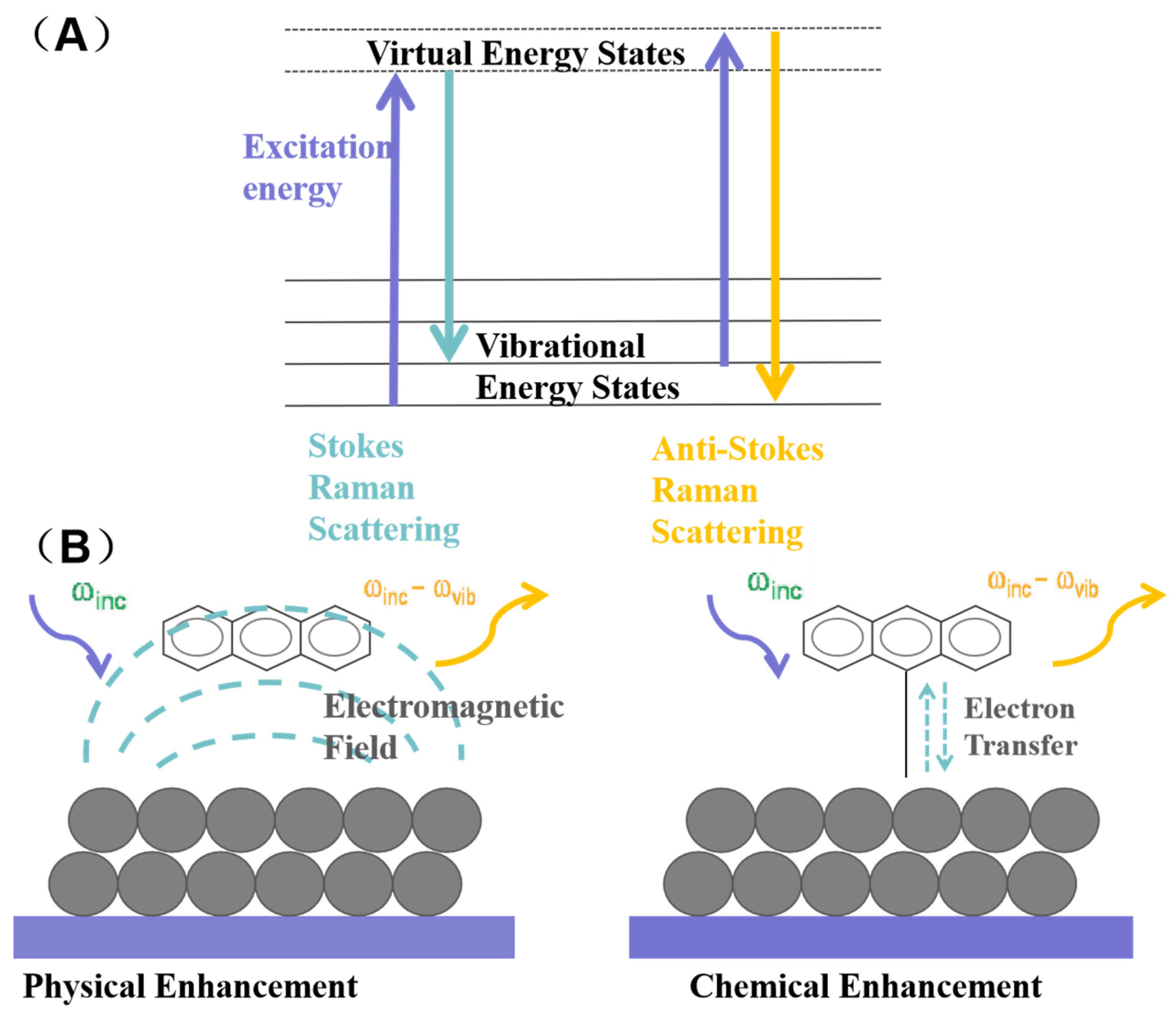
2. SERS Overview
3. Types and Principles of PCF-SERS Sensors
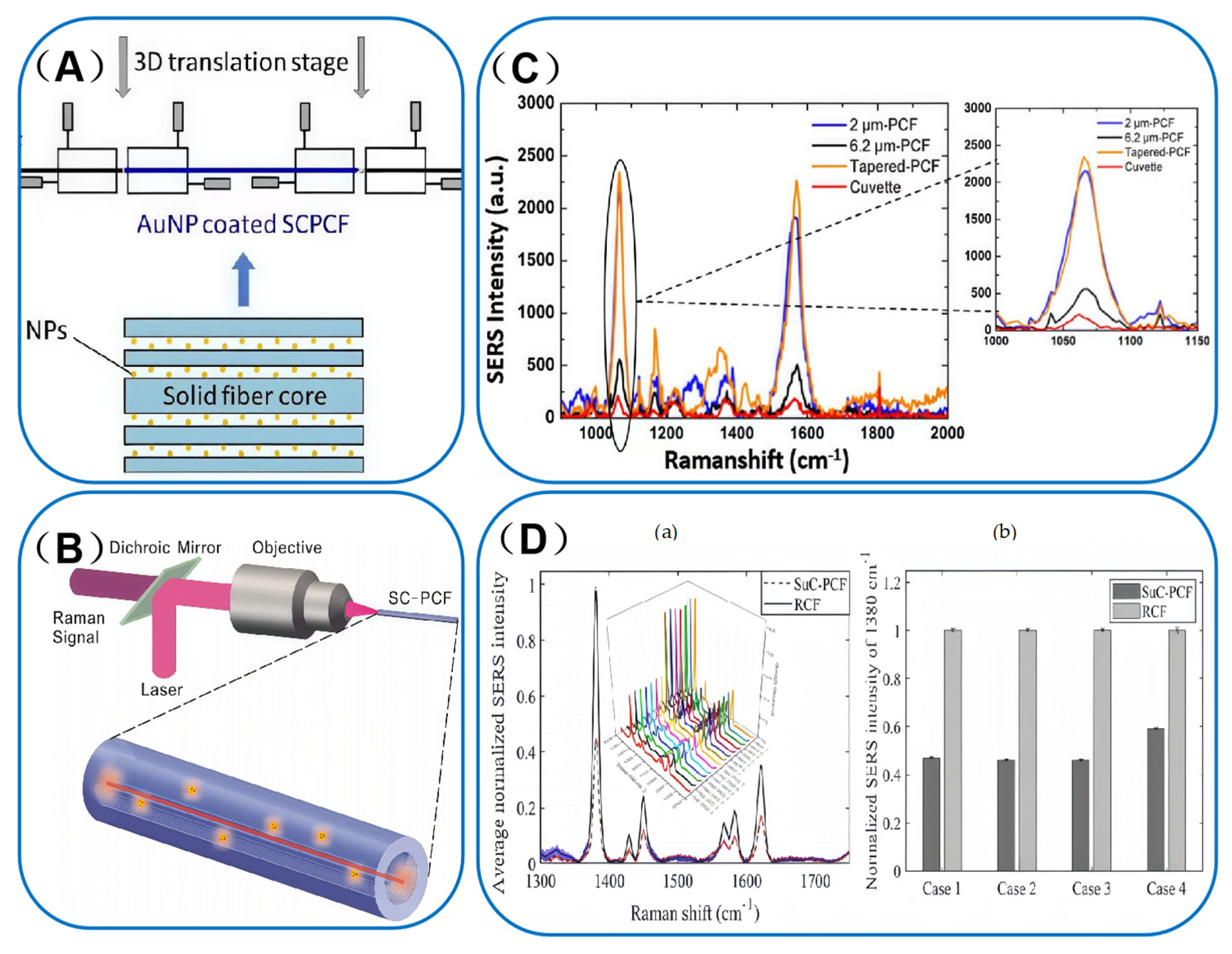
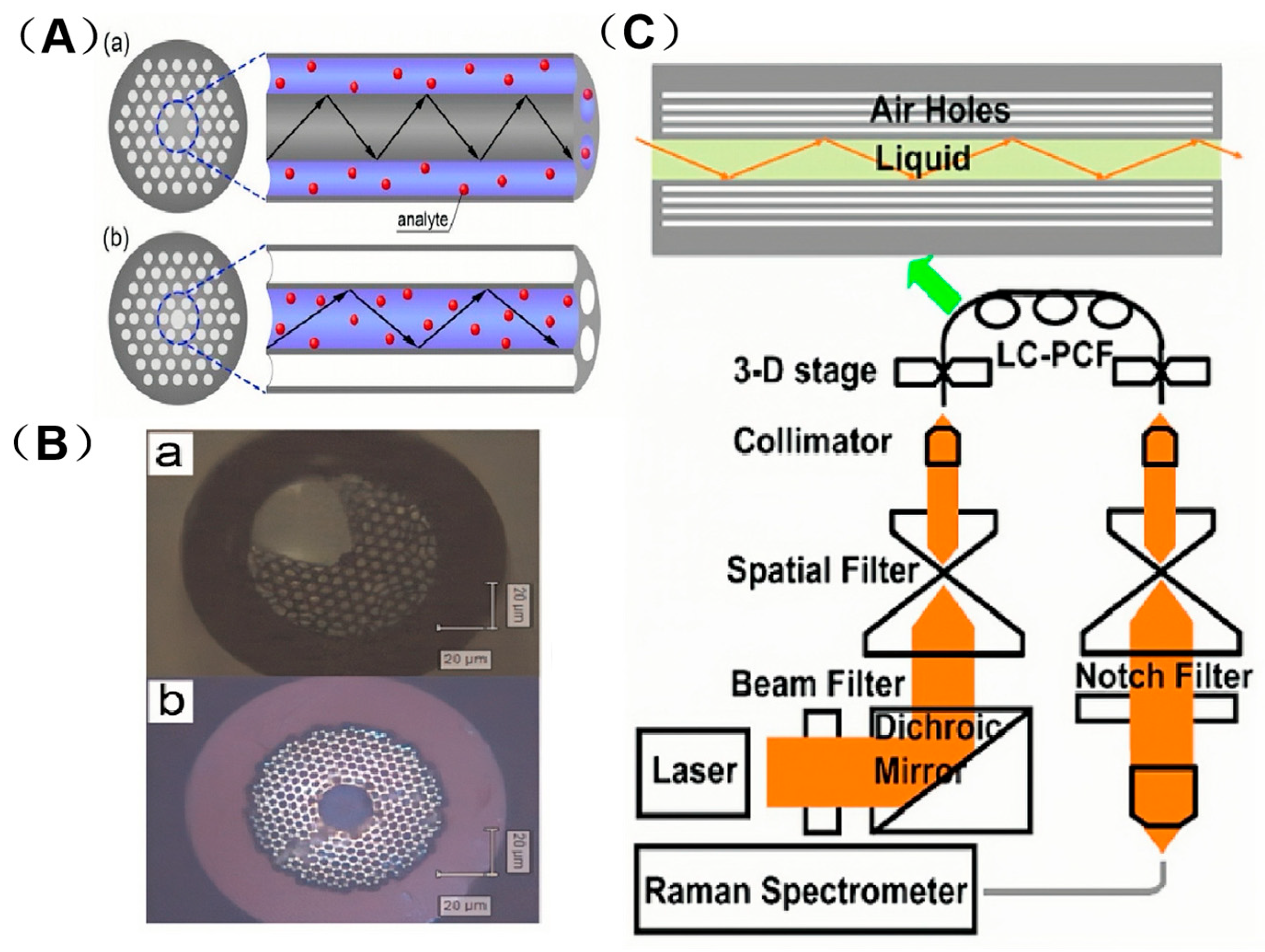
3.1. Solid-Core Photonic Crystal Fibers (SC-PCF)
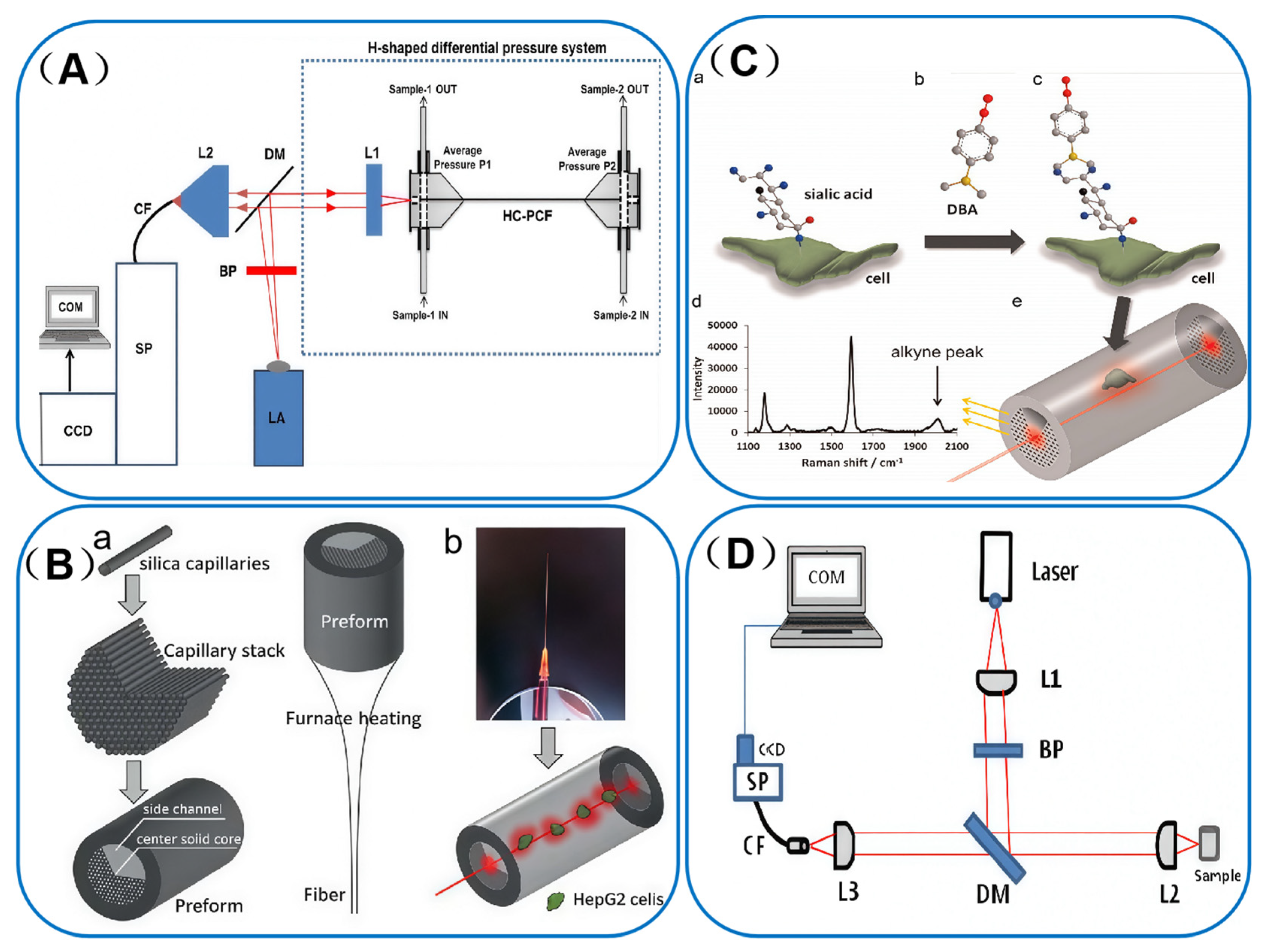
3.2. Hollow-Core Photonic Crystal Fibers (HC-PCF)
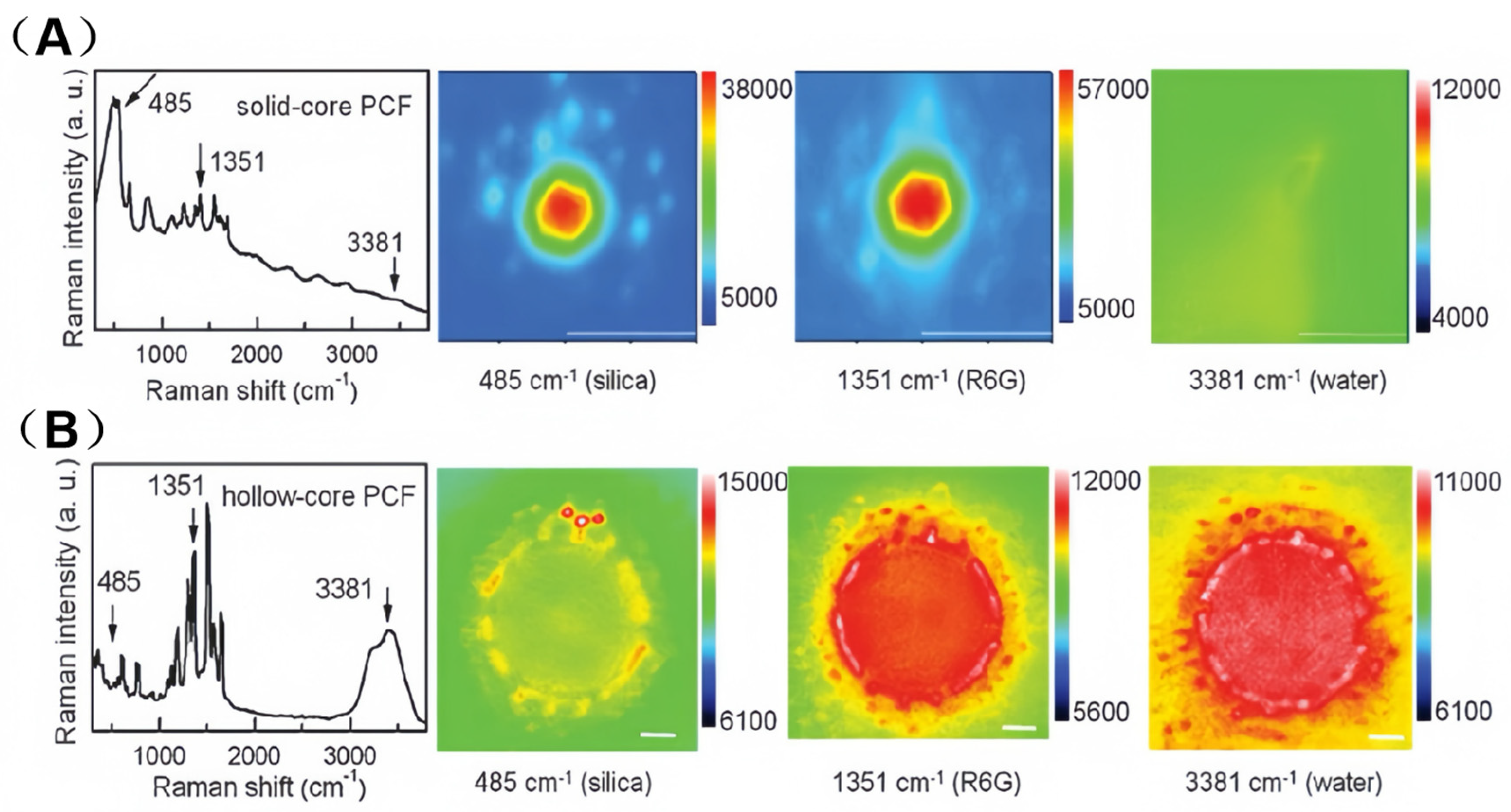
3.3. Comparison of SERS Signal Distribution Between SC-PCF and HC-PCF
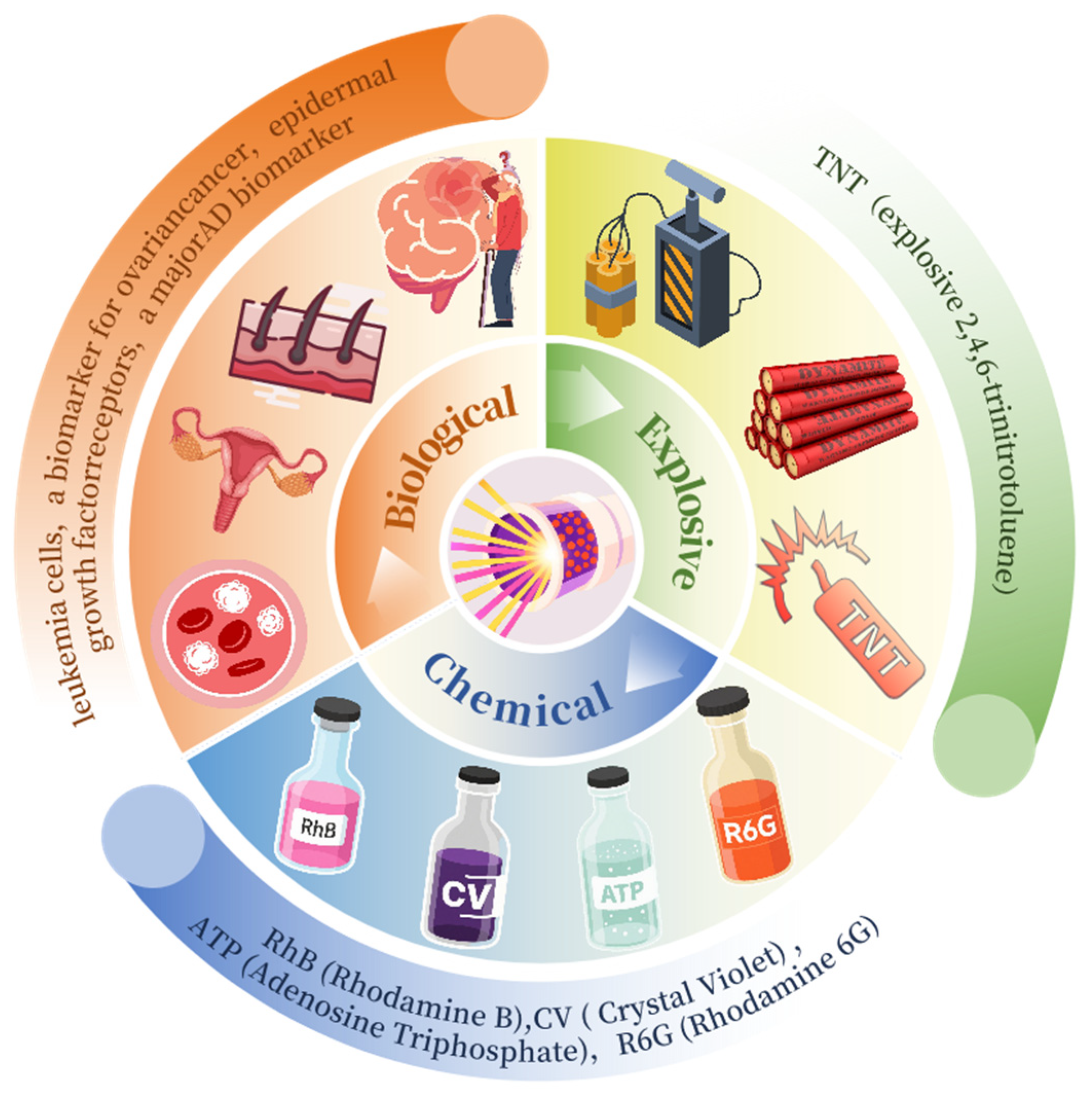
4. Application of PCF-SERS Sensors
4.1. Detection of Chemical Substances
4.2. Detection of Biomedicine
4.2.1. Disease Biomarkers
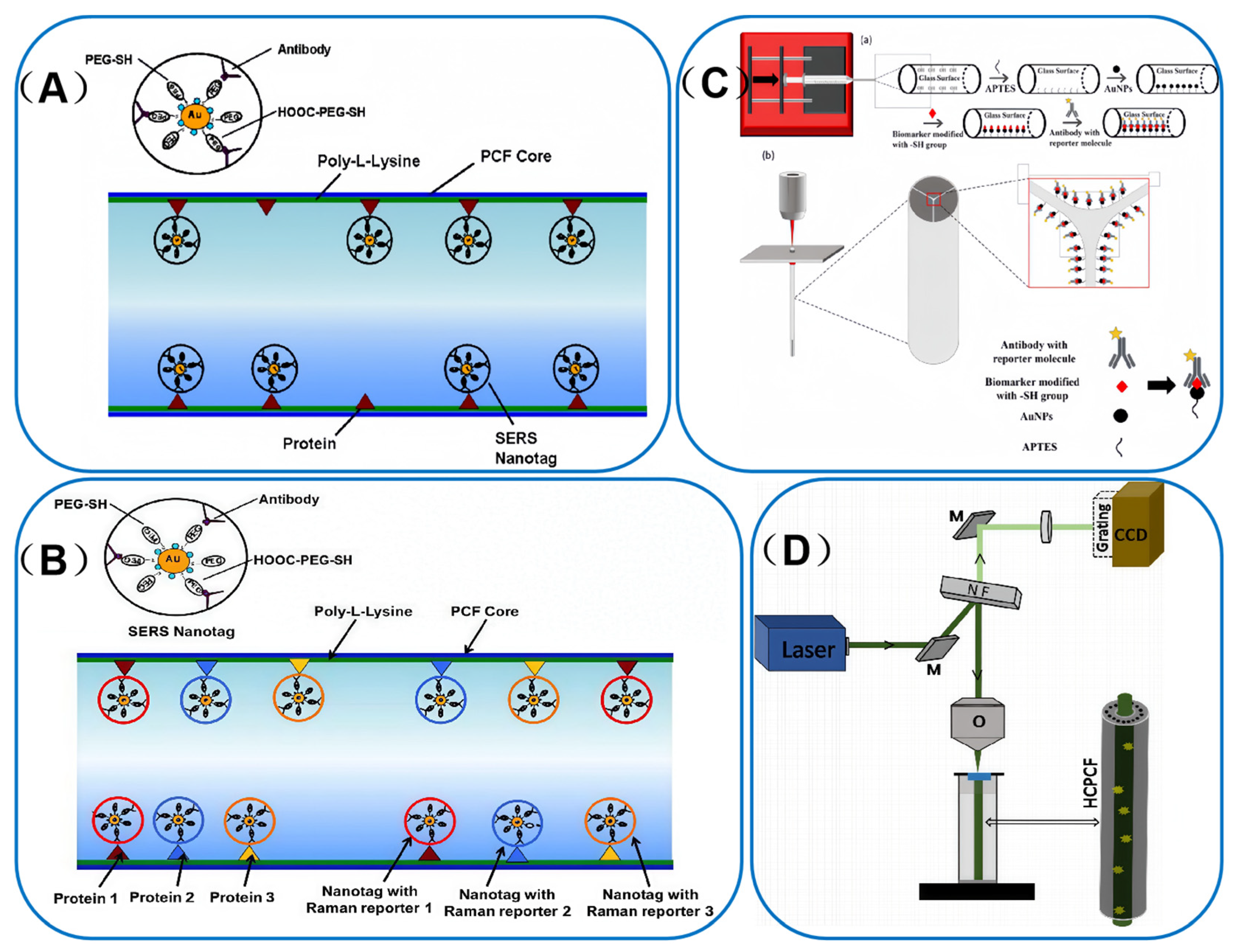
4.2.2. Cellular Correlation
| Analytes | Type of Optical Fiber | SERS Active Nanomaterials | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| epidermal growth factor receptors in a lysate solution from human epithelial carcinoma cells | Hollow core PCF | AuNP-MGITC-antibody | 100 pg/mL | [68] |
| hepatocellular carcinoma biomarkers-alpha fetoprotein and alpha-1-antitrypsin | Hollow core PCF | AuNP-Cy5 or AuNP-MGTIC antibody | N.A. | [69] |
| haptoglobin, a biomarker for ovarian cancer | Suspended core PCF | AuNPs | N.A. | [70] |
| amyloid β (1–42) peptide (Aβ42), a major AD biomarker | Hollow core PCF | AuBPs | 40 μg/mL | [71] |
| acute myeloid leukemia cells | Hollow core PCF | AgNPs | 300 cells/mL | [79] |
| lipid-peroxidation-derived protein modifications in cells | Side channel PCF | AuNPs | 0.7 µg/mL | [80] |
| sialic acid on single cell | Side channel PCF | AuNPs | 2.5 fM | [40] |
| amino acid neurotransmitters | Hollow core PCF | AuNPs | 10−4 M | [81] |
4.2.3. Antibiotics
4.3. Detection of Explosives
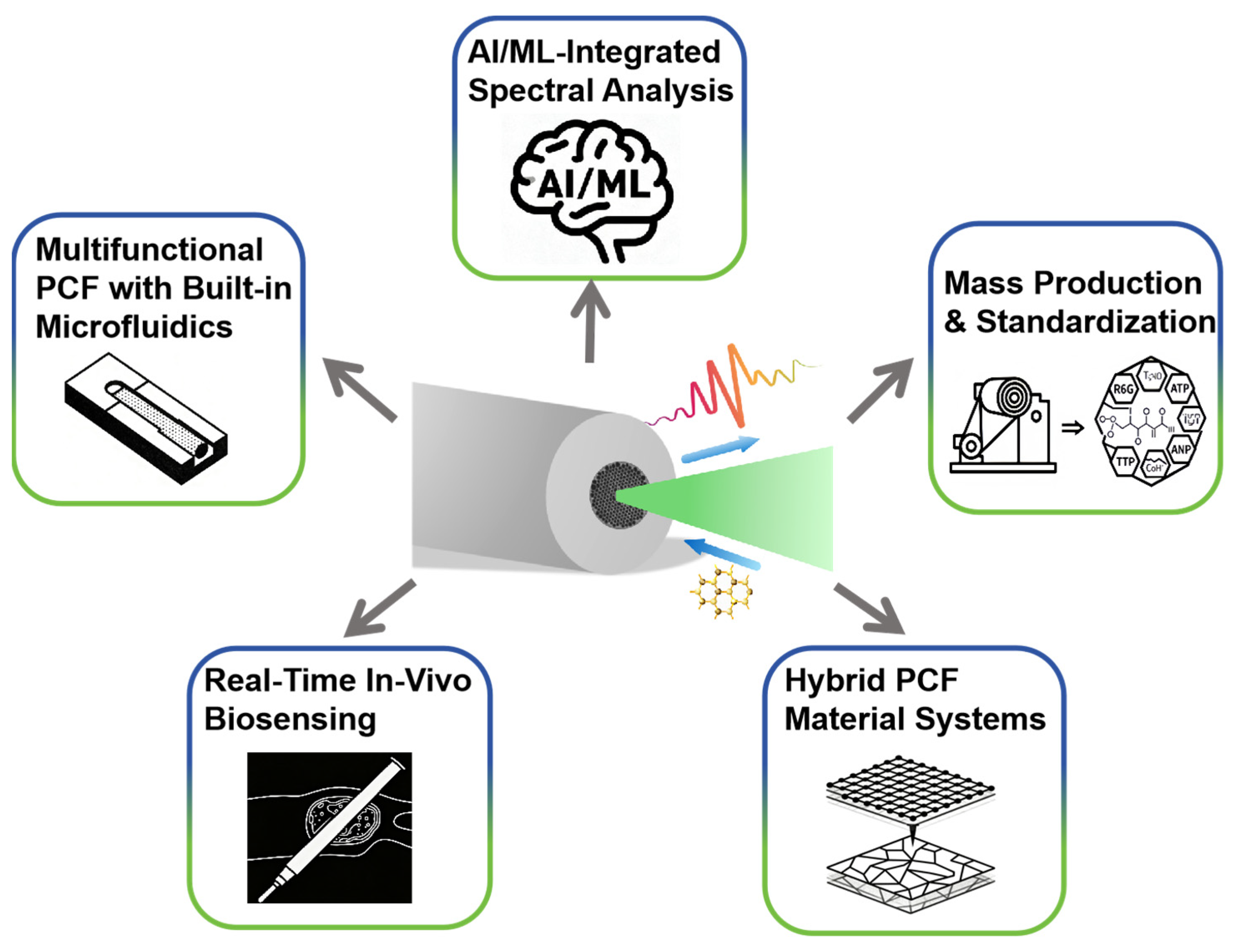
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
- 1.
- Precision structures
- 2.
- AI-driven multifunctional systems
- 3.
- Scalable manufacturing and field deployment
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langer, J.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguie, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.J.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G.; et al. Present and Future of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlücker, S. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Concepts and Chemical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4756–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Schluecker, S. Convergence of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering with Molecular Diagnostics: A Perspective on Future Directions. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 5998–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmaire, D.L.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1977, 84, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Etchegoin, P.G.; Meyer, M. Enhancement factor distribution around a single surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spot and its relation to single molecule detection. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 204701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Aizpurua, J.; Kall, M.; Apell, P. Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced raman scattering. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, T.K.; Murphy, C.J. Self-assembly patterns formed upon solvent evaporation of aqueous cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-coated gold nanoparticles of various shapes. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2005, 21, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Claire, G.; Fang, Q.; Yat, L.; Zhang, Z.J. Highly sensitive detection of proteins and bacteria in aqueous solution using surface-enhanced Raman scattering and optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5888–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y.J.; Hur, W.; Kang, H.M.; Jun, B.-H. In vivo surface-enhanced Raman scattering techniques: Nanoprobes, instrumentation, and applications. Light-Sci. Appl. 2025, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.N.; Du, J.J.; Shi, J.B. Research Progress in the Detection of Environmental Pollutants by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Bull. 2024, 87, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, K.; Majhi, S.; Tripathi, C.S.P.; Guin, D. Facile synthesis of Ag NPs@MgO nanosheets for quantitative SERS-based detection and removal of hazardous organic pollutants. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 323, 124885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Huang, L.; Shuai, Q.; Ouyang, L. Urchin-like covalent organic frameworks templated Au@Ag composites for SERS detection of emerging contaminants. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 8840–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, P.; Gao, D.; Yang, X.; Luo, M.; Kong, D.; Gao, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Yuan, L.; et al. In situ SERS detection of quinolone antibiotic residues in a water environment based on optofluidic in-fiber integrated Ag nanoparticles. Appl. Optics 2021, 60, 6659–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Jiang, Y.N.; Cao, J.Y.; Zheng, Q.T.; Wu, Y.P.; Guo, X.Y.; Ying, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H.F. Applications and Prospects of Metal-Organic Frameworks/Nanozyme Composite SERS Substrates in the Field of Biomedical Analysis. J. Light Scatt. 2024, 36, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lulu, L.; Wenrui, M.; Xiang, W.; Shunbo, L. Recent Progress of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Bacteria Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Yang, S.; Cheng, L.; QiaoYan, J.; Feng, C.; Yue, C. SERS-Based Biosensors Combined with Machine Learning for Medical Application. ChemistryOpen 2023, 12, e202200192. [Google Scholar]
- Khetani, A.; Riordon, J.; Tiwari, V.; Momenpour, A.; Godin, M.; Anis, H. Hollow core photonic crystal fiber as a reusable Raman biosensor. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 12340–12350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenlei, Z.; Tianyan, Y.; Xihui, O.; Meng, W. Recent progress in mycotoxins detection based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1887–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Fingerprinting and tagging detection of mycotoxins in agri-food products by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Principles and recent applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, H.M.; Muhammad, Z.; Yi, X.; Huanhuan, L.; Quansheng, C. SERS based sensor for mycotoxins detection: Challenges and improvements. Food Chem. 2020, 344, 128652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Surface enhanced Raman scattering effects of silver colloids with different shapes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12544–12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cialla-May, D.; Bonifacio, A.; Markin, A.; Markina, N.; Fornasaro, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Dib, T.; Farnesi, E.; Liu, C.; Ghosh, A.; et al. Recent advances of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) in optical biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 181, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Niu, M.H.; Lin, W.H.; Xue, C.L.; Hu, J.Q.; Lv, J.Q.; Hu, J.; Shao, L.Y.; Wang, G.H.; et al. Advances in Fiber Optic Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensors. ACS Photonics 2025, 12, 5312–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.K.; Pathak, A.K.; Chiavaioli, F.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Kamil, Y.M.; Mahdi, M.A.; Singh, V.K. Optical fiber SERS sensors: Unveiling advances, challenges, and applications in a miniaturized technology. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 510, 215861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.T.C.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, H.J.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, C.M.; Thotagamuge, R.; Mahadi, A.H.; Chau, Y.F.C. Improving Temperature-Sensing Performance of Photonic Crystal Fiber via External Metal-Coated Trapezoidal-Shaped Surface. Crystals 2023, 13, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzapulo, X.; Kassenova, A.; Bukasov, R. Immunoassays: Analytical and Clinical Performance, Challenges, and Perspectives of SERS Detection in Comparison with Fluorescent Spectroscopic Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P.J.; McQuillan, A.J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, J.; Wittig, B.; Bohr, H.; Kneipp, K. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: A new optical probe in molecular biophysics and biomedicine. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2010, 125, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Brolo, A.G. A review on recent advances in the applications of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1097, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huo, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Yang, H. Design and Synthesis of SERS Materials for In Vivo Molecular Imaging and Biosensing. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2202051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilot, R.; Signorini, R.; Durante, C.; Orian, L.; Bhamidipati, M.; Fabris, L. A Review on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Biosensors 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Enhancement Factors: A Comprehensive Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Chu, C.; Teng, P.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X. Review of Optical Fiber Optofluidic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. Photonic Sens. 2025, 15, 250134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongde, M. Preparation and Application of Surface-Enhanced Raman Substrates Based on Photonic Crystals. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, R.; Takei, K.; Hong, M. Toward Flexible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.E.J.; Charron, G.; Cortes, E.; Kneipp, J.; de la Chapelle, M.L.; Langer, J.; Prochazka, M.; Tran, V.; Schluecker, S. Towards Reliable and Quantitative Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS): From Key Parameters to Good Analytical Practice. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5454–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Experimental Research on Surface-Enhanced Raman Probes Based on Photonic Crystal Fibers. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dinish, U.S.; Flavien, B.; Georges, H.; Louis, A.J.; Malini, O. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active photonic crystal fiber probe: Towards next generation liquid biopsy sensor with ultra high sensitivity. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tan, S.; Oo, M.K.K.; Pristinski, D.; Sukhishvili, S.; Du, H. Towards Full-Length Accumulative Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Active Photonic Crystal Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2647–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.X.; Cui, Y.; Goh, D.; Voon, K.K.; Shum, P.P.; Humbert, G.; Auguste, J.L.; Dinh, X.Q.; Yong, K.T.; Olivo, M. Highly sensitive SERS detection and quantification of sialic acid on single cell using photonic-crystal fiber with gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beffara, F.; Humbert, G.; Auguste, J.L.; Olivo, M.; Dinish, U.S. Innovative suspended ring core fiber for SERS application. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 18216–18223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazza, A.; Beffara, F.; Auguste, J.L.; Olivo, M.; Dinish, U.S.; Humbert, G. Reliable and easy-to-use SERS spectroscopy probe using a tapered opto-fluidic photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issatayeva, A.; Mariyam, S.; Kho, K.W.; Andersson-Engels, S.; Cucinotta, A. Suspended-core photonic crystal fibers for SERS detection of biomolecules. J. Opt. 2025, 27, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Oo, M.K.K.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Demohan, M.S.; Jin, W.; Du, H. Index-guiding liquid-core photonic crystal fiber for solution measurement using normal and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Opt. Eng. 2008, 47, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yong, D.; Yu, X.; Xia, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y. Amplification of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in Photonic Crystal Fiber Using Offset Launch Method. Plasmonics 2013, 8, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Claire, G.; Changxi, Y.; Jie, L.; Guofan, J.; Jiatao, Z.; Lantian, H.; Yuan, Y. Hollow core photonic crystal fiber surface enhanced Raman probe. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 6433, 204101. [Google Scholar]
- Fatemeh, E.; Anna, L.; Eugenia, K.; Helmy, A.S. Examining metal nanoparticle surface chemistry using hollow-core, photonic-crystal, fiber-assisted SERS. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 680–682. [Google Scholar]
- Chuanyi, T.; Rong, C.; Jingke, L. Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensor Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering for Explosives Detection. In Advanced Sensor Systems and Applications VII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 10025, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.V.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. A high sensitive fiber SERS probe based on silver nanorod arrays. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12230–12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucotti, A.; Zerbi, G. Fiber-optic SERS sensor with optimized geometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 121, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yan, H.; Gu, C.; Ghosh, D.; Seballos, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Chen, B. A double substrate sandwich structure for fiber surface enhanced Raman scattering detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 103107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, M. Graphene-based SERS for sensor and catalysis. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2023, 58, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Chen, B. Innovative cellulose-lactone hybrid material for efficient rhodamine 6G dye adsorption: Synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Chao, S.; Damon, W.; Rebecca, N.; Bin, C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Claire, G. High-sensitivity molecular sensing using hollow-core photonic crystal fiber and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2010, 27, 977–984. [Google Scholar]
- Kyaw, K.O.M.; Yun, H.; Jiri, K.; Svetlana, S.; Henry, D. Structure fits the purpose: Photonic crystal fibers for evanescent-field surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Humbert, G.; Gong, T.; Shum, P.P.; Li, K.; Auguste, J.-L.; Wu, Z.; Hu, D.J.J.; Luan, F.; Dinh, Q.X.; et al. Side-channel photonic crystal fiber for surface enhanced Raman scattering sensing. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2016, 223, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhoutao, S. Rapid SERS Detection of Microfluidic Based on Suspended Core Fibers. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z. Advances in Protein Biomarker Assay via the Combination of Molecular Imprinting and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering. Acta Chim. Sin. 2021, 79, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.T.; Han, H.H.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Zhu, G.B.; Zang, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Yoon, J.; James, T.D.; Li, J.; He, X.P. Fluorescent probes for the detection of disease-associated biomarkers. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 853–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-W.; Song, Y.-Y. Fast Detection of Biomarker in Exhaled Breath Based on Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering Barcodes. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Distinguishing human characteristics based on hair metabolomics and proteomics: A review. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar]
- Wen-Jun, J.; Qu, T.; Xi-Juan, G.; Hai-Wei, J.; Li, W.; Yu-Ling, Q. Progress in Point-of-Care Testing of Disease Markers Based on Microfluidic Technology. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 51, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, G. Tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomics analysis of plasma and plasma exosomes in Parkinson’s disease. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2023, 41, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.R.; Hao, N.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, K. Cascade-catalyzed Enzyme-free Colorimetric Detection of Glucose Based on Manganese Dioxide-oxygen Doped Carbon Nitride Composites. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 727–732. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Dai, L.; Ren, X.; Wu, D.; Cao, W.; Wei, Q.; Ma, H. Protein-driven interaction enhanced electrochemiluminescence biosensor of hydrogen-bonded biohybrid organic frameworks for sensitive immunoassay of disease markers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 266, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, J.W.; Bergen, H.R., 3rd; Heegaard, N.H.H. On-line immunoaffinity-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for identification of amyloid disease markers in biological fluids. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Yu, R.J.; Jing, C.; Han, H.X.; Ma, W. Silver-amplified fluorescence immunoassay via aggregation-induced emission for detection of disease biomarker. Talanta 2021, 225, 121963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinish, U.S.; Fu, C.Y.; Soh, K.S.; Bhuvaneswari, R.; Kumar, A.; Olivo, M. Highly sensitive SERS detection of cancer proteins in low sample volume using hollow core photonic crystal fiber. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinish, U.S.; Ghayathri, B.; Tae, C.Y.; Malini, O. Sensitive multiplex detection of serological liver cancer biomarkers using SERS-active photonic crystal fiber probe. J. Biophotonics 2014, 7, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beffara, F.; Perumal, J.; Mahyuddin, A.P.; Choolani, M.; Khan, S.A.; Auguste, J.L.; Vedraine, S.; Humbert, G.; Dinish, U.S.; Olivo, M. Development of highly reliable SERS-active photonic crystal fiber probe and its application in the detection of ovarian cancer biomarker in cyst fluid. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201960120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eravuchira, P.J.; Banchelli, M.; D’Andrea, C.; de Angelis, M.; Matteini, P.; Gannot, I. Hollow core photonic crystal fiber-assisted Raman spectroscopy as a tool for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 077001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, R.; Zhan, Y.; Dong, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Gao, S.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; et al. Novel Ratiometric Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Quantitative Monitoring of Human Carboxylesterase-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Using Ag-Au Nanoflowers as SERS Substrate. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 18555–18563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Shen, Y.; Ouyang, G. Determination of circulating tumor cells by surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on molecularly imprinted polymers doped with silver nanoparticles. Anal. Sci. 2025, 41, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.E.; Lim, D.K. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering for HSP 70A mRNA detection in live cells using silica nanoparticles and DNA-modified gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 13, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyubin, A.; Lavrova, A.; Dogonadze, M.; Borisov, E.; Postnikov, E.B. Single-cell analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with diverse drug resistance using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). PeerJ 2025, 13, e18830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, X. Identifying Hepsin as a novel biomarker for human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its application in fluorescence imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 334, 125707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachon, E.; Bigot, J.; Cazelles, E.; Bidet, A.; Vial, J.P.; Dumas, P.Y.; Mimoun, A. Low Dimensional Representation of Multi-Patient Flow Cytometry Datasets Using Optimal Transport for Measurable Residual Disease Detection in Leukemia. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2025, 107, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovens, A.J.; Yu, D.; Dite, T.A.; Kemp, B.E.; Oakhill, J.S. Measuring Cellular Adenine Nucleotides by Liquid Chromatography-Coupled Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2882, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, K.; Ali, M.; Alarcon, E.I.; Hanan, A. Hollow core photonic crystal fiber for monitoring leukemia cells using surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 4599–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.X.; Zhang, N.; Kong, K.V.; Goh, D.; Ying, C.; Auguste, J.L.; Shum, P.P.; Wei, L.; Humbert, G.; Yong, K.T.; et al. Rapid SERS monitoring of lipid-peroxidation-derived protein modifications in cells using photonic crystal fiber sensor. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.S.; Khetani, A.; Monempour, A.T.; Smith, B.; Anis, H.; Trudeau, V.L. Detection of amino acid neurotransmitters by surface enhanced Raman scattering and hollow core photonic crystal fiber. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8233, 82330Q. [Google Scholar]
- Taccone, F.S.; Hites, M.; Beumier, M.; Scolletta, S.; Jacobs, F. Appropriate antibiotic dosage levels in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2011, 13, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletz, M.W.; Bloos, F.; Burkhardt, O.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Greer, M.W.; Stass, H.; Welte, T. Pharmacokinetics of moxifloxacin in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan, K.; Bartlett, M.G.; Stewart, J.T. Determination of moxifloxacin in human plasma by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, J.G.; Stass, H.; Heinig, R.; Blaschke, G. Capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence: A routine method to determine moxifloxacin in human body fluids in very small sample volumes. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 716, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.X.; Lai, K.Q.; Huang, Y.Q. Application of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to the determination of trace chemical hazards in food products. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2014, 34, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Ye, Q. Research Status and Progress of Antibiotic Drugs. World Notes Antibiot. 2019, 40, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Popp, J.; Pletz, M.W.; Frosch, T. Highly Sensitive Broadband Raman Sensing of Antibiotics in Step-Index Hollow-Core Photonic Crystal Fibers. ACS Photonics 2017, 4, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Wang, Y.S. Developments in Detection of Explosives Based on Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of Process Parameters on Double Absorption Resonance Peaks of Au Nanoparticles. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Hakonen, A.; Andersson, P.O.; Schmidt, M.S.; Rindzevicius, T.; Kall, M. Explosive and chemical threat detection by surface-enhanced Raman scattering: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Guan, G.; Zhang, K.; Mei, Q.; Liu, R.; Wang, S. Trinitrotoluene Explosive Lights up Ultrahigh Raman Scattering of Nonresonant Molecule on a Top-Closed Silver Nanotube Array. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6913–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, L.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S.; He, X. Utilizing an Automated SERS-Digital Microfluidic System for High-Throughput Detection of Explosives. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Pei, S.; Yang, D.; Guo, D.; Yang, M. Review on Hollow-Core Fiber Based Multi-Gas Sensing Using Raman Spectroscopy. Photonic Sens. 2024, 14, 240412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
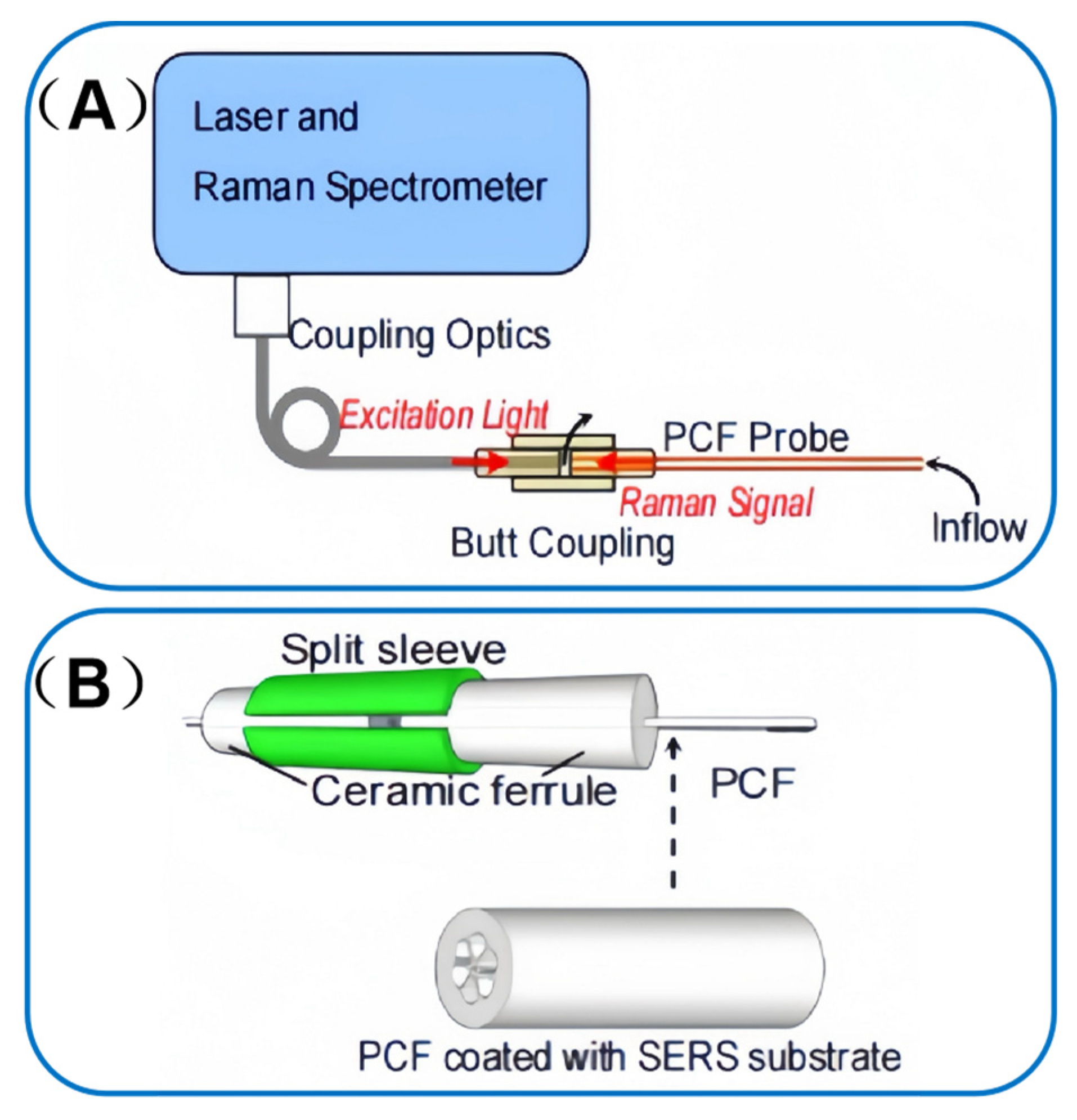
| Category | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| traditional SERS sensors | Rapid detection Reproducible | Lack of flexibility and compactness rigid and bulky design Limited application |
| PCF-SERS sensors | Flexible design Increase the volume of the active sensing area Anti-interference Lower Raman background High spectral certainty | The level of technological maturity needs to be improved Multi-parameter cross-sensitivity |
| Analytes | Type of Optical Fiber | SERS Active Nanomaterials | Limit of Detection | Analytical Enhancement Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RhB | Solid core PCF | AuNPs | 10−7 M | ~106 | [45] |
| R6G | Hollow core PCF | AgNPs | 10−10 M | ~108 | [54] |
| R6G | Solid core PCF | AgNPs | 10−10 M | ~107 | [55] |
| R6G | Side channel PCF | AuNPs | 5 × 10−14 M | ~109 | [56] |
| ATP | Tapered Suspended Core PCF | AuNPs | 1 × 10−7 M | ~107 | [42] |
| CV | Suspended core PCF | AgNPs | 10−12 M | ~1011 | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Ye, M. A Review of High-Sensitivity SERS-Active Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensors for Chemical and Biological Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226982
Luo J, Sun J, Chen H, Zhao C, Ye M. A Review of High-Sensitivity SERS-Active Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensors for Chemical and Biological Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226982
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jiaying, Jia Sun, Huacai Chen, Chunliu Zhao, and Manping Ye. 2025. "A Review of High-Sensitivity SERS-Active Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensors for Chemical and Biological Detection" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226982
APA StyleLuo, J., Sun, J., Chen, H., Zhao, C., & Ye, M. (2025). A Review of High-Sensitivity SERS-Active Photonic Crystal Fiber Sensors for Chemical and Biological Detection. Sensors, 25(22), 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226982






