A Review of the Expansion and Integration of Production Line Balancing Problems: From Core Issues to System Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Literature Selection
2.2. Literature Analysis
2.2.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
2.2.2. Keyword Cluster Analysis
3. C: Increased Internal Complexity
3.1. Diversified Production Line Layout
3.2. Optimization Objective Changes
3.3. Changes in Production Line Processes
4. H: Collaborative Optimization with the Workshop Level
4.1. Integration with Product Sequencing
4.2. Integration with Worker Assignment
4.3. Integration with Material Handling
5. V: Collaborative Optimization at the Enterprise Operational Level
5.1. Upstream Integration: Design and Process
5.2. Downstream Integration: Supply Chain and Warehousing
6. E: From Efficiency to Sustainability and Resilience
6.1. Sustainability
6.2. Resilience
7. Discussion and Future Research Directions
7.1. Discussion
7.2. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, S.-M.; Pei, W.; Chuang, M.-H. PV chart management innovation based on production balance ratio: A case study of Company S’s GaAs process improvement for compound semiconductors. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 2769–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, M.M.; Meles, T.Y.; Yang, C.-L. Productivity improvement through assembly line balancing by using simulation modeling in case of Abay garment industry Gondar. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H. Research on optimization and simulation of sand casting production line based on VSM. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2022, 13, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L. Research on Intelligent Production Line Design and Dynamic Balance for 3C Products. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 4136978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimeny, I.; Koltai, T. Comparison of MILP and CP models for balancing partially automated assembly lines. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 32, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breznik, M.; Buchmeister, B.; Herzog, N.V. Assembly Line Optimization Using MTM Time Standard and Simulation Modeling-A Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadarova, J.; Janekova, J.; Suhanyiova, A. Possibilities to Increase Assembly Line Productivity Using Different Management Approaches. Processes 2022, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroca, A.; Pereira, M.T.; Silva, F.J.G.; Oliveira, M.J.G.P. Optimization of an Air Conditioning Pipes Production Line for the Automotive Industry-A Case Study. Systems 2024, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaia, O.; Dolgui, A.; Guschinsky, N. An exact method for machining lines design with equipment selection and line balancing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Butterfield, J.; Murphy, A. A New Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm for Assembly Line Balancing. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2023, 23, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telemeci, Y.E.; Azizoglu, M. Type-II transfer line Balancing problem—A branch and bound approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 198, 110689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, S.; Masehian, E. An efficient solution to the simple assembly line balancing problem type 1 using iterated local search. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 144, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliktas, D.; Aydin, D. An artificial bee colony based-hyper heuristic algorithm with local search for the assembly line balancing problems. Eng. Comput. 2023, 40, 2453–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncayo-Martinez, L.A.; He, N.; Arias-Nava, E.H. Minimising by Simulation-Based Optimisation the Cycle Time for the Line Balancing Problem in Real-World Environments. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 2025, 41, e2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, A.; Fathi, M.; Ng, A.H.C. Balancing and scheduling human-robot collaborated assembly lines with layout and objective consideration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 187, 109775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaïa, O.; Dolgui, A. Hybridizations in line balancing problems: A comprehensive review on new trends and formulations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 250, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldi, L.D.; Galizia, F.G.; Bortolini, M. Balancing storage cost and customization time in product platform design: A bi-objective optimization model. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 136, 4933–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkul, O.; Selvi, I.H.; Şişci, M.; Öge, M. An integrated simulation-data envelopment analysis approach for impact of line-seru conversion. RAIRO—Oper. Res. 2024, 58, 4819–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Cao, N.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Deng, X. Balancing a U-Shaped Assembly Line with a Heuristic Algorithm Based on a Comprehensive Rank Value. Sustainability 2022, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelles-Chaouche, A.R.; Gurevsky, E.; Brahimi, N.; Dolgui, A. Optimizing modular equipment in the design of multi-product reconfigurable production lines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 192, 110226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, Q.; Chica, M.; Li, Z. Reinforcement Learning-Based Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm for Mixed-Model Multimanned Assembly Line Balancing Under Uncertain Demand. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 54, 2914–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.; Yang, T.; Huang, T.-L. Optimizing U-Shaped Production Line Balancing Problem with Exchangeable Task Locations and Walking Times. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, R.; Geng, X.; Hu, J.; Bao, H. Flower Pollination Algorithm with Ring Topology for Multisolution Spaces to Solve the Disassembly Line Balancing Problem. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng.-Trans. ASME 2025, 147, 021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.V.; Mohan, G.M.; Mohanasundaram, K.M. Design & implementation of the production line in garment industry. Ind. Textila 2022, 73, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Miranda, E.; Pereira, J.; Vargas, C.; Vilà, M. Variable-depth local search heuristic for assembly line balancing problems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 3102–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Z. Genetic Transfer Learning for Optimizing and Balancing of Assembly Lines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 7169–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Duan, J.J.; Zheng, R.P.; Shen, H.N.; Li, H.; Xu, J. Optimization and Simulation of Garment Production Line Balance Based on Improved GA. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2023, 22, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.T.; Karabay, G. Balancing The Shirt Production Line Under Different Operational Constraints Using An Integer Programming Model. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2022, 32, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, F.; Mammar, S. A hybrid constraint programming and cross-entropy approach for balancing U-Shaped disassembly line with flexible workstations and spatial constraints. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2025, 45, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didden, J.B.H.C.; Lefeber, E.; Adan, I.J.B.F.; Panhuijzen, I.W.F. Genetic algorithm and decision support for assembly line balancing in the automotive industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 3377–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Liu, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, C. Load Balancing of Two-Sided Assembly Line Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhomaidi, E.; Askin, R.G. Exact and approximation heuristic of mixed model assembly line balancing with parallel lines and task-dependent tooling consideration. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 193, 110265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilati, F.; Lelli, G.; Regattieri, A. Assembly line balancing and activity scheduling for customised products manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.T.; Arslankaya, S. Solution of the assembly line balancing problem using the rank positional weight method and Kilbridge and Wester heuristics method: An application in the cable industry. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Shen, S.; Cao, W.; Jiang, J.; Tang, W.; Hu, Y. Multi-objective optimization of the mixed-flow intelligent production line for automotive MEMS pressure sensors. Appl. Intell. 2024, 55, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Li, B.; Yu, Y. A bi-objective approach for the multi-skilled worker assignment of a hybrid assembly line-seru production system. RAIRO—Oper. Res. 2024, 58, 1187–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, F.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, K.-J.; Qian, X. Mixed Production Line Optimization of Industrialized Building Based on Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2411458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, Q.; Li, Z. Mixed-model assembly line balancing problem in multi-demand scenarios. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2023, 14, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, O. An investigation of mixed-model assembly line balancing problem with uncertain assembly time in remanufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 198, 110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Moroni, G.; Li, A.; Xu, L. Heuristic Approach for a Combined Transfer Line Balancing and Buffer Allocation Problem Considering Uncertain Demand. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Tian, G.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Pham, D.T.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, J. Human-Robot Collaboration in Mixed-Flow Assembly Line Balancing under Uncertainty: An Efficient Discrete Bees Algorithm. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 41, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xia, B.; Han, Y. Research on balancing and sequencing problems of flexible mixed model assembly lines with alternative precedence relations. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 8451–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, L. Combining balancing, sequencing and buffer allocation decisions to improve the efficiency of mixed-model asynchronous assembly lines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 194, 110357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangaro, F.; Minner, S.; Battini, D. The multi-manned joint assembly line balancing and feeding problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 5543–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, N.; Schulze, P.; Scholl, A. Assembly line balancing: What happened in the last fifteen years? Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 301, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Su, X.; Li, L.; Wu, Z. An improved ant colony optimization algorithm for two-sided U-type assembly line balancing problems. Eng. Optim. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, L.; Li, X. Dynamic Balancing of U-Shaped Robotic Disassembly Lines Using an Effective Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 6855–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiralay, Y.D.; Kara, Y. Profit-oriented balancing of two-sided disassembly lines with resource-dependent task times. Robot. Intell. Autom. 2024, 44, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-G.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Sang, C.-Y.; Liu, H. A genetic algorithm for balancing and sequencing of mixed-model two-sided assembly line with unpaced synchronous transfer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 146, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y. A Knowledge-Assisted Variable Neighborhood Search for Two-Sided Assembly Line Balancing Considering Preventive Maintenance Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 6859–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, T.; Liang, W. Mathematical formulation and an improved moth–flame optimization algorithm for parallel two-sided disassembly line balancing based on fixed common stations. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2022, 10, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Fang, K.; Huang, D. Balancing parallel assembly lines with human-robot collaboration: Problem definition, mathematical model and tabu search approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 63, 51–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Cao, J. Multi-Objective Optimization of Multi-Product Parallel Disassembly Line Balancing Problem Considering Multi-Skilled Workers Using a Discrete Chemical Reaction Optimization Algorithm. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 80, 4475–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Lee, C.K.M. A Benders’ Decomposition Algorithm for Balancing and Sequencing of the Mixed-Model Multi-Manned Assembly Lines. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Syst. 2024, 54, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhu, M.; Sun, Y. Multi-objective coupling optimization of electrical cable intelligent production line driven by digital twin. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2023, 86, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, S.; Guo, J.; Du, B.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K. A Pareto-based hybrid genetic simulated annealing algorithm for multi-objective hybrid production line balancing problem considering disassembly and assembly. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 4809–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Tao, L.; Su, B.; Javanmardi, E. Neighbourhood-search-enhanced non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-III for multi-objective assembly line balancing problem considering operator skill levels and carbon footprint. Eng. Optim. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Balancing and sequencing of mixed-model assembly line considering preventive maintenance scenarios: Mathematical model and a migrating birds optimization algorithm. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2023, 35, 1175–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Xie, N. Assembly line balancing and capacity evaluation based on interval grey processing time. Grey Syst.-Theory Appl. 2024, 14, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sikora, C.G.S.; Kucukkoc, I. Chance-constrained stochastic assembly line balancing with branch, bound and remember algorithm. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 335, 491–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, M.C.; Tural, M.K. Robotic stochastic assembly line balancing. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2023, 35, 1076–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S. Mathematical model and a variable neighborhood search algorithm for mixed-model robotic two-sided assembly line balancing problems with sequence-dependent setup times. Optim. Eng. 2023, 24, 989–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S. Two-sided resource-constrained assembly line balancing problem: A new mathematical model and an improved genetic algorithm. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2024, 90, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Multimanned partial disassembly line balancing optimization considering end-of-life states of products and skill differences of workers. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 66, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, R.; Guo, A.; Zhao, Q. Research on the balancing problem of human–robot collaborative assembly line in SMEs considering ergonomic risk and cost. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 204, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, C.; Bodin, U.; Schelen, O. Why decision support systems are needed for addressing the theory-practice gap in assembly line balancing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 79, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Research on workload balance problem of mixed model assembly line under parallel task strategy. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2025, 16, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraee, N.; Calzavara, M.; Finco, S.; Battaïa, O.; Battini, D. Assembly line balancing and worker assignment considering workers’ expertise and perceived physical effort. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 6939–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S. Effects of step-by-step line balancing in apparel assembly line. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2023, 18, 15589250231191196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, M.; Isler, M.; Guner, M. Optimizing the Material-Product Transformation Processes in the Clothing Manufacturing Line. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2022, 32, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.; Macedo, R.; Relvas, S.; Barbosa-Póvoa, A. Simulation of in-house logistics operations for manufacturing. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 35, 989–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, C.G.S. Balancing mixed-model assembly lines for random sequences. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 314, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Li, S.; Han, Z. Optimizing mixed-model assembly line efficiency under uncertain demand: A Q-Learning-Inspired differential evolution algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 200, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Guan, C. A multi-objective hybrid evolutionary search algorithm for parallel production line balancing problem including disassembly and assembly tasks. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2022, 30, 3508–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyasi, M.; Selcuk, Y.S.; Özener, O.Ö.; Coban, E. Imperialist competitive algorithm for unrelated parallel machine scheduling with sequence-and-machine-dependent setups and compatibility and workload constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 190, 110086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Zheng, L. Integrating real-time manufacturing data into a novel serial two-stage adaptive alternate genetic fireworks algorithm for solving stochastic type-II simple assembly line balancing problem. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 7075–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourabi, Z.; Khedher, F.; Babay, A.; Cheikhrouhou, M. Developing a metaheuristic model for the general assembly line balancing optimization based on a new workforce performance index: A case study in the garment industry. J. Text. Inst. 2024, 115, 2343–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-Y.; Yun, J.; Lee, C.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Noh, S.D. Data-driven analysis and human-centric assignment for manual assembly production lines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 188, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Wang, X. Human-robot collaboration assembly line balancing considering cross-station tasks and the carbon emissions. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2024, 19, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Wheelock, R.M.; Ou, W.; Yenradee, P.; Huynh, V.-N. A Demand-Driven Model for Reallocating Workers in Assembly Lines. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 80300–80320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhomaidhi, E. Enhancing efficiency and adaptability in mixed model line balancing through the fusion of learning effects and worker prerequisites. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2024, 15, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdous, M.-A.; Delorme, X.; Battini, D.; Sgarbossa, F. Scenario-based optimization and simulation framework for human-centered Assembly Line Balancing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2025, 282, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulac, S.; Kiraz, A. An integrated ergonomic risk assessment framework based on fuzzy logic and IVSF-AHP for optimising ergonomic risks in a mixed-model assembly line. Ergonomics 2024, 67, 2009–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, L. Assigning rest times to workers in assembly lines with ergonomically hazardous tasks: An approach to defend companies’ profitability. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 62, 1239–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Sun, J.; Yamamoto, H.; Dou, R.-L. A study of optimal assignment model considering quality and worker level in limited-cycle with multiple periods for smart manufacturing. Int. J. Ind. Eng.-Theory Appl. Pract. 2025, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-Y.; Lee, A.H.I.; Su, Y.-X. Multi-objective mixed-model assembly line balancing with hierarchical worker assignment: A case study of gear reducer manufacturing operations. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 2025, 16, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Fan, C.; Shirafuji, S.; Wang, Y.; Nishio, M.; Ota, J. Task allocation and scheduling to enhance human–robot collaboration in production line by synergizing efficiency and fatigue. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 80, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdous, M.A.; Delorme, X.; Battini, D.; Sgarbossa, F.; Berger-Douce, S. Assembly line balancing problem with ergonomics: A new fatigue and recovery model. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, J.; Minhas, K.A.; Rauf, M.; Yue, L.; Chen, Y. Solving line balancing and AGV scheduling problems for intelligent decisions using a Genetic-Artificial bee colony algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 189, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arik, O.A.; Yufka, P.N. A new mathematical model approach with assembly line feeding based Milk-Run system. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2025, 40, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, S. Assembly line balancing and optimal scheduling for flexible manufacturing workshop. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 2757–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Che, A. A note on integrated disassembly line balancing and routing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Pozo, R.; Bautista-Valhondo, J. Impact of limiting the ergonomic risk on the economic and productive efficiency of an assembly line. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aicha, M.; Belhadj, I.; Hammadi, M. Disassembly Process Planning and Its Lines Balancing Prediction. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2023, 10, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenzfurtner, W.; Pichler, E.; Gronalt, M. Increasing the output of mixed-model assembly lines for industrialised housebuilding: Learnings from a case-based simulation study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 63, 3192–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stade, D.; Spoor, J.M.; Manns, M.; Ovtcharova, J. Process time distribution simulation in robotic assembly line balancing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 63, 3467–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, C.G.S.; Tiacci, L. Incorporating car-sequencing rules in the planning of mixed-model assembly lines. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 63, 2114–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zou, G.; Su, Q.; Zou, S.; Deng, W.; Yu, A.; Zhang, H. Digital Twins-Based Production Line Design and Simulation Optimization of Large-Scale Mobile Phone Assembly Workshop. Machines 2022, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kádárová, J.; Kočišová, M.; Teplická, K.; Suhányiová, A.; Lachvajderová, L. Optimization of Costs and Production Process of Fire Dampers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittichotsatsawat, Y.; Wattanutchariya, W.; Jongjareonrak, A.; Seesuriyachan, P. Enhancing Manufacturing Operations Within the Supply Chain for Sustainable Frozen Shrimp Production. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, A.; Paprocka, I. The Influence of the Assembly Line Configuration and Reliability Parameter Symmetry on the Key Performance Indicators. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qin, Q. Intelligent manufacturing management system based on data mining in artificial intelligence energy-saving resources. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 4061–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X. Enhanced Hybrid Ant Colony Optimization for Machining Line Balancing Problem with Compound and Complex Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, Y. A Multi-Object Genetic Algorithm for the Assembly Line Balance Optimization in Garment Flexible Job Shop Scheduling. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 37, 2421–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chu, F.; Dolgui, A.; Anjos, M. Multi-objective disassembly line balancing and related supply chain management problems under uncertainty: Review and future trends. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 272, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, G.; Wang, W. U-shaped disassembly line balancing problem under interval Type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy set: Modeling and solution method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 145, 110211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y. A Novel Simulated Annealing-Based Hyper-Heuristic Algorithm for Stochastic Parallel Disassembly Line Balancing in Smart Remanufacturing. Sensors 2023, 23, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, B. Deep-Q-network-enhanced aquila-equilibrium hyper-heuristic algorithm for preventive maintenance integrated disassembly line balancing involving worker redeployment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 204, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelles-Chaouche, A.R.; Gurevsky, E.; Brahimi, N.; Dolgui, A. Minimizing task reassignments under balancing multi-product reconfigurable manufacturing lines. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 173, 108660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, X.; Gianessi, P. Line balancing and task scheduling to minimise power peak of reconfigurable manufacturing systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 5061–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, X.; Cerqueus, A.; Gianessi, P.; Lamy, D. RMS balancing and planning under uncertain demand and energy cost considerations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 261, 108873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, A.; Fathi, M.; Ng, A.H.C. Balancing and scheduling assembly lines with human-robot collaboration tasks. Comput. Oper. Res. 2022, 140, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkerdar, M.; ElMaraghy, W. Smart adaptable assembly line rebalancing and maintenance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Xu, Z. Integrated optimisation of dynamic scheduling and reconfiguration for distributed reconfigurable flowshops via iterated greedy algorithm. Int. J. Syst. Sci.-Oper. Logist. 2025, 12, 2467782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, X. Green and efficient-oriented human-robot hybrid partial destructive disassembly line balancing problem from non-disassemblability of components and noise pollution. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2024, 90, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, G.; Peng, T.; Pham, D.T. Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm with Machine Learning and Local Search for an Energy- Efficient Disassembly Line Balancing Problem in Remanufacturing. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng.-Trans. ASME 2023, 145, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Joint balancing and sequencing optimization for type-II robotic mixed-model assembly line considering energy consumption. Ann. Oper. Res. 2025. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmolouk, R.S.; El-Kharbotly, A.M.K.; Taha, R.B. Optimization of time and energy in straight one-sided robotic assembly lines. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zou, Y. Type-1 Robotic Assembly Line Balancing Problem That Considers Energy Consumption and Cross-Station Design. Systems 2022, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, C.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z. An Enhanced Social Engineering Optimizer for Solving an Energy-Efficient Disassembly Line Balancing Problem Based on Bucket Brigades and Cloud Theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 7148–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lu, W.; Sheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Human-Robot Collaboration on a Disassembly-Line Balancing Problem with an Advanced Multiobjective Discrete Bees Algorithm. Symmetry 2024, 16, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, L.; Qi, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Chatterjee, M.; Kang, Q. Multifactory Disassembly Process Optimization Considering Worker Posture. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2025, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Guo, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, S.; Tang, Y. A Multiobjective Discrete Harmony Search Optimizer for Disassembly Line Balancing Problems Considering Human Factors. IEEE Trans. Human-Mach. Syst. 2025, 55, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Guo, X. Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm for a Heterogeneous Multifactory Remanufacturing Optimization Problem. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2025, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, P.; Qi, L.; Qin, S.; Ji, Y.; Hu, B. An Evolutionary Learning Whale Optimization Algorithm for Disassembly and Assembly Hybrid Line Balancing Problems. Mathematics 2025, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharia, P.T.; Xidias, E.K.; Nearchou, A.C. The fuzzy human-robot collaboration assembly line balancing problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 187, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirabadi, M.; Keivanpour, S.; Chinniah, Y.A.; Frayret, J.-M. Human-robot collaboration in assembly line balancing problems: Review and research gaps. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 186, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Li, W.; Tan, Y.; Otto, K. A systematic energy-aware scheduling framework for manufacturing factories integrated with renewables. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 7644–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Ferraris, A.; Dhar, B.K. The contribution of circular economy practices on the resilience of production systems: Eco-innovation and cleaner production’s mediation role for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 424, 138806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, M.; Hornek, T.; Kraus, W. Towards scalability for resource reconfiguration in robotic assembly line balancing problems using a modified genetic algorithm. J. Intell. Manuf. 2025, 36, 1175–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, M.; Huber, M.F. Resource reconfiguration and optimization in brownfield constrained Robotic Assembly Line Balancing Problems. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 67, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Khan, R.; Saleem, W.; Salah, B.; Alkhatib, S. Modeling and Optimization of Assembly Line Balancing Type 2 and E (SLBP-2E) for a Reconfigurable Manufacturing System. Processes 2022, 10, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Meng, K.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z. An improved multi-objective multifactorial evolutionary algorithm for assembly line balancing problem considering regular production and preventive maintenance scenarios. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 68, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-K.; Chou, C.-W.; Wang, C.-H.; Ho, L.-A. Sustainable scheduling of TFT-LCD cell production: A hybrid dispatching rule and two-phase genetic algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 278, 109412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldar, P.; Fathi, M.; Nourmohammadi, A.; Delorme, X.; Battaïa, O.; Dolgui, A. Transfer line balancing problem: A comprehensive review, classification, and research avenues. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 201, 110913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, M.J.; Ostermeier, F.F. Dynamic line balancing in unpaced mixed-model assembly lines: A problem classification. Cirp J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 37, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Saldanha-Da-Gama, F.; Liu, M.; Yang, Z. A risk-averse two-stage stochastic programming model for a joint multi-item capacitated line balancing and lot-sizing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 304, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, L.; Tse, S.; May, M.C.; Lanza, G. Assisted production system planning by means of complex robotic assembly line balancing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 78, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Chi, Y.; Guo, L.; Yan, R. Robotic assembly line balancing considering the carbon footprint objective with cross-station design. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 190, 110045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcu, Y.K. Solution approach using heuristic and artificial neural networks methods in assembly line balancing problems: A case study in the lighting industry. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Bai, Z.; Liu, X.; Awais, M. Modelling and numerical analysis for seru system balancing with lot splitting. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 7410–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprocka, I.; Skolud, B. A Predictive Approach for Disassembly Line Balancing Problems. Sensors 2022, 22, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Chipusu, K. A deep learning approach for balance optimisation of patch panel assembly line. J. Eng. Des. 2024, 36, 1302–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xin, T.; Jia, S.; Ren, D.; Li, M. Production line balance problem identification and improvement based on decision tree: A case study of commercial air conditioner production line. Sci. Prog. 2024, 107, 00368504241238612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W.; Song, H. Modelling and optimization of line efficiency for preventive maintenance of robot disassembly line. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 79, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S. Development of a dedicated process simulator for the digital twin in apparel manufacturing: A case study. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2024, 36, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, N.; Algarni, A.D.; El-Hefnawy, N.A.; Abdel-Kader, H.; Abdelatey, A. Knowledge Graph-Enhanced Digital Twin Framework for Optimized Job Shop Scheduling in Smart Manufacturing. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 19863–19887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Singari, R.M. Analysing the Bottleneck in Crankcase Cover Manufacturing using Simulation and Modelling. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2024, 83, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Man–Robot Disassembly Line Balancing Optimization by Mixed-Integer Programming and Problem-Oriented Group Evolutionary Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 54, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Pham, D.T. Transfer Learning-Assisted Evolutionary Dynamic Optimisation for Dynamic Human-Robot Collaborative Disassembly Line Balancing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xue, H.; Zheng, C.; Shi, H. Improved dual-population genetic algorithm to solve human-robot collaborative assembly line balancing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 63, 6452–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Sepehri, A.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Tseng, M.-L. Balancing assembly lines with industrial and collaborative robots: Current trends and future research directions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 193, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wu, J.; Cao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Long, J. Multi-man–robot collaborative disassembly line balancing optimization via mixed-integer programming and genetic Jaya algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
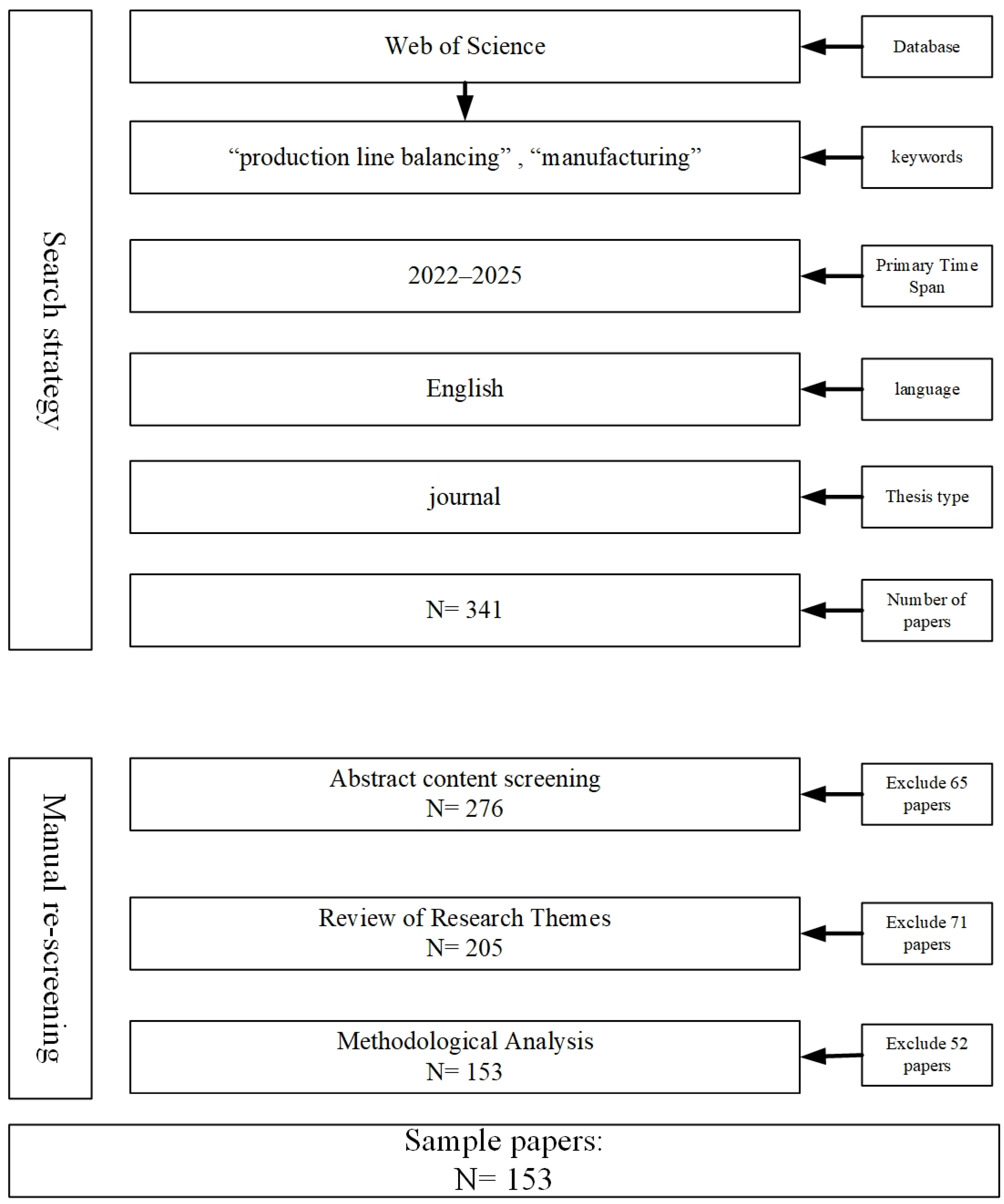
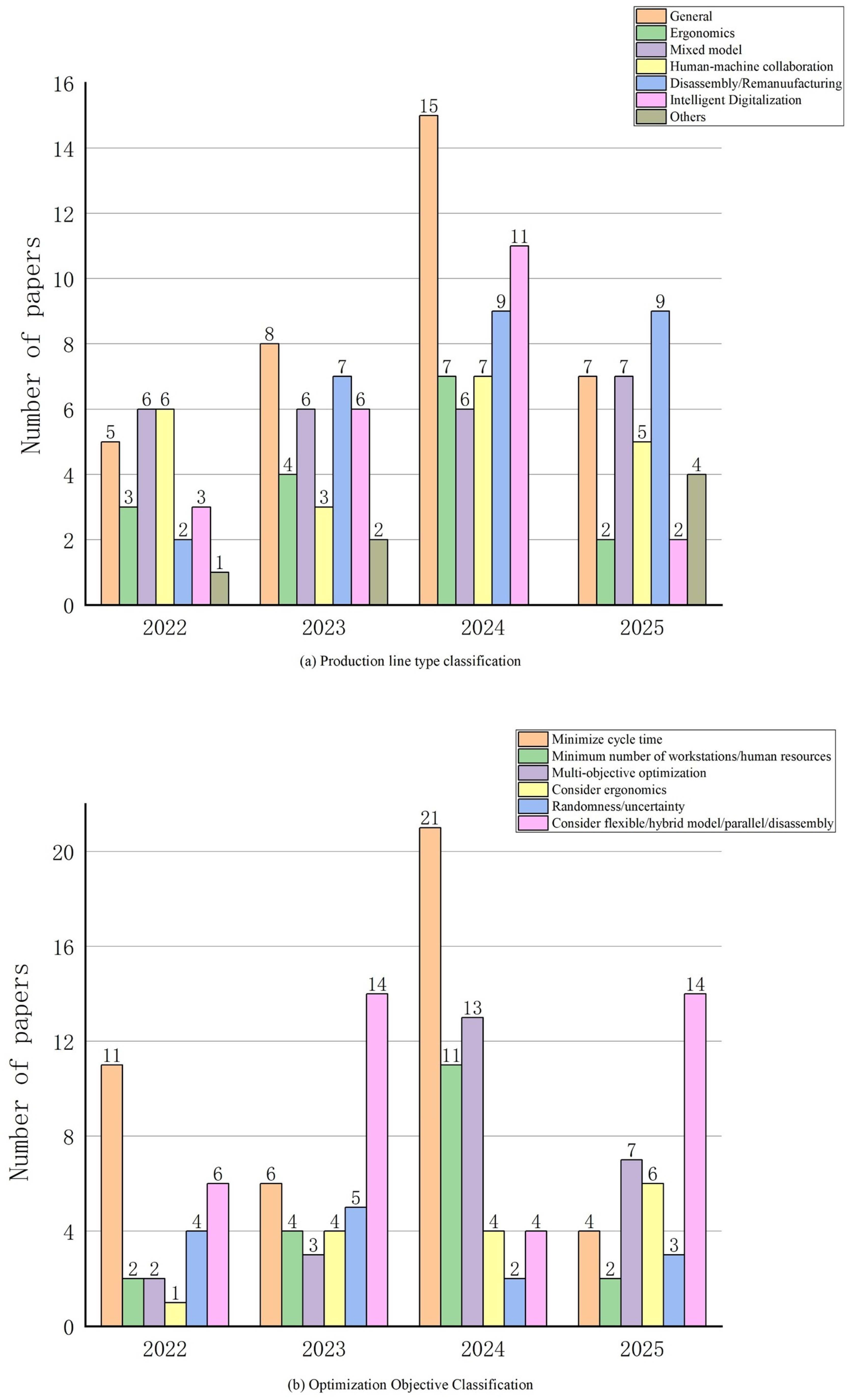
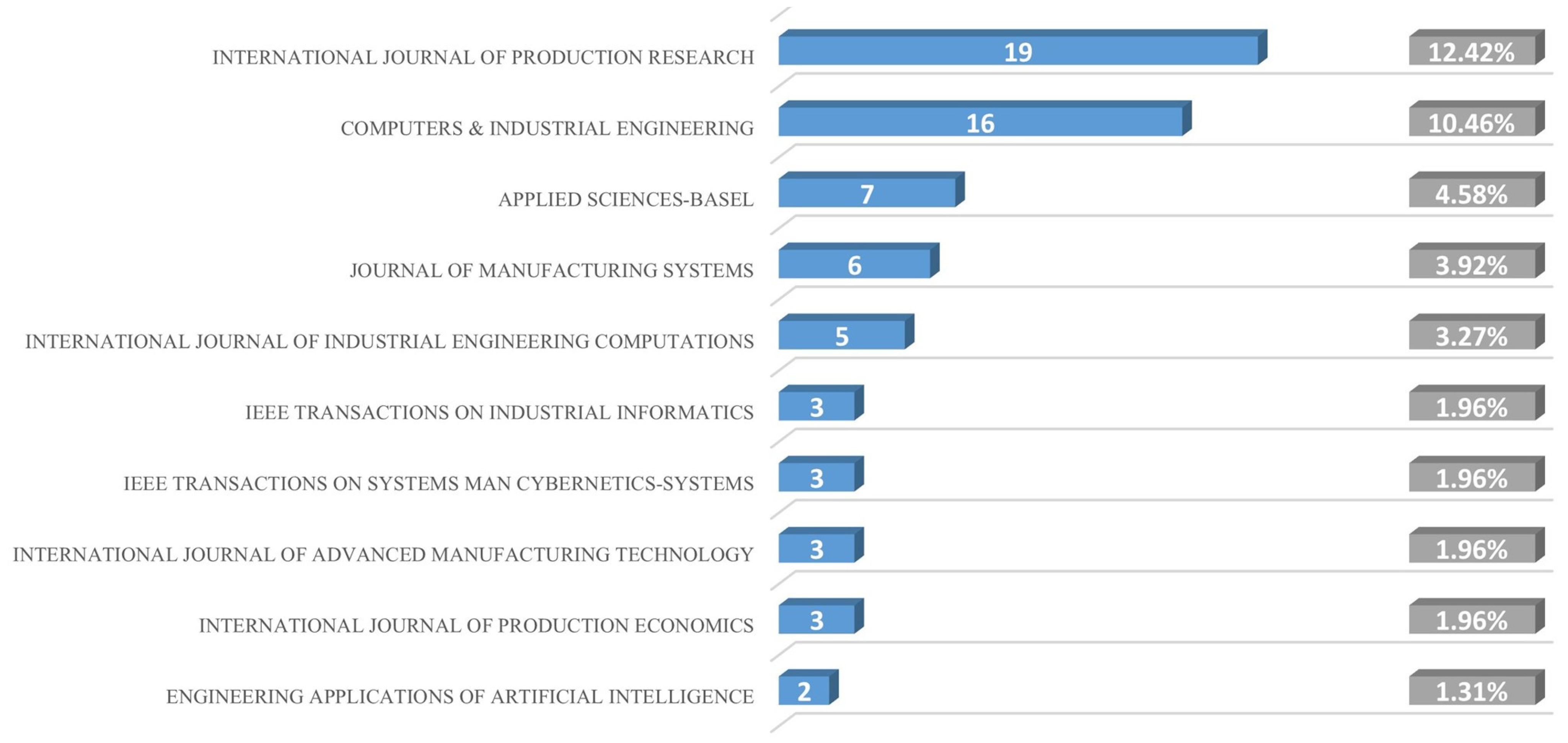
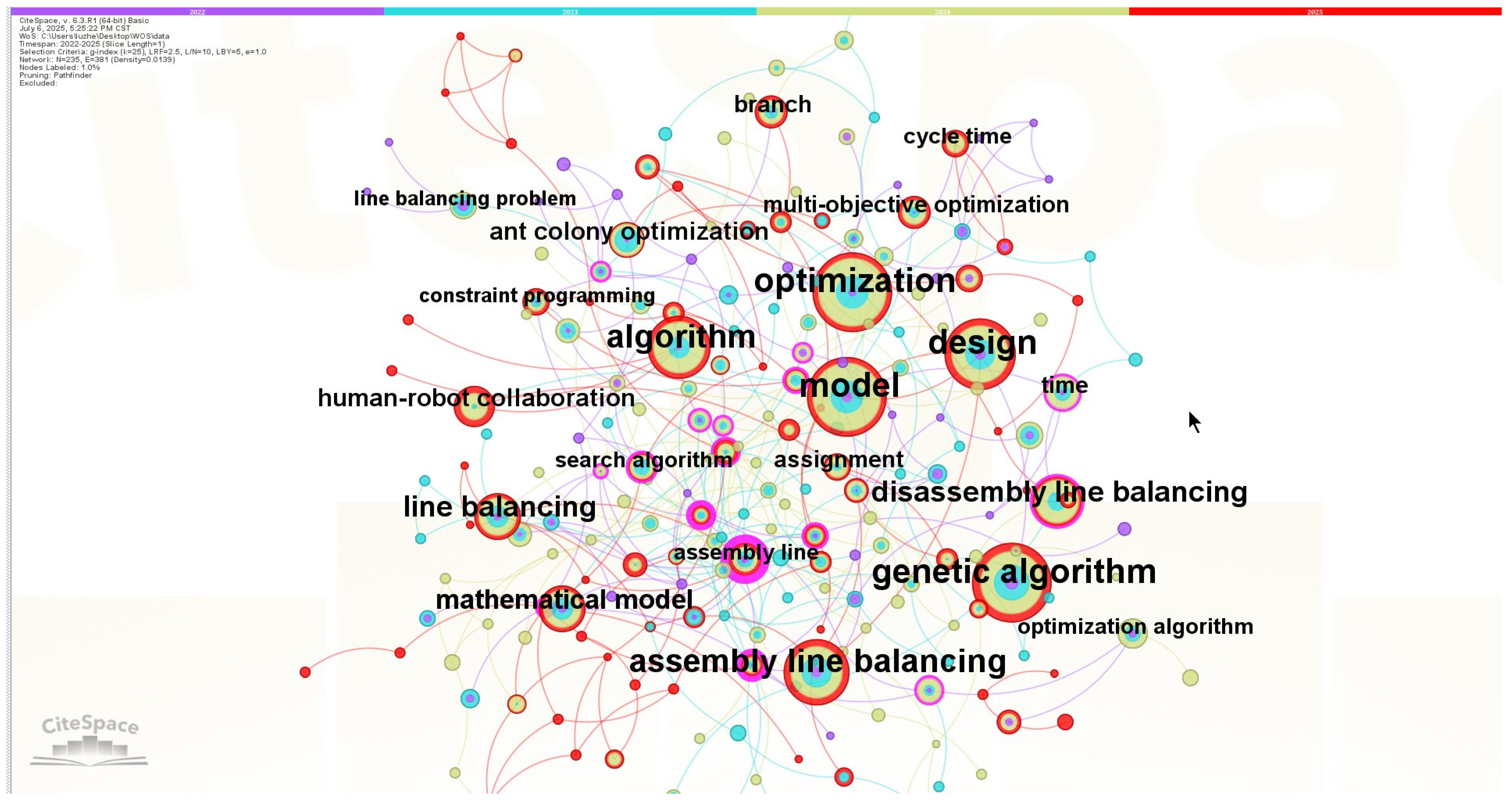
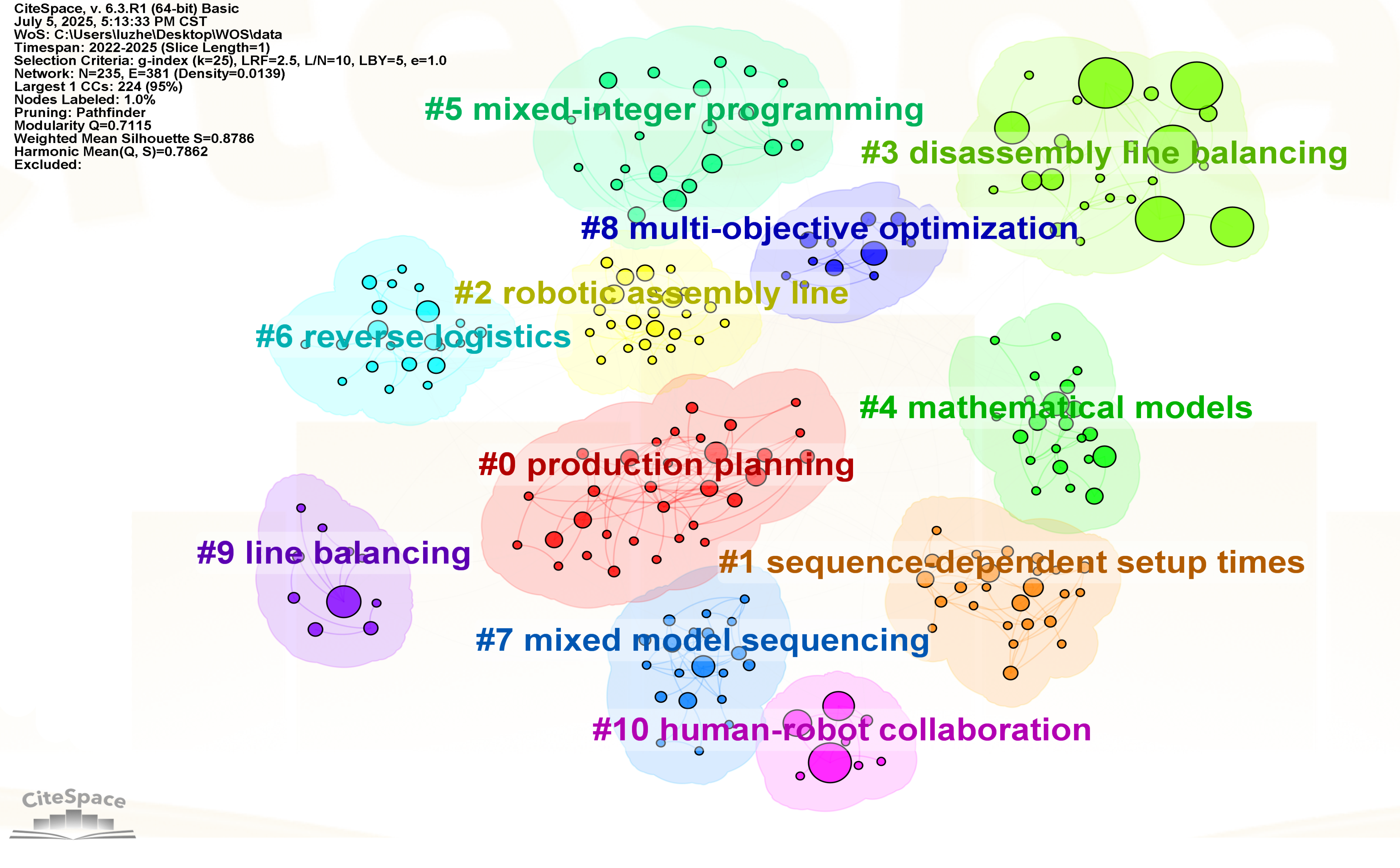
| Word Frequency Sorting | Centrality Sorting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Count | Keywords | Number | Centrality | Keywords |
| 1 | 108 | model | 1 | 0.43 | assembly line |
| 2 | 107 | optimization | 2 | 0.31 | job rotation |
| 3 | 100 | genetic algorithm | 3 | 0.3 | artificial bee colony algorithm |
| 4 | 91 | design | 4 | 0.2 | artificial bee colony |
| 5 | 74 | assembly line balancing | 5 | 0.17 | network design |
| 6 | 74 | algorithm | 6 | 0.16 | mixed-integer programming |
| 7 | 45 | disassembly line balancing | 7 | 0.14 | parallel workstations |
| 8 | 41 | line balancing | 8 | 0.13 | worker assignment |
| 9 | 35 | mathematical model | 9 | 0.13 | particle swarm optimization |
| 10 | 27 | human-robot collaboration | 10 | 0.12 | search algorithm |
| Cluster ID | Cluster Name | Size | Silhouette | Label (LLR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #0 | production planning | 32 | 0.859 | production planning, industry 4.0, mixed-model assembly line balancing, ergonomics, disassembly line balancing |
| #1 | sequence-dependent setup times | 25 | 0.907 | sequence-dependent setup times, two-sided assembly line balancing, artificial bee colony algorithm, local search, simple assembly line balancing |
| #2 | robotic assembly line | 24 | 0.874 | robotic assembly line, heuristic algorithms, data validation problem, domain generalization, decision support systems |
| #3 | disassembly line balancing | 23 | 0.864 | disassembly line balancing, disassembly planning, green manufacturing, collaborative robots, sustainable manufacturing |
| #4 | mathematical models | 22 | 0.896 | mathematical models, workstations, search problems, layout, costs |
| #5 | mixed-integer programming | 21 | 0.811 | disassembly line balancing, mixed-integer programming, assembly line balancing, recursive approach, human-robot interaction |
| #6 | reverse logistics | 21 | 0.841 | reverse logistics, chance-constrained programming, reconfiguration, decomposition heuristic, joint assembly line balancing and feeding problem |
| #7 | mixed model sequencing | 20 | 0.893 | mixed model sequencing, task sharing, reconfigurable manufacturing systems, classification scheme, dynamic line balancing |
| #8 | multi-objective optimization | 11 | 0.896 | multi-objective optimization, robotic assembly line balancing, industry 4.0, stochastic assembly line balancing |
| #9 | line balancing | 10 | 0.872 | line balancing, lean manufacturing, lean manufacturing, multi-objective optimization |
| #10 | human-robot collaboration | 8 | 1 | human-robot collaboration, resource sharing, u-shaped assembly line, hybrid disassembly line balancing, mathematical model |
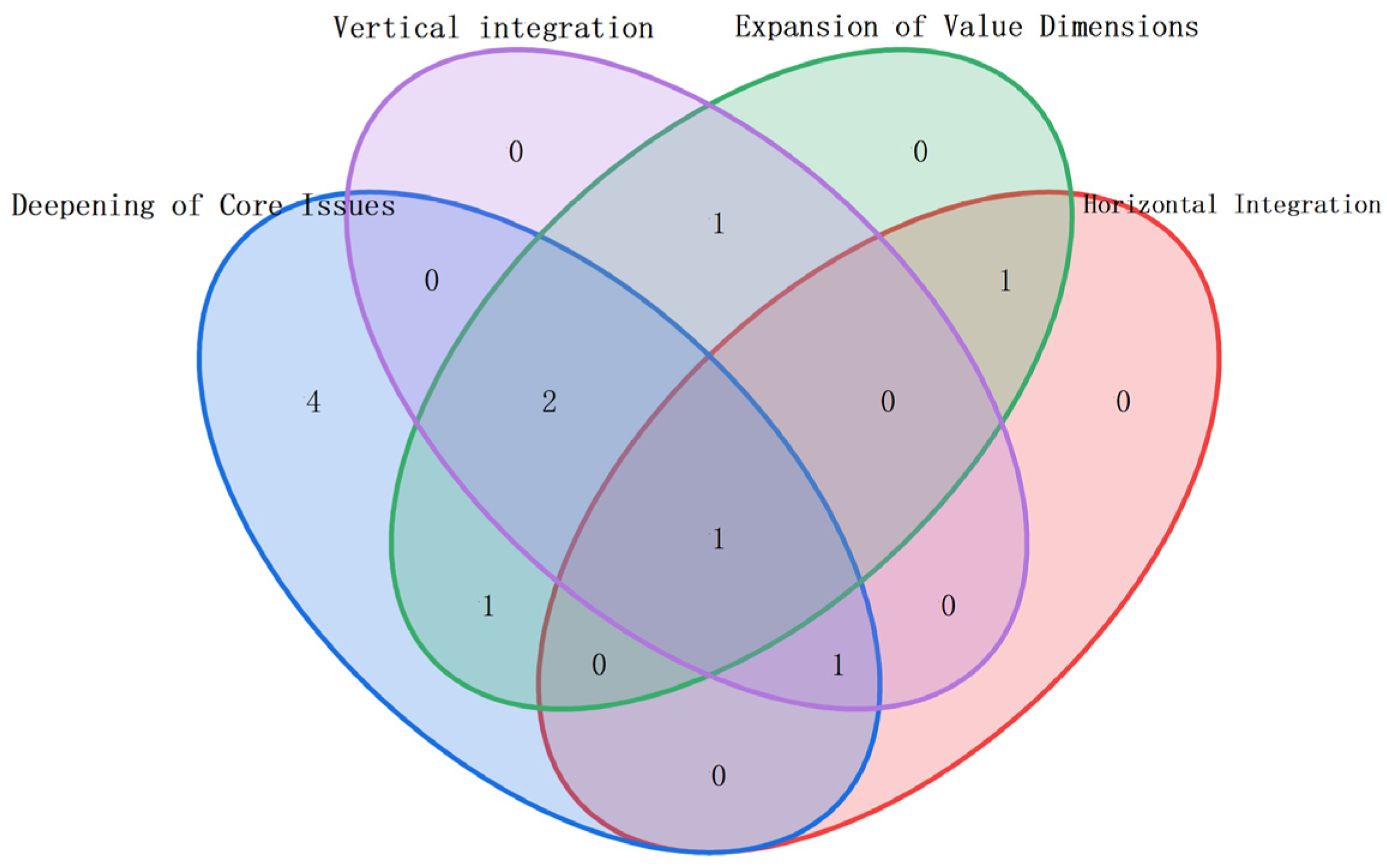
| Criteria | Contents | Cluster ID |
|---|---|---|
| C Deepening of core issues | Section 3.1 Layout expansion: from linear to U-shaped, two-sided, and parallel lines Section 3.2 Objective expansion: From single objective to mixed/multi-objective Section 3.3 Process uncertainty: from deterministic to random/fuzzy time; from simple to sequence-dependent | #0, #1, #4, #5, #6, #7, #8, #9, #10 |
| H horizontal integration | Section 4.1 Integration with Product Sequencing: Sorting Issues in Mixed-Flow Production Lines Section 4.2 Integration with Worker Assignment: Skills, fatigue, learning curves, etc. Section 4.3 Integration with material handling: feeding methods and costs | #2, #6, #10 |
| V vertical integration | Section 5.1 Upstream integration: product design, process planning Section 5.2 Downstream integration: integration with warehousing and supply chain (especially dismantling line balancing in reverse supply chains) | #0, #3, #5, #6, #10 |
| E Expansion of value dimensions | Section 6.1 Sustainability: energy consumption, carbon emissions, Human factors engineering, etc. Section 6.2 Resilience: Consideration of rebalancing issues in the event of disruptions | #0, #2, #3, #5, #9, #10 |
| References | Analytical Dimension | Research Objectives | Solution Approach | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layout | Production | Uncertainty | |||
| [22] | √ | Optimizing U-Shaped Production Line Balancing Problem | integer programming model, use Lingo to solve for the minimum production cycle. | ||
| [23] | √ | DLBP with Multiple Solution Space | Multi-objective mathematical model, ring topology pollination algorithm (RTFPA) | ||
| [24] | √ | Design & implementation of the production line in garment industry | Quantitative research methods, lean manufacturing tools, 5S | ||
| [25] | √ | SALBP | Variable depth local search algorithm, heuristic algorithm | ||
| [26] | √ | Assembly line optimization and balancing | GAB and genetic transfer learning (GTL) methods | ||
| [27] | √ | Clothing production line balancing optimization | Improvements in genetic algorithms and computer simulation technology | ||
| [28] | √ | Balancing The Shirt Production Line | Integer programming model considering dual constraints of manpower and machinery, ranking position weighting method | ||
| [29] | √ | balancing U-Shaped disassembly line with flexible workstations and spatial constraints | Hybrid integer nonlinear programming model and constraint programming model, hybrid constraint programming and cross-entropy approach | ||
| [30] | √ | Automobile assembly line balancing | GA, decision support systems | ||
| [31] | √ | Load balancing of dual-side assembly lines | Mathematical programming models, deep reinforcement learning algorithms | ||
| [32] | √ | Efficiently balancing assembly lines | Heuristic algorithms, multi-feature optimization models | ||
| [33] | √ | Customized product line balancing | Two-step process method, component grouping, task and worker allocation optimization model | ||
| [34] | √ | Cable production line balancing issues | Rank positional weight method, heuristic method, workstation load balancing | ||
| [35] | √ | Production cycle time and balance rate | Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II(NSGA-II) | ||
| [36] | √ | Uneven workload among workers | Dual-objective integer nonlinear programming model, | ||
| [37] | √ | Mixed Production Line Optimization of Industrialized Building | combining NSGA-II with multi-objective simulated annealing meta-heuristic method | ||
| [38] | √ | Balancing hybrid assembly lines in multi-demand scenarios | Genetic algorithms, sequence optimization, and buffer allocation for evaluating individual fitness functions | ||
| [39] | √ | Optimizing remanufacturing cycle time and overall balance rate (CBR) | Production rhythm optimization mathematical model, particle swarm optimization algorithm | ||
| [40] | √ | Balancing production lines with uncertain demand | Mixed-integer linear programming model, improved migratory bird optimization algorithm | ||
| [41] | √ | Balancing mixed-flow assembly lines in uncertain environments | Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Set Theory | ||
| [42] | √ | balancing and sequencing problems of flexible mixed model assembly lines | AND/OR graph modeling, iterative decomposition methods | ||
| [43] | √ | Efficiency of mixed assembly lines | Ant colony optimization algorithm, production line scheduling optimization | ||
| [44] | √ | The multi-manned joint assembly line balancing | heuristic algorithm based on adaptive large neighborhood search framework | ||
| References | Analytical Dimension | Research Objectives | Solution Approach | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Sequencing | Worker Assignment | Material Handling | |||
| [64] | √ | Optimization of disassembly line balancing considering worker skill differences | Mixed-integer programming (MIP) model, Based on incentive strategy NSGA-II | ||
| [65] | √ | Balancing human-machine collaboration assembly lines considering ergonomic risks | Multi-objective optimization mathematical model, improved multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm | ||
| [66] | √ | Automated allocation of production line tasks | Designing decision support systems for interactive and iterative workflows | ||
| [67] | √ | Assembly line design and load balancing under parallel task conditions | Mixed integer programming model, simulated annealing algorithm with improved strategy | ||
| [68] | √ | Assembly line balancing and worker allocation | Allocation strategy for worker performance variability, dual-objective linear programming model | ||
| [69] | √ | Clothing production line balancing | Task modularization, dual allocation of tasks and workers | ||
| [70] | √ | Optimizing the Material-Product Transformation Processes | string diagram, Minimization of resource movement, analysis of production activities, layout design | ||
| [71] | √ | Simulation of in-house logistics operations for manufacturing | Building a logistics simulation model for an automobile manufacturing factory | ||
| [72] | √ | Balance optimization of mixed-flow assembly lines under random sequences | Branch-and-bound algorithm, exact methods, heuristic extension schemes | ||
| References | Analytical Dimension | Research Objectives | Solution Approach | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | Downstream | |||
| [93] | √ | Consider the impact of ergonomic factors on production line efficiency during the design phase | Designing models that maximize production line efficiency, Linearization solution | |
| [94] | √ | Production line balancing during the design phase | Process Planning Forecasting Analysis Method | |
| [95] | √ | Production Efficiency of Mixed Flow Assembly Lines for Wall Components | A hybrid approach combining configuration modeling and discrete event simulation techniques | |
| [96] | √ | Robot assembly line balancing | Process time distribution simulation, Evaluating the impact of different process time distributions | |
| [97] | √ | Incorporating car-sequencing rules in the planning of mixed-model assembly lines | Design genetic algorithms combine balancing problems with semi-random production sequences | |
| [98] | √ | Mobile phone assembly line production process combination and workstation division | Dual production line mixing workshop, mixing workshop optimization model, heuristic algorithm | |
| [99] | √ | Research on Production Costs and Process Optimization | Measure workstation time consumption, balance workstation method | |
| [100] | √ | Optimize production processes, Reduce supply chain costs | Value stream mapping, line balancing method, ECRS | |
| [101] | √ | Production line fluctuation issues | Improving mathematical models, Segment work-in-process inventory | |
| [102] | √ | Waste of idle resources at production sites, Low production line balance rate | Artificial Intelligence-based Data Mining Intelligent Manufacturing Management System | |
| References | Analytical Dimension | Research Objectives | Solution Approach | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | Resilience | |||
| [106] | √ | U-shaped disassembly line balancing problem | Improved Fuzzy Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (FMOPSO), interval Type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy set (IT2TFS) | |
| [107] | √ | Remanufacturing dismantling line balancing | Random parallel disassembly line balancing model, high-order heuristic algorithm (HH) for simulated annealing | |
| [108] | √ | preventive maintenance integrated disassembly line balancing | Mixed integer programming model, Deep-Q-network-enhanced aquila-equilibrium hyper-heuristic algorithm | |
| [109] | √ | Minimizing task reallocation in multi-product reconfigurable production lines | Mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) model, MILP-based heuristic algorithm | |
| [110] | √ | Reconfigurable production line balancing, energy consumption minimization | Time-indexed integer linear programming model, heuristic algorithm | |
| [111] | √ | RMS balancing and planning | Double-layer optimization model, discrete whale optimization algorithm | |
| [112] | √ | Collaborative robot assembly line optimization | MILP model, neighborhood search simulated annealing algorithm (SA) | |
| [113] | √ | Intelligent adaptive production line rebalancing and maintenance | Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) | |
| [114] | √ | Dynamic Scheduling and Reconfiguration of Distributed Reconfigurable Production Lines | Heuristic dynamic rescheduling method, iterated greedy algorithm | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitahong, A.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Mo, P.; Ma, J. A Review of the Expansion and Integration of Production Line Balancing Problems: From Core Issues to System Integration. Sensors 2025, 25, 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206337
Sitahong A, Lu Z, Yuan Y, Mo P, Ma J. A Review of the Expansion and Integration of Production Line Balancing Problems: From Core Issues to System Integration. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206337
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitahong, Adilanmu, Zheng Lu, Yiping Yuan, Peiyin Mo, and Junyan Ma. 2025. "A Review of the Expansion and Integration of Production Line Balancing Problems: From Core Issues to System Integration" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206337
APA StyleSitahong, A., Lu, Z., Yuan, Y., Mo, P., & Ma, J. (2025). A Review of the Expansion and Integration of Production Line Balancing Problems: From Core Issues to System Integration. Sensors, 25(20), 6337. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206337





