A Modality Alignment and Fusion-Based Method for Around-the-Clock Remote Sensing Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- Most solutions lack robust mechanisms for handling severe feature quality deterioration under extreme weather conditions, where visible light images suffer from illumination insufficiency while infrared images are affected by thermal noise [30]. These limitations become particularly apparent in mission-critical applications requiring operational capability, where even state-of-the-art methods like CCFINet [31] and CrossFormer [32] show compromised accuracy during modality transitions or weather extremes [31,32].
- (1)
- We propose a comprehensive cross-modal detection framework that simultaneously addresses modality differences and feature degradation through synergistic module design.
- (2)
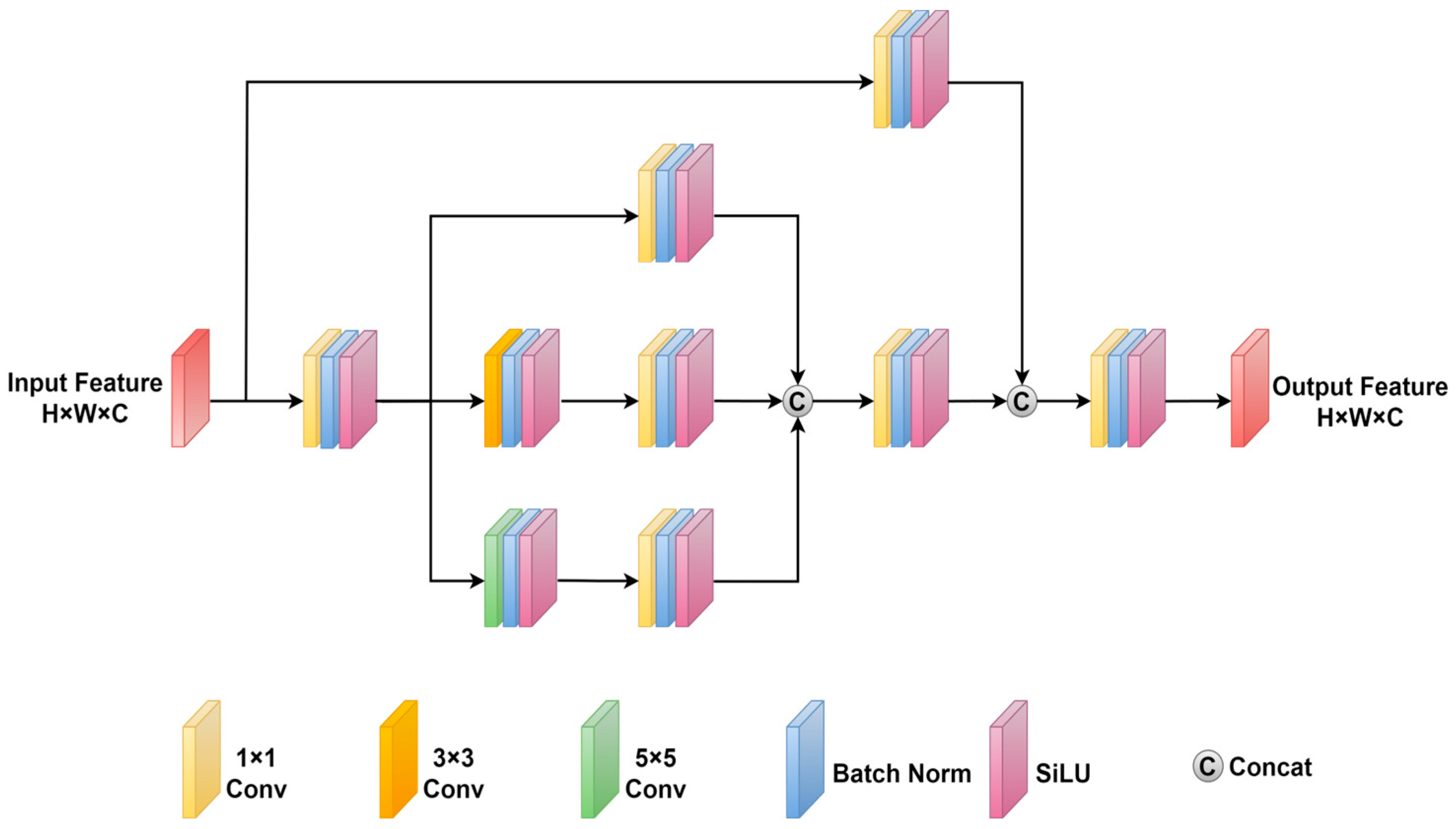
- We develop a multi-scale feature extraction module (MSFEM) with a multi-branch convolutional architecture that captures diverse receptive fields, effectively compensating for lost visible-light features in adverse conditions.
- (3)
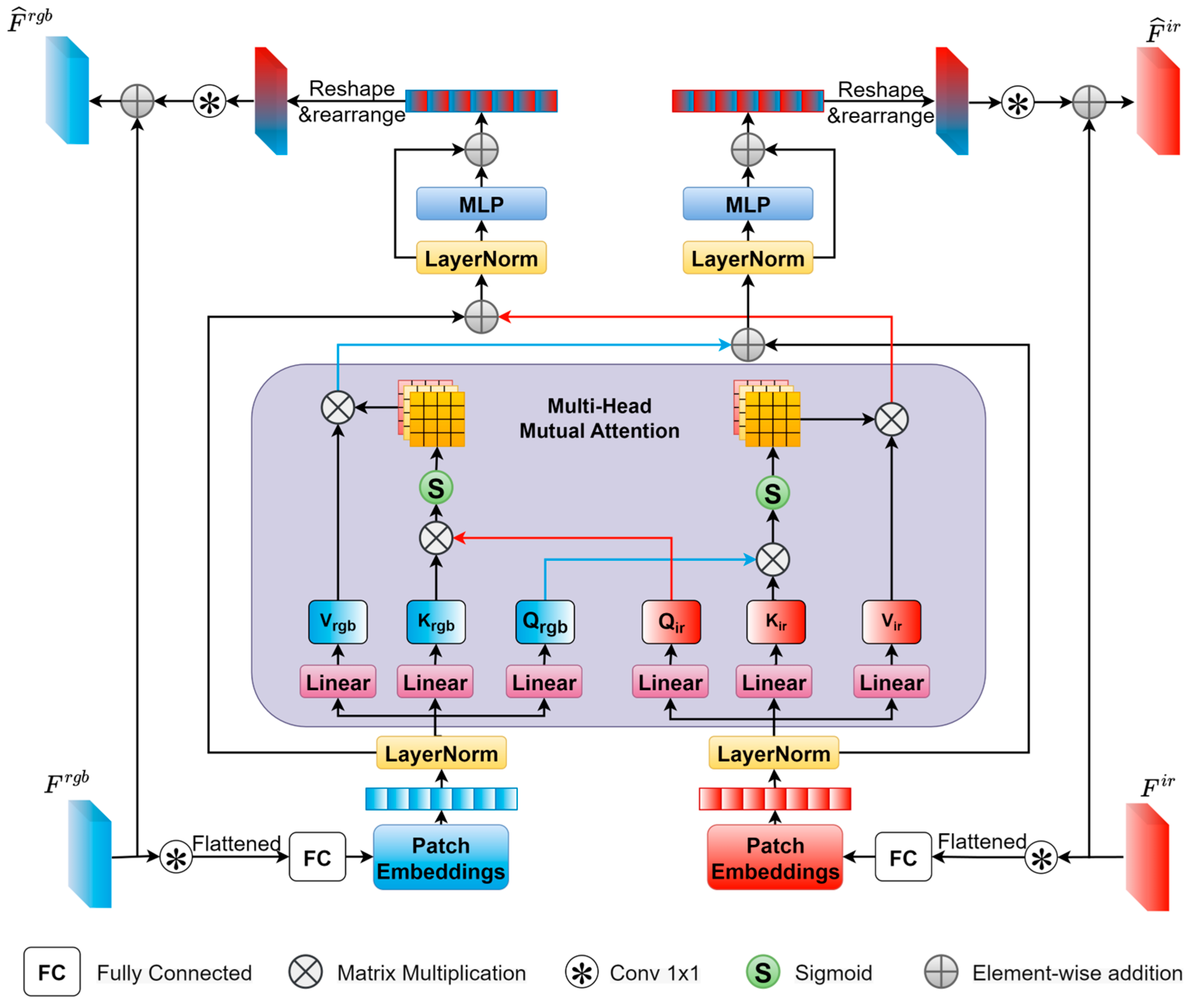
- We introduce a feature interaction module (FIM) employing cross-attention mechanisms to model long-range inter-modal dependencies while implementing dynamic feature selection for noise suppression.
- (4)
- We design a feature correction fusion module (FCFM) that performs spatial boundary alignment and channel-wise consistency optimization through novel correction mechanisms.
2. Methodology
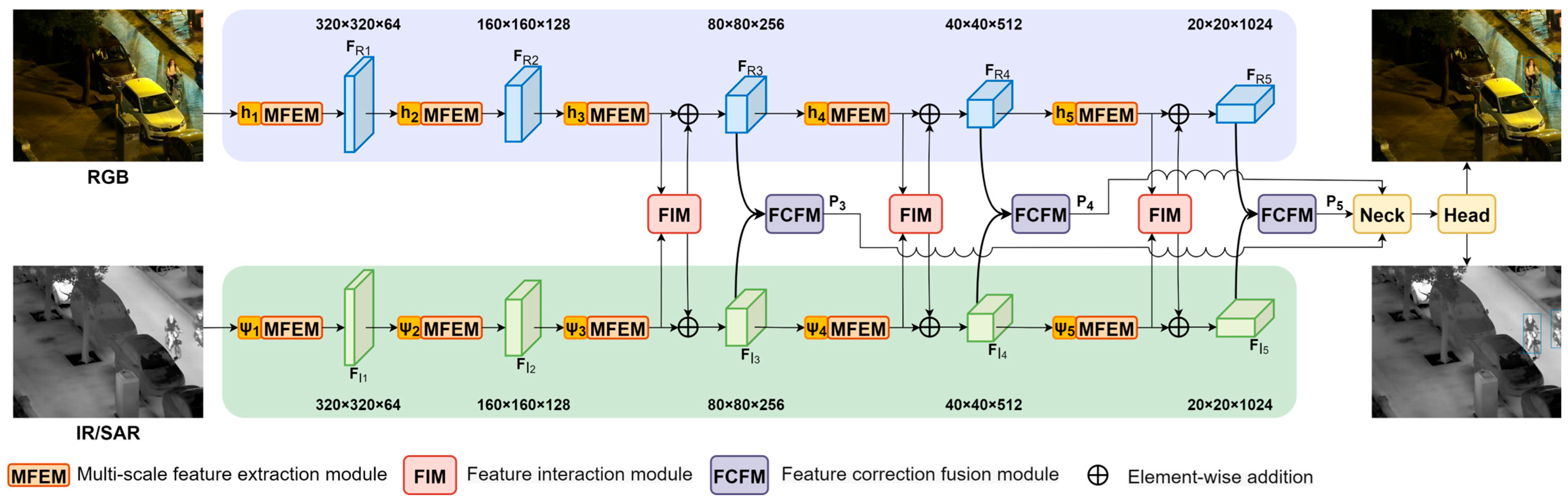
2.1. Problem Formulation and Network Overview
2.2. Multi-Scale Feature Extraction Module
2.3. Feature Interaction Module
2.4. Feature Correction Fusion Module
- (a)
- Spatial correction first processes concatenated features:
- (b)
- Channel correction then performs global optimization:
3. Experiments
3.1. Datasets
- (a)
- LLVIP. The LLVIP dataset is a highly challenging multi-spectral dataset for pedestrian detection under low-light conditions. Collected in low-light environments, this dataset makes accurate pedestrian detection in the RGB modality extremely challenging. The dataset comprises 12,025 pairs of aligned RGB-T images in the training set and 3463 pairs of images in the validation set, with each image having a resolution of 1024 × 1280.
- (b)
- OGSOD. The OGSOD dataset is a recently released optical-SAR paired dataset for cross-modal remote sensing object detection. It includes a training set with 14,665 image pairs and a test set with 3666 image pairs, containing over 48,000 instance annotations in total. All images have a size of 256 × 256. Three categories are annotated, including bridges, tanks, and ports.
- (c)
- Drone Vehicle. The Drone Vehicle dataset is a large-scale aerial optical-infrared dataset captured by drones, containing 28,439 image pairs and 953,087 vehicle annotation instances. This dataset covers a variety of scenes, including urban roads, residential areas, parking lots, and varying lighting conditions from day to night. The dataset is divided into five vehicle categories (cars, buses, trucks, vans, and cargo vehicles) and provides rich oriented bounding box annotations. To facilitate processing, the white borders of the images were removed, and the image size was uniformly adjusted to 640 × 512.
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.4. Comparison with Existing Methods
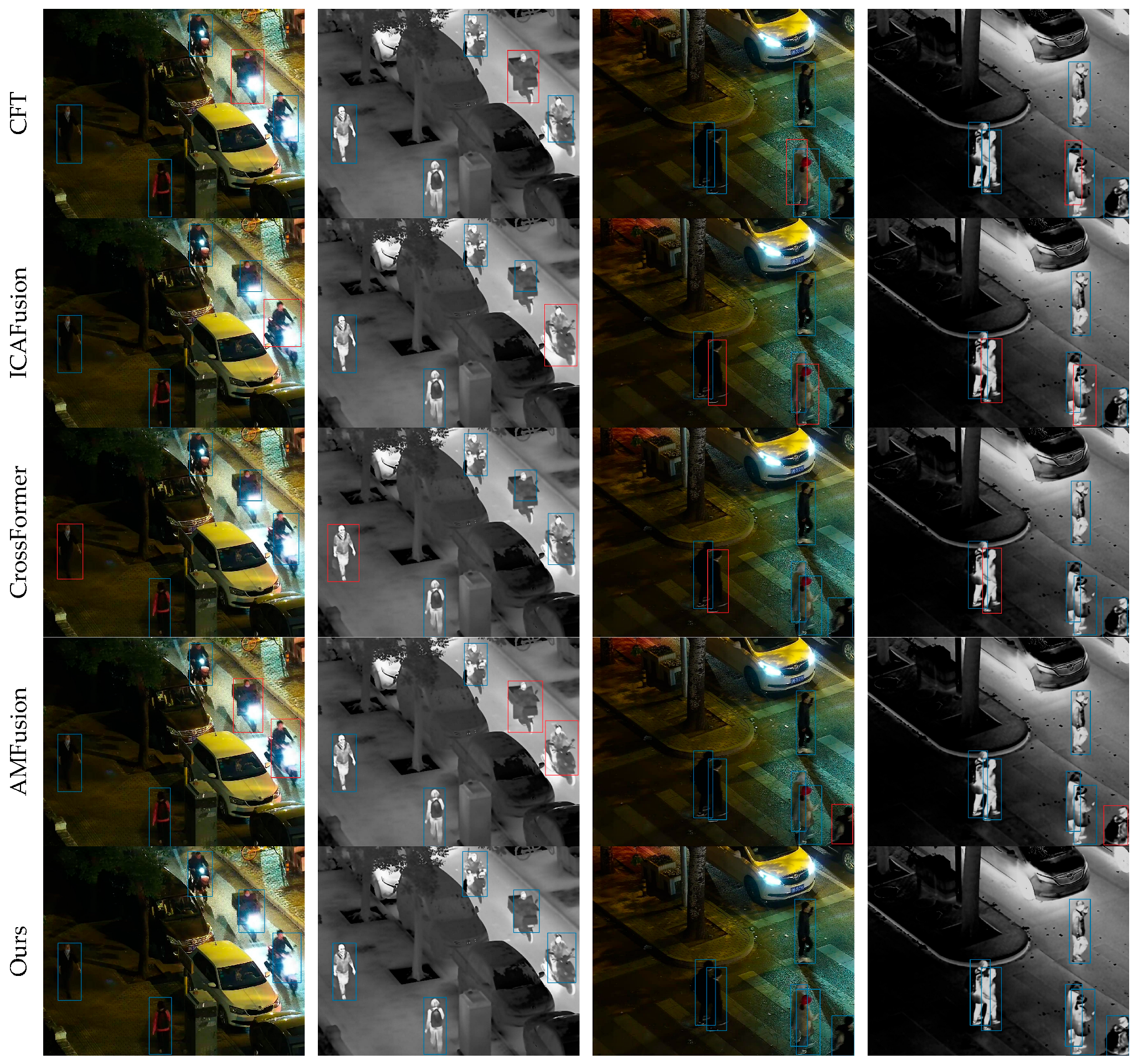
3.5. Visualization Results
3.6. Ablation Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.; Franklin, K.A.; Nicoll, M.A.; Cole, N.C.; Ruhomaun, K.; Tatayah, V.; Mackiewicz, M. Improving object detection for time-lapse imagery using temporal features in wildlife monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Tang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Feng, X.; Shi, H.; Hao, W. DCN-YOLO: A Small-Object Detection Paradigm for Remote Sensing Imagery Leveraging Dilated Convolutional Networks. Sensors 2025, 25, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. CenterNet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kieu, M.; Bagdanov, A.D.; Bertini, M.; Del Bimbo, A. Domain adaptation for privacy-preserving pedestrian detection in thermal imagery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Trento, Italy, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection via Simultaneous Detection and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2018, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kieu, M.; Bagdanov, A.D.; Bertini, M.; Del Bimbo, A. Task-conditioned domain adaptation for pedestrian detection in thermal imagery. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chi, Y.; Shen, T.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Improving RGB-Infrared Object Detection by Reducing Cross-Modality Redundancy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Huang, K.; Hussain, A. Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Q. Drone-based RGB-infrared cross-modality vehicle detection via uncertainty-aware learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6700–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Xue, X.; Wen, H.; Ji, Y.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. Misaligned visible-thermal object detection: A drone-based benchmark and baseline. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 7449–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wei, X. C2Former: Calibrated and complementary transformer for RGB-infrared object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5403712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Si, B.; Zhang, D.; Kou, R.; Yu, Y.; Feng, C. YOLOFIV: Object detection algorithm for around-the-clock aerial remote sensing images by fusing infrared and visible features. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 15269–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingyun, F.; Dapeng, H.; Zhaokui, W. Cross-Modality Fusion Transformer for Multispectral Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefevre, S.; Avignon, B. Multispectral fusion for object detection with cyclic fuse-and-refine blocks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.T.; Shi, J.; Ye, Z.; Mertz, C.; Ramanan, D.; Kong, S. Multimodal object detection via probabilistic ensembling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Bin, J.; Hamari, J.; Blasch, E.; Liu, Z. Multimodal object detection by channel switching and spatial attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 18–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Huang, M.; Hu, J.; Xiang, X. Dual-Dynamic Cross-Modal Interaction Network for Multimodal Remote Sensing Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5401013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Yeo, D.; Yim, J.; Kim, N.S.; Pyo, C.S.; Kim, J. Densely distilled flow-based knowledge transfer in teacher-student framework for image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5698–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Cui, Q.; Song, R.; Qiu, Y.; Liang, J. Decoupled knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Ye, R.; Wang, P.; Ren, D.; Zuo, W.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M. Localization distillation for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ruan, R.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Category-oriented localization distillation for SAR object detection and a unified benchmark. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5211314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.M.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Yu, Y. TransXNet: Learning Both Global and Local Dynamics with a Dual Dynamic Token Mixer for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 11534–11547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Improving Multispectral Pedestrian Detection by Addressing Modality Imbalance Problems. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. BAANet: Learning Bi-directional Adaptive Attention Gates for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, D. Cross-modality complementary information fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 10361–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.; Park, J. CrossFormer: Cross-guided attention for multi-modal object detection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 179, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot Multibox Detector. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G. YOLOv5 by Ultralytics. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Qi, Y.; Yang, S.; Jia, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. An Investigation of Infrared Small Target Detection by Using the SPT–YOLO Technique. Technologies 2025, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefèvre, S.; Avignon, B. Guided Attentive Feature Fusion for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Ma, J. DIVFusion: Darkness-free Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Fan, H.; Yang, W. ICAFusion: Iterative Cross-Attention Guided Feature Fusion for Multispectral Object Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, T.; Lin, C.W. Beyond Night Visibility: Adaptive Multi-scale Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01083. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F. MambaDFuse: A Mamba-based Dual-phase Model for Multi-modality Image Fusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.08406. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. RepPoints: Point Set Representation for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-Based and Anchor-Free Detection via Adaptive Training Sample Selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Savvides, M.; Zhang, X. Bounding Box Regression with Uncertainty for Accurate Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, T.; Xu, C.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-End Object Detection with Learnable Proposals. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zand, M.; Etemad, A.; Greenspan, M. ObjectBox: From Centers to Boxes for Anchor-Free Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align Deep Features for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q. Learning RoI Transformer for Oriented Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Althoupety, A.; Wang, L.Y.; Feng, W.C.; Rekabdar, B. DAFF: Dual Attentive Feature Fusion for Multispectral Pedestrian Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–24 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. COMO: Cross-Mamba Interaction and Offset-Guided Fusion for Multimodal Object Detection. Inf. Fusion 2026, 125, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Meng, F.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; He, M.; Li, H. GM-DETR: Generalized Multispectral Detection Transformer with Efficient Fusion Encoder for Visible-Infrared Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–24 June 2024. [Google Scholar]

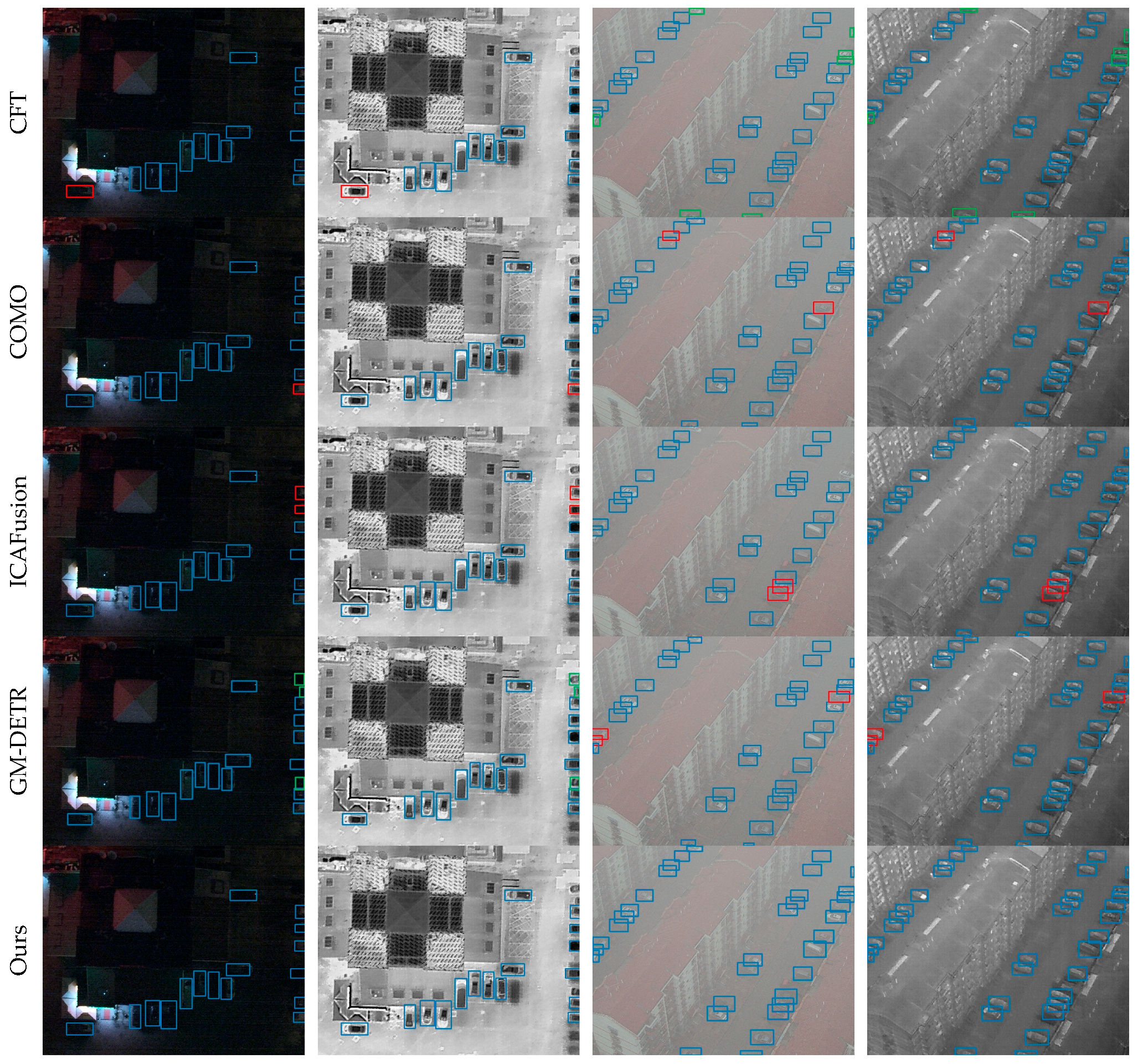
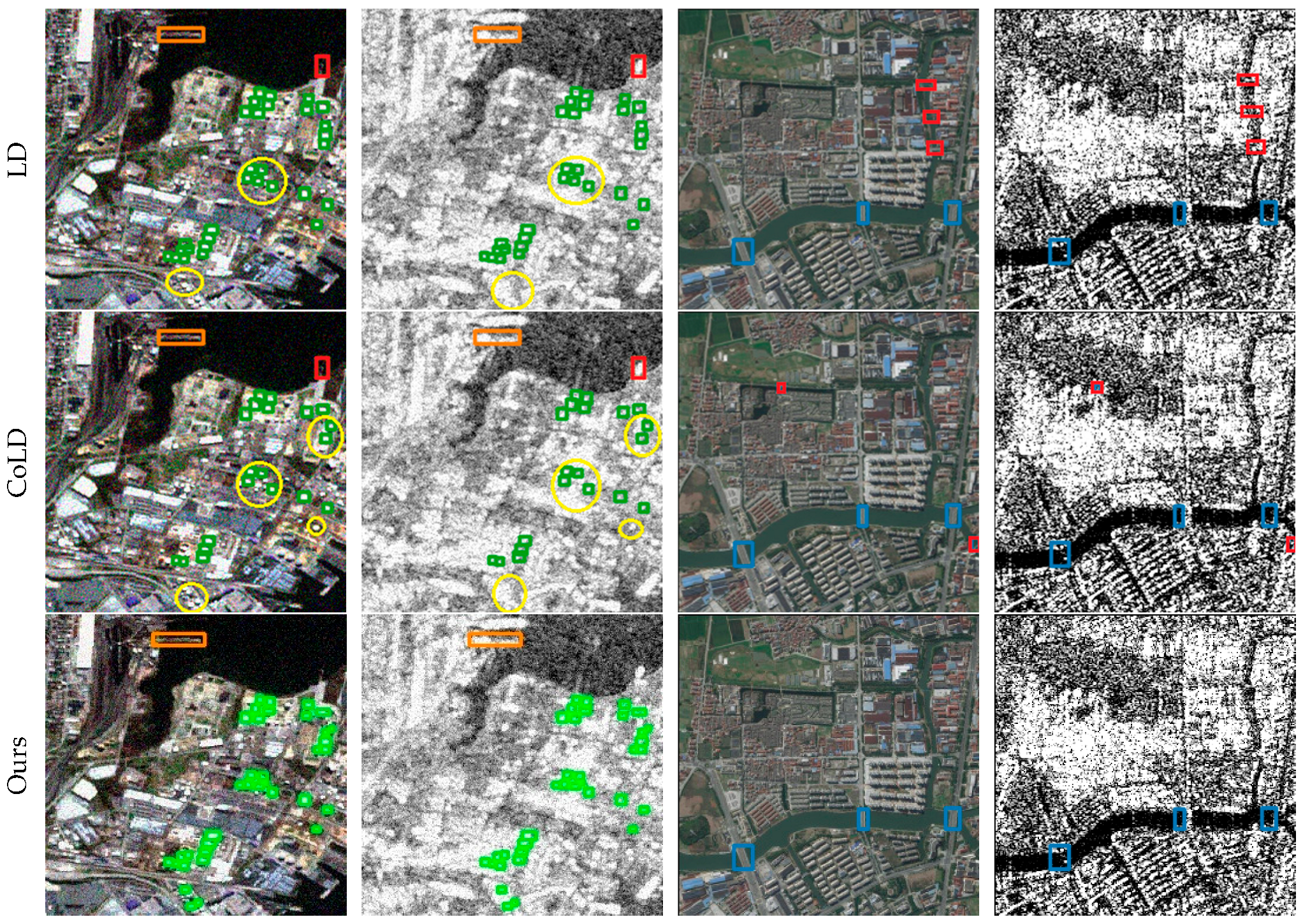

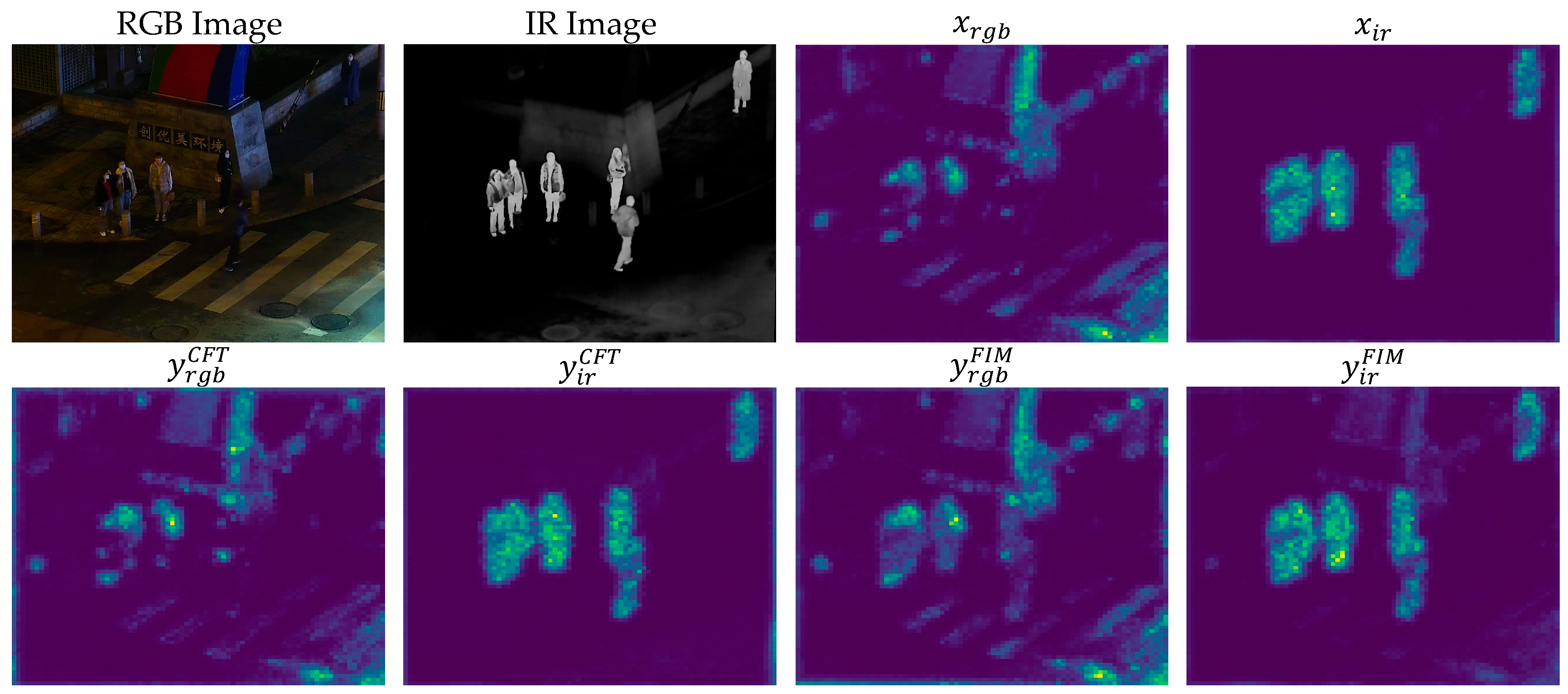

| Modality | Method | mAP50 | mAP75 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR | Faster R-CNN | 92.6 | 48.8 | 50.7 |
| SSD [35] | 90.2 | 57.9 | 53.5 | |
| YOLOv3 | 89.7 | 53.4 | 52.8 | |
| YOLOv5 [36] | 94.6 | 72.2 | 61.9 | |
| YOLOv8 [37] | 95.2 | - | 62.1 | |
| RGB | Faster R-CNN | 88.8 | 45.7 | 47.5 |
| SSD | 82.6 | 31.8 | 39.8 | |
| YOLOv3 | 85.9 | 37.9 | 43.4 | |
| YOLOv5 | 90.8 | 51.9 | 50.0 | |
| YOLOv8 | 91.9 | - | 54.0 | |
| RGB+IR | Halfway Fusion [38] | 91.4 | 60.1 | 55.1 |
| GAFF | 94.0 | 60.2 | 55.8 | |
| CFT | 97.5 | 72.9 | 63.6 | |
| ProbEN | 93.4 | 50.2 | 51.5 | |
| CSSA | 94.3 | 66.6 | 59.2 | |
| DIVFusion [39] | 89.8 | 59.9 | 52.0 | |
| CCFINet | 97.6 | 72.6 | 64.1 | |
| ICAFusion [40] | 96.9 | 71.5 | 62.2 | |
| CrossFormer | 97.4 | 76.3 | 66.1 | |
| AMFusion [41] | 96.5 | 70.1 | 60.3 | |
| MambaDFuse [42] | 95.6 | 66.4 | 59.3 | |
| Ours | 97.9 | 76.5 | 66.3 |
| Modality | Method | Year | Oil Tank | Bridge | Harbor | mAP50 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | RetinaNet | 2017 | 17.3 | 73.3 | 95.3 | 62.0 | 36.7 |
| YOLOv3 | 2018 | 32.4 | 76.0 | 97.0 | 68.5 | 39.5 | |
| ATSS [43] | 2019 | 26.2 | 78.0 | 96.3 | 66.8 | 38.6 | |
| YOLOv5 | 2020 | 57.7 | 87.2 | 97.9 | 80.9 | 46.3 | |
| RepPoints [44] | 2020 | 30.4 | 70.8 | 95.4 | 65.5 | 37.9 | |
| Generalized Focal [45] | 2020 | 33.4 | 72.8 | 96.5 | 67.6 | 41.8 | |
| Sparse R-CNN [46] | 2021 | 28.7 | 73.8 | 94.2 | 65.6 | 38.7 | |
| Object BOX [47] | 2022 | 51.0 | 82.4 | 96.5 | 76.6 | 40.1 | |
| YOLOv7 [48] | 2022 | 59.7 | 79.8 | 98.1 | 79.2 | 45.1 | |
| RGB+SAR | KD | 2020 | 60.3 | 88.4 | 98.8 | 82.6 | 48.4 |
| GI Imitation | 2021 | 69.2 | 92.9 | 99.1 | 87.1 | 55.9 | |
| DKD | 2022 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 98.7 | 83.4 | 49.8 | |
| LD | 2022 | 65.7 | 65.7 | 98.3 | 84.5 | 51.9 | |
| CoLD | 2023 | 69.8 | 69.8 | 99.5 | 87.6 | 56.7 | |
| Ours | 2025 | 94.9 | 99.3 | 99.7 | 94.5 | 58.6 |
| Modality | Method | Car | Truck | Freight Car | Bus | Van | mAP0.5 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR | YOLOv5 | 90.0 | 59.5 | 60.8 | 89.5 | 53.8 | 70.7 | - |
| YOLOV8 | 87.96 | 54.55 | 17.05 | 86.16 | 24.90 | 54.12 | - | |
| S2A-Net [49] | 89.7 | 51.0 | 50.2 | 89.0 | 44.0 | 64.8 | 67.5 | |
| Faster R-CNN | 89.4 | 53.5 | 48.3 | 87.0 | 42.6 | 64.2 | - | |
| ROI Transformer [50] | 89.6 | 51.0 | 53.4 | 88.9 | 44.5 | 65.5 | 70.3 | |
| Oriented R-CNN [51] | 89.6 | 53.9 | 53.9 | 89.2 | 41.0 | 65.5 | 67.0 | |
| RGB | YOLOv5 | 78.6 | 55.3 | 43.8 | 87.1 | 46.0 | - | 62.1 |
| YOLOv8 | 70.12 | 54.55 | 18.2 | 82.05 | 22.38 | 48.57 | - | |
| S2A-Net | 79.9 | 50.0 | 36.2 | 82.8 | 37.5 | 57.3 | 61.0 | |
| Faster R-CNN | 79.0 | 49.0 | 37.2 | 77.0 | 37.0 | - | 55.9 | |
| ROI Transformer | 61.6 | 55.1 | 42.2 | 85.5 | 44.8 | 61.6 | 61.6 | |
| Oriented R-CNN | 80.3 | 55.4 | 42.1 | 86.8 | 46.9 | 62.3 | 60.8 | |
| RGB+IR | CFT | 98.5 | 75.0 | 68.5 | 82.3 | 97.3 | 84.3 | 61.9 |
| DDCI | 91.0 | 78.9 | 66.1 | 90.7 | 65.5 | 78.4 | - | |
| CMADet | 98.2 | 70.4 | 66.4 | 78.3 | 96.8 | 82.0 | 59.5 | |
| DaFF [52] | 92.2 | 58.9 | 58.2 | 71.9 | 94.4 | 75.1 | 45.5 | |
| YOLOFIV | 95.89 | 64.23 | 34.57 | 91.56 | 37.29 | 64.71 | - | |
| C2Former | 90.2 | 68.3 | 64.4 | 89.8 | 58.5 | 74.2 | 70.0 | |
| ICAFusion | 96.1 | 46.4 | 34.0 | 57.1 | 92.2 | 65.1 | 44.0 | |
| COMO [53] | 98.6 | 78.9 | 71.5 | 84.1 | 97.4 | 86.1 | 65.5 | |
| UA-CMDet | 88.6 | 73.0 | 56.0 | 88.3 | 54.8 | 72.2 | 64.0 | |
| GM-DETR [54] | 92.4 | 75.3 | 64.9 | 80.8 | 90.8 | 80.8 | 55.9 | |
| Ours | 98.7 | 83.1 | 75.8 | 97.3 | 97.6 | 86.3 | 71.7 |
| Methods | Params (M) | Flops@640 (G) | FPS (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFT | 44.76 | 17.92 | 91.74 |
| SuperYOLO | 4.83 | 17.98 | 89.4 |
| GHOST | 7.06 | 20.36 | 125.6 |
| MFPT | 47.65 | 34.55 | 51.2 |
| ICAFusion | 20.15 | 14.93 | 217.4 |
| GM-DETR | 70.00 | 176.00 | 45.6 |
| DaFF | 45.42 | 18.45 | 85.2 |
| CMADet | 33.33 | 16.86 | 208.3 |
| Ours | 68.43 | 14.36 | 226.2 |
| Dataset | Modality | Method | mAP50 | mAP75 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLVIP | IR | Baseline | 94.6 | 72.2 | 61.9 |
| RGB | 90.8 | 51.9 | 50.0 | ||
| RGB+IR | + Two Stream | 95.8 | 71.4 | 62.3 | |
| + MSFEM | 96.3 | 73.5 | 63.5 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM | 97.1 | 75.3 | 64.7 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM + FCFM | 97.9 (3.3⬆) | 76.5 (4.3⬆) | 66.3 (4.4⬆) | ||
| OGSOD | RGB | Baseline | 80.9 | 50.31 | 46.3 |
| SAR | 78.7 | 35.5 | 40.2 | ||
| RGB+SAR | + Two Stream | 81.4 | 58.3 | 45.63 | |
| + MSFEM | 86.2 | 65.0 | 49.78 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM | 88.9 | 68.2 | 53.4 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM + FCFM | 94.5 (13.6⬆) | 74.3 (23.99⬆) | 58.6 (12.3⬆) | ||
| Drone Vehicle | IR | Baseline | 80.8 | 58.7 | 60.2 |
| RGB | 74.6 | 46.9 | 46.7 | ||
| RGB+IR | + Two Stream | 81.3 | 64.6 | 63.4 | |
| + MSFEM | 84.1 | 69.58 | 68.3 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM | 85.3 | 72.48 | 69.7 | ||
| + MSFEM + FIM + FCFM | 86.3 (5.5⬆) | 76.4 (17.7⬆) | 71.7 (8.1⬆) |
| FCFM | mAP50 | mAP75 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel → Spatial | 96.4 | 73.3 | 63.5 |
| Spatial → Channel | 97.9 | 76.5 | 66.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. A Modality Alignment and Fusion-Based Method for Around-the-Clock Remote Sensing Object Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164964
Qi Y, Yang S, Chen J, Zhang M, Zhu J, Liu X, Zheng H. A Modality Alignment and Fusion-Based Method for Around-the-Clock Remote Sensing Object Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164964
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yongjun, Shaohua Yang, Jiahao Chen, Meng Zhang, Jie Zhu, Xin Liu, and Hongxing Zheng. 2025. "A Modality Alignment and Fusion-Based Method for Around-the-Clock Remote Sensing Object Detection" Sensors 25, no. 16: 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164964
APA StyleQi, Y., Yang, S., Chen, J., Zhang, M., Zhu, J., Liu, X., & Zheng, H. (2025). A Modality Alignment and Fusion-Based Method for Around-the-Clock Remote Sensing Object Detection. Sensors, 25(16), 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164964





