Towards Intelligent Assessment in Personalized Physiotherapy with Computer Vision
Abstract
Highlights
- YOLO Pose can detect physiotherapy-relevant body keypoints with sufficient speed and efficiency for real-time applications.
- A semantic framework was developed to map pose estimation data into clinically interpretable parameters like strength, balance, and coordination.
- Automated motion analysis can improve objectivity and consistency in physiotherapy assessments.
- The proposed approach reduces the time spent on manual evaluation and supports data-driven clinical decision making.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Is the YOLO Pose algorithm suitable for detecting physiotherapy-relevant keypoints from sensor data obtained with cameras?
- If it is not sufficient, can its precision be improved through neural network modifications?
- Is it possible to develop a semantic model that translates keypoint data into meaningful clinical parameters?
2. Related Works
2.1. Evolution of Physiotherapy and the Role of Sensors
2.2. Clinical Assessment Scales in Physiotherapy
2.3. Challenges in Mapping Sensor Data to Clinical Scales
2.4. Applications of Computer Vision in Physiotherapy
2.5. YOLO Pose for Movement Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations in the Use of Advanced Technologies
2.7. Strategies for Improving Pose Estimation Algorithms
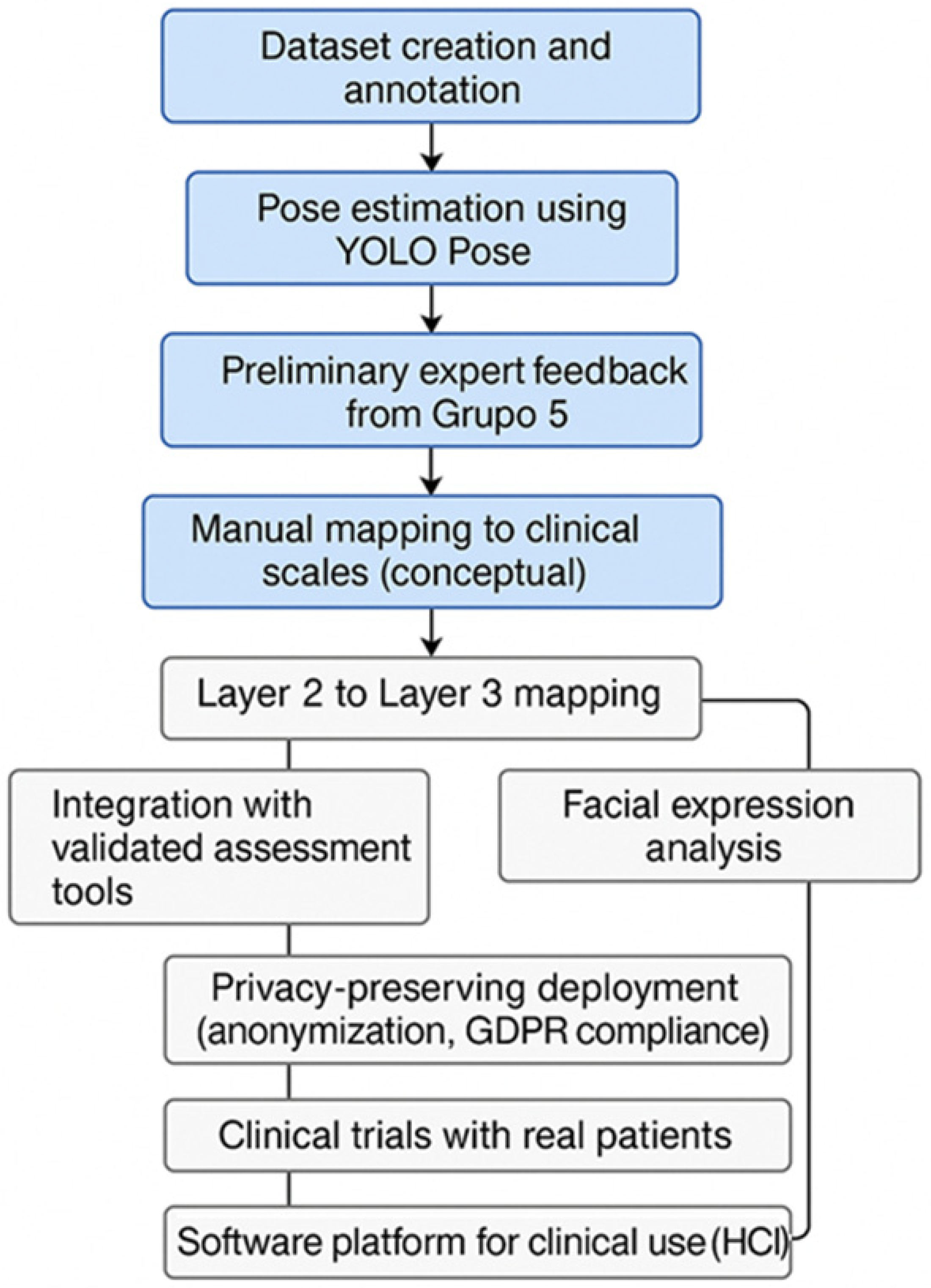
3. Methodology
3.1. Evaluating YOLO Pose to Address the Identified Issues
3.2. Creation of the Image Dataset
- A simple program was created in Visual Basic to segregate the images from different videos and to organize the datasets into training, validation, and test sets. Approximately 1000 images were selected as the dataset.
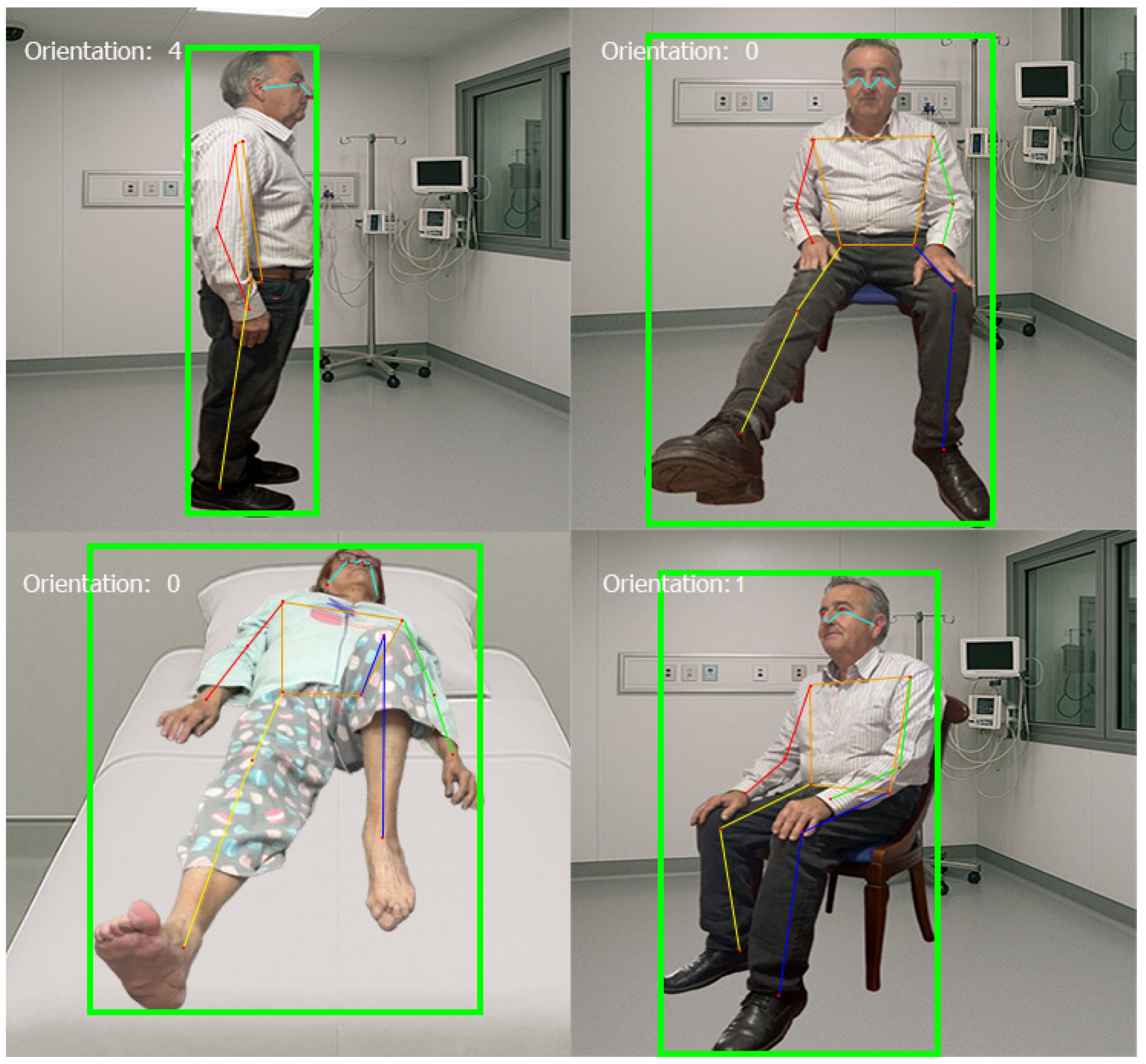
- Once the necessary images for training were obtained, they were annotated using Computer Vision Annotation Tool (CVAT) software. CVAT is an open-source annotation tool designed for creating labeled images and video datasets, specifically for computer vision tasks (see Figure 1). CVAT allows users to draw bounding boxes, polygons, and keypoints on images, thus facilitating data preparation for machine learning models. More information on CVAT can be found in its official GitHub repository (https://github.com/cvat-ai/cvat (accessed on 14 February 2025)).

3.3. Modifications to the YOLOv8-Pose-p6 Network
3.3.1. Original Network Configuration (YOLOv8-Pose-p6)
- Number of Classes (nc): Configured for a single class, considering the person as the only object of interest.
- Keypoint Shape (kpt_shape): Determines 17 keypoints with coordinates (X, Y) and a visibility indicator.
- Model Scale: Depth, width, and maximum number of channels set to [1.00, 1.25, 512].
- Architecture:
- ✓
- Backbone: Composed of convolutional layers and C2f blocks, with Spatial Pyramid Pooling—Fast (SPPF) to capture features at different scales.
- ✓
- Head: Includes upsampling operations and concatenations to integrate information from different levels, culminating in a structure specialized in pose estimation.
3.3.2. Modifications
3.4. Training Characteristics
- Data Parallelism: 8 Dataloader Workers to optimize data loading.
- Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP): Reduces memory consumption without affecting accuracy.
- Data Augmentation: Real-time transformations applied with Albumentations to enhance model generalization.
- Batch Size: Adjusted based on available memory (batch size of 64).
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use of TensorBoard for process adjustment and optimization.
3.5. Training Hyperparameters
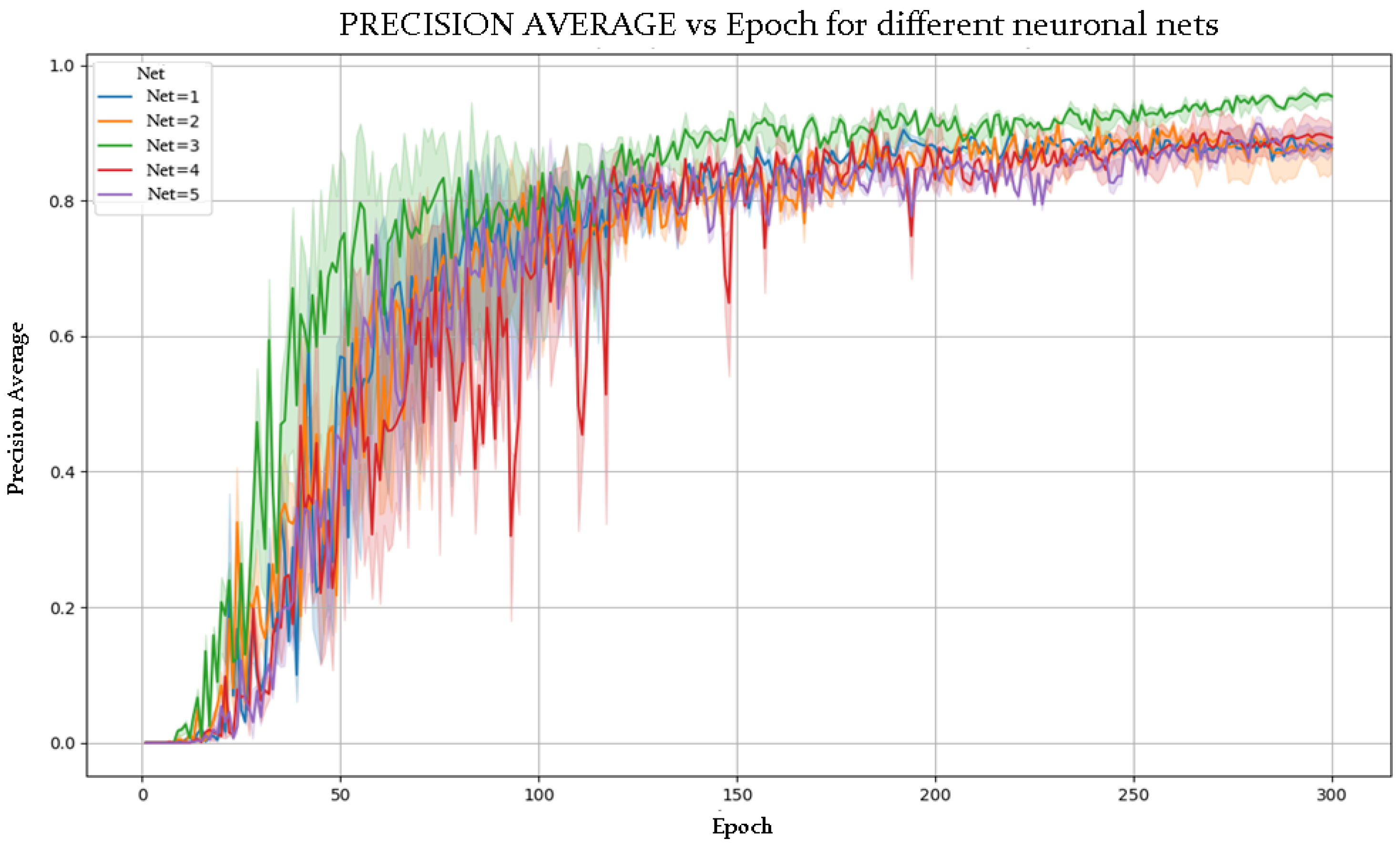
- Number of Epochs: 300, ensuring sufficient exposure to the data.
- Number of Runs: 5, to evaluate performance variance.
- Image Size: 640 × 640 px, balancing efficiency and small detail detection.
- Optimizer: AdamW with automatic learning rate and momentum adjustment.
- Data Augmentation: Application of Blur, MedianBlur, ToGray, and CLAHE to improve model robustness.
- Single-Class Training: Training with single_cls = True, optimizing detection for a single object type.
3.6. Data Extraction for a Common Semantics
3.6.1. Data Acquisition: Controlled Recording Environment
- Adequate space for unrestricted movement.
- Consistent lighting to avoid image distortions.
- Fixed high-resolution cameras to accurately capture movement.
- Specialized recording software for video analysis and data storage.
3.6.2. Data Extraction and Key Parameters
- Bounding Box Data: Position and size of the detected person.
- Keypoints: 17 skeletal keypoints (e.g., head, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, ankles).
- Timestamps: Capturing motion in milliseconds.
- Future Considerations: Facial expression analysis and finer joint detection.
3.6.3. Data Processing: Transformation into Physiotherapy Metrics
- Modification 1 (Increased Depth) aimed to improve the extraction of complex spatial features at the first and second layers, enhancing the quality of keypoint localization and movement trajectory accuracy.
- Modification 2 (Subsampling Adjustment and Activation Functions) targeted the retention of fine-grained spatial details and optimized gradient flow, improving the computation of joint angles and velocities at the second layer.
- Modification 3 (Incorporation of Normalization) focused on increasing the stability of feature extraction across training, ensuring more consistent pose detection relevant to all three layers.
- Modification 4 (Normalization and ReLU in Final Stage) enhanced the reliability of outputs at the third layer, facilitating better mapping of extracted metrics to clinical scales.
4. Results
4.1. Preliminary Evaluation of YOLO Pose to Address the Identified Issues
4.2. Modification and Training of the YOLOv8x-Pose-p6 Neural Network
4.3. Constructing a Common Semantics
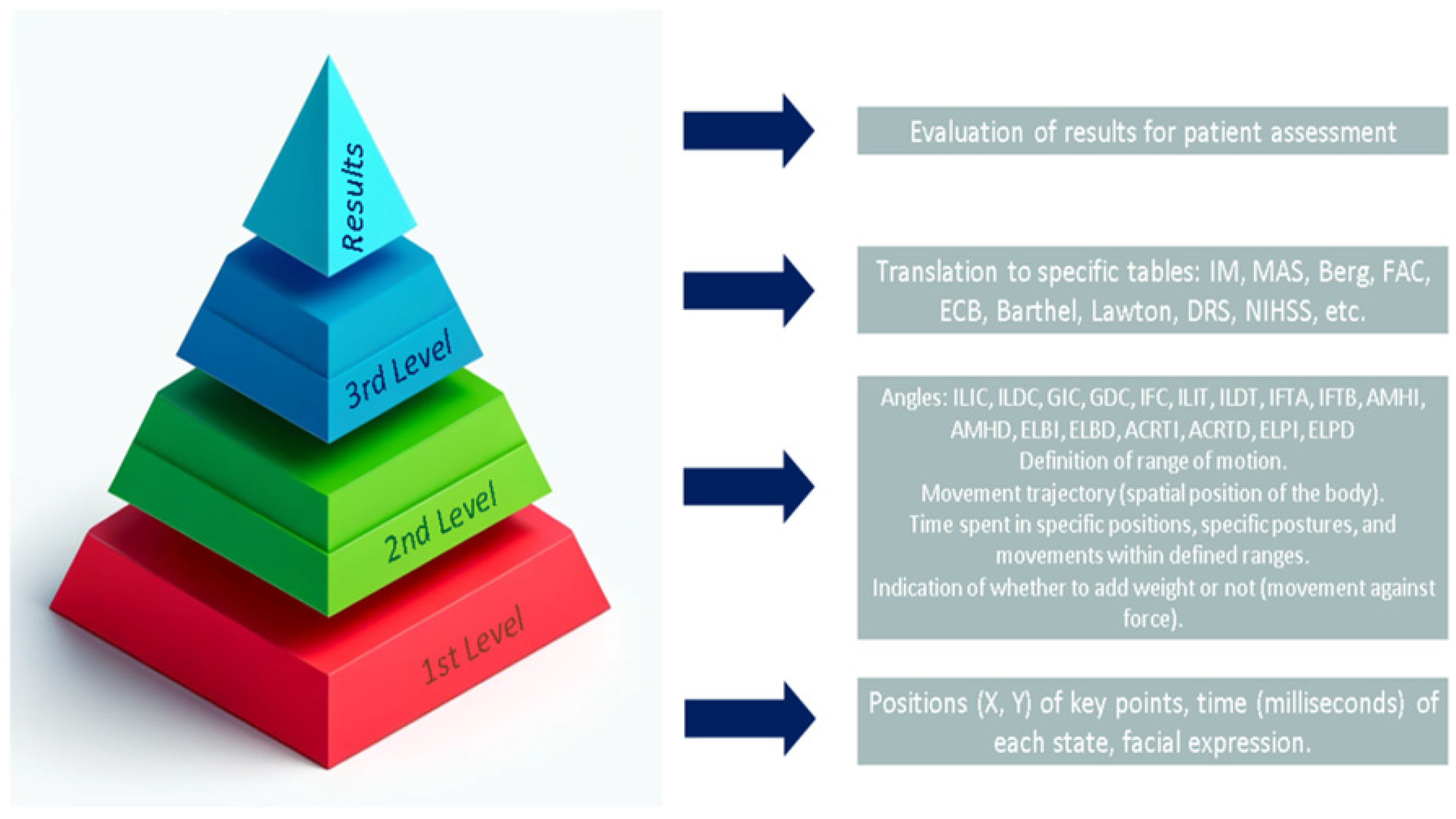
4.3.1. First Abstraction Layer
- Bounding Box: Position (X, Y) and width and height of the bounding box for the “person” class.
- Keypoints: Position (X, Y) of 17 keypoints: 0: Nose, 1: Left Eye, 2: Right Eye, 3: Left Ear, 4: Right Ear, 5: Left Shoulder, 6: Right Shoulder, 7: Left Elbow, 8: Right Elbow, 9: Left Wrist, 10: Right Wrist, 11: Left Hip, 12: Right Hip, 13: Left Knee, 14: Right Knee, 15: Left Ankle, and 16: Right Ankle.
- Time: The recorded time in milliseconds when the above parameters were obtained.
4.3.2. Second Abstraction Layer
The Importance of Setting the Orientation
- Inclination and Rotation Angles: Keypoints corresponding to the head, torso, arms, and legs are used to calculate inclination and rotation angles relative to anatomical axes. These angles (e.g., lateral head tilt, head rotation, lateral trunk tilt) allow for the evaluation of symmetry, posture control, and compensatory patterns (see Table 10, columns 1–3).
- Time: For each detected motion, the system computes the time spent within defined angular ranges (e.g., 0–30°, 30–60°, 60–90°). This provides an objective measure of endurance and postural stability, particularly important in balance and gait assessments.
- Angular Velocity and Acceleration: These parameters are derived by calculating the time derivatives of inclination and rotation angles. They quantify the speed and dynamic control of transitions between positions, which are critical for assessing neuromuscular coordination.
- Variation of Spatial Position Over Time: By tracking the changes in spatial position over successive frames, the system measures the stability of the patient’s posture and gait, identifying sways, tremors, or balance issues.
- With or Without Weight: Some assessments involve evaluating the patient’s movements under additional load (e.g., with weighted objects or resistance). This parameter indicates whether the performance differences observed are influenced by external force application, which is crucial for assessing strength and compensatory strategies.
General Solutions from Abstraction Layer 2
4.3.3. Third Layer
5. Discussion
5.1. Architectural Improvements in Pose Estimation
5.2. Superior Performance of NETWORK 3
5.3. Design of the Evaluation Environment in Physiotherapy
5.4. Technological Infrastructure and Parameter Analysis
5.5. Integration with Clinical Evaluation Tools
5.6. Levels of Abstraction and Clinical Usability
5.7. Scalability and Deployment Scenarios
5.8. Common Pose Estimation Errors and Mitigation Strategies
- Incorporating diverse training data with varied lighting, orientations, and morphologies.
- Modifying the network architecture to preserve spatial information and reduce feature loss through downsampling.
- Applying anatomical plausibility checks in post-processing to identify inconsistent joint configurations.
5.9. User Interaction and Workflow Integration
6. Conclusions
- Layer 1: Extraction of raw pose data (keypoints and bounding boxes) from camera input using YOLO Pose.
- Layer 2: Computation of biomechanical parameters (angles, velocity, orientation) through geometric analysis and machine learning.
- Layer 3: Mapping of computed parameters to standardized clinical scales (e.g., MAS, MI, BBS), enabling objective physiotherapy assessment.
7. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonanno, M.; De Nunzio, A.M.; Quartarone, A.; Militi, A.; Petralito, F.; Calabrò, R.S. Gait Analysis in Neurorehabilitation: From Research to Clinical Practice. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesar, T.M.; Reisman, D.S.; Perumal, R.; Jancosko, A.M.; Higginson, J.S.; Rudolph, K.S.; Binder-Macleod, S.A. Combined effects of fast treadmill walking and functional electrical stimulation on post-stroke gait. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.-S.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A Review of Wearable Sensors and Systems with Application in Rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ge, D.; Miao, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, L. Vision-Based Method for Automatic Quantification of Parkinsonian Bradykinesia. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippenberg, E.; Verbrugghe, J.; Lamers, I.; Palmaers, S.; Timmermans, A.; Spooren, A. Markerless motion capture systems as training device in neurological rehabilitation: A systematic review of their use, application, target population and efficacy. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordt, K.; Gerhardy, T.; Najafi, B.; Schwenk, M. Effects of Wearable Sensor-Based Balance and Gait Training on Balance, Gait, and Functional Performance in Healthy and Patient Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Gerontology 2017, 64, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulroy, S.; Gronley, J.; Weiss, W.; Perry, J. Use of cluster analysis for gait pattern classification of patients in the early and late recovery phases following stroke. Gait Posture 2003, 18, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Adkins, D.L. Motor System Reorganization After Stroke: Stimulating and Training Toward Perfection. Physiology 2015, 30, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.W.T.; Tang, Y.M.; Fong, K.N.K. A systematic review of the applications of markerless motion capture (MMC) technology for clinical measurement in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Virtual Reality Gait Training to Promote Balance and Gait Among Older People: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Geriatrics 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Nau, C.L.; Crawford, W.W.; Schatz, M.; Zeiger, R.S.; Rozema, E.; Koebnick, C. Developing a Predictive Model for Asthma-Related Hospital Encounters in Patients With Asthma in a Large, Integrated Health Care System: Secondary Analysis. JMIR Med. Inform. 2020, 8, e22689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrowsmith, C.; Burns, D.; Mak, T.; Hardisty, M.; Whyne, C. Physiotherapy Exercise Classification with Single-Camera Pose Detection and Machine Learning. Sensors 2022, 23, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Or, C.K.; Chen, T. Effectiveness of Using Virtual Reality-Supported Exercise Therapy for Upper Extremity Motor Rehabilitation in Patients With Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Malaviya, S.; Barker, S. Reliability and Validity of Computer Vision Software to Monitor Joint Movement for Postoperative Physiotherapy. Orthop. Proc. 2023, 105, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv8-Ultralytics YOLO Docs. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Ultralytics. Pose Estimation-YOLO Docs. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/pose/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.-E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie Mellon Perceptual Computing Lab. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields. 2018. Available online: https://cmu-perceptual-computing-lab.github.io/openpose/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Lugaresi, C.; Tang, J.; Nash, H.; McClanahan, C.; Uboweja, E.; Hays, M.; Zhang, F.; Chang, C.L.; Yong, M.G.; Lee, J.; et al. MediaPipe: A Framework for Building Perception Pipelines. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08172. [Google Scholar]
- Mathis, A.; Mamidanna, P.; Cury, K.M.; Abe, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Mathis, M.W.; Bethge, M. DeepLabCut: Markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xie, S.; Tai, Y.-W.; Lu, C. RMPE: Regional Multi-person Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2334–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.-C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. PersonLab: Person Pose Estimation and Instance Segmentation with a Bottom-Up, Part-Based, Geometric Embedding Model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.-C.; Tan, M.; Chu, G.; Vasudevan, V.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Noohu, M.M.; Verma, S.; Singla, D.; Hussain, M.E. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance measures and proprioception among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Gait Posture 2019, 74, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Aldana, A.C.; Callejas-Cuervo, M.; Bo, A.P.L. Upper Limb Physical Rehabilitation Using Serious Video Games and Motion Capture Systems: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basteris, A.; Nijenhuis, S.M.; Stienen, A.H.A.; Buurke, J.H.; Prange, G.B.; Amirabdollahian, F. Training modalities in robot-mediated upper limb rehabilitation in stroke: A framework for classification based on a systematic review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.; Lane, H.C. How Students Search Video Captions to Learn: An Analysis of Search Terms and Behavioral Timing Data. In Proceedings of the 11th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference (LAK ’21), Irvine, CA, USA, 12–16 April 2021; pp. 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samkari, E.; Arif, M.; Alghamdi, M.; Al Ghamdi, M.A. Human Pose Estimation Using Deep Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1612–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data (General Data Protection Regulation). Off. J. Eur. Union 2016, 4, 177–184. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Beauchamp, T.; Childress, J. Principles of Biomedical Ethics, 7th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Marmot, M.; Allen, J.; Bell, R.; Bloomer, E.; Goldblatt, P. WHO European review of social determinants of health and the health divide. Lancet 2012, 380, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelechi, T.J.; Prentice, M.A.; Mueller, M.; Madisetti, M.; Vertegel, A. A Lower Leg Physical Activity Intervention for Individuals With Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ethics and Governance of Artificial Intelligence for Health: WHO Guidance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Dai, H.; Ye, M.; Zhu, C. Distribution-Aware Coordinate Representation for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7091–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; Volume 97, pp. 6105–6114. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/tan19a.html (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- Cao, Z.; Hidalgo, G.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.-E.; Sheikh, Y. OpenPose: Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, D.; Nagori, S.; Mathew, M.; Poddar, D. YOLO-Pose: Enhancing YOLO for Multi-Person Pose Estimation Using Object Keypoint Similarity Loss. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, J.; Santos, O.C. Toward modeling psychomotor performance in karate combats using computer vision pose estimation. Sensors 2021, 21, 8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Casas-Ortiz, A.; Echeverria, J.; Jimenez-Tellez, N.; Santos, O.C. Exploring the impact of partial occlusion on emotion classification from facial expressions: A comparative study of XR headsets and face masks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 44613–44627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaz, M.; Manjarrés Riesco, Á.; Santos, O.C. Human-Centered Recommender Systems. In Human-Centered AI: An Illustrated Scientific Quest; Germanakos, P., Juhász, M., Kongot, A., Marathe, D., Sacharidis, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Scale | Assessed Dimension | Measurement Type | Objectivity Level | Primary Functional Domain | Possible Correlation with Keypoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berg Balance Scale | Static and dynamic balance | Observational (scoring) | Medium | Postural control and stability | High: posture, center of gravity, sway |
| Motor Index | Muscle strength and motor control | Observational (ordinal scale) | Medium–high | Muscle strength and coordination | Moderate: range of motion, segment alignment |
| NIHSS | General neurological deficit (post-stroke) | Observational with specific tasks | Medium | Severity of neurological damage | Variable: depends on the item, some may map to fine or gross movements |
| FIM | Independence in daily living activities | Multidimensional functional scale | Medium | General functionality and independence | Low–Moderate: broad movements in ADLs, full functional patterns |
| Model | Accuracy | Speed (FPS) | Device Requirements | 2D/3D | Open Source | Suitability for Rehab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenPose | High | Low | GPU required | 2D | Yes | High (precise joints) |
| MediaPipe | Medium | High | Works on CPU | 2D | Yes | Medium (lightweight) |
| AlphaPose | High | Medium | GPU recommended | 2D | Yes | High (multiperson) |
| YOLO Pose | Medium–high | Very high | GPU/Edge support | 2D | Yes | High (real-time) |
| Modifications | Network Variant | Changes Introduced | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | YOLOv8-pose-p6_NC_PB | Increased repetitions in C2f blocks (3→4 and 6→8); Increased channels in last head layer (1024→1280) | Enhance abstraction capacity and deep feature fusion |
| 2 | YOLOv8-pose-p6_TS_FA | Reduced subsampling in the backbone; Replaced activation functions with ReLU and LeakyReLU | Improve spatial detail retention and training efficiency |
| 3 | YOLOv8-pose-p6_CN | Integrated BatchNorm2d layers in the network head | Improve training stability and enable higher learning rates |
| 4 | YOLOv8-pose-p6_CN_FA | Added BatchNorm and ReLU in the final stage | Improve final stage activation and overall generalization |
| Abstraction Layer | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| First Layer: Direct Data Extraction | Extraction of raw pose information from keypoints and bounding boxes. | Identification of anatomical keypoints; recording of movement trajectories. |
| Second Layer: Computational Analysis | Processing raw data to compute derived biomechanical parameters. | Calculation of joint angles, range of motion, velocity, acceleration; orientation classification via ML models (decision trees, SVM, random forest). |
| Third Layer: Mapping to Clinical Scales | Transformation of computed parameters into physiotherapy evaluation frameworks to facilitate standardized clinical assessment. | Motor Index (IM), Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), Berg Balance Scale, Barthel Index. |
| Code | Description | Applied Modifications | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | Baseline YOLOv8x-pose-p6 | None | Serve as performance reference. |
| C1 | Increased Depth (NC_PB) | Increased C2f repetitions and head channels | Enhance feature abstraction and deep fusion. |
| C2 | Subsampling Adjustment + Activation Functions (TS_FA) | Reduced subsampling; ReLU and LeakyReLU activations | Improve spatial detail retention and training efficiency. |
| C3 | Head Normalization (CN) | Added BatchNorm2d layers in the head | Stabilize training and improve generalization. |
| C4 | Final Stage Normalization + ReLU (CN_FA) | Added BatchNorm and ReLU at final stage | Improve final activation quality and output stability. |
| C5 | Increased Depth + Subsampling Adjustment | Combined C2f depth increase and subsampling reduction | Maximize feature richness and spatial accuracy. |
| C6 | Increased Depth + Head Normalization | Combined depth increase with head normalization | Improve deep feature learning and training stability. |
| C7 | Subsampling Adjustment + Head Normalization | Combined subsampling reduction and head normalization | Enhance spatial extraction while stabilizing the network. |
| C8 | Subsampling Adjustment + Final Stage Normalization | Combined subsampling reduction with final normalization | Preserve fine details and reinforce output stability. |
| C9 | Increased Depth + Subsampling Adjustment + Head Normalization | Combined depth increase, subsampling adjustment, and normalization | Maximize abstraction, spatial retention, and robustness. |
| NET | LOSS | PRECISION | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Average | Max | σ | Min | Average | Max | σ | |
| 1 | 2.812 | 4.485 | 1.128 | 1.872 | 0.000 | 0.646 | 0.917 | 0.308 |
| 2 | 2.595 | 4.005 | 1.081 | 1.597 | 0.000 | 0.708 | 0.938 | 0.262 |
| 3 | 2.390 | 3.743 | 1.069 | 1.632 | 0.000 | 0.779 | 0.969 | 0.269 |
| 4 | 2.356 | 4.162 | 1.070 | 1.829 | 0.000 | 0.675 | 0.954 | 0.292 |
| 5 | 2.778 | 4.334 | 1.169 | 1.801 | 0.000 | 0.690 | 0.946 | 0.275 |
| Class/Keypoint | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 0.91 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Neck | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.87 |
| Right Shoulder | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| Left Shoulder | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.88 |
| Right Elbow | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| Left Elbow | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.87 |
| Right Wrist | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| Left Wrist | 0.86 | 0.9 | 0.88 |
| Right Hip | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.88 |
| Left Hip | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Right Knee | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.9 |
| Left Knee | 0.9 | 0.87 | 0.88 |
| Right Ankle | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Left Ankle | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 |
| Assessment Scale | Strength | Stability | Mobility | Pain | Coordination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Barthel Index | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Berg Balance Scale (BBS) | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Motor Index (MI) | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Functional Ambulation Classification (FAC) | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ |
| Lawton and Brody IADL Scale | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Scale | LR | DT | RF | NB | KNN | SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (%) | 0.84 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.91 |
| Body Part | Parameters | Description | Computer Vision Detection | Detection Strategy | Analyzed Motion Ranges | Score by Range | Normalized Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | LHTL, LHTR | Lateral head tilt to the left (L) and right (R) | Analysis of the relative position of the head in the frontal body position | Establishing body orientation using AI strategies and calculating torsion angles based on detected keypoints. | 0–30° 30–60° 60–90° | [0–25] [25–50] [50–75] | |
| HRL, HRR | Head rotation to the left or right | Analysis of head rotation relative to the body’s axis | Detection of head orientation and rotation using facial reference points and motion analysis. | ||||
| FHT | Frontal head tilt | Detection of forward or backward tilt of the head in relation to the body | Use of facial tracking algorithms to determine the frontal inclination of the head. | ||||
| Arms | WSAL, WSAR | Wrist–shoulder angle | Detection of joint angles between the wrist and shoulder | Tracking of keypoints in the wrist and shoulder to calculate the angle. | 0–60° 60–120° 120–180° | [0–25] [25–50] [50–75] | |
| AELL, AELR | Lateral elevation of extended arms | Detection of lateral elevation of the arms | Tracking of arm trajectory in a lateral plane using limb detection. | 0–30° 30–60° 60–90° | [0–25] [25–50] [50–75] | ||
| Legs | HAAL, HAAR | Hip–ankle angle | Detection of angles between the hip and ankle | Analysis of leg alignment from the hip to the ankle to calculate the angle. | 0–30° 30–60° 60–90° | [0–25] [25–50] [50–75] | |
| LELI, LELR | Lateral elevation of extended legs | Detection of lateral elevation of extended legs | Tracking of leg trajectory in lateral elevation to determine range of motion. | ||||
| Torso | LTTL, LTTR | Lateral trunk tilt | Detection of lateral tilt of the torso | Use of postural analysis to assess lateral trunk inclination through keypoints in the torso. | 0–30° 30–60° 60–90° | [0–25] [25–50] [50–75] | |
| FTIF, FTIB | Frontal trunk inclination | Detection of forward or backward trunk tilt | Tracking of trunk orientation in the frontal plane to determine inclination. | ||||
| Body | Overall score to establish a global conclusion about the patient’s mobility. | ||||||
| Clinical Scale | Clinical Purpose | Analyzed Information |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Index (MI) | Evaluate motor strength and mobility | Wrist–elbow–shoulder angle; Hip–knee–ankle angle; Time in specific positions |
| Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) | Measure muscle resistance to passive movement and stiffness | Facial expressions of pain; Wrist–elbow–shoulder and hip–knee–ankle angles (with/without weight); Angular velocity; Movement trajectory |
| Berg Balance Scale and Shortened Berg Balance Scale | Assess balance and postural control | Head tilt and rotation; Trunk tilt (lateral and frontal); Variations in posture stability |
| Functional Ambulation Classification (FAC) | Assess independence during gait and limb coordination | Relative distance between keypoints during gait; Movement phases and timing |
| Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) | Evaluate neglect and affected limb usage | Asymmetry analysis; Keypoint position monitoring |
| Barthel Index and/or Lawton and Brody Scale | Assess ability to perform activities of daily living | Body position changes; Time maintaining postures; Stability during tasks |
| Disability Rating Scale (DRS) | Evaluate disability severity and recovery prognosis | Posture maintenance and activity tracking (keypoints and timing) |
| National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) | Evaluate stroke severity | Facial expressions; Arm and leg movement capacity; Trunk stability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, V.; Santos, O.C. Towards Intelligent Assessment in Personalized Physiotherapy with Computer Vision. Sensors 2025, 25, 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113436
García V, Santos OC. Towards Intelligent Assessment in Personalized Physiotherapy with Computer Vision. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113436
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Victor, and Olga C. Santos. 2025. "Towards Intelligent Assessment in Personalized Physiotherapy with Computer Vision" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113436
APA StyleGarcía, V., & Santos, O. C. (2025). Towards Intelligent Assessment in Personalized Physiotherapy with Computer Vision. Sensors, 25(11), 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113436








