Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
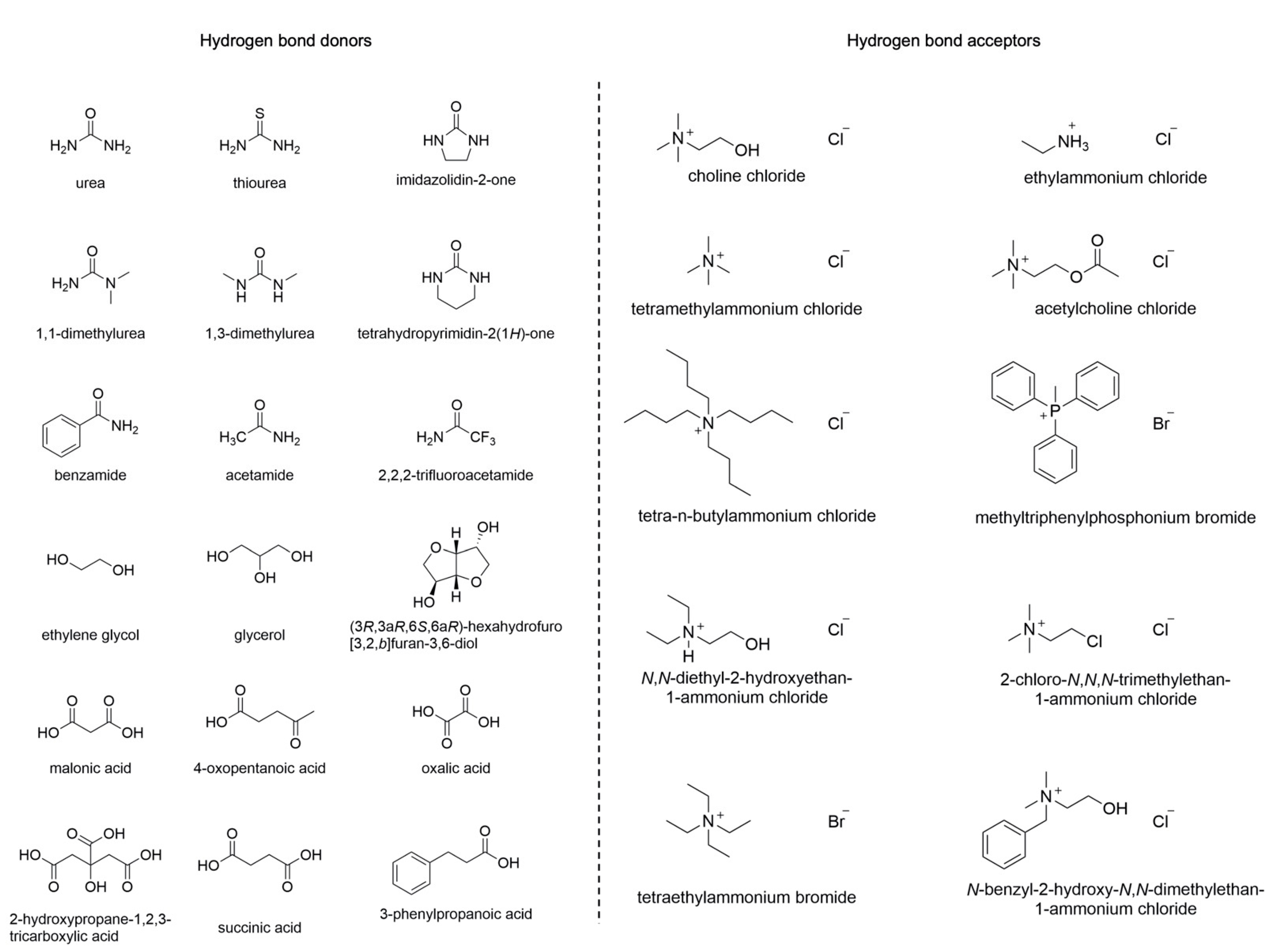
1.1. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs)
1.2. Biosensors
2. Synthesis of Electrode Materials in DESs
2.1. Graphene, Carbon Paste, and Carbon Nanotubes in DESs
2.2. Nano and Magnetic Particles in DESs
2.3. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in DESs
3. Biocompatibility of DESs
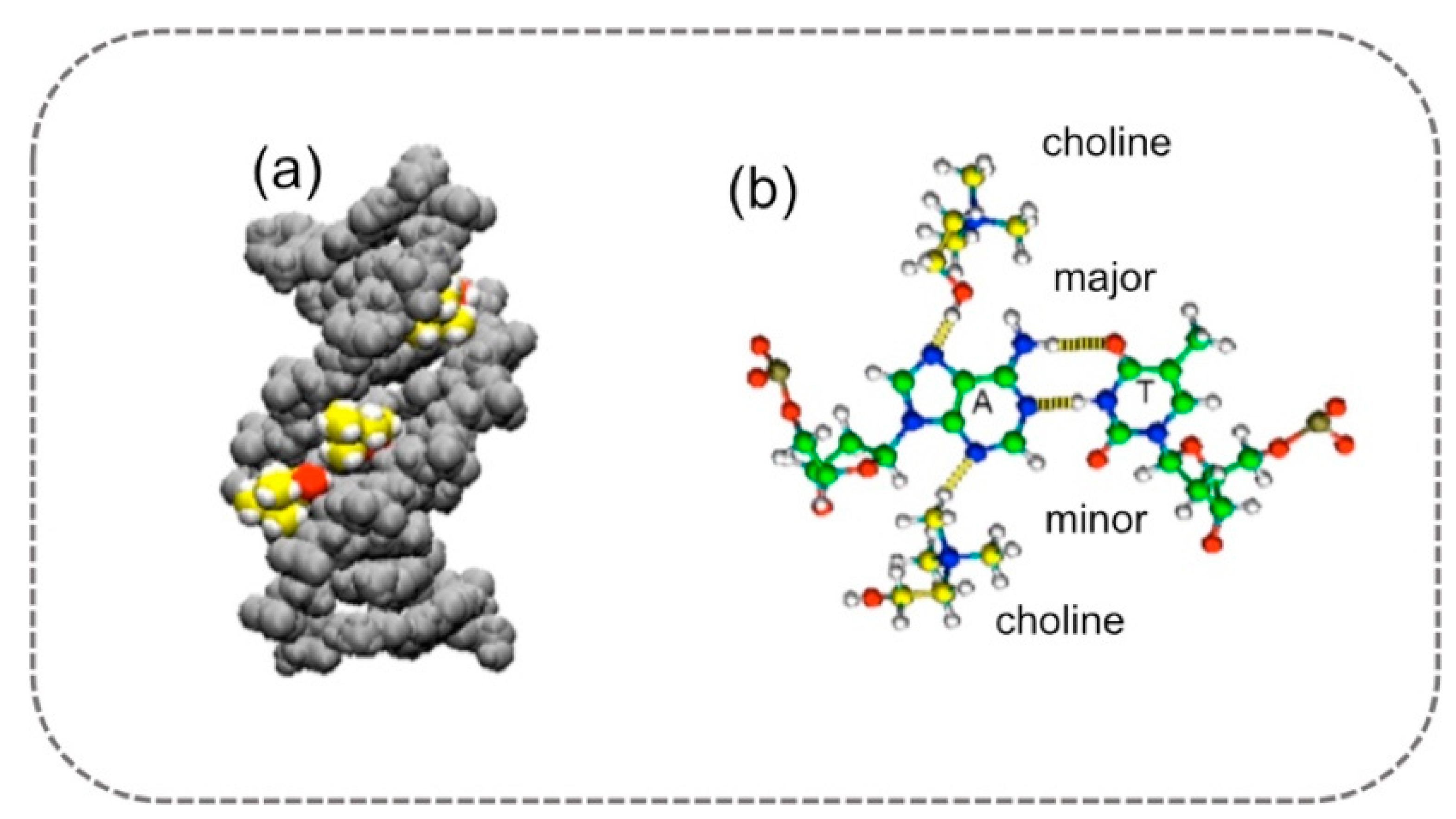
3.1. DNA Stability and Behavior in DESs
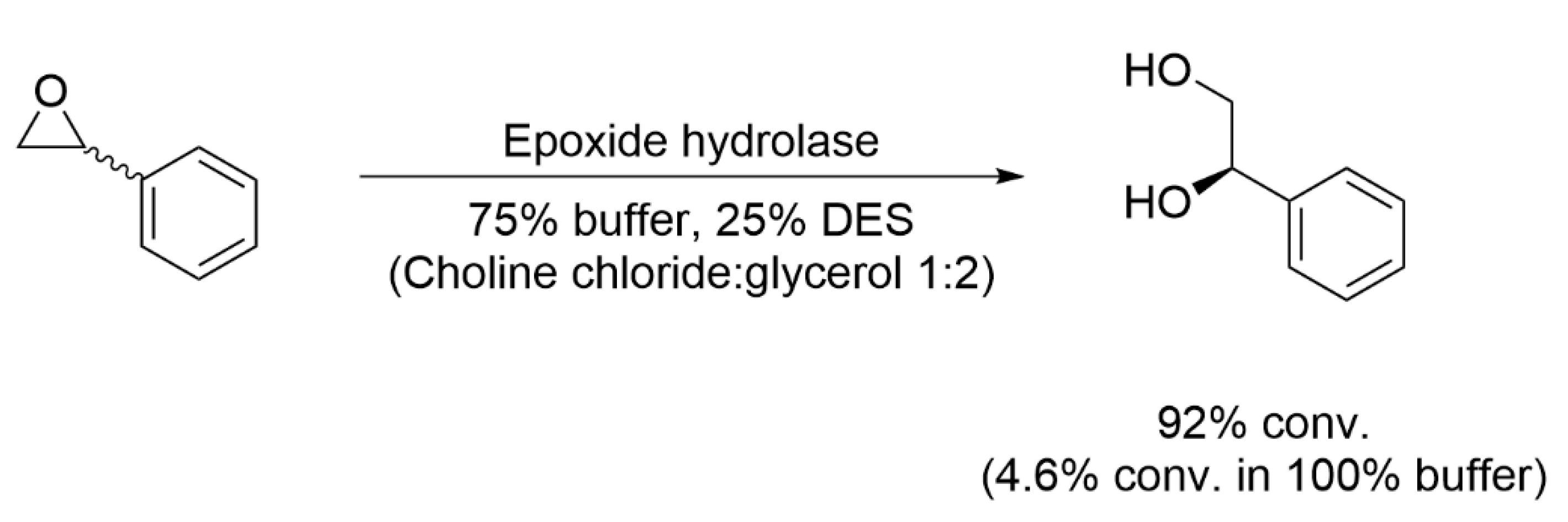
3.2. Enzyme Activity in DESs
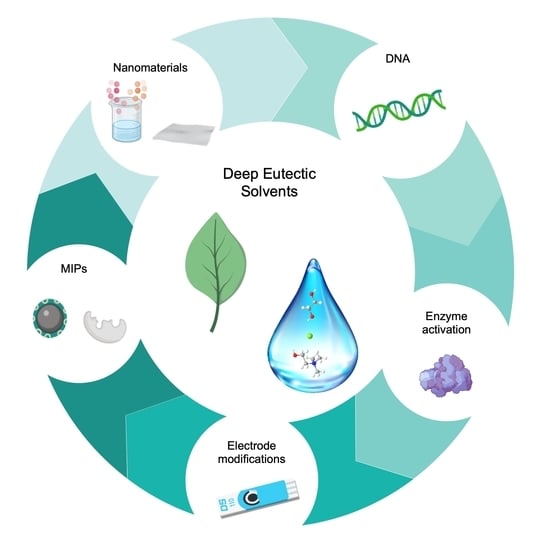
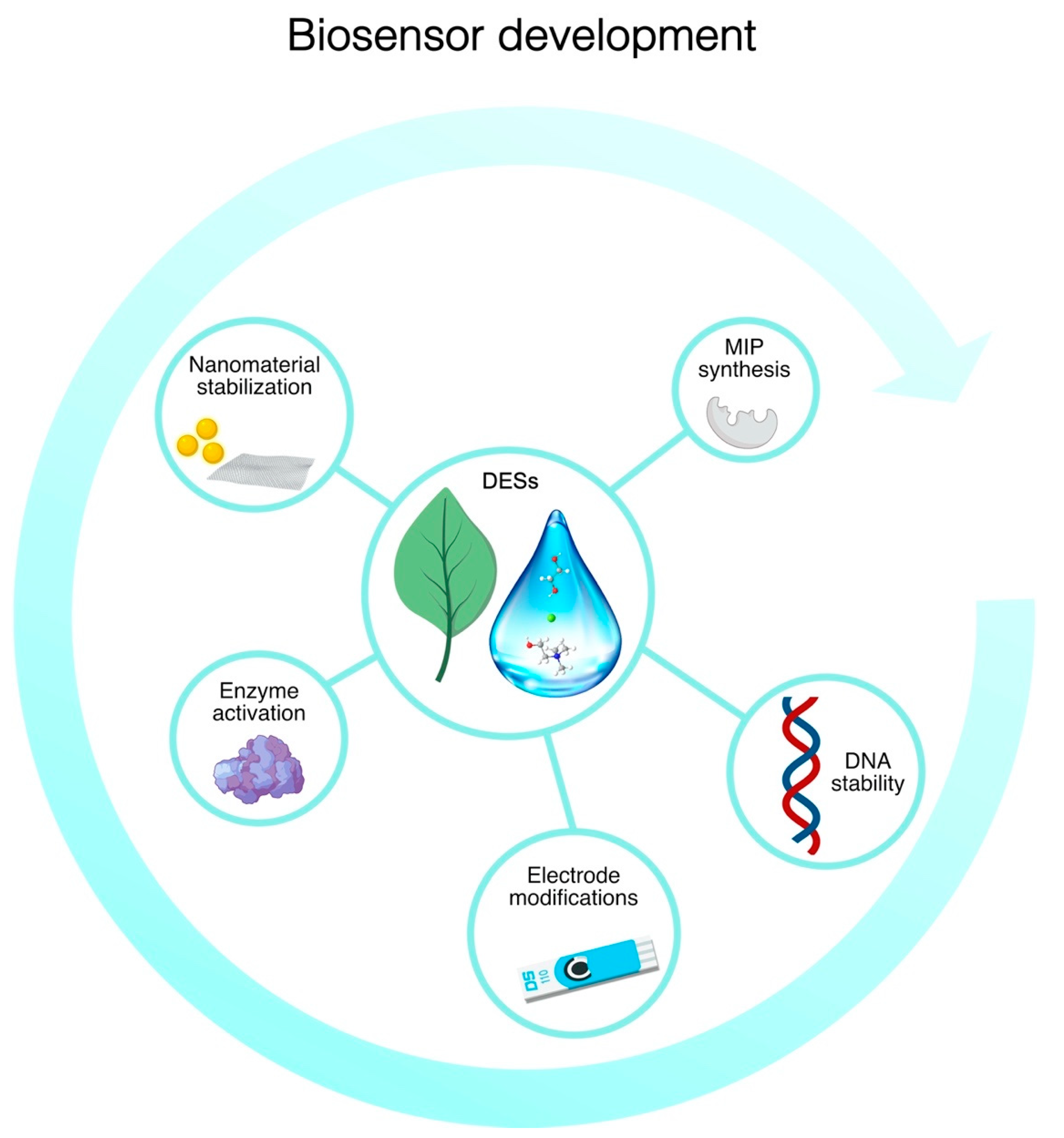
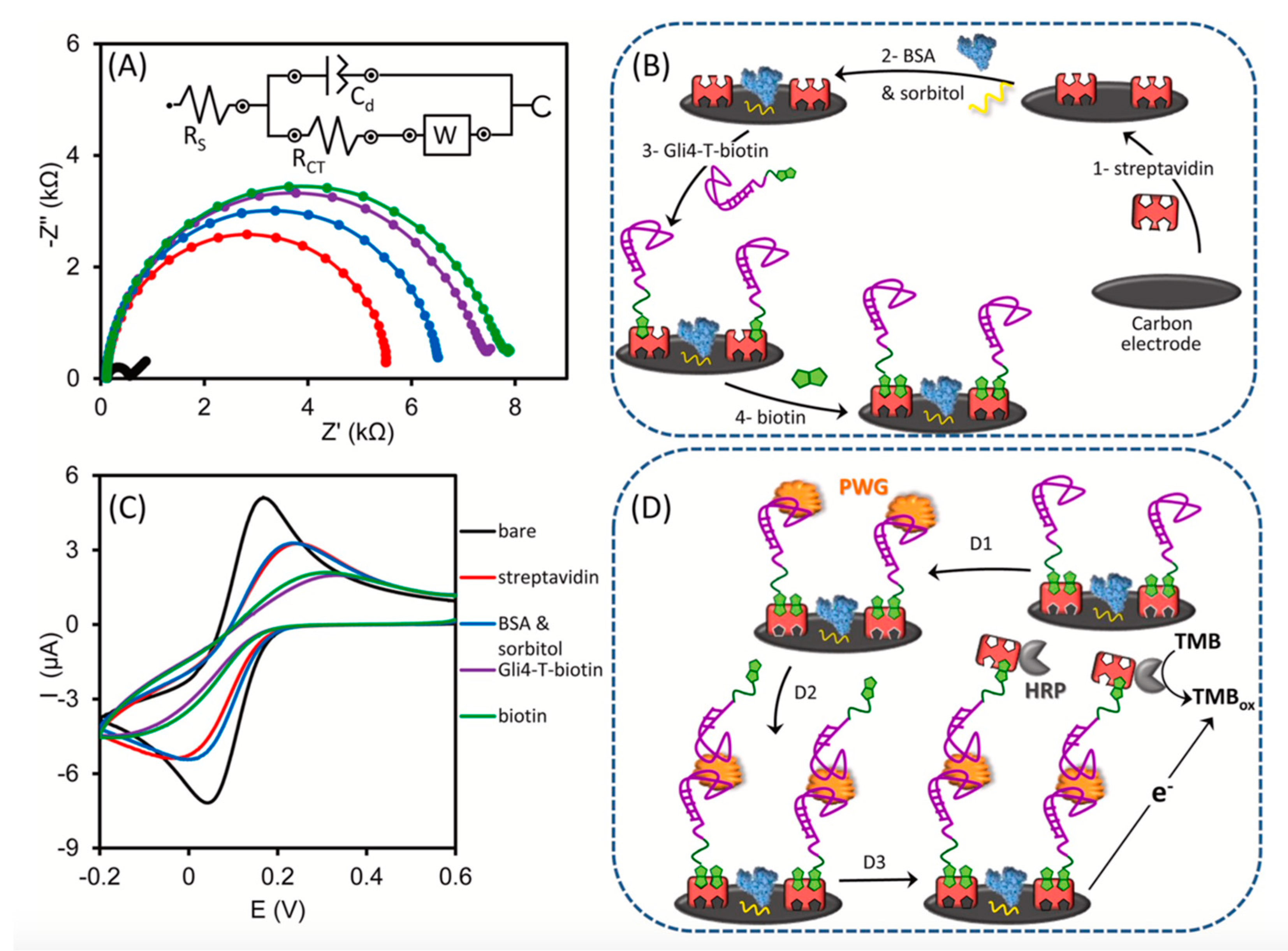
4. Application of DESs in the Development of Biosensors
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. From Green Chemistry to Nature: The Versatile Role of Low Transition Temperature Mixtures. Biochimie 2016, 120, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapiot, P.; Lagrost, C. Electrochemical Reactivity in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2238–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deetlefs, M.; Seddon, K.R. Assessing the Greenness of Some Typical Laboratory Ionic Liquid Preparations. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, K.; Szczepanska, N.; Plotka-Wasylka, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Shyshchak, O.; Bratychak, M.; Namiesnik, J. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Extraction Process. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2016, 10, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Potential Media for Green Technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hao, J.-W.; Mo, L.-P.; Zhang, Z.-H. Recent Advances in the Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Sustainable Media as Well as Catalysts in Organic Reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48675–48704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.D.O.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Row, K.H. Development of Deep Eutectic Solvents Applied in Extraction and Separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busato, M.; Migliorati, V.; Del Giudice, A.; Di Lisio, V.; Tomai, P.; Gentili, A.; D’Angelo, P. Anatomy of a Deep Eutectic Solvent: Structural Properties of Choline Chloride:Sesamol 1:3 Compared to Reline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 11746–11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, L.I.; Baiao, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Production and Application of New Materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigelj, R.; Bortolomeazzi, R.; Dossi, N.; Giacomino, A.; Bontempelli, G.; Toniolo, R. An Effective Gluten Extraction Method Exploiting Pure Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents (ChCl-DESs). Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, B.L.; Paveglio, G.C.; Silvestri, S.; Muller, E.I.; Enders, M.S.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Zanatta, N.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Radke, C.; Frizzo, C.P. TiO2 Nanoparticles Coated with Deep Eutectic Solvents: Characterization and Effect on Photodegradation of Organic Dyes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.-F.; George, M.; Govindasamy, M.; Benadict Joseph, X. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Manganese Molybdate Nanosheets for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Human Lethal Compounds: Comparing the Electrochemical Performances of M-Molybdate (M = Mg, Fe, and Mn) Electrocatalysts. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 19719–19731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Chromatography: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.-E.; Andreasidou, E.; Samanidou, V. Microextraction Techniques with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vian, M.; Breil, C.; Vernes, L.; Chaabani, E.; Chemat, F. Green Solvents for Sample Preparation in Analytical Chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2017, 5, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Tian, M.; Row, K.H. Evaluation of Alcohol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent in Extraction and Determination of Flavonoids with Response Surface Methodology Optimization. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Dou, L.-L.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.-H. Comprehensive Evaluation of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Extraction of Bioactive Natural Products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Rozema, E.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Application of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents to the Extraction of Anthocyanins from Catharanthus Roseus with High Extractability and Stability Replacing Conventional Organic Solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1434, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Silva, J.C.; Mano, F.; Ferreira, A.S.; Dionísio, M.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Dissolution Enhancement of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients by Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 98, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Li, M.-H. Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in a Choline Chloride–Ethylene Glycol Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 551, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to Biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alhadrami, H.A. Biosensors: Classifications, Medical Applications, and Future Prospective. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2018, 65, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asal, M.; Özen, Ö.; Şahinler, M.; Baysal, H.T.; Polatoğlu, İ. An Overview of Biomolecules, Immobilization Methods and Support Materials of Biosensors. Sens. Rev. 2019, 39, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha Santos, T.A.P. Recent Developments in Recognition Elements for Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhain, A.; Bonini, A.; Vivaldi, F.; Poma, N.; Di Francesco, F. Latest Developments in Non-Faradic Impedimetric Biosensors: Towards Clinical Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, A.; Crew, A.; Pemberton, R.; Hughes, G.; Doran, O.; Hart, J.P. Screen-Printed Carbon Based Biosensors and Their Applications in Agri-Food Safety. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Devadas, B.; Chen, S.-M. Direct Electrochemistry of Glucose Oxidase at Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide-Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Hybrid Material Modified Electrode for Glucose Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.J.; Baik, S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D. Enzyme-Based Glucose Sensor: From Invasive to Wearable Device. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.; Probst, D.; Klonoff, D.; Sode, K. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems—Current Status and Future Perspectives of the Flagship Technologies in Biosensor Research. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Dinesh, B.; Chen, S.-M.; Saraswathi, R. Direct Electrochemistry of Myoglobin at Reduced Graphene Oxide-Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes-Platinum Nanoparticles Nanocomposite and Biosensing towards Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitrite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, D.; Bayer, B.C.; Gupta, T.; Szabo, G.L.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Eder, D.; Meyer, J.C.; Steiner, S.; Gollas, B. Electrochemical Behavior of Graphene in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40937–40948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariati, L.S.S. Evaluation of Ionic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) Modified Binders towards the Chemical Properties of Carbon Paste Electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 109, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.K.; El-Shafie, A.; Hin, L.S.; Mohd, N.S.B.; Aljumaily, M.M.; Ibraim, S.; AlSaadi, M.A. A Clean Approach for Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes by Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Performance in the Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, S.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Insights on (C, BN, Si, Ge, MoS 2 ) Nanotubes in Reline Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-G.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.-P.; Sun, S.-G. Shape-controlled Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles in Deep Eutectic Solvents for Studies of Structure–Functionality Relationships in Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9100–9103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Ochmann, M.; Hoell, A.; Polzer, F.; Rademann, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Self-Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles: A SAXS, UV−Vis, and TEM Investigation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6038–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Selection of Anti-Gluten DNA Aptamers in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 13032–13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.-F.; George, M. Effect of Various Deep Eutectic Solvents on the Sustainable Synthesis of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Nitrofurantoin and 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Fu, N.; Zhang, C.; Hu, L.; Li, D.; Tang, B.; Zhu, T. Specific Recognition of Polyphenols by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1530, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Zhou, Y. Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on a Deep Eutectic Solvent as the Functional Monomer for Specific Recognition of Lysozyme. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, X.; Row, K.H. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Silica Modified by Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Rapid Simultaneous Magnetic-Based Solid-Phase Extraction of Salvia Miltiorrhiza Bunge, Glycine Max (Linn.) Merr and Green Tea. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Preston, K.; Krokhin, O.; Mellish, J.; Ens, W. Characterization of Wheat Gluten Proteins by HPLC and MALDI TOF Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 19, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gállego, I.; Grover, M.A.; Hud, N.V. Folding and Imaging of DNA Nanostructures in Anhydrous and Hydrated Deep-Eutectic Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6765–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Ballone, P. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids Meet Biomolecules: A Microscopic View of Structure and Dynamics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H. DNA Stability in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Tateishi-Karimata, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sugimoto, N. Choline Ion Interactions with DNA Atoms Explain Unique Stabilization of A–T Base Pairs in DNA Duplexes: A Microscopic View. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamajanov, I.; Engelhart, A.E.; Bean, H.D.; Hud, N.V. DNA and RNA in Anhydrous Media: Duplex, Triplex, and G-Quadruplex Secondary Structures in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6310–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Paul, S. Effect of Hydrated and Nonhydrated Choline Chloride–Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent (Reline) on Thrombin-Binding G-Quadruplex Aptamer (TBA): A Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11686–11698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Paul, S. Understanding The Role of Reline, a Natural DES, on Temperature-Induced Conformational Changes of C-Kit G-Quadruplex DNA: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor-Fernández, V.; Paul, C.E. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Redox Biocatalysis. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 293, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Application, and Focus on Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorke, J.T.; Srienc, F.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Hydrolase-Catalyzed Biotransformations in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, A.A.; Efstathiadou, E.; Patila, M.; Polydera, A.C.; Stamatis, H. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Media for Peroxidation Reactions Catalyzed by Heme-Dependent Biocatalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5145–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-P.; Wen, Q.; Xu, H.; Yang, Z. Insights into the Impact of Deep Eutectic Solvents on Horseradish Peroxidase: Activity, Stability and Structure. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 101, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, R.; Divsalar, A. Enzymatic Behavior of Bovine Liver Catalase in Aqueous Medium of Sugar Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarika, C.; Rekha, K.; Narasimha Murthy, B. Studies on Enhancing Operational Stability of a Reusable Laccase-Based Biosensor Probe for Detection of Ortho-Substituted Phenolic Derivatives. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bounegru, A.V.; Apetrei, C. Laccase and Tyrosinase Biosensors Used in the Determination of Hydroxycinnamic Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, M.L.; Pereira, M.M.; Freire, M.G.; Silva, J.P.A.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Tavares, A.P.M. Laccase Activation in Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.; Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. Novel Nanocomposite Film Modified Electrode Based on Poly(Brilliant Cresyl Blue)-Deep Eutectic Solvent/Carbon Nanotubes and Its Biosensing Applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 317, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.; Ghica, M.E.; Brett, C.M.A. Choline Oxidase Inhibition Biosensor Based on Poly(Brilliant Cresyl Blue)—Deep Eutectic Solvent/Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode for Dichlorvos Organophosphorus Pesticide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M.A. Novel Biosensor for Acetylcholine Based on Acetylcholinesterase/Poly(Neutral Red)—Deep Eutectic Solvent/Fe2O3 Nanoparticle Modified Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 872, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Krishnan, S.; Guadalupe-Ferreira García, M.; Prokhorov, E.; Estevez-González, M.; Pérez, R.; Esparza, R.; Meyyappan, M. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Functionalized Nanosilica Using Deep Eutectic Solvent for an Electrochemical Enzymatic Glucose Biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7072–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Xu, F.; Edwards, J.V.; Prevost, N.T.; Nam, S.; Condon, B.D.; French, A.D. Nanocellulose as a Colorimetric Biosensor for Effective and Facile Detection of Human Neutrophil Elastase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Pizzolato, S.; Toniolo, R.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Truncated Aptamers as Selective Receptors in a Gluten Sensor Supporting Direct Measurement in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, Z. A Composite Prepared from MnO2 Nanosheets and a Deep Eutectic Solvent as an Oxidase Mimic for the Colorimetric Determination of DNA. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tavengwa, N.T. Emerging Green Solvents and Their Applications during Pesticide Analysis in Food and Environmental Samples. Talanta 2021, 223, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| DESs | Salt/HBD Molar Ratio | Viscosity a Pa·s | Conductivity a μS·cm−1 | Density a g/cm3 | Tf/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl:urea | 1:2 | - | - | 1.25 | 12 |
| ChCl:acetamide | 1:2 | 0.127 | 2710 | 1.09 | 51 |
| ChCl:glycerol | 1:2 | 0.177 | 1647 | 1.19 | −40 |
| ChCl:1,4-butanediol | 1:4 | 0.047 | 2430 | 1.04 | - |
| ChCl:triethylene glycol | 1:4 | 0.044 | 1858 | 1.12 | −66 |
| ChCl:xylitol | 1:1 | 3.867 | 172.6 | 1.24 | - |
| ChCl:D-sorbitol | 1:1 | 13.736 | 63.3 | 1.28 | - |
| ChCl:oxalic acid | 1:1 | 0.089 | 2350 | 1.24 | 34 |
| ChCl:levulinic acid | 1:2 | 0.119 | 1422 | 1.13 | - |
| ChCl:malonic acid | 1:1 | 0.616 | 732 | 1.21 | 10 |
| ChCl:malic acid | 1:1 | 11.475 | 41.4 | 1.28 | - |
| ChCl:citric acid | 1:1 | 45.008 | 18.4 | 1.33 | 69 |
| ChCl:tartaric acid | 2:1 | 66.441 | 14.3 | 1.27 | 47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Grazioli, C.; Toniolo, R. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development. Sensors 2021, 21, 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134263
Svigelj R, Dossi N, Grazioli C, Toniolo R. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development. Sensors. 2021; 21(13):4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134263
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvigelj, Rossella, Nicolò Dossi, Cristian Grazioli, and Rosanna Toniolo. 2021. "Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development" Sensors 21, no. 13: 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134263
APA StyleSvigelj, R., Dossi, N., Grazioli, C., & Toniolo, R. (2021). Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Application in Biosensor Development. Sensors, 21(13), 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134263