Symmetry of Gait in Underweight, Normal and Overweight Children and Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Acquisition
- (1)
- spatio-temporal parameters of gait (namely gait speed, stride length and cadence);
- (2)
- HRs, which refer to AP (i.e., direction of motion), ML and V directions.
- (1)
- Gait speed: the mean velocity of progression (m/s);
- (2)
- Stride length: the longitudinal distance between successive ground contacts of the same foot (m);
- (3)
- Cadence: the rate at which a person walks (steps per minute).
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aparecida, S.; De Souza, F.; Faintuch, J.; Carlos, A.; Fernando, A.; Anna, S.; Gama, J.J.; Cristina, I.; Fonseca, D.B.; Souza, R.B.; et al. Gait cinematic analysis in morbidly obese patients. Obes. Surg. 2005, 15, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearing, S.C.; Hennig, E.M.; Byrne, N.M.; Steele, J.R.; Hills, A.P. Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: A biomechanical perspective. Obes. Rev. 2006, 7, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, P.; Menegoni, F.; Vismara, L.; Cimolin, V.; Grugni, G.; Galli, M. Characterisation of balance capacity in prader-willi patients. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, M.; Crivellini, M.; Sibella, F.; Montesano, A.; Bertocco, P.; Parisio, C. Sit-to-stand movement analysis in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibella, F.; Galli, M.; Romei, M.; Montesano, A.; Crivellini, M. Biomechanical analysis of sit-to-stand movement in normal and obese subjects. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, N.; Cimolin, V.; Galli, M.; Precilios, H.; Tacchini, E.; Santovito, C.; Capodaglio, P. Center of pressure displacements during gait initiation in individuals with obesity. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolin, V.; Vismara, L.; Galli, M.; Grugni, G.; Cau, N.; Capodaglio, P. Gait strategy in genetically obese patients: A 7-year follow up. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimolin, V.; Cau, N.; Galli, M.; Santovito, C.; Grugni, G.; Capodaglio, P. Gait initiation and termination strategies in patients with prader-willi syndrome. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimolin, V.; Capodaglio, P.; Cau, N.; Galli, M.; Santovito, C.; Patrizi, A.; Tringali, G.; Sartorio, A. Computation of spatio-temporal parameters in level walking using a single inertial system in lean and obese adolescents. Biomed. Tech. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.P.; Menegoni, F.; Vismara, L.; Galli, M.; Romei, M.; Bergamini, E.; Petroni, M.L.; Capodaglio, P. Balance in patients with anorexia and bulimia nervosa. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 45, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cimolin, V.; Galli, M.; Vismara, L.; Vimercati, S.L.; Precilios, H.; Cattani, L.; Fabris De Souza, S.; Petroni, M.L.; Capodaglio, P. Gait analysis in anorexia and bulimia nervosa. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2013, 11, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, S.; Kanekar, A. Childhood obesity: A global public health crisis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, V.J.; Fink, P.W.; Lark, S.D.; Shultz, S.P. Mass affects lower extremity muscle activity patterns in children’s gait. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, B.; McClenaghan, B.A.; Williams, H.G.; Dickerson, J.; Ward, D.S. Gait and postural stability in obese and nonobese prepubertal boys. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Parker, A.W. Gait characteristics of obese children. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1991, 72, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.C.T.; Barnes, C.M.; Holton, M.; Summers, H.D. Human movement science profiling movement quality and gait characteristics according to body-mass index in children (9–11 y). Hum. Mov. Sci. 2016, 49, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenon, A.; Gabrielli, F.; Lepvrier, J.; Faupin, A.; Allart, E.; Tiffreau, V.; Wieczorek, V. Collection of normative data for spatial and temporal gait parameters in a sample of french children aged between 6 and 12. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochu, N.J.; Prince, F. Locomotor strategies in obese and nonobese children. Obesity 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Garcia, P.; Migueles, J.H.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Plaza-Florido, A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Ortega, F.B. A systematic review on biomechanical characteristics of walking in children and adolescents with overweight/obesity: Possible implications for the development of musculoskeletal disorders. Obes. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shultz, S.P.; D’Hondt, E.; Lenoir, M.; Fink, P.W.; Hills, A.P. The role of excess mass in the adaptation of children’s gait. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 36, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, K.A.; Lokenvitz, N.; Smiley-Oyen, A.L. Age-and speed-related differences in harmonic ratios during walking. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanca, J.L.; Lowry, K.A.; VanSwearingen, J.M.; Brach, J.S.; Redfern, M.S. Harmonic ratios: A quantification of step to step symmetry. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brach, J.S.; McGurl, D.; Wert, D.; Van Swearingen, J.M.; Perera, S.; Cham, R.; Studenski, S. Validation of a measure of smoothness of walking. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluscio, V.; Bergamini, E.; Salatino, G.; Marro, T.; Gentili, P.; Iosa, M.; Morelli, D.; Vannozzi, G. Dynamic balance assessment during gait in children with down and prader-willi syndromes using inertial sensors. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2019, 63, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimolin, V.; Galli, M. Summary measures for clinical gait analysis: A literature review. Gait Posture 2014, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Lord, S.R.; Fitzpatrick, R.C. Acceleration patterns of the head and pelvis when walking on level and irregular surfaces. Gait Posture 2003, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Lord, S.R.; St George, R.; Fitzpatrick, R.C. Walking stability and sensorimotor function in older people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Mandaresu, S.; Pilloni, G.; Porta, M.; Coghe, G.; Giovanna, M.; Cocco, E. Gait & posture smoothness of gait detects early alterations of walking in persons with multiple sclerosis without disability. Gait Posture 2017, 58, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, K.A.; Smiley-Oyen, A.L.; Carrel, A.J.; Kerr, J.P. Walking stability using harmonic ratios in Parkinson’ s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 24, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liao, S.; Cao, S.; Wu, D.; Zhang, X. An acceleration-based gait assessment method for children with cerebral palsy. Sensors 2017, 17, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehle, A.W.; Nahhas, R.W.; Sherwood, R.J.; Duren, D.L. Age-related changes in spatiotemporal characteristics of gait accompany ongoing lower limb linear growth in late childhood and early adolescence. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Flegal, K.M.; Nicholls, D.; Jackson, A.A. Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: International survey. Br. Med. J. 2007, 335, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. Br. Med. J. 2000, 320, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N. Ethics in child research: Rights, reason and responsibilities. Child. Geogr. 2008, 6, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Mandaresu, S.; Leban, B.; Nussbaum, M.A. Short-term effects of backpack carriage on plantar pressure and gait in schoolchildren. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Leban, B.; Pilloni, G.; Porta, M.; Cubeddu, F.; Secci, C.; Piras, V.; Monticone, M. Trunk rotation alters postural sway but not gait in female children and early adolescents: Results from a school-based screening for scoliosis. Gait Posture 2018, 61, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasciuto, I.; Bergamini, E.; Iosa, M.; Vannozzi, G.; Cappozzo, A. Overcoming the limitations of the harmonic ratio for the reliable assessment of gait symmetry. J. Biomech. 2017, 53, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Misu, S.; Asai, T.; Doi, T.; Sawa, R.; Ueda, Y.; Saito, T.; Nakamura, R.; Murata, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Yamada, M.; et al. Association between gait abnormality and malnutrition in a community-dwelling elderly population. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, S.M.O.; Kuo, A.D. Direction-dependent control of balance during walking and standing. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 102, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, R.C.; Kram, R. Effects of obesity on the biomechanics of walking at different speeds. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelan, J.M.; Shipman, D.W.; Kram, R.; Kuo, A.D. Mechanical and metabolic requirements for active lateral stabilization in human walking. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.R.; Mara, A.; Muniz, D.S.; Cerqueira, L.S.; Nadal, J. Biomechanical alterations of gait on overweight subjects biomechanical alterations of gait on overweight subjects. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 34, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, M.A.D.; Menz, H.B.; Smith, S.T.; Delbaere, K.; Lord, S.R. Good lateral harmonic stability combined with adequate gait speed is required for low fall risk in older people. Gerontology 2015, 61, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Misu, S.; Sawa, R.; Doi, T.; Yamada, M. The Association between fear of falling and smoothness of lower trunk oscillation in gait varies according to gait speed in community-dwelling older adults. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, D.C.; Todd, M.H.; Della Croce, U. Gender differences in joint biomechanics during walking: Normative study in young adults. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 77, 9482373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Underweight | Normal Weight | Overweight | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants # (M,F) | 25 (13M, 12F) | 25 (13M, 12F) | 25 (13M, 12F) |
| Age (years) | 11.1 ± 1.0 | 11.2 ± 1.2 | 11.7 ± 1.8 |
| Height (cm) | 148.2 ± 9.9 | 147.8 ± 10.3 | 151.9 ± 14.6 |
| Body Mass (kg) | 31.6 ± 5.2 | 38.9 ± 7.7 | 71.5 ± 21.4 a,b |
| Body Mass Index (kg·m−2) | 14.3 ± 0.7 | 17.6 ± 1.9 a | 30.2 ± 5.4 a,b |
| Underweight | Normal Weight | Overweight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial-temporal parameters of gait | Gait speed (m·s−1) | 1.23 ± 0.29 | 1.22 ± 0.30 | 1.41 ± 0.39 |
| Stride length (m) | 1.18 ± 0.32 | 1.18 ± 0.23 | 1.27 ± 0.46 | |
| Cadence (steps min−1) | 127.59 ± 23.01 | 123.72 ± 18.35 | 146.13 ± 65.01 | |
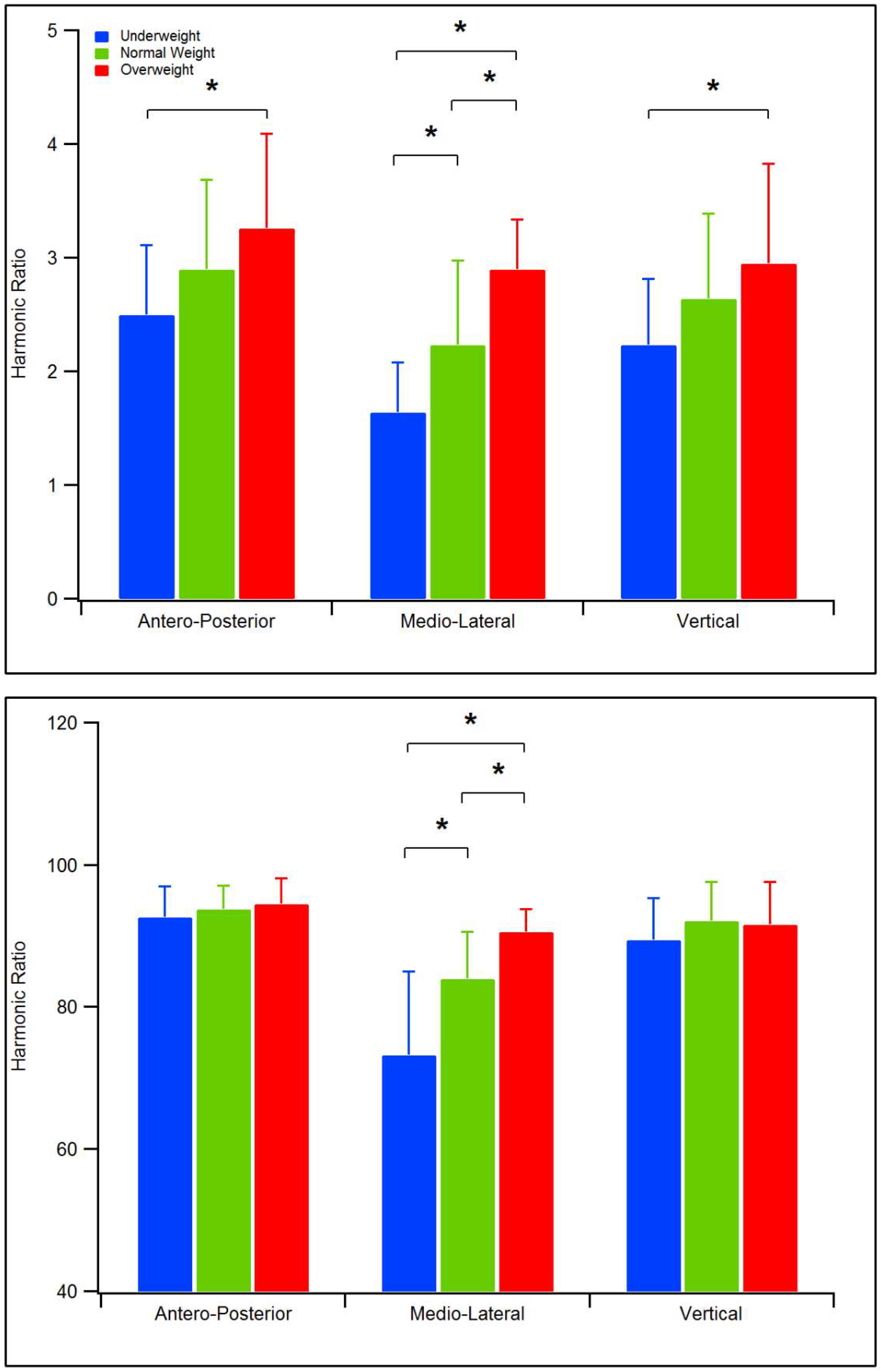
| Symmetry of gait (HR, Menz et al. [26]) | AP direction | 2.50 ± 0.80 | 2.90 ± 0.79 | 3.25 ± 0.83 a |
| ML direction | 1.64 ± 0.44 | 2.23 ± 0.74 a | 2.89 ± 0.44 a,b | |
| V direction | 2.23 ± 0.59 | 2.64 ± 0.75 | 2.95 ± 0.88 a | |
| Symmetry of gait (iHR, Pasciuto et al. [37]) | AP direction | 92.68 ± 4.34 | 93.74 ± 3.35 | 94.53 ± 3.64 |
| ML direction | 73.20 ± 11.80 | 83.98 ± 6.62 a | 90.58 ± 3.22 a,b | |
| V direction | 89.44 ± 5.90 | 92.09 ± 5.44 | 91.59 ± 6.01 |
| Menz et al. (2013) | Pasciuto et al. (2017) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
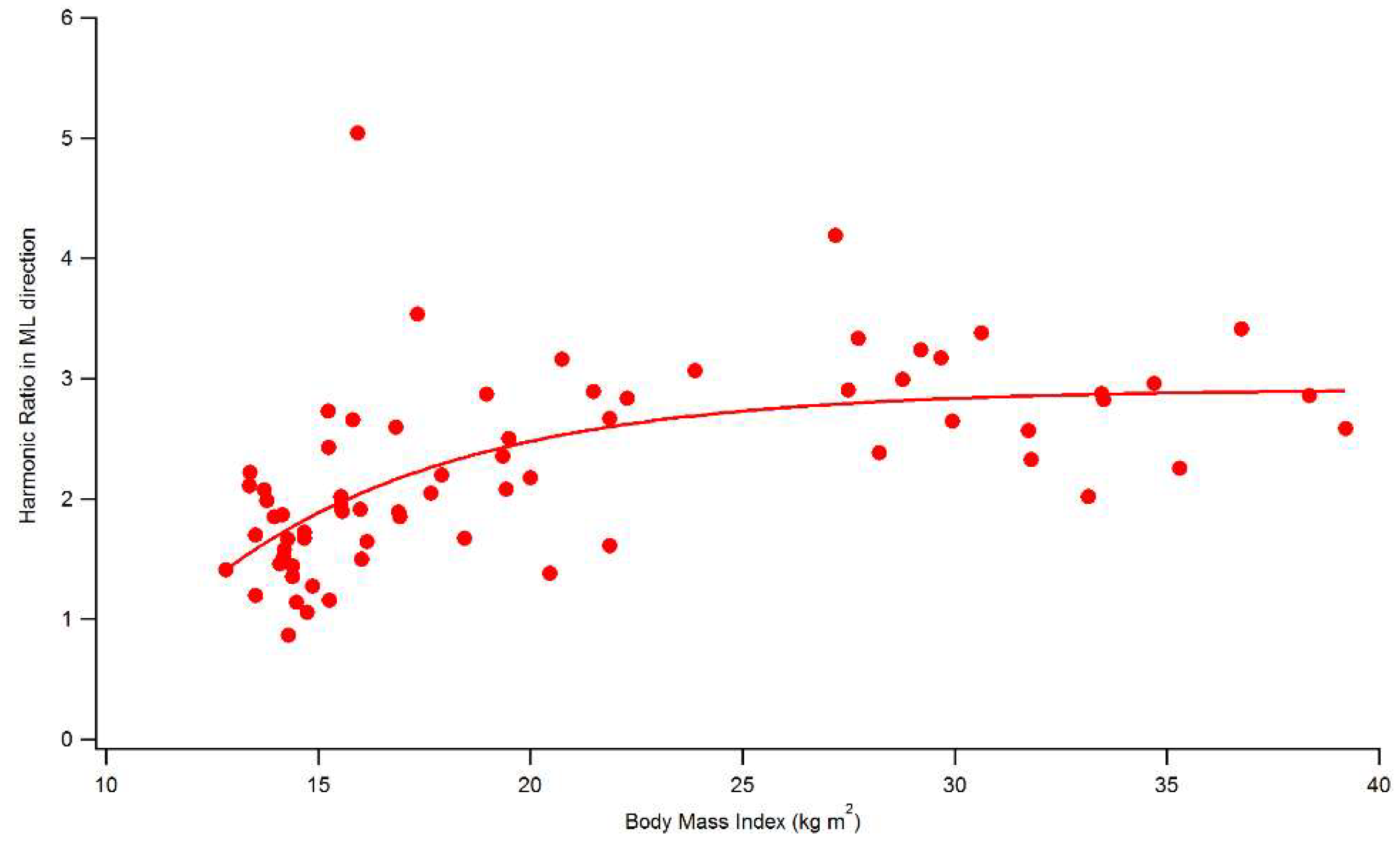
| BMI vs. | HR AP direction | 0.370 ** | 0.252 * |
| HR ML direction | 0.672 ** | 0.663 ** | |
| HR V direction | 0.375 ** | 0.213 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cimolin, V.; Cau, N.; Sartorio, A.; Capodaglio, P.; Galli, M.; Tringali, G.; Leban, B.; Porta, M.; Pau, M. Symmetry of Gait in Underweight, Normal and Overweight Children and Adolescents. Sensors 2019, 19, 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092054
Cimolin V, Cau N, Sartorio A, Capodaglio P, Galli M, Tringali G, Leban B, Porta M, Pau M. Symmetry of Gait in Underweight, Normal and Overweight Children and Adolescents. Sensors. 2019; 19(9):2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092054
Chicago/Turabian StyleCimolin, Veronica, Nicola Cau, Alessandro Sartorio, Paolo Capodaglio, Manuela Galli, Gabriella Tringali, Bruno Leban, Micaela Porta, and Massimiliano Pau. 2019. "Symmetry of Gait in Underweight, Normal and Overweight Children and Adolescents" Sensors 19, no. 9: 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092054
APA StyleCimolin, V., Cau, N., Sartorio, A., Capodaglio, P., Galli, M., Tringali, G., Leban, B., Porta, M., & Pau, M. (2019). Symmetry of Gait in Underweight, Normal and Overweight Children and Adolescents. Sensors, 19(9), 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19092054









