Abstract
‘Biodiversity’ means the variety of life and it can be studied at different levels (genetic, species, ecosystem) and scales (spatial and temporal). Last decades showed that marine biodiversity has been severely underestimated at all levels. In order to investigate diversity patterns and underlying processes, there is a need to know what species live in the marine environment. An emerging tool for species identification, DNA barcoding can reliably assign unknown specimens to known species, also flagging potential cryptic species and genetically distant populations. This paper will review the role of DNA barcoding for the study of marine biodiversity at the species level.
1. Introduction
‘Biodiversity’ is a broad and abstract concept, widely used by the scientific world but with reverberations at the economic, political and social levels. With more than 17,000,000 hits on Google search engine (February 2010), the concept of biodiversity is becoming a commonplace, even more so in 2010—The International Year of Biodiversity as proposed by the United Nations. But what does ‘biodiversity’ mean? Shorthand form of ‘biological diversity’, it literally means the ‘variety of life’ (Gk. ‘bios’, Lat. ‘diversitas’). It was officially mentioned for the first time at the National Forum on Biodiversity held in 1986 at Washington D.C. [1] and it became a funded research field in 1992 through the Convention on Biological Diversity (http://www.cbd.int). With three main levels accepted and usually investigated (genes, species, ecosystems), biodiversity must be conserved in order for our society to prosper, even more so that a ‘biodiversity crisis’ (highest human-induced extinction rates ever) was shown to occur [2]. However, a required step prior to protection is biodiversity assessment, usually conducted at the species level of biodiversity. Therefore, species identification has a paramount importance.
How many species are there and how do we recognize them? No precise species number can be provided but it is believed to approximate 1.9 million described species out of 11 million estimated [3]. Traditionally, morphology was a key factor in describing and naming species within the field of taxonomy. This long-standing approach, starting with Aristotle and becoming organized due to Linnaeus, can be very tedious and a matter of subjectivity since it is up to the taxonomist to choose those morphological characters believed to delineate species (whatever ‘species’ meant according to different views [4]). As a result, it took 250 years for traditional taxonomy to provide descriptions for less than quarter of the world species using as tools a variety of morphological keys, sometimes ‘written by those who don’t need them for those who can’t use them’ [5]. After centuries of acquiring knowledge, taxonomy started to lose popularity to other fields resulting in a worldwide shortage of trained personnel. Paradoxically enough, every biological study requires some taxonomic knowledge.
At the turn of the centuries, the original blend of ‘biodiversity crisis’ and ‘taxonomic impediment’ brought a stringent flavor to biodiversity studies. Although a solution is not envisaged yet, new approaches based on molecular markers might be of great help in advancing our knowledge of biodiversity. As opposed to morphological identifications and their ‘mediocrity’ in some cases [5], molecular methods are better tools for the identification of early life stages or partial specimens. One method in particular, DNA barcoding, was the incentive for a large debate on the current and future status of taxonomy. Here, we review the role of DNA barcoding for marine biodiversity studies at the species level. For this attempt, we searched the Web of Science by using ‘DNA barcod*’ and ‘marine’ as keywords and we retained only those papers that specifically dealt with species diversity and reference libraries of DNA barcodes. We provide an update regarding the progress in barcoding various marine groups and some future directions, as well as a plea for collaboration between barcoders and taxonomists.
2. Marine Biodiversity
By numbers, biodiversity in the sea seems to be quite reduced, varying between 167,817 valid species (or 318,004 taxa, species to phyla) according to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS; http://www.marinespecies.org) (February 2010), and 229,602 marine species described [6] (Table 1), but estimated to exceed 10 million [7].

Table 1.
Global numbers of marine species per taxon according to Bouchet [6] and WoRMS. Only taxa present on both lists were included.
| Marine group | Bouchet (2006) | WoRMS (February 2010) Valid species |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 4,800 | 625 |
| Fungi | 500 | 1,061 |
| Rhodophyta | 6,200 | 6,302 |
| Acanthocephala | 600 | 410 |
| Annelida | 12,148a | 12,631 |
| Arthropoda | 47,217b | 44,591 |
| Brachiopoda | 550 | 386 |
| Bryozoa | 5,700c | 1,525 |
| Chaetognatha | 121 | 208 |
| Cnidaria | 9,795 | 11,071 |
| Ctenophora | 166 | 170 |
| Cycliophora | 1 | 2 |
| Echinodermata | 7,000 | 5,764 |
| Echiura | 170 | 203 |
| Entoprocta | 165–170 | 161 |
| Gastrotricha | 390–400 | 524 |
| Gnathostomulida | 97 | 97 |
| Hemichordata | 106 | 106 |
| Mesozoa | 106d | 115 |
| Mollusca | 52,525 | 23,689 |
| Nematoda | 12,000 | 5,889 |
| Nemertea | 1,180–1,230 | 1,371 |
| Phoronida | 10 | 11 |
| Platyhelminthes | 15,000 | 3,348 |
| Porifera | 5,500 | 8,174 |
| Rotifera | 50 | 185 |
| Sipuncula | 144 | 158 |
| Tardigrada | 212 | 170 |
| Chordata | 21,517e | 21,944 |
| Total | 203,887 | 150,891 |
a it includes Pogonophora (separate taxon in [6])b as two taxa, Crustacea and Chelicerata, in [6]c as Ectoprocta in [6]d as two taxa, Rhombozoa and Orthonectida, in [6]e it includes Urochordata, Cephalochordata, Pisces and Mammalia (no reptiles)
The belief that oceans are a homogeneous environment in which speciation is not a common process resulted in only a fraction of the scientific attention being oriented towards marine compared to terrestrial biodiversity (Figure 1).
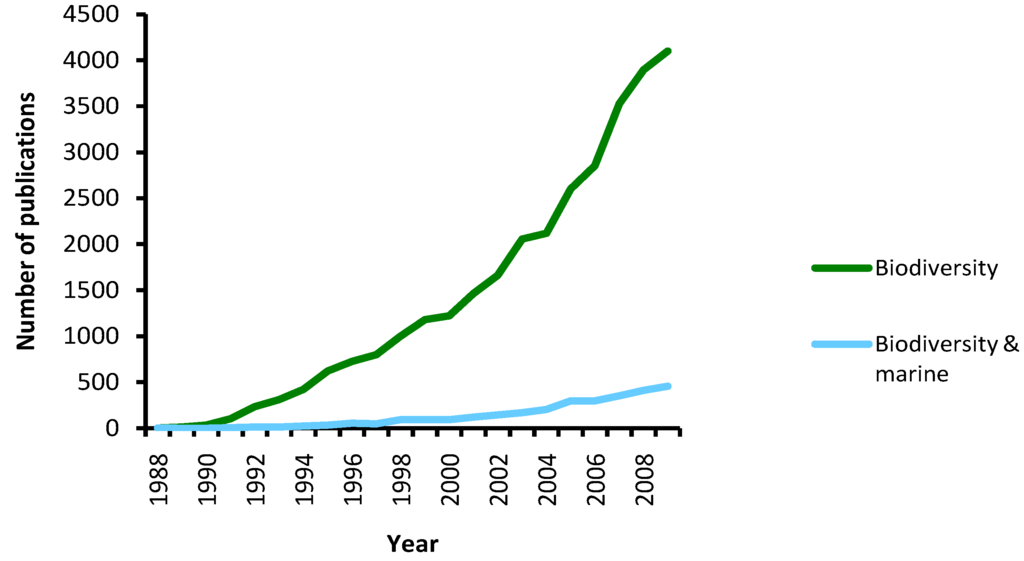
Figure 1.
The amount of articles focusing on marine biodiversity since 1988 (‘biodiversity’ and ‘marine’ used as keywords in Web of Science).
However, oceans cover more than 70% of our planet and it was a matter of improving technologies until new explorations of new habitats, especially deep-sea, allowed the discovery of new species [8], while cryptic species (morphologically similar but genetically distinct) were shown to be a common presence in marine systems [9]. Consequently, a more careful look at the world oceans might show, even by numbers, that biodiversity in the sea is as great as on land. On the other hand, an opposite situation occurs at higher taxonomic levels. Of the 35 animal phyla that have been described so far, all but one has living representatives in the oceans, while 14 phyla are marine endemics [10,11]. Within marine ecosystems, most diversity is benthic, consisting of invertebrates residing in (infauna) and on (epifauna) sediments. Brunel [12] mentioned that benthic animals, seaweeds and protists account for 98% of species diversity and the remaining 2% is pelagic. Other patterns of marine biodiversity include an increase in species diversity from Arctic to tropics and from coastal waters to deep-sea [11].
The importance of marine biodiversity can be translated at the economic or ecological level: source of food, biotechnological and non-living resources, as well as indicator of environmental health and ecosystem functioning (food webs). Major threats to marine biodiversity include overharvesting, habitat degradation, pollution, global warming, biological invasions and other anthropogenic stressors, most of them in coastal areas rather than in open ocean [11]. For instance, overfishing is predicted to cause a collapse of all fished taxa within the next 50 years [13], while marine invaders increased their ranges and are present in at least 84% of marine ecoregions worldwide [14]. Given these major concerns, it becomes more important than ever to know how many species are present in an ecosystem in order to understand and conserve species diversity.
There are significant disparities across marine taxa in terms of knowledge and status of taxonomic inventory. Larger organisms (e.g., fishes, mammals) are represented by fewer taxa in the world oceans and are usually well-studied groups. However, surprising findings can sometimes emerge, challenging our views on current knowledge. For instance, the number of marine mammals from Canadian waters currently reaches 52 species (Archambault et al., submitted) compared to 10 species listed in 1995 [15]. Considering how comparatively well known marine mammals are relative to most marine invertebrates, the inferred gaps in knowledge are particularly disconcerting when attempting to estimate the biodiversity of smaller organisms in poorly-sampled taxonomic groups, such as benthic and pelagic invertebrates, phytoplankton, and microbes. For marine invertebrates, the extent of taxonomic knowledge, including the number of species described every year, depends on the size of the taxonomic community studying various groups (Figure 2) [6].
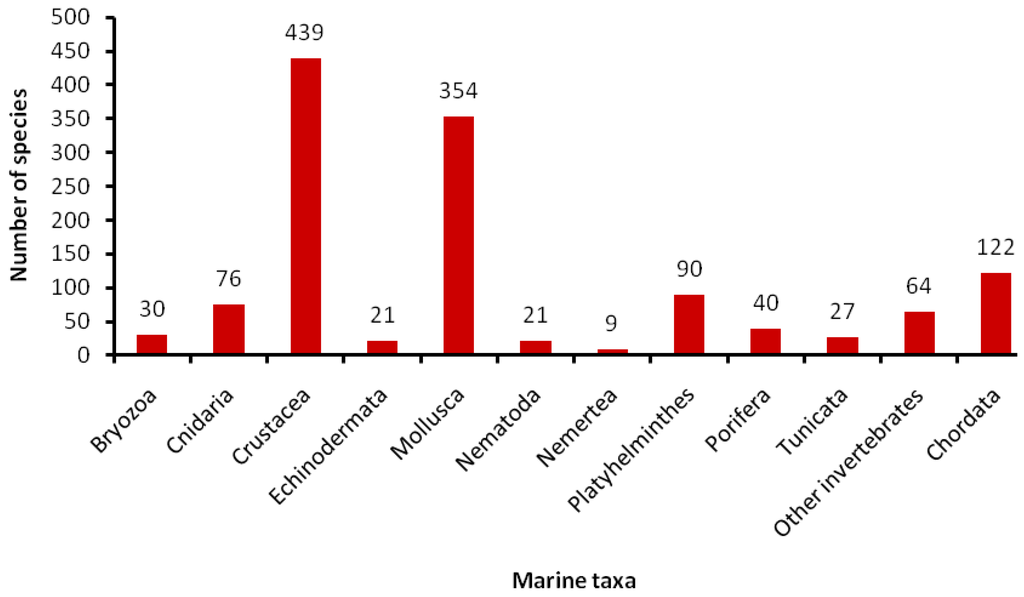
Figure 2.
Average number of marine animal species per taxon described every year (modified from [6]).
For instance, molluscs and crustaceans are the largest groups but probably due to large communities of malacologists and carcinologists, while polychaetes, believed to be one of the most abundant and species-rich macrobenthic taxa [7], are in great need of taxonomic work. With so many difficulties for biodiversity assessment, there is no wonder that marine faunal inventories usually fail to identify one third of specimens to the species level when using morphological methods [16].
3. Molecular Methods for Species Diversity
Given that morphological diagnosis poses a problem for the identification of all life stages (e.g., eggs, larvae), for sexually dimorphic species or those with large phenotypic plasticity and considering that cryptic species are widely distributed in marine systems [9], there is no surprise that scientists took the opportunity provided by the development of molecular methods to clarify many ambiguities in traditional taxonomy. Allozymes, alternative forms of enzymes coded by alleles at the same locus, were the first molecular markers widely used in population genetics to document patterns of genetic diversity in populations and also served as a useful tool in early molecular systematic studies [17]. For instance, Sévigny et al. [18] used the information provided by glucose phosphate isomerase to distinguish between closely related species of the planktonic copepod Pseudocalanus. Although electrophoretic patterns were not useful for species discrimination due to shared alleles, genetic analyses (heterozygosity, allele frequency, private alleles) showed that organisms previously grouped into species based on subtle morphological differences were also genetically isolated. Better resolution was found for larval identification of three oyster species [19]. However, protein-based approaches soon lost popularity in systematic studies due to several drawbacks such as the need to work with tissues that were either fresh or frozen and in reasonable quantity (i.e., very small eggs or larvae could not be analyzed). Furthermore, as this technique only detects nonsynonymous substitutions, the revealed polymorphism was often low. Consequently, the advent of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) allowing the amplification of various genes from small amounts of tissue, either fresh or preserved in ethanol, led to a boost in molecular-based identification of organisms. Various methods have been developed, including DNA hybridization, species-specific PCR, random amplified polymorphic DNA, restriction fragment length polymorphism, single strand conformational polymorphic DNA and sequencing of PCR products, with their advantages and disadvantages (see Table 1 in [20]). Of all these, sequencing methods, providing access to the most accurate genetic information (i.e., the string of nucleotides), were soon to become the method of choice for species identification.
One of the early sequencing-based studies in marine species looked at a mitochondrial gene, cytochrome b oxidase (cyt-b), and found that four species of tuna could be distinguished based on these sequences [21], while Medeiros-Bergen et al. [22] successfully identified three holothurian species with other mitochondrial sequences (16S). Bucklin et al. [23] sequenced yet another mitochondrial gene, cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI), in eight species from three genera of planktonic copepods and found the method to reliably discriminate even among sibling species. The authors acknowledged the need for a ‘rapid, simple, inexpensive and reliable’ molecular protocol for marine species identification.
4. DNA Barcoding for Species Identification and Discovery
4.1. The Concept: Advantages and Limitations
A ground-breaking approach to species identification was brought by Hebert et al. [24] who proposed the use of a small fragment from the mitochondrial genome for species identification across phyla from the entire animal kingdom and coined the term ‘DNA barcoding’ for this approach. Reasons for choosing mitochondrial (mtDNA) over nuclear DNA include uniparental inheritance (in a majority of animal phyla), high evolutionary rate, lack of introns, large copy numbers in every cell, and limited recombination (but see [25]). The proposal of COI as the target gene for DNA barcoding was not an arbitrary choice since decades of research showed a useful phylogenetic signal for both above- and below-species level and that ‘universal’ primers were capable to recover the 5’end of COI in most animal phyla. According to the barcoding approach, species could be identified based on a ‘barcoding gap’ between intra- and interspecific genetic distances by using a threshold value of 2−3% [24] or a 10-fold value [26] for species delimitation.
Although numerous studies used molecular methods for species identification prior to the DNA barcoding era, it is still a unique concept with manifold attributes. Initially proposed only for animal taxa, a DNA-based identification system was soon found to be successful in land plants [27], algae [28], fungi [29], whether using only COI and/or other DNA regions (mitochondrial, plastid, nuclear) for a better resolution. Besides the global scale involved, DNA barcoding brings a few major assets. It implies standardization (i.e., the same DNA fragment(s) used within a taxon), which allows comparisons between datasets of various researchers, revealing cases of synonymy, potential cryptic species or genetically distinct populations. Vouchers are permanently stored, ideally in a DNA-friendly manner, in museum collections, publicly accessible for future reference. This step is in contrast to most molecular studies conducted so far, which lack the possibility of specimen retrieval for sequences deposited in public databases (GenBank), therefore resulting in impossible taxonomic verifications and growing concerns about the documentation of scientific data ([30] and references therein). Vouchers can be stored under different forms (specimens, tissue, detailed photographs or stained slides for microscopy) and preservation methods (frozen, ethanol-preserved or dried specimens). DNA extracted from these vouchers is permanently stored in DNA banks available for future usage (e.g., inferring evolutionary patterns in different genes or proteins among taxa or habitats. The DNA Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD; http://www.boldsystems.org [31]) provides a unifying protocol for data acquisition, storage and analysis. Data stored in BOLD include sampling details with GPS coordinates, images, taxonomic information, DNA barcodes, primer sequences, electropherogram ‘trace’ files, and even detailed laboratory operations (with protocols for each step and gel images) for specimens processed at the Biodiversity Institute of Ontario (BIO, http://www.biodiversity.uoguelph.ca). Above all, this database if freely accessible and all data can be downloaded after publication or analyzed directly in BOLD with distance-based methods. Future taxonomic updates are possible. These attributes make BOLD a more advantageous tool to use when dealing with DNA barcodes than GenBank (notorious for hosting erroneous data [32]), proved by an eight-fold amount of barcodes produced at BIO and directly stored in BOLD (>650,000 barcodes) compared to GenBank (>90,000 barcodes) (February 2010).
Data scrutiny is vital since errors can occur at every step of DNA barcoding protocol, from sampling in the field to COI amplification, leading to surprising results such as amphipods identified as decapods according to DNA barcodes (A. Radulovici, unpublished). Any evidence of misidentification, mislabeling, cross-contamination between samples due to leaked DNA in ethanol jars with mixed samples [33] or during COI amplification, other contaminations (e.g., human, mouse, bacteria) or pseudogenes (nuclear copies of COI), is routinely investigated in barcoding studies. Once through the cleansing step, DNA barcodes can be used in various analyses.
DNA barcoding was initially faced with great criticism [34,35,36,37] by people who feared that a universal DNA-based approach for species identification will gain exclusivity over traditional methods and taxonomists would go extinct while funding would be vacuumed by high-throughput facilities in order to provide ‘barcode-species’ (i.e., species seen as strings of nucleotides). As with any other method, DNA barcoding has limitations, acknowledged by barcoders: low resolution in some cases (hybrids, recently diverged species, species complexes or slow evolving groups), the presence of pseudogenes [38], contaminants amplified with ‘universal’ primers [39] or cases of mitochondrial introgression [40] (see barcoding reviews [41,42]). Also, the functional group of many organisms is impossible to identify with DNA-barcodes. Thresholds have to be carefully considered due to variable mutation rate across taxa [25] or incomplete sampling of taxa [43,44]. Distance-based methods have been criticized and they are sometimes used in combination with character-based ones, but analytical tools are constantly being developed to incorporate the large body of information produced by DNA barcoding [45]. Moreover, critics have been oriented towards a new ‘barcode-species’ concept which will lead to an extreme amount of divergent clusters being arbitrary raised to the species level (taxon over-splitting). On the other hand, reproductive isolation, the requirement for the popular biological species concept, is a very difficult investigation in marine systems. However, Gómez et al. [46] tested this case in a cosmopolitan marine bryozoan and showed that divergent barcode clusters might indeed correspond to reproductively isolated groups, providing a link between DNA barcoding and the biological species concept.
Despite its limitations, DNA barcoding eventually became an appealing tool for biodiversity investigations, by identifying specimens during all life stages, from fresh or preserved material, cases of sexual dimorphism or potential cryptic species. Non-specialists are able to have a fast (express-barcoding in less than two hours [47]), cheap and reliable identification tool with many practical and fundamental applications. Moreover, there is an international Consortium for the Barcode of Life (CBOL; http://www.barcoding.si.edu) dedicated to establish DNA barcoding as a standard tool for species identification. The largest project currently envisaged is the International Barcode of Life Project (iBOL, http://www.ibol.org), to be launched in October 2010, with the goal of acquiring DNA barcodes for 500,000 species until 2015.
4.2. Practical Applications for the Marine Environment
In recent years, DNA barcodes have proved to be a valuable asset in identifying marine organisms, especially in the obvious cases where morphological identification is not possible, namely processed seafood. The famous example of fish sold as ‘red-snapper’ in the US and actually consisting of other species in 77% of cases (cyt-b sequences, [48]) was soon followed by other studies, which proved that seafood substitutions are common. The extent of this phenomenon on the global market of fresh, smoked or dried fish products varies across continents [20,49,50,51] and the possible explanations include genuine mislabeling due to morphological similarities between closely related species or fraudulent substitution of expensive species with cheaper variants. An extreme case of fish substitution had drastic consequences for public health, leading to food poisoning due to puffer fish toxin and the consequent recall of products [52]. With its power to reveal mislabeled products, DNA barcoding will have multiple implications from food safety and public health, to fisheries management (depletion of fish stocks) and conservation (protected species caught illegally).
Most marine organisms have larval stages difficult to identify based on morphological characters and DNA barcoding could have a great impact in this field, provided that a complete reference library for adults is developed [53,54,55]. Reliable identification of adults could have economic implications, for instance in aquarium fish trade regulations since many species originate in coral reefs [56], a highly threatened ecosystem. Moreover, routine DNA barcoding of marine organisms could identify invasive species [57], with special importance in cases of partial specimens which lost their key diagnostic characters [58].
4.3. Progress in DNA-based Inventories of Marine Groups
Many marine taxa represent an ideal target for DNA barcoding due to a lack of reliable morphological characters for easy diagnosis. Marine algae represent such a group due to simple morphology, phenotypic plasticity and alternative heteromorphic generations, among other factors [28]. The same standard marker as for animals (COI) proved to work well in red algae and revealed the presence of an invasive species in Canadian waters [57] as well as a large proportion of cryptic species [59]. Other invasive red algae with a negative impact on coral reefs were identified in Hawaii based on a multi-gene approach including COI [60]. Successful results with COI were shown in brown algae [61] but less so in green algae where other markers are being tested (G. Saunders, pers. comm.).
Diatoms represent a large component of the marine microbiota and another group where COI was not successful on large scale. A recent study including 114 diatom species found ITS to have 99.5% identification success [62], result that will surely lead to an increase in DNA-based inventories for this important marine group.
Due to low substitution rate in mtDNA, plant barcoding had a lower success rate compared to the animal kingdom. Alternative regions have been proposed and a final recommendation for a two-locus approach (plastid coding genes: matK and rcbL) has recently been made [27]. Consequently, seagrass species (e.g., Zostera spp., Posidonia spp.) with no reference in BOLD yet (February 2010), will soon be targeted by barcoding studies.
Sponges are an ancestral metazoan group with simple morphology but complex and important roles in marine ecosystems and pharmaceutical industry [63]. Currently, this is the only invertebrate phylum to be barcoded through a global campaign (Sponge Barcoding Project, http://www.spongebarcoding.org), although a COI fragment downstream of the ‘Folmer’ region was found to be more variable, hence more appropriate for species identification in sponges [64].
Cnidarians (e.g., corals, sea anemones) and sponges constitute the most important components of coral reefs. COI seems to evolve too slowly in both groups, therefore lacking the power to reliably identify species. And while in sponges another COI fragment than the standard 5’end might be useful, cnidarian barcoding might need another gene (<2% interspecific divergences in scleractinian corals [65]) (Table 2). Moura et al. [66] assessed the efficacy of 16S and showed that this gene could be a useful marker at the species and even population, genus and family levels in hydrozoans. Combining their own sequences with public ones from GenBank, the authors flagged problematic issues for hydroid systematics: potential cryptic species, conspecificity (low divergence between species) or cosmopolitan species consisting of species complexes. However, recent advances involving planktonic hydrozoans [67] indicate that this group might actually be successfully COI barcoded.

Table 2.
Levels of genetic divergence in marine taxa. Only studies using the 5’ end of COI and giving average K2P genetic divergences were included. NoS: number of species barcoded; Intra: mean genetic distances within species; Inter: mean genetic distances between species.
| Marine group | NoS | Intra (%) | Inter (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crustaceans | ||||
| Malacostracans | 80 | 0.91a | 13.6 | [58] |
| Decapods | 54 | 0.46 | 17.16 | [68] |
| Copepods | 24 | 0.75b | 27.05 | [67] |
| Molluscs | ||||
| Heteropods | 9 | 3.28 | 21.7 | [69] |
| Pteropods | 31 | 3.02 | 17.6 | [69] |
| Corals | 30 | 0.05 | 1.90 | [65] |
| Chaetognaths | 14 | 1.45 | 34.5 | [70] |
| Echinoderms | 191 | 0.62 | 15.33 | [71] |
| Fishes | 207 | 0.39 | 9.93 | [72] |
a if deeply divergent clades are removed, the mean intraspecific value becomes 0.51%.b mean intraspecific for the entire dataset (crustaceans, cnidarians, chaetognaths, one nemertean).
Molluscs represent the largest marine group with more than 50,000 described species (Table 1). One of the early studies to draw attention on the risks of using thresholds and incomplete sampling in barcoding approaches was tested on cowries, a very diverse and well-studied group of marine gastropods [43]. Results showed that overlap between intra- and interspecific divergences might lead to large errors in species identification when the taxon is undersampled. Species of intertidal gastropods were found to share haplotypes in NE Atlantic, potentially due to introgression or incomplete lineage sorting [40], while gastropod eggs from Philippines could not be identified to the species level due to a lack of comprehensive barcode databases [73]. Local-scale barcoding of species from four genera of Norwegian bivalves was a successful case, although larger datasets are needed to prove the applicability of barcodes in identifying bivalves [74]. A barcoding study of planktonic gastropods (pteropods and heteropods) from six oceans revealed the highest average values (> 3%) for genetic distances between individuals of the same species reported to date (Table 2) [69]. This is a strong indication that divisions below the species level (e.g., subspecies) might represent valid species and a taxonomic revision should be conducted.
Crustaceans are one of the largest (Table 1) and most diverse, morphologically and ecologically, marine groups. Playing important roles in marine food webs, crustaceans have representatives in all marine habitats. Costa et al. [68] used their own sequence data and public data in GenBank to perform a large-scale analysis in crustaceans (150 species from 23 orders). Besides successful species identification (Table 2), this study revealed cases of potential overlooked species and the need for taxonomic revisions (e.g., valid species that should be lumped). Taxon-specific barcoding studies were conducted on euphausiids [75] and stomatopod larvae [53]. While the former could identify all specimens to the species level, the latter showed that a large part of stomatopod species from Indo-Pacific coral reefs is unknown as adults. Reef-associated crustaceans, mainly decapods, stomatopods and peracarids, from French Polynesia have been recently barcoded, revealing a large proportion of singletons (i.e., species represented by one specimen) living in Pocillopora dead heads [76]. While undersampling is usually the cause for a bias towards singletons, this study used a semi-quantitative sampling design to show that associated fauna in coral reefs is largely composed of low-abundance species. In addition, no species barcoded in this study had a match in GenBank, highlighting once more the need for comprehensive reference libraries. Radulovici et al. [58] used a regional approach in barcoding malacostracan crustaceans from the Gulf of St. Lawrence and revealed the existence of an invasive amphipod species, Echinogammarus ischnus, which expanded its distribution since previous studies. Cryptic speciation was not found to be common (5% of cases) but it might be a result of incomplete taxon sampling (80 species representing only 20% of the regional malacostracan fauna) or geographical scale.
A large barcoding study was conducted on echinoderms (191 species from five classes) by including also public data from GenBank (70% of the final dataset) [71]. Based on shallow intraspecific versus deep congeneric divergences (Table 2), a large amount of specimens (97.9%) could be assigned to known species. Those who failed belonged to one genus, Amblypneustes, known to include morphologically and genetically similar species. Additionally, a few cases of potential cryptic species were recorded.
Smaller groups are also targeted in barcoding studies. For instance, sea spiders (Pycnogonida) were recently sampled as part of a marine inventory of the Ross Sea, Antarctica, and 25 species were identified based on morphological and molecular data (18S, 12S, 16S, COI) [77]. Although statistics related to the level of genetic divergence were not provided by this study, a general concordance between barcode clusters and morphospecies was reported (one case of misidentification or potential cryptic species) and no new species was revealed during the survey. However, with a larger geographic sampling for an abundant and circumpolar species, Krabbe et al. [78] found multiple cryptic mitochondrial lineages, geographically restricted, within one nominal species. A much smaller group than sea spiders (see Table 2.1 in [6]), chaetognaths are mostly planktonic invertebrates with simple morphology but complex roles in the pelagic realm together with large distribution areas at the global scale. Successful identification can be performed with standard COI barcodes, even though the level of intraspecific variation is slightly higher than in other marine groups (Table 2) [70].
A large and morphologically difficult group, therefore with underestimated diversity, but with potential roles as indicators of anthropogenic impact on marine systems, nematodes could greatly benefit from DNA barcoding (Table 1). So far, the 18S gene was found to amplify across many taxa and with 97% identification success [79].
Parasites are very often excluded from marine faunal inventories. However, they are very common and play important roles in marine ecosystems by affecting population dynamics of their hosts. Therefore, a reliable identification system would be of great utility in community ecology (e.g., identifying all life cycles in different hosts) as well as for public health (e.g., human parasites). In the marine realm, a recent attempt to barcode parasites of intertidal species from New Zealand targeted a group of trematode species, all of which could be distinguished based on DNA sequences [80]. Although the authors chose to amplify a short DNA fragment downstream of the ‘Folmer’ region, while the standard 5’ end can generally be amplified in this group [81], the study provided important ecological data on the trematode species analyzed with notes on new host-parasite interactions in intertidal mudflats.
Fishes are among the most studied marine groups and are currently barcoded within two global campaigns, FISH-BOL (http://www.fishbol.org) and SHARK-BOL (http://www.sharkbol.org) [82]. One of the early studies on barcoding marine life looked at 207 fish species from Australia and showed that all could be discriminated based on their COI sequence, including five species of Squalus previously described but not formally named [72]. Other studies found barcoding to be useful in identifying fishes from Pacific Canada [83], North Atlantic [84] or fish larvae from the Great Barrier Reef [55]. When including shared species between distant geographical areas, DNA barcodes could be useful to test the relationship between distance and intraspecific variation. For instance, Ward et al. [84] found only two out of 15 species shared between North Atlantic and Australasia with deep intraspecific divergence (2.75% and 7.44%). On the other hand, Zemlak et al. [85] showed that populations of commercial fish with inshore distribution in South Africa and Australia have high levels of genetic divergence (mean 5.10%) and estimated that one third of the 1,000 shared species between these two regions include cryptic taxa. As a general remark, DNA barcodes were shown to be a powerful tool in discriminating marine fishes (98% success). Rare cases of incongruence were due to potential cryptic species or species complexes (deeply divergent intraspecific clusters), or to cases of hybrids, recent radiation, taxonomic over-splitting or morphological misidentification (shared haplotypes) [82].
Sea turtles are represented by only seven species worldwide but are threatened across their entire distribution range, therefore DNA barcodes could be very useful in species conservation and wildlife forensics by identifying turtle meat and eggs illegally traded or carcasses stranded on beaches [86]. Although sea turtles represent an ancient group with slow mutation rate, all species were successfully identified and no cryptic species was revealed based on genetic distances and character-based methods [87]. Two recently radiated species showed the only interspecific distance below the threshold of 2−3% but even so, there was no overlap between intra- and interspecific values. Other marine reptiles, such as snakes, will be barcoded within a large iBOL project targeting all vertebrates (A. Borisenko, pers. comm.), while birds connected to the marine environment are already being barcoded within ‘All Birds Barcoding Initiative’ (http://www.barcodingbirds.org).
The most studied and charismatic marine vertebrates (whales, dolphins and the other cetaceans), lack a comprehensive library of DNA barcodes. However, a newly established campaign, Mammalia Barcode of Life (http://www.mammaliabol.org), has as goal to provide DNA barcodes for all mammals by 2015, marine species as well.
DNA barcoding is a tool for species identification and discovery (by flagging divergent clusters) and modern taxonomy and systematics is increasingly incorporating COI sequences as additional data into their fields [88,89,90,91,92]. DNA barcodes might become a standard character to be included with species description and low sequencing prices will soon make this tool widely available to researchers from economically poor but biodiversity rich countries. Although we saw a multitude of cases arguing for potential cryptic species (‘taxon-splitting’), there will definitely be cases of ‘taxon-lumping’ revealed with a DNA-based approach. For instance, two lumpsucker species with different morphology were found to have identical sequences for multiple genes and to actually represent one sexually dimorphic species [93]. Moreover, DNA barcodes could be incorporated into large phylogenies [94,95], or used for inferring preliminary phylogeographic patterns [96].
5. Current Status
5.1. How Many Marine Barcodes?
We attempted to make a synopsis of marine groups that have been targeted by DNA barcoding by focusing on published data. Some of the papers reviewed here were contributions to the Marine Barcode of Life Project (MarBOL, http://www.marinebarcoding.org), a joint effort of CBOL and Census of Marine Life (CoML; http://www.coml.org) to provide 50,000 barcodes for marine species by mid-2010. Since the project is still in progress, only preliminary results are available at this moment. However, with more than 37,000 barcodes produced (MarBOL website, February 2010), the project is moving fast forward confirming the usefulness of such an approach for marine systems (Figure 3).
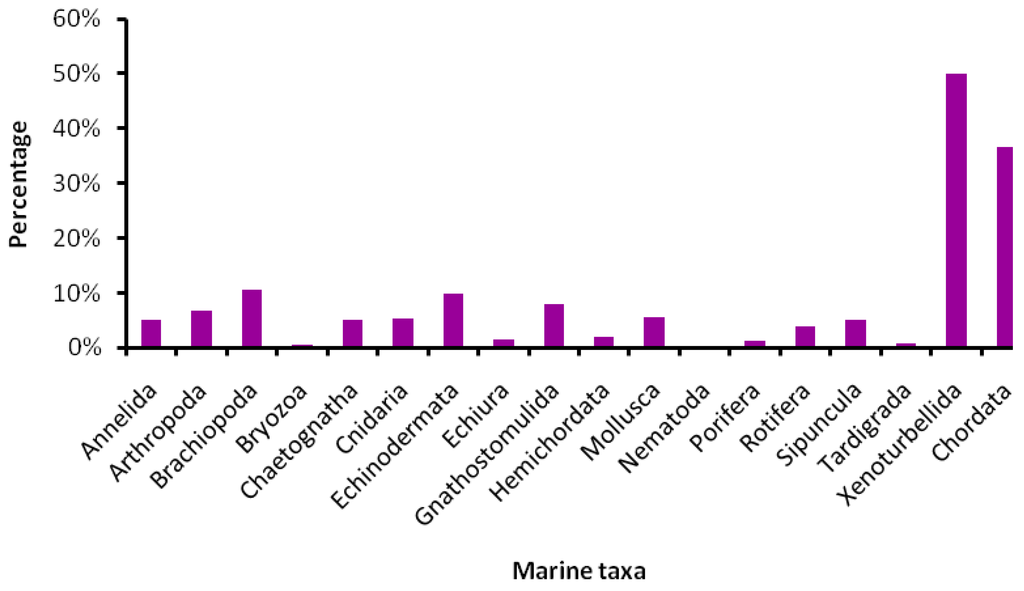
Figure 3.
Proportion of barcoded species across marine taxa (data provided by D. Steinke, MarBOL coordinator).
There is a wealth of on-going case-studies in the marine realm that will be published in the near future (http://www.bolinfonet.org/casestudy; Taxonomy Browser in BOLD). Whether taxon-oriented (FISH-BOL, SharkBOL, Sponge Barcoding Project), nationwide (Canada, Australia, Norway, India) or locally focused on entire biota (Churchill, Moorea), targeting ecosystems (ReefBOL), ecoregions (Polar Barcode of Life) or multiple taxa from the entire marine environment (MarBOL), large-scale barcoding campaigns will provide a vast amount of information in need for accurate treatment and analysis.
A first glimpse at the Canadian case-study might suggest that marine biodiversity has been severely underestimated even in a marine non-hotspot area. First, there is an enormous amount of marine species, mostly invertebrates, collected in the past and still awaiting formal description and naming (only 48% of marine species classified [15], Archambault et al., submitted). Second, the opening of the Northwest Passage due to climate change will lead to new Arctic explorations, most likely ending with new faunal discoveries, especially in less-known groups (e.g., polychaetes). Third, DNA barcodes indicate that cryptic speciation might take place even in well-known marine taxa (though to less extent) and geographical areas. For instance, DNA barcodes showed that one quarter of polychaete identified morphospecies actually consists of potential cryptic species when considering a nationwide scale with all three oceans, Atlantic, Arctic and Pacific, included (C. Carr, pers. comm.). Based on this result and knowing that there are at least 673 infaunal polychaetes for the three oceans (Archambault et al., submitted), this would mean that around 840 species of polychaetes are present in Canadian waters alone. Cryptic speciation seems to be common in different groups of marine algae (G. Saunders, pers. comm.) but less so in fish [83] or marine crustaceans [58]. However, marine crustaceans include a wide variety of groups with different potential for dispersal (hence different potential to speciate) and once a nationwide scale is included and taxonomic input provided, crustaceans might likely exhibit various extents of cryptic speciation (Radulovici et al., unpublished).
5.2. Special Issues with Marine Taxa
Where are we now? Recent developments provide non-invasive DNA extraction with total voucher recovery [97], as well as extraction of DNA leaked into the aquatic environment [98] or ethanol [33]. Primers are being developed for various taxa and additional markers or larger COI fragments used in cases of slow mutation rate (e.g., sponges, cnidarians). The BIO high-throughput facilities provide around 250,000 barcodes per year and will double the amount in the future (G. Singer, pers. comm.). We have the technological capacity to barcode the entire life, yet marine barcoding lags far behind the terrestrial counterpart (Figure 4). Why? The long-standing tradition of preserving marine material by using formalin, which prevents DNA amplification, represents a serious impediment in using museum specimens for DNA barcoding, in contrast to terrestrial taxa. Therefore, fresh material stored in ethanol must be collected during sampling cruises, which are very expensive and usually focused on one or a few particular groups of marine organisms. These specimens have to be identified by trained taxonomists who are drastically decreasing in number. Moreover, most marine groups do not benefit from the help of amateurs, in contrast to terrestrial groups such as birds or butterflies. Consequently, a greater effort is inevitable when barcoding marine taxa.
5.3. Taxonomy and Barcoding
At the moment we are unable to assess the impact of DNA barcoding on species diversity in terms of number of new species described as a result of this approach. The reason is simple: barcoding studies have the role to screen large sample sizes and flag cases of intraspecific deep divergence (‘cryptic species’). However, the task of investigating further the extent of this phenomenon (additional genetic, ecological, behavioral data) culminating in a new species description does not belong to a barcoder but to a taxonomist. And since the number of taxonomists is rapidly decreasing [99] while marine barcodes are rapidly accumulating, the majority of flagged cases stop at the level of ‘potential cryptic species’. Without a larger interest and involvement of highly trained taxonomists in marine barcoding studies, the advancement of the understanding of marine speciation will not be very rapid, potentially leading to another ‘tale of stupidity’ [100].
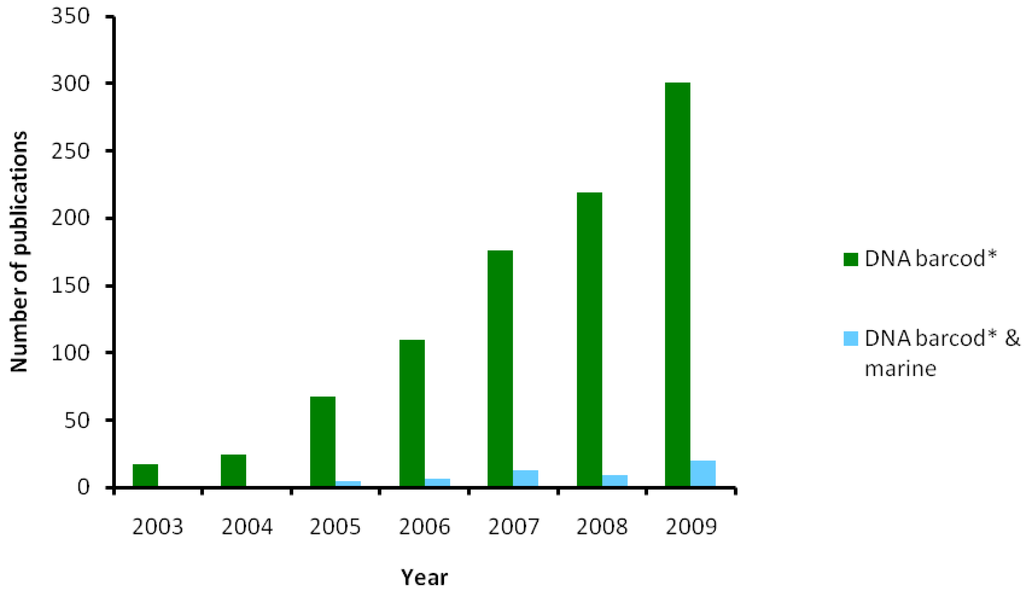
Figure 4.
The amount of barcoding studies targeting marine systems (‘DNA barcod*’ and ‘marine’ as keywords in Web of Science).
5.4. Future Directions
Most of the studies reviewed here did not flag a high amount of cryptic speciation but this discovery is contingent upon the scale of the studies. An increased geographic scale and the inclusion of groups with lower potential for dispersal will surely bring interesting results. Since a few cases of deep divergence have been found in fishes, the most popular marine group for barcoding, surveys of similar scales in understudied groups will be promising for species discovery.
New methods for sampling deep-sea will lead to the discovery of many new species. Sampling expeditions with on-board laboratories might become a commonplace. While most barcoding studies are still taxon-oriented, there are a few others opening new directions by targeting marine communities (e.g., zooplankton [67,101]). DNA microarrays (‘chips’) will be developed for certain marine groups [102], allowing reliable identification of known species. Once reference libraries are completed, next generation sequencing will allow reliable identification of environmental samples (e.g., water, sediment) or species diet, with reverberations for studying the ecosystem level of biodiversity.
5.5. Species as Currency for Biodiversity
This review looked at reliable methods for biological identifications. But do we need species names? The idea that species might not represent equal parts of the global diversity (‘some animals are more equal than others’ [103]), resulted in alternative approaches for biodiversity assessments, for instance including the diversity of higher taxa (e.g., taxonomic distinctness rather than species diversity [104]). Moreover, in functional ecology species names are not important but just the functional group (e.g., predator, prey). In this case, one might argue that barcodes are useless because they do not offer any functional information, while morphological characters (e.g., mouthparts in crustaceans) could be an indication of specimens’ functional group and their role in ecosystems. Alternatively, at the genetic level of biodiversity, species names are not crucial. Clusters of DNA barcodes might be used in biodiversity surveys by using a phylogenetic diversity analysis [105,106]. Therefore, we should take advantage of various methods for a holistic approach to biodiversity.
6. Conclusions
DNA barcoding is a unique concept with many innovative attributes undertaking continuous improvement. It is not the goal but the tool to be used in order to improve our understanding of the surrounding world. It is a fast, reliable and cheap method for species identification and discovery. It provides permanent tags unchanged during taxonomic revisions. It will have multiple applications for marine life: identification of larvae, invasive species, cryptic species, new species, illegal trade of protected species, stock management, biodiversity assessments, ecosystem monitoring, revisions of certain taxa, inference of phylogenetic relationships, phylogeographic and speciation patterns. Most of the studies reviewed here were published within the last two-three years and there was no sign that traditional taxonomy is being replaced by DNA barcoding, as once feared, but that they are complementary approaches. Not only that species are not seen as merely strings of nucleotides, but we are witnessing a renaissance of taxonomy due to the need (and curiosity) to understand how and why divergent barcode clusters are (if really) morphologically identical. As seen above, the apparent ‘failure’ of DNA barcoding to identify species is mainly due to a lack of comprehensive reference libraries and taxonomists will play a vital role in completing such a global database. Millions of barcodes will soon be generated and new species revealed, in need for proper taxonomic description. Furthermore, as marine inventories are not carried out by taxonomist experts at museums but by trained personnel at university or governmental institutions, there is a pressing need to make a concordance between taxonomy and DNA barcoding. Therefore, taxonomy is far from being extinct.
Whether DNA barcoding with the plethora of global and local campaigns will succeed in meeting close deadlines (500,000 species by 2015) or not, remains an open question. During the last ten years, CoML had the objective to assess and explain the diversity, distribution, and abundance of marine life, contributing significantly to an understanding of the marine environment and the inhabitants of the global oceans. However, even with the amount of new information generated by CoML, it is only the beginning. DNA barcoding might be of great help in this direction, leading to a shift in our view of marine biodiversity, patterns and processes included. But above all, DNA barcoding provides data freely accessible to everyone. And even if computers and Internet access, needed to browse data in BOLD, are not yet a commodity in many countries, DNA barcoding represents the largest experiment of open-access data sharing which could help decision making to preserve and protect marine biodiversity now and into the future.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the following people for sharing information with us: Dirk Steinke (BIO) provided data on the global progress of marine barcoding, graphically represented in Figure 3; David Porco (BIO) and Robert Jennings (UMB) sent us their papers ahead of print; Christina Carr (BIO) shared her interesting results on barcoding Canadian polychaetes and Gary Saunders (UNB) provided an update on barcoding marine algae; Alex Borisenko and Greg Singer (BIO) kindly provided details on new iBOL projects. We thank two anonymous reviewers for useful comments upon the manuscript. This work is a contribution to the Canadian Barcode of Life Network, as well as to the Canadian Healthy Oceans Network, both funded through the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council.
References
- Biodiversity; Wilson, E.O.; Peter, F.M. (Eds.) National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1988.
- Pimm, S.L.; Russell, G.J.; Gittleman, J.L.; Brooks, T.M. The future of biodiversity. Science 1995, 269, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, A.D. Numbers of Living Species in Australia and the World, 2nd ed.; Australian Biological Resources Study: Canberra, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, J.A.; Orr, H.A. Speciation; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, L.; Gibbs, J.; Sheffield, C.; Hanner, R. DNA barcoding and the mediocrity of morphology. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, P. The magnitude of marine biodiversity. In The Exploration of Marine Biodiversity: Scientific and Technological Challenges; Duarte, C.M., Ed.; Fundacion BBVA: Bilbao, Spain, 2006; pp. 31–64. [Google Scholar]
- Grassle, J.F.; Maciolek, N.J. Deep-sea species richness—regional and local diversity estimates from quantitative bottom samples. Am. Nat. 1992, 139, 313–341. [Google Scholar]
- Vrijenhoek, R.C. Cryptic species, phenotypic plasticity, and complex life histories: Assessing deep-sea faunal diversity with molecular markers. Deep-Sea Res. II 2009, 56, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N. Sibling species in the sea. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 189–216. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, J.C. Species-diversity—land and sea compared. Syst. Biol. 1994, 43, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.S. Marine biodiversity: patterns, threats and conservation needs. Biodivers. Conserv. 1997, 6, 153–175. [Google Scholar]
- Brunel, P. Visages de la biodiversite marine. VertigO 2005, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Worm, B.; Barbier, E.B.; Beaumont, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Folke, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Lotze, H.K.; Micheli, F.; Palumbi, S.R.; Sala, E.; Selkoe, K.A.; Stachowicz, J.J.; Watson, R. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 2006, 314, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquin, T.; Whiting, P.G.; McAllister, D.E. Canada’s Biodiversity: The Variety of Life, Its Status, Economic Benefits, Conservation Costs and Unmeet Needs; Canadian Museum of Nature: Ottawa, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Schander, C.; Willassen, E. What can biological barcoding do for marine biology? Mar. Biol. Res. 2005, 1, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Systematic value of electrophoretic data. Syst. Zool. 1975, 23, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sévigny, J.M.; McLaren, I.A.; Frost, B.W. Discrimination among and variation within species of Pseudocalanus based on the GPI locus. Mar. Biol. 1989, 102, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.P.; Lutz, R.A.; Vrijenhoek, R.C. Electrophoretic identification and genetic-analysis of bivalve larvae. Mar. Biol. 1992, 113, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.H.K.; Hanner, R.H. DNA barcoding detects market substitution in North American seafood. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.E.; Davidson, W.S. Identification of Thunnus tuna species by the polymerase chain-reaction and direct sequence-analysis of their mitochondrial cytochrome-b genes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 48, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Bergen, D.E.; Olson, R.R.; Conroy, J.A.; Kocher, T.D. Distribution of holothurian larvae determined with species-specific genetic probes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.; Guarnieri, M.; Hill, R.S.; Bentley, A.M.; Kaartvedt, S. Taxonomic and systematic assessment of planktonic copepods using mitochondrial COI sequence variation and competitive, species-specific PCR. Hydrobiologia 1999, 401, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtier, N.; Nabholz, B.; Glémin, S.; Hurst, G.D.D. Mitochondrial DNA as a marker of molecular diversity: a reappraisal. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Stoeckle, M.Y.; Zemlak, T.S.; Francis, C.M. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Forrest, L.L.; Spouge, J.L.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ratnasingham, S.; van der Bank, M.; Chase, M.W.; Cowan, R.S.; Erickson, D.L.; Fazekas, A.J.; Graham, S.W.; James, K.E.; Kim, K.J.; Kress, W.J.; Schneider, H.; van AlphenStahl, J.; Barrett, S.C.H.; van den Berg, C.; Bogarin, D.; Burgess, K.S.; Cameron, K.M.; Carine, M.; Chacón, J.; Clark, A.; Clarkson, J.J.; Conrad, F.; Devey, D.S.; Ford, C.S.; Hedderson, T.A.J.; Hollingsworth, M.L.; Husband, B.C.; Kelly, L.J.; Kesanakurti, P.R.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Lahaye, R.; Lee, H.L.; Long, D.G.; Madriñan, S.; Maurin, O.; Meusnier, I.; Newmaster, S.G.; Park, C.W.; Percy, D.M.; Petersen, G.; Richardson, J.E.; Salazar, G.A.; Savolainen, V.; Seberg, O.; Wilkinson, M.J.; Yi, D.K.; Little, D.P. A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12794–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, G.W. Applying DNA barcoding to red macroalgae: a preliminary appraisal holds promise for future applications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, K.A.; Samson, R.A.; deWaard, J.R.; Houbraken, J.; Levesque, C.A.; Moncalvo, J.M.; Louis-Seize, G.; Hebert, P.D.N. Prospects for fungus identification using CO1 DNA barcodes, with Penicillium as a test case. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3901–3906. [Google Scholar]
- Pleijel, F.; Jondelius, U.; Norlinder, E.; Nygren, A.; Oxelman, B.; Schander, C.; Sundberg, P.; Thollesson, M. Phylogenies without roots? A plea for the use of vouchers in molecular phylogenetic studies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.J. Can you bank on GenBank? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokralla, S.; Singer, G.A.C.; Hajibabaei, M. Direct PCR amplification and sequencing of specimens’ DNA from preservative ethanol. BioTechniques 2010, 48, 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Will, K.W.; Mishler, B.D.; Wheeler, Q.D. The perils of DNA barcoding and the need for integrative taxonomy. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, K.W.; Rubinoff, D. Myth of the molecule: DNA barcodes for species cannot replace morphology for identification and classification. Cladistics 2004, 20, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinoff, D.; Cameron, S.; Will, K. A genomic perspective on the shortcomings of mitochondrial DNA for ‘barcoding’ identification. J. Hered. 2006, 97, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinoff, D. Utility of mitochondrial DNA barcodes in species conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Buhay, J.E.; Whiting, M.F.; Crandall, K.A. Many species in one: DNA barcoding overestimates the number of species when nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes are coamplified. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13486–13491. [Google Scholar]
- Siddall, M.E.; Fontanella, F.M.; Watson, S.C.; Kvist, S.; Erséus, C. Barcoding bamboozled by Bacteria: convergence to metazoan mitochondrial primer targets by marine microbes. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemppainen, P.; Panova, M.; Hollander, J.; Johannesson, K. Complete lack of mitochondrial divergence between two species of NE Atlantic marine intertidal gastropods. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frézal, L.; Leblois, R. Four years of DNA barcoding: Current advances and prospects. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A. DNA barcoding demystified. Aust. J. Entomol. 2008, 47, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.P.; Paulay, G. DNA barcoding: Error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Ekrem, T.; Willassen, E.; Stur, E. A comprehensive DNA sequence library is essential for identification with DNA barcodes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Matz, M. Statistical approaches for DNA barcoding. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.; Wright, P.J.; Lunt, D.H.; Cancino, J.M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Hughes, R.N. Mating trials validate the use of DNA barcoding to reveal cryptic speciation of a marine bryozoan taxon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Borisenko, A.V.; Hebert, P.D.N. Express barcodes: racing from specimen to identification. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, P.B.; Lee, S.C.; Rice, A.M.; Gramling, J.M.; Fitzhenry, T.M.; McAlister, J.S.; Harper, G.R.; Moran, A.L. Mislabelling of a depleted reef fish. Nature 2004, 430, 309–310. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.J.; McVeagh, S.M.; Steinke, D. DNA barcoding for the identification of smoked fish products. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuto, M.; Galimberti, A.; Ferri, E.; Labra, M.; Malandra, R.; Galli, P.; Casiraghi, M. DNA barcoding reveals fraudulent substitutions in shark seafood products: the Italian case of ‘palombo’ (Mustelus spp.). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.H.; Steinke, D.; Ward, R.D. Identification of shark and ray fins using DNA barcoding. Fish. Res. 2009, 95, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.J.; Deeds, J.R.; Wong, E.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Yancy, H.F.; White, K.D.; Thompson, T.M.; Wahl, M.; Pham, T.D.; Guichard, F.M.; Huh, I.; Austin, C.; Dizikes, G.; Gerber, S.I. Public health response to puffer fish (tetrodotoxin) poisoning from mislabeled product. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 810–817. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, P.; Boyce, S.L. Estimating diversity of Indo-Pacific coral reef stomatopods through DNA barcoding of stomatopod larvae. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, K.E.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Clark, M.S.; Bowden, D.A. DNA barcoding: a molecular tool to identify Antarctic marine larvae. Deep Sea Res. II 2006, 53, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegg, G.G.; Sinclair, B.; Briskey, L.; Aspden, W.J. MtDNA barcode identification of fish larvae in the southern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Steinke, D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Barcoding Nemo: DNA-based identifications for the ornamental fish trade. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, G.W. Routine DNA barcoding of Canadian Gracilariales (Rhodophyta) reveals the invasive species Gracilaria vermiculophylla in British Columbia. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovici, A.E.; Sainte-Marie, B.; Dufresne, F. DNA barcoding of marine crustaceans from the Estuary and Gulf of St Lawrence: a regional-scale approach. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, G.W. A DNA barcode examination of the red algal family Dumontiaceae in Canadian waters reveals substantial cryptic species diversity. 1. The foliose Dilsea-Neodilsea complex and Weeksia. Botany-Botanique 2008, 86, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, K.Y.; Kurihara, A.; Sherwood, A.R. A molecular method for identification of the morphologically plastic invasive algal genera Eucheuma and Kappaphycus (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) in Hawaii. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevit, D.C.; Saunders, G.W. On the utility of DNA barcoding for species differentiation among brown macroalgae (Phaeophyceae) including a novel extraction protocol. Phycol. Res. 2009, 57, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniz, M.B.J.; Kaczmarska, I. Barcoding of diatoms: nuclear encoded ITS revisited. Protist 2010, 161, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörheide, G.; Erpenbeck, D. DNA taxonomy of sponges—progress and perspectives. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2007, 87, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Erpenbeck, D.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Wörheide, G. CO1 phylogenies in diploblasts and the ‘Barcoding of Life’—are we sequencing a suboptimal partition? Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, T.L.; Coffroth, M.A. Barcoding corals: limited by interspecific divergence, not intraspecific variation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, C.J.; Harris, D.J.; Cunha, M.R.; Rogers, A.D. DNA barcoding reveals cryptic diversity in marine hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) from coastal and deep-sea environments. Zool. Scr. 2008, 37, 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bucklin, A.; Hopcroft, R.R.; Kosobokova, K.N.; Nigro, L.M.; Ortman, B.D.; Jennings, R.M.; Sweetman, C.J. DNA barcoding of Arctic Ocean holozooplankton for species identification and recognition. Deep-Sea Res. II 2010, 57, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.O.; DeWaard, J.R.; Boutillier, J.; Ratnasingham, S.; Dooh, R.T.; Hajibabaei, M.; Hebert, P.D.N. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes: the case of the Crustacea. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 272–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, R.M.; Bucklin, A.; Ossenbrügger, H.; Hopcroft, R.R. Species diversity of planktonic gastropods (Pteropoda and Heteropoda) from six ocean basins based on DNA barcode analysis. Deep-Sea Res. II. 2010. accepted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, R.M.; Bucklin, A.; Pierrot-Bults, A. Barcoding of arrow worms (Phylum Chaetognatha) from three oceans: genetic diversity and evolution within an enigmatic phylum. PLoS One 2010. accepted for publication. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; O’Hara, T.D. DNA barcoding discriminates echinoderm species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Strong, E.E.; Bouchet, P.; Boisselier, M.C.; Couloux, A.; Samadi, S. Identifying gastropod spawn from DNA barcodes: possible but not yet practicable. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, N.T.; Schander, C.; Willassen, E. Local scale DNA barcoding of bivalves (Mollusca): a case study. Zool. Scr. 2007, 36, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.; Wiebe, P.H.; Smolenack, S.B.; Copley, N.J.; Beaudet, J.G.; Bonner, K.G.; Farber-Lorda, J.; Pierson, J.J. DNA barcodes for species identification of euphausiids (Euphausiacea, Crustacea). J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisance, L.; Knowlton, N.; Paulay, G.; Meyer, C. Reef-associated crustacean fauna: biodiversity estimates using semi-quantitative sampling and DNA barcoding. Coral Reefs 2009, 28, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.F.; Lavery, S.; Lorz, A.N. Synopsis of a new collection of sea spiders (Arthropoda: Pycnogonida) from the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabbe, K.; Leese, F.; Mayer, C.; Tollrian, R.; Held, C. Cryptic mitochondrial lineages in the widespread pycnogonid Colossendeis megalonyx Hoek, 1881 from Antarctic and Subantarctic waters. Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, P.; Austen, M.C.; Bilton, D.T.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Rogers, A.D.; Smerdon, G.R. Development and evaluation of a DNA-barcoding approach for the rapid identification of nematodes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 320, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.L.F.; Donald, K.M.; Keeney, D.B.; Koehler, A.V.; Peoples, R.C.; Poulin, R. Trematode parasites of Otago Harbour (New Zealand) soft-sediment intertidal ecosystems: life cycles, ecological roles and DNA barcodes. N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2009, 43, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, S.A.; McLaughlin, J.D.; Dayanandan, S.; Marcogliese, D.J. Diversity and specificity in Diplostomum spp. metacercariae in freshwater fishes revealed by cytochrome c oxidase I and internal transcribed spacer sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Hanner, R.; Hebert, P.D.N. The campaign to DNA barcode all fishes, FISH-BOL. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 329–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Boutillier, J.A.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding of Pacific Canada’s fishes. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Costa, F.O.; Holmes, B.H.; Steinke, D. DNA barcoding of shared fish species from the North Atlantic and Australasia: minimal divergence for most taxa, but Zeus faber and Lepidopus caudatus each probably constitute two species. Aquatic Biol. 2008, 3, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zemlak, T.S.; Ward, R.D.; Connell, A.D.; Holmes, B.H.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding reveals overlooked marine fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S.M.; Araujo, F.C.F.; Santos, F.R. DNA barcoding of Brazilian sea turtles (Testudines). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naro-Maciel, E.; Reid, B.; Fitzsimmons, N.N.; Le, M.; DeSalle, R.; Amato, G. DNA barcodes for globally threatened marine turtles: a registry approach to documenting biodiversity. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 10, 252–263. [Google Scholar]
- Järnegren, J.; Schander, C.; Sneli, J.A.; Rønningen, V.; Young, C.M. Four genes, morphology and ecology: distinguishing a new species of Acesta (Mollusca; Bivalvia) from the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, P.J.; Ellingson, R.A.; Burton, R.; Valdés, Á. A new Poecilogonous species of sea slug (Opisthobranchia: Sacoglossa) from California: comparison with the planktotrophic congener Alderia modesta (Loven, 1844). J. Molluscan Stud. 2007, 73, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derycke, S.; Fonseca, G.; Vierstraete, A.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vincx, M.; Moens, T. Disentangling taxonomy within the Rhabditis (Pellioditis) marina (Nematoda, Rhabditidae) species complex using molecular and morhological tools. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 152, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, P.; Menegola, C.; Rapp, H.T.; Diaz, M.C. Morphological description and DNA barcodes of shallow-water Tetractinellida (Porifera: Demospongiae) from Bocas del Toro, Panama, with description of a new species. Zootaxa 2009, 2276, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, P.; Rota, E.; Erséus, C. Grania (Annelida: Clitellata: Enchytraeidae) of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia, including four new species and a re-description of Grania trichaeta Jamieson, 1977. Zootaxa 2009, 2165, 16–38. [Google Scholar]
- Byrkjedal, I.; Rees, D.J.; Willassen, E. Lumping lumpsuckers: molecular and morphological insights into the taxonomic status of Eumicrotremus spinosus (Fabricius, 1776) and Eumicrotremus eggvinii Koefoed, 1956 (Teleostei: Cyclopteridae). J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 111–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kappner, I.; Bieler, R. Phylogeny of venus clams (Bivalvia: Venerinae) as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.; Ahmadzadeh, A.; Jondelius, U. DNA taxonomy of Swedish Catenulida (Platyhelminthes) and a phylogenetic framework for catenulid classification. Org. Divers. Evol. 2008, 8, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.O.; Henzler, C.M.; Lunt, D H.; Whiteley, N.M.; Rock, J. Probing marine Gammarus (Amphipoda) taxonomy with DNA barcodes. Syst. Biodivers. 2009, 7, 365–379. [Google Scholar]
- Porco, D.; Rougerie, R.; Deharveng, L.; Hebert, P.D.N. Coupling non-destructive DNA extraction and voucher retrieval for small soft-bodied Arthropods in a high-throughput context: the example of Collembola. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar]
- Packer, L.; Grixti, J.C.; Roughley, R.E.; Hanner, R. The status of taxonomy in Canada and the impact of DNA barcoding. Can. J. Zool. 2009, 87, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, F. The study of species in the era of biodiversity: a tale of stupidity. Diversity 2010, 2, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, R.J.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Nishida, M.; Nishida, S. Zooplankton diversity analysis through single-gene sequencing of a community sample. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 438. [Google Scholar]
- Kochzius, M.; Nölte, M.; Weber, H.; Silkenbeumer, N.; Hjörleifsdottir, S.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Marteinsson, V.; Kappel, K.; Planes, S.; Tinti, F.; Magoulas, A.; Vazquez, E.G.; Turan, C.; Hervet, C.; Falgueras, D.C.; Antoniou, A.; Landi, M.; Blohm, D. DNA microarrays for identifying fishes. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M.; Somerfield, P.J. All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R. New ‘biodiversity’ measures reveal a decrease in taxonomic distinctness with increasing stress. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 129, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Phylogenetic pattern and the quantification of organismal biodiversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P.; Baker, A.M. Phylogenetic diversity (PD) and biodiversity conservation: some bioinformatics challenges. Evol. Bioinform. 2006, 2, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).