Abstract
The blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna) is suffering from higher roadkill rates (RK) at the Emas National Park (ENP), an important Brazilian National Park in the Cerrado biome. This species is also a victim of nest poaching for illegal trade. We modeled the blue-and-yellow macaw population’s viability in ENP and how this viability is affected by roadkill and nest poaching. We hereby report that the species is critically at risk and could be extinct in about a decade when considering both threats. Without considering any threat, 150 individuals are necessary to maintain a viable population. When individuals are harvested at a roadkill rate of 0.008 individuals/km/year and at twice this level, the viability figures increase to 4500 and 7500 birds, respectively. For nest poaching, we estimated that 2000 individuals are required to maintain a viable population. When both threats are present, 5000 individuals are necessary. The dynamics of the population are highly sensitive to the age at which females reproduce for the first time and the proportion of reproducing adult females, followed by the rate of adult survival. Our model demonstrates how even a non-threatened highly mobile species, such as the blue-and-yellow macaw, may be at risk due to human activities.
1. Introduction
Conservation biology has two main goals: assessment and management of biological diversity [1]. The assessment involves defining the current status of a population, predicting its future trends, and identifying risks to its persistence. Management encompasses identifying and implementing solutions that ensure the population’s persistence. In this sense, population viability analyses have been commonly used to assess the impact of human activities upon natural populations [2,3,4]. Understanding the underlying causes of population decline, as well as the processes contributing to the extinction of species, are important steps towards identifying the species that are at greatest risk [5].
Wildlife roadkill is a threat to the survival of several species [6,7]. Roadkill data combined with population viability analyses can promote greater knowledge about the possible impacts of highways on a given species/population [8]. While for some species, the effects of roadkill can be insignificant, such as for small rodents in Spain [9], for others, roadkill can be a threat to their existence, including the jaguar [10], the giant anteater [4,11], and the maned wolf [12].
More than 8 million birds die victim of roadkill in Brazil every year [13]. Despite the various risks, birds are typically considered able to avoid roadkill [14]. Perhaps for this reason, only 12% of the roadkill research carried out in Latin America has had birds as the object of study, and 31% of that research looked at more than one taxon. In fact, most of the studies carried out on that continent have produced lists of the roadkill species. However, there is still a need for further research that seeks to understand how roadkill influences population viability in order to define (i) the species that are conservation priorities and (ii) effective roadkill mitigation strategies [15].
Brazil is recognized as a biologically megadiverse country, being the habitat of almost 20% of the 10,000 bird species identified worldwide [16]. In the Cerrado biome alone, 837 species have been registered, which is equivalent to 43.6% of all Brazilian birds [17]. Psittacidae, a family composed of macaws, parakeets, and parrots [18], includes 33 species occurring in the Cerrado [17], with the blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna) being one of the most emblematic.
The blue-and-yellow macaw occurs in Venezuela, Guyana, Peru, Bolivia, eastern Panama, western Ecuador, northern Colombia, Argentina, and Paraguay [19]. In Brazil, it is found mainly in the Cerrado, Pantanal, and Amazon biomes [18]. It is commonly found in the canopy of gallery forests, floodplains with palm trees, and the interior and edges of high forests at about a 500 m altitude. It feeds on seeds, fruits, and nuts [20,21], and travels long distances during the day between resting and eating places [22,23]. It migrates at certain times of the year, probably in search of food [20,21,23]. They nest between August and December in holes inside the trunks of large dead palm trees, at approximately 10 and 25 m in height, laying an average of two eggs, which are incubated for 24–26 days [24,25]. The reproductive success of the nests varies from 92.3% [24], 72% [25], to 50% [26]. Within 77 days, the fledglings fly [25]. Of the eggs produced, 46% ([24] to 33% [25] are successful. They live in pairs or in groups of 3 individuals. They can also form larger groups of up to 30–50 individuals, as observed at the Emas National Park (ENP) [22].
The blue-and-yellow macaw is not considered an endangered species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature—IUCN [19] or by the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation—ICMBio [27]. The last is responsible for assessing the extinction risk in Brazil. However, the population is decreasing and the number of individuals of reproductive age is still unknown [19]. In addition to direct threats such as deforestation and fragmentation of habitats, the species has suffered for decades from excessive harmful legal and illegal trades, with each unit costing up to US $4000 [28]. In South America, it is the second most traded animal (considering parrots) [29]. It is among the most traded species internationally [30] and domestically [31]. Although more than one third of blue-and-yellow macaw that are internationally traded are captive-bred, wild caught and unknown sources also represent a great number of them [30]. Another worrying feature of illegal trade is that it is not opportunistic, nor abundance dependent, but due to the species’ attractiveness and a function of species size, coloration, and ability to talk [31]. In Brazil, macaw species area illegally traded in more than half of the surveyed cities [32]. The Wild Animal Recovery Center (Centro de Recuperação de Animais Silvestres—CRAS) of São Paulo received 298 individuals of the species between the years 2003 and 2013 [33]. Unfortunately, nest poaching also occurs inside Brazilian areas designated to conservation. In 2020, during seven days, the ICMBio in a joint action with the police force captured 374 birds in a conservation area [34]. Although nest poaching is not documented in the ENP, blue-and-yellow macaws nest inside and on the boundaries of the park [25]. The last areas are easily accessible for anyone. Additionally, the species can be observed leaving the park and flying to native areas by passing through agriculture areas [35].
Roadkill is not cited by the IUCN as a threat to the blue-and-yellow macaw, but recent studies demonstrate it is certainly an additional risk for the species. For instance, in the ENP conservation unit, 36 individuals were identified as roadkill (during 90 consecutive days), representing 54% of the registered birds killed. These fatalities usually kill adults, only two were identified as non-adults (5.5%). Although blue-and-yellow macaws fly in groups, in just two occasions more than one individual was identified as roadkill (5.5% of the casualties). Roadkill of this species is temporally and spatially aggregated. All roadkill happened exclusively in the dry season in specific stretches of the highway [36]. When extrapolating these data to 6 months of the dry season, 69 individuals die in one year, with a roadkill rate (RK) of 0.008 animals/km/day. Studies that evaluate the effects of roadkill on population viability are still rare and, as far as we know in Brazil, none have assessed a bird species.
This study aimed: (1) to estimate the viability of the population of the blue-and-yellow macaw in the ENP, (2) to estimate the impacts of roadkill and nest poaching on population viability, and (3) to propose measures to promote the species’ survival.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
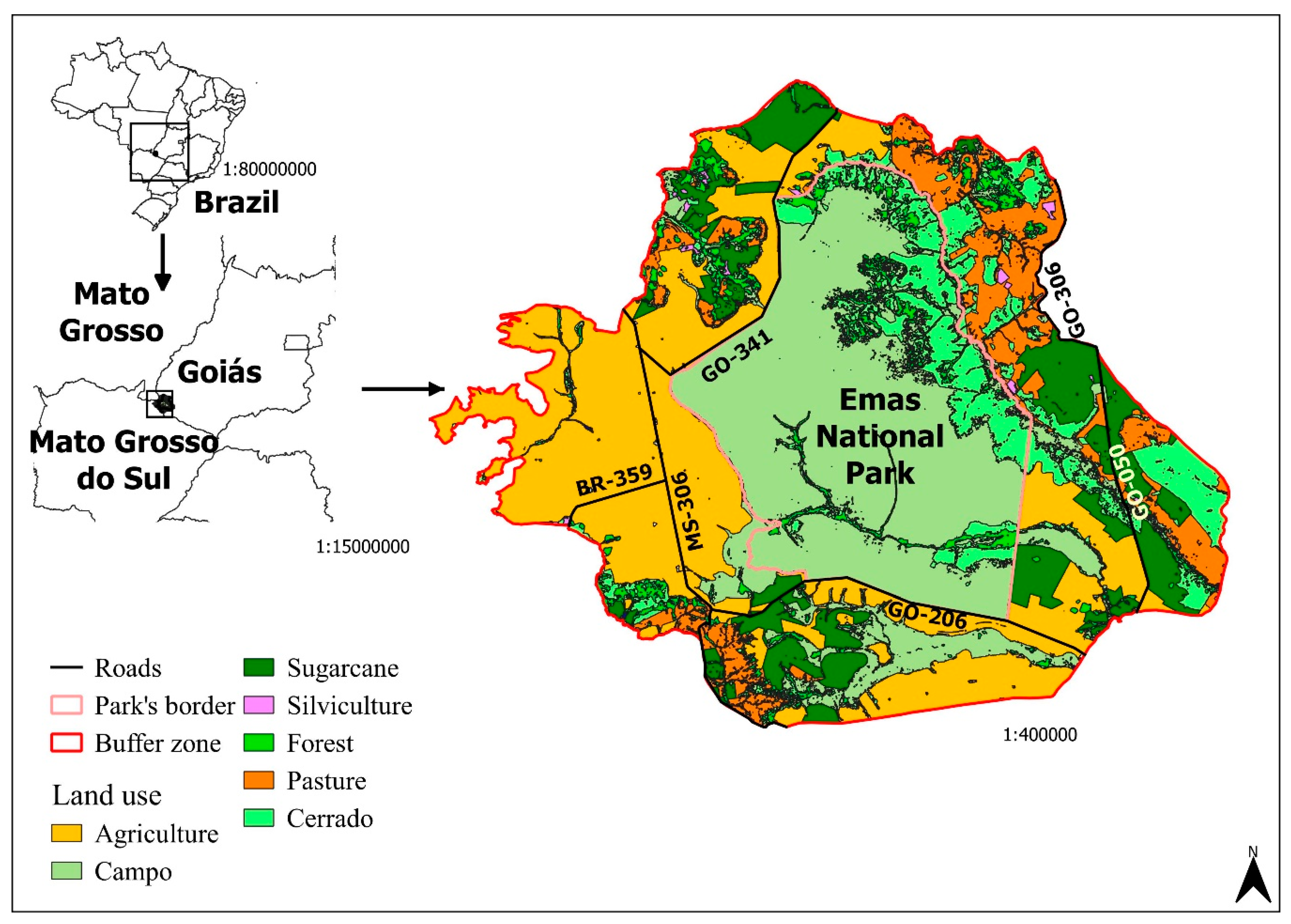
The ENP is located in the southwest of the State of Goiás, it borders the states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul (Figure 1). The park has a total area of 1320 km2 (131386 ha) and is one of the few Brazilian National Parks that encompasses the different types of Cerrado within the state of Goiás, such as campo limpo, campo sujo, veredas and riparian forests [37]. The park is home to 85 species of mammals [38], 353 birds, and 88 reptiles [37]. The ENP presents the largest number of endemic species of birds among Brazilian national parks.
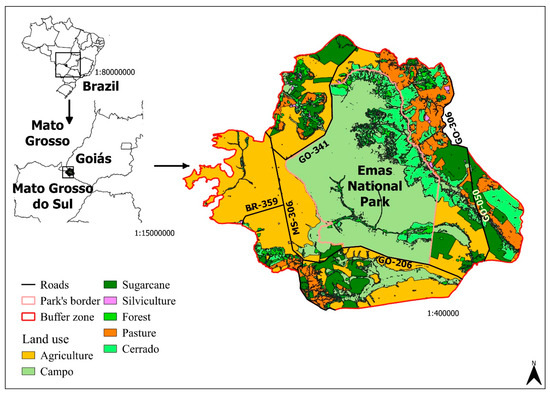
Figure 1.
Location of the Emas National Park (ENP), with emphasis on its buffer zone, the highways in the area, and land use. Sources: [39,40].
The park is surrounded on all sides by crops, as well as state and municipal highways with high truck traffic [37]. The roads that pass through the buffer zone are two-lane, totaling 76.5 km of paved roads (GO-050 (31.7 km) and GO-341 (44.8 km)), and 114.6 km of unpaved roads (GO-206 (47.1 km), GO-306 (27.1 km), MS-306 (56.1 km), MT-100 (2.7) and BR-359 (13.3 km)). The ENP buffer zone totals 2634 km2; 63.7% of this area is occupied by agricultural activities, mainly production of grains, 11.2% is pasture, and 25% is still preserved natural area. Due to the ENP’s importance, these natural areas in the buffer zone are considered to be of reduced size [40].
According to the Köppen classification, the region fits into the Aw type, tropical humid climates, with two well-defined seasons: dry, in winter, and humid, in summer. The total annual rainfall varies between 1200 and 3000 mm. The average temperature of the hot months varies between 24 and 26 °C, while in the cold months, it is between 15 and 24 °C [37].
2.2. Modeling
To model the threats to blue-and-yellow macaw viability in the ENP, we used the software VORTEX 10 [41]. VORTEX performs a simulation based on the individual of deterministic as well as demographic, environmental, and genetic forces of stochastic events in populations. The software models population dynamics as discrete and sequential events that occur according to probabilities that are random variables following distributions specified by the user. The user can examine the current status of a given species and determine which factors, if changed or manipulated, may have the greatest effect on causing or preventing extinction [42].
We modeled the blue-and-yellow macaw viability in the ENP for 100 years; the model was run 1000 times. The species is monogamous and couples remain together for life [18] (Table 1). On average, offspring are born when adults are 10.69 years old [43]. The maximum age of reproduction is 34 years and they can live up to 49 years. [43]. As these data are available only for female captive blue-and-yellow macaws, we used the same values for males. The maximum number of broods per year is one and progeny per brood is two; with a mean of 1.2 offspring per year (± 0.4) [25], it is more common to have one offspring per nest. For these input parameters, we only considered fledglings that left the nest [44]. The sex ratio at birth is 1:1 [45]. The information above is relative to the local ENP population. There are no data about the proportion of reproducing blue-and-yellow macaws. For the blue-throated macaw (Ara glaucogularis), this value is 36.5% [46], 20% for the red-fronted macaw (Ara rubrogenys) [47], and for Lear’s macaw (Anodorhynchus leari), it varies from 20% [48] to 37.5% [44]. Considering that young can be seen with their parents during one to two years and that during this period parents will not reproduce [18], the value of 36.5% seems very reasonable [46]; these species are also closely related. The blue-throated macaw has an average length of 85 cm and its mass ranges from 600 to 1000 g. Reproduction parameters are also comparable; females lay one to three eggs per clutch and incubate for 26 days [49]. No data are available about environmental variation in female reproduction. Since assuming that there is no variation in breeding might be less realistic than assuming there is a small variation [41], we opted for a value of 5%. There is no mortality rate available for the blue-and-yellow macaw. As with previous input data, we only considered fledglings that left the nest; we accounted for a 48% mortality between hatching and fledgling [44]. Therefore, we opted to add an additional 7% mortality from 0 to 1 year, 5% from age 1 to 2, 2% from age 2 to adult, and 1% for adults. These data are available for Lear‘s macaw [44]. In monogamous species, all adult males are considered potential breeders [44]; therefore, we considered that 100% of the males are capable of reproducing.

Table 1.
Life history parameters used to model the viability of the blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna) population in Emas National Park, Brazil. For a detailed description of input parameters, see [41].
There are no data about the blue-and-yellow macaw population size in the ENP. In south-east Peru, its density is 1.1 individuals/km2 in primary seasonality flooded swamp forest and 3.4 individuals/km2 in primary middle/upper floodplain forest with Guadua bamboo [50]. Another study shows lower values; this survey was performed in neotropical regions on unpaved and low-transit paved roads, where the density of this species ranged between 0.22 and 1.18 individuals/km2 (mean 0.48), with a value of 0.34 for the Brazilian Cerrado. The lower density estimates are from different landscape types, varying from well-preserved areas to urban areas [51], and the higher rates are from a large protected area [50]. Therefore, we decided to use 1.18 individuals/km2. As we have no data about the ENP population distribution across and around the park, we simply estimated the ENP population size by multiplying the value of density by the park’s extent (1320 km2), totaling 1558 individuals. We did not add migration to our simulation because these data are not available; however, we expect that we are not dealing with a closed population. The carrying capacity was considered to be the same as the initial population size.
The model included harvest by roadkill and illegal trade. The annual RK for paved roads was calculated by multiplying the daily estimate (0.008 individuals/km) by the number of days of the dry season (this species did not suffer roadkill in rainy months [36]), totaling 1.47 blue-and-yellow macaws/km/year. Considering the 76.5 km of paved roads within the ENP buffer zone, 112 individuals die every year (the annual roadkill rate multiplied by road extent, 1.47 × 76.5). In contrast to paved roads, the RK on unpaved roads is six times smaller (0.245) [52]. Therefore, the number of blue-and-yellow macaw roadkill on unpaved roads was calculated by multiplying 0.245 by 114.6 (total extension of unpaved roads within the ENP buffer zone), totaling 28 individuals. Thus, the final number of blue-and-yellow macaw roadkill is simply a sum of the number of individuals killed on paved and unpaved roads, totaling 140 individuals (9% of the population). Of these, only 5.5% were recognized as non-adults and the remaining 8.3% were unidentifiable; thus, we decided to consider that adults represent 92% of the roadkill events [36]. We also simulated a scenario where the RK was twice this number., There is no information about the rate of illegal trade in the ENP; however, in a protected area located in the northeastern Peruvian Amazon, 29.4% of the nestlings are harvested in a year [53]. Considering that these data are over almost two decades and that nest poaching is not documented for ENP, we used a 5% level (affecting 78 individuals). Finally, we simulated an interaction of 5% nest poaching in addition to roadkill.
The minimum viable population (MVP) analysis is an estimate of the minimum number of organisms of a particular species to constitute a viable population over the long term [54]. We simulated the MVP with and without harvest. We considered the MVP when the probability of extinction is zero and genetic diversity is 95% [42].
We performed a sensitivity analysis to assess the population’s sensitivity to certain parameters of the baseline model. This analysis is important because uncertainty regarding the biological parameters of a given population occurs at several levels, especially for parameters that have never been measured in the population. Sensitivity of population dynamics to certain parameters indicates that those parameters describe factors that could be critical determinants of population viability [42]. We evaluated the effect of reproductive and mortality parameters on stochastic growth rate (stoch-r) of the blue-and-yellow macaw population in ENP. We varied one parameter at a time, using lower and higher values than those of the baseline model (Table 2). Regarding the proportion of blue-and-yellow macaws reproducing, we also used values available in the literature for the blue-throated macaw (Ara rubrogenys) [47]. About the age of first offspring, we used real data for the species (available for captive animals)—the 25–75% confidence intervals—as lower and higher values [43]. We did not consider roadkill and nest poaching.

Table 2.
Lower and higher values used for sensitivity analysis.
3. Results
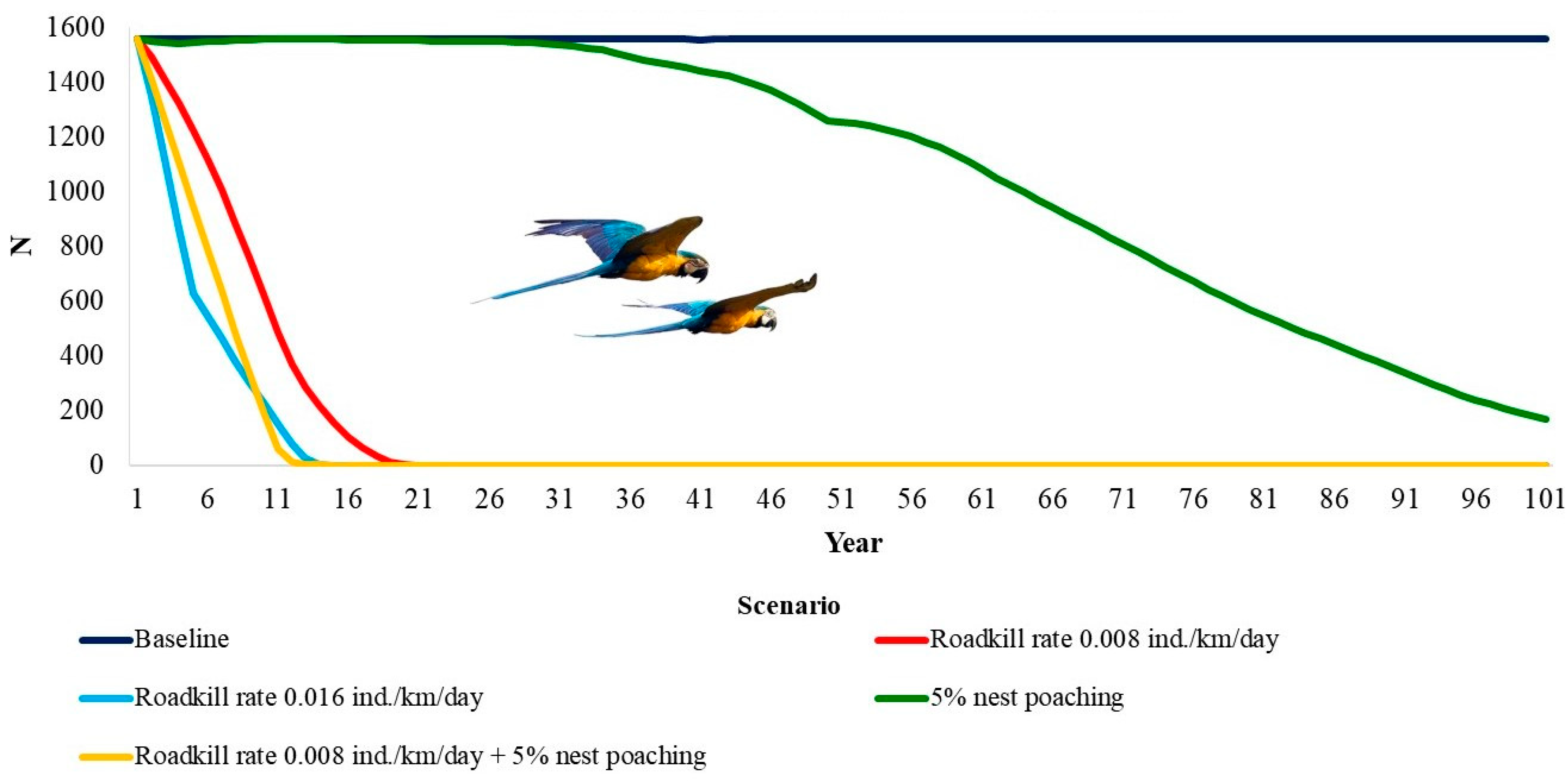
The deterministic growth rate (rdet) was 0.045. This means a potential annual growth rate of about 4.5% when below carrying capacity. The blue-and-yellow macaw population is only viable within the 100 years of the simulation in the baseline model (Table 3, Figure 2). The genetic diversity was almost equal to the initial values. When considering all other scenarios, the population would go extinct. For a RK rate of 0.008 individuals/km/day, extinction would take 19 years, 13 years for twice that rate of RK (2 RK), and 98 years for 5% of nest poaching. This number decreases to 12 years when considering both nest poaching and RK.

Table 3.
Results of mean rate of stochastic population growth (stoch_r), probability of extinction (PE), population size at the end of simulations (N-extant), genetic diversity (GeneDiv), and mean time to extinction (meanTE) for populations of blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna) in Emas National Park, Brazil, suffering from different levels of roadkill (RK) and nest poaching.
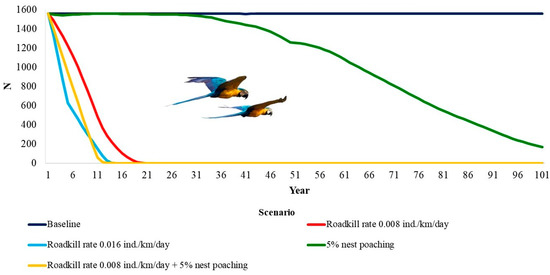
Figure 2.
Time to extinction of the blue-and-yellow macaw, Ara ararauna (Aves: Psittaciformes) in Emas Natural Park, Brazil, under the impacts of roadkill and nest poaching.
Without considering any threats, 150 individuals are necessary to maintain a viable population for the next 100 years (Table 4). When individuals are harvested at RK and 2 RK this value increases to 4000 and 7500 individuals. When birds are poached for illegal trade, the number of individuals required to maintain a viable population would increase to 2000. If both threats happen concomitantly, a viable population must have 5000 individuals.

Table 4.
Results of minimum viable population for blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna) in Emas National Park, Brazil, suffering from different levels of roadkill (RK) and nest poaching. Stoch_r: mean rate of stochastic population growth, PE: probability of extinction, N-extant: population size at the end of simulations, GeneDiv: genetic diversity, meanTE: mean time to extinction.
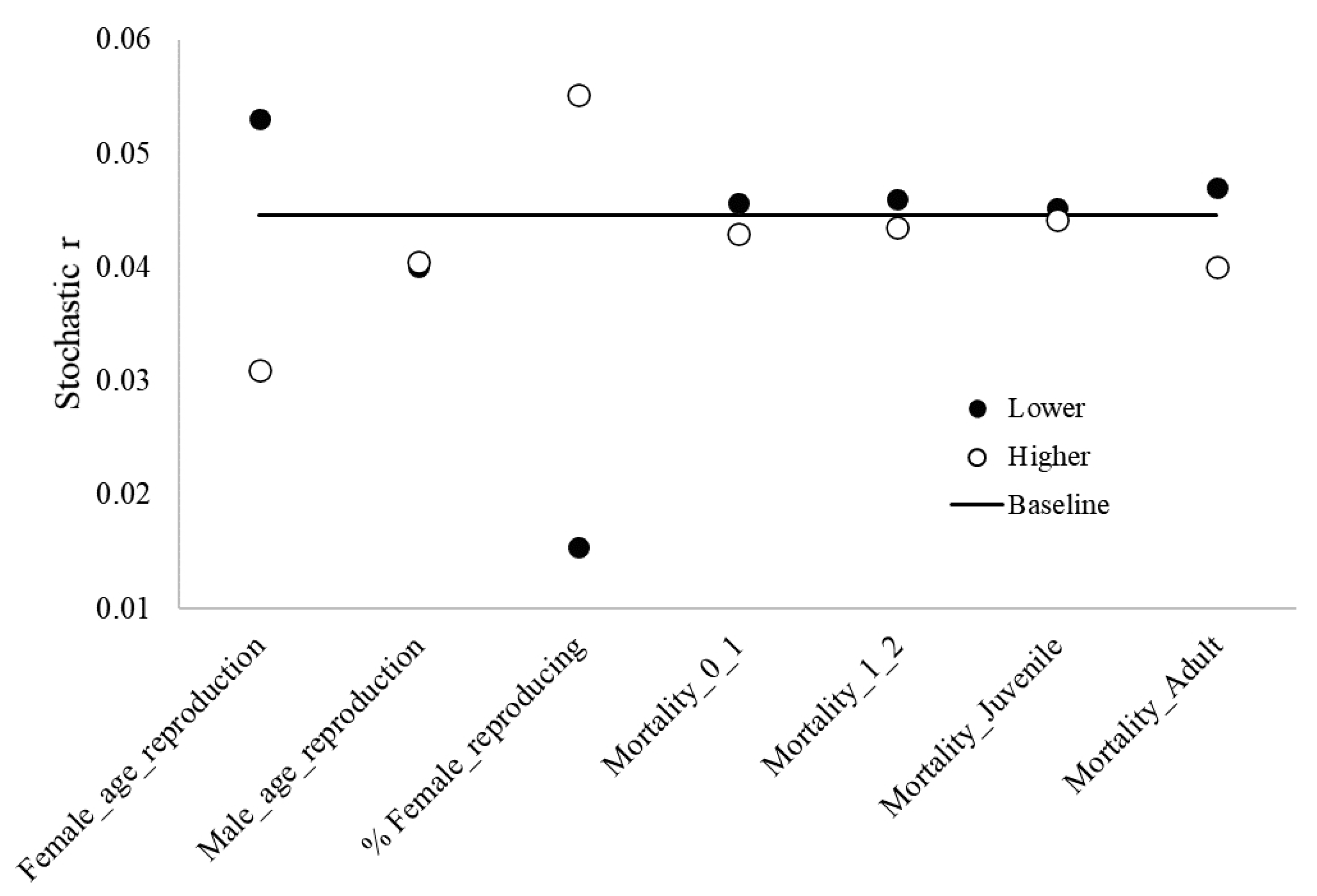
The age females reproduce for the first time and the proportion of reproducing adult females had the strongest influence on the dynamics of the blue-and-yellow macaw population. Mortality rates for adults were the third strongest influencer (Figure 3).
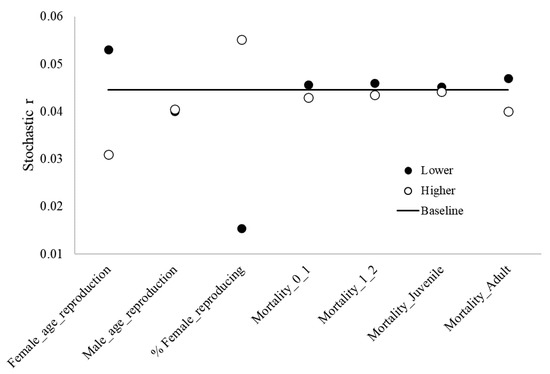
Figure 3.
Results from sensitivity analysis, highlighting the baseline stochastic r values and lower and higher values regarding different reproduction and mortality parameters of blue-and-yellow macaw (Ara ararauna). Female_age_reproduction: age of first offspring females, Male_age_reproduction: age of first offspring males, % _reproducing females: % reproducing adult females; Mortality_0_1: mortality rates from age 0 to 1, Mortality_1_2: mortality rates from age 1 to 2, Mortality_Juveniles: mortality rates for juveniles, Mortality_Adult: mortality rates for adults.
4. Discussion
The predictions derived from our simulations are extremely worrying for blue-and-yellow macaw population survival in ENP. The population will be extinct in all scenarios that included some level of threat. The most important factor in determining the blue-and-yellow macaw vulnerability seems to be the population size. It is of crucial importance to assess the real population size in ENP. If this value is close to 1558 individuals, the population is critically at risk and can be extinct in just 12 years.
Roadkill is the most important threat to blue-and-yellow macaw population persistence. The blue-and-yellow macaw population in ENP is surrounded by two-lane roads (Figure 1). As a consequence, individuals dispersing or trying to forage in adjoining areas must cross these roads, becoming vulnerable to incoming traffic. This scenario would be aggravated by 100% if all the extension of the roads were paved. This would allow drivers to travel faster and could also increase the vehicle traffic in the area. For instance, people that avoid travelling on unpaved roads may choose to travel through them if they were paved. In consequence, this would increase RK, as this metric is positively correlated to vehicle traffic [55].
While nest poaching seems to be a less important threat, the number of individuals harvested are not comparable (5% and 9% for nest poaching and roadkill, respectively). As nest poaching targets chicks, in the long term, adults will not be added to the population, consequently leading to decreased reproduction and thereby decreasing the population size faster. Roadkill, on the other hand, impacts mostly adults. Chicks may still survive to become adults and generate some offspring until possibly becoming roadkill victims.
Population dynamics is highly sensitive to the age females reproduce for the first time and the proportion of reproducing adult females. Adult survival rates are also significant. Any threats modulating these parameters will have a major impact on the population. These results show the importance of obtaining accurate values of blue-and-yellow macaw mortality rates in the wild and reinforce the need for long-term studies [42].
Another alarming information about the species is that a genetic study conducted at the ENP concluded that the species had a mean genetic diversity similar to that in species considered vulnerable to extinction [45]. Therefore, future research should also target the population’s genetic diversity because the population could easily be threatened by an unpredicted threat (e.g., disease epidemic or hunting) or an increase in a current threat [42].
We must consider that there is a lack of data about the blue-and-yellow macaw species. For this reason, we had to use the information available for other close species or for captive animals. Similarly, as in other publications that evaluated population viability, we needed to make a series of assumptions in our model due to the lack of quantitative information [10,46,56]. This may be a reason why, for threatening scenarios, our results may be overestimating the species’ time to extinction. When relevant information becomes available, it can be used to produce more reliable models [10].
We also did not model scenarios evaluating other known threats to the blue-and-yellow macaw population in the study area, such as fire, severe drought, and migration across metapopulations. Fires caused declines in populations, and also resulted in greater loss of genetic diversity in giant anteater populations in the Brasília National Park [11]. Migration between patches may happen since the species can move long distances daily and seasonally [23]. ENP can serve as a source of blue-and-yellow macaws for other remnants of Cerrado in the surrounding matrix. Individuals from other areas could even come to ENP during some periods of the year. While this migration between patches and the ENP can increase genetic diversity, on the other hand, it also can increase roadkill rates.
The blue-and-yellow macaw in ENP seems to be at risk of becoming extinct due to roadkill and nest poaching. This conclusion is heavily dependent on the natural history and ecological parameters used for modelling. Henceforth, we advise that the following metrics should be further investigated, namely: nest poaching rate, population size in ENP, the mean age at which offspring are born, the maximum age of reproduction, lifespan, the proportion of blue-and-yellow macaw reproducing, and the mortality rate for the blue-and-yellow macaw. The first two metrics are the most urgent.
Our results are extremely worrisome and show that even non-threatened and highly mobile species may be at risk of extinction due human activities. One cheap measure to prevent the aggravation of this scenario is forbidding the paving of the remaining unpaved roads [57]. To help prevent roadkill, the stretches with higher roadkill values for blue-and-yellow macaw (also called roadkill hotspots, roadkill aggregations) need to be identified for the entire buffer zone. Accordingly, mitigation measures should be determined and implemented. For birds, flight diverters may reduce the likelihood of roadkill. Wildlife crossing structures can decrease roadkill and the barrier effect as well as roadsides should be managed to make them less attractive to birds [14]. Finally, crops that attract the species, as soybean and corn, should be avoided near the road. Efforts to decrease and avoid nest poaching and illegal trade are advocated regionally, nationally, and internationally. Many actions are demanded regionally. I is necessary to develop behavior change campaigns aiming (i) to facilitate the understanding of the threats posed by nest poaching to the macaw species as well as its overall biological importance [32,33] and (ii) to reduce the demand for wild-caught macaws [30,58]. Furthermore, communities living in close proximity to conservation units must have other sources of income in order to stop nest poaching from being a desirable activity [29,32,33]. Law enforcement is also necessary to reduce nest poaching and for this, it is essential to form a comprehensive basic and general knowledge of the trade chain [58]. More intervention efforts and monitoring are important to prohibit captive facilities from acting as laundering for wild-caught animals [30]. Finally, Brazil’s government should create an international alliance to stop the illegal trade [29,32,33].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.F.C.-R.; methodology, C.F.C.-R.; formal analysis C.F.C.-R.; investigation, C.F.C.-R.; data curation, C.F.C.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.F.C.-R. and O.M.J.; writing—review and editing, C.F.C.-R. and O.M.J.; visualization, C.F.C.-R. and O.M.J.; supervision, O.M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Giselle Bastos Alves for providing information about roadkill, Renato Alves Moreira and the NGO Oréades Núcleo de Geoprocessamento for the ENP land use map, Marcos Cunha for local information about the species, the Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa e Pós-Graduação from the Federal University of Uberlândia for the financial support given to this publication and the reviewers for their extremely relevant suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Primack, R.B.; Rodrigues, E. Biologia da Conservação; Planta: Londrina, Brazil, 2001; ISBN 8590200213. [Google Scholar]
- Brook, B.W.; O’Grady, J.J.; Chapman, A.P.; Burgman, M.A.; Resit Akçakaya, H.; Frankham, R. Predictive accuracy of population viability analysis in conservation biology. Nature 2000, 404, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hileman, E.T.; King, R.B.; Faust, L.J. Eastern massasauga demography and extinction risk under prescribed-fire scenarios. J. Wildl. Manage. 2018, 82, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.A.S.; Bager, A.; Clevenger, A.P.; Grilo, C. Giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) conservation in Brazil: Analysing the relative effects of fragmentation and mortality due to roads. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 228, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, M.; Mace, G.M.; Jones, K.E.; Bielby, J.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Sechrest, W.; Orme, C.D.L.; Purvis, A. Evolution: Multiple causes of high extinction risk in large mammal species. Science 2005, 309, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, N.C.; Hannibal, W.; Freitas, D.R.; Silva, E.L.; Roman, C.; Casella, J. Mammal occurrence and roadkill in two adjacent ecoregions (Atlantic Forest and Cerrado) in south-western Brazil. Zoologia 2010, 27, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceia-Hasse, A.; Borda-de-Água, L.; Grilo, C.; Pereira, H.M. Global exposure of carnivores to roads. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.L.W.; Shilling, F.M.; Perkins, S.E. The value of monitoring wildlife roadkill. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2020, 66, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, P.; Mata, C.; Malo, J.E. How many rodents die on the road? Biological and methodological implications from a small mammals’ roadkill assessment on a Spanish motorway. Ecol. Res. 2015, 30, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, L.; Stanton, J.C.; Lima, F.; Uezu, A.; Perilli, M.L.L.; Resit Akcakaya, H. Implications of fine-grained habitat fragmentation and road mortality for jaguar conservation in the atlantic forest, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.F.; Brito, D. Threats to and viability of the giant anteater, Myrmecophaga tridactyla (Pilosa: Myrmecophagidae), in a protected Cerrado remnant encroached by urban expansion in central Brazil. Zoologia 2013, 30, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.; Schumaker, N.H.; Brandon, K.R.; Bager, A.; Grilo, C. Simulating the consequences of roads for wildlife population dynamics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 193, 103672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Suárez, M.; Zanchetta, F.F.; Grilo, C. Spatial and species-level predictions of road mortality risk using trait data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kociolek, A.; Grilo, C.; Jacobson, S. Flight doesn’t solve everything: Mitigation of road impacts on birds. In Handbook of Road Ecology; van der Ree, R., Smith, D.J., Grilo, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, F.A.S.; Clevenger, A.P.; Grilo, C. Effects of roads on terrestrial vertebrate species in Latin America. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, T.M.; Prado, P.I. How many species are there in Brazil? Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.C. Birds of the Cerrado Region, South America. Steenstrupia 1995, 21, 69–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sick, H. Ornitologia brasileira; Nova Fronteira: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997; ISBN 8520908160. [Google Scholar]
- BirdLife International. Ara ararauna. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22685539/131917270 (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Ragusa-Netto, J. Dry fruits and the abundance of the Blue-and-Yellow Macaw (Ara ararauna) at a cerrado remnant in central Brazil. Ornitol. Neotrop. 2006, 17, 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tubelis, D.P. Feeding ecology of Ara ararauna (Aves, Psittacidae) at firebreaks in western Cerrado, Brazil. Biotemas 2011, 22, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gwynne, J.A.; Ridgely, R.S.; Argel, M.; Tudor, G. Aves do Brasil. Pantanal & Cerrado; Editora Horizonte: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010; ISBN 9788588031296. [Google Scholar]
- Brightsmith, D.J.; Boyd, J.D.; Hobson, E.A.; Randel, C.J. Satellite telemetry reveals complex migratory movement patterns of two large macaw species in the western amazon basin. Avian Conserv. Ecol. 2021, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, L.T. Avaliação do Sucesso Reprodutivo da Arara-Canindé (Ara ararauna—Psittacidae) e o Desenvolvimetno de Campo Grande. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidade Anhanguera-Uniderp, Campo Grande, MS, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C.A.C. Biologia Reprodutiva da Arara Canindé (Ara ararauna, Psittacidae) No Parque Nacional das Emas. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidade de Brasília, Brasília, GO, Brazil, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brightsmith, D.; Bravo, A. Ecology and management of nesting blue-and-yellow macaws (Ara ararauna) in Mauritia palm swamps. Biodivers. Conserv. 2006, 15, 4271–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICMBio. Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade. Livro Vermelho da Fauna Brasileira Ameaçada de Extinção25; ICMBio: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 9788561842796. [Google Scholar]
- Renctas. 1st National Report on the Traffic of Wild Animals; Renctas: Brasília, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Halle, B.O. Bird ’s-Eye View: Lessons from 50 Years of Bird Trade Regulation & Conservation in Amazon Countries; TRAFFIC: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, D.T.C.; Poon, E.S.K.; Wong, A.T.C.; Sin, S.Y.W. Global trade in parrots—Influential factors of trade and implications for conservation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 30, e01784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Vidal, P.; Hiraldo, F.; Rosseto, F.; Blanco, G.; Carrete, M.; Tella, J.L. Opportunistic or non-random wildlife crime? Attractiveness rather than abundance in the wild leads to selective parrot poaching. Diversity 2020, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.R.N.; Lima, J.R.d.F.; Araujo, H.F.P. The live bird trade in Brazil and its conservation implications: An overview. Bird Conserv. Int. 2012, 23, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charity, S.; Ferreira, J.M. Wildlife Trafficking in Brazil; TRAFFIC International: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, D. Operação Contra Tráfico de Fauna e Caça em Unidades de Conservação de AL: 376 Animais Resgatados. Available online: https://faunanews.com.br/2020/07/03/operacao-contra-trafico-de-fauna-e-caca-em-unidades-de-conservacao-de-al-376-animais-resgatados/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Tubelis, D.P. When a large reserve is not large enough to protect part of a population: Blue-and-yellow Macaws (Ara ararauna) in central Brazil. Rev. Biotemas Biotemas 2010, 23, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho-Roel, C.F.; Alves, G.B.; Almeida, A.T.D.; Moreira, R.A.; Tôrres, N.M.; Silveira, L. Wildlife roadkill in the surroundings of Emas National Park, Cerrado Biome, Brazil. Oecologia Aust. 2021, 25, 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- IBAMA—Instituto Brasileiro de Meio Ambiente e Recursos Naturais Renováveis. Plano de Manejo—Parque Nacional das Emas; IBAMA: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.H.G.; Silveira, L.; Jácomo, A.T.A.; Carmignotto, A.P.; Bezerra, A.M.R.; Coelho, D.C.; Garbogini, H.; Pagnozzi, J.; Hass, A. Composição e caracterização da fauna de mamíferos do Parque Nacional das Emas, Goias, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2002, 19, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oréades, N.d.G. Mapa de Uso e Cobertura Do Solo; NGO Oréades Núcleo de Geoprocessamento: Mineiros, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.P.; Damasceno, C.E.; Oliveira, B.J.S. Análise da paisagem na zona de amortecimento do Parque Nacional das Emas –Brasil. Geog Ens Pesq. 2020, 24, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, R.C.; Miller, P.S.; Traylor-Holzer, K. Vortex 10 User’s Manual; IUCN SSC Conservation Planning Specialist Group, and Chicago Zoological Society: Apple Valley, MN, USA, 2020; ISBN 0120137046. [Google Scholar]
- Medici, E.P.; Desbiez, A.L.J. Population viability analysis: Using a modeling tool to assess the viability of tapir populations in fragmented landscapes. Integr. Zool. 2012, 7, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Hobsona, E.A.; Lackey, L.B.; Wrighta, T.F. Survival on the ark: Life history trends in captive parrots. Anim. Conserv. 2012, 15, 28–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.B.; Lugarini, C.; de Sousa, A.E.B.; Barbosa, A.E.A.; Miyaki, C.Y.; Aguilar, T.M.; do Amaral, A.C.A.; Linares, S.F.T.P.; do Nascimento, J.L.X.; de Barros, Y.; et al. De Análise de viabilidade populacional de uma população de arara-azul-de-lear. In Plano de Ação Nacional para Conservaçaõ da Arara-Azul-de-Lear; Lugarini, C., Barbosa, A.E.A., de Oliveira, K.G., Eds.; Instituo Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade—ICMBio: Brasília, Brazil, 2012; pp. 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Caparroz, R.; Guedes, N.M.R.; Bianchi, C.A.; Wajntal, A. Analysis of the genetic variability and breeding behaviour of wild populations of two Macaw species (Psittaciformes, Aves) by DNA fingerprinting. Ararajuba 2001, 9, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Strem, R.I.; Bouzat, J.L. Population viability analysis of the Blue-throated Macaw (Ara glaucogularis) using individual-based and cohort-based PVA programs. Open Conserv. Biol. J. 2012, 6, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, J.L.; Rojas, A.; Carrete, M.; Hiraldo, F. Simple assessments of age and spatial population structure can aid conservation of poorly known species. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 167, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacífico, E.C.; Barbosa, E.A.; Filadelfo, T.; Oliveira, K.G.; Silveira, L.F.; Tella, J.L. Breeding to non-breeding population ratio and breeding performance of the globally Endangered Lear’s Macaw Anodorhynchus leari: Conservation and monitoring implications. Bird Conserv. Int. 2014, 24, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, S. Ara Ara glaucogularis. Anim. Divers. Web. 2011, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Ara_glaucogularis/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Lloyd, H. Habitat and population estimates of some threatened lowland forest bird species in Tambopata, south-east Peru. Bird Conserv. Int. 2004, 14, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, J.L.; Romero-Vidal, P.; Dénes, F.V.; Hiraldo, F.; Toledo, B.; Rossetto, F.; Blanco, G.; Hernández-Brito, D.; Pacífico, E.; Díaz-Luque, J.A.; et al. Roadside car surveys: Methodological constraints and solutions for estimating parrot abundances across the world. Diversity 2021, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.G.; Assis, J.d.R.; Basile, I.S.; Custódio, A.E.I.; Veloso, A.C.; Carvalho-Roel, C.F. Sazonalidade e Pavimentação Afetam as Taxas de Atropelamento de Animais Silvestres na Rodovia MGC-455, Uberlândia-Rio Do Peixe; Unpublished Manuscript, Last Modified; 11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- González, J.A. Harvesting, local trade, and conservation of parrots in the Northeastern Peruvian Amazon. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 114, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, M.S. Population viability analysis. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.L.; Bliss-ketchum, L.L.; Rivera, C.E.D.; Smith, W.P. A behavior-based framework for assessing barrier effects to wildlife from vehicle traffic volume. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, M.L.; Ferrati, R.; Berkunsky, I. Evaluating management strategies in the conservation of the critically endangered Blue-throated Macaw (Ara glaucogularis). Ecol. Modell. 2017, 361, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Goosem, M.; Laurance, S.G.W. Impacts of roads and linear clearings on tropical forests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Mercado, A.; Ferrer-Paris, J.R.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Tella, J.L. A literature synthesis of actions to tackle illegal parrot trade. Diversity 2021, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).