Abstract
The community composition of decapods associated with subtidal tropical seagrass meadows was analyzed in a pristine reef lagoon on the Mexican Caribbean coast in the summer of 1995 and winter of 1998. The macrophyte community was dominated by Thalassia testudinum followed by Syringodium filiforme, with interspersed rhyzophytic macroalgae and large patches of drift algae. In each season, 10 one-min trawls were made with an epibenthic sled (mesh aperture 1 mm) during the day and 10 during the night on each of five sites. In all, 53,211 decapods belonging to 119 species were collected. The most diverse taxa were Brachyura and Caridea, but the most abundant were Caridea and Anomura. Dominance was high, with three species (Latreutes fucorum, Cuapetes americanus, and Thor manningi) accounting for almost 50% of individuals, and 10 species accounting for nearly 90% of individuals. There was great similarity in community composition and ecological indices between seasons, but significantly more individuals and species in night versus day samples. In the 20+ years elapsed since the samples were taken, the reef lagoon has undergone substantial environmental changes due to extensive coastal development and, more recently, the decay of massive beachings of floating Sargassum macroalgae. This study constitutes a valuable baseline for future studies investigating the potential impact of these stressors on tropical seagrass-associated communities.
1. Introduction
Seagrass ecosystems occur in many coastal regions of the world, where they provide valuable ecosystem functions. Seagrasses stabilize sediments and coastlines, sequester carbon, filter water, and provide habitat for a wide variety of species, including virtually all major groups of invertebrates as well as juveniles of many fishery resources (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5]). However, recent reviews [6,7] have revealed that more information on the relative importance of different groups is available for temperate zones than for the tropics, from the intertidal than for the subtidal, for large species than for the small to very small, and for those associated with the seabed or swimming in the water column than for those living on the seagrass leaves.
Crustaceans are one of the most abundant groups of epifauna in all marine ecosystems, including seagrass meadows, in terms of diversity, abundance, biomass, and energy flow [8,9,10,11]. Within this group, dominant taxa include the decapods, which have an important regulatory function in seagrass ecosystems because they include mesograzers and predators of small fauna [1,12,13,14,15] while constituting a significant portion of the diet of many seagrass-associated fishes [16,17,18,19].
The species composition and temporal variations in abundance of the decapod fauna associated with seagrasses have been more studied in temperate and subtropical ecosystems (e.g., [9,14,15,20,21]) than in tropical ecosystems, such as Caribbean meadows dominated by Thalassia testudinum [8,13,19,22,23,24,25]. In particular, ecological studies on the seagrass decapod fauna are very limited in the Mexican Caribbean coast, where previous studies have generally consisted of species lists with a few ecological observations (e.g., [26,27,28,29]), or have focused on one species [30] or a limited group of species [31].
The Puerto Morelos coral reef system is located on the northern portion of the Yucatan peninsula, in the state of Quintana Roo (Mexican Caribbean coast), and is part of the Mesoamerican Reef that runs along the western Caribbean Sea. Puerto Morelos became one of UNESCO’s Caribbean Coral Reef Productivity Program (CARICOMP) sites in 1993 [32,33,34], and information on the status of local seagrasses in the reef lagoon has been obtained on a regular basis ever since [35,36]. In 1998, the reef system was declared a protected area—the Puerto Morelos Reef National Park (PMRNP) [37]. As the information on the motile benthic fauna was very scarce at the time, a study on the seagrass-associated epifauna in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon was conducted in the late 1990s. The data were partially presented in two theses [38,39], and a list of species was included in the PMRNP Management Program [40]. However, except for analyses of the distribution of juveniles of spiny lobster (Panulirus argus) [30] and their feeding ecology as related to the benthic epifauna [41], the full ecological data remained unpublished. This was unfortunate because, at the time of sampling, the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon was considered pristine [36] and the local seagrass-associated decapod community had not been previously or has been since investigated.
After 1998, the northern coast of Quintana Roo, including Puerto Morelos, became one of the most rapidly developing coastlines in the world [37,42,43]. In the 20+ years since the present data were collected, the coastal systems have undergone gradual environmental changes, mainly due to eutrophication resulting from the explosive coastal development [33,35,36,37] and, more recently, from the decay of massive influxes of floating macroalgae Sargassum spp. that die upon getting beached along the shoreline [44,45]. Therefore, the aim of the present study is to provide a baseline characterization of the seagrass-associated decapod community in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon in terms of species composition, assemblage structure, and diel and seasonal variations, as a representative example of the decapod biodiversity in western Caribbean reef lagoons prior to the substantial environmental changes undergone during the past 20+ years.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The reef lagoon at Puerto Morelos (centered at 20°48′ N, 86°51′ W) is a shallow (<5 m in depth) body of water extending from the shoreline to a coral reef tract that lies slightly diagonally to the coast at a distance of 500–1300 m. The reef lagoon is well flushed; the average water residence time is 3 h under normal wave conditions but can decrease to 0.35 h during extreme hurricane swell [46]. In the late 1990s, the water in the lagoon was highly oligotrophic [32,47], and the bottom was covered by a well-developed seagrass community dominated by the turtle grass Thalassia testudinum. The manatee seagrass Syringodium filiforme and a variety of rhyzophytic macroalgae grew interspersed with T. testudinum [48]. Based on its vegetation, the reef lagoon was divided into three zones [32]: (1) a narrow coastal fringe, 20–50 m wide, dominated either by T. testudinum or S. filiforme, (2) a mid-lagoon zone, 200–1000 m wide, dominated by either T. testudinum with long blades or algae, and (3) a zone of back-reef vegetation, 100–400 m wide, where S. filiforme was virtually absent, and T. testudinum had variable densities of mostly short blades.
Five sampling sites were selected throughout the reef lagoon, three located in the mid-lagoon zone at depths of 3–3.5 m and two located closer to the back-reef zone, at depths of 4 and 3 m, respectively (Figure 1). At the time of sampling, blades of T. testudinum in the mid-lagoon zone reached 20–25 cm long, and typical values of standing crop of T. testudinum were 20–35 g dry weight (DW) m−2, which were low compared to other areas throughout the Caribbean [48]. Standing crops of S. filiforme were even lower (2–30 g m−2 DW). Extensive ephemeral mats up to 500 m in diameter of the drift ochrophyte Lobophora variegata abounded over the sandy mid-lagoon zone, whereas Laurencia spp. and other rhodophytes only occurred in small, isolated patches of hard bottom (exposed calcareous pavement) [32]. In the back-reef zone, the standing crop of T. testudinum was 15–30 g DW m−2 but the maximum height of its blades was only 9–10 cm [48]. Most algae, as well as S. filiforme, were typically absent, but Halimeda spp. occurred in certain areas. Despite the differences in vegetation between the mid-lagoon and back-reef zones, previous analyses did not find an effect of lagoon zone on epifauna richness or abundance [38,39]; therefore, the five sampling sites were considered as replicates.
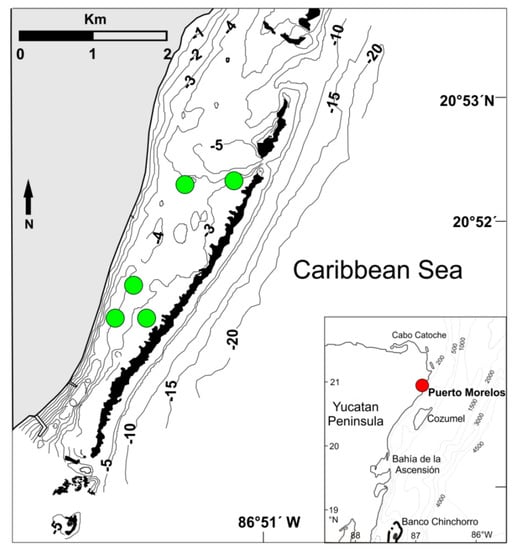
Figure 1.
Location of the five sampling sites (green dots) in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, Mexico. The black areas denote the reef crest. Isobaths are in meters. Inset shows the location of Puerto Morelos on the Mexican Caribbean coast (red dot).
2.2. Epifauna Sampling
In the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, biomass, growth rates, and productivity of seagrasses are higher in the summer than in the winter [33,48,49]. Therefore, we sampled the seagrass-associated epifauna in summer (June–July 1995) and winter (February–March 1998). We used an epibenthic sled with a mesh aperture of 1 mm, a length of 1.19 m, and a mouth 0.57 m wide × 0.25 m high. On each site, 10 trawls were made during the day (11:00–13:00 h), and 10 trawls were made during the night (20:00–22:00 h). Each trawl lasted for one min at a speed of 1 m s−1. A scuba diver monitored the trawls to ensure that the net performed properly. The diver also supervised that successive trawls in each site did not go over the same place twice, and measured the distance traveled by the sled with a 100 m-long tape. These data were used to obtain the average area trawled by the sled in order to estimate the density of decapods. On average, the area covered by the 10 trawls on each sampling site was ~342 m2 [30]. Individual samples were placed into plastic bags, transported to the laboratory within the hour, and frozen at −20 °C pending further processing. After thawing, the samples were washed, hand-sorted into morphospecies, quantified, and preserved in 70% ethanol. All decapods were identified to the lowest possible taxon using multiple sources [26,27,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58].
2.3. Data Analyses
The analysis of the community composition of decapods was done with multivariate techniques using the software PRIMER 6 v6.1.9 (PRIMER-E Ltd.). The k-dominance curves were used to visualize diversity profiles (the distribution of numbers of individuals among species) averaged over all replicates for each combination of season and time of day. A k-dominance curve is constructed by plotting cumulative proportional abundance against a log species rank. The higher the curve, the less diverse (and more dominated) is the assemblage it represents [59]. Differences in the community composition between day and night, between seasons, and combining both factors (season-time of the day) were analyzed via non-metric multidimensional scaling (MDS). For these analyses, the Bray–Curtis similarity measure was used on a fourth-root transformation of the abundance data, which lessens the influence of highly abundant species [60]. A one-way analysis of similarity (ANOSIM) was used in all cases to test the statistical significance of the observed differences in the decapod assemblages. ANOSIM provides an R-value indicative of the degree of difference between samples as well as a p-value for the significance of that difference. R values close to 0 indicate little difference, while values close to 1 indicate a large difference in assemblage composition [61]. Results from the MDS plots were cross-checked against those from a cluster analysis with average group linkage, as recommended when stress values are moderately high (i.e., between 0.1 and 0.2) [61,62]. A similarity profile analysis (SIMPROF) was used to further test the significance of the cluster findings. SIMPROF tests the null hypothesis that the set of samples contains no multivariate structure that can be further examined [63]. Finally, the species responsible for the observed differences in the community composition were identified with a similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER) [60].
For each sampling site, in addition to abundance (N), the following ecological indices were estimated by season and time of day—species richness (S, number of species), Shannon–Wiener’s diversity (H′), Pielou’s evenness (J′), and Simpson’s dominance (D). S is an informative index that constitutes the basis of biodiversity estimates. H′, J′, and D are compound indices that combine richness and abundance of species, hence providing greater ability to discriminate samples than S alone [64,65]. The results of each ecological index were subjected to a separate general linear model (GLM) to test the effects of season, time of day, and their interaction. The data on density (No. of individuals m−2) of each of the 10 most abundant species of decapods were transformed to log (x + 1) and subjected to a similar GLM analysis. In all cases, a Tukey HSD test was applied to significant GLM results.
3. Results
3.1. Decapod Species and Abundance
In total, we collected 53,211 decapods, of which 52,799 were identified to species level, 377 to genus level, and 35 to family or superfamily level. The full database is provided in Table S1. There were representatives of 119 species, of which 19 (mostly xanthoid crabs) were only identified to some taxon above the genus. Of the 119 species, 36 were represented by only one individual, and eight by two individuals (Table A1). The more diverse infraorders were Brachyura (54 species) and Caridea (41), followed by Anomura (16 species), whereas the superfamily Penaeoidea was represented by only five species, and the infraorders Achelata, Gebiidea, and Stenopodidea by one species each. The more diverse families were Alpheidae (15 species), Mithracidae (14), Diogenidae (9), and Hippolythidae (7). However, the most abundant taxa were Caridea (64.4% of all individuals) and Anomura (30%), followed at a distance by Brachyura (3.1%), Penaeoidea (2.3%) and Achelata (0.14%), with Gebiidea and Stenopodidea represented by only one individual each. Ten species (in decreasing order of abundance: Latreutes fucorum, Cuapetes americanus, Thor manningi, Pagurus annulipes, Pagurus brevidactylus, Clibanarius tricolor, Thor dobkini, Alpheus normanni, Tozeuma carolinense, and Processa bermudensis) accounted for nearly 90% of all individuals collected (Table A1), with the first three accounting for almost 50% of all individuals, as shown by the k-dominance curves (Figure 2). However, these curves did not reveal meaningful differences in diversity or dominance among the four combinations of season and time of day, as further confirmed by comparisons of the ecological indices.
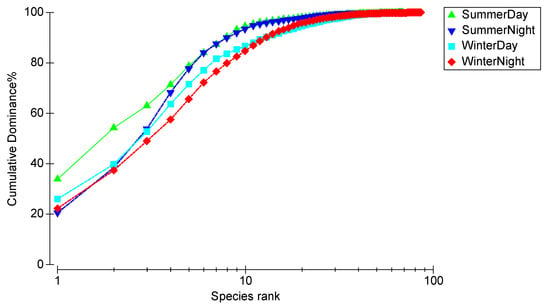
Figure 2.
k-Dominance curves for samples of seagrass-associated decapod crustaceans from the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon. Each curve is based on average abundances at five replicate sites. Samples from each site were obtained in 10 trawls conducted with an epibenthic sled in the day and in 10 the night, in the summer of 1995 and the winter of 1998.
3.2. Ecological Indices
Of the five ecological indices estimated, species richness (S) and abundance (N) varied significantly with time of day, with overall higher values in night samples than in day samples, but were not affected by season. In contrast, evenness (J’), diversity (H’), and dominance (D) did not vary significantly with either the time of day or season (Table 1, Figure 3).

Table 1.
Results of General Linear Models (α = 0.05) on data of five ecological indices of decapod diversity (S: species richness; N: abundance; H’: Shannon–Wiener’s diversity; J’: Pielou’s evenness; 1-lambda: Simpson’s dominance) in two seasons (summer 1995, winter 1998) and two times of the day (day, night) in seagrass meadows of the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon (N = 5 sites per season and time of day).
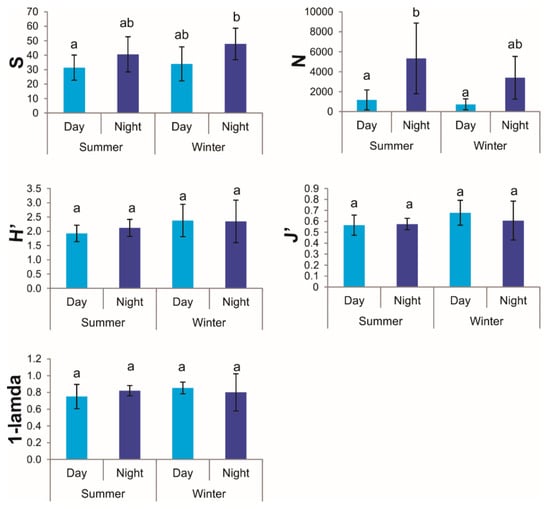
Figure 3.
Mean ecological indices of decapod diversity (S: species richness; N: abundance; H’: Shannon–Wiener’s diversity; J’: Pielou’s evenness; 1-lambda: Simpson’s dominance) estimated in seagrass meadows of the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon during the day (light blue columns) and night (dark blue columns) in two seasons (summer 1995, winter 1998) (N = 5 sites per time of the day and season). Error bars are 95% confidence intervals. In each panel, the same letter indicates similar means (α = 0.05).
3.3. Community Composition
Decapod assemblages varied significantly with time of the day (ANOSIM test: R = 0.544, p = 0.001), but not with the season (ANOSIM: R = 0.093, p = 0.075). The combined effect of both factors was also significant (R = 0.452, p = 0.001), but pairwise ANOSIM tests confirmed a stronger effect of the time of the day (R values: 0.444–0.752) compared with the season (R values: 0.164–0.200). The MDS plot exploring the effects of both factors, cross-checked against results from the cluster analysis and SIMPROF test, revealed that all samples formed a single group at 40% similarity but several groups at 60% similarity. One of the latter groups included all night samples from both seasons, except for one winter night sample, whereas the day samples formed several groups with no clear pattern (Figure 4). The SIMPER results showed high similarity among sites within seasons (summer: 58.3%; winter: 58.27%) and within the time of the day (day: 56.9%; night: 68.1%), with a dissimilarity of 43.2% between seasons and of 47.1% between day and night. The species that contributed more to the dissimilarity between seasons was Clibanarius tricolor (3.4%), which was six times as abundant in winter as in summer, and Cuapetes americanus (3.3%), which was 3.6 times more abundant in the summer than in the winter. Most species were more abundant at night than during the day, but those species contributing more to the dissimilarity between day and night were Processa bermudensis (3.9%), A. normanni (3.8%), and C. tricolor (3.3%).
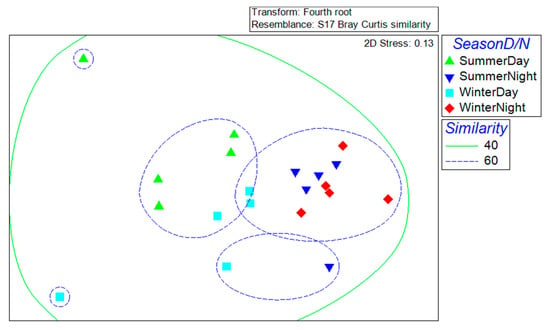
Figure 4.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (MDS) ordination of the community structure of seagrass-associated decapods in samples from Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, taken in the summer of 1995 and the winter of 1998, during the day and during the night. The analysis was based on species abundances. Each symbol denotes a sampling site. Shown are groups of samples within 40% (continuous green line) and 60% (broken blue line) similarity contours given by the sequence of similarity profile analysis (SIMPROF) tests on hierarchical clustering dendrograms (not shown).
3.4. Changes in Density of the 10 Most Abundant Species
Of the 10 most abundant species, only the density of L. fucorum, Pagurus annulipes, and Thor dobkini varied with both the time of the day and season, with no interaction (Table 2). All three species were more abundant in the summer than in the winter and at night than during the day. None of the other species showed significant changes in density with the season, but five exhibited changes in density with time of day, being more abundant at night than during the day (Cuapetes americanus, Thor manningi, Pagurus brevidactylus, A. normanii, and Processa bermudensis). Two of the 10 species (Clibanarius tricolor and Tozeuma carolinense) showed no changes in density with either season or time of day.

Table 2.
Mean density (No. individuals m−2) of the 10 most abundant seagrass-associated decapod species by season (summer, winter) and time of day (day, night) in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon. The numbers in parentheses are 95% confidence intervals. Across each row, the same superscript (a,b) indicates similar values (α = 0.05).
4. Discussion
The present study provides a baseline of the seagrass-associated epibenthic decapod community in Puerto Morelos at a time when this shallow Caribbean reef lagoon was in a relatively pristine state. We found 119 species of decapods, which exceeds the number of decapod species generally reported in other studies in tropical seagrass ecosystems (e.g., [8,13,19,22,23,66]). However, species richness is a function of both sampling duration and sampling area [67], and we sampled a larger area per site (340 m2) than most other studies did (≤10 m2). We did this because, as noted by Heck [68] and García-Raso et al. [21], sampling small areas may be insufficient (even with replicates) for the study of the communities of epibenthic seagrass-associated decapods, which are highly mobile and encompass a wide size range. Indeed, although 10 of the 119 species that we found accounted for nearly 90% of individuals, almost 50% (54 species) were rare (≤3 individuals). The time of sampling (day vs. night) affected the community composition because both the richness and abundance of species were higher at night, but did not affect other ecological indices, and season had no effect on either the community composition or any ecological index.
It is difficult to compare our results with studies conducted at other sites because the faunal assemblages vary with factors such as seagrass and associated macroalgal species [10,11,66,69,70,71,72], proximity to other types of habitats (e.g., coral reefs, mangroves, sand, mud) [68,73], freshwater runoff, temperature regime, and the local predator guild [17,24,74]. For example, there are broad differences in the fauna associated with Thalassia seagrass beds between the northern Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, although the most abundant genera in both regions tend to be represented by congeneric species [14]. Even in the Caribbean Sea, comparisons of decapod communities associated with seagrass meadows dominated by T. testudinum are limited by differences in the sampled area, type of sampling gear, and mesh size, although caridean shrimps and hermit crabs tend to dominate these communities [8,13,19,22,24,25,75]. In the 1980s, Bauer [13,22,23] obtained day and night samples from two T. testudinum sites in Puerto Rico over 13 months, using a push-net with the same mesh size as ours (1 mm). Interestingly, the three most abundant species in Bauer’s samples were the same as in our samples, and in the same order, suggesting a high similarity in the composition of decapod assemblages in both locations at the time of sampling.
Structural characteristics of the marine vegetation are not good predictors of the abundance or species richness of the associated faunal assemblages, in particular when macrophytes with different morphologies co-occur [10]. For example, in some studies, the abundance of faunal assemblages has shown no correlation with seagrass parameters [15,76]. This appears to be the case in Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, where despite the differences in the above-ground seagrasses density and biomass between the mid-lagoon and the back-reef lagoon zones [48,49], a preliminary analyses found no spatial pattern in abundance or diversity indices of invertebrates in general [38] and decapods in particular [30,39]. This lack of pattern may reflect the patchy configuration of the seagrass landscape [77,78]. Although the density of small decapods tends to be higher in small versus large seagrass patches [18,79,80,81,82], the large area per site that our samples covered may have included patches of different sizes interspersed in different types of matrices (e.g., sand or hard bottoms).
Diel variation in the abundance of seagrass-associated decapods is well known, with overall greater abundances in night samples than in day samples. This pattern reflects the nocturnal habits of many decapods, which remain inactive or burrow under the vegetation during the day [9,12,13,21,22,23,83]. In particular, dominant caridean species in seagrass meadows exhibit an activity peak during the first two hours after sunset [75]. Therefore, it has been suggested that studies on decapod assemblages in seagrasses should incorporate nocturnal samples [9,13,75]. In the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, the mean abundance of decapods was indeed much greater at night, and so was the variability. For example, among the 20 most abundant species (accounting for 97% of all individuals), the abundance of some was up to one order of magnitude higher in the night samples (e.g., Latreutes fucorum, Cuapetes americanus, Thor manningi, Pagurus annulipes, P. brevidactylus), whereas the abundance of others was 2–3 orders of magnitude higher in the night samples (e.g., Processa bermudensis, Alpheus normanni, Clibanarius tricolor, Sicyonia parri, Paguristes tortugae, Processa fimbriata). Only two of these 20 species exhibited slightly higher abundances in the day than in the night (Tozeuma carolinense and Mithraculus forceps). These two species were among the main contributors to the dissimilarity between the day and night decapod assemblages. Based on these results, we suggest that future comparative studies in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon give priority to night samples.
Seasonal differences in seagrass-associated faunal assemblages, including decapods, commonly occur in subtropical and temperate seagrass meadows (e.g., [1,12,84]). For example, in the western Mediterranean Sea, a significant temporal trend was found in decapod assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica, mainly related to recruitment events of the dominant species [15]. At Puerto Morelos, the annual range in monthly average sea surface temperatures is narrow (25.1–29.9 °C) [33], which is why we chose to sample in the two most contrasting seasons (summer and winter) during which T. testudinum shows differences in the above-ground biomass [48]. However, seasons had no significant effect on abundance, ecological indices, or community composition of seagrass-associated decapods. In most tropical seagrass meadows, decapod assemblages are dominated by small caridean shrimps and hermit crabs that have short lifespans as well as year-round reproduction and recruitment [8,85]; therefore, seasonality may be less influential than in temperate seagrass ecosystems. Yet Bauer [13,22] found seasonal variation in the abundance of the dominant species of shrimps and hermit crabs in T. testudinum meadows in Puerto Rico. However, Bauer’s sampling sites were very shallow (0.4–1 m) compared to ours (3–4 m), and shallow seagrass meadows are more susceptible to temperature variations than deeper meadows [86]. Changes in salinity may also drive changes in abundance of some taxa in tropical and subtropical seagrass meadows [68,87]. Many Caribbean seagrass ecosystems are subjected to seasonal riverine discharge (e.g., Panama: [8]; Guatemala: [25]; Venezuela: [19]), but Puerto Morelos has little influence of freshwater because there are no rivers in the Yucatan peninsula and the local wetlands are separated from the sea by a sand bar 2–3 m in height and 100–200 m in width. Therefore, annual salinity variations are minimal around an average value of 36 ppt [32,33].
In the 20+ years since this study was conducted, the Puerto Morelos reef system has changed from a nearly pristine to a more eutrophic system due to rapid coastal development as tourism became the main economic activity. Between 1998 and 2019, the population of Puerto Morelos increased six times (from ~5000 to 29,168), and the number of hotel rooms experienced a 14-fold increase (from 401 to 5600) [https://puertomorelos.gob.mx/]. Along with coastal development, nutrients and pollutant levels typically increase in adjacent waters. In Puerto Morelos, this was further aggravated by the paucity of sewage treatment plants in the area (with the exception of some hotels), an underground water circulation system that discharges in mangrove wetlands and submarine springs, and infiltration through the sand bar after heavy rain inputs [33,37]. Gradual changes in the seagrass community have occurred in time, including an increasing abundance of the faster-growing seagrass S. filiforme and rooted and drifting fleshy algae, shifts of relatively higher biomass invested in above-ground tissues of T. testudinum and S. filiforme, and an increase in phosphorus content in T. testudinum leaves [33,35]. Together with the discovery of high phosphorus additions through groundwater discharges into the reef lagoon after heavy rain [88], these changes are consistent with increasing levels of nutrient input. Hurricanes have also affected the seagrass meadows. After major hurricane Wilma (category 5) hit Puerto Morelos in October 2005, the narrow coastal fringe of vegetation was buried under sand and has not yet recovered [35,43].
Furthermore, since 2011, the Caribbean Sea has been affected by massive influxes of floating Sargassum spp. algae, which, upon reaching the shore, get stranded and die. At Puerto Morelos, these influxes were particularly large in 2015 and 2018. In July and August 2015, when the beachings of Sargassum peaked, accumulations of the seaweed amounted to an average of 9726 m3 per month per km of coastline [89]. These accumulations resulted in the build-up of decaying beach-cast material and nearshored murky brown waters [43]. These so-called Sargassum brown tides reduced light, oxygen, and pH while increasing levels of nitrogen and phosphorous. As a result, nearshore seagrass meadows were replaced by a community dominated by calcareous rhizophytic algae and drifting algae and epiphytes, resulting in 61.6–99.5% loss of below-ground biomass [43]. Sargassum brown tides also provoked the mortality of seagrass-associated fauna, including at least 18 species of decapods [90].
Macroalgae growing interspersed with seagrasses can increase the habitat value of a seagrass meadow [30,70], but in eutrophic systems, fleshy macroalgae can outcompete seagrasses, increase water-column hypoxia, and reduce animal abundance and production [87,91]. Seagrass loss has been found to induce changes in infaunal communities [92,93]. In Florida Bay mud banks, the seagrass-associated fish and crustacean communities changed between the 1980s and the late 1990s following seagrass (Thalassia and Halodule) die-offs, phytoplankton blooms, and other ecosystem changes [94]. In temperate Zostera marina meadows in Canada, eutrophication resulted in the loss of sensitive species and decreases in species richness, but the effects varied with geographic region [95]. In contrast, no effects of coastal development in lower Chesapeake Bay (USA) were detected on communities associated with Z. marina, including crustacean grazer biomass [96]. Therefore, the present baseline study may prove helpful to investigate whether the changes in the seagrass community of the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon over the last two decades have resulted in changes in the associated invertebrate communities.
5. Conclusions
In the late 1990s, the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon held a rich community of at least 119 species of seagrass-associated decapods. The dominance was high, with three species accounting for nearly 50% of individuals, whereas almost 50% of the species were rare, with 1–3 individuals in total. Species richness and abundance were significantly higher in night samples than in day samples, but seasons had no significant effect on ecological indices or community composition in this tropical ecosystem. The reef lagoon was considered pristine at the time of sampling, and has since been subjected to gradual eutrophication and presumably habitat degradation; therefore, these results provide a baseline to test for potential changes in community composition and ecological indices of seagrass-associated decapods.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/12/5/205/s1, Table S1. Database used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B.-F. and E.L.-Á.; Data curation, P.B.-F.; Formal analysis, P.B.-F., L.V.M.-V. and J.E.-O.; Funding acquisition, P.B.-F. and E.L.-Á.; Investigation, P.B.-F., L.V.M.-V., J.E.-O. and E.L.-Á.; Methodology, P.B.-F., L.V.M.-V., J.E.-O. and E.L.-Á.; Resources, P.B.-F. and E.L.-Á.; Supervision, P.B.-F. and E.L.-Á.; Visualization, P.B.-F.; Writing—original draft, P.B.-F.; Writing—review & editing, P.B.-F., L.V.M.-V., J.E.-O. and E.L.-Á. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (Research Grant No. 1171-N awarded to P.B.-F. and M.Sc. scholarship awarded to L.V.M.-V.).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the invaluable technical assistance provided by Fernando Negrete-Soto and Cecilia Barradas-Ortiz throughout the study. Surya Garza-Garza, Verónica Castañeda, Daniella Guevara, and Erick Cadena-Barrientos provided additional help in the field and laboratory. Edgar Escalante-Mancera provided the draft of Figure 1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Number of species and individuals of seagrass-associated decapod crustaceans on five sampling sites in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, Mexico. Samples were taken with an epibenthic sled during the day and during the night in the summer of 1995 and the winter of 1998.
Table A1.
Number of species and individuals of seagrass-associated decapod crustaceans on five sampling sites in the Puerto Morelos reef lagoon, Mexico. Samples were taken with an epibenthic sled during the day and during the night in the summer of 1995 and the winter of 1998.
| Summer | Winter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Species | Day | Night | Day | Night | Total | % | Cumulative % |
| 1 | Latreutes fucorum | 1998 | 5504 | 949 | 2554 | 11005 | 20.68 | 20.68 |
| 2 | Cuapetes americanus | 1209 | 4764 | 286 | 1375 | 7634 | 14.35 | 35.03 |
| 3 | Thor manningi | 519 | 4073 | 200 | 1435 | 6227 | 11.70 | 46.73 |
| 4 | Pagurus annulipes | 488 | 3893 | 507 | 767 | 5655 | 10.63 | 57.36 |
| 5 | Pagurus brevidactylus | 308 | 2509 | 400 | 1976 | 5193 | 9.76 | 67.12 |
| 6 | Clibanarius tricolor | 185 | 478 | 171 | 3807 | 4641 | 8.72 | 75.84 |
| 7 | Thor dobkini | 166 | 1671 | 49 | 314 | 2200 | 4.13 | 79.97 |
| 8 | Alpheus normanni | 15 | 911 | 8 | 1103 | 2037 | 3.83 | 83.80 |
| 9 | Tozeuma carolinense | 436 | 348 | 467 | 277 | 1528 | 2.87 | 86.67 |
| 10 | Processa bermudensis | 4 | 693 | 6 | 452 | 1155 | 2.17 | 88.84 |
| 11 | Leander tenuicornis | 5 | 82 | 33 | 537 | 657 | 1.23 | 90.08 |
| 12 | Processa fimbriata | 7 | 422 | 14 | 169 | 612 | 1.15 | 91.23 |
| 13 | Ancylomenes pedersoni | 198 | 171 | 62 | 104 | 535 | 1.01 | 92.23 |
| 14 | Sicyonia laevigata | 8 | 85 | 11 | 380 | 484 | 0.91 | 93.14 |
| 15 | Sicyonia parri | 1 | 84 | 3 | 355 | 443 | 0.83 | 93.98 |
| 16 | Trachycaris restrictus | 20 | 148 | 45 | 122 | 335 | 0.63 | 94.61 |
| 17 | Metapenaeopsis goodei | 0 | 65 | 20 | 208 | 293 | 0.55 | 95.16 |
| 18 | Portunus sp. | 2 | 74 | 19 | 135 | 230 | 0.43 | 95.59 |
| 19 | Mithraculus forceps | 80 | 42 | 31 | 27 | 180 | 0.34 | 95.93 |
| 20 | Mithraculus sculptus | 23 | 61 | 54 | 40 | 178 | 0.33 | 96.26 |
| 21 | Paguristes tortugae | 3 | 58 | 1 | 80 | 142 | 0.27 | 96.53 |
| 22 | Nikoides schmitti | 0 | 8 | 6 | 124 | 138 | 0.26 | 96.79 |
| 23 | Mithrax sp. 1 | 35 | 54 | 27 | 21 | 137 | 0.26 | 97.05 |
| 24 | Pitho aculeata | 9 | 67 | 17 | 38 | 131 | 0.25 | 97.29 |
| 25 | Panopeus occidentalis | 48 | 24 | 25 | 13 | 110 | 0.21 | 97.50 |
| 26 | Mithraculus coryphe | 3 | 5 | 69 | 23 | 100 | 0.19 | 97.69 |
| 27 | Chorinus heros | 0 | 27 | 8 | 63 | 98 | 0.18 | 97.87 |
| 28 | Latreutes parvulus | 6 | 78 | 2 | 11 | 97 | 0.18 | 98.05 |
| 29 | Achelous ordwayi | 1 | 32 | 5 | 52 | 90 | 0.17 | 98.22 |
| 30 | Pagurus sp. 1 | 0 | 43 | 10 | 29 | 82 | 0.15 | 98.38 |
| 31 | Panulirus argus | 0 | 25 | 6 | 45 | 76 | 0.14 | 98.52 |
| 32 | Calcinus tibicen | 0 | 1 | 6 | 61 | 68 | 0.13 | 98.65 |
| 33 | Pagurus sp. 2 | 0 | 26 | 16 | 24 | 66 | 0.12 | 98.77 |
| 34 | Mithrax pleuracanthus | 8 | 10 | 18 | 21 | 57 | 0.11 | 98.88 |
| 35 | Dardanus venosus | 0 | 13 | 1 | 39 | 53 | 0.10 | 98.98 |
| 36 | Podochela macrodera | 10 | 9 | 13 | 20 | 52 | 0.10 | 99.08 |
| 37 | Omalacantha bicornuta | 9 | 19 | 8 | 15 | 51 | 0.10 | 99.171 |
| 38 | Hippolyte zostericola | 18 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 30 | 0.06 | 99.228 |
| 39 | Clibanarius sp. | 2 | 6 | 1 | 21 | 30 | 0.06 | 99.284 |
| 40 | Paguristes puncticeps | 1 | 5 | 2 | 19 | 27 | 0.05 | 99.335 |
| 41 | Pitho sp. | 1 | 22 | 0 | 2 | 25 | 0.05 | 99.382 |
| 42 | Macrocoeloma diplacanthum | 2 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 24 | 0.05 | 99.427 |
| 43 | Gnathophyllum americanum | 7 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 23 | 0.04 | 99.470 |
| 44 | Micropanope nuttingi | 12 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 21 | 0.04 | 99.509 |
| 45 | Thor amboinensis | 0 | 0 | 14 | 4 | 18 | 0.03 | 99.543 |
| 46 | Macrocoeloma subparelellum | 0 | 0 | 7 | 11 | 18 | 0.03 | 99.577 |
| 47 | Eurypanopeus dissimilis | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 15 | 0.03 | 99.605 |
| 48 | Neopanope packardii | 9 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 14 | 0.03 | 99.632 |
| 49 | Thersandrus compressus | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 0.02 | 99.652 |
| 50 | Moreiradromia antillensis | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 0.02 | 99.671 |
| 51 | Calappa sulcata | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 10 | 0.02 | 99.690 |
| 52 | Teleophrys sp. | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 9 | 0.02 | 99.707 |
| 53 | Alpheus peasei | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 9 | 0.02 | 99.724 |
| 54 | Xanthoid G | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0.013 | 99.737 |
| 55 | Petrolisthes galatinus | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0.013 | 99.750 |
| 56 | Cyclozodium angustum | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 0.013 | 99.763 |
| 57 | Alpheus armatus | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 0.013 | 99.776 |
| 58 | Hippolyte obliquimanus | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 0.011 | 99.788 |
| 59 | Tuleariocaris neglecta | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.009 | 99.797 |
| 60 | Panopeus herbsti | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.009 | 99.806 |
| 61 | Mithrax sp. 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0.009 | 99.816 |
| 62 | Xanthoid H | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0.008 | 99.823 |
| 63 | Xanthoid B | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0.008 | 99.831 |
| 64 | Macrocoeloma laevigatum | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0.008 | 99.838 |
| 65 | Alpheus sp. 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0.008 | 99.846 |
| 66 | Xanthoid L | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.852 |
| 67 | Sicyonia brevirostris | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.857 |
| 68 | Sicyonia stimpsoni | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.863 |
| 69 | Panopeus sp. 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.868 |
| 70 | Paguristes sp. 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.874 |
| 71 | Hexapanopeus angustifrons | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.880 |
| 72 | Euryplax nitida | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.885 |
| 73 | Epialtus longirostris | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.891 |
| 74 | Diogenid A | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.897 |
| 75 | Alpheus armillatus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0.006 | 99.902 |
| 76 | Xanthoid F | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.906 |
| 77 | Xanthoid A | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.910 |
| 78 | Xanthoid M | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.914 |
| 79 | Xanthoid I | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.917 |
| 80 | Thoe puella | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.921 |
| 81 | Hippolyte sp. | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.925 |
| 82 | Anomuran A | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.929 |
| 83 | Alpheus sp. 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0.004 | 99.932 |
| 84 | Xanthoid E | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.934 |
| 85 | Xanthoid D | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.936 |
| 86 | Xanthoid C | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.938 |
| 87 | Xanthoid N | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.940 |
| 88 | Xanthoid K | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.942 |
| 89 | Xanthoid J | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.944 |
| 90 | Upogebia affinis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.945 |
| 91 | Synalpheus fritzmülleri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.947 |
| 92 | Synalpheus sp. 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.949 |
| 93 | Synalpheus sp. 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.951 |
| 94 | Synalpheus sp. 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.953 |
| 95 | Stenorhynchus seticornis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.955 |
| 96 | Stenopus hispidus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.957 |
| 97 | Speloeophorus pontifer | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.959 |
| 98 | Porcellanid A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.961 |
| 99 | Pilumnus sp. 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.962 |
| 100 | Pilumnus sp. 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.964 |
| 101 | Pachygrapsus gracilis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.966 |
| 102 | Periclimenes iridiscens | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.968 |
| 103 | Mithrax sp. 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.970 |
| 104 | Majoid A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.972 |
| 105 | Macrocoeloma trispinosum | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.974 |
| 106 | Lysmata anchisteus | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.976 |
| 107 | Lobopilumnus agassizii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.977 |
| 108 | Latreutes inermis | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.979 |
| 109 | Gnathophyllum sp. | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.981 |
| 110 | Discias atlanticus | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.983 |
| 111 | Diogenid B | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.985 |
| 112 | Caridean B | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.987 |
| 113 | Caridean A | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.989 |
| 114 | Alpheus sp. 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.991 |
| 115 | Alpheus sp. 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.992 |
| 116 | Alpheopsis trispinosus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.994 |
| 117 | Alpheopsis trigonus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.996 |
| 118 | Acanthonyx petiverii | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.002 | 99.998 |
| 119 | Alpheus websteri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.002 | 100 |
References
- Gore, R.H.; Gallaher, E.E.; Scotto, L.E.; Wilson, K.A. Studies on decapods of the Indian River region off Florida. XI. Community composition, structure, biomass and species-area relationship of seagrass and drift algae-associated macrocrustaceans. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1981, 12, 458–503. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, E.L.; Rowden, A.A.; Attrill, M.J.; Bossey, S.J.; Jones, M.B. The importance of seagrass beds as a habitat for fishery species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2001, 39, 269–303. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, K.H.; Hays, G.C.; Orth, R. Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 253, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Middelburgi, D.J.; Caraco, N. Major role of marine vegetation on the oceanic carbon cycle. Biogeosciences 2005, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.; Baird, M.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.; Larkum, A.; Ralph, P. Quantifying and modelling the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrass meadows—A critical assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.; York, P.H.; Rasheed, M.A.; Northfield, T.D. Does biodiversity–ecosystem function literature neglect tropical ecosystems? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, P.H.; Hyndes, G.; Bishop, M.J.; Barnes, R. Faunal Assemblages of Seagrass Ecosystems. In Seagrasses of Australia; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 541–588. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, K.L. Comparative species richness, composition, and abundance of invertebrates in Caribbean seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) meadows (Panamá). Mar. Biol. 1977, 41, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, H.; Livingston, R. Diel variation in the structure of seagrass-associated epibenthic macroinvertebrate communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1982, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.G. Crustacean epifauna of seagrass and macroalgae in Apalachee Bay, Florida, USA. Mar. Biol. 1987, 94, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, L.L.; Bell, S.S. The influence of habitat structure in faunal-habitats associations in a Tampa Bay seagrass system, Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1998, 62, 781–794. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, K.L.; Orth, R.J. Structural components of eelgrass (Zostera marina) meadows in the lower Chesapeake Bay: Decapod Crustacea. Estuaries 1980, 3, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.T. Diel and seasonal variation in species composition and abundance of the caridean shrimps (Crustacea, Decapoda) from seagrass meadows on the north coast of Puerto Rico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 36, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist, J.; Powell, G.V.N.; Sogard, S.M. Decapod and stomatopod assemblages on a system of seagrass-covered mud banks in Florida Bay. Mar. Biol. 1989, 100, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, Á.M.; Urra, J.; Marina, P.; Rueda, J.L.; Raso, J.E.G. Crustacean decapod assemblages associated with fragmented Posidonia oceanica meadows in the Alboran Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea): Composition, temporal dynamics and influence of meadow structure. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 37, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, G.J.; Shaw, C. The production and trophic ecology of shallow-water fish assemblages in southern Australia II. Diets of fishes and trophic relationships between fishes and benthos at Western Port, Victoria. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1995, 194, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, V.; Nelson, W.G. Factors influencing the association patterns of Hippolyte zostericola and Palaemonetes intermedius (Decapoda: Natantia) with seagrasses of the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. Mar. Biol. 1999, 134, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boada, J.; Pagès, J.F.; Gera, A.; MacPherson, E.; Santana, Y.; Romero, J.; Alcoverro, T. The richness of small pockets: Decapod species peak in small seagrass patches where fish predators are absent. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 142, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, J.; Mendoza, M.D.; Sánchez, B.L. Composition and abundance of decapod crustaceans in mixed seagrass meadows in the Paraguaná Peninsula, Venezuela. Iheringia Série Zool. 2018, 108, 2018004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, J.G.; Powell, G.V.N.; Sogard, S.M. Decapod and stomatopod communities of seagrass-covered mud banks in Florida Bay: Inter-and intra-bank heterogeneity with special reference to isolated subenvironments. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1989, 44, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Raso, J.E.G.; Martin, M.J.; Diaz, V.; Cobos, V.; Manjón-Cabeza, M.E. Diel and seasonal changes in the structure of a decapod (Crustacea: Decapoda) community of Cymodocea nodosa from Southeastern Spain (West Mediterranean Sea). Hydrobiologia 2006, 557, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.T. Hermit crab fauna from seagrass meadows in Puerto Rico: Species composition, diel and seasonal variation in abundance. J. Crust. Biol. 1985, 5, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.T. Penaeoid shrimp fauna from tropical seagrass meadows: Species composition, diurnal and seasonal variation in abundance. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1985, 98, 177–190. [Google Scholar]
- Barba Macías, E. Faunistic analysis of the caridean shrimps inhabiting seagrasses along the NW coast of the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrivillaga, A.; Baltz, D.M. Comparison of fishes and macroinvertebrates on seagrass and bare-sand sites on Guatemala’s Atlantic coast. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1999, 65, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Chace, F.A. The shrimps of the Smithsonian-Bredin Caribbean Expeditions with a summary of the West Indian shallow-water species (Crustacea: Decapoda: Natantia). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1972, 1–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, J.C.; Donath-Hernández, F.E.; Villalobos-Hiriart, J.L.; Cantú Díaz-Barriga, A. Notes on the shallow-water marine Crustacea of the Caribbean coast of Quintana Roo, México. An. Inst. Biol. Univ. Nal. Autón. México Ser. Zool. 1990, 61, 405–446. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Contreras, R.; Martínez-Mayén, M. Shallow water hippolytid shrimps (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea) from the Mexican Caribbean coast. Hidrobiológica 2009, 19, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Contreras, R.; Martínez-Mayén, M. Palaemonidae (Crustacea: Decapoda: Caridea) de las aguas someras de Quintana Roo, Caribe mexicano. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2010, 81, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Fourzán, P.; Lozano-Álvarez, E. The importance of Lobophora variegata (Phaeophyta: Dictyotales) as a habitat for small juveniles of Panulirus argus (Decapoda: Palinuridae) in a tropical reef lagoon. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2001, 68, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Briones-Fourzán, P.; Pérez-Ortiz, M.; Negrete-Soto, F.; Barradas-Ortiz, C.; Lozano-Álvarez, E. Ecological traits of Caribbean sea anemones and symbiotic crustaceans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 470, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Rentería, F.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Puerto Morelos, Quintana Roo, México. In CARICOMP–Caribbean Coral Reef, Seagrass, and Mangrove Sites; Kjerve, B., Ed.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Ruíz-Rentería, F.; Van Tussenbroek, B.; Barba-Santos, G.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Jordán-Garza, G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Environmental state and tendencies of the Puerto Morelos CARICOMP site, Mexico. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2010, 58, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortés, J.; Oxenford, H.A.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E.; Cróquer, A.; Bastidas, C.; Ogden, J.C. The CARICOMP network of Caribbean marine maboratories (1985–2007): History, key findings, and lessons learned. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I. Dynamics of seagrasses and associated algae in coral reef lagoons. Hidrobiológica 2011, 21, 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Cortes, J.; Collin, R.; Fonseca, A.C.; Gayle, P.M.H.; Guzman, H.M.; Jácome, G.E.; Juman, R.; Koltes, K.H.; Oxenford, H.A.; et al. Caribbean-wide, long-term study of seagrass beds reveals local variations, shifts in community structure and occasional collapse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R. Community involvement in marine protected areas: The case of Puerto Morelos reef, México. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Olivo, J.J. Riqueza Específica y Abundancia de la Macrofauna Béntica Asociada a Pastizales Marinos en la Laguna Arrecifal de Puerto Morelos, Quintana Roo, México. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Monroy-Velázquez, L.V. Variaciones en la Composición y Abundancia de la Fauna de Decápodos Asociados a Pastizales Marinos en el Caribe Mexicano. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Ecología. Programa de Manejo Parque Nacional Arrecife de Puerto Morelos; Secretaría del Medio Ambiente, Recursos Naturales y Pesca: Cd. de México, Mexico, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Briones-Fourzán, P.; Castañeda-Fernández de Lara, V.; Lozano-Álvarez, E.; Estrada-Olivo, J. Feeding ecology of the three juvenile phases of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus in a tropical reef lagoon. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G. Constructing paradise: The impacts of big tourism in the Mexican coastal zone. Coast. Manag. 2007, 35, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchley, A.; Alvarez-Filip, L. Local human activities limit marine protection efficacy on Caribbean coral reefs. Conserv. Lett. 2018, 11, e12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Hernández-Arana, H.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Espinoza-Avalos, J.; Canizales-Flores, H.M.; González-Godoy, C.E.; Barba-Santos, M.G.; Vega-Zepeda, A.; Collado-Vides, L. Severe impacts of brown tides caused by Sargassum spp. on near-shore Caribbean seagrass communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Roy, P.D.; Torrescano-Valle, N.; Cabanillas-Terán, N.; Carrillo-Domínguez, S.; Collado-Vides, L.; García-Sánchez, M.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I. Element concentrations in pelagic Sargassum along the Mexican Caribbean coast in 2018–2019. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, C.; Candela, J.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; Sheinbaum, J.; Lopez, M.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J. On the circulation in the Puerto Morelos fringing reef lagoon. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, M.; Otero, L. Atlas Ambiental Costero, Puerto Morelos-Quintana Roo; Centro de Investigaciones de Quintana Roo: Chetumal, Mexico, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I. Thalassia testudinum leaf dynamics in a Mexican Caribbean coral reef lagoon. Mar. Boil. 1995, 122, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I. Above- and below-ground biomass and production by Thalassia testudinum in a tropical reef lagoon. Aquat. Bot. 1998, 61, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbun, M.J. The spider crabs of America. Bull. United States Natl. Mus. 1925, 129, 1–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbun, M.J. The cancroid crabs of America of the families Euryalidae, Portunidae, Atelecyclidae, Cancridae, and Xanthidae. Bull. United States Natl. Mus. 1930, 152, 1–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, A.J., Jr. The shallow water hermit crabs of Florida. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1959, 9, 349–420. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, D.L. An Annotated Key to Crabs and Lobsters (Decapoda, Reptantia) from Coastal Waters of the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico; Louisiana St. University Publication No. LSU-SG-73-02: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, G. Los Crustáceos Decápodos de Venezuela; Instituto Venezolano de Investigaciones Científicas: Caracas, Venezuela, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.B. Shrimps, Lobsters, and Crabs of the Atlantic Coast of the Eastern United States, Maine to Florida; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Abele, L.G.; Kim, W. An Illustrated Guide to the Marine Decapod Crustaceans of Florida; Florida State University: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Humann, P. Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas; New World Publications: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Aguilera, J.L.; Toral-Almazán, R.E.; Ruiz-Nilo, J.A. Especies Catalogadas de Crustáceos Estomatópodos y Decápodos para el Golfo de México, Río Bravo, Tamps., a Progreso, Yuc.; Secretaría de Marina y CONABIO: Cd. de México, México, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, R.; Dashfield, S.; Somerfield, P. The integral structure of a benthic infaunal assemblage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E.; Dornelas, M. Biological diversity in a changing world. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3593–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.K.; Caruso, T.; Buscot, F.; Fischer, M.; Hancock, C.; Maier, T.S.; Meiners, T.; Mueller, C.; Obermaier, E.; Prati, D.; et al. Choosing and using diversity indices: Insights for ecological applications from the German Biodiversity Exploratories. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, B.R.; Johnson, M.W.; Cammarata, K.; Smee, D.L. Changes in seagrass species composition in Northwestern Gulf of Mexico estuaries: Effects on associated seagrass fauna. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azovsky, A.I. Species–area and species–sampling effort relationships: Disentangling the effects. Ecography 2011, 34, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.L., Jr. Some determinants of the composition and abundance of motile macro-invertebrates species in tropical and temperate turtlegrass (Thalassia testudinum) meadows. J. Biogeogr. 1979, 6, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F. Distribution of macrobenthic crustaceans associated with Thalassia, Halodule and bare sand substrata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 19, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.W.; Lewis, F. The influence of quantitative and qualitative aspects of habitat complexity in tropical sea-grass meadows. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 94, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virnstein, R.W.; Howard, R.K. Motile epifauna of marine macrophytes in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. II. Comparisons between drift algae and three species of seagrasses. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 41, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Leopardas, V.; Uy, W.; Nakaoka, M. Benthic macrofaunal assemblages in multispecific seagrass meadows of the southern Philippines: Variation among vegetation dominated by different seagrass species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 457, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Arbi, U.Y.; Lin, H.; Azkab, M.H.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Mou, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S. An ecological survey of the abundance and diversity of benthic macrofauna in Indonesian multispecific seagrass beds. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.D.; Duffy, J.; Orth, R. Plant species diversity and composition: Experimental effects on marine epifaunal assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 224, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grave, S.; Livingston, D.; Speight, M. Diel variation in sea grass dwelling shrimp: When to sample at night? J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2006, 86, 1421–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.K.; Young, M.W. Macrobenthic invertebrates in bare sand and seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) at Carrie Bow Cay, Belize. In The Atlantic Barrier Reef Ecosystem at Carrie Bow Cay, Belize, 1: Structure and Communities; Rützler, K., Macintyre, I.G., Eds.; Smithsonian Contributions Marine Science 12: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Boström, C.; Jackson, E.; Simenstad, C.A. Seagrass landscapes and their effects on associated fauna: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J. Landscape ecology of interactions between seagrass and mobile epifauna: The matrix matters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, D.B.; Etherington, L.L.; Elis, W.E. Organism response to habitat patchiness: Species and habitat-dependent recruitment of decapod crustaceans. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 223, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, D.; Hovel, K.A. Seagrass bed patchiness: Effects on epifaunal communities in San Diego Bay, USA. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 313, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Heck, K.L., Jr. Effects of habitat fragmentation per se on decapods and fishes inhabiting seagrass meadows in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 306, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Marion, S.R.; Lombana, A.V.; Orth, R.J. Faunal communities are invariant to fragmentation in experimental seagrass landscapes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.K. Diel variation in the abundance of epifauna associated with seagrasses of the Indian River, Florida, USA. Mar. Biol. 1987, 96, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, R.; Pertusati, M.; Batistini, F.; Piazzi, L. Spatial and temporal variation of motile macro-invertebrate assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica meadows. Acta Adriat. 2011, 52, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, R.T. Continuous reproduction and episodic recruitment in nine shrimp species inhabiting a tropical seagrass meadow. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1989, 127, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.A.; Unsworth, R.K.F. Long-term climate-associated dynamics of a tropical seagrass meadow: Implications for the future. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 422, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.O.; Lirman, D.; Pittman, S.J.; Serafy, J. Spatial patterns of seagrasses and salinity regimes interact to structure marine faunal assemblages in a subtropical bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 594, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, T.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Dennison, W. Influence of submarine springs and wastewater on nutrient dynamics of Caribbean seagrass meadows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Afluencia masiva de sargazo pelágico a la costa del Caribe mexicano (2014–2015). In Florecimientos Algales Nocivos en México; García-Mendoza, E., Quijano-Scheggia, S.I., Olivos-Ortiz, A., Núñez-Vázquez, E.J., Eds.; CICESE: Ensenada, México, 2016; pp. 352–365. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Medina-Valmaseda, A.; Blanchon, P.; Monroy-Velázquez, L.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Delgado-Pech, B.; Vásquez-Yeomans, L.; Francisco, V.; García-Rivas, M. Faunal mortality associated with massive beaching and decomposition of pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, L.A.; Wright, A.; Ayvazian, S.G.; Finn, J.T.; Golden, H.; Merson, R.R.; Harrison, J.A. Nitrogen loading alters seagrass ecosystem structure and support of higher trophic levels. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2002, 12, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, R.D.; Lewis, C.J.E. Loss of seagrass results in changes to benthic infaunal community structure and decreased secondary production. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2018, 94, 1273–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaiga, M.N.; Frouws, A.M.; Kairo, J.G.; Huxham, M. Seagrass removal leads to rapid changes in fauna and loss of carbon. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, R.E.; Camp, D.K.; Sogard, S.M.; Bjorgo, K.A. Changes in seagrass-associated fish and crustacean communities on Florida Bay mud banks: The effects of recent ecosystem changes? Estuaries 1999, 22, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.L.; Coll, M.; Lotze, H.K. Regional-scale differences in eutrophication effects on eelgrass-associated (Zostera marina) macrofauna. Estuar. Coasts 2017, 40, 1096–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.; Duffy, J.E.; Richardson, J.P. Patterns of seagrass community response to local shoreline development. Estuar. Coasts 2014, 37, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).