Abstract
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a phenolic natural product with diverse biological activities, notably anticancer properties. However, its ester group is metabolically unstable. The amide derivative, CAPA, offers improved metabolic stability to esterases but still possesses a metabolically liable catechol group. In this work, we describe the synthesis of a novel CAPA analogue in which the catechol is replaced with a benzimidazole bioisostere via a water-mediated Wittig reaction.
1. Introduction
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) (Figure 1) is a phenolic compound derived from bee propolis; it exhibits a wide range of biological activities such as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunostimulatory effects [1,2,3,4,5]. This has led to CAPE’s application in chronic wound healing [6], protection from ischemia–reperfusion injury [7], and other applications [8]. However, CAPE’s metabolic instability has prompted efforts to develop more stable analogues by replacing CAPE’s metabolically unstable ester bond with an amide group yielding caffeic acid phenethyl amide (CAPA) (Figure 1). This substitution of an ester with an amide should lead to increased stability for carboxylesterases, which generally hydrolyze amides much slower than esters [9,10]. While this modification addresses the instability of CAPE towards esterases, both CAPE and CAPA contain catechol groups that can also serve as sites of metabolic instability [11] as well as toxophores due to redox cycling and covalent modification of the ortho-quinone form [12,13].
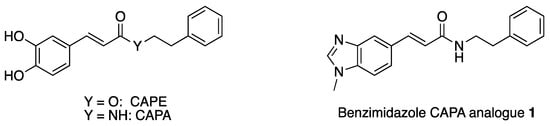
Figure 1.
Structure of CAPE and CAPA and the benzimidazole CAPA analogue 1.
To address these limitations, we sought to design a CAPA analogue with a bioisostere for the catechol group. Benzimidazoles have been reported to serve as catechol bioisosteres in the context of catecholamines [14,15] and other biologically active phenols [16]. Thus, we report the preparation of one such benzimidazole CAPA analogue, (E)-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-N-phenethyl acrylamide (1) (Figure 1).
Usually, CAPE and CAPA analogues are constructed using ester or amide coupling of caffeic acid precursors or the Wittig olefination reaction of the corresponding aldehyde to generate CAPE and CAPA [17,18,19]. For acid coupling approaches using organic solvents, high-purity reagents and specific activating agents are often required to achieve desired yields and selectivity. In contrast, we elected to employ the Wittig olefination route by employing an on-water reaction of the appropriate phosphonium salt with 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde, following our recently reported procedure for the preparation of biologically active CAPA analogs [20]. Water has proven to be an effective medium for Wittig reactions involving a broad range of stabilized ylides and aldehydes. This type of Wittig reaction performs well when large hydrophobic groups, such as aromatic and heterocyclic aromatic carboxaldehydes, are paired with phosphonium salts. Although the reactants may sometimes exhibit poor solubility, the reactions typically result in high yields, with E-selectivity reaching up to 99% [21,22,23]. In this method, the aqueous Wittig reaction stabilized ylides are relatively straightforward, catalyst-free, and sustainable, achieve high E-selectivity, and minimize the environmental impact by reducing reliance on organic solvents.
2. Results and Discussion
The required aldehyde for the Wittig route to 1, 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde 7 (Scheme 1), has previously been prepared via the reduction of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbonitrile [24]; however, the yield for this reduction was not high (51% yield). Aldehyde 7 has also been prepared as a mixture of 5- and 6-carbaldehydes via the methylation of 1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde [16]. We elected to prepare 7 through Swern oxidation of the primary alcohol 6 which was prepared from the corresponding methyl ester 5 (Scheme 1).
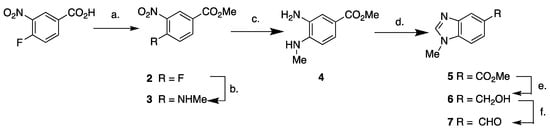
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde 7. Conditions: a. MeOH, H2SO4, 60 °C (95%); b. MeNH2, MeOH, (quant.); c. Zn, NH4Cl, THF/H2O/MeOH, 0 °C (91%); d. formic acid, 150 °C (µwave), (77%); e. LAH, THF (81%); f. DMSO, (ClCO)2, Et3N, DCM, (85%).
The benzimidazole methyl ester 5 was synthesized using a modified literature procedure [25]. Starting with 4-fluoro-3-nitrobenzoic acid, Fisher esterification in methanol affords the methyl ester 2 in 95% yield (Scheme 1). The conversion of fluoro compound 2 to methylamine 3 was achieved in quantitative yield using 40% methylamine solution. Reduction of 3 with zinc metal affords methyl 3-amino-4-(methylamino) benzoate (4) in 91% yield. Subjecting 4 to microwave irradiation in the presence of formic acid at 150 °C for 15 min gives ester 5 (77% yield). LAH reduction of ester 5 affords the hydroxymethyl compound 6 in 81% yield. Swern oxidation of 6 affords the required aldehyde 7 in 85% yield.
The synthesis of benzimidazole CAPA analogue 1 proceeded through the Wittig reaction of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde (7) and phosphonium bromide (8) in water using sodium hydroxide as a base at 70 °C for 3 h (Scheme 2). After extraction with dichloromethane, purification via flash chromatography, and recrystallization from DCM in hexane, the CAPA analogue was obtained as a single isomer of (E)-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-N-phenethyl acrylamide (1) in 64% yield (Scheme 2).
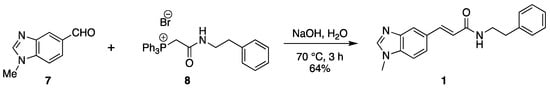
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of(E)-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-N-phenethylacrylamide.
3. Materials and Methods
Unless otherwise noted, all materials were obtained from commercial suppliers and were used without further purification. (2-Oxo-2-(phenethyl amino) ethyl) triphenyl phosphonium bromide (8) was prepared using a method from the literature [26]. Flash chromatography was performed on a Teledyne Combi-Flash with RediSep Rf silica gel (230–400 mesh) using the mobile phase indicated. Melting points (open capillary) were determined on an Electrothermal series IA 9000 digital melting point apparatus and were uncorrected. Unless otherwise noted, 1H and 13C NMR spectra were obtained on Bruker Advance Spectrometers operating at 400 MHz (100 MHz for 13C) or 500 MHz (126 MHz for 13C) and were determined in CDCl3 and DMSO-d6. Chemical shifts are reported in ppm using solvent as an internal standard (7.26 ppm for 1H and 77.0 ppm for 13C in CDCl3 and 2.50 ppm for 1H and 39.52 ppm for 13C in DMSO-d6). Low-resolution mass spectra were obtained on an Advion Expression L compact mass spectrometer with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) or electrospray ionization (ESI). High-resolution mass spectra were obtained on a Waters Synapt XS spectrometer with ESI. Copies of all NMR, IR, and HRMS spectra are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Synthesis of methyl 4-fluoro-3-nitrobenzoate (2): To a solution of 4-fluoro-3-nitrobenzoic acid (1 g, 5.45 mmol) in methanol (10 mL), concentrated H2SO4 (0.5 mL) was added. The reaction mixture was heated to 60 °C for 8 h. After completion of the reaction (monitored using the TLC), the solution was concentrated under reduced pressure, diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 50 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with sodium bicarbonate solution (20 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under vacuum to afford an off-white solid, 1.1 g, 95% yield; mp = 62–64 °C; IR 2952, 2885, 1726, 1268, 1072, 835 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.74 (dd, J = 7.2, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.33 (ddd, J = 8.7, 4.2, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 10.1, 8.8 Hz, 1H), 3.99 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.1, 158.0 (d, J = 271 Hz), 136.5 (d, J = 10 Hz), 127.8, 127.8, 127.2 (d, J = 4 Hz), 118.8 (d, J = 21 Hz), 52.9; APCI MS m/z: 200.1 (MH+). Matches lit [27].
Synthesis of methyl 4-(methylamino)-3-nitrobenzoate (3): To a solution of 4-fluoro-3-nitro-benzoic acid (1 g, 5.02 mmol) in MeOH (10 mL) at 0 °C, 40% methylamine solution in water (5 mL) was added dropwise with vigorous stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred at ambient temperature for 4 h, during which time an orange precipitate formed. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (20 mL) and cooled to 5 °C in an ice bath. The reaction mixture was adjusted to pH 4 through the slow addition of conc. HCl. The precipitate that formed was collected by filtration and washed with 2 × 10 mL of distilled water. Drying in vacuo for 18 h gave 4-methylamino-3-nitrobenzoic acid as a yellow solid, 1.15 g, quantitative yield, mp = 138–140 °C; IR 2950, 1705, 1230, 1005, 972, 835 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.56 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 2H), 7.94 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 2.99 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.4, 148.5, 136.1, 130.8, 128.7, 115.9, 115.0, 52.4, 30.3; APCI MS m/z: 211.1 (MH+). Matches lit [28].
Synthesis of methyl 3-amino-4-(methylamino) benzoate (4): To a solution of methyl 3-(methylamino)-4-nitrobenzoate (900 mg, 4.28 mmol) in THF/water/MeOH (1:1:1) (10 mL) at 0 °C, zinc dust (1.4 g, 21.41 mmol) and ammonium chloride (1.14 g, 21.41 mmol) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at rt for 30 min. The reaction mixture was filtered on a bed of Celite and extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL); the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum to afford a light brown solid, 700 mg, 91% yield; mp = 95–97 °C; IR 3403, 2948, 2525, 1692, 1599, 1296, 1166, 766 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.25 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 6.40 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 5.39 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 4.66 (s, 2H), 3.73 (s, 3H), 2.78 (d, J = 3.9 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.4, 142.1, 134.5, 121.3, 117.0, 114.3, 107.9, 51.6, 30.1; APCI MS m/z: 181.2 (MH+). Matches lit [29].
Synthesis of methyl 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylate (5): A solution of methyl 3-amino-4-(methyl amino) benzoate (500 mg, 2.77 mmol) in 3 mL of formic acid in a microwave vial was subjected to microwave heating to 150 °C for 15 min. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 20 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (20 mL) followed by brine solution (20 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under vacuum. The crude product was triturated with a DCM/hexane mixture to obtain an orange solid, 400 mg, 77% yield; mp = 124–126 °C; IR 2984, 2908, 1735, 1478, 1283, 1234, 1043 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.34 (s, 1H), 8.26 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.3, 147.3, 143.2, 138.3, 123.8, 123.6, 121.5, 110.9, 52.5, 31.4; APCI MS m/z: 191.1 (MH+). Matches lit [25].
Synthesis of (1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl) methanol (6): To a solution of methyl 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylate (300 mg, 1.74 mmol) in 15 mL of THF under argon at 0 °C, LAH (38 mg, 2.55 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred at rt for 6 h. After complete consumption of the starting material (monitored using the TLC), the reaction mixture was carefully quenched with water (20 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 50 mL). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum. The crude product was purified using Combi–Flash chromatography using 12% methanol in DCM as an eluant to obtain the product as a white solid, 163 mg, 83% yield; mp = 120–122 °C; IR 3379, 3256, 2949, 1758, 1246, 1043 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.13 (s, 1H), 7.58 (d, J = 0.5 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (dd, J = 8.3, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (s, 1H), 4.60 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H), 3.82 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 145.1, 143.7, 136.4, 134.0, 122.1, 117.6, 110.1, 63.8, 31.1; APCI MS m/z: 163.4 (MH+); HR CIMS calcd. for C9H11N2O (MH+) 163.0866, found 163.0883.
Synthesis of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde (7): To a solution of oxalyl chloride 165 mg in DCM (15 mL) at −78 °C under argon, DMSO (202 mg in DCM 10 mL) was added dropwise, followed by stirring at −78 °C for 30 min. Alcohol (150 mg in DCM 10 mL) was added dropwise to the reaction mixture and stirred for 30 min at −78 °C. Triethylamine (0.72 mL) was added to the reaction mixture and stirred at 0 °C for 30 min. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to rt and stirred for an additional 1 h. The reaction mixture was quenched with water (50 mL) and extracted with DCM (2 × 25 mL), and the combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated under vacuum to afford the crude product. The crude product was dissolved in 1 mL of DCM; then, 25 mL of hexane was added and the mixture was stirred for 20 min during which the product precipitated as a solid. The solids were filtered and dried under vacuum to afford a brown solid, 125 mg, 85% yield; mp = 119–121 °C; IR 3510, 3383, 1732, 1687, 1372, 1249 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.06 (s, 1H), 8.39 (s, 1H), 8.25 (s, 1H), 7.85 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.2, 147.7, 143.4, 139.3, 131.5, 123.6, 123.1, 111.6, 31.5; APCI MS m/z: 161.1 (MH+); HR CIMS calcd. for C9H9N2O (MH+) 161.0709, found 161.0720. Matches lit [16,24].
Synthesis of (E)-3-(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-N-phenethyl acrylamide (1): To a stirred solution of phosphonium salt 8 (113.3 mg, 0.22 mmol) in 2 mL of water at 0 °C, sodium hydroxide (30.0 mg, 0.75 mmol) was added portion-wise followed by the addition of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde 7 (30 mg, 0.18 mmol). The resulting mixture was stirred at 70 °C for 3 h. After the completion of the reaction (monitored using the TLC), the reaction mixture was diluted with water (10 mL) and extracted with dichloromethane (2 × 25 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with 20 mL of brine solution, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford the crude product. The crude product was purified via flash chromatography using (10% MeOH in DCM) is an eluant to afford the obtained compound, which was recrystallized from DCM (1 mL) in hexane (10 mL) to afford an off-white solid, 35 mg, 64% yield; mp = 151–153 °C; IR 3292, 3062, 2362, 1652, 1614, 1249 cm−1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.22 (s, 1H), 8.16 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.60 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (t, J = 13.1 Hz, 2H), 7.36–7.18 (m, 5H), 6.62 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.54–3.50 (m, 2H), 2.80 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.8, 146.2, 144.0, 140.2, 139.9, 136.0, 129.2, 129.1, 128.8, 126.6, 122.3, 120.6, 119.5, 111.2, 40.8, 35.6, 31.3; HR CIMS calcd. for C19H20N3O (MH+) 306.1601, found 306.1622.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we report a stereoselective on-water Wittig reaction of 1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carbaldehyde (7) with phosphonium salt (8) in the presence of a base to afford the novel benzimidazole CAPA analogue 1 in good yield. Biological studies of 1 are ongoing.
Supplementary Materials
1H and 13C NMR spectra of all compounds, IR spectra of all compounds, HRMS copies of compound 6, 7, and 9, and DEPT spectra of compound 1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.K.; methodology and investigation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and S.M.K.; supervision, S.M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by grants from the National Science Foundation (1955432, to S.M.K.). We also acknowledge support from the Texas State University Postdoctoral Researcher Catalyst Program (M.S.).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to David Schilter from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Texas State University for the HRMS data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Olgierd, B.; Kamila, Z.; Anna, B.; Emilia, M. The Pluripotent Activities of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester. Molecules 2021, 26, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaha, M.; De Filippis, B.; Cataldi, A.; di Giacomo, V. CAPE and neuroprotection: A review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdemli, H.K.; Akyol, S.; Armutcu, F.; Akyol, O. Antiviral properties of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its potential application. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 4, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittala, V.; Salerno, L.; Romeo, G.; Acquaviva, R.; Di Giacomo, C.; Sorrenti, V. Therapeutic potential of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) in diabetes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4827–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, M.F.; Omar, H.A.; Azab, S.S.; Khalifa, A.E.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Abdel-Rahman, S.Z. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester: A Review of Its Antioxidant Activity, Protective Effects against Ischemia-reperfusion Injury and Drug Adverse Reactions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaha, M.; Cataldi, A.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Cacciatore, I.; De Filippis, B.; Di Stefano, A.; Maccallini, C.; Rapino, M.; Korona-Glowniak, I.; Przekora, A.; et al. CAPE derivatives: Multifaceted agents for chronic wound healing. Archiv. Pharm. 2024, 357, e2400165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarauskaite, J.; Baniene, R.; Trumbeckas, D.; Strazdauskas, A.; Trumbeckaite, S. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects kidney mitochondria against ischemia/reperfusion induced injury in an in vivo rat model. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shuai, X.; Zhou, X.; Yin, D. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) inhibits cross-kingdom biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01578-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, S.D.; Berthelemy, M.; Jamita, S.G.; Hammock, B.; Morisseau, C. Development of amide-based fluorescence probes for selective measurement of carboxylesterase1 activity in tissue extracts. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 539, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, P.; Shaihutdinova, Z.; Lockridge, O. Drug and pro-drug substrates and pseudo-substrates of human butyrylcholinesterase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 218, 115910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velderrain-Rodriguez, G.R.; Palafox-Carlos, H.; Wall-Medrano, A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Chen, C.Y.O.; Robles-Sanchez, M.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A. Phenolic compounds: Their journey after intake. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.L.; Dunlap, T.L.; Dietz, B.M. Formation and biological targets of botanical o-quinones. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndreu, L.; Hurben, A.K.; Nyman, G.S.A.; Tretyakova, N.Y.; Karlsson, I.; Hagvall, L. Investigation into Propolis Components Responsible for Inducing Skin Allergy: Air Oxidation of Caffeic Acid and Its Esters Contribute to Hapten Formation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, C.D.; Wright, J.; Zenker, N. Synthesis and Adrenergic Activity of Benzimidazole Bioisosteres of Norepinephrine and Isoproterenol. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriga, M.; Paglietti, G.; Sparatore, F.; Pinna, G.; Sisini, A. Synthesis of Substituted Di-3(5-Benzazolyl) Alanines as DOPA and Alpha-Methyl DOPA Analogs and their Effects on Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase, Tyrosinase and Diphenoloxidase. Il Farm. 1991, 47, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, R.; Gajate, C.; Puebla, P.; Mollinedo, F.; Medarde, M.; Pelaez, R. Substitution at the Indole 3 position Yields Highly Potent Indole combretastatins Against Human Tumor Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Armas-Ricard, M.; Ruiz-Reyes, E.; Ramirez-Rodriguez, O. Caffeates and Caffeamides: Synthetic Methodologies and Their Antioxidant Properties. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2592609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.G.; Warren, S. Synthesis of New Water-soluble Phosphonium Salts and Their Wittig Reactions in Water. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2000, 4, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambacher, J.; Zhao, W.; El-Batta, A.; Arness, R.; Jiang, C.; Berdgahl, M. Water is an Efficient Medium for Wittig Reactions Employing Stabilized Ylides and Aldehydes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 4473–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, A.; Subbarao, M.; Jemal, M.; Mesa-Diaz, N.L.; Smith, J.; Vernaza, A.; Du, L.; Kerwin, S.M. Flow and On-Water Synthesis and Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Amide (CAPA) Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Batta, A.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, W.; Anness, R.; Cooksy, A.L.; Bergdahl, M. Wittig reactions in water media employing stabilizedylides with aldehydes. Synthesis of α, β-unsaturated esters from mixing aldehydes, α-bromoesters, and Ph3P in aqueous NaHCO3. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 5244–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Engberts, J.B.F.N. Hydrophobic interactions and chemical reactivity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 2809–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.J.B.; Fallot, L.B.; Gustafson, J.L.; Bergdahl, B.M. Water Mediated Wittig Reactions of Aldehydes in the Teaching Laboratory: Using Sodium Bicarbonate for the inSitu Formation of Stabilized Ylides. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deau, E.; Lindberg, M.F.F.; Miege, F.; Roche, D.; George, N.; George, P.; Kramer, A.; Knapp, S.; Meijer, L. Leucettinibs, a Class of DYRK/CLK Kinase Inhibitors Inspired by the Marine Sponge Natural Product Leucettamine B. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 10694–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Breit, B. Cu-Catalyzed C-H Allylation of Benzimidazoles with Allenes. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 6765–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Marriner, G.A.; Wang, X.; Bowman, P.D.; Kerwin, S.M.; Stavchansky, S. Synthesis of a Series of Caffeic Acid PhenethylAmide (CAPA) Fluorinated Derivatives: Comparison of Cytoprotective Effects to Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5032–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintre, S.A.; Ramjugernath, D.; Singh, P.; Mocktar, C.; Koorbanally, N.A. Microwave Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Docking Studies of 2-Substituted Methyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-5-carboxylates. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munack, S.; Leroux, V.; Roderer, K.; Ökvist, M.; van Eerde, A.; Gundersen, L.-L.; Krengel, U.; Kast, P. When Inhibitors do not Inhibit: Critical Evaluation of Rational Drug Design Targeting Chorismate Mutase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biodiv. 2012, 9, 2507–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Chen, X.X.; Yang, K.; Cui, H.; Qian, R.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, L.Q.; Su, X.; Zhao, M.Y.; et al. Design and Synthesis of 1H-benzo[d]imidazole Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors with Potential Therapy for Multiple Myeloma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 261, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).