Abstract
The subject of this article is new potential hypoxia-sensitive azo-thiacalix[4]arenes derivatives in the 1,3-alternate configuration. Previously, it was shown that azo derivatives of calix[4]arene in the cone conformation form complexes with rhodamine dyes. The present work is devoted to the synthesis of new azo derivatives using the thiacalix[4]arene platform. A new highly productive method for the synthesis of thiacalixarene with four anionic sulfonate azo fragments on the lower rim (compounds 2a–b) for further complexation with the most common cationic dyes is reported. The chemical structures of the products obtained were established based on 1H and 13C NMR, IR spectroscopy, MALDI TOF mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis.
1. Introduction
Hypoxia is a pathological process that develops as a result of an insufficient oxygen supply to tissues or a violation of its use by tissues [1,2]. It accompanies many diseases and pathophysiological states in the human body [3,4]. Particularly, hypoxia can be regarded as an indicator of tumor aggressiveness [5]. For this reason, there is a great interest in developing hypoxia visualization tools. Changes in the vascular system and blood flow resulting from tumor growth lead to the appearance of rapidly growing tumors of hypoxic regions, which in turn is accompanied by an increase in reductase activity [6]. The susceptibility of the azo bond to reduction by azoreductase formed the basis for the development of methods for visualizing hypoxia [7,8,9,10,11]. In this regard, the creation of hypoxia-sensitive systems based on complexes of azo derivatives of calixarenes seems promising [12]. Previously, it was shown that the calix[4]arenes with anionic carboxyl and sulfonate azo fragments in the cone configuration form complexes with rhodamine dyes [13]. The resulting complexes do not luminesce, but luminescence is recovered under hypoxic conditions. The present work is devoted to the synthesis of thiacalix[4]arenes 2a–b with anionic sulfonate azo groups in the 1,3-alternate conformation for further complexation with cationic dyes and the creation of signaling systems based on them for detecting hypoxia.
2. Results and Discussion
We synthesized new O-substituted thiacalix[4]arenes 2a–b in the 1,3-alternate conformation containing azo fragments linked by methylene spacers of different lengths (three and four units) (Scheme 1).
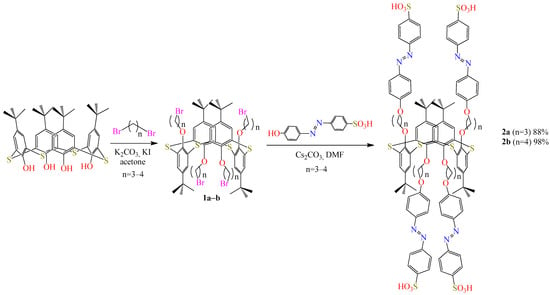
Scheme 1.
Synthetic pathway for thiacalixarenes 2a–b.
The synthesis of the initial bromopropyl thiacalixarene derivative 1a–b [14] as well as 4-[4-hydroxyphenylazo]-benzenesulfonic acid [15] was carried out using methods from the literature. We synthesized new derivatives of tetra-azo-thiacalix[4]arene 2a–b in 1,3-alternate form from the reaction of 1a–b with azo fragments. Compounds 2a–b were obtained after refluxing the reaction mixture for 5 days with 88% and 98% yield, respectively. Azo derivatives 2a–b were obtained as a result of the nucleophilic substitution reaction of the OH-nucleophile of the phenolic azo derivative with haloalkyl-thiacalixarene 1a–b in a basic medium.
The structures of 2a–b were decisively assigned based on IR, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, MALDI TOF mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis. The 1H NMR spectrum of 25,26,27,28-tetrakis-4-[4-(4′-sulfonylphenyldiazinyl)phenoxy]butoxy-5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)thiacalix[4]arene 2b displayed four aromatic protons as two apparent doublet and two singlet signals at δ 7.88, 7.79, 7.41, and 7.07 and four methylene protons as multiplet signals at δ 3.96, 3.91, 1.67, and 1.34 in addition to one methyl proton signal at δ 1.24 ppm. Additionally, the substitution reaction was confirmed by the 13C NMR spectrum that showed the four sp3-methylene carbons at δ 69.63, 68.98, 36.77, and 34.91 (see Figures S1–S8).
3. Materials and Methods
The NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker Avance 400 and 500 Nanobay (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) instruments with signals from residual protons of DMSO-d6 solvent as the internal standard. MALDI mass spectra were obtained using an UltraFlex III TOF/TOF spectrometer in the linear mode; p-nitroaniline or 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid was used as the matrix. Elemental analysis was performed using a PerkinElmer PE 2400 CHNS/O analyzer.
All reagents and solvents were purchased from either Acros (Geel, Belgium) or Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, VT, USA) and used without further purification. 5,11,17,23-tetra-tert-butyl-25,26,27,28-tetrakis-[(3-bromopropoxy)]2,8,14,20-tetrathiacalix[4]arene 1a, 5,11,17,23-tetra-tert-butyl-25,26,27,28-tetrakis-(4-bromobutoxy)-2,8,14,20-tetrathiacalix[4]arene 1b [14], and 4-[4-hydroxyphenylazo]-benzenesulfonic acid [15] were synthesized according to reported methods.
Synthesis of azo-thiacalix[4]arenes 2a–b.
25,26,27,28-Tetrakis(p-bromalkoxy)-5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)thiacalix[4]arene 1a–b (0.1 mmol) in DMF (10 mL) was added to 4-[4′-hydroxyphenylazo]benzenesulfonic acid (0.6 mmol) and Cs2CO3 (1 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated to 85 °C for 5 days. Then, the solvent was removed under vacuum; water was added to the residue. The precipitate formed was filtered off, washed with water, and dried in the air.
25,26,27,28-tetrakis-3-[4-(4′-sulfonylphenyldiazinyl)phenoxy]propoxy-5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)thiacalix[4]arene 2a.
Yield 88 %, orange powder, mp > 360 °C. Rf (ethyl acetate:hexane = 10:1) 0.26. IR: 1440 (N=N); 1191; 1143; 1120; 1006 (SO2). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C) δ, ppm: 7.90 (app d, 8H, Arazo-H), 7.79 (s, 16H, Arazo-H), 7.46 (s, 8H, ArH), 7.09 (app d, 8H, ArHazo-H), 3.98–4.07 (m, 16H, OCH2), 1.49 (m, 8H, CH2), 1.23 (s, 36H, t-Bu). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C): δ 163.32, 162.34, 157.16, 152.73, 151.26, 147.19, 146.96, 128.35, 128.13, 127.66, 127.23, 125.70, 122.74, 120.79, 116.00, 66.08, 36.78.78, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.00, 35.78, 35.00, 35.00. 31.80, 29.28. Mass spectrum MALDI (DHB), m/z: 2028.4 [M − 4H + K]+. Found, %: C 58.79; H 5.71; N 6.45. C100H104N8O20S8·3H2O·2(CH3)2NC(O)H. Calculated, %: C 58.87; H 5.78; N 6.48.
25,26,27,28-tetrakis-4-[4-(4′-sulfonylphenyl-diazinyl)phenoxy]butoxy-5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)thiacalix[4]arene 2b.
Yield 98 %, orange powder, mp > 360 °C. Rf (ethyl acetate:hexane = 10:1) 0.56. IR: 1440 (N=N); 1237; 1194; 1120; 1007 (SO2). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C) δ, ppm: 7.88 (app d, 8H, Arazo-H), 7.79 (s, 16H, Arazo-H), 7.41 (s, 8H, ArH), 7.07 (app d, 8H, ArHazo-H), 3.91–3.96 (m, 16H, OCH2), 1.67 (m, 8H, CH2), 1.34 (m, 8H, CH2), 1.24 (s, 36H, t-Bu). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C): δ 163.31, 162.41, 157.84, 152.69, 151.29, 147.18, 146.43, 128.95, 128.71, 127.65, 125.64, 122.73, 115.92, 69.63, 68.98, 36.77, 34.91, 31.95, 31.78. Mass spectrum MALDI (p-NA), m/z: 2145.5 [M + H]+. Found, %: C 60.95; H 5.60; N 6.05. C104H112N8O20S8·(CH3)2NC(O)H. Calculated, %: C 60.98; H 5.69; N 5.98.
4. Conclusions
Thus, we have demonstrated the synthesis of thiacalix[4]arenes 2a–b with anionic sulfonate azo groups in the 1,3-alternate conformation in high yields. The chemical structures of the products obtained were established based on 1H and 13C NMR, IR spectroscopy, MALDI TOF mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded. Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2a (DMSO-d6, 40 MHz, 25 °C); Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 2a (DMSO-d6, 101 MHz, 25 °C); Figure S3: MALDI TOF mass spectrum of compound 2a (DHB); Figure S4: IR spectrum of compound 2a (KBr tablet); Figure S5: 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2b (DMSO-d6, 500 MHz, 25 °C); Figure S6: 13C NMR spectrum of compound 2b (DMSO-d6, 101 MHz, 25 °C); Figure S7: MALDI TOF mass spectrum of compound 2b (p-NA); Figure S8: IR spectrum of compound 2b (KBr tablet).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.B.G. and S.E.S.; investigation, M.A.K., E.S.C. and S.R.K.; data curation, F.B.G., M.A.K. and S.R.K.; writing—original draft preparation, F.B.G.; writing—review and editing, F.B.G. and S.E.S.; supervision, S.E.S. and I.S.A.; project administration, F.B.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 22-73-00138.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are contained within the article or in the Supplementary Materials or are available on request from the corresponding author Farida Gabdrakhmanova.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Assigned Spectral-Analytical Center of Shared Facilities for Study of Structure, Composition and Properties of Substances and Materials of the Federal Research Center of Kazan Scientific Center of Russian Academy of Sciences (CSF-SAC FRC KSC RAS) for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P. Hypoxia and metabolism. Hypoxia, DNA repair and genetic instability. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; Wilson, W.R. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Ko, J.; Ju, C.; Eltzschig, H.K. Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellinger, I.N.; Cordasic, N.; Panesar, J.; Buchholz, B.; Jacobi, J.; Hartner, A.; Klanke, B.; Jakubiczka-Smorag, J.; Burzlaff, N.; Heinze, E.; et al. Hypoxia inducible factor stabilization improves defective ischemia-induced angiogenesis in a rodent model of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Span, P.N.; Bussink, J.B. Biology of Hypoxia. WB Saunders 2015, 45, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Qin, F.; Chen, C. Designing Hypoxia-Responsive Nanotheranostic Agents for Tumor Imaging and Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, A.; Mercier, C.; Saurel, L.; Orenga, S.; Renard, P.Y.; Romieu, A. The first latent green fluorophores for the detection of azoreductase activity in bacterial cultures. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8815–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Dwivedi, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Hypoxia-induced activity loss of a photo-responsive microtubule inhibitor azobenzene combretastatin A4. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, L.; Hu, J.; Tan, S. Novel designed azo substituted semi-cyanine fluorescent probe for cytochrome P450 reductase detection and hypoxia imaging in cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21572–21577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.B.; Ha, W.; Gao, K.; Shi, Y.P. Precisely Traceable Drug Delivery of Azoreductase-Responsive Prodrug for Colon Targeting via Multimodal Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9039–9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Li, J.; Lan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Light-Enhanced Hypoxia-Response of Conjugated Polymer Nanocarrier for Successive Synergistic Photodynamic and Chemo-Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21909–21919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.-C.; Jia, S.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Guo, D.-S. A noncovalent fluorescence turn-on strategy for hypoxia imaging. Agewandte Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironova, D.; Burilov, B.; Galieva, F.; Khalifa, M.A.M.; Kleshnina, S.; Gazalieva, A.; Nugmanov, R.; Solovieva, S.; Antipin, I. Azocalix[4]arene-rhodamine supramolecular hypoxia-sensitive systems: A search for the best calixarene hosts and rhodamine guests. Molecules 2021, 26, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyuftin, A.A.; Solovieva, S.E.; Muravrev, A.A.; Polyantsev, F.M.; Latypov, S.H.K.; Antipin, I. Synthesis and fluorescent properties of thiacalix[4]arenes containing terpyridyl fragments at the lower rim. Chem. Bull. Int. Ed. 2009, 58, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Bai, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, L. Nanosized Difunctional Photo Responsive Magnetic Imprinting Polymer for Electrochemically Monitored Light-Driven Paracetamol Extraction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44114–44123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).