Abstract
The E ring of betulin rearranges and forms a cyclic ether when treated with an acid. Treatment of betulin with iodine generated hydrogen iodide in situ, which went on to promote the rearrangement at C-19 and C-20, followed by cyclization to form allobetulin. A reaction of allobetulin with 2-furoyl chloride yielded 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol-2-furoate.
1. Introduction
Betulin (lup-20(29)-ene-3β,28-diol), a pentacyclic triterpenoid, is an abundant, biologically active secondary metabolite that is found in birch species (Betula ssp.) [1]. The amount of betulin from different birch species ranges from more than 15% of dry weight in B. populifolia and B. payrifera to about 30% in B. verrucosa. Betulin is readily extracted from the bark of Betula ssp. and is an attractive starting material for making different derivatives, including betulinic acid. Betulinic acid and other betulin derivatives have been shown to exhibit multiple biological activities [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. In addition to the selective oxidation of betulin to produce betulinic acid, other modifications have been carried out at C-3 and C-28 of betulin to make novel compounds for biological testing. Allobetulin (19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol), (Scheme 1), is one of the compounds that is readily obtained from betulin. Acid-catalyzed rearrangement of betulin produces allobetulin in one step and in good yield, making it a valuable candidate for additional modifications. The ease with which betulin is converted to allobetulin has led to the syntheses of novel compounds that include esters, amines, and glycosides by transforming the 3-OH of allobetulin, along with novel modifications to ring A [18,19]. In our study, allobetulin was obtained from betulin by using hydrogen iodide as a catalyst for the transformation. The hydrogen iodide was generated in solution by the reaction of the primary alcohol on the substrate, betulin, with iodine. The synthesis of 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol-2-furoate was accomplished by reacting allobetulin with 2-furoyl chloride in dry dichloromethane.
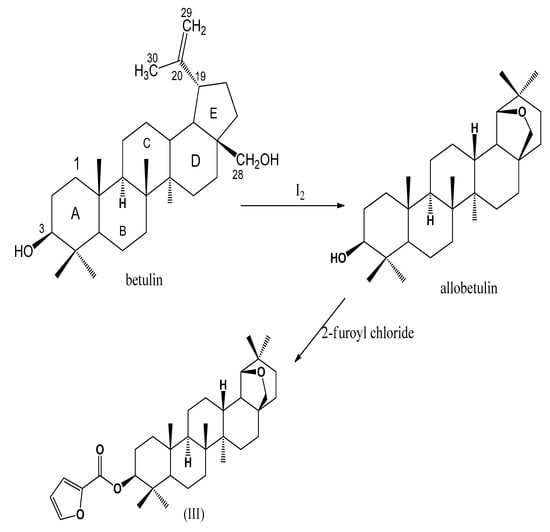
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol-2-furoate (III).
2. Results and Discussion
Allobetulin was synthesized from betulin by using hydrogen iodide (Scheme 1). The hydrogen iodide was generated in solution by reacting the C-28 hydroxy group of the substrate with iodine. The intermediate produced was R-O-I [Scheme 2]. Protonation of a double bond generated a tertiary carbocation that underwent the Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement.
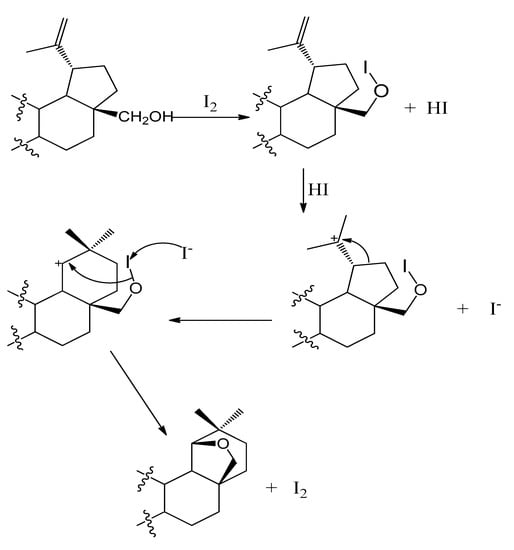
Scheme 2.
Hydrogen iodide-catalyzed conversion of betulin to allobetulin.
Green et al. used p-toluenesulfonic acid and proposed a mechanism for the rearrangement and cyclization [20]. Recently, Grymel and Adamek used a tetrafluoroboric acid diethyl ether complex to accomplish a similar transformation [21]. The iodide produced during protonation attacks R-O-I, and as the I–I bond is being formed, a new bond develops between oxygen and the carbocation to complete the cyclization. The reaction of iodine with different alcohols has previously been reported [22,23,24]. The coupling of the first step to the cyclization to produce the final product under mild conditions was not surprising and was in line with past observations. Allobetulin was reacted with 2-furoyl chloride to produce 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol-2-furoate (III). The chemical 1H-NMR chemical shifts for most protons did not change much from those of allobetulin. The 3-Ha chemical shift moved from 3.22 ppm to 4.79 ppm because of the ester group at that position. The three additional aromatic protons were centered at 6.51 ppm, 7.15 ppm, and 7.59 ppm, all as doublets of doublets with small coupling constants, in agreement with the findings of Abraham et al. [25] and Bardsley et al. [26]. The 13C-spectra consisted of five new carbons due to the ester -C=O at 158.71, and four aromatic carbons at 111.68 ppm, 117.32 ppm, 145.23 ppm, and 146.13 ppm.
The 13C-DEPT indicated twenty-seven carbon atoms consisting of CH, CH2 and CH3 leaving out C1′, C2′ and six quaternary carbons that are part of the triterpene skeleton.
3. Experimental
Betulin was isolated from white birch bark that was collected from York County, Pennsylvania. Dichloromethane, iodine, 2-furoyl chloride, and solvents were purchased from Aldrich. Dichloromethane was dried using molecular sieves (3 Å) that had been activated at 90 °C. 1H and 13C spectra were obtained using a Varian Gemini 500 NMR and recorded at 500 MHz and 125.74 MHz. The spectra are provided as Supplementary Materials. Elemental analysis was performed by Robertson Microlit Laboratories Inc., Legdewood, NJ, USA. Pulverized dry bark (100 g) was suspended in 375 mL of acetic acid: ethyl acetate: ethanol: water (1.5:1:0.5 v/v). After 48 h at room temperature, the mixture was filtered, and the filtrate was concentrated under vacuum. The solid (17.2 g) was recrystallized from isopropyl alcohol to give pure betulin, m.p. 252–253 °C, (lit. m.p. 254 °C) [27].
3.1. 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol (II) (Allobetulin)
To the solution of betulin (0.11 g, 0.034 mmol) in dry dichloromethane (10 mL) molecular sieves (2 g) and iodine (0.04 g, 0.16 mmol) were added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 16 h, followed by the addition of a 5% solution of sodium thiosulfate (10 mL). The colorless dichloromethane layer was washed with 5% sodium bicarbonate and then water, dried (Na2SO4) and concentrated under vacuum. The solid residue was re-crystallized from ethyl acetate to give the product (0.79 g, 70%) as white flakes, m.p. 258–260 °C, (lit. m.p. 260–261 °C) [28]. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, Me2SO-d6) d 0.78 (s, -CH3), 0.81 (s, -CH3), 0.86 (s, -CH3), 0.93 (s, -CH3), 0.95 (s, -CH3), 0.99 (s, -2CH3), 1.25–1.94 (m, -CH2), 3.22 (dd, J = 5.0 Hz, J = 11.5 Hz, 3-Ha), 3.46 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, H-19), 3.55 (s, 28-H), 3.8 (dd, J = 7.5 Hz, J = 1.5 Hz, H-19). 13C-NMR (125.74 MHz, Me2SO-d6) d 13.52, 15.39, 15.72, 16.49, 18.27, 21.00, 24.56, 26.27, 26.45, 26.46, 27.42, 27.99, 28.82, 32.72, 33.92, 34.16, 36.28, 36.76, 37.27, 38.90, 38.93, 40.62, 40.72, 41.49, 46.84, 51.09, 55.50, 71.28 (C-28), 78.97 (C-3), 87.95 (C-19).
3.2. 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol-2-furoate (III)
2-Furoyl chloride (0.13 g, 1 mmol) was added dropwise over 5 min to a stirred ice-cold solution of 19β,28-Epoxy-18α-olean-3β-ol (0.22 g, 0.5 mmol) in dry pyridine (4 mL). The reaction mixture was kept at room temperature for 1 h. Ether (20 mL) was added, followed by 5 mL of 1 M HCl solution. The organic layer was washed with 5 % sodium bicarbonate, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the ether was removed under vacuum to give a white solid (0.22 g, 84%). Pure crystals were obtained after recrystallization from a mixture of ethyl acetate and hexane (m.p. 300–302 °C). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, Me2SO-d6) d 0.82 (s, -CH3), 0.93 (s, -CH3), 0.94 (s, -CH3), 0.95 (s, -CH3), 0.97 (s, -CH3), 01.01 (s, -CH3), 1.26–1.99 (m, -CH2), 3.46 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, H-28), 3.55 (s, 19-H), 3.80 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, H-28), 4.73 (dd, J = 9.0 Hz, J = 5.5 Hz, 3-Ha), 6.51 (dd, J = 3.5 Hz, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, aromatic), 7.15 (dd, J = 3.50 Hz, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H, aromatic), 7.594 (dd, J = 1.5 Hz, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H, aromatic). 13C-NMR (125.74 MHz, Me2SO-d6) d 13.51, 15.73, 16.58, 16.63, 18.17, 21.04, 23.82, 24.56, 26.27, 26.44, 26.45, 28.02, 28.82, 32.73, 33.86, 34.17, 36.29, 36.76, 37.21, 38.18, 38.60, 40.66, 40.75, 41.50, 46.84, 51.02, 55.59, 71.30, 81.64, 87.98 (-O-C=O), 111.68 (C-aromatic), 117.32 (C-aromatic), 145.23 (C-aromatic), 146.13 (C-aromatic), 158.71 (C=O). C35H52O4 requires: C, 78.31%; H, 9.76%; O, 11.92%. Found: C, 78.29; H, 9.77%, O, 11.95%.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded online. Copies of 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra.
Funding
Funds from the Pennsylvania State University–York Advisory Board were used for this work.
Data Availability Statement
Copies of 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Krol, S.K.; Kiełbus, M.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Stepulak, A. Comprehensive Review on Betulin as a Potent Anticancer Agent. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 584189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, A.; Taru, M.; Salme, K.; Jari, Y.-K. Pharmacological properties of the ubiquitous natural product betulin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, F.; Poujade, C.; Evers, M.; Carry, J.-C.; Hénin, Y.; Bousseau, A.; Huet, T.; Pauwels, R.; De Clercq, E.; Mayaux, J.-F.; et al. Betulinic Acid Derivatives: A New Class of Specific Inhibitors of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Entry. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwada, Y.; Hashimoto, F.; Cosentino, L.M.; Chen, C.-H.; Garrett, P.E.; Lee, K.-H. Betulinic Acid and Dihydrobetulinic Acid Derivatives as Potent Anti-HIV Agents. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1016–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstikov, G.A.; Flekhter, O.B.; Shultz, E.E.; Baltina, L.A.; Tolstikov, A.G. Betulin and Its Derivatives. Chemistry and Biological Activity. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 13, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.-M.; Xu, H.-G.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.-J.; Sun, P.-H.; Wu, X.-M.; Wang, G.-J.; Chen, W.-M.; Ye, W.-C. Betulinic Acid and its Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 1127–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bori, I.D.; Hung, H.-Y.; Qian, K.; Chen, C.-H.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.-H. Anti-AIDS agents 88. Anti-HIV conjugates of betulin and betulinic acid with AZT prepared via click chemistry. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordyjewska, A.; Ostapiuk, A.; Horecka, A.; Kurzepa, J. Betulin and betulinic acid: Triterpenoids derivatives with a powerful biological potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 929–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommera, H.; Kaluđerović, G.N.; Kalbitz, J.; Paschke, R. Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Novel Betulinic acid and Betulin Derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2010, 343, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soica, C.M.; Dehelean, C.A.; Peev, C.; Aluas, M.; Zupkó, I.; Kása, P., Jr.; Alexa, E. Physico-chemical comparison of betulinic acid, betulin and birch bark extract and in vitro investigation of their cytotoxic effects towards skin epidermoid carcinoma (A431), breast carcinoma (MCF7) and cervix adenocarcinoma (HeLa) cell lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Pawlak, A.; Henklewska, M.; Sysak, A.; Wen, L.; Yi, J.E.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B. Antitumor Activity of Bet-ulinic Acid and Betulin in Canine Cancer Cell Lines. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubek, B.; Mituła, P.; Niezgoda, N.; Kempińska, K.; Wietrzyk, J.; Wawrzeńczyk, C. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity of New Betulin and Betulinic Acid Esters with Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Tang, N.; Yan, W.-D. Synthesis and cytotoxicity of triterpenoids derived from betulin and betulinic acid via click chemistry. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 17, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvasnica, M.; Sarek, J.; Klinotova, E.; Dzubak, P.; Hajduch, M. Synthesis of phthalates of betulinic acid and betulin with cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, G.; Yokoyama, T.; Sagara, Y.; Manabe, M.; Kodama, H. Effect of three triterpenoids, lupeol, betulin, and betulinic acid on the stimulus-induced superoxide generation and tyrosyl phosphorylation of proteins in human neutrophils. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 325, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, C.; Legault, J.; Lavoie, S.; Rondeau, S.; Tremblay, S.; Pichette, A. Synthesis and Cytotoxicity of Bidesmosidic Betulin and Betulinic Acid Saponins. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 72, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloyede, H.; Ajiboye, H.; Salawu, M. Influence of oxidative stress on the antibacterial activity of betulin, betulinic acid and ursolic acid. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrous, I.; Boudebouz, O.; Voronova, O.; Plotnikov, E.; Bakibaev, A. Synthesis and antioxidant evaluation of some new allobetulin esters. Rasayan J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaen, W.; Mashentseva, A.A.; Seitembetov, T.S. Allobetulin and Its Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Activity. Molecules 2011, 16, 2443–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.; Bentley, M.D.; Chung, B.Y.; Lynch, N.G.; Jensen, B.L. Isolation of Betulin and Rearrangement to Allobetulin. A Biomimetic Natural Product Synthesis. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grymel, M.; Adamek, J. Allobetulin. Molbank 2022, 2022, M1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasa, A.; Varala, R.; Swami, P.M.; Zubaidha, P. Selective and efficient etherification of secondary cinnamyl alcohols in the presence of iodine catalyst and evaluation of their anti-candida activity. Chem. J. 2013, 03, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kasashima, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Mino, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Fujita, T. An Efficient Synthesis of Five-membered Cyclic Ethers from 1,3-Diols Using Molecular Iodine as a Catalyst. J. Oleo Sci. 2008, 57, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kasashima, Y.; Uzawa, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Murakami, K.; Mino, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Fujita, T. Synthesis of Cinnamyl Ethers from .ALPHA.-Vinylbenzyl Alcohol Using Iodine as Catalyst. J. Oleo Sci. 2010, 59, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, R.J.; Bernstein, H.J. The proton resonance spectra of furan and pyrrole. Can. J. Chem. 1959, 37, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardsley, B.; Smith, M.S.; Gibbon, B.H. Structure elucidation and spectroscopic analysis of photodegradants of the anti-rhinitis drug fluticasone furoate. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 1876–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, H.; Pierok, K. Zur Kenntnis des Betulins. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1922, 55, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Green, B.; Bowyer, W.J. Steroids and Related Natural Products. VI. The Structure of α-Apoallobetulin. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 8, 2879–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).