miR-369-3p Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
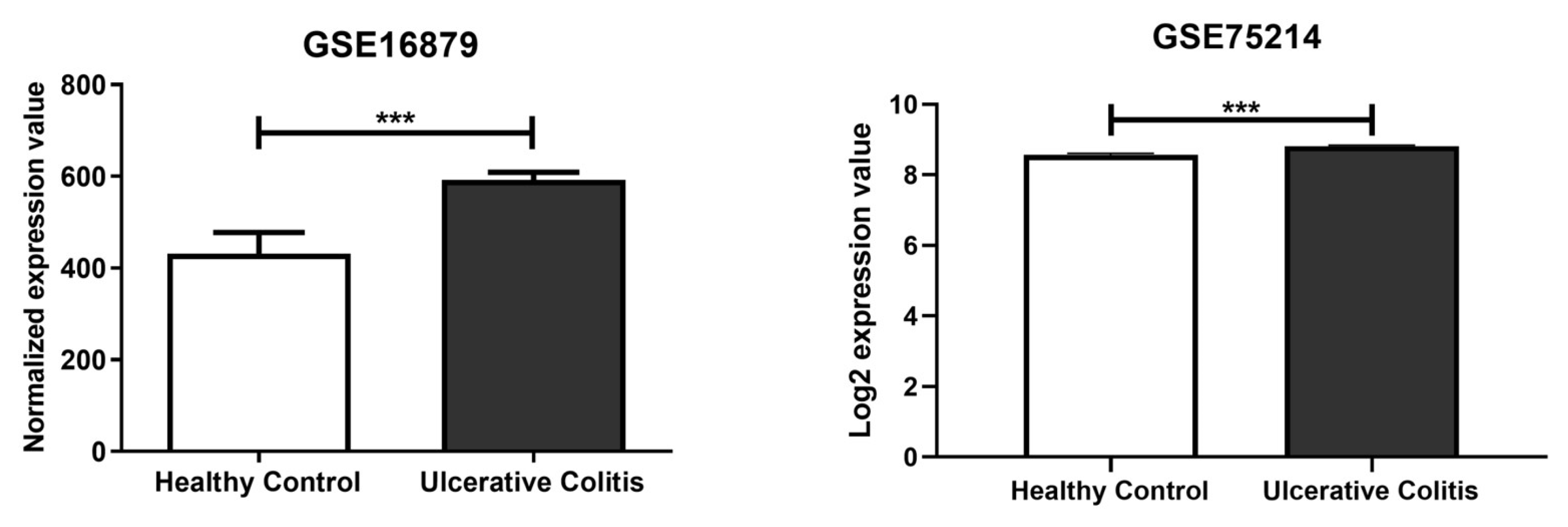
2.1. In Silico Identification of miR-369-3p Target Gene
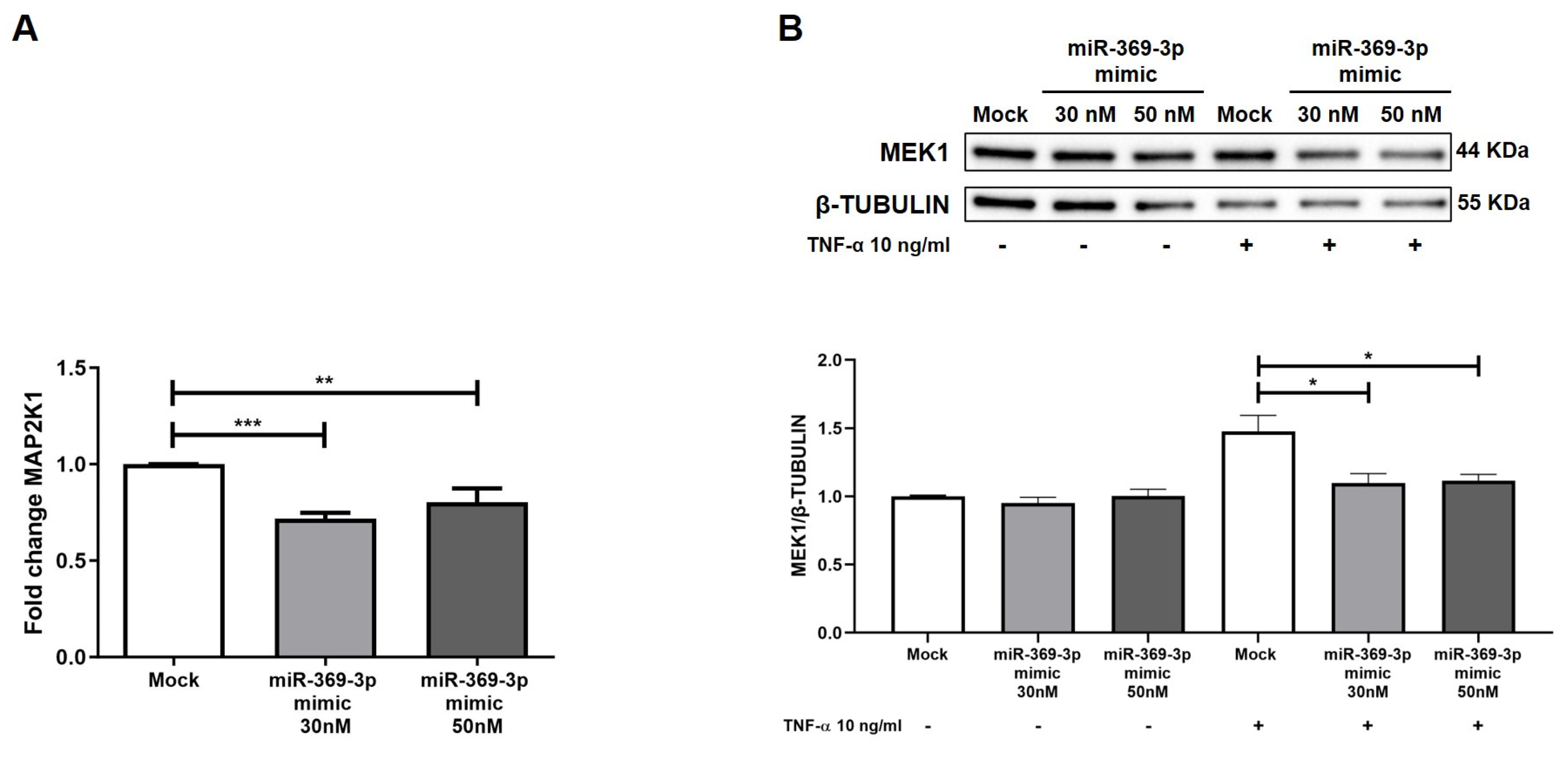
2.2. miR-369-3p Mimic Influences MAP2K1 Expression
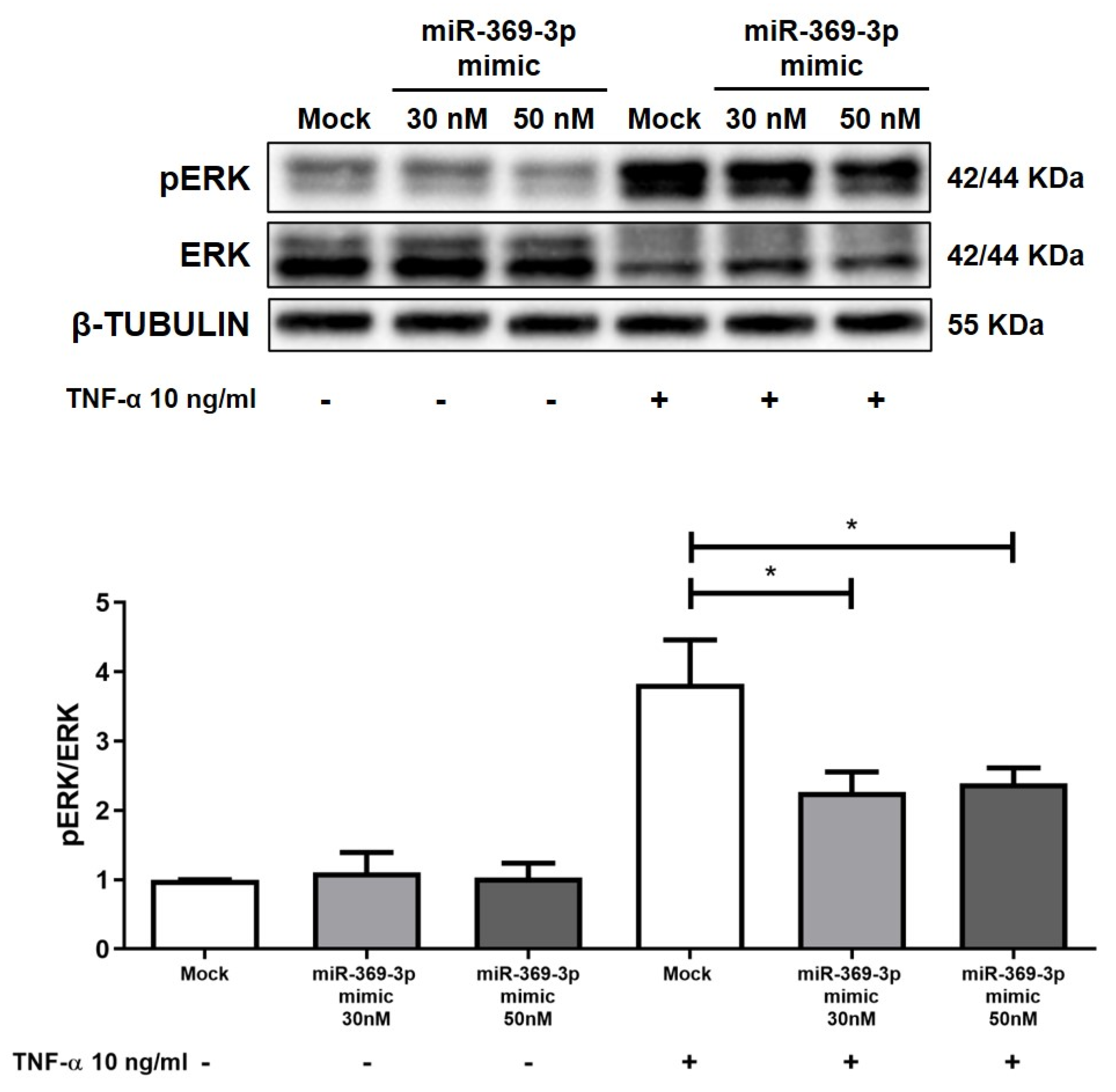
2.3. The Modulation of MEK1 Reduces the Activation of ERK
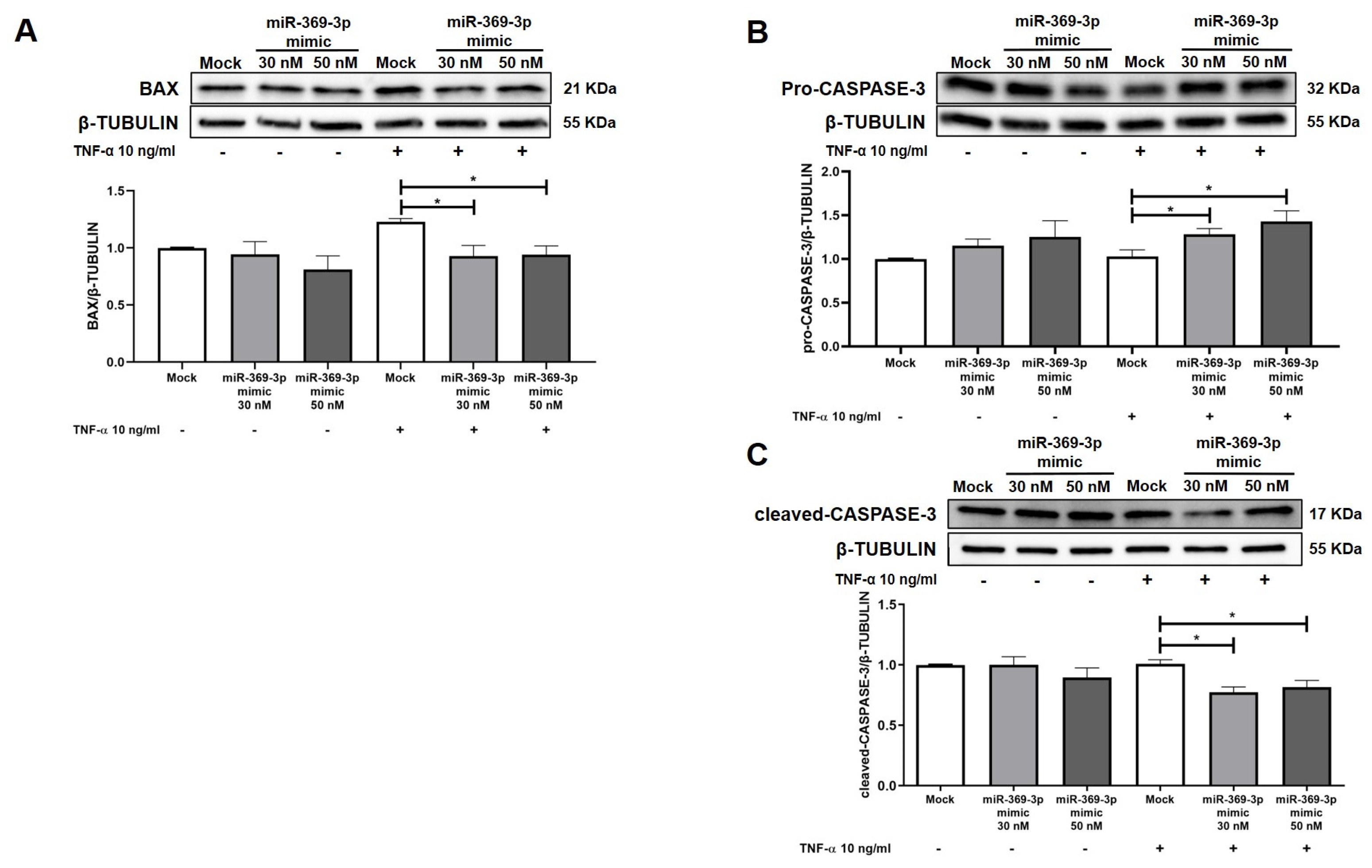
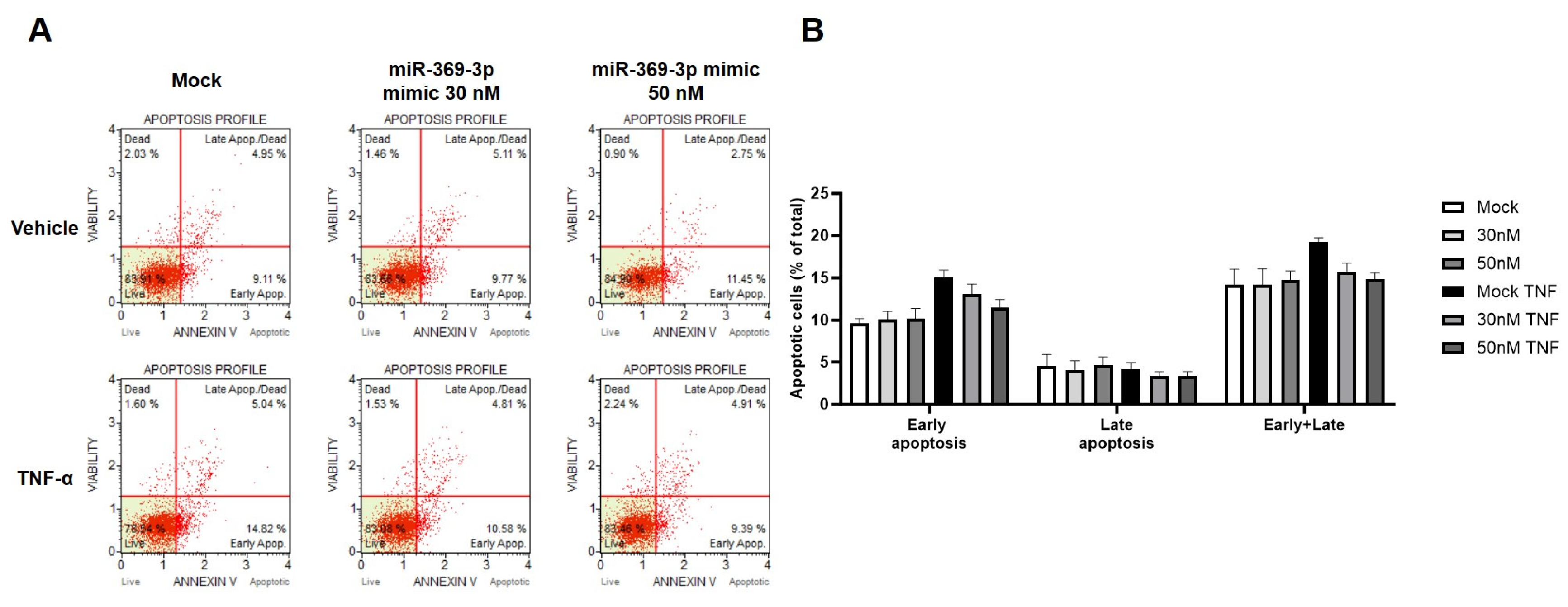
2.4. The Modulation of MEK1 by miR-369-3p Shows a Significant Impact on the Apoptosis Pathway
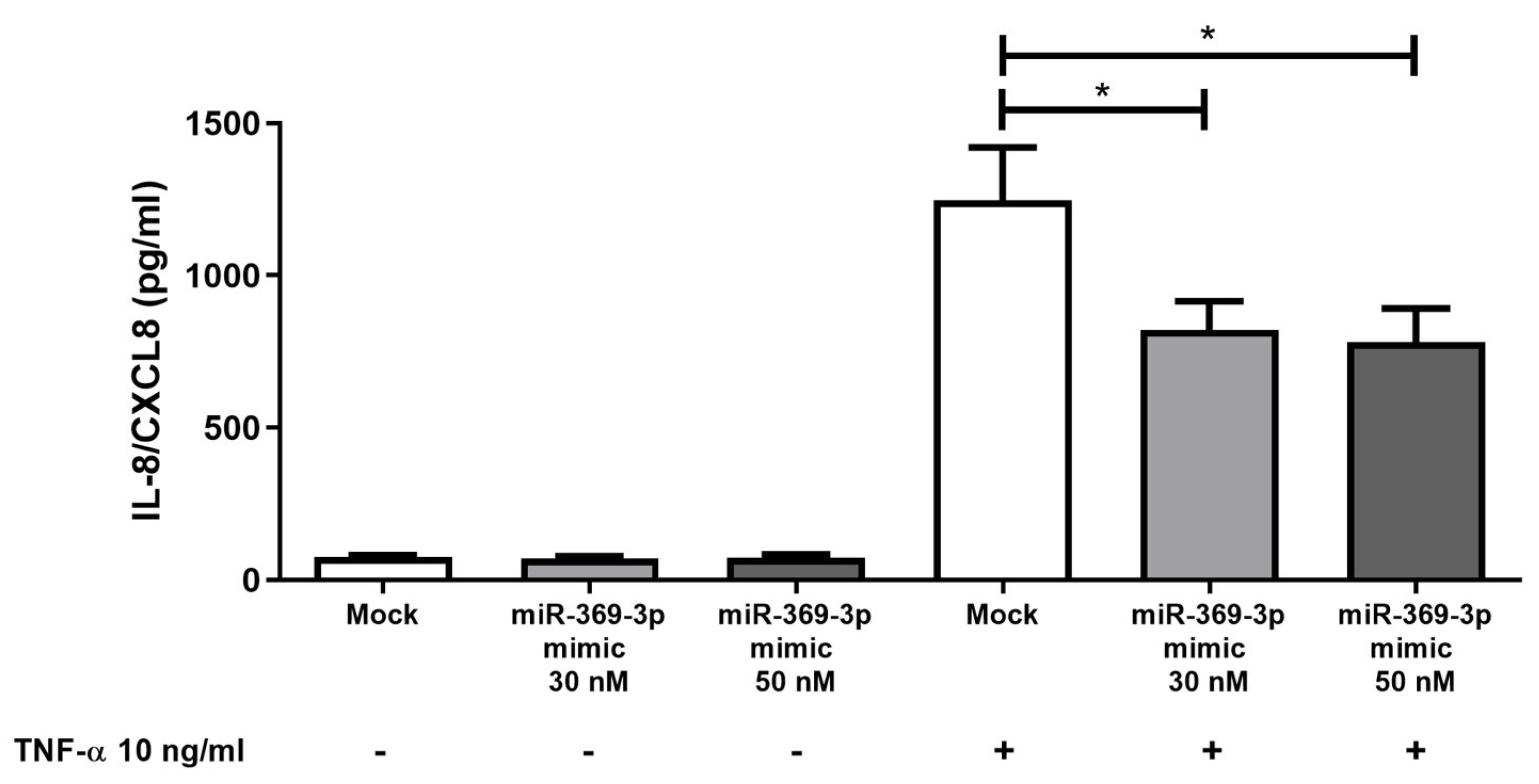
2.5. Effect of miR-369-3p on Release of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and miRNA Mimic Transfection
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.3. Immunoblot Analysis
4.4. Annexin V Assay
4.5. Cytokines Production
4.6. Bioinformatics Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Q. A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7247238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.P.; Papadakis, K.A. Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.; Ghazi, P.C.; Starchenko, A.; Tovaglieri, A.; Baldwin, K.R.; Poulin, E.J.; Gierut, J.J.; Genetti, C.; Yajnik, V.; Breault, D.T.; et al. The Colonic Epithelium Plays an Active Role in Promoting Colitis by Shaping the Tissue Cytokine Profile. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2002417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, E.; Haller, D. Intestinal Epithelial Cell Metabolism at the Interface of Microbial Dysbiosis and Tissue Injury. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal Epithelial Cells: Regulators of Barrier Function and Immune Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zallot, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Deep Remission in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Looking Beyond Symptoms. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2013, 15, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, R.; Watanabe, M. Role of Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, M.; Olsen, J.; Seidelin, J.B.; Nielsen, O.H. MAP Kinases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, O.J.; Widjaya, B.; Troelsen, J.; Olsen, J.; Nielsen, O.H. Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases: A Role in Inflammatory Bowel Disease? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 158, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blander, J.M. On Cell Death in the Intestinal Epithelium and Its Impact on Gut Homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 34, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Natural Products Modulate Cell Apoptosis: A Promising Way for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 806148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Excessive Apoptosis in Ulcerative Colitis: Crosstalk Between Apoptosis, ROS, ER Stress, and Intestinal Homeostasis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. MicroRNAs in Action: Biogenesis, Function and Regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbant, E.; Akkaya-Ulum, Y.Z. Exploring Regulatory Mechanisms on MiRNAs and Their Implications in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, A.I.; Batool, W.; Ahmed, A.; Zafar, S.; Patel, S.K.; Mohan, A.; Zia, U.; Aminpoor, H.; Kumar, V.; Tejwaney, U. Role of MicroRNA in Colorectal Carcinoma (CRC): A Narrative Review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. MiR-195-5p Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression via KRT23 Regulation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; De Marinis, L.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. Identification of a Novel MiR-195-5p/PNN Axis in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; Bianco, G.; Savino, M.T.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. Downregulation of γ-Catenin by MiR-195-5p Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression, Regulating Desmosome Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, Y.N.; Kamel, A.M.; Medhat, M.A.; Hetta, H.F. MicroRNA Signatures in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnachaitanya, S.S.; Liu, M.; Fujise, K.; Li, Q. MicroRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Lacalamita, A.; Tafaro, A.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. MiR-195-5p Regulates Tight Junctions Expression via Claudin-2 Downregulation in Ulcerative Colitis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Bianco, G.; Schena, N.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. The Increase of MiR-195-5p Reduces Intestinal Permeability in Ulcerative Colitis, Modulating Tight Junctions’ Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galleggiante, V.; De Santis, S.; Liso, M.; Verna, G.; Sommella, E.; Mastronardi, M.; Campiglia, P.; Chieppa, M.; Serino, G. Quercetin-Induced MiR-369-3p Suppresses Chronic Inflammatory Response Targeting C/EBP-β. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Valentini, A.M.; Schena, N.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. MiR-369-3p Modulates Intestinal Inflammatory Response via BRCC3/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis. Cells 2023, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Valentini, A.; Mastronardi, M.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. A Novel Mechanism of Immunoproteasome Regulation via MiR-369-3p in Intestinal Inflammatory Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Labarile, N.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of MiR-369-3p via PDE4B in Intestinal Inflammatory Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Farré, R.; Verstockt, S.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Schuit, F.; Vermeire, S.; Arijs, I.; et al. Genetic and Transcriptomic Bases of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijs, I.; De Hertogh, G.; Lemaire, K.; Quintens, R.; Van Lommel, L.; Van Steen, K.; Leemans, P.; Cleynen, I.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Mucosal Gene Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Before and After First Infliximab Treatment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeissig, S.; Bergann, T.; Fromm, A.; Bojarski, C.; Heller, F.; Guenther, U.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J. Altered ENaC Expression Leads to Impaired Sodium Absorption in the Noninflamed Intestine in Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. ERK1/2 MAP Kinases: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipieter, F.; Cappe, B.; Leray, A.; De Schutter, E.; Bridelance, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Van Camp, G.; Declercq, W.; Héliot, L.; Vincent, P.; et al. Characteristic ERK1/2 Signaling Dynamics Distinguishes Necroptosis from Apoptosis. iScience 2021, 24, 103074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, I.; Mayer, L. Immunopathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2002, 18, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.O.; Satsu, H.; Shimizu, M. Histidine Inhibits Oxidative Stress- and TNF-α-induced Interleukin-8 Secretion in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4671–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vebr, M.; Pomahačová, R.; Sýkora, J.; Schwarz, J. A Narrative Review of Cytokine Networks: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Implications for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Ma, C.; Su, F.; Jiang, Y.; Lai, R.; Zhang, T.; Sun, K.; Fan, L.; Cai, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein Mediates Intestinal Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Promotes IBDs in Humans and Mice. Gut 2017, 66, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Mukaisyo, K.; Sugihara, H.; Fujiyama, Y.; Hattori, T. Increased Apoptosis and Decreased Proliferation of Colonic Epithelium in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. Oncol. Rep 2010, 24, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Vaux, L.; Patterson, A.M.; Modasia, A.; Muraro, D.; Fletcher, A.G.; Byrne, H.M.; Maini, P.K.; Watson, A.J.M.; Pin, C. Elevated Apoptosis Impairs Epithelial Cell Turnover and Shortens Villi in TNF-Driven Intestinal Inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamo, K.; Okuzono, Y.; Yabuki, M.; Ochi, T.; Sugimura, K.; Sato, Y.; Sagara, M.; Hayashi, H.; Ishimura, Y.; Nishimoto, Y.; et al. Gene Signature–Based Approach Identified MEK1/2 as a Potential Target Associated With Relapse After Anti-TNFα Treatment for Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Gong, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. N-Acetyl-Seryl-Aspartyl-Lysyl-Proline Mitigates Experimental Colitis Through Inhibition of Intestinal Mucosal Inflammatory Responses via MEK-ERK Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dai, L.-M.; Shen, H.; Gu, P.-Q.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.-F. Qing Chang Hua Shi Granule Ameliorate Inflammation in Experimental Rats and Cell Model of Ulcerative Colitis through MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalavino, V.; Liso, M.; Cavalcanti, E.; Gigante, I.; Lippolis, A.; Mastronardi, M.; Chieppa, M.; Serino, G. MiR-369-3p Modulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Is Involved in Regulation of Chronic Inflammatory Response. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Yan, F.; Yamaoka, T.; Polk, B.D. Regulation of Apoptosis during Homeostasis and Disease in the Intestinal Epithelium. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Gong, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Du, P.; Chen, Y. MiR-200b Inhibits TNF-α-Induced IL-8 Secretion and Tight Junction Disruption of Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G123–G132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, H.; Sato, N.; Mizuno, N.; Ikawa, Y. The Influence of Cytokines on the Complex Pathology of Ulcerative Colitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejnar, C.E.; Zdobnov, E.M. MiRmap: Comprehensive Prediction of MicroRNA Target Repression Strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Kanellos, I.; Papadimitriou, D.; Kavakiotis, I.; Maniou, S.; Skoufos, G.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v8: A Decade-Long Collection of Experimentally Supported MiRNA–Gene Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. miR-369-3p Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094288
Scalavino V, Piccinno E, Giannelli G, Serino G. miR-369-3p Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094288
Chicago/Turabian StyleScalavino, Viviana, Emanuele Piccinno, Gianluigi Giannelli, and Grazia Serino. 2025. "miR-369-3p Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094288
APA StyleScalavino, V., Piccinno, E., Giannelli, G., & Serino, G. (2025). miR-369-3p Ameliorates Inflammation and Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094288







