Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of CTX-M β-Lactamase Genes and Proteins Confers Ampicillin Resistance in Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. Isolation and Quantification of Vesicles
2.2. DNA Quantification
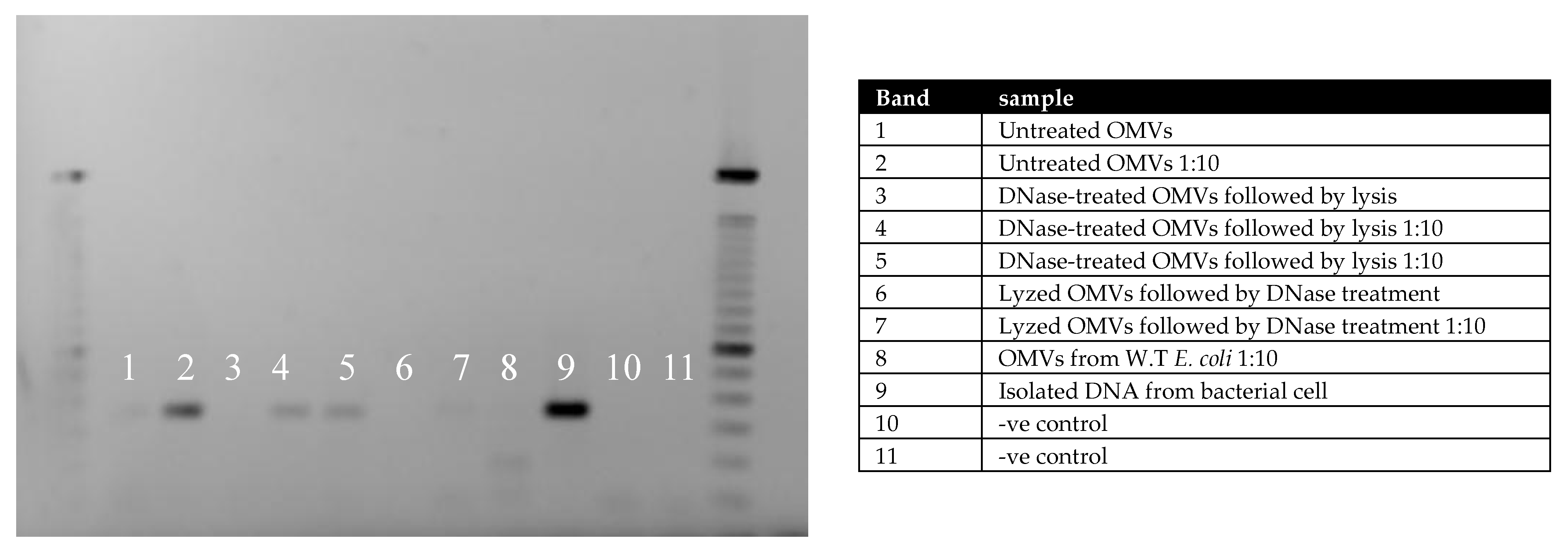
2.3. PCR Analysis
2.4. β-Lactamase Activity
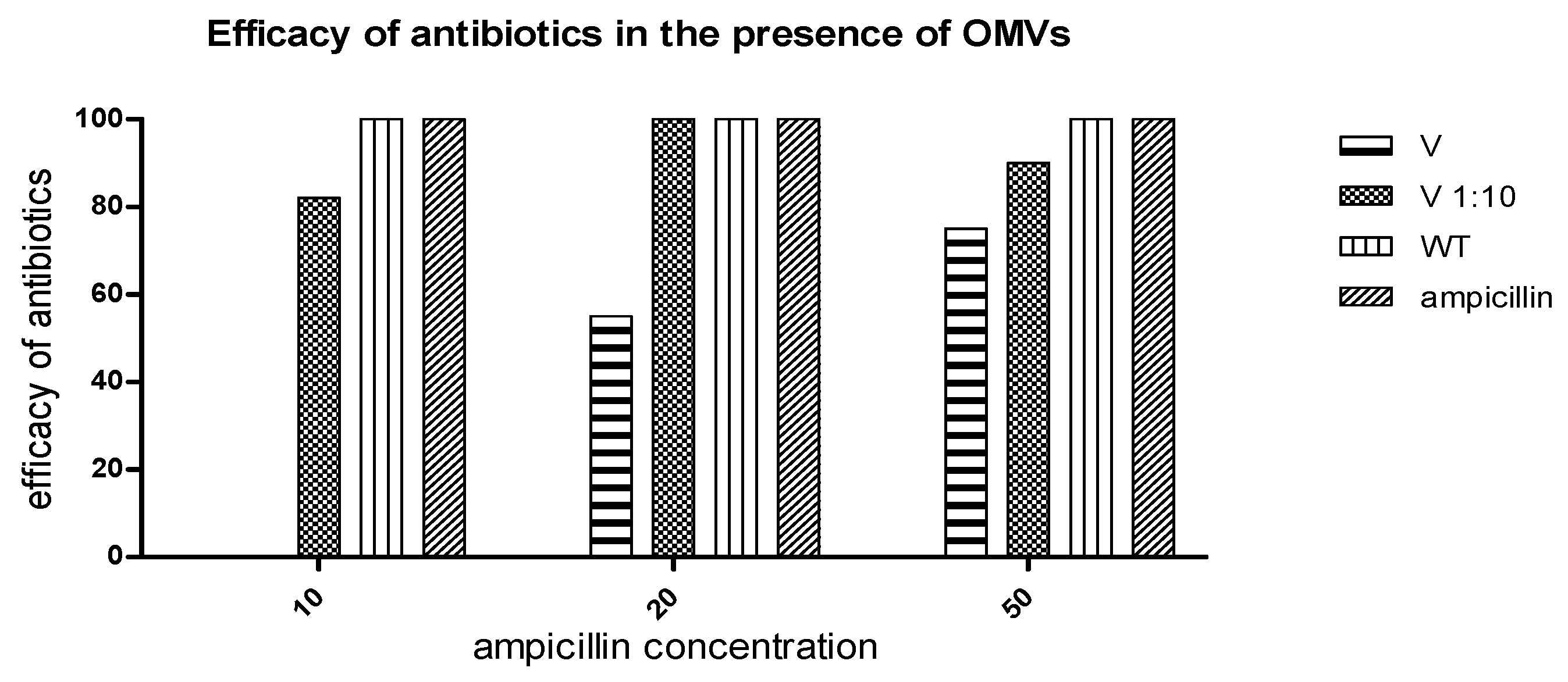
2.5. Measurement of Ampicillin Efficacy in the Presence of OMVs
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Condition
4.2. Isolation and Purification of Vesicles
4.3. Vesicle Quantification and Verification
4.4. DNase Treatment and DNA Quantification
4.5. PCR Analysis for Resistant Genes
4.6. Quantification of OMVs β-Lactamase Activity
4.7. The Effect of OMVs on Antibiotics
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance, C. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchaim, D.; Zaidenstein, R.; Lazarovitch, T.; Karpuch, Y.; Ziv, T.; Weinberger, M. Epidemiology of bacteremia episodes in a single center: Increase in Gram-negative isolates, antibiotics resistance, and patient age. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Fatima, J.; Shakil, S.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Kamal, M.A. Antibiotic resistance and extended spectrum beta-lactamases: Types, epidemiology and treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L.; Bonomo, R.A. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A clinical update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 657–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, R.P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton, P.J.; Lundon, D.J.; McWade, R.; Scanlon, N.; Hannan, M.M.; O’Kelly, F.; Lynch, M. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli urinary isolates and comparison with antibiotic consumption data over 10 years, 2005–2014. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 186, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe: Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net); ECDC: Solna, Sweden, 2010.
- Bajaj, P.; Singh, N.S.; Virdi, J.S. Escherichia coli beta-Lactamases: What Really Matters. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.A.; Kuehn, M.J. Offense and defense: Microbial membrane vesicles play both ways. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renelli, M.; Matias, V.; Lo, R.Y.; Beveridge, T.J. DNA-containing membrane vesicles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and their genetic transformation potential. Microbiology 2004, 150 Pt 7, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameli, N.; Becker, H.E.F.; Welbers, T.; Jonkers, D.; Penders, J.; Savelkoul, P.; Stassen, F.R. Metagenomic Profiling of Fecal-Derived Bacterial Membrane Vesicles in Crohn’s Disease Patients. Cells 2021, 10, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolling, G.L.; Matthews, K.R. Export of virulence genes and Shiga toxin by membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaar, V.; Uddback, I.; Nordstrom, T.; Riesbeck, K. Group A streptococci are protected from amoxicillin-mediated killing by vesicles containing beta-lactamase derived from Haemophilus influenzae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaar, V.; Nordstrom, T.; Morgelin, M.; Riesbeck, K. Moraxella catarrhalis outer membrane vesicles carry beta-lactamase and promote survival of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae by inactivating amoxicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3845–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Alcantud, B.S.; Piersma, S.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Maass, S.; Becher, D.; Azeredo, J.; Bathoorn, E.; van Dijl, J.M. Outer membrane vesicles of carbapenem-resistant clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates protect both the vesicle-producing bacteria and non-resistant bacteria against carbapenems. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 297, 128175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, L.; Ji, Q.; Gao, F.; Yang, S.; Fu, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. NDM-5-carried outer membrane vesicles impair the efficacy of antibiotics against bacterial infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2025, 69, e0180524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M.; Schild, S.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Eberl, L. Composition and functions of bacterial membrane vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Yang, A.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Jian, Z.; Chen, X.; Yan, Q.; Liang, X.; Liu, W. Outer Membrane Vesicles Transmitting bla(NDM-1) Mediate the Emergence of Carbapenem-Resistant Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0144422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qin, J.; Xiang, G.; Chen, T.; Nurxat, N.; Gao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Outer membrane vesicles mediating horizontal transfer of the epidemic bla(OXA-232) carbapenemase gene among Enterobacterales. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2290840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentz, R.; Horn, N.; Cross, K.; Salt, L.; Brearley, C.; Livermore, D.M.; Carding, S.R. Cephalosporinases associated with outer membrane vesicles released by Bacteroides spp. protect gut pathogens and commensals against beta-lactam antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Park, S.B.; Im, S.P.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, J.W.; Gong, T.W.; Lazarte, J.M.S.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Outer membrane vesicles from beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli enable the survival of beta-lactam-susceptible E. coli in the presence of beta-lactam antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5402. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; He, T.; Ji, X.; Wei, R.; Yu, M.; Wang, R. Sub-MIC Antibiotics Modulate Productions of Outer Membrane Vesicles in Tigecycline-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, D.; Maitra, R.; Bormon, R.; Czekanska, M.; Meiers, J.; Titz, A.; Verma, S.; Chopra, S. Tackling the outer membrane: Facilitating compound entry into Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. NPJ Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 1, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Wei, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, F. A critical role of outer membrane vesicles in antibiotic resistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameli, N.; Borman, R.; López-Iglesias, C.; Savelkoul, P.; Stassen, F.R.M. Characterization of Feces-Derived Bacterial Membrane Vesicles and the Impact of Their Origin on the Inflammatory Response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 667987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, C.I.; Ludlam, H.A.; Woodford, N.; Brown, D.F.; Brown, N.M.; Roberts, M.T.; Milner, N.; Curran, M.D. Real-time TaqMan PCR for rapid detection and typing of genes encoding CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56 Pt 1, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kameli, N. Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of CTX-M β-Lactamase Genes and Proteins Confers Ampicillin Resistance in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110601
Kameli N. Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of CTX-M β-Lactamase Genes and Proteins Confers Ampicillin Resistance in Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110601
Chicago/Turabian StyleKameli, Nader. 2025. "Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of CTX-M β-Lactamase Genes and Proteins Confers Ampicillin Resistance in Escherichia coli" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110601
APA StyleKameli, N. (2025). Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of CTX-M β-Lactamase Genes and Proteins Confers Ampicillin Resistance in Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110601





