Evaluation of the Effect of Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Prolactin Secretion Using the Clonidine Test in the Diagnosis of Children with Short Stature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
- -
- ISS group—children with normal GH secretion (GHmax values ≥ 10 ng/mL in at least one test); n = 29 children
- -
- GHD group—children with decreased GH secretion (GHmax values < 10 ng/mL in both tests); n = 20 children.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dehkhoda, F.; Lee, C.M.M.; Medina, J.; Brooks, A.J. The Growth Hormone Receptor: Mechanism of Receptor Activation, Cell Signaling, and Physiological Aspects. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bole-Feysot, C.; Goffin, V.; Edery, M.; Binart, N.; Kelly, P.A. Prolactin (PRL) and Its Receptor: Actions, Signal Transduction Pathways and Phenotypes Observed in PRL Receptor Knockout Mice. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 225–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.E.; Kanyicska, B.; Lerant, A.; Nagy, G. Prolactin: Structure, Function, and Regulation of Secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1523–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Dobolyi, Á. Prolactin in Sleep and EEG Regulation: New Mechanisms and Sleep-Related Brain Targets Complement Classical Data. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2025, 169, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arey, B.J.; Freeman, M.E. Oxytocin, Vasoactive-Intestinal Peptide, and Serotonin Regulate the Mating-Induced Surges of Prolactin Secretion in the Rat. Endocrinology 1990, 126, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo-Castro, M.; Marazuela, M.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Biagetti, B. Prolactin and Growth Hormone Signaling and Interlink Focused on the Mammosomatotroph Paradigm: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilton, B.S.; Hewetson, A. Prolactin and Growth Hormone Signaling. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2005, 68, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ad, I.; Topper, E.; Laron, Z. Oral Clonidine as a Growth Hormone Stimulation Test. Lancet 1979, 2, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginalska-Malinowska, M.; Malinowska, A. Arginine, clonidine and L-Dopa test for growth hormone secretion – an assessment and interpretation of the results. Endokrynol. Ped. 2009, 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Thorner, M.O.; Hartman, M.L.; Vance, M.L.; Pezzoli, S.S.; Ampleford, E.J. Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth Hormone Secretion. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1995, 19, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara-Moszyńska, M.; Kedzia, A.; Korman, E.; Niedziela, M. Usefulness of Growth Hormone (GH) Stimulation Tests and IGF-I Concentration Measurement in GH Deficiency Diagnosis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 21, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tissier, P.R.; Grattan, D.R. Physiology Is All about Interactions: The Prolactin and Growth Hormone Systems as Exemplars. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2024, 36, e13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Nishiyama, M.; Corcoran, D.; Araki, T. Biological Roles of Growth Hormone/Prolactin from an Evolutionary Perspective. Endocr. J. 2024, 71, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorczak, A.; Lewiński, A.; Stawerska, R. Involvement of Sirtuin 1 in the Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Signal Transduction and Its Impact on Growth Processes in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorczak, A.; Kowalik, D.; Kopciuch, J.; Głowacka, E.; Mikołajczyk, K.; Tkaczyk, M.; Lewiński, A.; Stawerska, R. Relationship between Serum Sirtuin 1 and Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Concentrations in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D.A.; Frawley, L.S.; Neill, J.D. Neuroendocrine Control of Prolactin Secretion. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1983, 45, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, D.R. 60 YEARS OF NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY: The Hypothalamo-Prolactin Axis. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, T101–T122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjalbert, A.; Bertrand, P.; Le Dafniet, M.; Epelbaum, J.; Hugues, J.N.; Kordon, C.; Moyse, E.; Peillon, F.; Shu, C. Somatostatin and Regulation of Prolactin Secretion. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1986, 11, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stawerska, R.; Smyczyńska, J.; Hilczer, M.; Lewiński, A. Changes in Circadian Rhythm of Prolactin in Short Children Are Dependent on Growth Hormone Secretion. Ann. Agric. Environ.Med. 2014, 21, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stawerska, R.; Lewiński, A.; Smyczyńska, J.; Hilczer, M.; Kowalska, E.; Kaniewska, D.; Karasek, M. Circadian Pattern of Prolactin Secretion in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency and Congenital Organic Lesions in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Region. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2007, 28, 765–774. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Daliot, J.; Laron-Kenet, T.; Wattad, M.; Ben-Dor, A.; Lilos, P.; Laron, Z. The Relationship between Serum Levels of Prolactin and Growth Hormone in the Early Postnatal Period. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laron, Z.; Efros, O. Serum Prolactin in Untreated and IGF-I Treated Patients with Laron Syndrome. In Laron Syndrome—From Man to Mouse: Lessons from Clinical and Experimental Experience; Laron, Z., Kopchick, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 247–254. ISBN 978-3-642-11183-9. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Völkl, T.M.K.; Haas, S.; Dörr, H.G. Spontaneous Prolactin Secretion in Growth Hormone-Deficient Children. Horm. Metab. Res. 2005, 37, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, A.; Barazani, C.; Laron, Z. Prolactin Response to Growth Hormone Stimulation Tests. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2022, 65, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devesa, J.; Arce, V.; Lois, N.; Tresguerres, J.A.; Lima, L. Alpha 2-Adrenergic Agonism Enhances the Growth Hormone (GH) Response to GH-Releasing Hormone through an Inhibition of Hypothalamic Somatostatin Release in Normal Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.D.; Chapin, L.T.; Radcliff, R.P.; Lookingland, K.J.; Tucker, H.A. Somatostatin Inhibits Alpha-2-Adrenergic-Induced Secretion of Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone. Neuroendocrinology 2001, 73, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnati, L.F.; Benfenati, F.; Cortelli, P.; D’alessandro, R.; Ghisoli, E.; Zampa, G.A. A Study on the Effects of Interaction between Naloxone and 2-Br-Alpha-Ergocryptine or Clonidine on Luteinizing Hormone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, Prolactin and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels in Normal Man Serum. Neurosci. Lett. 1979, 12, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, E.L.; Morrison, A.; Kassarich, J.; Sullivan, D. Alpha-2-Adrenergic Control of Prolactin Release. Neuroendocrinology 2008, 44, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasinski, F.; Chaves, F.M.; Pedroso, J.A.B.; Mansano, N.S.; Camporez, J.P.; Gusmão, D.O.; List, E.O.; Kopchick, J.J.; Frazão, R.; Szawka, R.E.; et al. Growth Hormone Receptor in Dopaminergic Neurons Regulates Stress-Induced Prolactin Release in Male Mice. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palczewska, I.; Niedzwiedzka, Z. Somatic development indices in children and youth of Warsaw. Med. Wieku Rozwoj. 2001, 5, 18–118. [Google Scholar]
- Majewska, K.A.; Tchorzewska-Skrobich, M.; Wais, P.; Majewski, D.; Naskręcka, M.; Kędzia, A. Deficient or Normal Growth Hormone Secretion in Polish Children with Short Stature: Searching for Clinical Differences. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | GHD, n = 20 | ISS, n = 29 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronological age (years) | 10.78 ± 2.79 | 9.39 ± 3.60 | 0.173 |
| HSDS | −2.26 ± 0.95 | −2.46 ± 1.12 | 0.579 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 16.82 ± 2.70 | 16.45 ± 3.62 | 0.732 |
| TSH (mIU/mL) | 2.51 ± 1.51 | 2.51 ± 1.01 | 0.999 |
| FT4 (ng/mL) | 1.37 ± 0.18 | 1.21 ± 0.20 | 0.009 * |
| FT3 (ng/mL) | 4.09 ± 0.65 | 4.09 ± 0.50 | 0.980 |
| IGF-1 (pg/mL) | 104.13 ± 49.18 | 158.49 ± 103.67 | 0.050 |
| IGF-1 SDS | −2.42 ± 1.27 | −1.01 ± 0.70 | 0.001 * |
| IGFBP-3 (ng/mL) | 3.87 ± 1.38 | 4.52 ± 1.50 | 0.161 |
| IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.08 | 0.066 |
| Bone age (years) | 8.89 ± 3.18 | 8.16 ± 4.02 | 0.531 |
| GH-0′ (ng/mL) | 0.94 ± 1.52 | 1.50 ± 2.25 | 0.358 |
| GH-30′ (ng/mL) | 1.35 ± 1.86 | 3.03 ± 3.17 | 0.050 |
| GH-60′ (ng/mL) | 4.77 ± 3.29 | 12.22 ± 6.02 | 0.001 * |
| GH-90′ (ng/mL) | 4.58 ± 2.06 | 10.90 ± 4.32 | 0.001 * |
| GH-120′ (ng/mL) | 2.67 ± 1.70 | 6.30 ± 3.21 | 0.001 * |
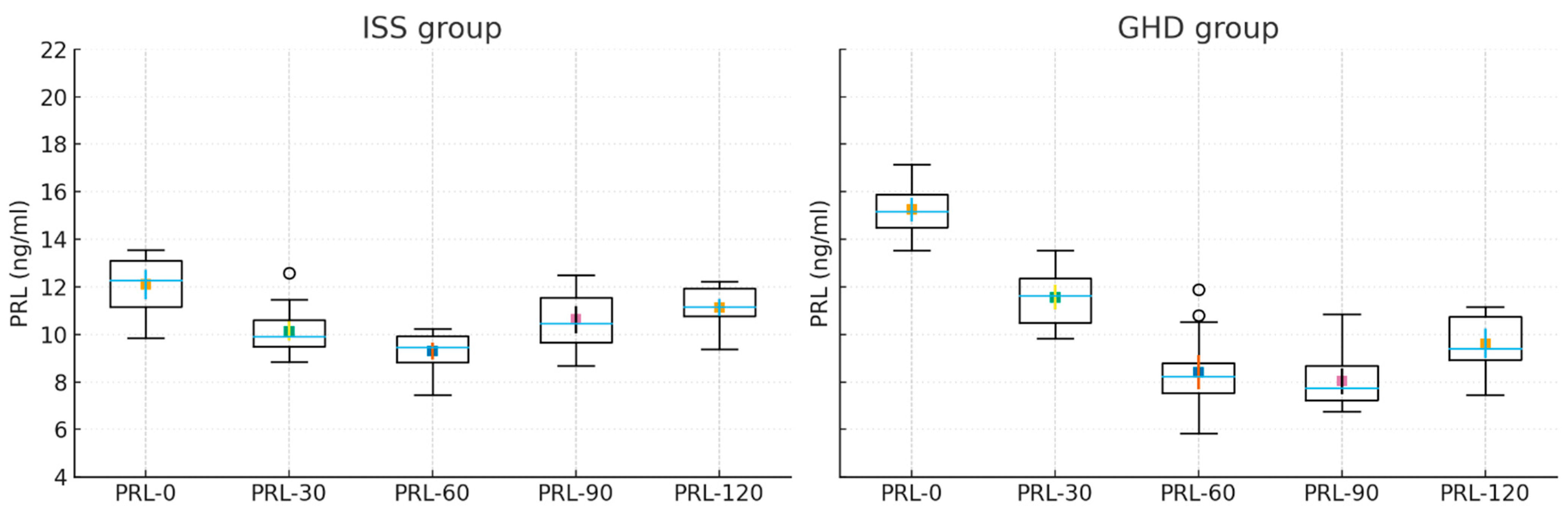
| PRL-0′ (ng/mL) | 15.81 ± 10.73 | 13.34 ± 5.29 | 0.310 |
| PRL-30′ (ng/mL) | 10.63 ± 6.26 | 9.85 ± 4.16 | 0.618 |
| PRL-60′ (ng/mL) | 7.90 ± 3.20 | 8.88 ± 3.62 | 0.359 |
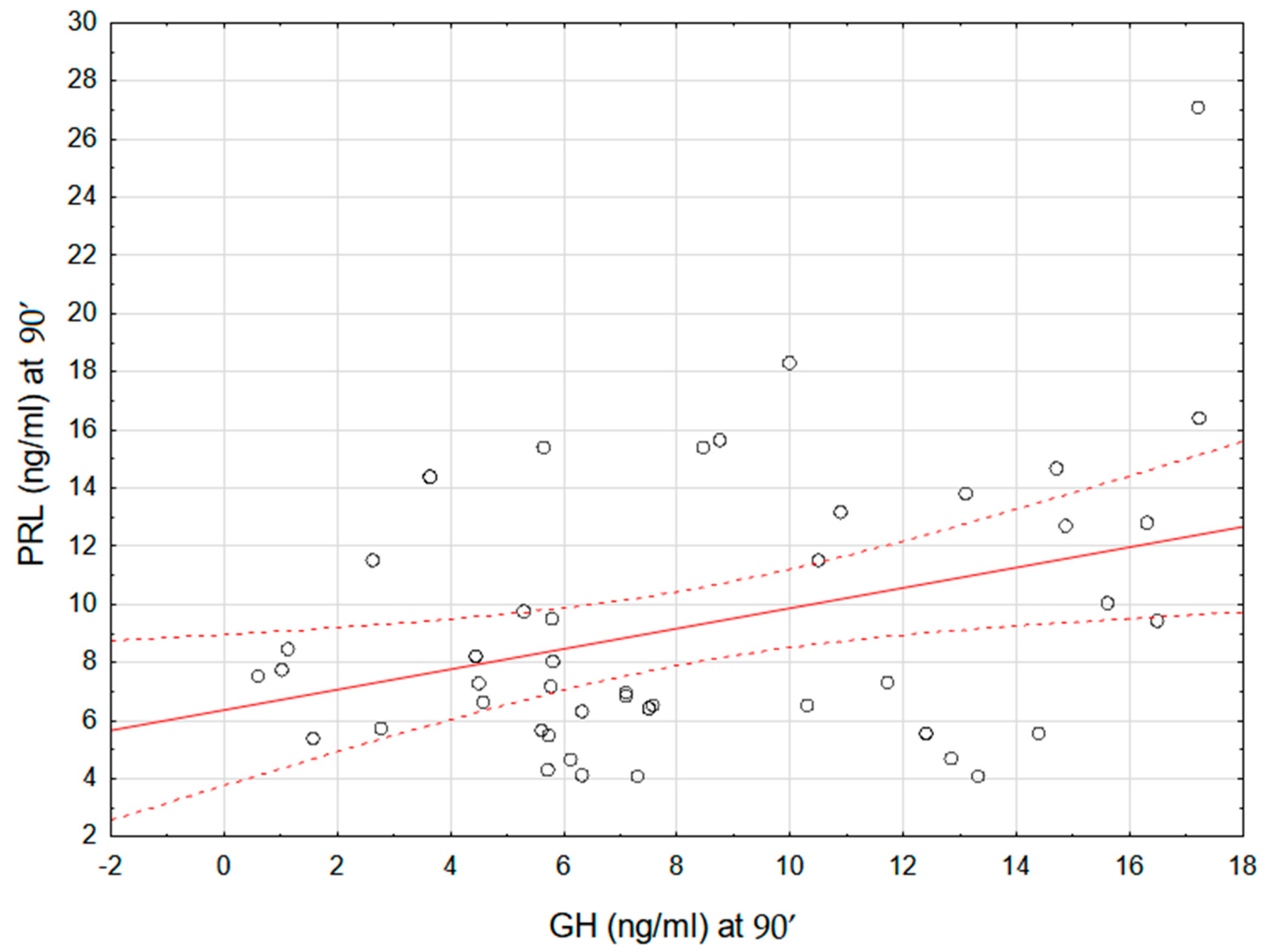
| PRL-90′ (ng/mL) | 7.68 ± 3.25 | 10.39 ± 5.31 | 0.059 |
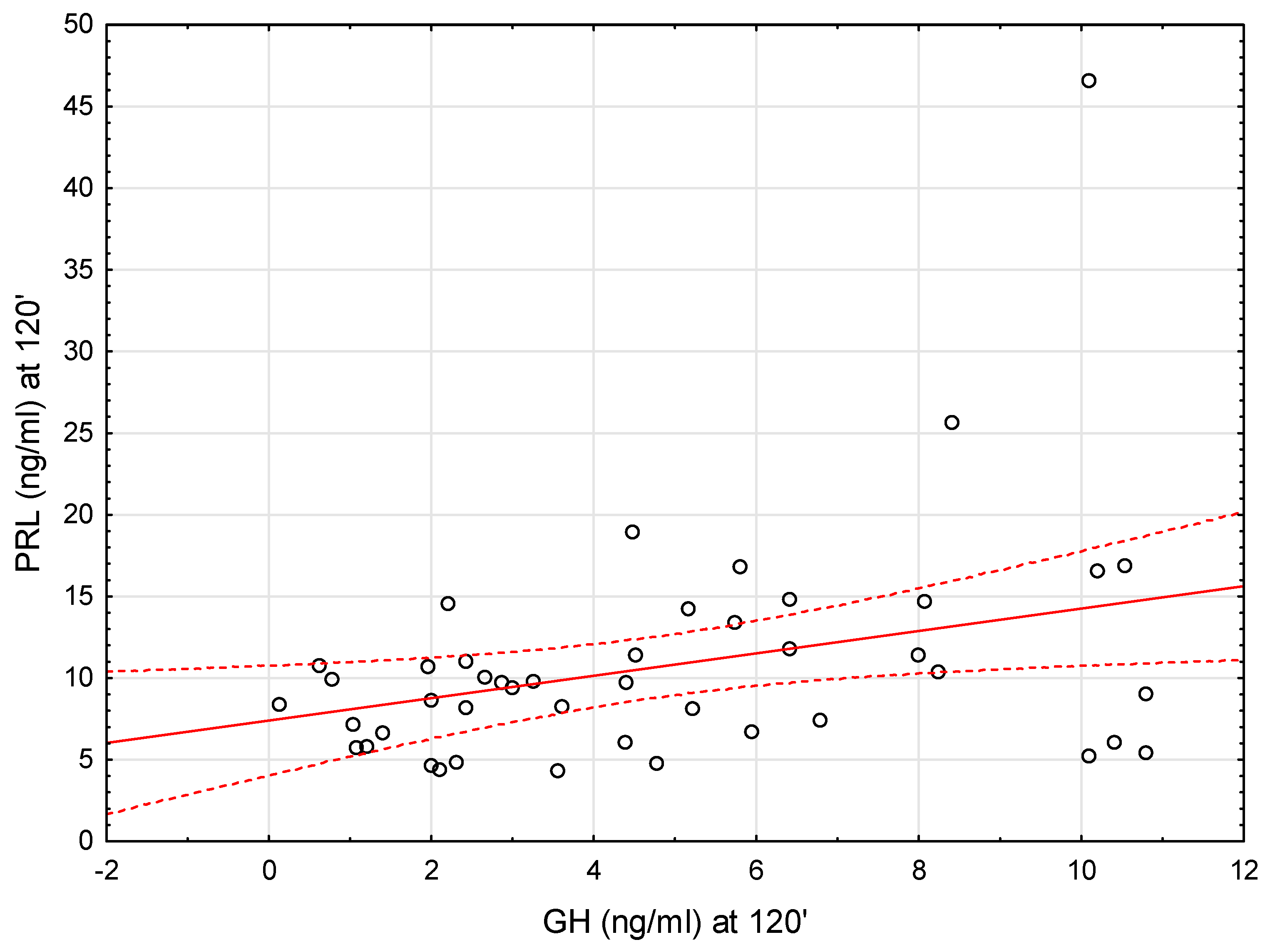
| PRL-120’ (ng/mL) | 8.44 ± 3.45 | 12.34 ± 8.37 | 0.069 |
| GHD, p-Value | ISS, p-Value | Total Group, p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRL-0 & PRL-30 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| PRL-0 & PRL-60 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * |
| PRL-0 & PRL-90 | 0.005 * | 0.019 * | 0.001 * |
| PRL-0 & PRL-120 | 0.022 * | 0.151 | 0.011 * |
| PRL-30 & PRL-60 | 0.006 * | 0.058 | 0.001 * |
| PRL-30 & PRL-90 | 0.043 * | 0.904 | 0.221 |
| PRL-30 & PRL-120 | 0.396 | 0.113 | 0.463 |
| PRL-60 & PRL-90 | 0.896 | 0.012 * | 0.041 * |
| PRL-60 & PRL-120 | 0.199 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| PRL-90 & PRL-120 | 0.084 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pakuła, A.; Fedorczak, A.; Kolasa-Kicińska, M.; Łupińska, A.; Hilczer, M.; Zygmunt, A.; Stawerska, R. Evaluation of the Effect of Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Prolactin Secretion Using the Clonidine Test in the Diagnosis of Children with Short Stature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209939
Pakuła A, Fedorczak A, Kolasa-Kicińska M, Łupińska A, Hilczer M, Zygmunt A, Stawerska R. Evaluation of the Effect of Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Prolactin Secretion Using the Clonidine Test in the Diagnosis of Children with Short Stature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209939
Chicago/Turabian StylePakuła, Angelika, Anna Fedorczak, Marzena Kolasa-Kicińska, Anna Łupińska, Maciej Hilczer, Arkadiusz Zygmunt, and Renata Stawerska. 2025. "Evaluation of the Effect of Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Prolactin Secretion Using the Clonidine Test in the Diagnosis of Children with Short Stature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209939
APA StylePakuła, A., Fedorczak, A., Kolasa-Kicińska, M., Łupińska, A., Hilczer, M., Zygmunt, A., & Stawerska, R. (2025). Evaluation of the Effect of Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation on Prolactin Secretion Using the Clonidine Test in the Diagnosis of Children with Short Stature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209939





