The Esc(1-21)-1c Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits a Specific Transcriptional Activator of the MexAB–OprM Efflux Pump in P. aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mechanism of Action of Esc(1-21)-1c
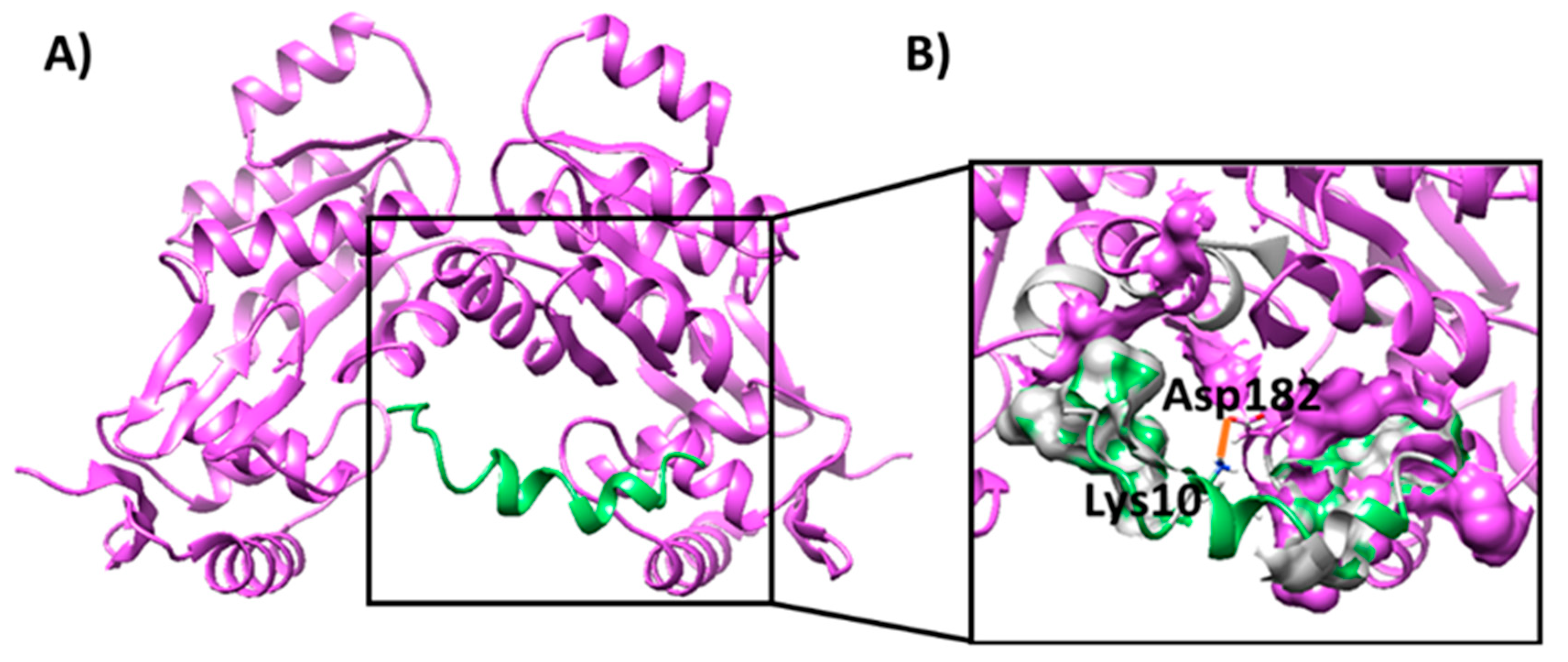
2.2. Molecular Docking Analysis
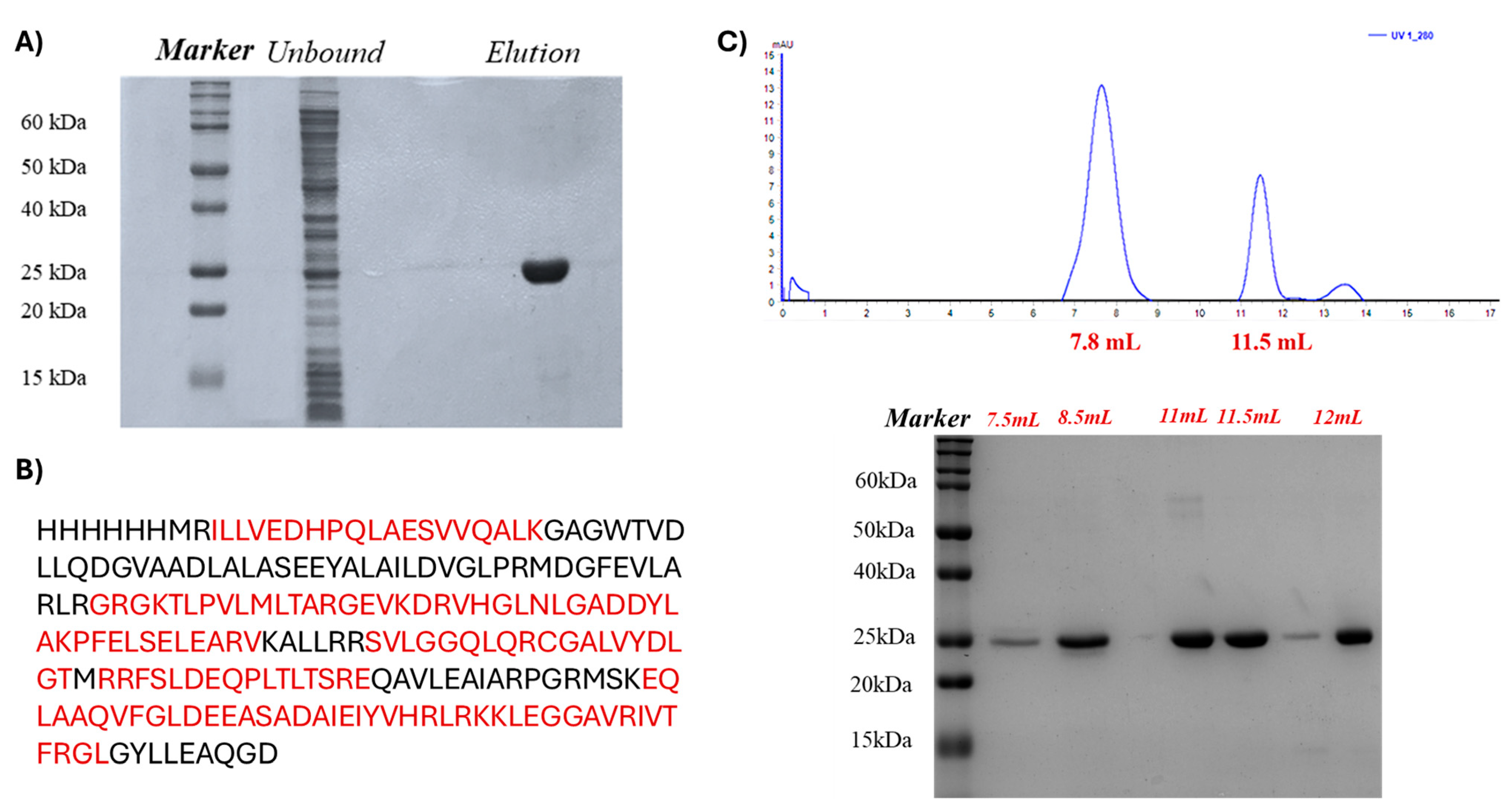
2.3. Recombinant Production and Purification of Q9I5H3 in E. coli
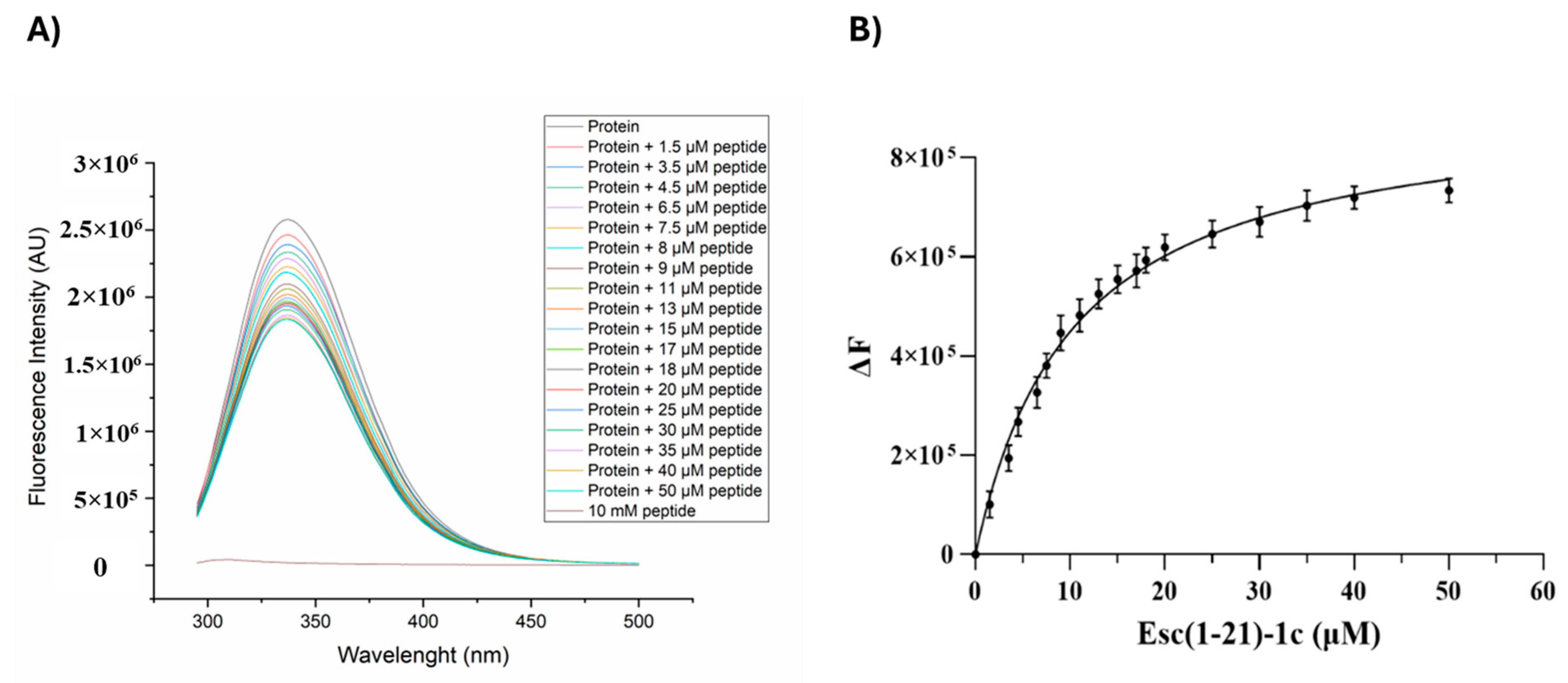
2.4. Fluorescence Binding Experiments Between Esc(1-21)-1c and Q9I5H3
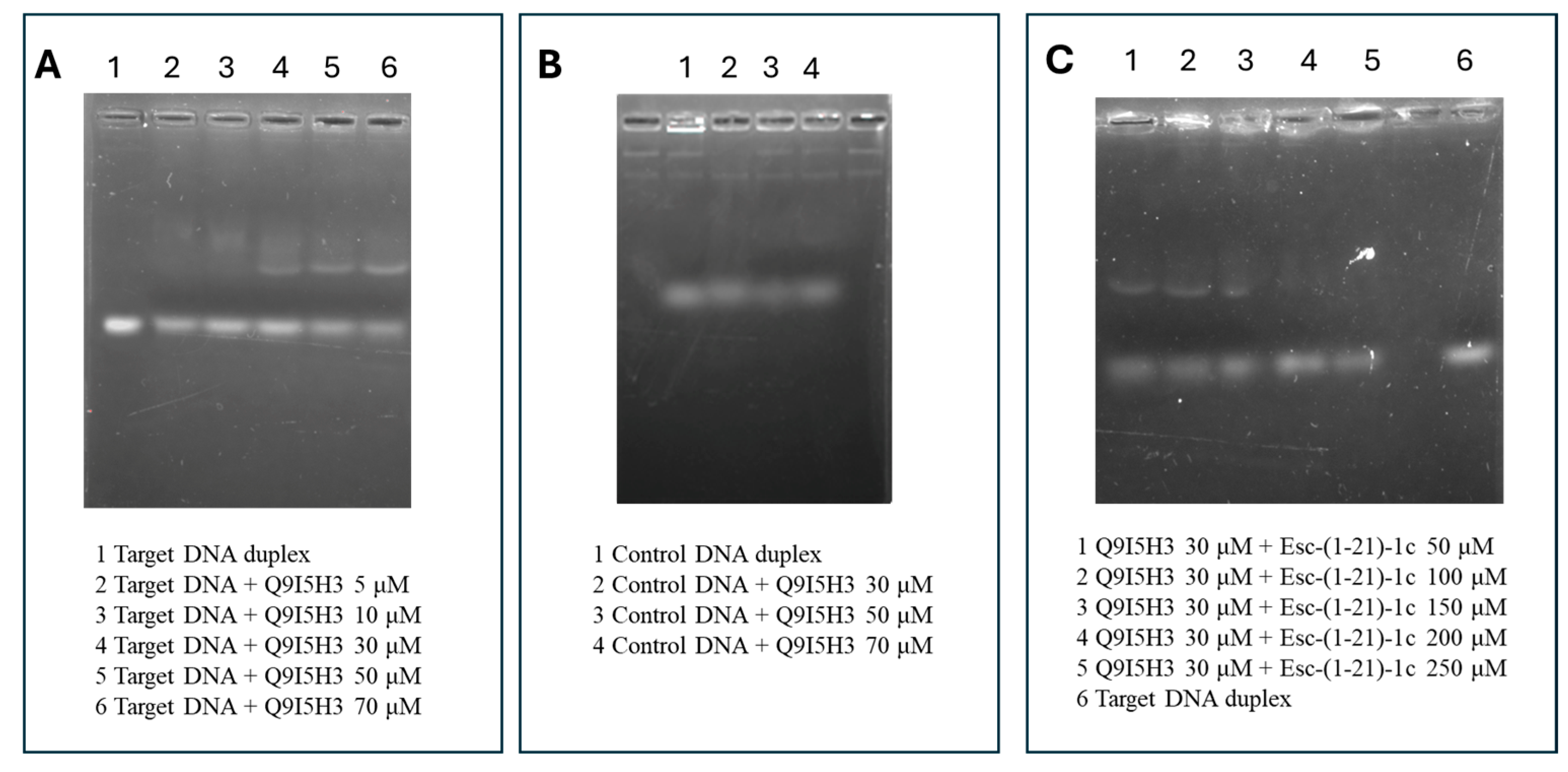
2.5. EMSA-Based Binding Experiments Between Q9I5H3 and Duplex DNA
3. Discussion
3.1. Mechanistic Interpretation: Role of Two-Component Systems in Bacterial Regulation
3.2. Q9I5H3 as a Novel Transcriptional Regulator of MexAB–OprM
3.3. Therapeutic Implications of Targeting Q9I5H3
3.4. Summary of Findings
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis
4.2. Bacterial Growths
4.3. Functional Proteomics Experiment
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. Recombinant Production and Purification of Protein Q9I5H3
4.6. Binding Experiment by Fluorescence Spectroscopy
4.7. Protein–DNA Interaction by Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinemerem Nwobodo, D.; Ugwu, M.C.; Oliseloke Anie, C.; Al-Ouqaili, M.T.; Chinedu Ikem, J.; Victor Chigozie, U.; Saki, M. Antibiotic resistance: The challenges and some emerging strategies for tackling a global menace. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria—A review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüssow, H. The antibiotic resistance crisis and the development of new antibiotics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R. The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2022, 399, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, V.; Stringaro, A.; Colone, M.; Pini, A.; Mangoni, M.L. Esculentin (1-21), an amphibian skin membrane-active peptide with potent activity on both planktonic and biofilm cells of the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2773–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, E.; Fernández-Muñoz, A.; Zamorano, L.; Oliver, A.; Horcajada, J.P.; Juan, C.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S. Impact of multidrug resistance on the virulence and fitness of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A microbiological and clinical perspective. Infection 2024, 52, 1235–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of efflux pumps on antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, M.; Rajeev, A.; Chattopadhyay, I. Application of antimicrobial peptides as next-generation therapeutics in the biomedical world. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2022, 40, 2458–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Qin, Z.; Xu, L.; He, N.; Tan, Y.; Dessie, W. Advancements, challenges and future perspectives on peptide-based drugs: Focus on antimicrobial peptides. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 181, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagandeep, K.R.; Narasingappa, R.B.; Vyas, G.V. Unveiling mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide: Actions beyond the membranes disruption. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canè, C.; Tammaro, L.; Duilio, A.; Di Somma, A. Investigation of the Mechanism of Action of AMPs from Amphibians to Identify Bacterial Protein Targets for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Grazia, A.; Cappiello, F.; Cohen, H.; Casciaro, B.; Luca, V.; Pini, A.; Di, Y.P.; Shai, Y.; Mangoni, M.L. D-Amino acids incorporation in the frog skin-derived peptide esculentin-1a (1-21) NH 2 is beneficial for its multiple functions. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2505–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, B.; Lin, Q.; Afonin, S.; Loffredo, M.R.; de Turris, V.; Middel, V.; Ulrich, A.S.; Di, Y.P.; Mangoni, M.L. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and expression of virulence genes by selective epimerization in the peptide Esculentin-1a (1-21) NH 2. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3874–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, B.; Loffredo, M.R.; Luca, V.; Verrusio, W.; Cacciafesta, M.; Mangoni, M.L. Esculentin-1a derived antipseudomonal peptides: Limited induction of resistance and synergy with aztreonam. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canè, C.; Casciaro, B.; Di Somma, A.; Loffredo, M.R.; Puglisi, E.; Battaglia, G.; Mellini, M.; Cappiello, F.; Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide Esc(1-21)-1c increases susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to conventional antibiotics by decreasing the expression of the MexAB-OprM efflux pump. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1271153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, D.; Han, X.; Du, W.; Kou, Z.; Jiang, F. Trp-containing antibacterial peptides impair quorum sensing and biofilm development in multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and exhibit synergistic effects with antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 611009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrophanov, A.Y.; Groisman, E.A. Signal integration in bacterial two-component regulatory systems. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; El-Garawany, Y.; Anagreyyah, S.; Alnafea, Y.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Alwarhi, W.; Rawway, M.; Draz, A. The development of technology to prevent, diagnose, and manage antimicrobial resistance in healthcare-associated infections. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auda, I.G.; Salman, I.M.A.; Odah, J.G. Efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria in brief. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, J.J.; Metallo, S.J.; Schneider, T.L.; Schepartz, A. DNA specificity enhanced by sequential binding of protein monomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11735–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.X.; Yi, X.X.; Cho, A.; O’Gara, F.; Wang, Y.P. CpxR activates MexAB-OprM efflux pump expression and enhances antibiotic resistance in both laboratory and clinical nalB-type isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Gerstein, M. Binding geometry of α-helices that recognize DNA. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1995, 23, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagirath, A.Y.; Li, Y.; Patidar, R.; Yerex, K.; Ma, X.; Kumar, A.; Duan, K. Two Component Regulatory Systems and Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Arya, R.; Kim, K.K. Roles of Two-Component Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecki, P.; Jensen, V.; Schulze, W.; Gödeke, J.; Strehmel, J.; Eckweiler, D.; Nicolai, T.; Bielecka, A.; Wille, T.; Gerlach, R.G.; et al. Cross Talk between the Response Regulators PhoB and TctD Allows for the Integration of Diverse Environmental Signals in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6413–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, C.M.; Wu, T.; Stock, A.M. Comprehensive Analysis of OmpR Phosphorylation, Dimerization, and DNA Binding Supports a Canonical Model for Activation. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xue, M.; Yu, L.; Qi, K.; Ni, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, R.; Shang, F.; Xue, T. QseBC Is Involved in the Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia Coli Isolated from Bovine Mastitis. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K.; Tetro, K.; Zhao, Q.; Neshat, S.; Heinrichs, D.E.; Bianco, N. Expression of the Multidrug Resistance Operon MexA-MexB-OprM in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: MexR Encodes a Regulator of Operon Expression. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Srikumar, R.; Poole, K. MexAB-OprM Hyperexpression in NalC-Type Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification and Characterization of the NalC Gene Encoding a Repressor of PA3720-PA3719. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Cao, L.; Gould, V.C.; Avison, M.B.; Poole, K. NalD Encodes a Second Repressor of the MexAB-OprM Multidrug Efflux Operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8649–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafti, F.A.; Eslami, G.; Zandi, H.; Barzegar, K. Mutations in Nalc Gene of Mex AB-OprM Efflux Pump in Carbapenem Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Burn Wounds in Yazd, Iran. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2020, 12, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Bertoni, D.; Magana, P.; Paramval, U.; Pidruchna, I.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Tsenkov, M.; Nair, S.; Mirdita, M.; Yeo, J.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database in 2024: Providing structure coverage for over 214 million protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D368–D375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Bera, S.; Shai, Y.; Mangoni, M.L.; Bhunia, A. NMR structure and binding of esculentin-1a (1–21) NH2 and its diastereomer to lipopolysaccharide: Correlation with biological functions. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-García, B.; Pons, C.; Fernández-Recio, J. pyDockWEB: A web server for rigid-body protein–protein docking using electrostatics and desolvation scoring. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1698–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lumbreras, L.A.; Jiménez-García, B.; Giménez-Santamarina, S.; Fernández-Recio, J. pyDockDNA: A new web server for energy-based protein-DNA docking and scoring. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 988996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, G.E. The Dominance of Symmetry in the Evolution of Homo-oligomeric Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein–protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, J.; Platella, C.; Iachettini, S.; Zizza, P.; Musumeci, D.; Cosconati, S.; Pagano, A.; Novellino, E.; Biroccio, A.; Randazzo, A.; et al. Tailoring a lead-like compound targeting multiple G-quadruplex structures. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
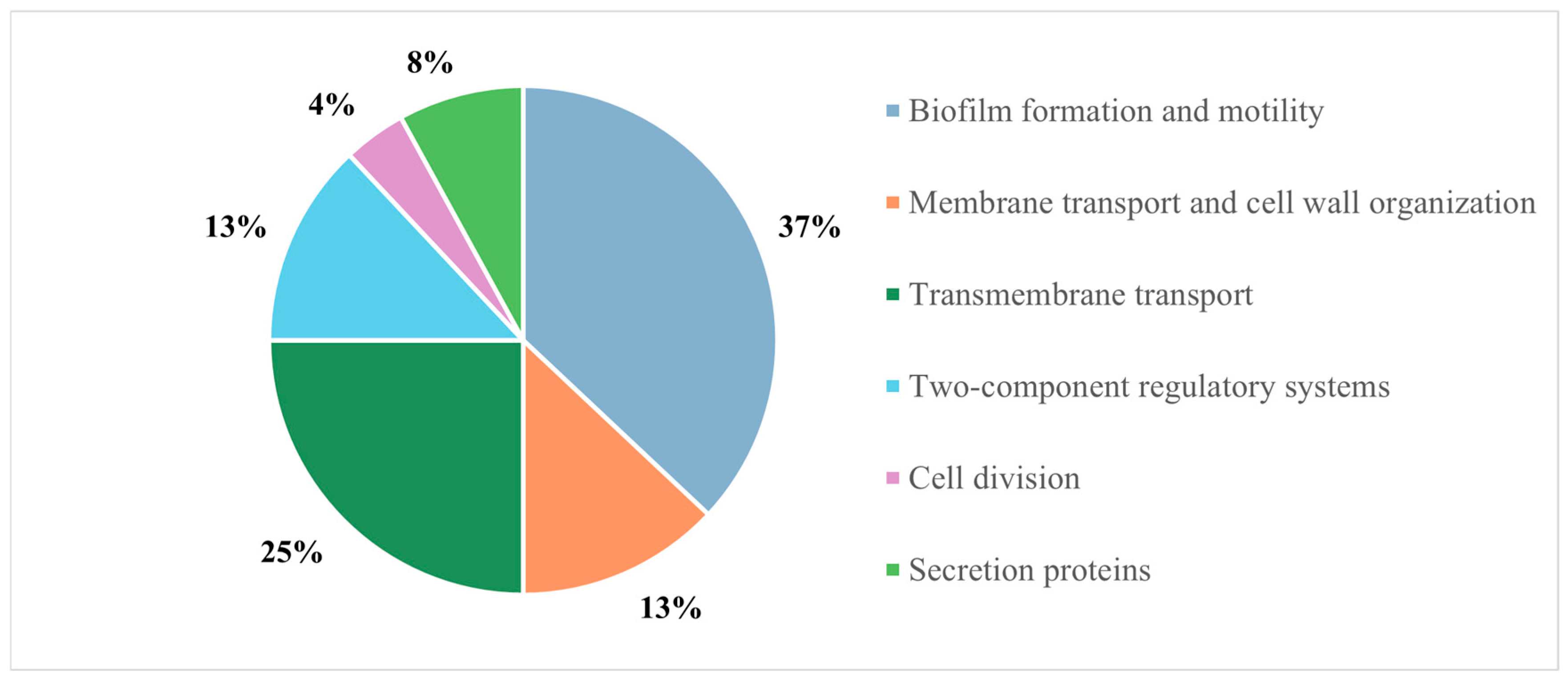

| UniProt Code | Protein Name | Gene | Peptides | Biological Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9I2U3 | Two-component response regulator ParR | parR | 3(1) | Two-component regulatory system |
| Q9HU59 | DNA-binding transcriptional regulator NtrC | ntrC | 3(1) | Regulation of biofilm formation |
| Q9HV31 | Sensor protein kinase PmrB | pmrB | 4(1) | Two-component regulatory system |
| G3XCT6 | Chemotaxis protein CheA | PA1458 | 1(1) | Chemotaxis |
| Q9HX42 | histidine kinase | ladS | 3(1) | Biofilm process |
| Q9HYE4 | histidine kinase | PA3462 | 2(1) | Sensor kinase activity |
| Q9I5H3 | Probable two-component response regulator | PA0756 | 5(2) | Two-component regulatory system |
| Q9HWI4 | Histidine kinase | bfiS | 4(1) | Biofilm formation |
| P24908 | Putative transcriptional regulator | PA0034 | 7(1) | Two-component regulatory system |
| Q9I6K5 | EAL domain-containing protein | PA0285 | 4(1) | Regulation of DNA-templated transcription |
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Fixed Modifications | Carbamidomethyl (C) |
| Variable Modifications | Oxidation (M) Gln-> pyro-Glu (N-Term Q) |
| Enzyme | Trypsin |
| Max Missed Cleavages | 3 |
| Minimum Number of Peptides | 5 |
| False Discovery Rate (FDR) | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canè, C.; Casciaro, B.; Vetrano, C.; Tammaro, L.; Platella, C.; Musumeci, D.; Mangoni, M.L.; Duilio, A.; Di Somma, A. The Esc(1-21)-1c Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits a Specific Transcriptional Activator of the MexAB–OprM Efflux Pump in P. aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209940
Canè C, Casciaro B, Vetrano C, Tammaro L, Platella C, Musumeci D, Mangoni ML, Duilio A, Di Somma A. The Esc(1-21)-1c Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits a Specific Transcriptional Activator of the MexAB–OprM Efflux Pump in P. aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209940
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanè, Carolina, Bruno Casciaro, Carlo Vetrano, Lidia Tammaro, Chiara Platella, Domenica Musumeci, Maria Luisa Mangoni, Angela Duilio, and Angela Di Somma. 2025. "The Esc(1-21)-1c Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits a Specific Transcriptional Activator of the MexAB–OprM Efflux Pump in P. aeruginosa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209940
APA StyleCanè, C., Casciaro, B., Vetrano, C., Tammaro, L., Platella, C., Musumeci, D., Mangoni, M. L., Duilio, A., & Di Somma, A. (2025). The Esc(1-21)-1c Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits a Specific Transcriptional Activator of the MexAB–OprM Efflux Pump in P. aeruginosa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209940












