The Importance of Molecular Size, Concentration, and Thermal Conditions in Enhancing Lignin Derivatives’ Interactions with Skin-like Membranes: Implications for Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
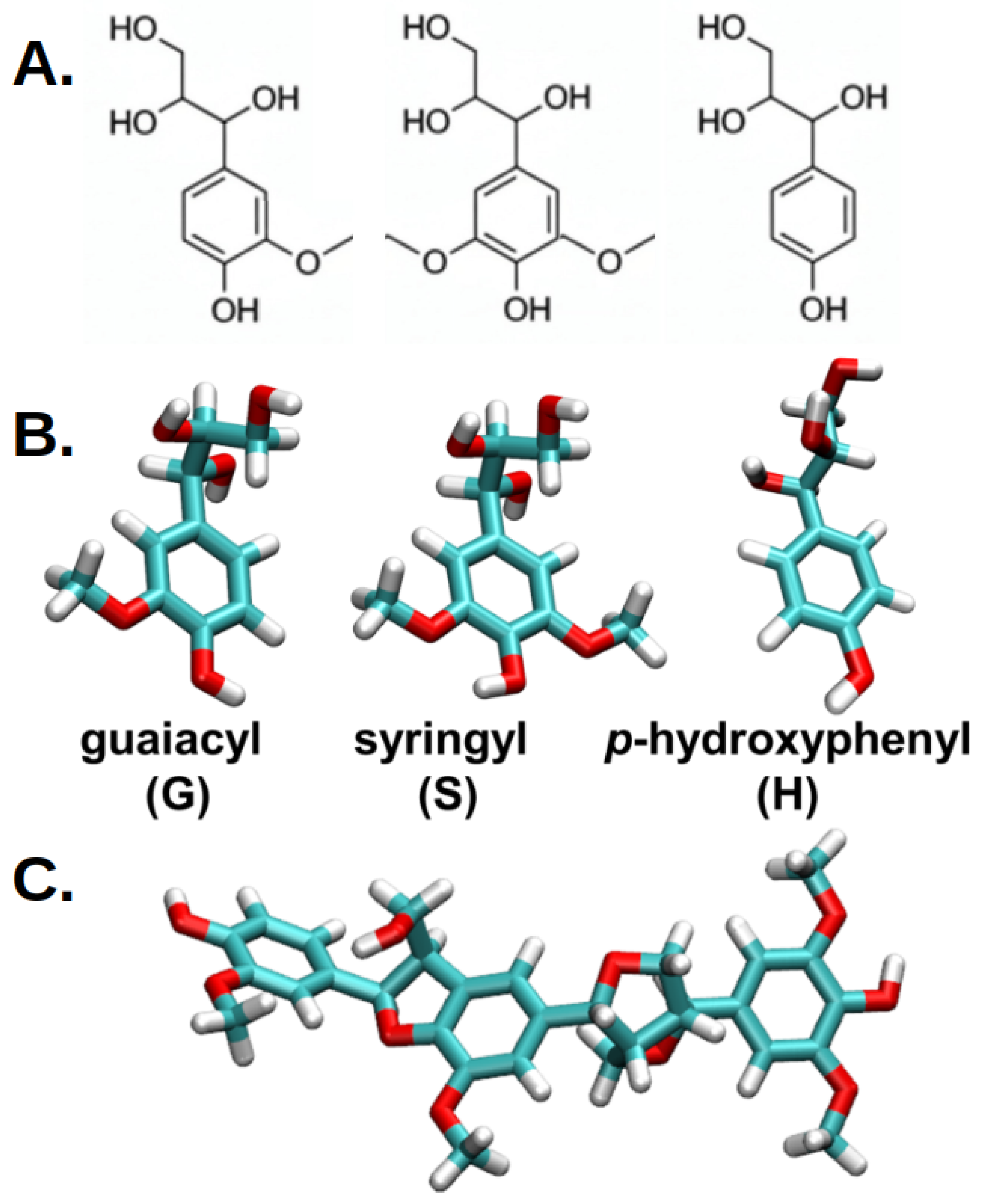
1. Introduction
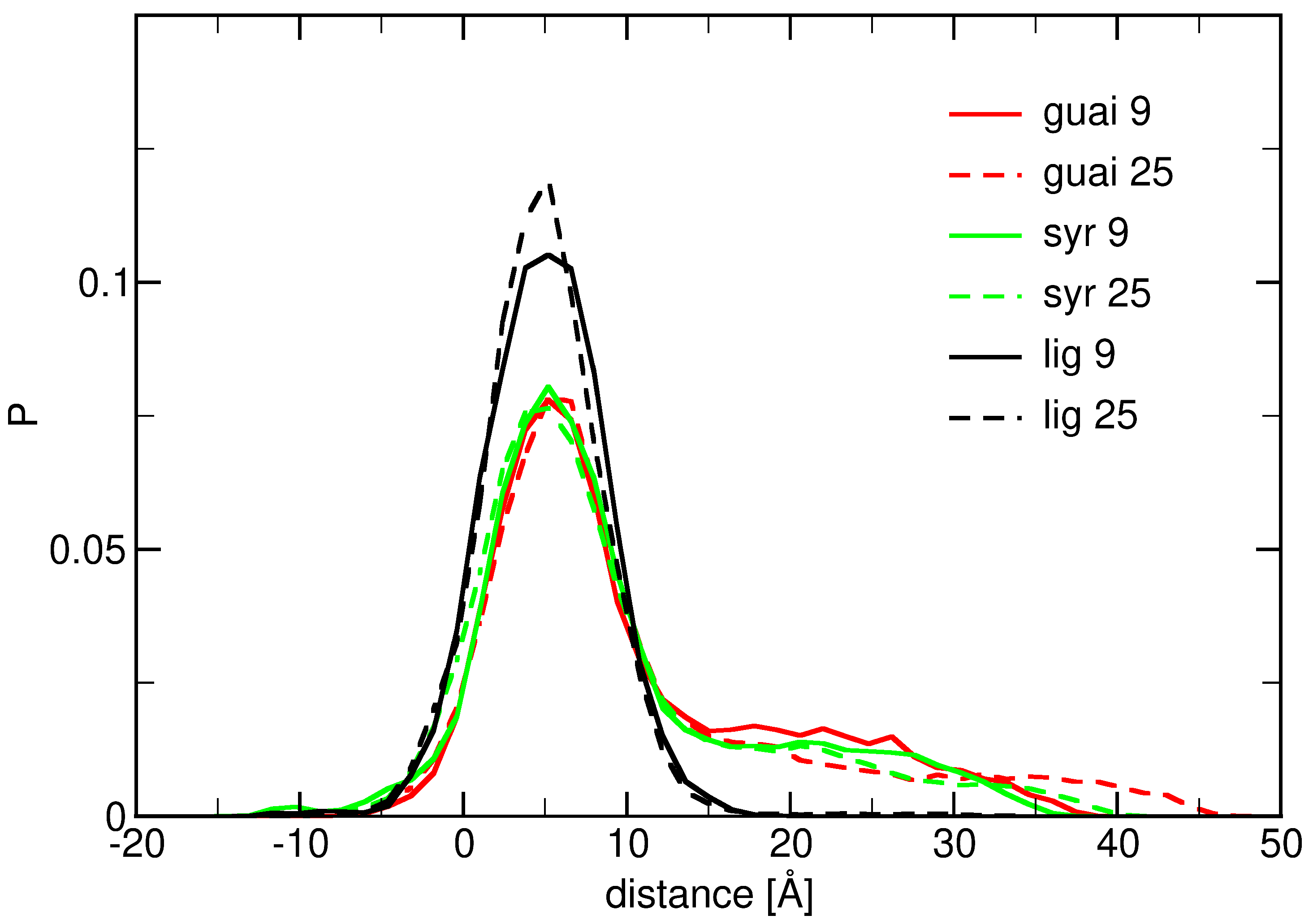
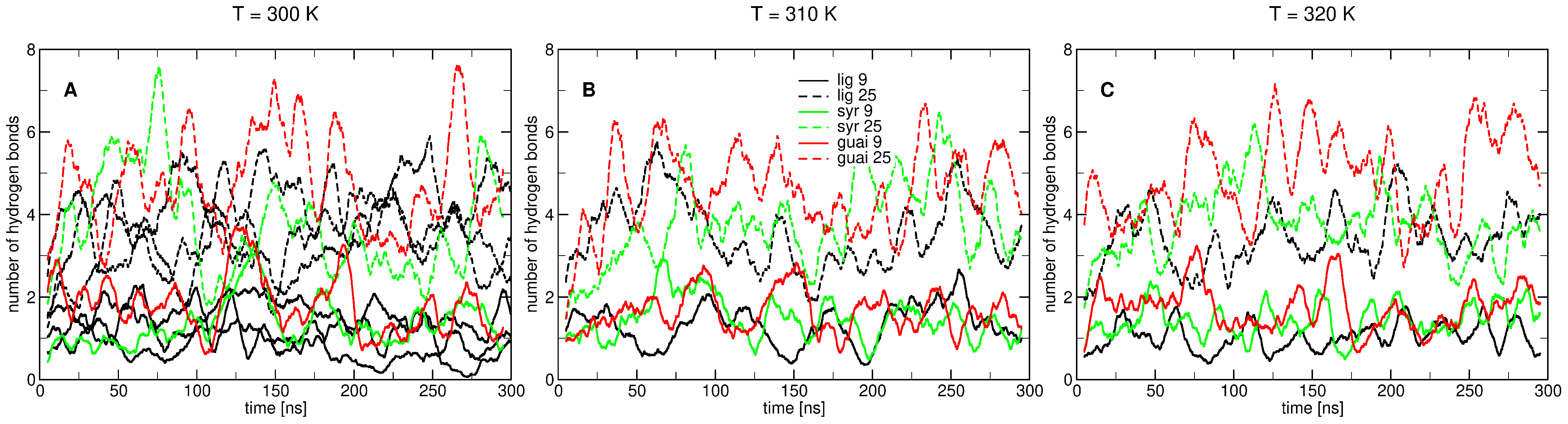
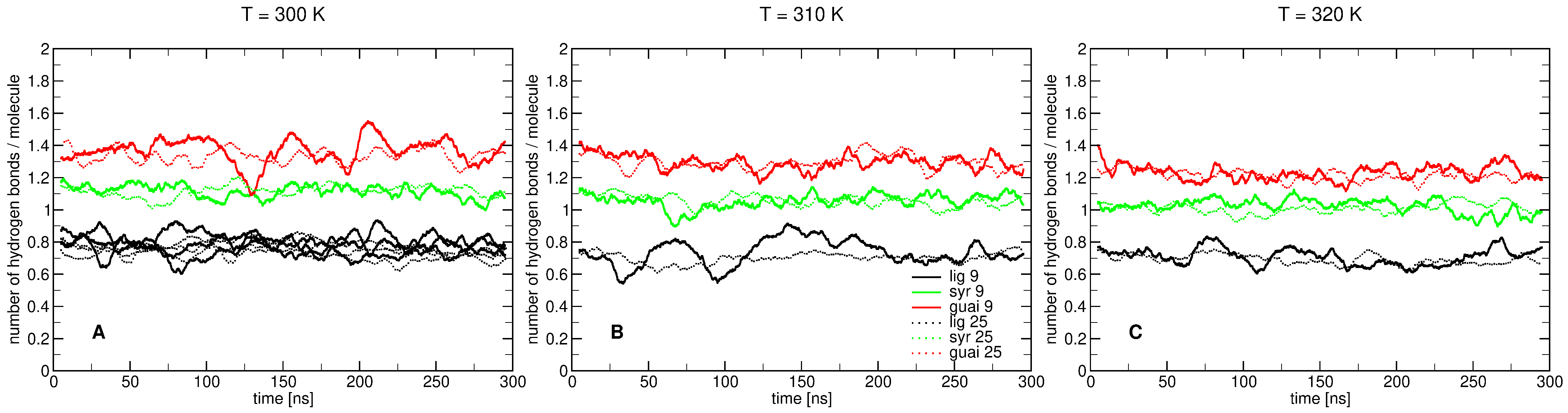
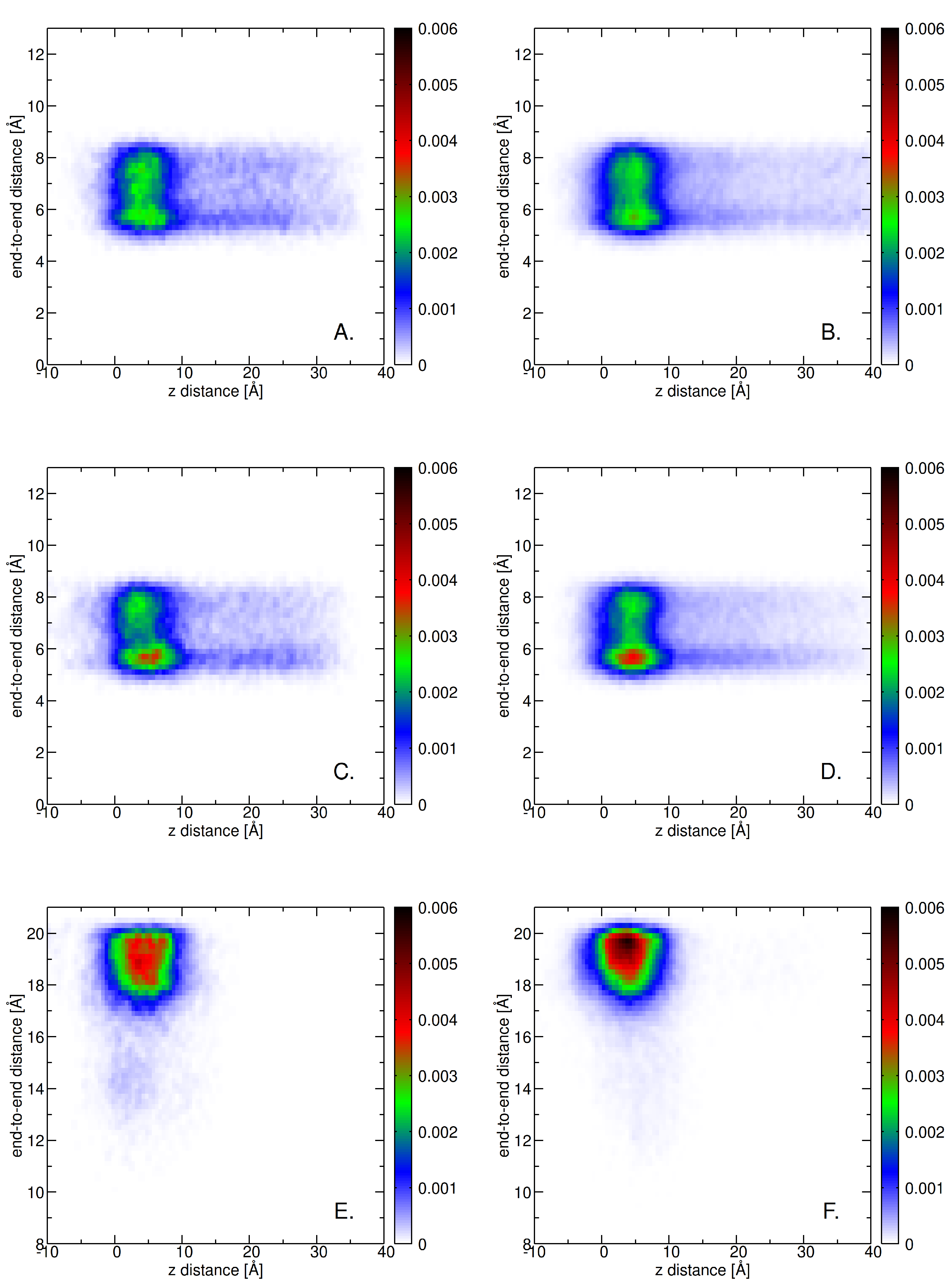
2. Results
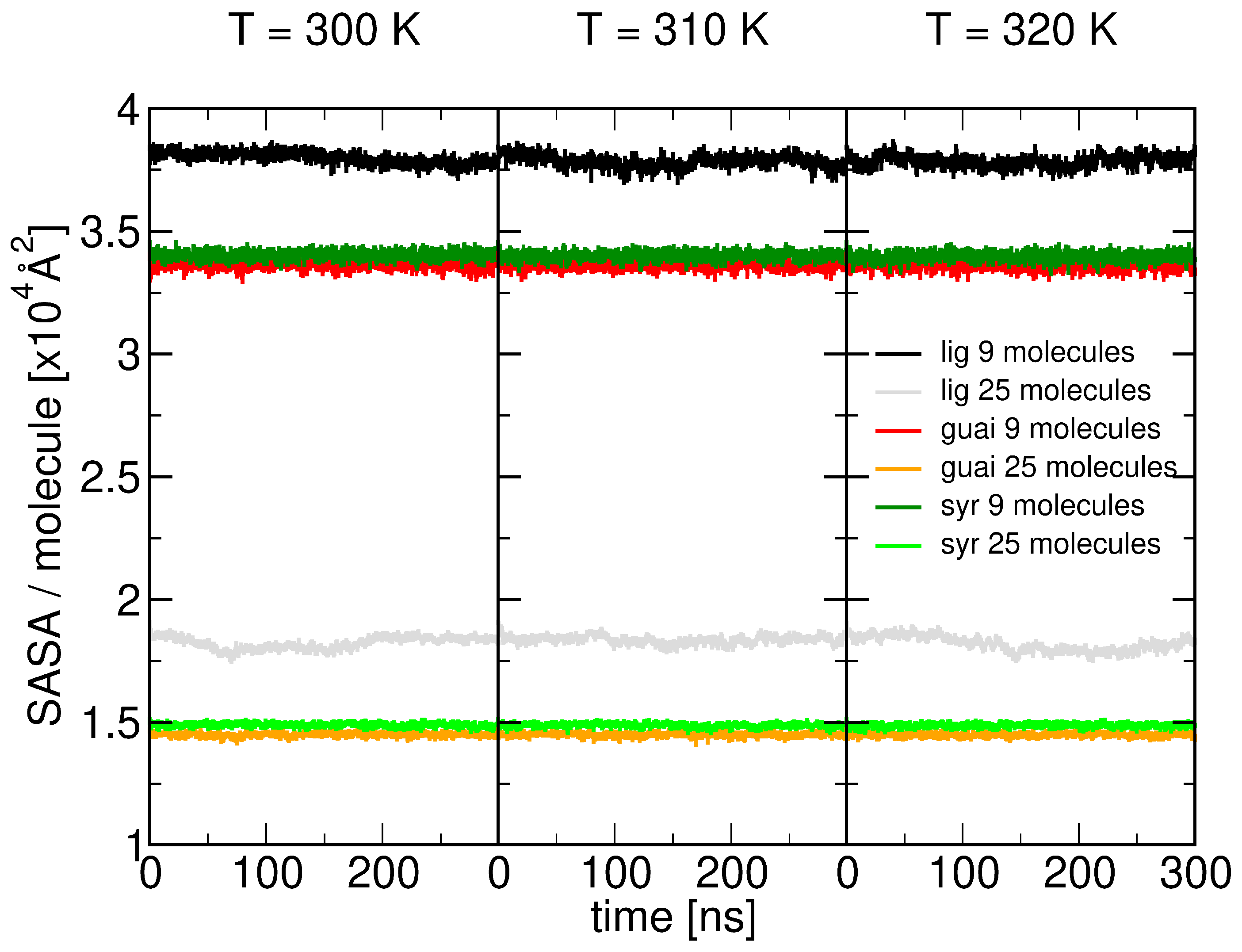
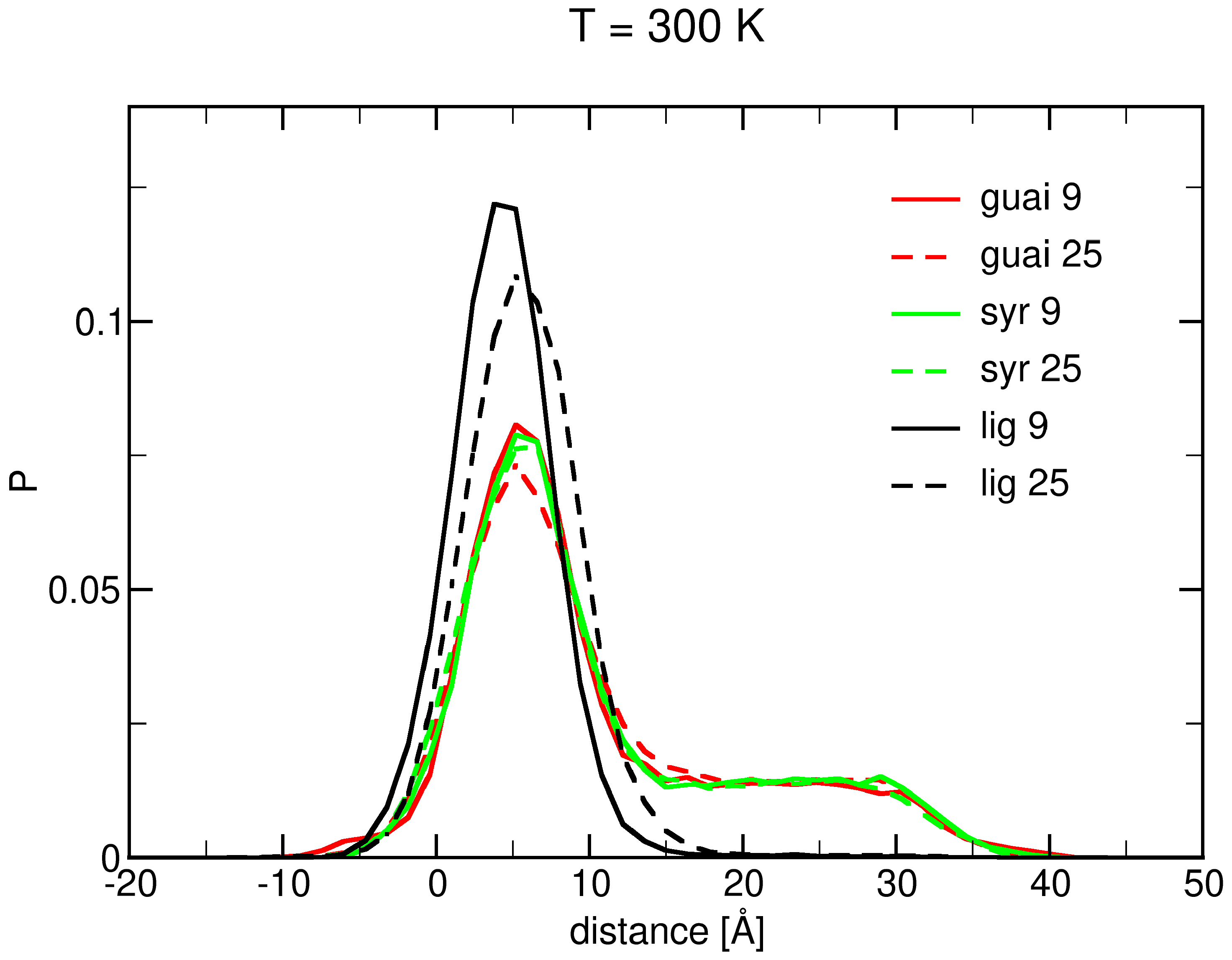
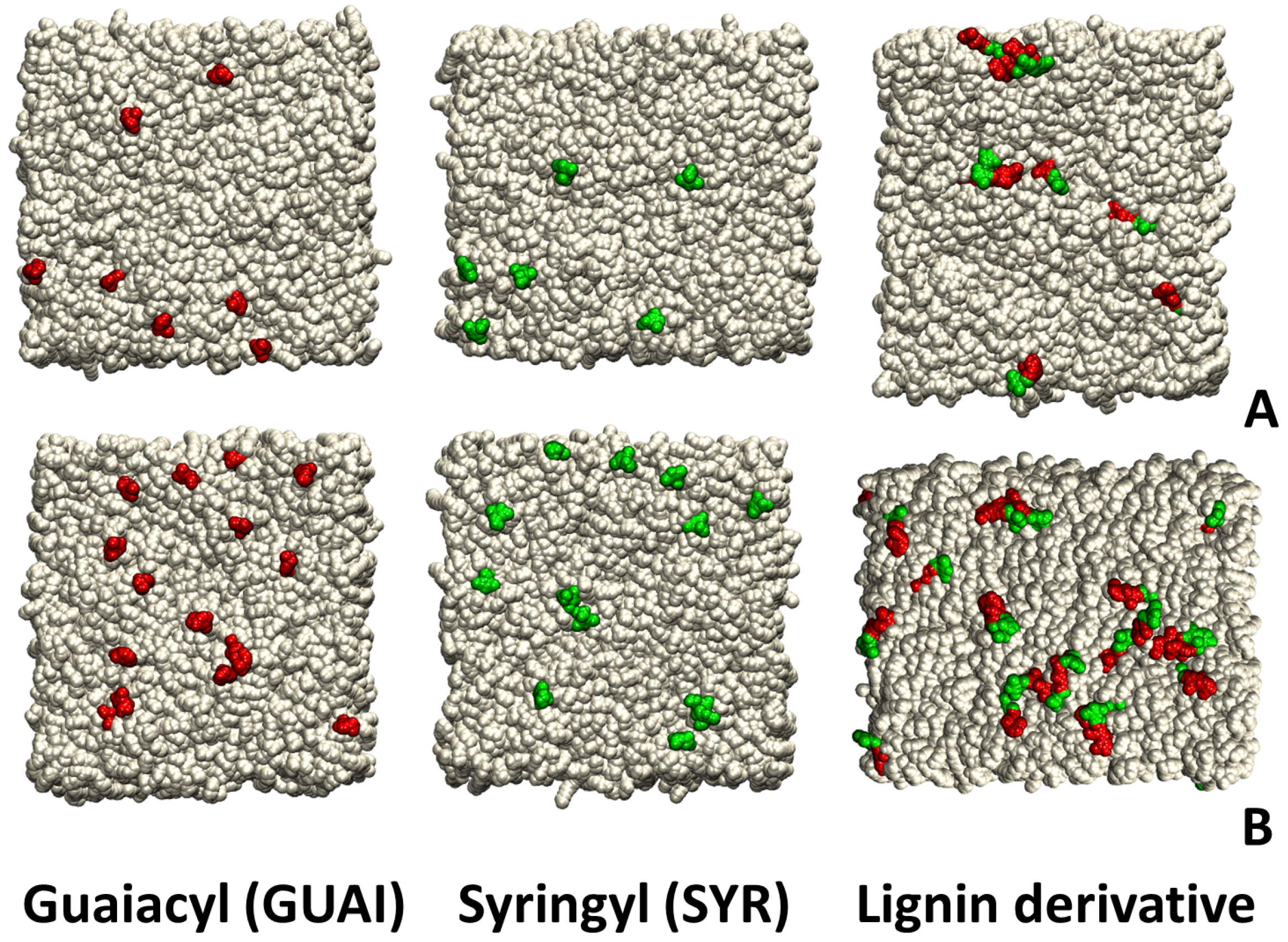
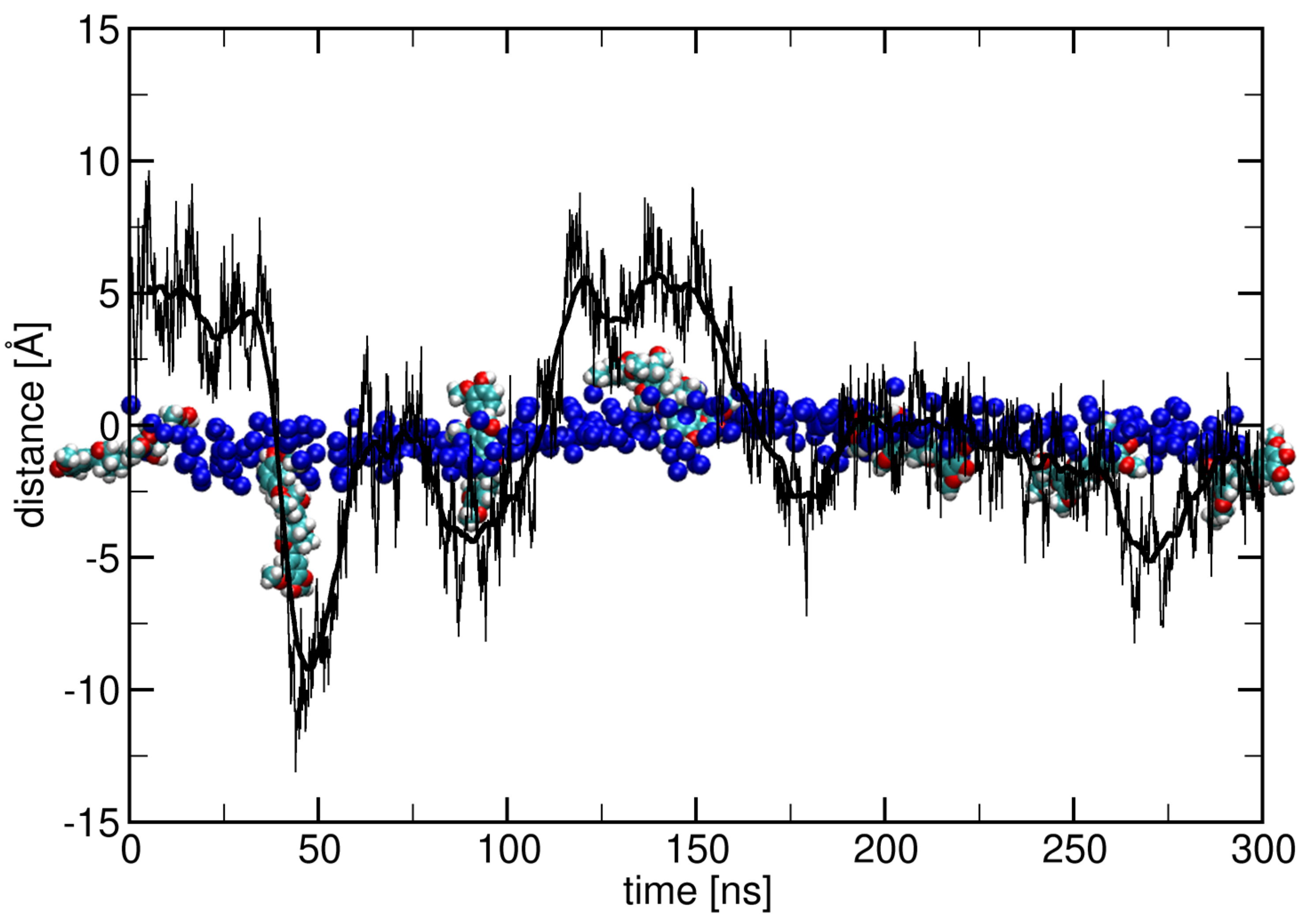
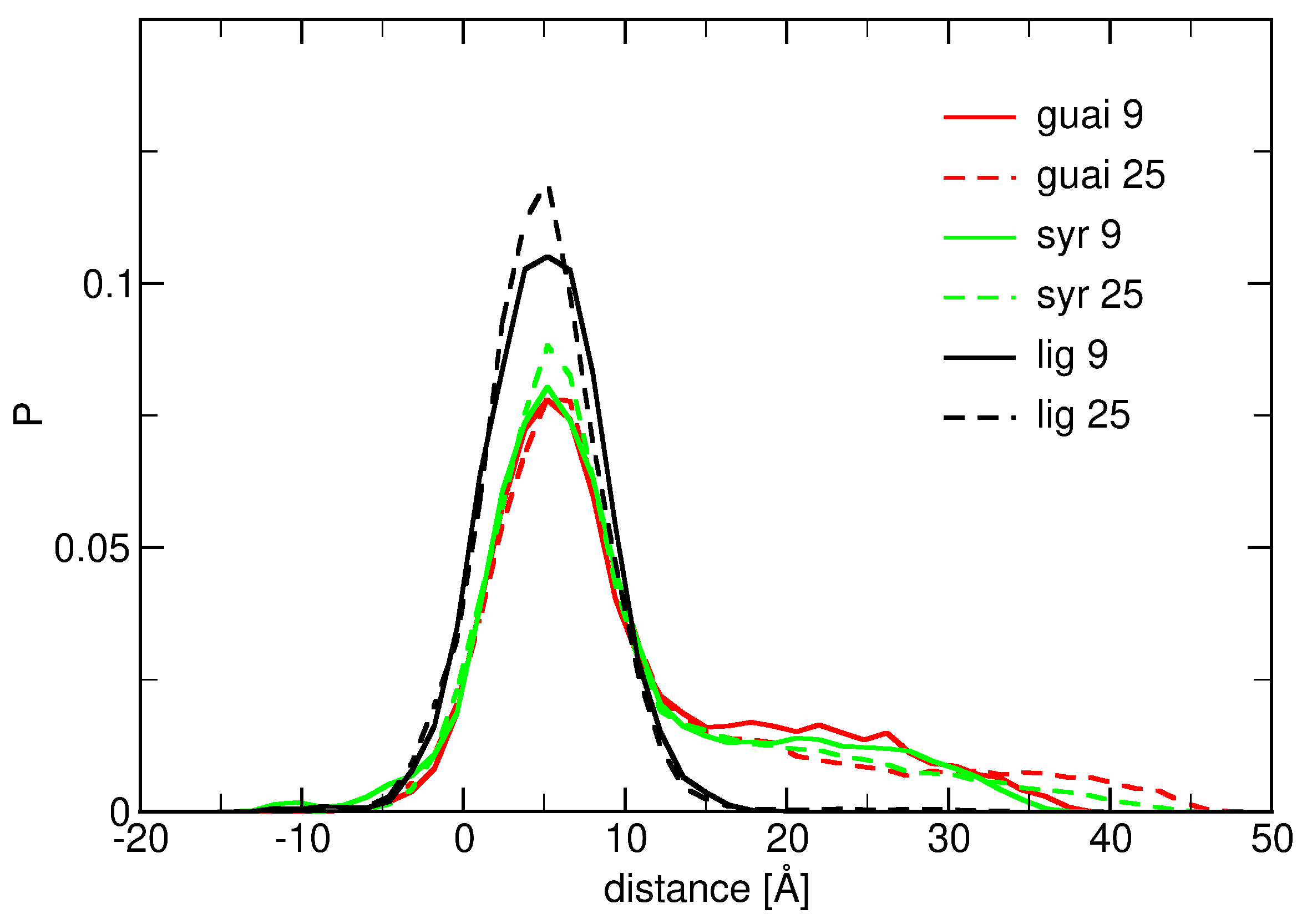
2.1. Surface Adhesion of Lignin
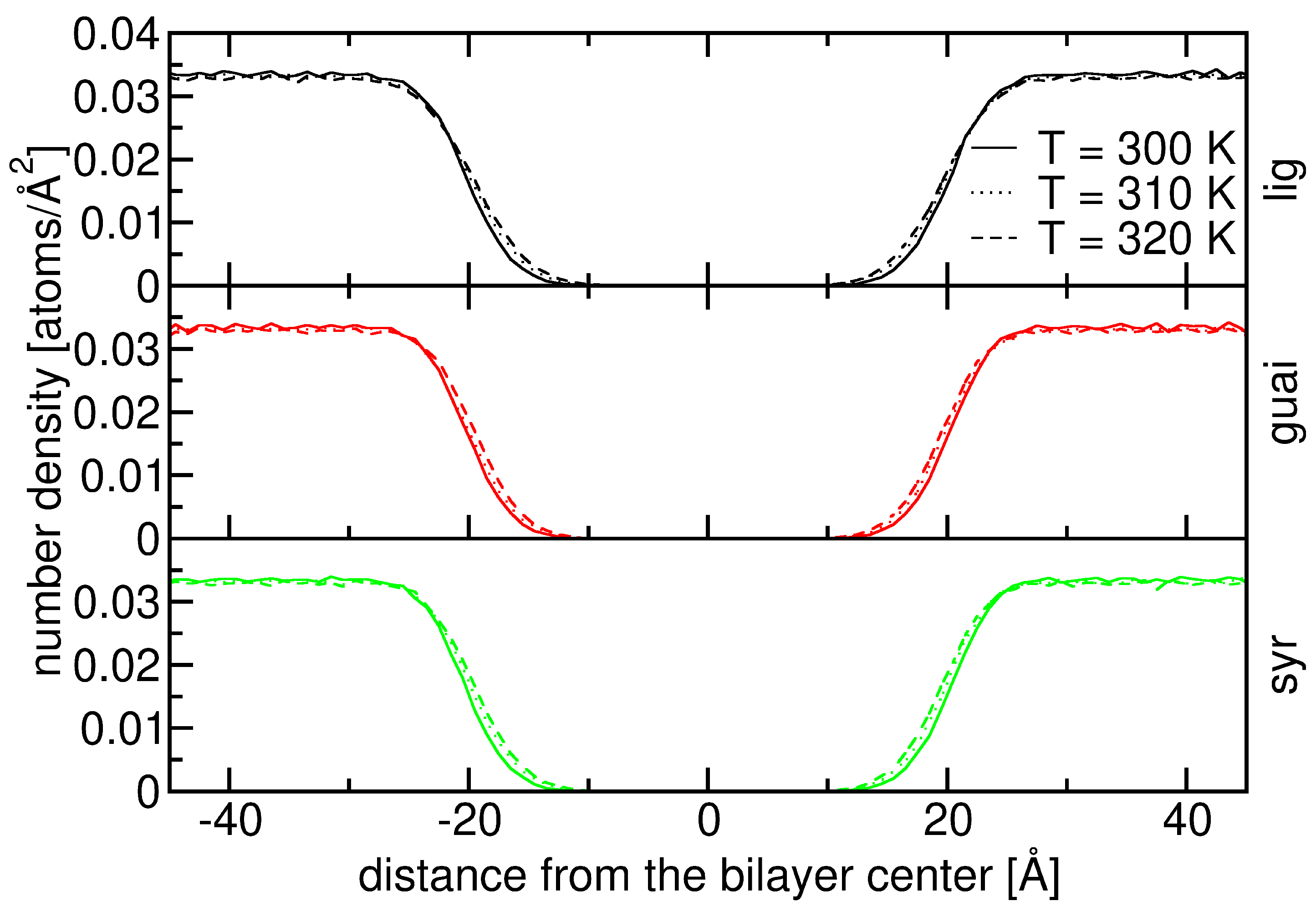
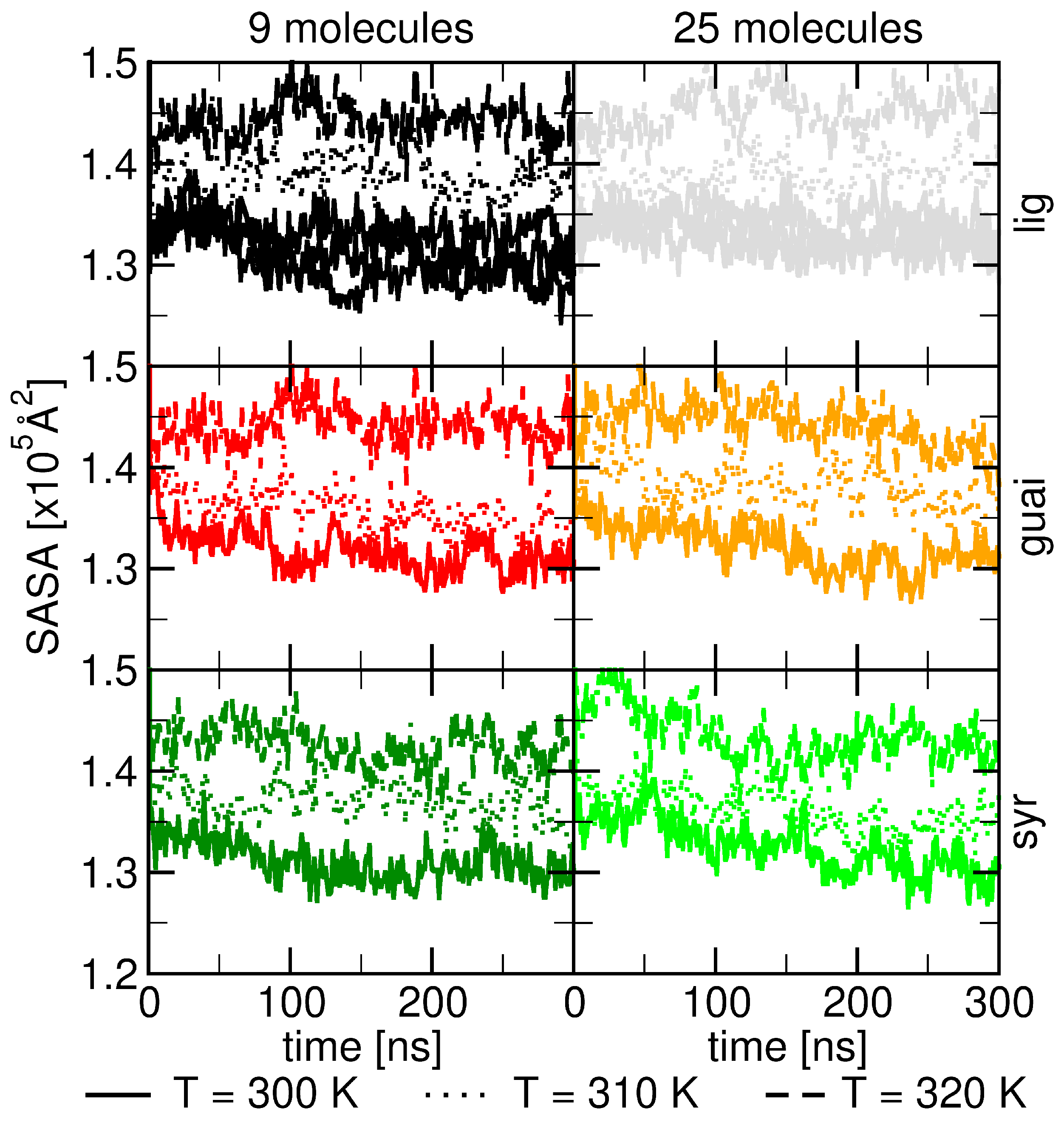
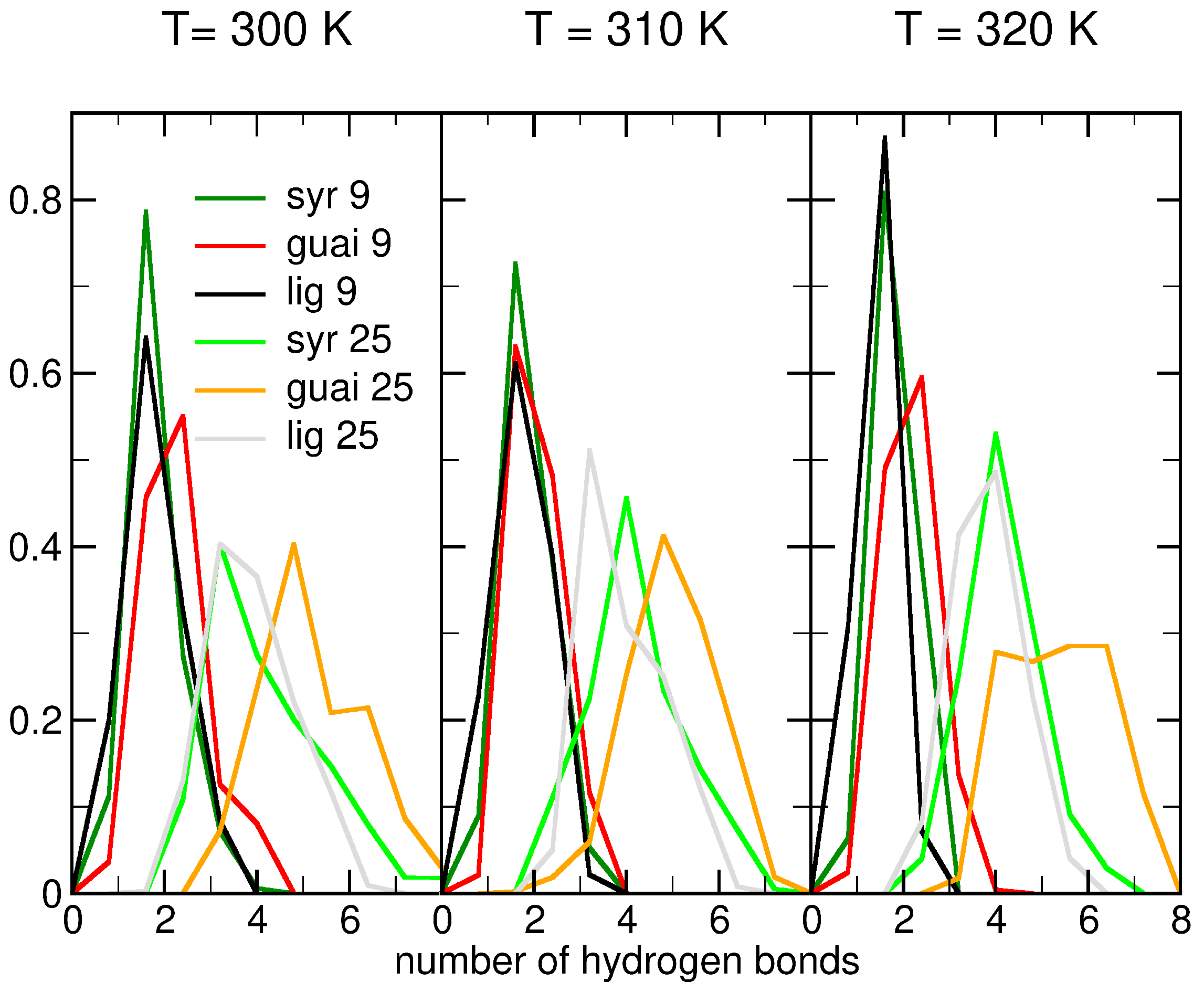
2.2. Influence of Hydration on Lignin–Membrane Interactions
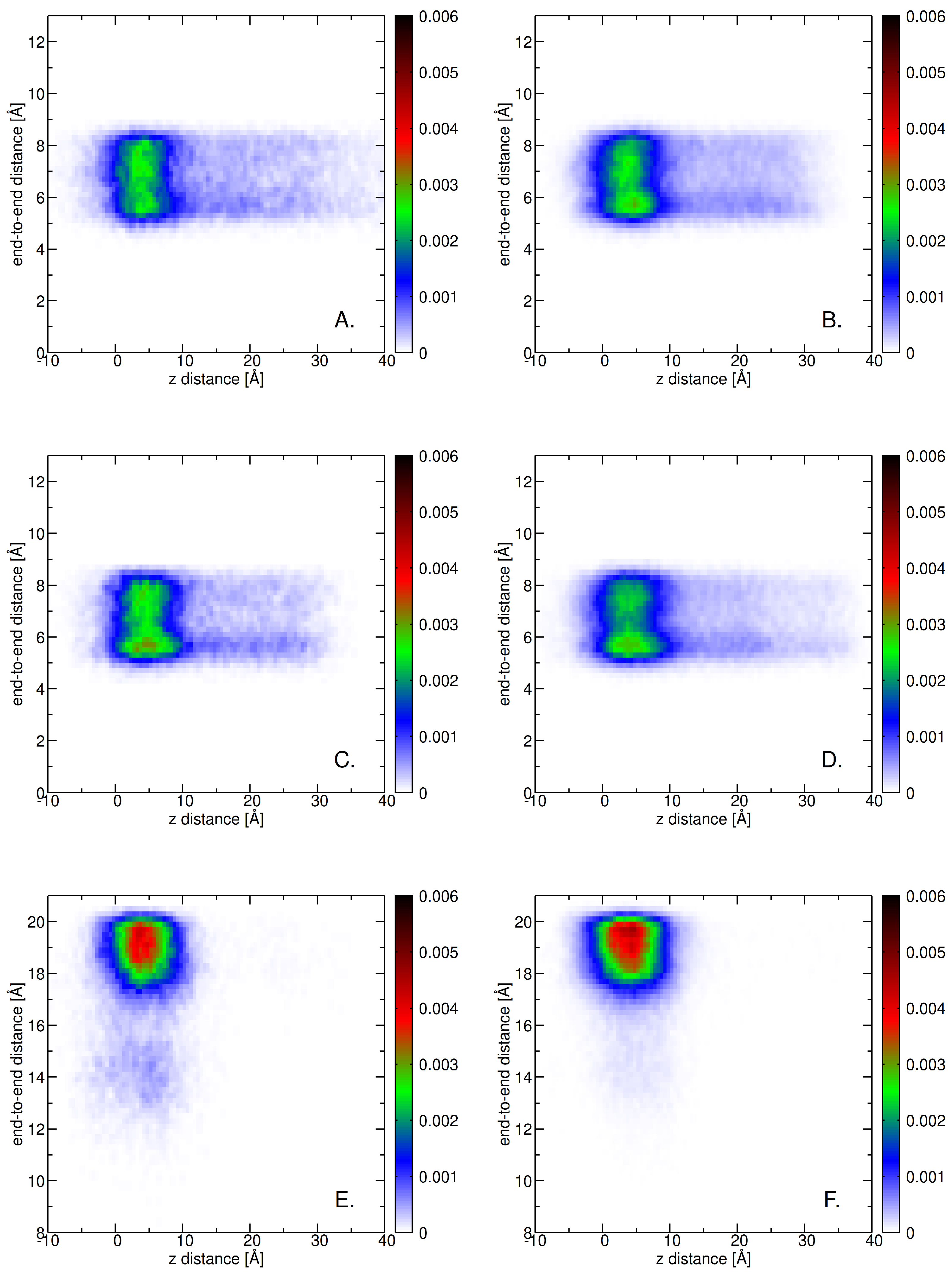
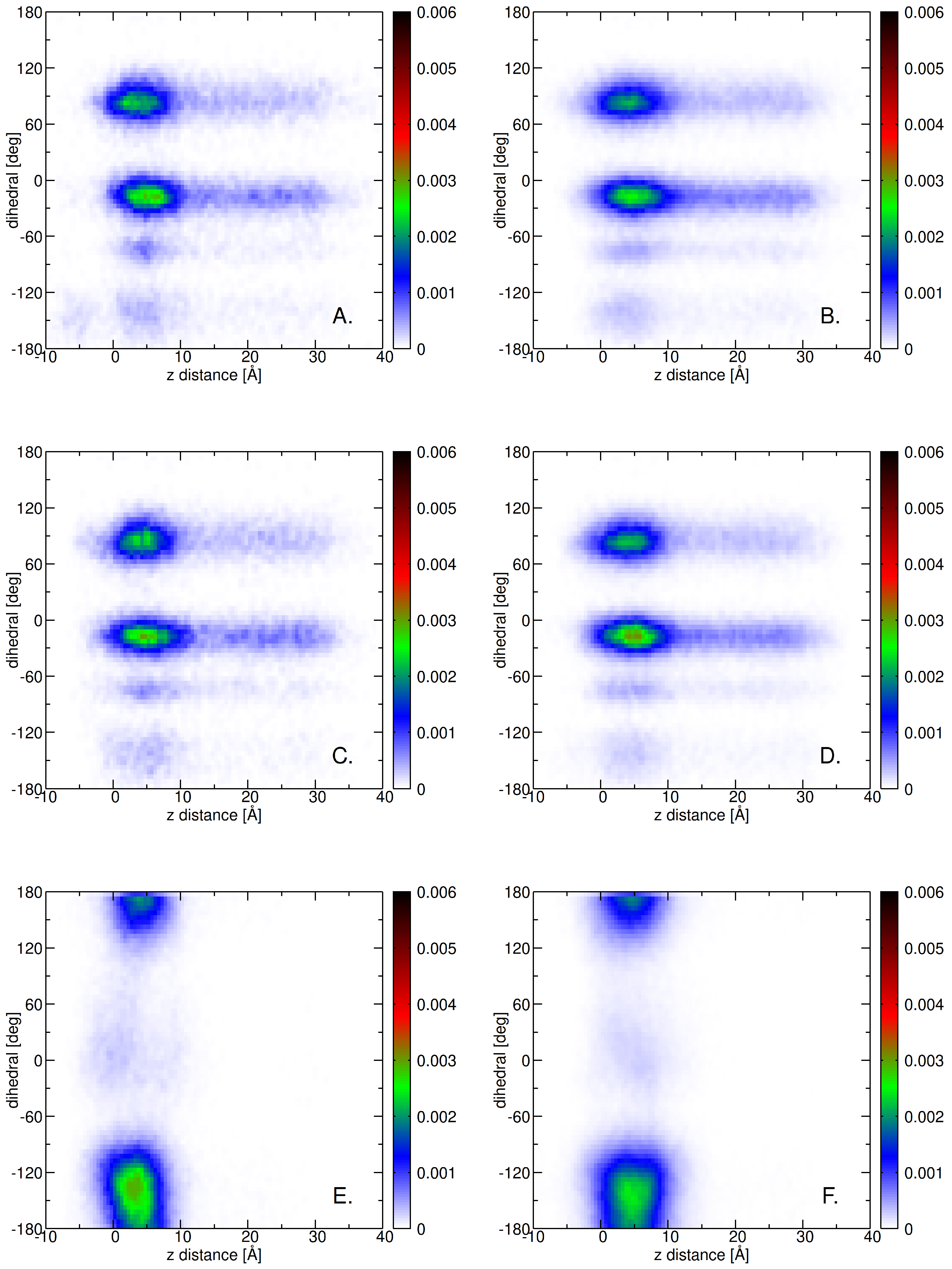
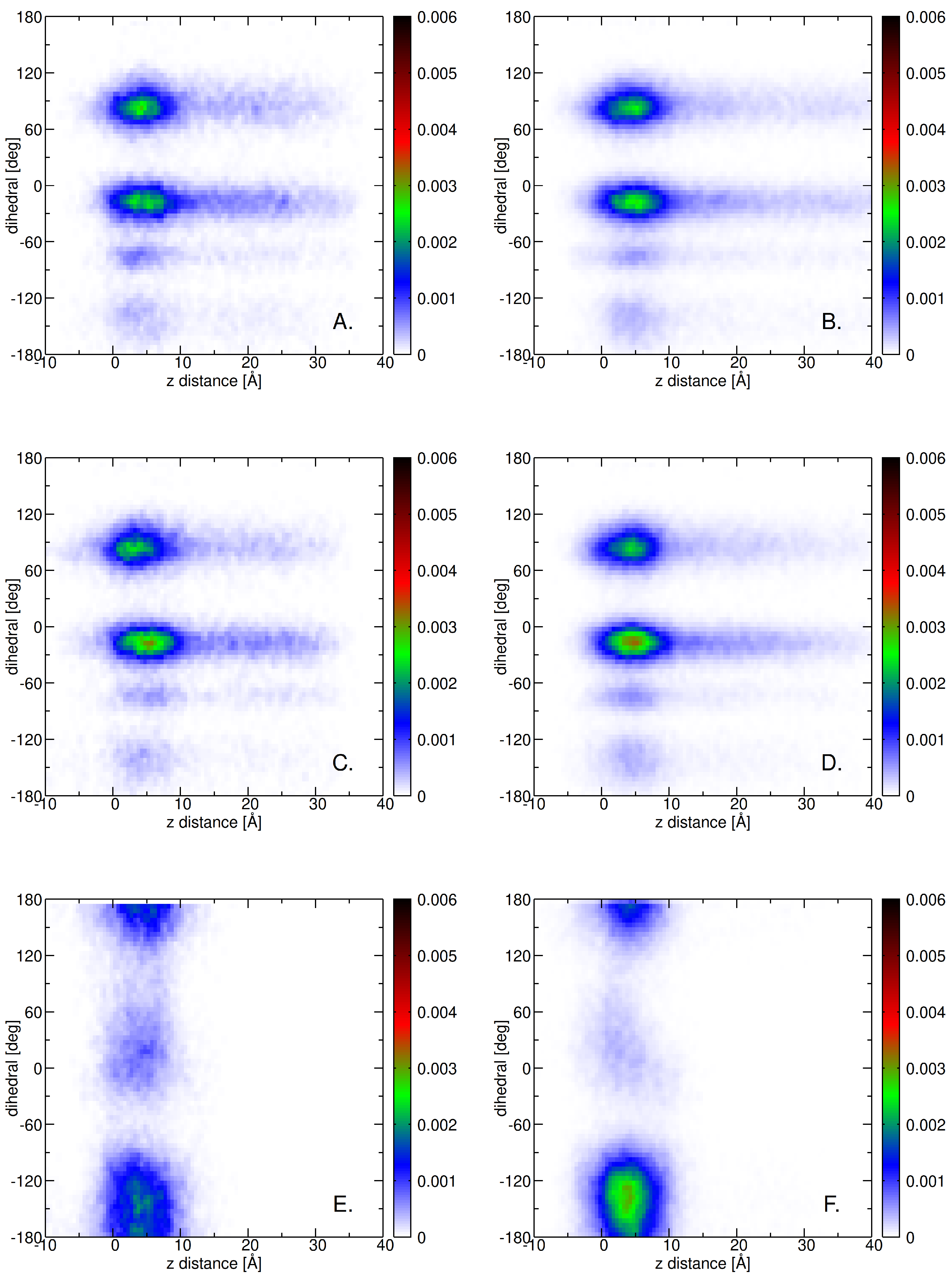
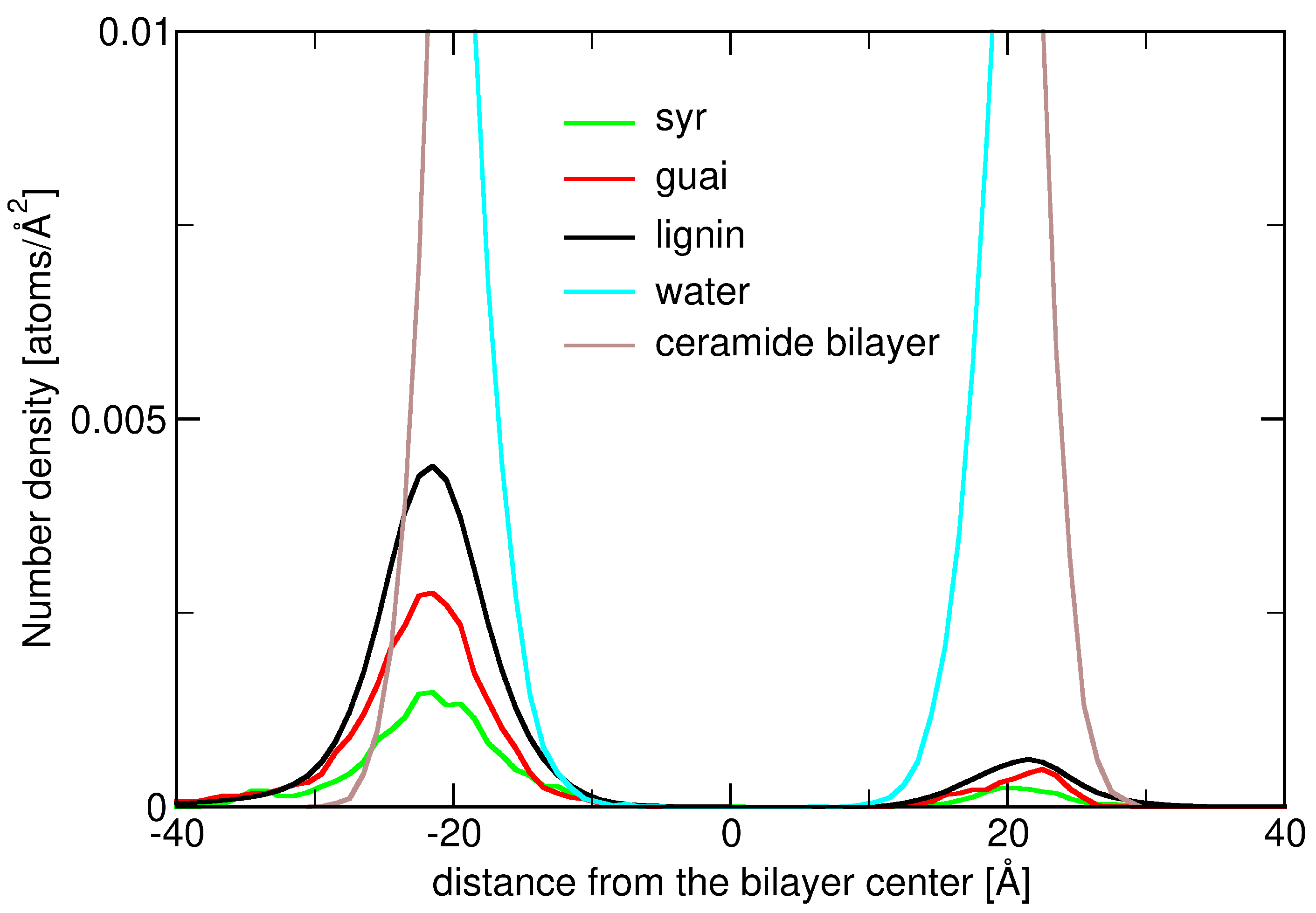
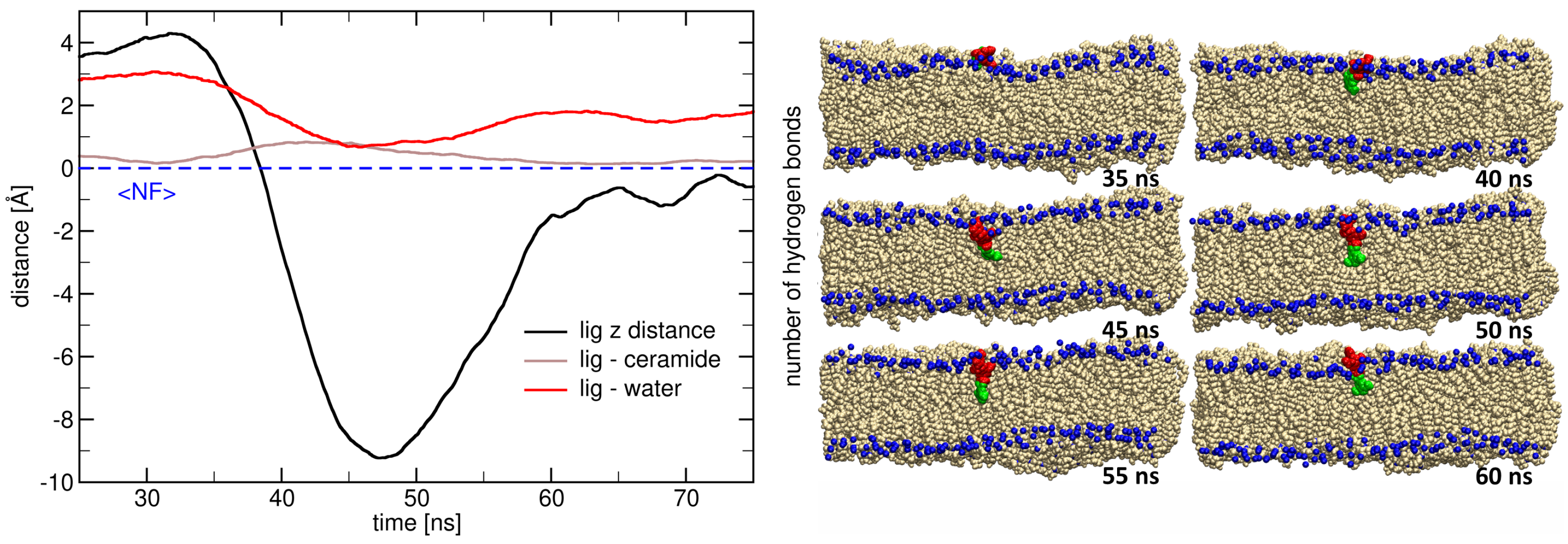
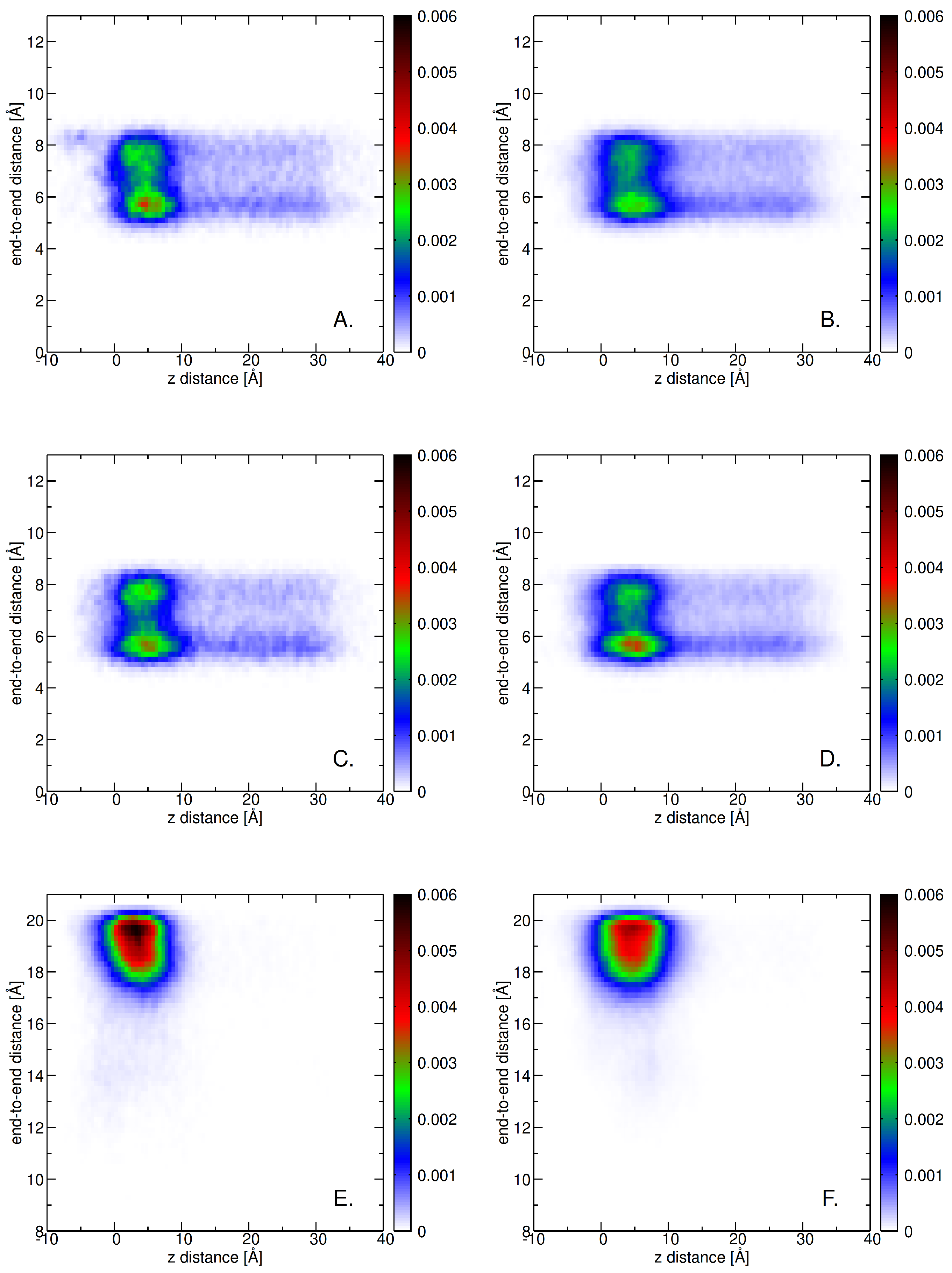
2.3. Insertion into Skin-like Membranes
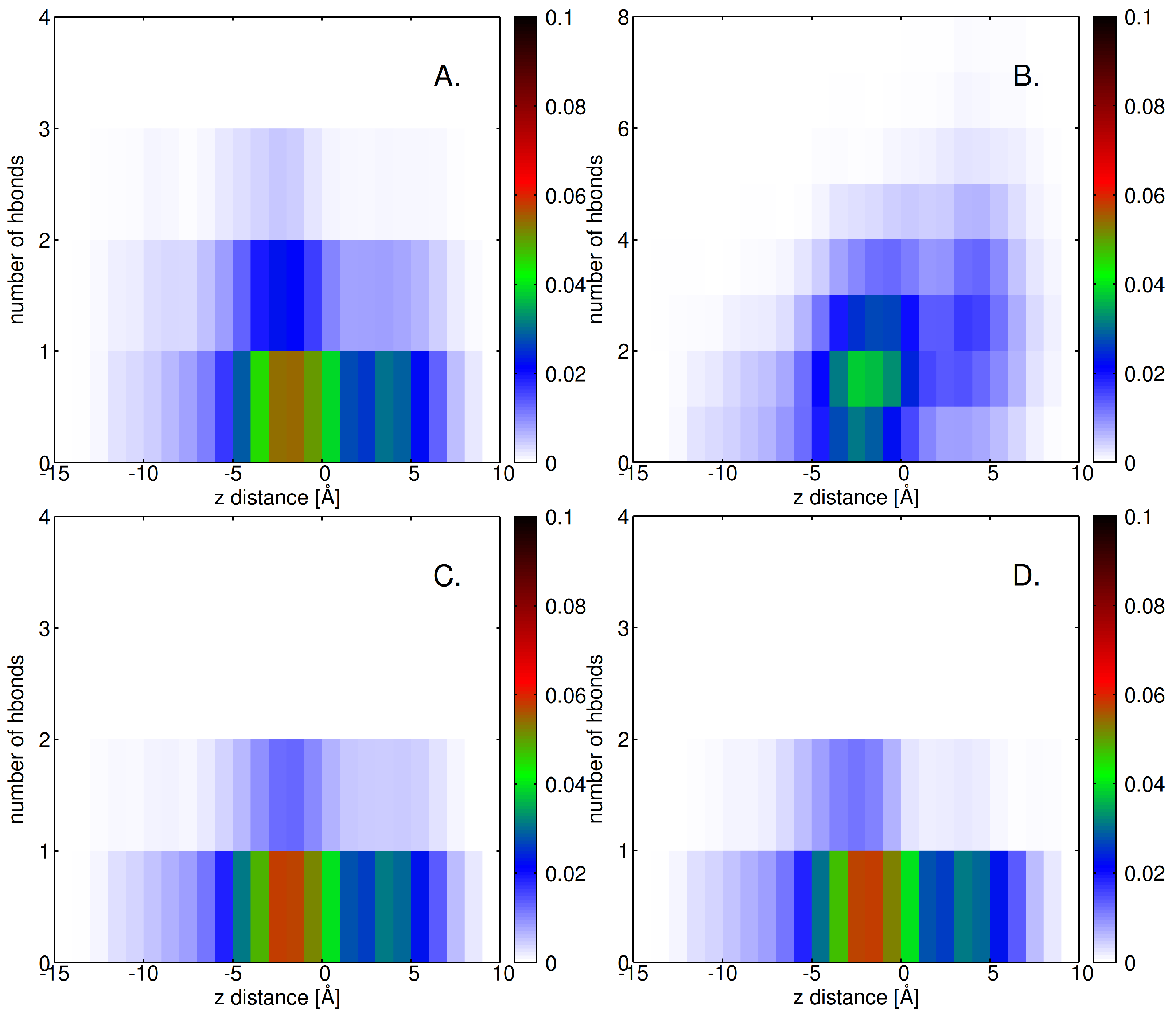
2.4. Factors Facilitating Lignin Insertion
2.5. Role of Surface Clusters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Dynamics
4.2. Potential of Mean Force Calculations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Cárcamo-Martínez, Á.; Stewart, S.A.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E.; Borrega, M. Lignin for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications – Could this become a reality? Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasounian, R.; Martinez, R.M.; Lopes, A.M.; Giarolla, J.; Rosado, C.; Magalhães, W.V.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. Innovative approaches to an Eco-friendly cosmetic industry: A review of sustainable ingredients. Clean Technol. 2024, 6, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, M.; Jin, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Lee, J.S.; Luan, G.; et al. A comprehensive review of unlocking the potential of lignin-derived biomaterials: From lignin structure to biomedical application. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beu, T.A.; Farcaş, A. CHARMM force field and molecular dynamics simulations of protonated polyethylenimine. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, R.; Fernandes, M.; Fangueiro, R. Biopolymers in Medical Implants: A Brief Review. Procedia Eng. 2017, 200, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordobil, O.; Olaizola, P.; Banales, J.M.; Labidi, J. Lignins from Agroindustrial by-Products as Natural Ingredients for Cosmetics: Chemical Structure and In Vitro Sunscreen and Cytotoxic Activities. Molecules 2020, 25, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creteanu, A.; Lungu, C.N.; Lungu, M. Lignin: An adaptable biodegradable polymer used in different formulation processes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Butreddy, A.; Kommineni, N.; Reddy, P.G.; Bunekar, N.; Sarkar, C.; Dutt, S.; Mishra, V.K.; Aadil, K.R.; Mishra, Y.K.; et al. Lignin: Drug/gene delivery and tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2419–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Ringu, T.; Ghosh, S.; Pramanik, N. A comprehensive review on recent advances in preparation, physicochemical characterization, and bioengineering applications of biopolymers. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7247–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolore, R.S.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. A comprehensive review on sustainable lignin extraction techniques, modifications, and emerging applications. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 235, 121696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawoko, M.; Samec, J.S.M. Kraft lignin valorization: Biofuels and thermoset materials in focus. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 40, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, D.S.; Pourhashem, G.; Ullah, A.H.; Bajwa, S.G. A concise review of current lignin production, applications, products and their environmental impact. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 139, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Abu-Omar, M. Chemicals from Lignin. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlekar, N.; Cayla, A.; Rault, F.; Giraud, S.; Salaun, F.; Malucelli, G.; Guan, J. Thermal stability and fire retardant properties of polyamide 11 microcomposites containing different lignins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13704–13714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolarski, N. High-Value Opportunities for Lignin: Unlocking Its Potential. In Market Insights; Frost Sullivan: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dessbesell, L.; Paleologou, M.; Leitch, M.; Pulkki, R.; Xu, C.C. Global lignin supply overview and kraft lignin potential as an alternative for petroleum-based polymers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 123, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthäuser, J.; Biziks, V.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Lignin and Lignin-Derived Compounds for Wood Applications—A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaas, J.V.; Petridis, L.; Ralph, J.; Crowley, M.F.; Beckham, G.T. Systematic parameterization of lignin for the CHARMM force field. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preet, J.; Pathania, K.; Kaur, J.; Singh, R.; Salunke, D.B.; Pawar, S.V. A lignin-based biocomposite hydrogel for antimicrobial and wound healing applications. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 9445–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgundi, A.S.; Chauhan, J.; Sharma, R.K. Synthesis and characterization of Eco-friendly lignin nanoparticles for antimicrobial and UV barrier applications in textiles and possible sunscreen formulations. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e00345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.V.; Tran, N.T.; Nguyen, P.L.M.; Nguyen, N.N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Van Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, V.P.; Thai, H.T.; Hoang, D. Sustainable lignin-based nano hybrid biomaterials with high-performance antifungal activity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 37540–37548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, R.; Fardim, P. Lignin-based materials for emerging advanced applications. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 41, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudet, A.M. Lignins and lignification: Selected issues. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 38, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, E. Lignin chemistry—Past, present and future. Wood Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 169–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boija, E.; Johansson, G. Interactions between model membranes and lignin-related compounds studied by immobilized liposome chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, A.M.; Gatto, E.; Lettieri, R.; Bokharaie, H.; Caravella, A.; D’Ottavi, C.; di Bartolomeo, E.; Domenici, F.; Sima, S.; Correia, A.; et al. Biomass-derived Lignin Nanoparticles for the Sustained Delivery of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-C. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2025, 216, 114860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Jiang, B.; Huang, C.; Jin, Y. Dual regulation of sulfonated lignin to prevent and treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, T.; Kai, J.; Sugiarto, S.; Yu, Y.; Soo, D.X.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Merzaban, J.; Kai, D. Nano-strategies for lignin biomaterials toward cancer therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinardell, M.; Mitjans, M. Lignins and Their Derivatives with Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Mukai, Y.; Tokuoka, Y.; Mikame, K.; Funaoka, M.; Fujita, S. Effect of lignin-derived lignophenols on hepatic lipid metabolism in rats fed a high-fat diet. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Ansari, N.; Moriya, Y.; Joshi, K.; Prasad, D.; Sajwan, G.; Shukla, S.; Kumar, S.; Varma, R.S. Nanobiopolymers in cancer therapeutics: Advancing targeted drug delivery through sustainable and controlled release mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 11887–11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, A.; Janosi, L.; Astilean, S. Size and surface coverage density are major factors in determining thiol modified gold nanoparticles characteristics. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2022, 1209, 113581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikeli, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; D’Annibale, A.; Capitani, D.; Romagnoli, M.; Mugnozza, G.S. Preparation of Lignin Nanoparticles from Wood Waste for Wood Surface Treatment. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Greener synthesis of lignin nanoparticles and their applications. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 612–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabellone, S.; Piccinino, D.; Filippi, S.; Castrignanò, T.; Zippilli, C.; Del Buono, D.; Saladino, R. Lignin Nanoparticles Deliver Novel Thymine Biomimetic Photo-Adducts with Antimelanoma Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Khan, S.S.; Singh, S.; Yu, C.; Cheng, G. Recent advances in biological activities of lignin and emerging biomedical applications: A short review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, S.; Leow, Y.; Tan, C.L.; Wang, G.; Kai, D. How far is Lignin from being a biomedical material? Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przetaczek-Rożnowska, I.; Fortuna, T. Effect of conditions of modification on thermal and rheological properties of phosphorylated pumpkin starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, C.; González-Martínez, C.; Vilaplana, F.; Diretto, G.; Chiralt, A. Incorporation of natural antioxidants from rice straw into renewable starch films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Fu, S.; Chen, Y. High-value utilization of kraft lignin: Color reduction and evaluation as sunscreen ingredient. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugleva, V.; Ivanova, N.; Sotirova, Y.; Andonova, V. Dermal Drug Delivery of Phytochemicals with Phenolic Structure via Lipid-Based Nanotechnologies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaas, J.V.; Dixon, R.A.; Chen, F.; Mansfield, S.D.; Boerjan, W.; Ralph, J.; Crowley, M.F.; Beckham, G.T. Passive membrane transport of lignin-related compounds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23117–23123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, F.; Mota, I.F.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Lopes, G.; Pintado, M.; Costa, P.S. From sugarcane to skin: Lignin as a multifunctional ingredient for cosmetic application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.A.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, J. Lignin-based antioxidant hydrogel patch for the management of atopic dermatitis by mitigating oxidative stress in the skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 33135–33148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyamoorthy, V.; Jacop, J.P.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Ibrahim, H.I.M.; Kandhasamy, S. The synergic impact of lignin and Lactobacillus plantarum on DSS-induced colitis model via regulating CD44 and miR 199a alliance. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, C.; Busuttil, V.; Botto, J.M. Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of human skin melanogenesis and pigmentation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 328–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Singh, S.P.; Rajpoot, A.S.; Chauhan, S.; Meraj, A.; Jawaid, M.; Varghese, E.; Kumar, V.; Awad, S.A. Preparation and applications of nanoparticles from lignocellulosic biomass: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 321, 146138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rani, A.; Dar, M.; Qaisrani, M.; Noman, M.; Yoganathan, K.; Asad, M.; Berhanu, A.; Barwant, M.; Zhu, D. Recent Advances in Characterization and Valorization of Lignin and Its Value-Added Products: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Biomass 2024, 4, 947–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolore, R.S.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. Green and sustainable pretreatment methods for cellulose extraction from lignocellulosic biomass and its applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 7, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Baican, M. Lignins as Promising Renewable Biopolymers and Bioactive Compounds for High-Performance Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kelley, S.S.; Venditti, R.A. Lignin-Based Thermoplastic Materials. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternberg, J.; Pilla, S. Thermoplastic Polymer from Lignin: Creating an Extended Polyamide Network through Reactive Kraft Lignin Derivatives. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 40110–40118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderch, L.; Lopez, O.; de la Maza, A.; Parra, J.L. Ceramides and Skin Function. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E.; Kaykın, M.; Şahin Bektay, H.; Güngör, S. Recent advances on topical application of ceramides to restore barrier function of skin. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdyshev, E. Skin lipid barrier: Structure, function and metabolism. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2024, 16, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullmannová, P.; Čuříková Kindlová, B.A.; Ondrejčeková, V.; Kováčik, A.; Dvořáková, K.; Dulanská, L.; Georgii, R.; Majcher, A.; Maixner, J.; Kučerka, N.; et al. Polymorphism, Nanostructures, and Barrier Properties of Ceramide-Based Lipid Films. ACS Omega 2022, 8, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.; Huang, C.; Radi, R.; Moll, S.B.; Jules, E.; Arbiser, J.L. Skin Barrier Function: The Interplay of Physical, Chemical, and Immunologic Properties. Cells 2023, 12, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Jiang, Z.; Lin, X.; Wei, X. Application of plant extracts cosmetics in the field of anti-aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. Cosmet. Technol. 2024, 1, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, W.; Jin, Y.; Wu, W. Exploring the relationship between lignin structure and antioxidant property using lignin model compounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Chaffee, A.; Yarovsky, I. Investigation of Lignin-water interactions by molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2002, 28, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.; Joseph, E.; Lian, G.; Lunter, D.J. Presence of Different Ceramide Species Modulates Barrier Function and Structure of Stratum Corneum Lipid Membranes: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 4280–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Foulon, L.; Chabbert, B.; Aguié-Béghin, V.; Molinari, M. Atomic force microscopy reveals how relative humidity impacts the Young’s modulus of lignocellulosic polymers and their adhesion with cellulose nanocrystals at the nanoscale. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghifar, H.; Ragauskas, A.J. Lignin as a Natural Antioxidant: Chemistry and Applications. Macromol 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, L.; Guccini, V.; Heise, K.; Solala, I.; Niinivaara, E.; Xu, W.; Mihhels, K.; Kröger, M.; Meng, Z.; Wohlert, J.; et al. Understanding Nanocellulose–Water Interactions: Turning a Detriment into an Asset. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 1925–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.R.; Alves, M.F.; Cunha, J.P.; Costa, J.L.; Silva, C.A.; Fernandes, M.H.; Vilarinho, P.M.; Ferreira, P. Nanostructured transparent solutions for UV-shielding: Recent developments and future challenges. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Lim, J.B.; Klauda, J.B.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder for Mixed Bilayers and Its Application to Yeast Membranes. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kale, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauda, J.B.; Venable, R.M.; Freites, J.A.; O’Connor, J.W.; Tobias, D.J.; Mondragon-Ramirez, C.; Vorobyov, I.; MacKerell, A.D.; Pastor, R.W. Update of the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Force Field for Lipids: Validation on Six Lipid Types. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7830–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, R.M.; Sodt, A.J.; Rogaski, B.; Rui, H.; Hatcher, E.; MacKerell, A.D.; Pastor, R.W.; Klauda, J.B. CHARMM All-Atom Additive Force Field for Sphingomyelin: Elucidation of Hydrogen Bonding and of Positive Curvature. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kollman, P.A. Settle: An analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithm for rigid water models. J. Comput. Chem. 1992, 13, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, S.E.; Zhang, Y.; Pastor, R.W.; Brooks, B.R. Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, N.V.; Tsygankov, P.Y.; Menshutina, N.V. Facile Lignin Extraction and Application as Natural UV Blockers in Cosmetic Formulations. ChemEngineering 2024, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosztin, I.; Barz, B.; Janosi, L. Calculating potentials of mean force and diffusion coefficients from nonequilibrium processes without Jarzynski’s equality. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 064106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorila, B.; Necula, G.; Janosi, L.; Turcu, I.; Bacalum, M.; Radu, M. Interaction of Arginine and Tryptophan-Rich Short Antimicrobial Peptides with Membrane Models: A Combined Fluorescence, Simulations, and Theoretical Approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2025, 65, 3723–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, A.; Wrachtrup, J.; Schulten, K.; Tietz, C. Possible pathway for ubiquinone shuttling in Rhodospirillum rubrum revealed by molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamloo, A.; Pedram, M.Z.; Heidari, H.; Alasty, A. Computing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) diffusion coefficient: A molecular dynamics approach. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 410, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundborg, M.; Wennberg, C.L.; Narangifard, A.; Lindahl, E.; Norlén, L. Predicting drug permeability through skin using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Control. Release 2018, 283, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosi, L.; Keer, H.; Kosztin, I.; Ritz, T. Influence of subunit structure on the oligomerization state of light-harvesting complexes: A free energy calculation study. Chem. Phys. 2006, 323, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Forney, M.W.; Janosi, L.; Kosztin, I. Calculating free-energy profiles in biomolecular systems from fast nonequilibrium processes. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 051913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, E.; Boiteux, C.; Lev, B.; Vorobyov, I.; Allen, T.W. Atomistic simulations of membrane ion channel conduction, gating, and modulation. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7737–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevick, E.M.; Prabhakar, R.; Williams, S.R.; Searles, D.J. Fluctuation theorems. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 603–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y. Nonequilibrium fluctuation-dissipation theorem of Brownian dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 144113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, C.P.; Janosi, L.; Kosztin, I. Using stochastic models calibrated from nanosecond nonequilibrium simulations to approximate mesoscale information. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 144908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmurugan, M. Generalized detailed fluctuation theorem under nonequilibrium feedback control. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 031129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NategholEslam, M.; Holland, B.W.; Gray, C.G.; Tomberli, B. Drift-oscillatory steering with the forward-reverse method for calculating the potential of mean force. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 021114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.D.L.; Adib, A.B. Optimized free energies from bidirectional single-molecule force spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 180602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| System | Molecule | No. of Molecules | No. of Lipids | No. of Water Molecules | No. of Na+ | No. of Cl− | Total No. of Atoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 163,585 | |
| 2 | guai | 9 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 207,417 |
| 3 | guai | 25 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 207,881 |
| 4 | syr | 9 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 207,417 |
| 5 | syr | 25 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 20,7881 |
| 6 | lig | 9 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 209,031 |
| 7 | lig | 25 | 800 | 39,910 | 113 | 113 | 209,031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farcas, A.; Farcas, A.-A.; Janosi, L. The Importance of Molecular Size, Concentration, and Thermal Conditions in Enhancing Lignin Derivatives’ Interactions with Skin-like Membranes: Implications for Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209906
Farcas A, Farcas A-A, Janosi L. The Importance of Molecular Size, Concentration, and Thermal Conditions in Enhancing Lignin Derivatives’ Interactions with Skin-like Membranes: Implications for Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209906
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarcas, Alexandra, Alex-Adrian Farcas, and Lorant Janosi. 2025. "The Importance of Molecular Size, Concentration, and Thermal Conditions in Enhancing Lignin Derivatives’ Interactions with Skin-like Membranes: Implications for Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209906
APA StyleFarcas, A., Farcas, A.-A., & Janosi, L. (2025). The Importance of Molecular Size, Concentration, and Thermal Conditions in Enhancing Lignin Derivatives’ Interactions with Skin-like Membranes: Implications for Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209906







