Abstract
Agarwood, valued for its resin, has long been used in perfumery, incense, and traditional medicine. Its resin is primarily derived from species of Aquilaria and is produced through a still-unknown process in response to biotic or abiotic stress. Concerns regarding agarwood’s sustainability and conservation have emerged because of the substantial loss of natural resources due to overharvesting and illegal trade. To address these concerns, artificial techniques are being used to produce agarwood. The mechanism underlying agarwood production must be elucidated to enhance yield. The authentication of agarwood species is challenging because of morphological similarities between pure and hybrid Aquilaria species. Techniques such as DNA barcoding, molecular marker assessment, and metabolomics can ensure accurate identification, facilitating conservation. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can support this process by enabling rapid, automated identification on the basis of genetic and phytochemical data. Advances in resin induction methods (e.g., fungal inoculation) and chemical induction treatments are improving yield and quality. Endophytic fungi and bacteria promote resin production at minimal harm to the tree. Agarwood’s pharmacological potential—antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects—has driven research into bioactive compounds such as sesquiterpenes and flavonoids for the development of novel drugs. This systematic review synthesized current evidence on species authentication, induction techniques, and pharmacological properties. The findings may guide future research aimed at ensuring sustainable use and enhancing the medicinal value of agarwood.
Keywords:
agarwood; Aquilaria; authentication; medicinal plant; DNA barcoding; sesquiterpene; chromone 1. Introduction
1.1. Importance of Agarwood
Agarwood, also known as oud, aloeswood, or gharuwood, is a fragrant dark resinous wood formed in the heartwood of Aquilaria trees, particularly when they are wounded or infected by a fungus. Agarwood, formed due to microbial infection, secretes a dark, aromatic resin, which is produced through secondary metabolism by the Aquilaria tree. Agarwood is used in incense, perfumes, cosmetics, and medicine and is known by various names such as “agar” (in various South Asian languages), “Oudh” (in Arabic), and “jinkoh” (in Japanese).
Agarwood is among the most expensive natural products, with a kilogram of pure agarwood costing as much as US$30,000 []. The cost of agarwood varies globally; the price per kilogram of wood chips ranges from US$20 to US$6000 depending on quality, whereas the cost of the wood itself is US$10,000 per kilogram. An estimated US$6–US$8 billion is traded annually on the global agarwood market, yet many transactions are unrecorded [].
In Asia, agarwood has long been used in religious rituals and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Agarwood leaves are used in religious ceremonies, perfumery, and aromatherapy. Regarding medicinal value, agarwood contains various compounds with neuroprotective, sedative, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidative properties [,].
Healthy Aquilaria trees can only generate a limited quantity of agarwood before sustaining severe damage or becoming overrun by microbes. Wild agarwood has become scarce because of overharvesting []. In 2004, a list of all Aquilaria species was included in supplementary materials of the CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) treaty []. In response to external stress, healthy Aquilaria produces sesquiterpenes (C15) and 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones, which accumulate over time to form high-quality resin. This slow process makes natural agarwood increasingly rare []. Thus, research efforts have been directed toward the large-scale production of agarwood through artificial means.
1.2. Challenges in Authenticating and Manufacturing Agarwood
Resin quality is key to agarwood authenticity. However, to the best of our knowledge, no standardized system is available for grading resin quality. DNA barcoding and related molecular tools are essential for accurately differentiating species with overlapping morphology, ensuring product authenticity, and reducing adulteration. Standardization is difficult to achieve because quality depends on fragrance, wood density, and resin content, which vary across batches. They provide a scientific basis for quality standardization, support conservation and regulatory efforts, and enable early species verification to prevent financial loss from cultivating non-resin-producing plants. Natural agarwood can be accurately differentiated from synthetic agarwood only with the help of sophisticated and inaccessible procedures such as spectroscopy or DNA analysis []. Resin production through artificial stimulation of cultivated trees remains challenging. Stressors such as physical injury or fungal inoculation do not guarantee the production of high-quality resin []. Even under stress, not all trees produce agarwood, making large-scale production challenging. Resin yield and quality vary depending on climate, tree genetics, and induction technique [].
The market for agarwood and its derivatives, particularly agarwood oil, is substantial, with top-grade products commanding prices higher than that of gold []. Authenticity certification not only preserves market integrity but also ensures fair-trade and consumer protection [].
The trade of agarwood is governed by various legal frameworks aimed at protecting consumers and ensuring ethical sourcing []. Ethical sourcing of agarwood not only supports local communities involved in its production but also adheres to international conservation efforts []. Advances in chemical analysis and DNA profiling techniques are necessary for accurate authentication of the origin, species, and quality of agarwood []. Furthermore, improvements in inoculation strategies and other resin induction methods are essential for ensuring reliable and sustainable agarwood production. Overcoming these obstacles in agarwood production requires balancing technology, ecofriendly cultivation, and quality control [].
2. Species Authentication and DNA Barcoding Technology
The identification of Aquilaria spp. is a complex and laborious process. First, samples from different places are gathered to determine the primary morphological traits of a given species, especially species common to China, Malaysia, and Southeast Asia. Morphological, anatomical, and genetic methods are used to identify Aquilaria sp., from which agarwood is derived []. The morphological identification of a plant species relies on the characteristics of its fruit as well as its size and leaves. An anatomical assessment of the plant’s cellular organization and resin ducts is also required. Molecular approaches such as DNA barcoding on the basis of specific gene sections—for example, maturase K (matK), ribulose−1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit (rbcL), or internal transcribed spacer—have been used to accurately differentiate between species []. With the current development of molecular and bioinformatics tools, DNA barcoding of agarwood (Aquilaria and Gyrinops spp.) can reliably provide information on species identification and authentication. The most commonly used loci for agarwood authentication are matK, rbcL, ITS, and trnH–psbA, which have proven discriminatory power in differentiating closely related Aquilaria species (e.g., A. malaccensis, A. crassna, A. sinensis) that are often morphologically similar. DNA barcoding is commonly used across various taxonomic levels (Figure 1) []. A study focusing on IUCN Red-listed Aquilaria species evaluated five DNA barcode loci—ITS, matK, psbA-trnH, rbcL, and trnL-trnF—both individually and in various combinations. The findings demonstrated that the combination of ITS2, psbA-trnH, and matK provided 100% species-level discrimination, whereas individual loci showed lower accuracy, ranging from 60% to 85% []. DNA identification of agarwood species is crucial for accurately and rapidly determining the correct variety. First, only genuine agarwood trees can produce resin, making it essential to confirm whether the tree belongs to the agarwood species. Second, identifying the exact variety is also important. Although there is a certain correlation between the species of agarwood and the quality of its aroma, the relationship is not absolute, as aroma quality can be influenced by external environmental factors and is also subject to individual perception. Nevertheless, it is undeniable that non-agarwood trees will not produce agarwood resin. Advanced techniques such as super-barcoding and meta-barcoding offer improved accuracy in identifying species at lower taxonomic levels but are mainly used to confirm results from standard single- or multilocus barcoding. Mini-barcoding is increasingly preferred for analyzing degraded DNA samples, allowing broader application in plant identification. Chemical profiling of sesquiterpenes is another technique occasionally used to differentiate between species with similar exterior traits [].
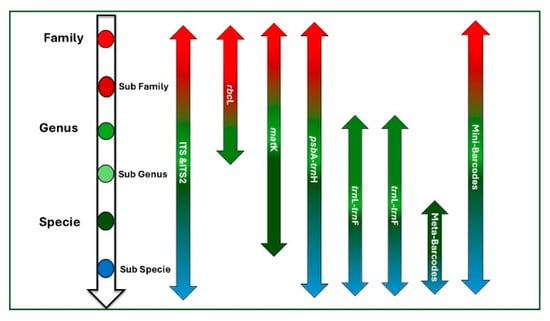
Figure 1.
Taxonomic resolution of common plant DNA barcodes from family to subspecies level. Figure inspired by [] and created by the authors.
3. Identification of Aquilaria sp.
Aquilaria sp. are identified through sequence analysis, genetic distance calculation, and phylogenetic tree construction. BLAST (version 2.17.0) is commonly used to align sequences and validate matches against the GenBank database. The TaxonDNA software (v.1.10) is used to calculate the rate of species identification, whereas the Figtree (version 1.4.3) and R (version 4.0.0) software are used to visualize and refine the construction of phylogenetic trees. DNA barcoding is a vital tool for species identification, conservation, quality control, research, and legal compliance [,].
In DNA barcoding, a short, species-specific genetic sequence is used to differentiate between plant species. This technique is widely used for taxonomic and forensic analyses, medicinal plant verification, and endangered species authentication []. It is extensively used for identifying Aquilaria. Standardized DNA segments are used in DNA barcoding for rapid and accurate species identification []. Although DNA barcoding is essential for distinguishing one Aquilaria sp. from another, different barcode regions may be required for different materials. DNA barcoding enhances identification accuracy when combined with traditional methods and used on appropriately collected samples. Standard methods cannot be used to trace the species origin of resinous products, but barcode sequences can help identify the source species of commercially sold agarwood []. Reported that Aquilaria sinensis was closely related to Aquilaria yunnanensis when chloroplast DNA barcodes were used and to Aquilaria crassna when both nuclear and chloroplast barcodes were used. In Southeast Asia, Aquilaria malaccensis is the primary source of premium agarwood. Thus, reliable tracking and authentication are required for this species []. DNA barcoding, based on DNA regions such as matK and rbcL, in chloroplast DNA can be used to effectively identify agarwood species.
Molecular markers, such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms and simple sequence repeats, can aid in agarwood species identification []. Generated DNA sequences are compared with reference databases or phylogenetic trees to accurately determine the species or variety []. DNA barcoding enables the determination of taxonomic position, supports efforts toward species conservation, and facilitates the authentication of agarwood in the market. Furthermore, it ensures sustainable use and protection of agarwood resources while preventing the exploitation of endangered species.
4. Assessment of Agarwood Authenticity
Agarwood’s distinct scent and traits are attributable to resinous chemicals, particularly sesquiterpenes and chromones, whose quantity and composition determine the quality of the wood []. Agarwood from different Aquilaria species and different geographic origins can vary significantly in value, uses, and market demand. These differences are mainly due to variations in resin composition, aroma profile, and cultural preferences, which directly affect grading and pricing. Resin accumulates as the tree responds to infection, with higher-quality agarwood containing more resin. Factors such as location, fungal species, and soil strongly influence resin production, affecting the quality, scent, and market value of the agarwood []. Accurate authentication of agarwood resin now combines traditional analyses with modern technologies. Recent advances in chemical profiling, AI, and machine vision have enhanced precision and objectivity. Table 1 summarizes these methods, key principles, findings, and applications. Characteristic chemicals in agarwood, identified through liquid extraction surface analysis (LESA)–mass spectrometry (MS), include 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones (m/z 319.1), which can facilitate the rapid identification of agarwood []. LESA–MS can effectively analyze agarwood samples from various sources. The distinct woody scent of agarwood results from sesquiterpenes, such as eudesmane and agarofuran. Chromones, particularly 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones, imbue agarwood with fruity, sweet, and balsamic notes. Phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, enhance the stability and durability of resin by affecting its oxidative characteristics [,]. Higher-quality agarwood has a more complex and potent chemical composition, which affects its grade and market value [].
Essential oil fragrances are identified using electronic sensors or by a human evaluator through sensory evaluations []. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are emerging tools in agarwood research for species identification, resin detection, and quality assessment. Deep learning segmentation has been used to detect resin zones in cross-sectional images and guide computer numerical control (CNC) machines in automatically removing resin []. ML-based machine vision can help identify resinous parts of an agarwood tree. Additionally, ML techniques can be applied to data obtained through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography (GC)–MS to classify agarwood species and predict resin quality; this approach facilitates a rapid and objective phytochemical analysis. Electronic sensors, such as electronic tongues or noses, enable objective, reproducible measurements of fragrance (Table 1). Both sensor-based and ML-based methods are crucial for determining the quality of essential oils [].

Table 1.
Overview of scientific and AI-based techniques used in the authentication and quality assessment of agarwood resin.
Table 1.
Overview of scientific and AI-based techniques used in the authentication and quality assessment of agarwood resin.
| Method/Technique | Key Factor | Findings | Implications for Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical analysis | Phloem | Presence of resin in phloem [] | Non-chemical, microscopic test for identifying fake or resin-coated wood |
| Deep learning segmentation method | Segmentation of cross-sectional images; control of a CNC machine with G-code script | Automated CNC-guided resin removal through accurate resin boundary detection [] | Machine vision method for identifying genuine resinous parts |
| Metabolite profiling through GC–MS and LC–MS | Discrimination between wild agarwood and cultivated agarwood | Difference in biochemical signature between wild agarwood and cultivated agarwood [] | Chemical fingerprinting for authenticating origin |
| Artificial neural networks for oil grading | Use of artificial neural networks to process data on chemical profiles | High accuracy in classification across five oil grades [,] | AI-assisted grading for greater objectivity |
| LESA–MS | Rapid surface authentication | Non-invasive chemical evaluation [] | Verification of resin authenticity |
5. Natural Versus Induced Agarwood Production
Agarwood resin forms near wounds or rotting sections of trees in response to stressors such as lightning, fire, insects, or microbes. It rarely develops in young, healthy trees and is scarce even in older ones, with yields of only 1–2%. The resin takes 25–30 years to form naturally in the roots, stems, or branches, which makes it a highly valuable product [].
The demand for agarwood has outstripped the pace at which agarwood naturally regenerates in forests. The defense mechanism of Aquilaria is triggered to stop additional harm in the face of stressors. This results in the formation of secondary metabolites such as sesquiterpenes and 2-(2-phenylmethyl) chromone compounds. These compounds accumulate over the years to form agarwood []. Agarwood forms when Aquilaria trees respond to fungal infection or injury. To accelerate this slow natural process, artificial methods such as wounding, chemical treatment, and fungal inoculation are used; these methods are more sustainable than wild harvesting [].
6. Artificial Induction Techniques
Agarwood can be artificially produced by inducing resin formation through fungal inoculation (e.g., Fusarium sp.) or by physically wounding the Aquilaria tree []. Fungal induction boosts agarwood yield but risks infection by pathogens. Physical methods (drilling and girdling) rely on the tree’s natural defenses, but the outcomes of these methods are less predictable []. Chemical induction carries the risks of pollution, tree damage, and toxicity. A safer alternative is fungal inoculation, which mimics natural infection without harmful effects. In a relevant study, Aquilaria trees were infected with Xylaria sp. for 2 months to induce agarwood production []. After 6 months of inoculation, Lasiodiplodia theobromae boosted the production of agarwood in healthy Aquilaria trees. Fungal inoculation–induced agarwood yields high-quality essential oils rich in sesquiterpenes and is highly similar to natural agarwood in terms of chemical and antimicrobial properties. The required fungi are easy to cultivate and can produce consistent results in a sustainable manner []. Fusarium solani is highly effective in inducing high resin yields. Trichoderma harzianum is another frequently used species, recognized for its dual role in inducing resin production and suppressing pathogen infection. Lasiodiplodia theobromae, commonly associated with naturally infected agarwood trees, induces localized necrosis, which prompts oleoresin secretion. Other genera such as Penicillium and Aspergillus can also induce resin production, but their effectiveness varies depending on the strain and tree species. These fungi stimulate the tree’s natural defense response, leading to the biosynthesis of aromatic resin components [].
Agarwood quality depends on the fungal strain used, but endophytic fungi often lead to low yields and thus have limited commercial viability. Nonetheless, the resin resulting from fungal infection is similar to natural resin []. Artificial agarwood production is challenging and expensive because induction techniques can kill or severely damage the tree. Plant hormones such as jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid(SA) activate defense pathways, mimicking biotic stress. Ethephon, a synthetic chemical that releases ethylene gas, is widely used in plantations for its ability to efficiently induce a stress response. Other compounds such as hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid, and sulfuric acid induce oxidative or chemical stress to initiate resin production. Mild chemical stressors such as fermented sugar solutions (e.g., molasses mixed with yeast) are sometimes used to increase the effectiveness of fungal inoculation [].
An ideal solution should balance efficiency, tree health, and high-quality resin output []. Non-traditional induction techniques, such as injecting trunks with solvents containing ions or microbial additions or those containing ions but no microbial additions, are often used to produce agarwood []. These techniques are easier to use and more accessible than traditional ones but may yield inconsistent outcomes in terms of resin output and quality. Furthermore, their misuse can damage or even kill the trees. Numerous tools and techniques have recently been developed for inducing agarwood production—for example, the whole-tree agarwood inducing technique (Agar-Wit), a biological induction technique (Agar-Bit), and the cultured agarwood kit (CA-kit) []. The CA-kit infuses an inducing agent into a wound with the help of an aeration device, thereby combining physical wounding with chemical induction. Although high-quality agarwood is produced using this kit, its environmental and public health implications remain unclear.
Figure 2 depicts the induction process involved in transforming healthy agarwood trees into resinous agarwood through both artificial and conventional means.
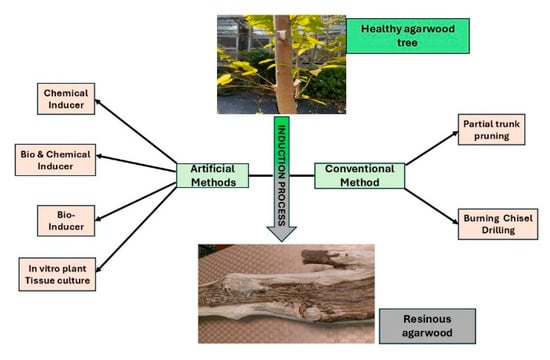
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of artificial and conventional methods used for agarwood resin induction.
7. Advances in Resin Induction Techniques
Organic farming, chemical induction, biological inducers, and controlled inoculation are modern methods for producing agarwood []. Controlled fungal inoculation—inserting specific fungi into drilled holes in Aquilaria trees—reduces resin formation time from decades to just a few years. Chemical inducers such as ethylene and methyl jasmonate are often combined with fungal methods to accelerate resin production []. These approaches enable large-scale agarwood production in environment-friendly plantations, guaranteeing a consistent supply while protecting wild populations and meeting the demands of the incense and perfume industries.
Accounting for technological advances, we extend Table 1 to present a more thorough overview and comparison of current induction methods, pharmaceutical studies, and their future evolution in Table 2.

Table 2.
Fungal induction versus physical induction.
8. The State of the Art and Future Prospects
The use of agarwood is most common in East Asia and the Middle East []. Recent research on agarwood production techniques has focused on improving sustainability, efficiency, and resin quality. Modern inoculation techniques and mindful forestry management are being incorporated into sustainable planting practices to facilitate large-scale agarwood production without overexploiting native tree populations. Traceability and certification are also becoming crucial to maintaining industry standards on ethics and sustainability. Sustainable agarwood production is imperative to avoid the overharvesting of wild Aquilaria species. Biotechnology offers effective solutions by enabling in vitro propagation (e.g., tissue culture) for cultivating plants without damaging natural populations []. In the future, synthetic biology and metabolic engineering can be combined to produce resin compounds in microbial systems, reducing the pressure on natural agarwood resources.
The manufacturing process of agarwood is expected to become even more efficient with the use of precision agriculture and AI. AI-powered models (Table 1) may be used to track and forecast the ideal circumstances for resin production, and precision agriculture can guarantee that every tree receives the appropriate care required for optimal resin yield []. Agarwood manufacturing may become a sustainable sector if environment-friendly processing techniques and sustainable harvesting technology are developed.
9. Chemical Composition and Quality Evaluation
Sesquiterpenes and chromones are the primary chemical components of agarwood. This class of terpenes has the chemical formula C15H24 and comprises three isoprene units. Sesquiterpenes constitute the majority of the chemical composition of agarwood, which greatly enhances its scent as shown in Table 3 []. Structurally, these compounds can be classified as alcohol, ketones, aldehydes, and hydrocarbons on the basis of functional groups present. On the basis of molecular structure, the sesquiterpenes found in agarwood can be classified as follows: candinanes, guaianes, eudesmanes, agarospiranes, agarofurans, and prezizanes [].
Advanced analytical techniques such as GC–MS have been used to identify sesquiterpenes in agarwood. Among the most well-known sesquiterpenes is α-guaiene; it is the most prevalent sesquiterpene in agarwood. This bicyclic compound has a woody and spicy scent []. Another key sesquiterpene is β-caryophyllene, which is known for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It has a spicy, woody scent. Agarospirol is a characteristic sesquiterpene alcohol that provides agarwood with its distinct, nuanced fragrance []. Selinene, found in α and β forms, has been associated with the woody, fresh scent of agarwood [].
Agarwood also contains chromones at considerable levels. These compounds are produced by a few plant species, such as Aquilaria spp., Eremophila georgei, and Bothriochloa ischaemum (Gramineae) []. The 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromone derivatives that agarwood are renowned for have been found in approximately 40 types of agarwood. On the basis of their molecular skeleton, chromones can be divided into 5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydro-2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones, diepoxy-tetrahydro-2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones, and related chromones []. Chromones vary considerably across species. To extract and isolate the monomers in agarwood extracts—often ethanol extracts—researchers studying chromones use various techniques, such as nuclear magnetic resonance and liquid chromatography (LC)–MS, which facilitate the identification of the chromone structures [].
Agarwood’s scent changes according to its quality. The scent of premium agarwood is usually earthy, sweet, and woody with a rich and long-lasting fragrance. However, low-quality agarwood may have faint or overpowering notes or even an overly pungent smell. Olfactory analysis, a sensory assessment method, can yield a qualitative profile of the fragrance. A small sample of agarwood is burned in traditional methods of evaluation. High-quality agarwood burns slowly and produces rich, fragrant smoke; by contrast, low-quality agarwood produces light smoke with a mild fragrance []. The gradual release of aromatic compounds after burning indicates the purity and richness of the resin. The defense system of the tree influences the development of resin, and resin that is left longer to grow has a richer scent. Thus, older agarwood tends to have a stronger, more pleasant scent, which raises its grade [].
Agarwood’s essential oils are intricate blends of volatile substances, such as monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, and aromatic substances, such as phenyl ethyl chromones. The composition of essential oils varies depending on plant species, tree age, and extraction technique. Both traditional medicine and perfumery hold these oils in great regard. Steam distillation is the most common technique for extracting essential oils from agarwood; however, other techniques such as solvent extraction and supercritical fluid extraction are also used. GC–MS is commonly used to investigate the essential oil and chemical composition of agarwood. The main ingredients of agarwood essential oils are α-guaiene and β-caryophyllene; these compounds are the main sources of the oil’s scent. Jinkoh-eremol and agarospirol are oxygenated sesquiterpenes that provide premium agarwood oil with its characteristic rich, woody, and deep scent []. Notably, 2-(2-Phenylethyl) chromones enhance the aromatic richness of essential oils by conferring a flowery and pleasant scent [].
Researchers exploring the metabolite profiles of agarwood have indicated metabolites such as 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones as key aromatic compounds []. Techniques such as LC–MS and nuclear magnetic resonance facilitate chromone profiling. Three main chromones have been identified thus far: tetrahydro-2-(2-phenylethyl), epoxy (2-phenylethyl), and diepoxy-(2-phenylethyl) chromones []. Chromones and sesquiterpenes markedly contribute to the aromatic and medicinal properties of agarwood. The chromone content in agarwood varies throughout the production process. Higher-quality agarwood is characterized by higher contents of 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones []. The primary compounds in agarwood—sesquiterpenes and chromones—are categorized by their molecular structures and the plant species they originate from (Figure 3). Sesquiterpenes identified from different agarwood species are listed in Table 2 [].
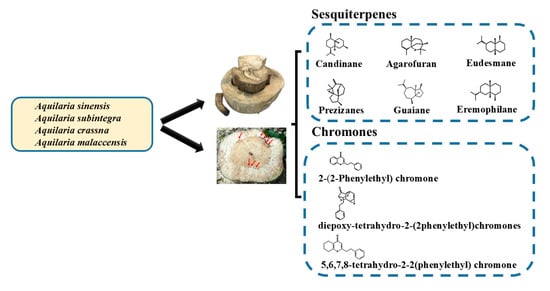
Figure 3.
Primary compounds in agarwood (sesquiterpenes and chromones) and their molecular skeletons.

Table 3.
Sesquiterpenes are from different agarwood species.
Table 3.
Sesquiterpenes are from different agarwood species.
| Sesquiterpenes | A. sinensis | A. subintegra | A. crassna | A. malaccensis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Agarofurans | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| α-Agarofuran | + [] | --- | + [] | + [] |
| Dihydro-β-agarofuran | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Epoxy-β-agarofuran | + [] | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Baimuxinol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Isobaimuxinol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Dehydrobaimuxinol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Baimuxifuranic acid | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Nor-keto-agarofuran | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| 4-Hydroxyl-baimuxinol | + [] | ---- | ----- | ---- |
| Agarospiranes | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Isoagarospirol | ----- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Oxo-agarospirol (baimuxinal) | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Baimuxinic acid (Bai Mu Xiang acid) | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Acorenone B | ---- | + [] | + [] | ---- |
| 4-epi-15-Hydroxyacorenone | + [] | + [,] | + [,] | ---- |
| 4-epi-10-Hydroxyacoronene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 15-Hydroxyacorenone | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Eudesmanes | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| (5S,7S,10S)-()-Selina-3,11-dien-9-on | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Agarol (11(13)-eudesmen-12-ol) | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Selina-3,11-dien-14-ol | ---- | + [] | + [] | ---- |
| Isolongifolene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Eudesmol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Copaen-11-ol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| β-Eudesmol | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| g-Selinene | + + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| d-Selinene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Copaene-8-ol 43 | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| β-Maaliene 36 | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| β-Eudesmol acetate | ---- | + [] | + [] | ---- |
| α-Selinene | + [] | ---- | + [,] | ---- |
| Eudesm-7(11)-en-4a-ol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Eremophilanes | + [] | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| (+ )-(4S,5R)-Dihydrokaranone | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Dehydro-jinkoh-eremol | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Calarene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 7b-H-9(10)-ene-11,12- poxy-8-oxoeremophilane | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 11-Hydroxy-valenc-1(10)-en-2-one | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Ligudicin C | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| (+)-11-Hydroxyvalenc-1(10),8-dien-2-one | + [] | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Valencene | + [] | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Nootkatone | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Guaianes | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| α-Bulnesene | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| (-)-Epoxyguai-11-ene (epoxybulnesene) | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| (-)-Guaia-1(10),11-dien-15-ol | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| (-)-Guaia-1(10),11-dien-15-al | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| (-)-Guaia-1(10),11-diene-15-carboxylic acid | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Rotundone | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Sinenofuranol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Sinenofuranal | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Viridifloorol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Ledol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Longifolene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Aromadendrene | ---- | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Guaiol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Chamaejasmone | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Chamaejasmone | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Candinanes | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Gmelofuran | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| (7b,8b,9b)-8,9-Epoxycalamenen-10-one | ---- | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Prezizanes | ---- | ---- | ---- | + l [] |
| Jinkohol | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Daphnauranol B | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Daphnauranol C | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Daphnauranol D | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Others | ||||
| Patchoulialcohol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| (+)-8b-Hydroxy-longicamphenylone | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Valerenol | ---- | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Valerenic acid | + [] | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Valerenal | + [] | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| Dihydro-neoclovene | ---- | ---- | + [] | ---- |
| 2,6-Dimethyl-10-methylene-12-oxatricyclo tridec-2-ene 2 | + [,] | ---- | ----- | ---- |
| β-Elemene | ---- | + [] | + [] | ---- |
| α-Bisabolol acetate | ---- | + [] | ---- | ---- |
| α-Caryophyllene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Humulene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Humulene diepoxide A | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Kobusone | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Santalol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| (E)-Nerolidol | ---- | + [] | + [] | + [] |
| Caryophyllenol-II | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Caryophylleneoxide | + [] | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Baldrina | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| α-Muurolene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Elemol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| cis-Z-α-Bisabolene epoxide | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Cubenol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 1,2,5,5,8 α-Pentamethyl-1,2,3,5,6,7,8,8 α -octahydronaphthalen-1-ol | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 1,5,9-Trimethyl-1,5,9-cyclododecatriene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| Aquilanol A | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| Aquilanol B | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| 12-Hydroxyhumula-2Z,6E,9E-triene | ---- | ---- | ---- | + [] |
| 14-Hydroxy-α-humulene | + [] | ---- | ---- | ---- |
10. Exploration of Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Agarwood Production
Effective agarwood manufacturing requires an understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways involved in resin production. Plant metabolomics has been extensively used to assess dynamic changes in metabolites across species, tissues, and developmental stages. In Rhodiola imbricata, RNA-seq-based molecular bioprospecting techniques are used to identify regulatory genes and explain how variations in biosynthetic gene expression profiles influence metabolite content []. Combined analysis of transcriptomic and metabolic data may reveal functional genes as well as primary and secondary metabolic pathways in plants [,].
Metabolomic analyses are performed to identify key secondary metabolites essential for the distinct scent of agarwood—for example, chromones and sesquiterpenes. These analyses unveil the biosynthetic pathways induced by stressors such as fungal infection and mechanical damage, as illustrated in Figure 4. Stress signals such as pathogen attack or mechanical injury are perceived by plant receptors, activating downstream signaling cascades. NADPH oxidase triggers the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), while calcium influx via Ca2+–calmodulin complexes further amplifies defense responses. These signals stimulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, leading to salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA) pathway activation, as well as programmed cell death (PCD). The interplay of JA, SA, and ethylene (ET) signaling regulates transcription factors such as WRKY, MYB, and MYC, which bind to cis-regulatory elements of terpene biosynthesis genes. Activation of mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways plays a central role in sesquiterpene biosynthesis, involving key enzymes such as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) []. Studies have shown that sesquiterpene synthase genes like ASS1 and ASS2 are upregulated in response to mechanical wounding and fungal infection, which are commonly used methods to induce agarwood formation []. Additionally, transcription factors such as WRKY, MYC2, and bHLH are known to regulate gene expression under stress conditions that lead to resin accumulation. These responses are often mediated by signal transduction pathways involving JA and SA, which activate genes involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis [,].
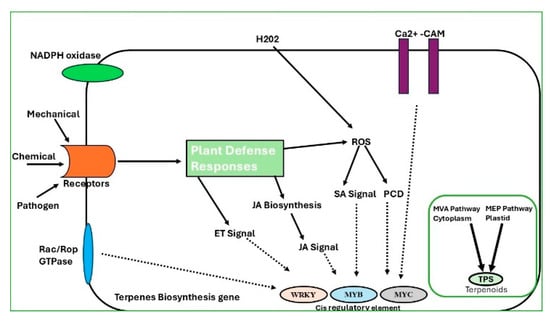
Figure 4.
Overview of plant defense signaling pathways regulating terpene biosynthesis. Pathogen or mechanical stimuli activate receptors, triggering ROS, JA, SA, and ET signaling. Transcription factors (WRKY, MYB, and MYC) regulate terpene biosynthetic genes via MVA and MEP pathways, leading to terpenoid production.
A study [] performed transcriptomic and metabolic analyses of six tissue types (root, stem, leaf, seed, husk, and callus) from A. sinensis to evaluate their potential as alternatives in agarwood cultivation. GC–MS performed in the aforementioned study revealed 331 distinct metabolites, with terpenoids being the most prevalent group (22.89%). Sesquiterpenes constituted 51% of the total terpenoid content. Notably, most sesquiterpenes were detected in callus tissue []. The biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes and terpenoids from agarwood leaf–derived callus tissue is illustrated in Figure 5. This figure depicts the process from leaf to callus induction and presents the major classes of compounds. The figure was prepared on the basis of original experimental data from our laboratory. The highest variability in metabolite content was observed in the husk and callus tissues. RNA-seq data production genes involved in sesquiterpene production were markedly enriched, particularly in the callus tissue. The aforementioned study revealed similar transcriptional profiles between the roots and stems and highlighted a predominance of sesquiterpene synthase genes in callus tissue (60%). These results offer valuable insights into sesquiterpene production and may guide the search for alternative agarwood sources [].
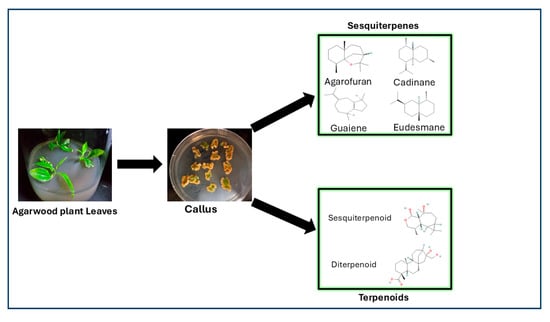
Figure 5.
Production of sesquiterpenes and terpenoids from agarwood callus.
The integrated approach opens new avenues for synthetic biology applications and sustainable production techniques, which may reduce the reliance on natural agarwood sources and thus support conservation efforts.
11. Pharmacological Properties
Agarwood essential oil has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, anti-asthmatic, anti-convulsive, and analgesic properties, which make it valuable for use in pharmaceutical as mentioned in Table 4. Evidence suggests that agarwood essential oil holds promise in the treatment of prostate, pancreas, breast, and colorectal cancers []. Agarwood was demonstrated to exert hepatoprotective effects in a mouse model of chemically induced liver injury [].
Most pharmacological applications of agarwood remain confined to traditional medicine systems, particularly Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Ayurveda, and Unani []. Within these systems, agarwood has been used for centuries to manage a variety of ailments, including asthma, digestive disorders, pain, and anxiety.
To date, no agarwood-based pharmaceuticals have been approved as registered drugs by major international regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA). However, in several Asian countries—notably China, Japan, Korea, and parts of Southeast Asia—agarwood is used as an active ingredient in registered herbal formulations or licensed traditional medicine preparations [].
For example, in China, agarwood (沉香, Chen Xiang) is officially listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia [] and is included in formulations for treating gastrointestinal conditions and inducing sedation. In Japan, agarwood is used in Jinkō-To aimed at treating digestive discomfort and qi stagnation. Similarly, in Malaysia and Indonesia, agarwood extracts are available as over-the-counter herbal supplements and essential oils, regulated by local traditional medicine authorities []. A major limitation on the medical application of agarwood lies in its high cost and limited availability. Agarwood resin forms slowly and unpredictably, and even with artificial induction, yields remain low. These factors hinder large-scale production, standardization, and cost-effective development for modern medicine.

Table 4.
Agarwood’s bioactive compounds and their potential therapeutic applications.
Table 4.
Agarwood’s bioactive compounds and their potential therapeutic applications.
| Property | Aquilaria Species | Key Findings | Mechanism/Active Compounds | Potential Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedative and anxiolytic | A.malaccensisA. sinensis | Modulates central nervous system activity and reduces stress and insomnia | GABAergic interaction; sesquiterpenes (agarospirol and jinkoh-eremol) | Anxiety and sleep disorders |
| Analgesic and anti-inflammatory | A.crassna A.malaccensis | Alleviates pain and inflammation in animal models | Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 []; various compounds (linalool, 10-epi-γ-eudesmol, and agarospirol) [,] | Arthritis [] and inflammatory conditions |
| Antioxidative | A.sinensisA. agallocha | Scavenge free radicals [] and prevents oxidative damage | Phenolic compounds and DPPH radical reduction | Oxidative stress-related diseases |
| Antimicrobial | A.agallocha | Effective against bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli) and fungi (e.g., Candida albicans) [] | Baimuxinol, agarospirol, and essential oils | Bacterial/fungal infections [] |
| Antidiabetic | A.malaccensis | Reduces blood glucose level and improves insulin sensitivity [] | Iriflophenone 3-C-β-glucoside and ethanol/methanol extracts | Diabetes management [] |
| Anticancer | A.crassna | Inhibits angiogenesis and induces apoptosis in cancer cells | β-caryophyllene [] and phenanthrene derivatives | Adjunct cancer therapy [] |
Table 3 presents key bioactive compounds present in agarwood and their potential therapeutic applications. Preclinical studies have indicated various pharmacological benefits of Aquilaria. The diversity of bioactive compounds in agarwood highlights its potential for exerting multitarget effects. In the future, well-designed pharmacokinetic studies should be conducted to investigate dose–response relationships. Moreover, human trials should be conducted to validate the safety and efficacy of agarwood’s bioactive compounds.
12. Agarwood Extract: Variability, Contaminants, and Regulatory Challenges
Agarwood extract is a highly valuable ingredient in traditional medicine, fragrance, and incense. It is extracted from the resinous wood of the Aquilaria spp. The chemical composition of agarwood extract, as well as corresponding biological activity and possible toxicity, varies depending on the plant species, agarwood origin, and extraction technique. Agarwood contains phenolic chemicals, several sesquiterpenes, and other bioactive compounds that can be toxicologically hazardous when ingested in high amounts [,]. The risk of adulteration cannot be ignored because unlicensed harvesting and agarwood processing may lead to contamination by heavy metals, synthetic compounds, or other plant elements. The lack of international standards limits efforts to ensure the safety of agarwood extracts. Despite centuries of traditional use, few solutions for the aforementioned problems are available. Thus, agarwood products should be used sparingly, particularly when consumed or administered topically. Agarwood consumption should not be a substitute for consultation with a health-care professional, especially if the individual has a medical history or is on other drugs [].
13. Key Insights from Major Studies
Agarwood formation is a complex biochemical process induced by biotic and abiotic stressors, which activate the secondary metabolism of the plant and lead to the production of key aromatic compounds such as sesquiterpenes and 2-(2-phenylethyl) chromones. Despite advances in artificial induction techniques—for example, physical wounding, fungal inoculation, and chemical elicitation—the quality, yield, and consistency of resin production remain variable and highly dependent on genetic, environmental, and methodological factors. Tools such as the CA-kit and Agar-Bit are major steps forward, but their long-term ecological impact requires further assessment.
Ensuring the authenticity and traceability of agarwood products is another critical challenge. The lack of standardized grading systems and the prevalence of synthetic or adulterated products have compromised consumer trust and fair-trade practices. DNA barcoding and molecular identification methods—focusing on the matK, rbcL, internal transcribed spacer, and trnL-trnF regions—have emerged as effective tools for species authentication. These techniques, particularly when combined with chemical profiling and metabolomics, offer promising solutions for quality control, regulatory compliance, and conservation efforts.
Chemical analysis through GC–MS and LC–MS has accurately identified bioactive compounds, supporting quality assessment and pharmacological exploration. Sesquiterpenes and chromones not only define the aromatic profile of agarwood but also exhibit potent antibacterial, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, hepatoprotective, and anticancer activities. These pharmacological attributes underscore agarwood’s therapeutic potential and justify its inclusion in both traditional and modern pharmacopeias.
Recent advances in transcriptomic and metabolomic studies have deepened our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying resin biosynthesis, particularly the roles of sesquiterpene synthase genes and stress-related pathways. These insights may inform targeted genetic and biotechnological strategies for enhancing resin production in a sustainable manner, thereby expanding agarwood’s availability while reducing pressure on wild plants.
Because of overharvesting, illegal trade, and habitat loss, sustainability is a major concern in agarwood production. This challenge may be overcome by adopting in situ and ex situ conservation, plantation-based cultivation, and agroforestry, which would reduce pressure on wild plant populations. Biotechnological tools, such as microbial or chemical resin induction, tissue culture for mass propagation, and genetic profiling, can enhance yield while protecting biodiversity. Regulatory support through CITES and traceability methods such as DNA barcoding can further promote legal and ethical trade. Together, these strategies can balance the increasing global demand for agarwood with a commitment to long-term environmental sustainability.
14. Conclusions
The future of agarwood production lies at the intersection of sustainable cultivation, molecular authentication, and innovative biological techniques. Continued interdisciplinary research integrating plant biology, chemistry, genomics, and environmental science is essential for optimizing agarwood production, ensuring ethical trade, preserving endangered Aquilaria sp., and realizing the medicinal and commercial potential of this precious natural resources.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26178468/s1.
Author Contributions
M.-K.L. conceptualized the manuscript. A.B. and A.A. wrote the first draft. A.B., A.A. and M.-K.L. reviewed and edited the manuscript. Three authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Council (MOST 111-2320-B-039-023-MY3) and China Medical University (CMU112-MF-52).
Data Availability Statement
All necessary data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MatK | Maturase K |
| Rbcl | ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit |
| ITS | internal transcribed spacer |
| LESA–MS | liquid extraction surface analysis |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| LC | liquid chromatography |
| CA-Kit | culture agarwood kit |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| TDFs | transcript-deprived fragments |
| GABA | gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| TrnL-trnF | RNA leucine-transfer RNA phenylalamine |
| ML | machine learning |
| CNC | computer numerical record |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| JA | jasmonic acid |
| SA | salicyclic acid |
| ROS | relative oxygen species |
| MVA | mevalonate |
| MEP | methylerythritol phosphate |
References
- Ma, S.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, P.; Liu, Z. The formation and quality evaluation of agarwood induced by the fungi in Aquilaria sinensis. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 173, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, M.J. The Agar Wood Industry: Yet to Utilize in Bangladesh. Int. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. Effects of various artificial agarwood-induction techniques on the metabolome of Aquilaria sinensis. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, Y.Z.; Phirdaous, A.; Azura, A. Screening of anticancer activity from agarwood essential oil. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 6, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Mohamed, R. The Origin and Domestication of Aquilaria, an Important Agarwood-Producing Genus; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Temporal characteristics of agarwood formation in Aquilaria sinensis after applying whole-tree agarwood-inducing technique. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.R.; Li, W.; Luo, S.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.H.; Liu, S.X. GC-MS Study of the Chemical Components of Different Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilgorgans and Agarwood from Different Asian Countries. Molecules 2018, 23, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, J. A Review of Quality Assessment and Grading for Agarwood. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.M.W.A.I.; Jinendra, B.M.S. Design, Development and Performance Evaluation of Pneumatic Type Agarwood Inoculum Injector (PAII). J. Agro-Technol. Rural Sci. 2024, 3, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Agricultural, P.; Council, R.; Pakistan, I. Boosting up the economy of Pakistan through agarwood production. Int. J. Hortic. Food Sci. 2020, 2, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.D.; Lim, T.; Turjaman, M. Expensive, Exploited and Endangered: A Review of the Agarwood-Producing Genera Aquilaria and Gyrinops: CITES Considerations, Trade Patterns, Conservation, and Management; ITTO Technical Series; International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO): Yokohama, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.M. Regulatory and quality issues with the essential oils supply chain. ACS Symp. Ser. 2016, 1218, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Isa, N.M.; Ismail, I.; Zainal, Z. Agarwood Induction: Current Developments and Future Perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Wong, T.H.; Liu, K.Y.E.; Tsang, H.L.R.; Lau, D.T.W. 3D documentation and classification of incense tree Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng. wounds by photogrammetry and its potential conservation applications. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, T.W.J.; Stephen, I.; Wombwell, E.; Fisher, M.C. The Amphibian trade: Bans or best practice? Ecohealth 2009, 6, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakansing, S.M.; Sahri, M.H.; Liew, K.C. Wood Anatomical Structure of Aquilaria malaccensis Associated with Agarwood Occurrence and the Uses of Agarwood. In Prospects and Utilization of Tropical Plantation Trees; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 179–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulik, M.; Jura-Morawiec, J. An arrangement of secretory cells involved in the formation and storage of resin in tracheid-based secondary xylem of arborescent plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1268643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Dai, J.; Gao, X. DNA barcoding: An efficient technology to authenticate plant species of traditional Chinese medicine and recent advances. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitikornpong, W.; Palanuvej, C.; Ruangrungsi, N. DNA barcoding for authentication of the endangered plants in genus Aquilaria. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 42, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadacek, F. Secondary metabolites as plant traits: Current assessment and future perspectives. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2002, 21, 273–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Wong, W.Y.; Koo, C.; Tien, W.P.; Yeo, G.; Rajarethinam, J.; Tan, E.; Chiang, S.; Chong, C.S.; Tan, C.H.; et al. Transient transmission of Chikungunya virus in Singapore exemplifies successful mitigation of severe epidemics in a vulnerable population. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 110, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishamuddin, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Syazwan, S.A.; Ramlee, S.I.; Lamasudin, D.U.; Mohamed, R. Highly divergent regions in the complete plastome sequences of Aquilaria are suitable for DNA barcoding applications including identifying species origin of agarwood products. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsiou, S.; Madesis, P.; Vasdekis, E.; Montemurro, C.; Grigoriou, M.E.; Skavdis, G.; Moussis, V.; Koutelidakis, A.E.; Tzakos, A.G. DNA Barcoding as a Plant Identification Method. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y. Molecular identification of Aquilaria species with distribution records in China using DNA barcode technology. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, Y.Z.H.Y.; Kerr, P.G.; Abbas, P.; Salleh, H.M. Aquilaria spp. (agarwood) as source of health beneficial compounds: A review of traditional use, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 331–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Du, R.; Wu, K.; Chen, J. Development of SSR markers related to agarwood production and genetic diversity of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng wild populations. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2024, 42, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarza, P.; Richter, M.; Peplies, J.; Euzeby, J.; Amann, R.; Schleifer, K.H.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O.; Rosselló-Móra, R. The All-Species Living Tree project: A 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 31, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, R.; Kaushik, N. A review of chemistry, quality and analysis of infected agarwood tree (Aquilaria sp.). Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 1045–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D. The Cultural Biography of Agarwood—Perfumery in Eastern Asia and the Asian Neighbourhood1. J. R. Asiat. Soc. 2013, 23, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Rapid authentication of agarwood by using liquid extraction surface analysis mass spectrometry (LESA-MS). Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Janitha, P.K.; Wanasundara, P.D. Phenolic antioxidants. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 32, 67–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Xie, A.; Wei, J. Resinous included phloem as a key indicator of authentic or fake agarwood. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlı, A.N.M.; Yusof, S.; Bhuyar, P.; Amınan, A.W.; Tajuddın, S.N. Fungi mediated agarwood (A. malaccensis) production and their pharmaceutical applications: A systematic review. Int. J. Plant Based Pharm. 2022, 2, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ni, C.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. A novel data fusion strategy based on multiple intelligent sensory technologies and its application in the quality evaluation of Jinhua dry-cured hams. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipiny, I.; Abdullah, J.; Bolhassan, N.A. Image-based Agarwood Resinous Area Segmentation using Deep Learning. April 2024. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.05129 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Martinez-Velasco, J.D.; Filomena-Ambrosio, A.; Garzón-Castro, C.L. Technological tools for the measurement of sensory characteristics in food: A review. F1000Research 2023, 12, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Qi, L.; Zhong, F.; Li, N.; Ma, Y. An integrated chemical characterization based on FT-NIR, GC–MS and LC-MS for the comparative metabolite profiling of wild and cultivated agarwood. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1188, 123056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Taib, M.N.; Ali, N.A.M.; Jamil, M.; Tajuddin, S.N. Application of ANN in agarwood oil grade classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 10th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, CSPA, Langkawi, Malaysia, 1–2 March 2024; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.L.; Yang, D.L.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.L.; Zeng, Y.B.; Guo, Z.K.; Dong, W.H.; Li, W.; Dai, H.F. Characterization and Determination of 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromones in Agarwood by GC-MS. Molecules 2013, 18, 12324–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiang-Zhao, M.; Ran, J.; Gao, M.; Li, N.X.; Ma, Y.M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Fusarium oxysporum infection-induced formation of agarwood (FOIFA): A rapid and efficient method for inducing the production of high quality agarwood. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chi, X.; Huang, L. Agarwood wound locations provide insight into the association between fungal diversity and volatile compounds in Aquilaria sinensis. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanand, P.; Arbie, N.F.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Ahmad, N. Agarwood—The Fragrant Molecules of a Wounded Tree. Molecules 2022, 27, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.Q.; Chen, H.Q.; Liu, Y.J. Production of high-quality agarwood in Aquilaria sinensis trees via whole-tree agarwood-induction technology. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.-Y.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Zhang, X.; Dai, D.-Q.; Mapook, A.; Suwannarach, N.; Xu, J.-C.; Stephenson, S.L.; Elgorban, A.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.; et al. Endophytic Fungi Associated with Aquilaria sinensis (Agarwood) from China Show Antagonism against Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, M.; Feng, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y. 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromones increase in Aquilaria sinensis with the formation of agarwood. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1437105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; Meng, H.; Chen, W.; Feng, J.; Gan, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Whole-tree Agarwood-Inducing Technique: An Efficient Novel Technique for Producing High-Quality Agarwood in Cultivated Aquilaria sinensis Trees. Molecules 2013, 18, 3086–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, L. Characteristic quality analysis for biologically induced agarwood columns in Aquilaria sinensis. Env. Res. 2023, 235, 116633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, G. Chemical Profiles of Cultivated Agarwood Induced by Different Techniques. Molecules 2019, 24, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, X.; Zas, R.; Sampedro, L. Methyl jasmonate as chemical elicitor of induced responses and anti-herbivory resistance in young conifer trees. In Plant Defence: Biological Control; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, A.; Martín, J.A.; López, R.; Sanz, A.; Gil, L. Effect of four tapping methods on anatomical traits and resin yield in Maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 86, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J. Isolation and screening of fungi for enhanced agarwood formation in Aquilaria sinensis trees. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, X.; Cui, Z.; Hong, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Hu, H.; Xu, D. Anatomical, chemical and endophytic fungal diversity of a Qi-Nan clone of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng with different induction times. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1320226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sui, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J. Agarwood Formation Induced by Fermentation Liquid of Lasiodiplodia theobromae, the Dominating Fungus in Wounded Wood of Aquilaria sinensis. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, H.; Kaushik, N. Fungal and bacterial diversity isolated from Aquilaria malaccensis tree and soil, induces agarospirol formation within 3 months after artificial infection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangareswari@Nagajothi, M.; Parthiban, K.T.; Kanna, S.U.; Karthiba, L.; Saravanakumar, D. Fungal Microbes Associated with Agarwood Formation. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vaan, M.D.; Eikelder, M.L.T.; Jozwiak, M.; Palmer, K.R.; Davies-Tuck, M.; Bloemenkamp, K.W.; Mol, B.W.J.; Boulvain, M. Mechanical methods for induction of labour. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD001233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, F.O.P.; Hamelin, R.C. Current state of genetically modified plant impact on target and non-target fungi. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 441–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sampson, A.; Page, T. History of Use and Trade of Agarwood. Econ. Bot. 2018, 72, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashant, S.P.; Bhawana, M. An update on biotechnological intervention mediated by plant tissue culture to boost secondary metabolite production in medicinal and aromatic plants. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ng, D.W.H.; Park, H.S.; McAlpine, M.C. 3D-printed multifunctional materials enabled by artificial-intelligence-assisted fabrication technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 6, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyita, A.; Sari, R.M.; Astuti, A.D.; Yasir, B.; Rumata, N.R.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Simal-Gandara, J. Terpenes and terpenoids as main bioactive compounds of essential oils, their roles in human health and potential application as natural food preservatives. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Meng, H.; Gao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Overview of sesquiterpenes and chromones of agarwood originating from four main species of the genus Aquilaria. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4113–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Yamagata, E.; Yoneda, K.; Nagashima, T.; Kawasaki, I.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, H.; Miura, I. Three fragrant sesquiterpenes of agarwood. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2066–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeta, Y.; Ito, M. Characterization of delta-guaiene synthases from cultured cells of Aquilaria, responsible for the formation of the sesquiterpenes in agarwood. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.-L.; Dong, W.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, J.-Z.; Wang, H.; Mei, W.-L.; Dai, H.-F. The Characteristic Fragrant Sesquiterpenes and 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromones in Wild and Cultivated ‘Qi-Nan’ Agarwood. Molecules 2021, 26, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pripdeevech, P.; Khummueng, W.; Park, S.K. Identification of odor-active components of agarwood essential oils from thailand by solid phase microextraction-GC/MS and GC-O. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2011, 23, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Mei, W.-L.; Dong, W.-H.; Gai, C.-J.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.-P.; Dai, H.-F. 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromone Derivatives of Agarwood Originating from Gyrinops salicifolia. Molecules 2016, 21, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Han, X.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Simultaneous determination of multiple active 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone analogues in agarwood by HPLC, QAMS, and UPLC-MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2021, 32, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ador, M.A.H.; Farabi, F.; Ahmed, R.; Khatun, R.; Haque, M.M.U. Agar (Aquilaria agallocha Roxb.) based small-scale enterprises in Bangladesh: Management, production, marketing and role in socio-economic development. Trees For. People 2021, 6, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.-G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.-F.; Song, X.-Q.; Zhu, G.-P.; Hu, X.-W. Dynamic accumulation of sesquiterpenes in essential oil of Pogostemon cablin. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2014, 24, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okugawa, H.; Ueda, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Kawanishi, K.; Kato, A. Effect of jinkoh-eremol and agarospirol from agarwood on the central nervous system in mice. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Mei, W.L.; Kong, F.D.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.Z.; Dai, H.F. 5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones from artificial agarwood of Aquilaria sinensis and their inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase. Phytochemistry 2017, 139, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.-L.; Dong, W.-H.; Li, W.; Wang, P.; Cao, X.; Yuan, J.-Z.; Chen, H.-Q.; Mei, W.-L.; Dai, H.-F. Sesquiterpenoids and 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones respectively acting as α-glucosidase and tyrosinase inhibitors from agarwood of an Aquilaria plant. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Wu, Y.; Tong, R. Asymmetric total syntheses of sarglamides A, C, D, E, and F. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 12856–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chung, M.-I.; Sung, P.-J.; Shu, C.-W.; Cheng, M.-J.; Chen, J.-J. New Flavones, a 2-(2-Phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Derivative, and Anti-Inflammatory Constituents from the Stem Barks of Aquilaria sinensis. Molecules 2015, 20, 20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monggoot, S.; Kulsing, C.; Wong, Y.F.; Pripdeevech, P. Incubation of Aquilaria subintegra with Microbial Culture Supernatants Enhances Production of Volatile Compounds and Improves Quality of Agarwood Oil. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Peng, K.; Tan, L.H.; Dai, H.F. Aquilarin A, a New Benzenoid Derivative from the Fresh Stem of Aquilaria sinensis. Molecules 2010, 15, 4011–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büchi, G.; Wittenau, M.S.V.; White, D.M. Terpenes. X.1, 2 The Constitution of Maaliol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 1968–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quli, S.M.S. Biodiversity conservation: Analysis of problems & extension strategy for securing people’s participation. Adv. For. Res. India 2000, 22, 24–50. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xing, C.; Zhao, L.; Chan, K.; Lu, G. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Li, J.; Gu, Y.-F.; Huo, H.-X.; Li, S.-S.; Song, Y.-L.; Zhu, Z.-X.; Tu, P.-F. GYF-21, an Epoxide 2-(2-Phenethyl)-Chromone Derivative, Suppresses Innate and Adaptive Immunity via Inhibiting STAT1/3 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näf, R.; Velluz, A.; Brauchli, R.; Thommen, W. Agarwood oil (Aquilaria agallocha Roxb.). Its composition and eight new valencane-, eremophilane-and vetispirane-derivatives. Flavour Fragr. J. 1995, 10, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-H.; Wang, H.; Guo, F.-J.; Mei, W.-L.; Chen, H.-Q.; Kong, F.-D.; Li, W.; Zhou, K.-B.; Dai, H.-F. Three New 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromone Derivatives of Agarwood Originated from Gyrinops salicifolia. Molecules 2019, 24, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Kitahara, T.; Mori, K. Stereocontrolled synthesis of (-)-prezizanol,(-)-prezizaene, their epimers and (-)-allokhusiol. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Peng, Q.; Han, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Three New Sesquiterpenoids and One New Sesquiterpenoid Derivative from Chinese Eaglewood. Molecules 2016, 21, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.-L.; Zeng, Y.-B.; Wu, J.; Cui, H.-B.; Dai, H.-F. Chemical composition and anti-MRSA activity of the essential oil from Chinese eaglewood. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 17, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Perng, M.H.; Chen, C.Y. The antioxidation and antiproliferation activity of flavonoids from aquilaria agallocha and Aquilaria sinensis. Biomed. Res. 2018, 29, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guxasekera, S.P.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Cordell, G.A.; Farnsworth, N.R. Plant anticancer agents. XIX Constituents of Aquilaria malaccensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W. Spasmolytic activity of Aquilariae Lignum Resinatum extract on gastrointestinal motility involves muscarinic receptors, calcium channels and NO release. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. Comparison of Compositions and Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oils from Chemically Stimulated Agarwood, Wild Agarwood and Healthy Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg Trees. Molecules 2011, 16, 4884–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebayo, M.A.; Lawal, O.A.; Sikiru, A.A.; Ogunwande, I.A.; Avoseh, O.N. Chemical Constituents and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oil of Senna podocarpa (Guill. et Perr.) Lock. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, K.R.; Maheshwari, M.L.; Bhattacharyya, S.C. Terpenoids—LXII: The constitution of agarospirol, a sesquiterpenoid with a new skeleton. Tetrahedron 1965, 21, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, H.; Ito, M.; Shiraki, T.; Yagura, T.; Honda, G. Sedative effects of vapor inhalation of agarwood oil and spikenard extract and identification of their active components. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Chung, M.I.; Chen, J.J. 2-(2-Phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Derivatives from the Resinous Wood of Aquilaria sinensis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects in LPS-Induced Macrophages. Molecules 2018, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornpunyapat, J.; Chetpattananondh, P.; Tongurai, C. Mathematical modeling for extraction of essential oil from Aquilaria crassna by hydrodistillation and quality of agarwood oil. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2011, 6, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, M.; Tsuneya, T.; Shiga, M.; Uneyama, K. Three sesquiterpenes from agarwood. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Rastogi, R.P. Agarol, a new sesquiterpene from Aquilaria agallocha. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 1869–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristanti, A.N.; Tanjung, M.; Aminah, N.S. Review: Secondary Metabolites of Aquilaria, a Thymelaeaceae Genus. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2018, 15, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Dong, W.-H.; Yang, J.-L.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Mei, W.-L.; Dai, H.-F. Monitoring the Chemical Profile in Agarwood Formation within One Year and Speculating on the Biosynthesis of 2-(2-Phenylethyl)Chromones. Molecules 2018, 23, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hussain, M.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Ye, F.; Mao, R.; Li, H. Aquilaria Species (Thymelaeaceae) Distribution, Volatile and Non-Volatile Phytochemicals, Pharmacological Uses, Agarwood Grading System, and Induction Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattan, S.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, E.; Sood, A.; Acharya, V.; Warghat, A.R. Comparative transcriptome and tissue-specific expression analysis of genes reveal tissue-cultured plants as an alternative source for phenylethanoids and phenylpropanoids in Rhodiola imbricata (Edgew.). Gene 2022, 836, 146672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Du, X.; Liang, X.; Han, R.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Blazquez, M.A. Different Roles of the Mevalonate and Methylerythritol Phosphate Pathways in Cell Growth and Tanshinone Production of Salvia miltiorrhiza Hairy Roots. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, B.; Li, M. Biosynthesis and the Transcriptional Regulation of Terpenoids in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlemann, J.K.; Klempien, A.; Dudareva, N. Floral volatiles: From biosynthesis to function. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1936–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, J.; Huang, L. Comparative Analysis of Metabolome and Transcriptome in Different Tissue Sites of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. Molecules 2024, 29, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; He, Q.; Feng, J.; Chen, D.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y. Chemical Composition and Potential Properties in Mental Illness (Anxiety, Depression and Insomnia) of Agarwood Essential Oil: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Mujahid, M.; Badruddeen; Jahan, Y.; Bagga, P.; Rahman, M.A. Hepatoprotective potential of ethanolic extract of Aquilaria agallocha leaves against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in SD rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 7, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Litscher, G.; Gao, S.-H.; Yu, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-Q.; Zhang, S.-F.; Tang, M.-K.; Sun, J.-N.; Ko, K.-M.; Chan, K. Historical Perspective of Traditional Indigenous Medical Practices: The Current Renaissance and Conservation of Herbal Resources. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 525340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Guo, P.; Wei, J. Chemical constituents and pharmacological activity of agarwood and aquilaria plants. Molecules 2018, 23, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, H.Q.; Wang, H.; Mei, W.L.; Dai, H.F. Natural products in agarwood and: Aquilaria plants: Chemistry, biological activities and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 38, 528–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.; Haron, M.N.; Komilus, C.F.; Lananan, F.; Chew, H.H.; Yaakub, N.; Kari, A. Effect of Karas (Aquilaria malaccensis) on Male Reproductive Organs and Sperm Quality in Adult Sprague Dawley Rats. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2023, 34, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, J.; He, M.; Melvin, T.M.; Osborn, T.J.; Briffa, K.R. A 3,500-year tree-ring record of annual precipitation on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2903–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.C.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, W.K.; Ha, J.H.; Gu, M.J.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of Pyeongwisan on LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages and Mouse Models of Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Response and Xylene-Induced Ear Edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Song, X.; Jia, R.; Yin, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, L.; He, C.; Liang, X.; Yue, G.; et al. Evaluation of Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Water Extract of Galla Chinensis In Vivo Models. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 6784032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamil, J.M.R.; Paudel, K.R.; Chan, Y.; Xenaki, D.; Panneerselvam, J.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Jha, N.K.; Kumar, D.; Prasher, P.; et al. Rediscovering the Therapeutic Potential of Agarwood in the Management of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Chiang, W.; Liu, G.-P.; Chien, Y.-L.; Chang, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Lo, J.-M.; Huang, S.-L.; Shih, M.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H. 2,2’-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging active components from adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) hulls. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5850–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils—Present Status and Future Perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamonwannasit, S.; Nantapong, N.; Kumkrai, P.; Luecha, P.; Kupittayanant, S.; Antibacterial, N.C. activity of Aquilaria crassna leaf extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis by disruption of cell wall. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2013, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Ata, A.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Sharopov, F.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Ruiz-Ortega, A.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Kobarfard, F.; Zakaria, Z.A.; et al. Antidiabetic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Active Components. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gong, B.; Peng, D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J. Agarwood extract mitigates alcoholic fatty liver in C57 mice via anti oxidation and anti inflammation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okugawa, H.; Ueda, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Kawanishi, K.; Kato, K. Effects of sesquiterpenoids from ‘Oriental incenses’ on acetic acid-induced writhing and D2 and 5-HT2A receptors in rat brain. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, H.; Basu, P.; Nesari, T.; Huddar, V.G.; Ray, K.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, S.; Mehrotra, R.; Tripathi, R. Therapeutic and pharmacological efficacy of plant-derived bioactive compounds in targeting breast cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2024, 16, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nester, T.M.; Hale, L.D.S. Effectiveness of a pharmacist-acquired medication history in promoting patient safety. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2002, 59, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).