B Cell-Derived and Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains: From Generation to Biological and Pathophysiological Roles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains
2.1. Genomic Organization and Rearrangement of B Cell-Derived FLCs
2.1.1. Gene Structure of B Cell-Derived FLCs
2.1.2. Biased Gene Segment Usage in Health and Disease
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of B Cell-Derived FLCs
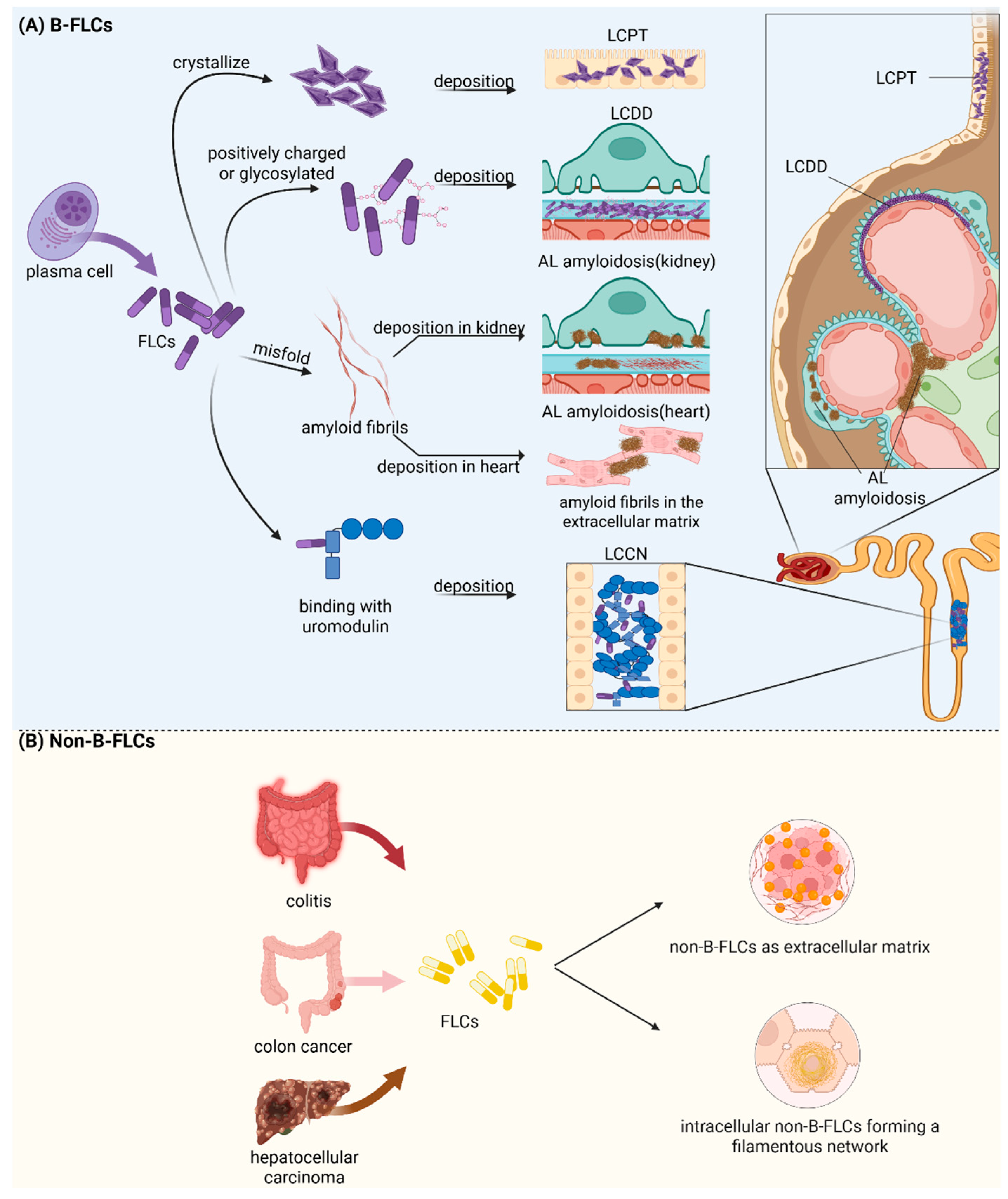
2.3. Biological Functions and Pathogenesis Features of B Cell-Derived FLCs
3. Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains
3.1. Genomic Features of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
3.2. Synthesis Regulation of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
3.3. Physicochemical Properties and Morphological Forms of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
3.4. Biological Functions and Pathogenesis Features of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
3.4.1. Physiological Functions of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
3.4.2. Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs in Inflammation and Inflammation-Mediated Carcinogenesis
3.4.3. Pathological Role of Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs in Malignancies
4. Comparative Analysis of B Cell-Derived FLCs vs. Non-B Cell-Derived FLCs
5. Clinical and Therapeutic Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3′E | 3′ enhancer |
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| ACOX1 | peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 |
| AL amyloidosis | light chain-derived amyloidosis |
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| APO1 | optic atrophy-1 |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis Signal-regulating Kinase 1 |
| Bcl-xL | B cell Lymphoma-extra Large |
| B-FLC | B cell-derived free light chain |
| CAC | Colitis Associated Cancer |
| CDR | complementarity-determining region |
| ConA | concanavalin A |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| CXCL | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| ETFA | Electron Transfer Flavoprotein A |
| FAK/Src | Focal Adhesion Kinase/Src Kinase |
| FcγR | Fc Gamma Receptor |
| FcεR | Fc Epsilon Receptor |
| FLC | Free light chain |
| FS | Fanconi syndrome |
| HC | Heavy chains |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| iE | Intronic enhancer |
| IGK | Immunoglobulin κ light-chain locus |
| IGL | Immunoglobulin λ light-chain locus |
| JAK-STAT | Janus Kinase-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| JRA | Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis |
| LC | Light chains |
| LCCN | Light-chain cast nephropathy |
| LCDD | Light-chain deposition disease |
| LCPT | Light-chain proximal tubulopathy |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| LMP | Latent membrane protein |
| LOX-1 | Lectin-like Oxidized LDL Receptor 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MC | Mast cell |
| MGUS | Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| NAR | Nonallergic rhinitis |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 |
| non-B-FLC | Non-B cell-derived free light chain |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| NP-KLH | 4-Hydroxy-3-nitrophenylacetyl-Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin |
| PCNA | Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen |
| RAG | Recombination-Activating Gene |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RPL7/S3 | Ribosomal Protein L7/S3 |
| RSS | Recombination Signal Sequences |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TNP25-BSA | Trinitrophenyl 25-Bovine Serum Albumin |
References
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fan, T.; Yin, S. The Structure Characteristics and Function of Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulin. In Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulins: The Structure, Characteristics and the Implication on Clinical Medicine; Qiu, X., Huang, J., Xu, X., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 59–71. ISBN 978-981-97-0511-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.B. Some Account of a New Animal Substance Occurring in the Urine of a Patient Labouring under Mollities Ossium. Edinb. Med. Surg. J. 1850, 74, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delman, G.M.; Gally, J.A. The nature of bence-jones proteins: Chemical similarities to polypeptide chains of myeloma globulins and normal γ-globulins. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 116, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.H.; Edelman, G.M. Comparisons of Bence-Jones Proteins and L Polypeptide Chains of Myeloma Globulins after Hydrolysis with Trypsin. J. Exp. Med. 1963, 118, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, D.; Provençal, M.; Gendron, S.; Ratel, D.; Demeule, M.; Gingras, D.; Béliveau, R. Purification and Characterization of a Stimulator of Plasmin Generation from the Antiangiogenic Agent Neovastat: Identification as Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chain. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 431, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.; Waldmann, T.A.; Fahey, J.L.; Mcfarlane, A.S. Metabolism of bence jones proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1964, 43, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wochner, R.D.; Strober, W.; Waldmann, T.A. The Role of the Kidney in the Catabolism of Bence Jones Proteins and Immunoglobulin Fragments. J. Exp. Med. 1967, 126, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V. Multiple Myeloma: 2024 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1802–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, M.J.; Madsen, M.J.; Davis, E.; Garner, C.D.; Curtin, K.; Jones, B.; Williams, J.A.; Tomasson, M.H.; Camp, N.J. Elevated IgM and Abnormal Free Light Chain Ratio Are Increased in Relatives from High-Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Pedigrees. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Sanchorawala, V.; Schönland, S.O.; Palladini, G.; Hawkins, P.N.; Gertz, M.A. Systemic Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Buros, A.; Mathur, P.; Gokden, N.; Singh, M.; Susanibar, S.; Jo Kamimoto, J.; Hoque, S.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Matin, A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors in Multiple Myeloma Patients with Light Chain Deposition Disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Rigante, D.; Stefanile, A.; Gulli, F.; Marino, M.; Basile, V.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Basile, U. Free Light Chains and Autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekeyser, C.; De Kesel, P.; Cambron, M.; Vanopdenbosch, L.; Van Hijfte, L.; Vercammen, M.; Laureys, G. Inter-Assay Diagnostic Accuracy of Cerebrospinal Fluid Kappa Free Light Chains for the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1385231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, I.; Axelsson, M.; Novakova, L.; Malmeström, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Lycke, J. Intrathecal Kappa Free Light Chain Synthesis Is Associated with Worse Prognosis in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 4800–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levraut, M.; Laurent-Chabalier, S.; Ayrignac, X.; Bigaut, K.; Rival, M.; Squalli, S.; Zéphir, H.; Alberto, T.; Pekar, J.-D.; Ciron, J.; et al. Kappa Free Light Chain Biomarkers Are Efficient for the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilf-Yarkoni, A.; Alkalay, Y.; Brenner, T.; Karni, A. High κ Free Light Chain Is a Potential Biomarker for Double Seronegative and Ocular Myasthenia Gravis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.K.; Alt, F.W.; Yeap, L.-S. Related Mechanisms of Antibody Somatic Hypermutation and Class Switch Recombination. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, L.M.; Schatz, D.G. New Insights into the Evolutionary Origins of the Recombination-Activating Gene Proteins and V(D)J Recombination. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manso, T.; Folch, G.; Giudicelli, V.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Kushwaha, A.; Nguefack Ngoune, V.; Georga, M.; Papadaki, A.; Debbagh, C.; Pégorier, P.; et al. IMGT® Databases, Related Tools and Web Resources through Three Main Axes of Research and Development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1262–D1272. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/50/D1/D1262/6455007?login=false (accessed on 30 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A. Light Chains of Immunoglobulins: Structural-Genetic Correlates. Blood 1986, 68, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Zachau, H.G. Expression and Hypermutation of Human Immunoglobulin Kappa Genes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 764, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatovich, O.; Tomlinson, I.M.; Jones, P.T.; Winter, G. The Creation of Diversity in the Human Immunoglobulin Vλ Repertoire. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 268, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farner, N.L.; Dörner, T.; Lipsky, P.E. Molecular Mechanisms and Selection Influence the Generation of the Human V Lambda J Lambda Repertoire. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuisinier, A.M.; Fumoux, F.; Moinier, D.; Boubli, L.; Guigou, V.; Milili, M.; Schiff, C.; Fougereau, M.; Tonnelle, C. Rapid Expansion of Human Immunoglobulin Repertoire (VH, V Kappa, V Lambda) Expressed in Early Fetal Bone Marrow. New Biol. 1990, 2, 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoi, H.; Naito, K.; Ohno, R.; Saito, H.; Naoe, T. Characterization of the Immunoglobulin Light Chain Variable Region Gene Expressed in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 1998, 12, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kosmas, C.; Viniou, N.; Stamato Poulos, K.; Courtenay-Luck, N.S.; Papadaki, T.; Kollia, P.; Paterakis, G.; Anagnostou, D.; Yataganas, X.; Loukopoulos, D. Analysis of the κ Light Chain Variable Region in Multiple Myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 94, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahota, S.S.; Leo, R.; Hamblin, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K. Myeloma VL and VH Gene Sequences Reveal a Complementary Imprint of Antigen Selection in Tumor Cells. Blood 1997, 89, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, V.; Palladini, G.; Casarini, S.; Navazza, V.; Rognoni, P.; Obici, L.; Invernizzi, R.; Perlini, S.; Klersy, C.; Merlini, G. The Repertoire of λ Light Chains Causing Predominant Amyloid Heart Involvement and Identification of a Preferentially Involved Germline Gene, IGLV1-44. Blood 2012, 119, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourelis, T.V.; Dasari, S.; Theis, J.D.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Kurtin, P.J.; Gertz, M.A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Zenka, R.M.; Dogan, A.; Dispenzieri, A. Clarifying Immunoglobulin Gene Usage in Systemic and Localized Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Amyloidosis by Mass Spectrometry. Blood 2017, 129, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comenzo, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Martinez, C.; Osman, K.; Herrera, G.A. The Tropism of Organ Involvement in Primary Systemic Amyloidosis: Contributions of Ig VL Germ Line Gene Use and Clonal Plasma Cell Burden. Blood 2001, 98, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevone, A.; Girelli, M.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Paiva, B.; Milani, P.; Cascino, P.; Piscitelli, M.; Speranzini, V.; Cartia, C.S.; Benvenuti, P.; et al. An N-Glycosylation Hotspot in Immunoglobulin κ Light Chains Is Associated with AL Amyloidosis. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletten, K.; Natvig, J.B.; Husby, G.; Juul, J. The Complete Amino Acid Sequence of a Prototype Immunoglobulin-Lambda Light-Chain-Type Amyloid-Fibril Protein AR. Biochem. J. 1981, 195, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, A.; Khamlichi, A.A.; Aucouturier, P.; Noël, L.H.; Denoroy, L.; Preud’homme, J.L.; Cogné, M. Primary Structure of a Variable Region of the V Kappa I Subgroup (ISE) in Light Chain Deposition Disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 91, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, V.; Stoppini, M.; Merlini, G.; Zapponi, M.C.; Meloni, M.L.; Banfi, G.; Ferri, G. Amino Acid Sequence of k Sci, the Bence Jones Protein Isolated from a Patient with Light Chain Deposition Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 1991, 1097, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Structure of a Monoclonal Kappa Chain of the V Kappa IV Subgroup in the Kidney and Plasma Cells in Light Chain Deposition Disease. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1904072/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Morbach, H.; Richl, P.; Faber, C.; Singh, S.K.; Girschick, H.J. The Kappa Immunoglobulin Light Chain Repertoire of Peripheral Blood B Cells in Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3840–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girschick, H.J.; Grammer, A.C.; Nanki, T.; Vazquez, E.; Lipsky, P.E. Expression of Recombination Activating Genes 1 and 2 in Peripheral B Cells of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurasov, S.; Tiller, T.; Tsuiji, M.; Velinzon, K.; Pascual, V.; Wardemann, H.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Persistent Expression of Autoantibodies in SLE Patients in Remission. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, X. Expression of Immunoglobulin Gene with Classical V-(D)-J Rearrangement in Mouse Testis and Epididymis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shao, W.; Wang, P.; Gong, X.; Ma, J.; Qiu, X.; Wang, B. Immunoglobulin M, a Novel Molecule of Myocardial Cells of Mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 88, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Shi, Q.; Shao, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J. Hepatocyte-Derived Igκ Exerts a Protective Effect against ConA-Induced Acute Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, M.; Sun, X.; He, Z.; Hu, F.; Chen, L.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Qiu, X.; Yin, C. IGK with Conserved IGKappaV/IGKappaJ Repertoire Is Expressed in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Promotes Leukemic Cell Migration. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 39062–39072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Geng, Z.; Chu, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, H.; et al. A Widely Expressed Free Immunoglobulin κ Chain with a Unique Vκ4-1/Jκ3 Pattern Promotes Colon Cancer Invasion and Metastasis by Activating the Integrin Β1/FAK Pathway. Cancer Lett. 2022, 540, 215720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Gu, H.; Yin, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Xian, X.; et al. Hepatocyte-Derived Igκ Promotes HCC Progression by Stabilizing Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Subunit α to Facilitate Fatty Acid β-Oxidation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2024, 43, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Ye, J.; Pan, P.; Cao, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Su, M.; Huang, C.; Gu, J. Immunoglobulin G Is Present in a Wide Variety of Soft Tissue Tumors and Correlates Well with Proliferation Markers and Tumor Grades. Cancer 2010, 116, 1953–1963. Available online: https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/cncr.24892 (accessed on 6 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Leboulleux, M.; Lelongt, B.; Mougenot, B.; Touchard, G.; Makdassi, R.; Rocca, A.; Noel, L.-H.; Ronco, P.M.; Aucouturier, P. Protease Resistance and Binding of Ig Light Chains in Myeloma-Associated Tubulopathies. Kidney Int. 1995, 48, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiaen, T.; Deret, S.; Mougenot, B.; Bridoux, F.; Dequiedt, P.; Dion, J.J.; Makdassi, R.; Meeus, F.; Pourrat, J.; Touchard, G.; et al. Adult Fanconi Syndrome Secondary to Light Chain Gammopathy: Clinicopathologic Heterogeneity and Unusual Features in 11 Patients. Medicine 2000, 79, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, A.; Sirac, C.; Terryn, S.; Javaugue, V.; Prange, J.A.; Bender, S.; Bonaud, A.; Cogné, M.; Aucouturier, P.; Ronco, P.; et al. Impaired Lysosomal Function Underlies Monoclonal Light Chain-Associated Renal Fanconi Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnayake, K.; Stringer, S.J.; Hutchison, C.A.; Cockwell, P. The Biology of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains and Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruccoleri, R.E.; Haber, E.; Novotný, J. Structure of Antibody Hypervariable Loops Reproduced by a Conformational Search Algorithm. Nature 1988, 335, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, I.S.; Bradwell, A.R.; Olson, A.J. Structure, Function and Properties of Antibody Binding Sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 217, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chothia, C.; Lesk, A.M. Canonical Structures for the Hypervariable Regions of Immunoglobulins. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 196, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, B.; Livneh, A.; Sela, B.-A. Immunoglobulin Free Light Chain Dimers in Human Diseases. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 901843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Clark, R.J.; Abraham, R.S.; Bryant, S.; Lymp, J.F.; Bradwell, A.R.; Kyle, R.A. Serum Reference Intervals and Diagnostic Ranges for Free Kappa and Free Lambda Immunoglobulin Light Chains: Relative Sensitivity for Detection of Monoclonal Light Chains. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.; Golderman, S.; Yahalom, G.; Yeskaraev, R.; Ziv, T.; Aizenbud, B.M.; Sela, B.-A.; Livneh, A. Free Light Chain Monomer-Dimer Patterns in the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 390, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, B.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Sikkink, L.; Golderman, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Livneh, A.; Gallo, G. Free Light Chains in Plasma of Patients with Light Chain Amyloidosis and Non-Amyloid Light Chain Deposition Disease. High Proportion and Heterogeneity of Disulfide-Linked Monoclonal Free Light Chains as Pathogenic Features of Amyloid Disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sølling, K.; Sølling, J.; Lanng Nielsen, J. Polymeric Bence Jones Proteins in Serum in Myeloma Patients with Renal Insufficiency. Acta Med. Scand. 1984, 216, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wall, J.S.; Meyer, J.; Murphy, C.; Randolph, T.W.; Manning, M.C.; Solomon, A.; Carpenter, J.F. Thermodynamic Modulation of Light Chain Amyloid Fibril Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimtchuk, E.S.; Gursky, O.; Patel, R.S.; Laporte, K.L.; Connors, L.H.; Skinner, M.; Seldin, D.C. The Critical Role of the Constant Region in Thermal Stability and Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9848–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberti, L.; Rognoni, P.; Barbiroli, A.; Lavatelli, F.; Russo, R.; Maritan, M.; Palladini, G.; Bolognesi, M.; Merlini, G.; Ricagno, S. Concurrent Structural and Biophysical Traits Link with Immunoglobulin Light Chains Amyloid Propensity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deret, S.; Chomilier, J.; Huang, D.B.; Preud’homme, J.L.; Stevens, F.J.; Aucouturier, P. Molecular Modeling of Immunoglobulin Light Chains Implicates Hydrophobic Residues in Non-Amyloid Light Chain Deposition Disease. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1997, 10, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weichman, K.; Dember, L.M.; Prokaeva, T.; Wright, D.G.; Quillen, K.; Rosenzweig, M.; Skinner, M.; Seldin, D.C.; Sanchorawala, V. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Patients with Non-Amyloid Light Chain Deposition Disorders, and Outcome Following Treatment with High-Dose Melphalan and Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2006, 38, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preud’homme, J.-L.; Aucouturier, P.; Touchard, G.; Striker, L.; Khamlichi, A.A.; Rocca, A.; Denoroy, L.; Cogné, M. Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition Disease (Randall Type). Relationship with Structural Abnormalities of Immunoglobulin Chains. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymenis, M.; Stollar, B.D. Domain Interactions and Antigen Binding of Recombinant Anti-Z-DNA Antibody Variable Domains. The Role of Heavy and Light Chains Measured by Surface Plasmon Resonance. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franek, F.; Nezlin, R.S. Recovery of Antibody Combining Activity by Interaction of Different Peptide Chains Isolated from Purified Horse Antitoxins. Folia Microbiol. 1963, 8, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.R.; Weir, R.C. Subunits of Immunoglobulins and Their Relationship to Antibody Specificity. J. Cell Physiol. 1966, 67 (Suppl. S1), 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, M.; Groot Kormelink, T.; Fischer, M.J.; Blokhuis, B.R.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Redegeld, F.A. Antigen Binding Characteristics of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains: Crosslinking by Antigen Is Essential to Induce Allergic Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redegeld, F.A.; Van Der Heijden, M.W.; Kool, M.; Heijdra, B.M.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Loveren, H.V.; Roholl, P.; Saito, T.; Verbeek, J.S.; et al. Immunoglobulin-Free Light Chains Elicit Immediate Hypersensitivity-like Responses. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Haag-Weber, M.; Mai, B.; Deicher, R.; Hörl, W.H. Effect of Immunoglobulin Light Chains from Hemodialysis and Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients on Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Functions. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Rudnicki, M.; Deicher, R.; Hörl, W.H. Immunoglobulin Light Chains Modulate Polymorphonuclear Leucocyte Apoptosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Rudnicki, M.; Hörl, W.H. Uremic Toxins Modulate the Spontaneous Apoptotic Cell Death and Essential Functions of Neutrophils. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, S48–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikura, H.; Endo, J.; Kitakata, H.; Moriyama, H.; Sano, M.; Fukuda, K. Molecular Mechanism of Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies for AL Amyloidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G.; Kumar, S. Systemic Amyloidosis Due to Clonal Plasma Cell Diseases. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 34, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomede, L.; Romeo, M.; Rognoni, P.; Beeg, M.; Foray, C.; Ghibaudi, E.; Palladini, G.; Cherny, R.A.; Verga, L.; Capello, G.L.; et al. Cardiac Light Chain Amyloidosis: The Role of Metal Ions in Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Guan, J.; Jiang, B.; Brenner, D.A.; del Monte, F.; Ward, J.E.; Connors, L.H.; Sawyer, D.B.; Semigran, M.J.; Macgillivray, T.E.; et al. Amyloidogenic Light Chains Induce Cardiomyocyte Contractile Dysfunction and Apoptosis via a Non-Canonical P38α MAPK Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4188–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Mishra, S.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, J.; Trudeau, K.; Las, G.; Liesa, M.; Shirihai, O.S.; Connors, L.H.; Seldin, D.C.; et al. Lysosomal Dysfunction and Impaired Autophagy Underlie the Pathogenesis of Amyloidogenic Light Chain-Mediated Cardiotoxicity. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1493–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.W.; Booker, B.B. Pathobiology of Cast Nephropathy from Human Bence Jones Proteins. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, J.; Teng, J.; Herrera, G.A. AL-Amyloidosis and Light-Chain Deposition Disease Light Chains Induce Divergent Phenotypic Transformations of Human Mesangial Cells. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 1322–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Russell, W.J.; Gu, X.; Cardelli, J.; Jones, M.L.; Herrera, G.A. Different Types of Glomerulopathic Light Chains Interact with Mesangial Cells Using a Common Receptor but Exhibit Different Intracellular Trafficking Patterns. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.J.; Cardelli, J.; Harris, E.; Baier, R.J.; Herrera, G.A. Monoclonal Light Chain–Mesangial Cell Interactions: Early Signaling Events and Subsequent Pathologic Effects. Lab. Investig. 2001, 81, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanders, P.W. Mechanisms of Light Chain Injury along the Tubular Nephron. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.-Z.; Li, X.; Rangarajan, S.; Feng, W.; Curtis, L.M.; Sanders, P.W. Immunoglobulin Light Chains Generate Proinflammatory and Profibrotic Kidney Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.-Z.; Wang, P.-X.; Aaron, K.J.; Basnayake, K.; Sanders, P.W. Immunoglobulin Light Chains Activate Nuclear Factor-κB in Renal Epithelial Cells through a Src-Dependent Mechanism. Blood 2011, 117, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Dannenbring, R.; Matsuura, K.; Tramontano, A.; Gololobov, G.; Paul, S. Monoclonal Antibody Light Chain with Prothrombinase Activity. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6459–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gao, Q.S.; Li, L.; Paul, S. Proteolytic Activity of an Antibody Light Chain. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 5121–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Li, L.; Kalaga, R.; Wilkins-Stevens, P.; Stevens, F.J.; Solomon, A. Natural Catalytic Antibodies: Peptide-Hydrolyzing Activities of Bence Jones Proteins and VL Fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15257–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains and Mast Cells: Pivotal Role in T-Cell-Mediated Immune Reactions? Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12697449/ (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Gao, E.; Shao, W.; Zhang, C.; Yu, M.; Dai, H.; Fan, T.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Lung Epithelial Cells Can Produce Antibodies Participating In Adaptive Humoral Immune Responses. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, D.; Gong, X.; Shao, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W.; Qiu, X. Free Immunoglobulin Light Chain (FLC) Promotes Murine Colitis and Colitis-Associated Colon Carcinogenesis by Activating the Inflammasome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Ding, H.; Ma, J.; Zhong, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Peng, H. Functional Analysis of Tumor-Derived Immunoglobulin Lambda and Its Interacting Proteins in Cervical Cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, L.; Gao, Q.S.; Paul, S. Antigen Recognition by an Antibody Light Chain. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Takahashi, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Kawai, S.; Shinozaki, R.; Komoda, T.; Nagata, A. Antigen-Specific Free Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Antibodies: Could It Be a New Diagnostic Marker for Patients with Allergy? Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, R.G.; Sage, H.J.; Tanford, C. Contributions of Heavy and Light Chains of Rabbit Immunoglobulin G to Antibody Activity. I. Binding Studies on Isolated Heavy and Light Chains. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahana, W.; Jacquemart, F.; Ermonval, M. A Murine Monoclonal Multireactive Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chain. Scand. J. Immunol. 1994, 39, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Simpler Sort of Antibody. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/epdf/10.1073/pnas.91.3.893 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Schechter, I.; Ziv, E. Binding of 2,4-Dinitrophenyl Derivatives by the Light Chain Dimer Obtained from Immunoglobulin A Produced by MOPC-315 Mouse Myeloma. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 2785–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and Mast Cells in Allergic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Association between Neutrophils and Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Available online: https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/epdf/10.1164/rccm.201104-0761OC?role=tab (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Judde, J.G.; Max, E.E. Characterization of the Human Immunoglobulin Kappa Gene 3′ Enhancer: Functional Importance of Three Motifs That Demonstrate B-Cell-Specific in Vivo Footprints. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992, 12, 5206–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Duan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Hu, D.; Li, M.; Tao, Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; Cao, Y. EBV-Encoded LMP1 Upregulates Igκ 3′enhancer Activity and Igκ Expression in Nasopharyngeal Cancer Cells by Activating the Ets-1 through ERKs Signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Duan, Z.; Hu, D.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, M.; et al. LMP1-Augmented Kappa Intron Enhancer Activity Contributes to Upregulation Expression of Ig Kappa Light Chain via NF-kappaB and AP-1 Pathways in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Hu, D.; Tang, M.; Cao, Y. Upregulated Expression of Kappa Light Chain by Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded Latent Membrane Protein 1 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via NF-kappaB and AP-1 Pathways. Cell Signal 2007, 19, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.-Y.; Hu, C.; Prayaga, S.; Khaidakov, M.; Sawamura, T.; Seung, K.-B.; Mehta, J.L. LOX-1 Dependent Overexpression of Immunoglobulins in Cardiomyocytes in Response to Angiotensin II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Min, M.; Bao, J.-K. Induction of Apoptosis by Concanavalin A and Its Molecular Mechanisms in Cancer Cells. Autophagy 2009, 5, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantner, F.; Leist, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Germann, P.G.; Tiegs, G. Concanavalin A-Induced T-Cell-Mediated Hepatic Injury in Mice: The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor. Hepatology 1995, 21, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eifan, A.O.; Durham, S.R. Pathogenesis of Rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powe, D.G.; Groot Kormelink, T.; Sisson, M.; Blokhuis, B.J.; Kramer, M.F.; Jones, N.S.; Redegeld, F.A. Evidence for the Involvement of Free Light Chain Immunoglobulins in Allergic and Nonallergic Rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 139–145.e1-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Sha, J.; Li, L.; An, L.; Zhu, X.; Meng, X.; Zhu, D.; Dong, Z. The Expression and Significance of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chain in the Patients with Allergic Rhinitis and Nonallergic Rhinitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, D.-Y.; Ren, W.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, H.; Tang, M.; Cao, Y. Expression of Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chain Constant Region in Abnormal Human Cervical Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot Kormelink, T.; Powe, D.G.; Kuijpers, S.A.; Abudukelimu, A.; Fens, M.H.A.M.; Pieters, E.H.E.; Kassing van der Ven, W.W.; Habashy, H.O.; Ellis, I.O.; Blokhuis, B.R.; et al. Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains Are Biomarkers of Poor Prognosis in Basal-like Breast Cancer and Are Potential Targets in Tumor-Associated Inflammation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schiffelers, R.M.; Metselaar, J.M.; Fens, M.H.A.M.; Janssen, A.P.C.A.; Molema, G.; Storm, G. Liposome-Encapsulated Prednisolone Phosphate Inhibits Growth of Established Tumors in Mice. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoszuk, M.; Corwin, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Nalcioglu, O.; Su, M.-Y. Inhibition of Thrombosis in Melanoma Allografts in Mice by Endogenous Mast Cell Heparin. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, S.; Freeman, S.; Gold, M.J.; Baker, J.H.E.; Minchinton, A.I.; Gold, M.R.; Roskelley, C.D.; McNagny, K.M. Opposing Roles for CD34 in B16 Melanoma Tumor Growth Alter Early Stage Vasculature and Late Stage Immune Cell Infiltration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-B.; Chen, X.; Wu, B.-Y.; Wang, M.-W.; Cai, C.-H.; Cho, D.-B.; Chong, J.; Li, P.; Tang, S.-G.; Yang, P.-C. Immunoglobulin Kappa and Immunoglobulin Lambda Are Required for Expression of the Anti-Apoptotic Molecule Bcl-xL in Human Colorectal Cancer Tissue. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Kwon, I.-S.; Park, J.; Lee, K.-H.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.Y.; Cho, S.-W.; Ahn, J.-Y. Ribosomal Protein S3, a New Substrate of Akt, Serves as a Signal Mediator between Neuronal Apoptosis and DNA Repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29457–29468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Hardwidge, P.R. Ribosomal Protein S3: A Multifunctional Target of Attaching/Effacing Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, E.; Maaliki, L.; Nasr, Z. Ribosomal Protein S3 Selectively Affects Colon Cancer Growth by Modulating the Levels of P53 and Lactate Dehydrogenase. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6083–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockers, K.; Schneider, R. Histone H1, the Forgotten Histone. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachaturov, V.; Xiao, G.-Q.; Kinoshita, Y.; Unger, P.D.; Burstein, D.E. Histone H1.5, a Novel Prostatic Cancer Marker: An Immunohistochemical Study. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends, M.; Engmann, O. Linker Histone H1.5 Is an Underestimated Factor in Differentiation and Carcinogenesis. Environ. Epigenet. 2020, 6, dvaa013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tani, R.; Nishitani, K.; Tanaka, S. Linker Histone Variant H1T Functions as a Chromatin De-Condenser on Genic Regions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 528, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, G. AL Amyloidosis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Targeted Therapies. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, G.A.; Teng, J.; Turbat-Herrera, E.A.; Zeng, C.; del Pozo-Yauner, L. Understanding Mesangial Pathobiology in AL-Amyloidosis and Monoclonal Ig Light Chain Deposition Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1870–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparvarinha, M.; Nickho, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Majidi, J. The Role of Free Kappa and Lambda Light Chains in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Abraham, R.S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lust, J.A.; Kyle, R.A. Diagnostic Performance of Quantitative κ and λ Free Light Chain Assays in Clinical Practice. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Ying, L.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, M. Serum Free Light Chain Is Associated with Histological Activity and Cirrhosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novel Biomarkers of Inflammation for the Management of Diabetes: Immunoglobulin-Free Light Chains. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/10/3/666 (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Gottenberg, J.-E.; Aucouturier, F.; Goetz, J.; Sordet, C.; Jahn, I.; Busson, M.; Cayuela, J.-M.; Sibilia, J.; Mariette, X. Serum Immunoglobulin Free Light Chain Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarto, C.; Intra, J.; Fania, C.; Brivio, R.; Brambilla, P.; Leoni, V. Monoclonal Free Light Chain Detection and Quantification: Performances and Limits of Available Laboratory Assays. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 95, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradwell, A.R.; Carr-Smith, H.D.; Mead, G.P.; Tang, L.X.; Showell, P.J.; Drayson, M.T.; Drew, R. Highly Sensitive, Automated Immunoassay for Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in Serum and Urine. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, L.; Romiti, N.; Koni, E.; Fiore, A.D.; Paolicchi, A.; Franzini, M. Inter-Assay Variability in Automated Serum Free Light Chain Assays and Their Use in the Clinical Laboratory. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, H.T.; Drayson, M.; Campbell, J.P. Measurement of Free Light Chains with Assays Based on Monoclonal Antibodies. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2016, 54, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, H.V.; Wechalekar, A.; Pratt, G. The Potential Role of Mass Spectrometry for the Identification and Monitoring of Patients with Plasma Cell Disorders: Where Are We Now and Which Questions Remain Unanswered? Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.V.; Rao, N.; Bhutani, D.; Mapara, M.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Shames, S.; Maurer, M.S.; Leng, S.; Solomon, A.; Lentzsch, S.; et al. Phase 1a/b Study of Monoclonal Antibody CAEL-101 (11-1F4) in Patients with AL Amyloidosis. Blood 2021, 138, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Burritt, M.F.; Therneau, T.M.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Lust, J.A.; Rajkumar, S.V.; et al. Serum Cardiac Troponins and N-Terminal pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide: A Staging System for Primary Systemic Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3751–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, M.; Blokhuis, B.R.; Nijkamp, F.P.; Redegeld, F.A. Free Immunoglobulin Light Chains: A Novel Target in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| FLC Origin | Condition | Gene Segment Usage | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-FLCs | Plasma cells | Physiological | IGKV1, IGKV2, IGKV3, IGKV4;IGKJ1, IGKJ2, IGKJ4;IGLV1, IGLV2, IGLV3;IGLJ7 | [20,21,22,23] |
| Multiple Myeloma | IGKV1, IGKV2, IGKV3 | [24,25,26,27] | ||
| Systemic Amyloidosis | IGLV3 (IGVL3-1), IGLV6 (IGLV6-57), IGLV1(IGLV1-44) | [28,29,30,31] | ||
| Light-Chain Deposition Disease | IGKV4 (IGKV4-1), IGKV1(IGKV1-5), IGKV3(IGKV3-11 and IGKV3-15), IGLV2(IGLV2-23 and DPL12) | [32,33,34,35] | ||
| Light-Chain Fanconi Syndrome | IGKV1 | [32,33,34,35] | ||
| Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis | IGKJ1, IGKJ2 | [36,37,38] | ||
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | IGKJ1, IGKJ2 | [36,37,38] | ||
| Non-B-FLCs | Primary spermatocytes(mouse) | Physiological | Igkvbv9/Igkj1, Igkv21-10/Igkj2 | [39] |
| Epididymal epithelial cells(mouse) | Physiological | Igkvbw20/Igkj5 | [39] | |
| Cardiomyocytes(mouse) | Physiological | Igkv17-121, Igkv9-120, Igkv14-100 | [40] | |
| Hepatocytes(mouse) | Physiological | Igkv1-135*01/Igkj1, Igkv12–44*01/Igkj5 | [41] | |
| Myeloblasts | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | IGKV15*03/IGKJ1*01, IGKV1-5*03/IGKJ3*01, IGKV1-NL1*01/IGKJ5*01 | [42] | |
| Carcinoma cells | Lung Cancer, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cervical Cancer | IGKV4-1/IGKJ3 | [43,44] | |
| Sarcoma cells | Fibrosarcoma, Leiomyoma, Rhabdomyosarcoma, Leiomyosarcoma | IGKV3D-20*01; IGKJ1 | [45] |
| FLC Origin | Biological Function | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-FLC | Plasma cells | Contributing to the formation of the antigen-binding region | [64,65,66] |
| Activating mast cells | [67,68] | ||
| Promoting activation and inhibiting the apoptosis of neutrophils | [69,70,71] | ||
| Cardiotoxicity | [10,72,73,74,75,76] | ||
| Renal toxicity | [77,78,79,80,81,82,83] | ||
| Enzymatic activity | [5,84,85,86] | ||
| Non-B-FLC | Nasal mucosal cells (not assured) | Potential interaction with mast cells | [87] |
| Hepatocytes | Protecting hepatocytes | [41] | |
| Lung epithelial cells | Facilitating the secretion of TD-Ag-specific antibodies of lung epithelial cells | [88] | |
| Colon cancer cells | Promoting colon cancer | [43] | |
| Colon cancer cells | Promoting colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis | [89] | |
| Hepatocyte carcinoma cells | Promoting hepatocyte carcinoma | [44] | |
| Cervical cancer cells | Promoting cervical cancer | [90] | |
| Myeloblasts of AML | Promoting acute myelocytic leukemia | [42] | |
| Mesenchymal tumor cells | Correlating with hyperproliferative phenotypes in mesenchymal tumors | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Gu, H.; Qiu, X.; Huang, J. B Cell-Derived and Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains: From Generation to Biological and Pathophysiological Roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157607
Li L, Gu H, Qiu X, Huang J. B Cell-Derived and Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains: From Generation to Biological and Pathophysiological Roles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157607
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Linyang, Huining Gu, Xiaoyan Qiu, and Jing Huang. 2025. "B Cell-Derived and Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains: From Generation to Biological and Pathophysiological Roles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157607
APA StyleLi, L., Gu, H., Qiu, X., & Huang, J. (2025). B Cell-Derived and Non-B Cell-Derived Free Light Chains: From Generation to Biological and Pathophysiological Roles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157607






