Development and Characterization of a Novel α-Synuclein-PEST H4 Cell Line for Enhanced Drug Screening in α-Synucleinopathies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
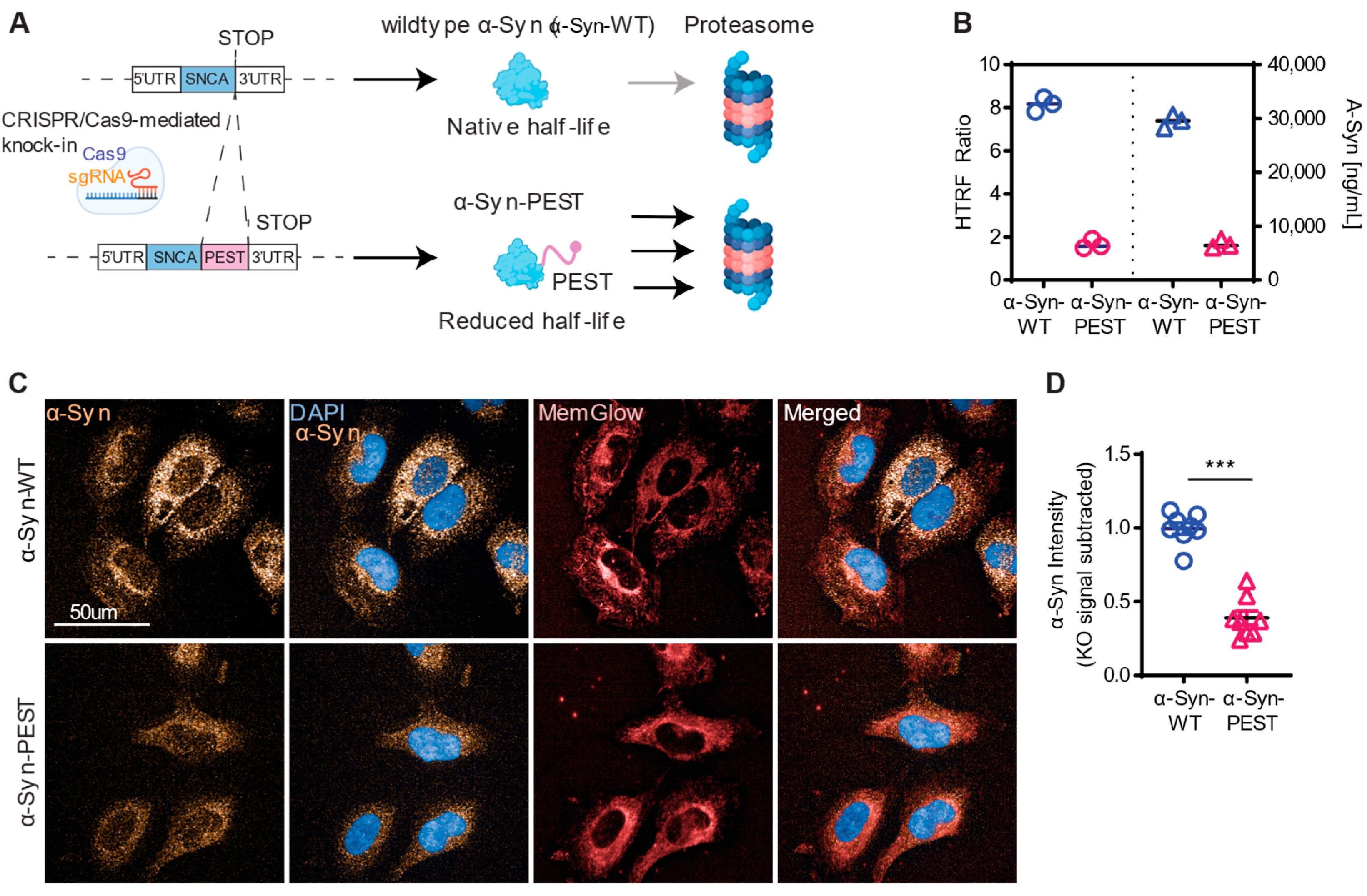
2.1. CRISPR/Cas9-Engineered H4 Cell Line Expressing PEST-Tagged α-Syn
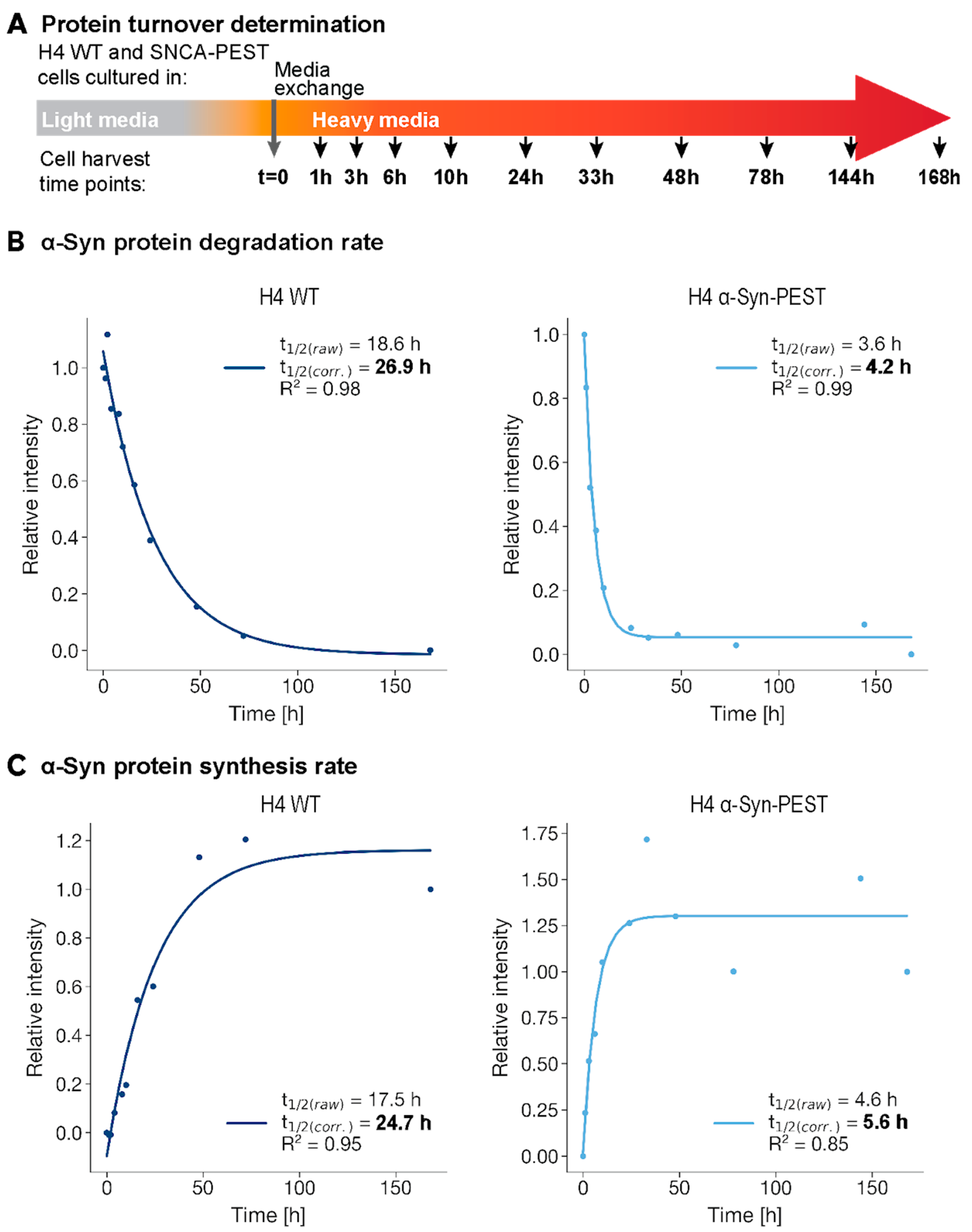
2.2. In Vitro Validation of Rapid α-Syn Protein Turnover
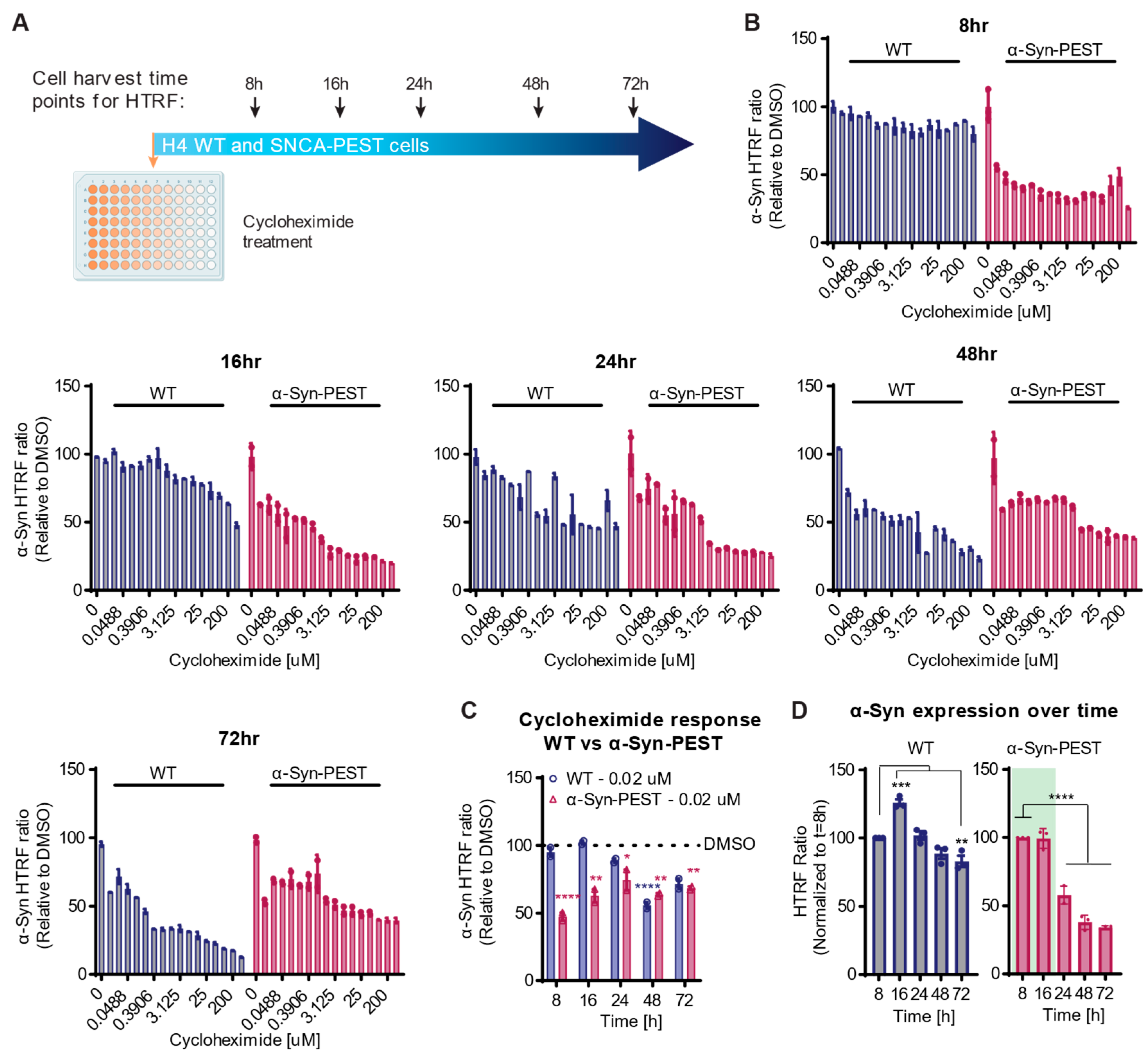
2.3. Evaluating the Effect of Translational Inhibition on Short-Lived α-Syn Expression
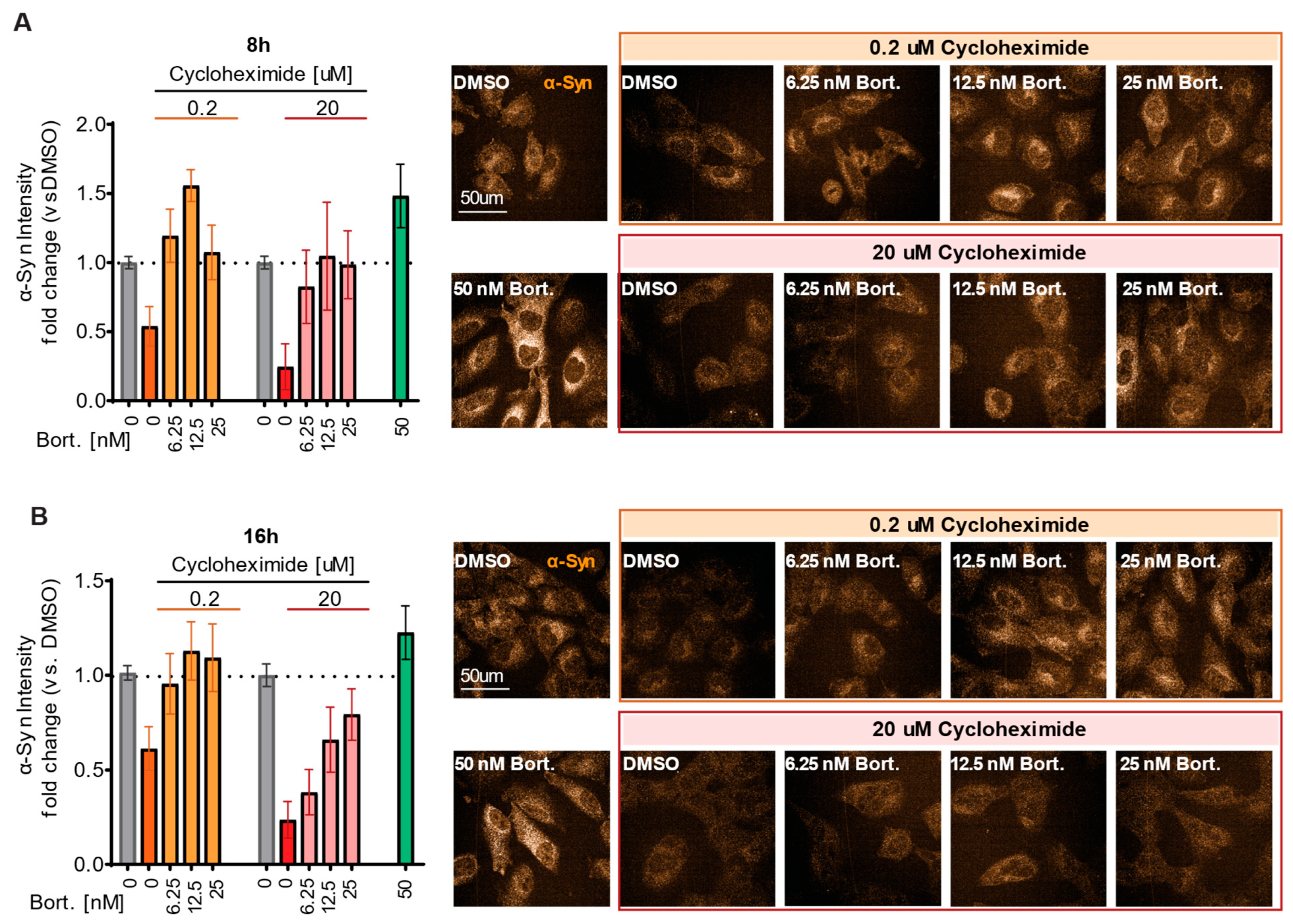
2.4. Detection of Rapid α-Syn Reduction and Rescue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. HTRF Protein Detection Assay
4.3. Protein Half-Life Determination Using SILAC
4.4. Immunocytochemistry
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-Syn | Alpha-Synuclein |
| PEST | Proline, glutamic acid, serine, threonine |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| ICC | Immunocytochemistry |
| α-Syn-PEST | PEST-tagged α-Syn |
| WT | Wild type |
| SILAC | Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino acids in Cell culture |
| bRP | basic reverse-phase |
| HTRF | Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence |
| Bort. | Bortezomib |
| DRB | 5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole |
| Act.D | Actinomycin D |
References
- Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Identification of Two Distinct Synucleins from Human Brain. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, A.; Masliah, E.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ge, N.; Flanagan, L.; de Silva, H.A.R.; Kittel, A.; Saitoh, T. The Precursor Protein of Non-Aβ Component of Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Is a Presynaptic Protein of the Central Nervous System. Neuron 1995, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.; Scheller, R. Synuclein: A Neuron-Specific Protein Localized to the Nucleus and Presynaptic Nerve Terminal. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein Promotes SNARE-Complex Assembly in Vivo and in Vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeliovich, A.; Schmitz, Y.; Fariñas, I.; Choi-Lundberg, D.; Ho, W.-H.; Castillo, P.E.; Shinsky, N.; Verdugo, J.M.G.; Armanini, M.; Ryan, A.; et al. Mice Lacking α-Synuclein Display Functional Deficits in the Nigrostriatal Dopamine System. Neuron 2000, 25, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, K.; Li, D.; Brunger, A.; Li, C.; Burré, J.; Diao, J. α-Synuclein Condensation in Synaptic Vesicle Function and Synucleinopathies. Trends Cell Biol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Qiao, L.; Li, M.; Wen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Global, Regional, National Epidemiology and Trends of Parkinson’s Disease from 1990 to 2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 16, 1498756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Darweesh, S.; Llibre-Guerra, J.; Marras, C.; Luciano, M.S.; Tanner, C. The Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Südhof, T.C. Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalino, E.; Stine, L.B.; Corin, A.J.; Thai, C.-T.; Quiroz, J.; Wilson, S.C.; Labow, M.; Mittal, S. A Novel High-Throughput Screening Strategy for Targeting Alpha-Synuclein and Other Long-Lived Proteins. SLAS Discov. 2022, 27, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macarrón, R.; Hertzberg, R.P. Design and Implementation of High-Throughput Screening Assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 565, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, J.A.; Gomes, A.V. PEST Sequences in Calmodulin-Binding Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1995, 149–150, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechsteiner, M. Regulation of Enzyme Levels by Proteolysis: The Role of Pest Regions. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1988, 27, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechsteiner, M. PEST Sequences Are Signals for Rapid Intracellular Proteolysis. Semin. Cell Biol. 1990, 1, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, M. Functional and Quantitative Proteomics Using SILAC. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Grollman, A.P. Cycloheximide Resistance in Yeast: A Property of the 60s Ribosomal Subunit. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967, 29, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.; Shaw, P.D. Antibiotics: Volume I Mechanism of Action; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783662384398. [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover, A.; Kwon, Y.T. Degradation of Misfolded Proteins in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Therapeutic Targets and Strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truscott, R.J.W.; Schey, K.L.; Friedrich, M.G. Old Proteins in Man: A Field in Its Infancy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, B.H.; Hetzer, M.W. Protein Homeostasis: Live Long, Won’t Prosper. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaud, S.; Malany, S.; Mehta, A.; Vasile, S.; Smith, L.H.; McLean, P.J. Targeting α-Synuclein Oligomers by Protein-Fragment Complementation for Drug Discovery in Synucleinopathies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatti, E.; Khawaja, S.; Weis, K. The Dark Side of Fluorescent Protein Tagging—The Impact of Protein Tags on Biomolecular Condensation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2025, 36, br10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, L.M.; Fossati, M.; Francolini, M.; Snapp, E.L. Assessing the Tendency of Fluorescent Proteins to Oligomerize Under Physiologic Conditions. Traffic 2012, 13, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.Y. β-Naphthoflavone, an Inducer of Xenobiotic Metabolizing Enzymes, Inhibits Firefly Luciferase Activity. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 304, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.M.M.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Firefly Luciferase Inhibition. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, A.J.; Braunschweig, U.; Wu, M.; Farhangmehr, S.; Pasculescu, A.; Lim, J.J.; Comsa, L.C.; Jen, M.; Wang, J.; Datti, A.; et al. High-Throughput Sensitive Screening of Small Molecule Modulators of Microexon Alternative Splicing Using Dual Nano and Firefly Luciferase Reporters. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, A.; Davis, M.I. Interference with Fluorescence and Absorbance; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Masato, A.; Bubacco, L. The ASynuclein Half-Life Conundrum. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 196, 106524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougman, A.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Suspension Trapping (STrap) Sample Preparation Method for Bottom-up Proteomics Analysis. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecha, J.; Satpathy, S.; Kanashova, T.; Avanessian, S.C.; Kane, M.H.; Clauser, K.R.; Mertins, P.; Carr, S.A.; Kuster, B. TMT Labeling for the Masses: A Robust and Cost-Efficient, In-Solution Labeling Approach* [S]. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Zheng, R.; Bayer, F.P.; Wong, C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Meng, C.; Zolg, D.P.; Reinecke, M.; Zecha, J.; Wiechmann, S.; et al. Robust, Reproducible and Quantitative Analysis of Thousands of Proteomes by Micro-Flow LC–MS/MS. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.P. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carullo, N.; Haellman, V.; Gutbier, S.; Schlicht, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Blum Marti, R.; Hartz, P.; Lindemann, L.; Schukur, L. Development and Characterization of a Novel α-Synuclein-PEST H4 Cell Line for Enhanced Drug Screening in α-Synucleinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157205
Carullo N, Haellman V, Gutbier S, Schlicht S, Nguyen TT, Blum Marti R, Hartz P, Lindemann L, Schukur L. Development and Characterization of a Novel α-Synuclein-PEST H4 Cell Line for Enhanced Drug Screening in α-Synucleinopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157205
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarullo, Nancy, Viktor Haellman, Simon Gutbier, Sonja Schlicht, Thien Thuong Nguyen, Rita Blum Marti, Philippe Hartz, Lothar Lindemann, and Lina Schukur. 2025. "Development and Characterization of a Novel α-Synuclein-PEST H4 Cell Line for Enhanced Drug Screening in α-Synucleinopathies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157205
APA StyleCarullo, N., Haellman, V., Gutbier, S., Schlicht, S., Nguyen, T. T., Blum Marti, R., Hartz, P., Lindemann, L., & Schukur, L. (2025). Development and Characterization of a Novel α-Synuclein-PEST H4 Cell Line for Enhanced Drug Screening in α-Synucleinopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157205





