MSTN Regulates Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation via PSMA6-Mediated AKT Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Subsection
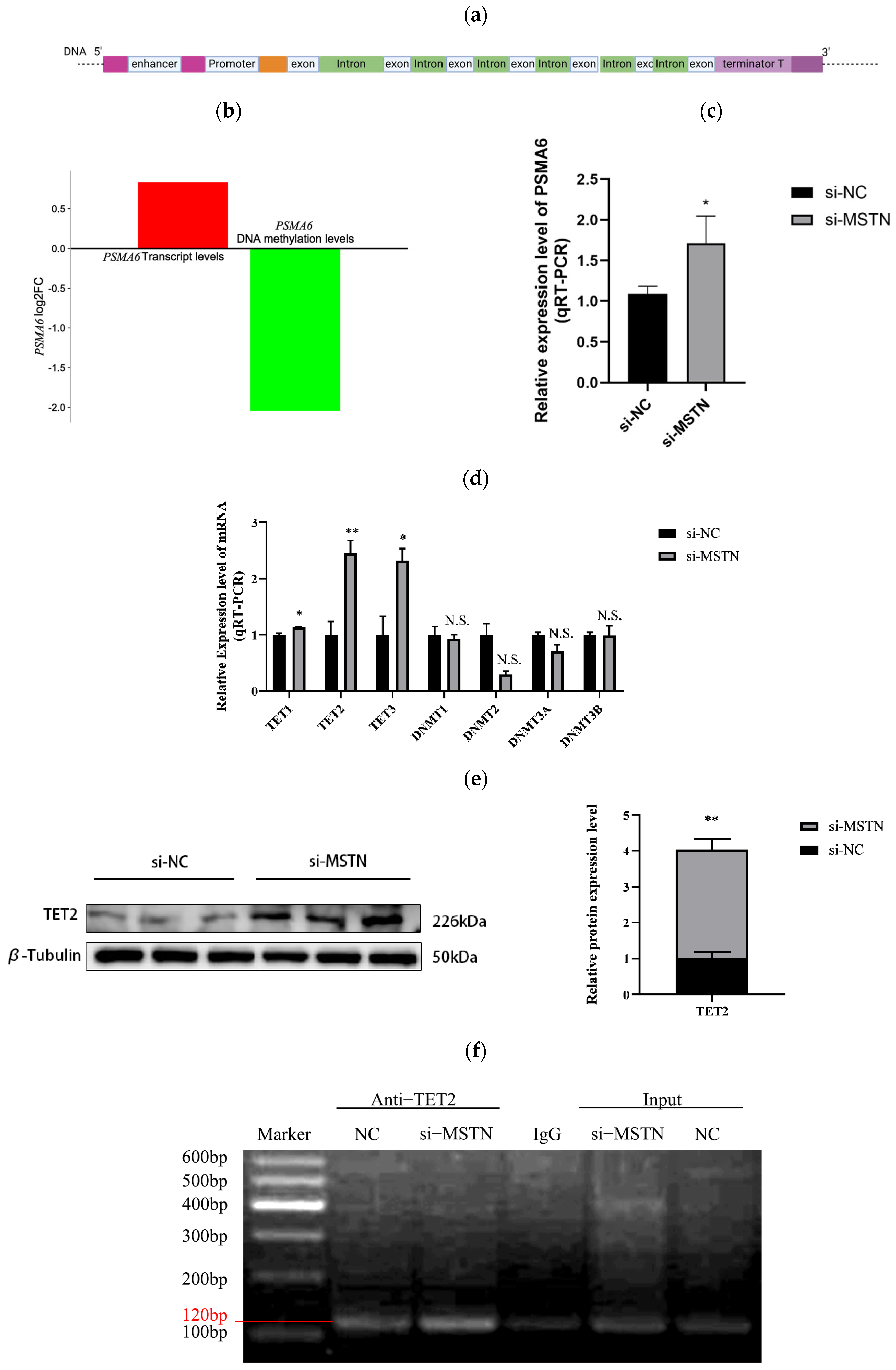
2.1.1. MSTN Negatively Regulates PSMA6 Gene and TET2 Protein Expression
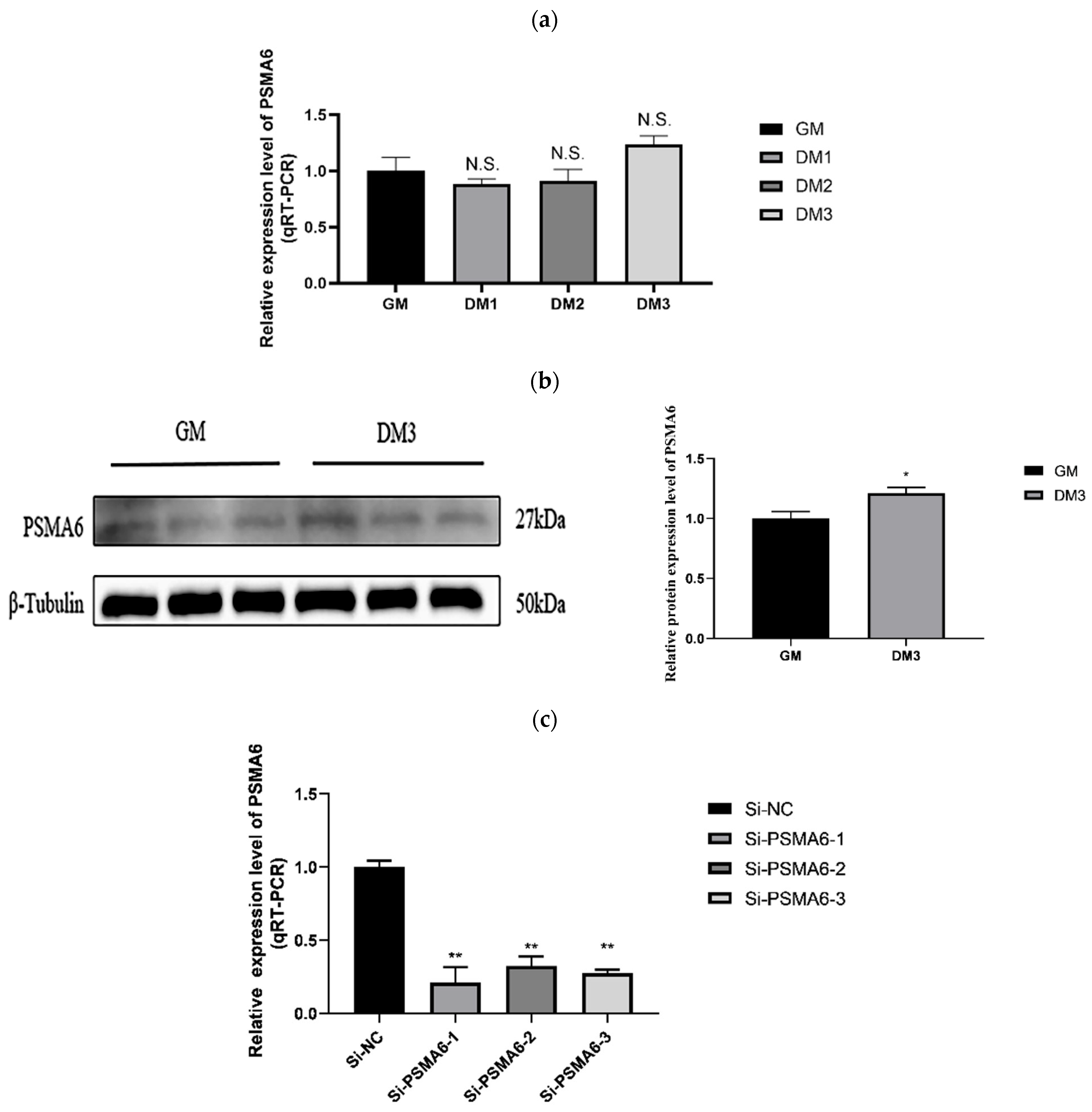
2.1.2. PSMA6’s Impact on the Growth of Satellite Cells in Bovine Skeletal Muscle PSMA6 Gene Expression over Time
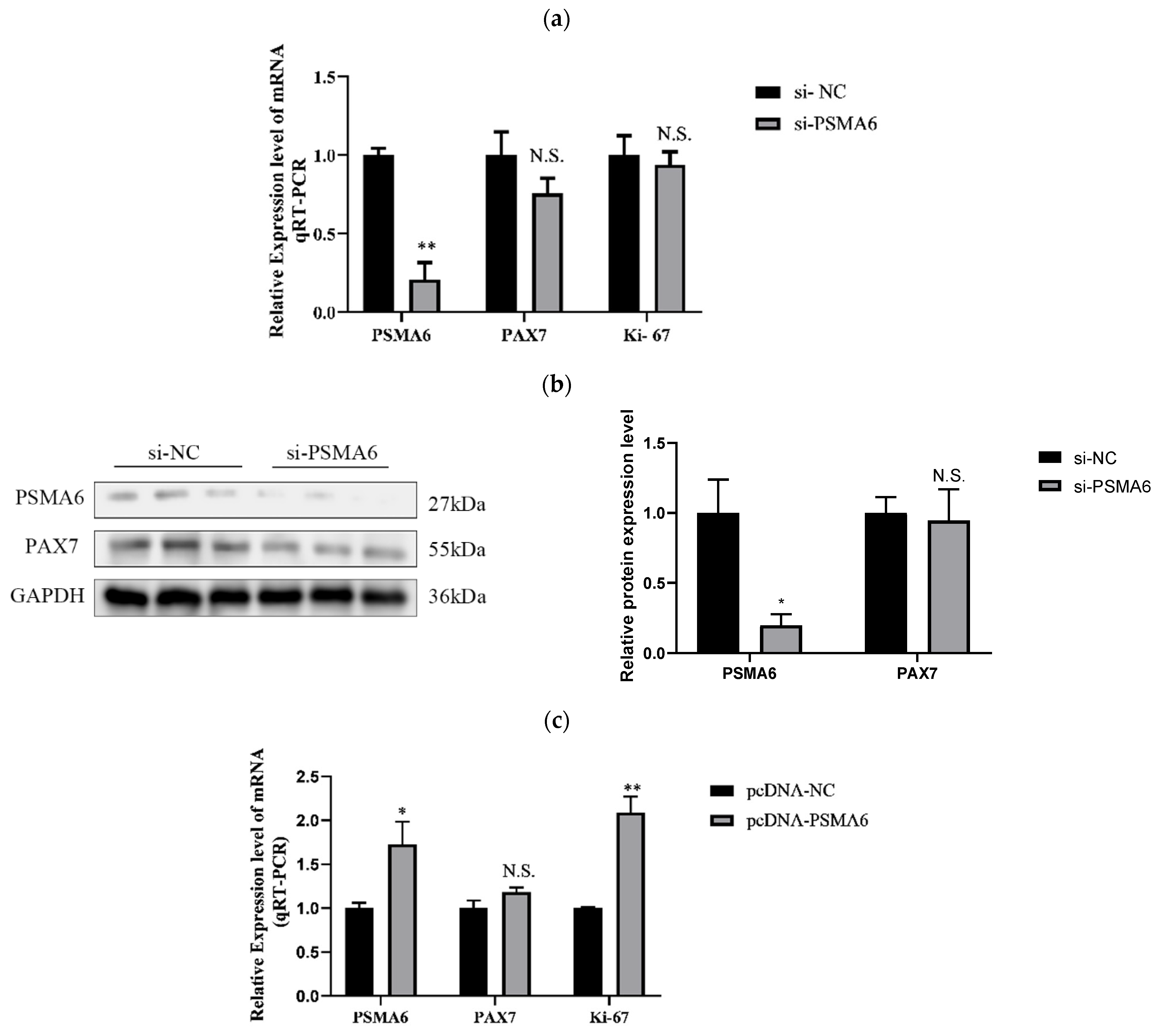
Regulatory Effects of PSMA6 on Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Proliferation
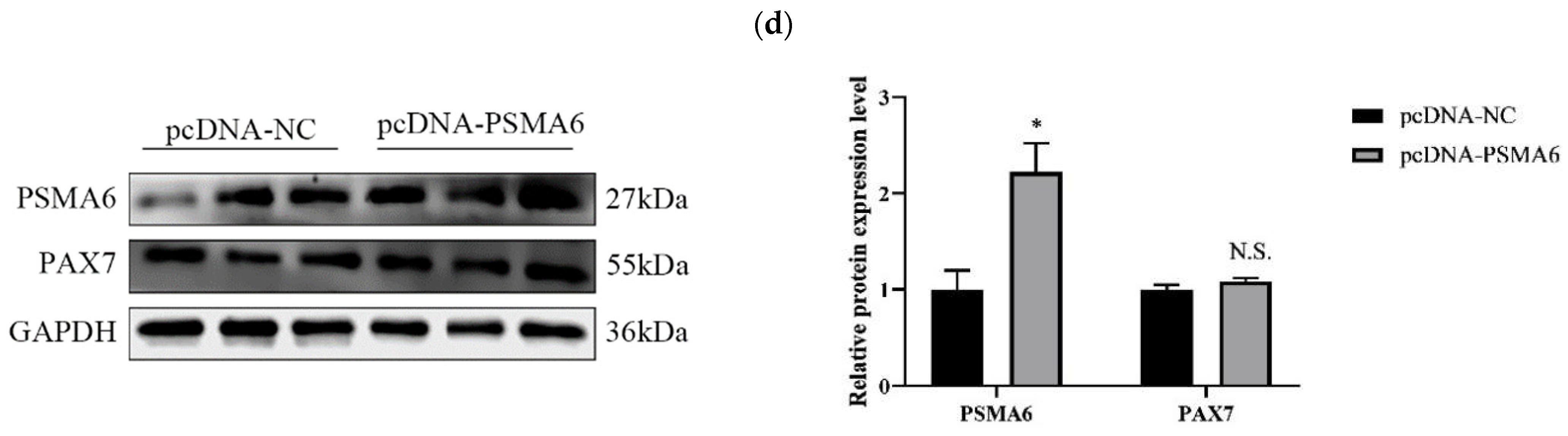
PSMA6 Modulates Differentiation in Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells
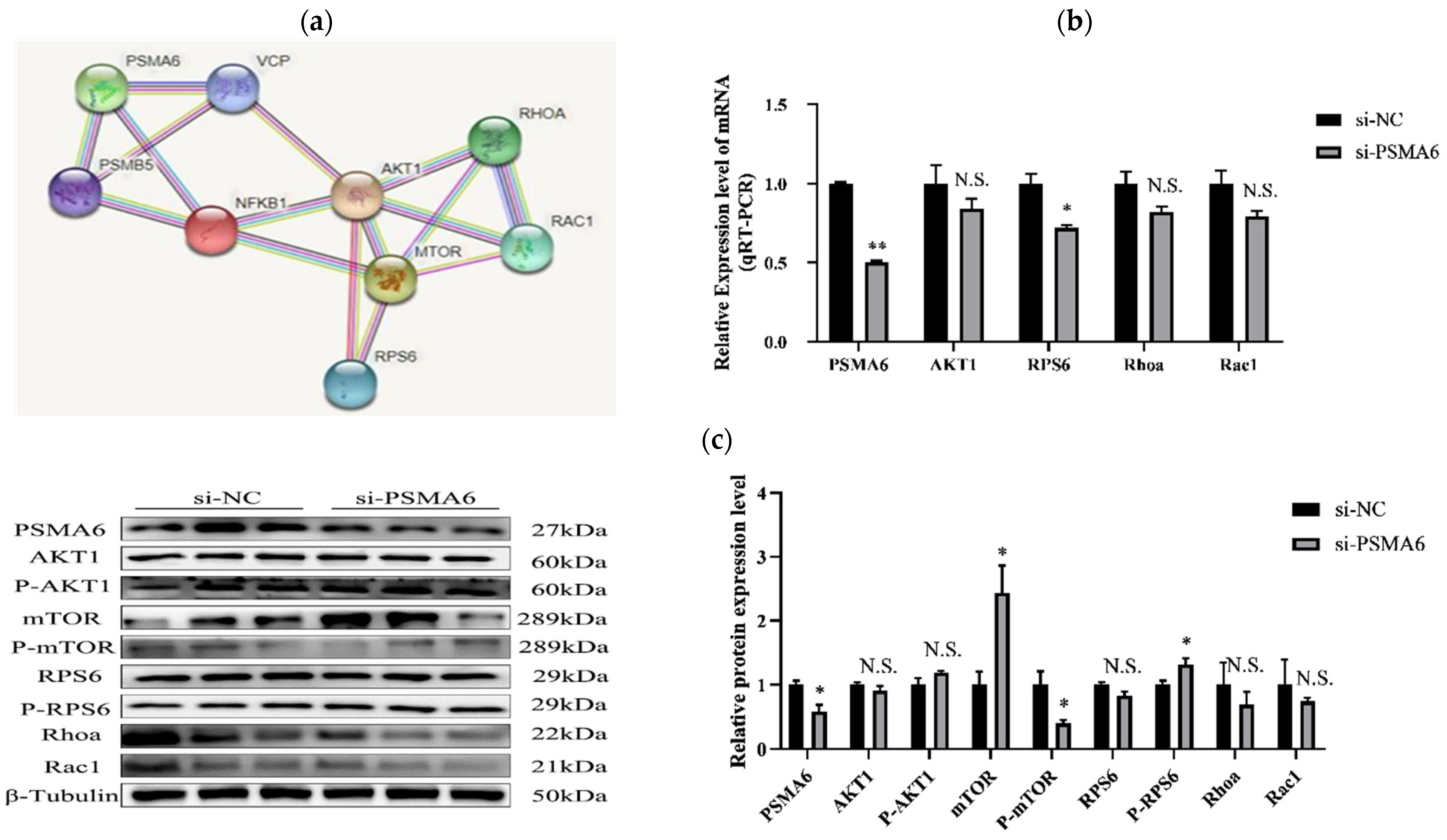
2.1.3. Effects of Interference and Overexpression of PSMA6 on AKT/mTOR Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Isolation and Culture
4.2. The Extraction of Total RNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.3. Overexpression Vectors and siRNA Synthesis
4.4. Plasmid In Vitro Transformation
4.5. Cell Transfection
4.6. Extraction of Protein & Western Blot Analysis
4.7. CHIP
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSTN | Myostatin |
| PSMA6 | Proteasome 20S subunit alpha-6 |
| TET1 | Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase-1 |
| TET2 | Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase-2 |
| TET3 | Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase-3 |
| DNMT1 | DNA methyltransferase-1 |
| DNMT2 | DNA methyltransferase-2 |
| DNMT3 | DNA methyltransferase-3 |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| CHIP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay |
| AKT/mTOR | Protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MyoG | Myogenin |
| MyHC | Myosin heavy chain |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| PAX7 | Paired Box 7 |
| Ki-67 | More than a proliferation marker |
| AKT1 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 gene |
| RPS6 | Ribosomal protein S6 |
| RhoA | Ras homolog family member A |
| Rac1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
References
- Zhang, J.; Sheng, H.; Pan, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Hu, C.; Wei, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y. Identification of Key Genes in Bovine Muscle Development by Co-Expression Analysis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Chen, H. CircINSR Regulates Fetal Bovine Muscle and Fat Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 615638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Mariano, E., Jr.; Joo, S.-T.; Choi, I.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, G.-D.; Hur, S.J. Improved Culture Procedure for Bovine Muscle Satellite Cells for Cultured Meat. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, P.J. The Roles of miRNAs in Adult Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 209, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle FIBERS. J. Cell Biol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, K. Skeletal Muscles Do More than the Loco-motion. Acta Physiol. 2022, 234, e13791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabadi, M.; Bordbar, F.; Jensen, J.; Du, M.; Guo, W. Key Genes Regulating Skeletal Muscle Development and Growth in Farm Animals. Animals 2021, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakati, R.; DiMario, J.X. Repression of Myoblast Proliferation and Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Promoter Activity by KLF10 Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13876–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Son, H.J.; Kim, J.-S.; Jung, C.H.; Ahn, J.; Hur, J.; Ha, T.Y. Coffee Consumption Promotes Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Myoblast Differentiation. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.M.; Subramaniyam, N.; Sim, C.M.; Ge, X.; Sathiakumar, D.; McFarlane, C.; Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R. Irisin Is a Pro-Myogenic Factor That Induces Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and Rescues Denervation-Induced Atrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Langley, B.; Berry, C.; Sharma, M.; Kirk, S.; Bass, J.; Kambadur, R. Myostatin, a Negative Regulator of Muscle Growth, Functions by Inhibiting Myoblast Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40235–40243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speese, A.; Padgett, C.A.; Rosewater, C.L.; Corley, Z.L.; Mintz, J.D.; Fulton, D.J.; Stepp, D.W. Myostatin Deletion Reverses Myosteatosis and Improves Angiogenesis in Obese Mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, cvac066.175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, S.; Subramanian, S.; Sathiakumar, D.; Venkatesh, R.; Salerno, M.S.; McFarlane, C.D.; Kambadur, R.; Sharma, M. Modulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Skeletal Muscle by Myostatin Is Mediated through NF-κB. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Luo, T.; Rong, H.; Lu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, C.; Yi, D.; Peng, Y.; Lei, E.; Xiong, X.; et al. Maternal Rodent Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate Decreases Muscle Mass in the Offspring by Increasing Myostatin. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Miao, M.; Tan, H.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Li, G.; et al. Proteomic Studies on the Mechanism of Myostatin Regulating Cattle Skeletal Muscle Development. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 752129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-M.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, S.-L.; Yu, K. Regulation of Myostatin on the Growth and Development of Skeletal Muscle. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 785712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.R. Muscle Regeneration through Myostatin Inhibition. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2005, 17, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Cao, Y.; Qiu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Wei, Q.; Xia, X.; et al. Establishment and Phenotypic Analysis of an MSTN Knockout Rat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Choe, H.M.; Lv, S.; Chang, S.; Yin, X. Esophageal Striated Muscle Hypertrophy and Muscle Fiber Type Transformation in MSTN Knockout Pigs. Transgenic Res. 2022, 31, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, H.; Han, C.; Xu, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhu, J.; Qin, C.; Luo, H.; Chen, K.; Jiang, S.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of MSTN Knockout in the Early Differentiation of Chicken Fetal Myoblasts. Genes 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kalds, P.; Luo, Q.; Sun, K.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Cai, B.; Huang, S.; Kou, Q.; Petersen, B.; et al. Optimized Cas9:sgRNA Delivery Efficiently Generates Biallelic MSTN Knockout Sheep without Affecting Meat Quality. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennebry, A.; Berry, C.; Siriett, V.; O’Callaghan, P.; Chau, L.; Watson, T.; Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R. Myostatin Regulates Fiber-Type Composition of Skeletal Muscle by Regulating MEF2 and MyoD Gene Expression. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 296, C525–C534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, M.; Wei, Z.; Gu, M.; Yang, L.; Bai, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, G. MSTN Mutant Promotes Myogenic Differentiation by Increasing Demethylase TET1 Expression via the SMAD2/SMAD3 Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Bai, C.; Su, G.; Yang, L.; Li, G. Myostatin Knockout Affects Mitochondrial Function by Inhibiting the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α Pathway in Skeletal Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Song, Y.; Ahn, J.; Kim, E.; Chen, P.; Yang, S.; Suh, Y.; Lee, K. A Novel Mechanism of Myostatin Regulation by Its Alternative Splicing Variant during Myogenesis in Avian Species. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C650–C659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, Q.; Hu, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Guo, H.; Guo, Y. Myostatin Mutation Enhances Bovine Myogenic Differentiation through PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signalling via Removing DNA Methylation of RACK1. Cells 2022, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, K.; Sato, H.; Iida, A.; Mizuno, H.; Nakamura, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Tsunoda, T.; Ikegawa, S.; Kamatani, N.; et al. A Functional SNP in PSMA6 Confers Risk of Myocardial Infarction in the Japanese Population. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumu, T.; Sato, M.; Goto, D.; Kato, T.; Yogo, N.; Hase, T.; Morise, M.; Fukui, T.; Yokoi, K.; Sekido, Y.; et al. Identification of Proteasomal Catalytic Subunit PSMA6 as a Therapeutic Target for Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J. The Potential Role of PSMA6 in Modulating Fat Deposition in Pigs by Promoting Preadipocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Gene 2021, 769, 145228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liao, Y.; Luo, W.; Peng, Z.; Ren, R.; Wang, H. Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis and Myogenesis Caused by TET2 Deletion in Muscle Stem Cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Y. Inactivation of the MSTN Gene Expression Changes the Composition and Function of the Gut Microbiome in Sheep. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Gao, L.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, G.; Bai, C.; Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Inactivation of Myostatin Delays Senescence via TREX1-SASP in Bovine Skeletal Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Gu, M.; Zhu, L.; Hai, C.; Di, A.; Wu, D.; Bai, C.; Su, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Loss of Myostatin Alters Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation, TCA Cycle Activity, and ATP Production in Skeletal Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grade, C.V.C.; Mantovani, C.S.; Alvares, L.E. Myostatin Gene Promoter: Structure, Conservation and Importance as a Target for Muscle Modulation. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Zhang, X.; Liao, L.; Zhang, N.; Liu, M. Regulatory Role of Nfix Gene in Sheep Skeletal Muscle Cell Development and Its Interaction Mechanism with MSTN. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yulin, B.; Tang, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Jin, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, R.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Sheep MSTN Gene Knockout and Promote sSMSCs Differentiation. J Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Dong, X.; Gong, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, F. Mutation in Myostatin 3′UTR Promotes C2C12 Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Blocking the Translation of MSTN. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Han, C.X.; Zhou, H.; Ding, J.M.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.Y.; He, C.; Akinyemi, F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Qin, C.; et al. Effective MSTN Gene Knockout by AdV-Delivered CRISPR/Cas9 in Postnatal Chick Leg Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gim, G.; Kwon, D.; Eom, K.; Moon, J.; Park, J.; Lee, W.; Jung, D.; Kim, D.; Yi, J.; Ha, J.; et al. Production of MSTN -mutated Cattle without Exogenous Gene Integration Using CRISPR-Cas9. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 17, 2100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Yuan, L.; Deng, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Lai, L. Efficient Generation of Myostatin Gene Mutated Rabbit by CRISPR/Cas9. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhang, R.; Tesfaye, D.; Tholen, E.; Looft, C.; Hölker, M.; Schellander, K.; Cinar, M.U. Sulforaphane Causes a Major Epigenetic Repression of Myostatin in Porcine Satellite Cells. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostusiak, P.; Slósarz, J.; Gołębiewski, M.; Grodkowski, G.; Puppel, K. Polymorphism of Genes and Their Impact on Beef Quality. CIMB 2023, 45, 4749–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, K. Myostatin Gene Role in Regulating Traits of Poultry Species for Potential Industrial Applications. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, Y.-G.; Zhao, S.-M.; Deng, W.-D.; Gao, S.-Z. Molecular Characterization and Tissue Expression of Ovine PSAM6 Gene from Muscle Full-Length cDNA Library of Black-Boned Sheep. Anim. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Xi, Y.; Xue, M.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Lei, M. Dynamic Transcriptome Profiles of Skeletal Muscle Tissue across 11 Developmental Stages for Both Tongcheng and Yorkshire Pigs. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, F.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, W.; Miao, M.; Gong, J. SHMT2 Promotes Liver Regeneration Through Glycine-Activated Akt/mTOR Pathway. Transplantation 2019, 103, e188–e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, M.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Myostatin-1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Inhibiting the mTOR Signal Pathway and MRFs, and Activating the Ubiquitin-Proteasomal System in Skeletal Muscle Cells of Japanese Flounder Paralichthys Olivaceus. Cells 2020, 9, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann, K.; Le Nihouannen, D.; Fong, J.E.; Hussein, O.; Barralet, J.E.; Komarova, S.V. Regulation of Osteoclast Growth and Fusion by mTOR/Raptor and mTOR/Rictor/Akt. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSMA6 | F | GCCCGAGATTGTGCTTGGAA | 149 |
| R | GATGTAAGGCCACCCTGGTT | ||
| MyHC | F | TGCTCATCTCACCAAGTTCC | 105 |
| R | CACTCTTCACTCTCATGGACC | ||
| MyoG | F | CAAATCCACTCCCTGAAA | 140 |
| R | GCATAGGAAGAGATGAACA | ||
| PAX7 | F | AGCCAGAGTTTCAACGGGAG | 93 |
| R | GTCGCCAACAGACAACACAC | ||
| Ki-67 | F | GAGGTGGCTCAGGTTCGTC | 97 |
| R | AAAGGGTTGGTGGTAAGTGGC | ||
| GAPDH | F | TGTTGTGGATCTGACCTGCC | 135 |
| R | AAGTCGCAGGAGACAACCTG | ||
| PSMA6-promoter | F | ATGGCAGGTCAAACCAAAGG | 120 |
| R | ATGGCACGGTCACTGGAAAG | ||
| Rac1 | F | ACCCGCAGACAGATGTATTCT | 121 |
| R | AGGATGATGGGTGTGTTGGG | ||
| RhoA | F | TCTTCGAAACGACGAGCACA | 100 |
| R | AGCACCAATCCTGTTTGCCA | ||
| RPS6 | F | ATGTTGTGCGAAAGCCCCTA | 91 |
| R | TGCAGAACTCGTGGAGTCAC | ||
| TET1 | F | TATCAAAACCAGGTGGCGCT | 160 |
| R | GTTTTATTTCCACTGTGCTCCCA | ||
| TET2 | F | GAAAGGAGACCCGACTGCAA | 215 |
| R | TGAATGAATTCAGCAGCTCTGTC | ||
| TET3 | F | GGACTCTGCCTTCTGGTGAC | 187 |
| R | GAGGAGAGTTGTGTGAGGGC | ||
| DNMT1 | F | TATCGGCTGTTCGGCAACAT | 198 |
| R | TCTGGTGGCAGAAACATGGG | ||
| DNMT2 | F | CAGCGATCTCTCTGTGCGAA | 388 |
| R | TCCAAGTAGACGGTAACGCTG | ||
| DNMT3A | F | TTGTCTTGCGTCTCCTTCCC | 111 |
| R | GGAGGAACTGCACTGTCGAA | ||
| DNMT3B | F | GACAAGCACGCCAACAGAAG | 188 |
| R | CTGGAGACCTCCCTCTTGGA | ||
| Fragment Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| si-bta-PSMA6_001 | GAAGAAAGTACCTGACAAA |
| si-bta-PSMA6_002 | CCTCTTGGTTGTTGTATGA |
| si-bta-PSMA6_003 | GCAGCAGGAGTTAAACAAA |
| Antibody Name | Manufacturer | Catalog Number | Host | Final Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TET2 | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | PS04133 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| PSMA6 | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | TD6911 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| MyoG | DSHB (America) | F5D | Mouse | 1:100 |
| MyHC | DSHB (America) | MF20 | Mouse | 0.5 μg/mL |
| GAPDH | Zhongshan Golden Bridge (Beijing, China) | TA-08 | Mouse | 1:1000 |
| AKT1 | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | T55561 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| p-AKT1 | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | T55885 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| RPS6 | Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China) | D291353 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| P-RPS6 | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | TA7331 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| mTOR | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | TA6308 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| P-mTOR | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | S2448 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| Rac1 | NewEast (America) | 26005 | Mouse | 1:1000 |
| RhoA | NewEast (America) | 26007 | Mouse | 1:1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, T.; Miao, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, D. MSTN Regulates Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation via PSMA6-Mediated AKT Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114963
Ma T, Miao M, Liu X, Zhang L, Guo Y, Li X, Ding X, Guo H, Hu D. MSTN Regulates Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation via PSMA6-Mediated AKT Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114963
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Tengxia, Meiling Miao, Xiangquan Liu, Linlin Zhang, Yiwen Guo, Xin Li, Xiangbin Ding, Hong Guo, and Debao Hu. 2025. "MSTN Regulates Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation via PSMA6-Mediated AKT Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114963
APA StyleMa, T., Miao, M., Liu, X., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Li, X., Ding, X., Guo, H., & Hu, D. (2025). MSTN Regulates Bovine Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation via PSMA6-Mediated AKT Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114963







