Abstract
The objective was to evaluate the current evidence regarding the etiology of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). This study systematically reviewed the literature by searching PubMed, Web of Science, and ProQuest databases for genes, proteins, and microRNAs associated with MRONJ from the earliest records through April 2023. Conference abstracts, letters, review articles, non-human studies, and non-English publications were excluded. Twelve studies meeting the inclusion criteria involving exposure of human oral mucosa, blood, serum, saliva, or adjacent bone or periodontium to anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic agents were analyzed. The Cochrane Collaboration risk assessment tool was used to assess the quality of the studies. A total of 824 differentially expressed genes/proteins (DEGs) and 22 microRNAs were extracted for further bioinformatic analysis using Cytoscape, STRING, BiNGO, cytoHubba, MCODE, and ReactomeFI software packages and web-based platforms: DIANA mirPath, OmicsNet, and miRNet tools. The analysis yielded an interactome consisting of 17 hub genes and hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424. A dominance of cytokine pathways was observed in both the cluster of hub DEGs and the interactome of hub genes with dysregulated miRNAs. In conclusion, a panel of genes, miRNAs, and related pathways were found, which is a step toward understanding the complexity of the disease.
1. Introduction
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) encompasses osteonecrosis of the jaw associated with bisphosphonates, denosumab, and anti-resorptive agents [1,2,3,4]. It is a rare but serious drug reaction associated often with receiving high doses of anti-angiogenic and anti-resorptive medication, including mTOR inhibitors [5,6,7]. Anti-resorptive drugs, namely bisphosphonate and denosumab, are monoclonal antibodies that target the receptor activator of the tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 [8,9]. Under conditions of accelerated skeletal turnover, bisphosphonates are selectively absorbed at sites of active bone remodeling [10]. Anti-angiogenic drugs, namely sunitinib and bevacizumab, are humanized monoclonal antibodies that impede the creation of novel blood vessels by suppressing the function of tyrosine kinases and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) [11].
MRONJ is a recognized phenomenon in nearly 1% of cancer patients and in 0.1% of those suffering from metabolic bone diseases [12]. The prevalence of MRONJ reported in studies varies widely, with incidence rates ranging from as low as 0.01% following low-dose oral bisphosphonate therapy to as high as 14.4% in high dose intravenous bisphosphonate treatment [13]. Dental extractions, implant procedures, oral and maxillofacial surgeries, periodontal disease, and invasive periodontal procedures have been identified as risk factors for MRONJ, with local inflammation being of greatest importance [14]. The etiology of MRONJ is multifactorial, encompassing multiple deficiencies that synchronize to result in bone resorption suppression [15], infection/inflammation [16], immune system dysfunction [17], angiogenesis inhibition [18], soft tissue toxicity [19], and systemic disorders related to conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes mellitus [20]. Although there is no conclusive pathophysiology supported by scientific data, numerous fundamental queries persist. Even though there has been a decades-long investigation, the exact reason MRONJ is more frequently observed in the jawbone remains unclear.
Oral disorders encompass a range of conditions with worldwide prevalence and clinical significance. These ailments can have mutilating effects and significantly diminish the quality of life, as they affect a restricted area with critical physiological and social functions. Although crucial, several oral illnesses remain inadequately understood and frequently receive ineffective treatment. It is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms at play in oral diseases to identify dependable, mechanistic indicators of clinical results, establish targeted therapeutic strategies, and customize prevention and treatment techniques. Conventional analysis of diseases only provides surface-level interpretations. Gaining a comprehensive knowledge of complex human disorders necessitates collating all pertinent data and scrutinizing biomarkers that are genetically associated with disease susceptibility. To facilitate the identification of innovative underlying molecular disease mechanisms, unbiased screening methods have been employed at various molecular levels to produce large-scale datasets. Numerous biological research areas, such as the investigation of oral conditions, gain advantages from recognizing these processes and biomarkers in single-omics analysis [21]. The application of multi-omics approaches, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, provides comprehensive molecular insights beyond single-omics methods. Therefore, the analysis aimed to pool existing data on the pathophysiological processes of MRONJ in humans, provided by multi-omics techniques such as high-throughput sequencing, gene expression arrays, and mass spectroscopy, to identify groups of biomarkers differentially expressed between cohorts and worthy of further investigation. At the same time, the objective of the work was to reveal altered signaling pathways and to create a multidimensional, layered configuration of MRONJ that would provide new insights into its pathobiology.
2. Materials and Methods
The results presented in this systematic analysis followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines [22].
2.1. Study Selection
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
To be included, studies had to involve human oral mucosa, blood, serum, saliva, or adjacent bone or periodontium exposed to anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic agents. The date of publication was not restricted, but only English language articles were considered.
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
Studies that have been retracted previously, along with reviews, conference abstracts, case reports, letters to the editor, case studies, and studies involving non-human animal studies, have been excluded.
2.1.3. Screening Process
The screening process was conducted with predetermined, objective inclusion criteria after the completion of a literature search. Figure 1 represents the procedure outlined. The survey was conducted between 7 and 10 March 2023. From inception until April 2023, two evaluators independently searched the databases of PubMed, Web of Science (WoS), and ProQuest. The data were pooled from those source articles that were related to mRNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs), proteins, and metabolites. The study merged key phrases with the logical operator “OR” and the results with the logical operator “AND”. The following terms were used in the search strategy: “mronj”, “bronj”, “aronj”, “dronj”, “medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw”, “bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw”, “antiresorptive agent-related osteonecrosis of the jaw”, and “denosumab-related osteonecrosis of the jaw”. In addition, the search terms for transcriptomics were “microRNA” or “miRNA” and “transcriptome”, “transcriptomics” or “mRNA”. Proteomics was searched using the terms “proteomics” or “proteome”, while metabolomics was obtained by searching for “metabolome”, “metabolomics” or “metabolite”. No year restrictions were applied for article publication.
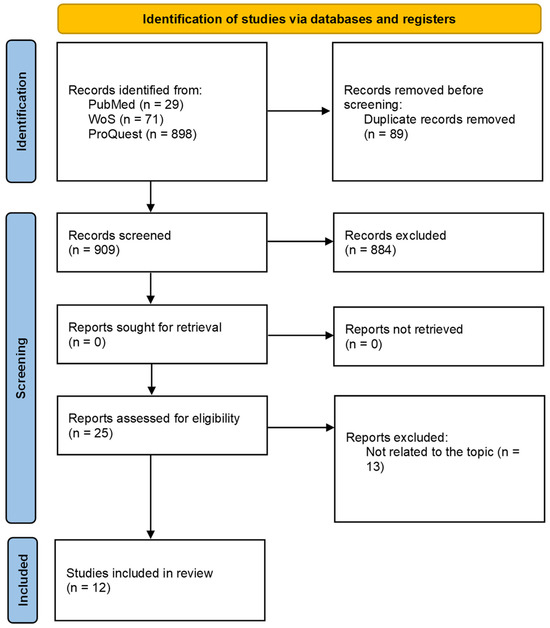
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of literature for a systematic review on the screening of medication-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Further, the screening process involved manually removing duplicate results from the analysis. Two reviewers independently analyzed the titles and abstracts of the papers and evaluated the remaining articles to determine their eligibility. If a study’s suitability could not be determined solely from its title and abstract, its full text was examined. Citations for the included papers were tracked using Google Scholar or PubMed. A manual review of the reference lists of the included articles was conducted to select relevant articles. The results were then summarized from the articles that satisfied the inclusion criteria. The Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2, https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/current-version-of-rob-2, accessed on 14 November 2023) was used to assess the risk of bias in domains related to the randomization process, deviations from the intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result.
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
The GeneCards human gene database (https://www.genecards.org, accessed on 10 July 2023) was used to verify and revise the list of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) compiled from eligible articles. Protein accession numbers were mapped to genes using the UniProt mapping tool (https://www.uniprot.org, accessed on 14 July 2023) [23]. The downloaded matching genes were then used for further investigation.
To investigate DEGs for overrepresentation in the hierarchical gene ontology (GO), the extensions of Cytoscape 3.10.0 [24] and BiNGO 3.0.5 [25] were used. The enrichment analysis for cell components, molecular function, and biological process terms was performed using the Benjamini and Hochberg multiple testing procedure. The significance level was set at 0.05 (p < 0.05).
2.2.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Network and Module Analysis
The network of DEGs was created using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING) database, which presents both insights and predictions regarding protein–protein interactions (PPIs). The network itself was constructed with the help of StringApp, Version 2.0.1 [26].
CytoHubba 0.1 [27] and Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) 2.0.3 [28] allowed the exploration of hub genes and clusters within the network. All CytoHubba plug-in algorithms, including Maximum Neighborhood Component (MNC), Maximal Clique Centrality (MCC), Density of Maximum Neighborhood Component (DMNC), Degree (Deg), Betweenness (BC), Bottleneck (BN), Closeness (Clo), EcCentricity (EC), Edge Percolated Component (EPC), Stress (Str), and Radiality (Rad), were used to detect the hub genes [27]. The MCODE clustering was performed with a degree cutoff of 2, a node score cutoff of 0.2, a maximum depth of 20, and a k-score of 5.
2.2.3. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
The ReactomeFI plug-in pathway database version 8.0.6 [29] was used for pathway enrichment analysis.
The mirPath v.4 database from DIANA Tools (https://diana-lab.e-ce.uth.gr/app/miRPathv4, accessed on 17 July 2023) was utilized to identify genes that could serve as miRNA target candidates.
2.2.4. Multi-Omics Network
The multi-omics data were integrated using web-based platforms such as OmicsNet (https://www.omicsnet.ca, accessed on 19 July 2023) [30] and miRNet (https://www.mirnet.ca, accessed on 21 July 2023) [31]. If the multi-omics network consisted of more than 3000 nodes, we implemented the minimum network setting, i.e., the algorithms that generate the minimum network connecting all specified nodes.
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review of Screening for MRONJ
The search strategy produced 998 articles. Twenty-five articles underwent full-text review following a screening of their titles and abstracts. Twelve articles were ultimately included in the library after thirteen articles were excluded following a thorough examination of their full text (Figure 2). Exclusion criteria comprised such items as conference abstracts, letters, and review articles; non-human studies; and publications in languages other than English. Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the studies on MRONJ that were included. Nine of the twelve studies that met the inclusion criteria were found to have an overall risk of bias of some concern, and three were found to have a high overall risk of bias.
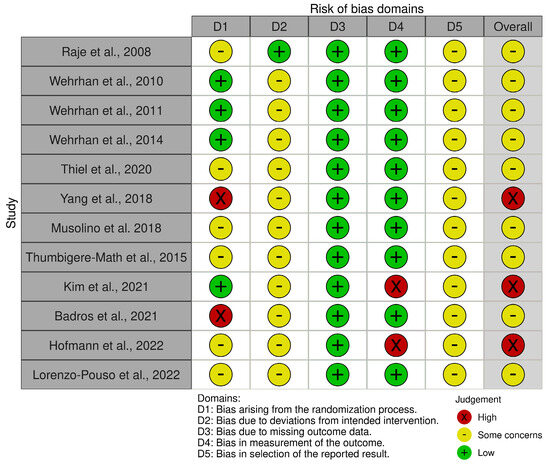
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. According to the Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2, https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/current-version-of-rob-2, accessed on 14 November 2023).

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies on medication-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws.
No relevant studies have been found regarding the metabolomics of MRONJ.
3.2. Network Analysis of Protein Interaction Data
To investigate the protein interactions involved in MRONJ pathogenesis, we utilized STRING databases to analyze the 824 identified genes/proteins and created an interactive network via Cytoscape. Figure 3 depicts the resulting network consisting of 701 genes and 3993 edges, while Table 2 summarizes the network topology.

Figure 3.
The STRING network formed from the dysregulated genes/proteins in MRONJ.

Table 2.
The most relevant topological parameters of the STRING network.
The network topology was analyzed using the cytoHubba (Version 0.1) extension of Cytoscape. The highly linked hub genes were extracted from the main complex network of DEGs by using the algorithms of cytoHubba. Subsequently, 24 genes were extracted that occurred at the intersection of at least three methods: ALB, ANXA5, ATM, CCL2, CD44, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, GART, HSP90AB1, HSPA4, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, LMNA, MMP9, PTPRC, RAB5A, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Hub genes identified by the cytoHubba plug-in algorithms. The crucial hub genes that occurred at the intersection of at least three methods are highlighted in red.
In complement to the cytoHubba algorithms, MCODE clustering was employed to detect the molecular complexes and the seeds—the hub genes with a high degree of connectivity. In a complex PPI network of DEGs, MCODE identified five of the intra-connected regions/clusters and five hub genes/seeds with a high degree of connectivity (see Table 4).

Table 4.
MCODE-interconnected clusters generated from the Cytoscape-derived gene interaction network. The seed node with the highest score within the cluster is marked with an asterisk.
In conjunction with cluster 1, the highest scoring MCODE clustering module, with the cytoHubba analysis results, a total of 17 hub genes were retrieved, comprising ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA.
3.3. GO Enrichment Analysis
A survey of how genes and gene products are represented in the biological domains concerning three aspects of molecular biology was conducted using Gene Ontology (GO). To associate GO terms with gene and protein sets, a series of enrichment analyses were performed in Cytoscape with the help of the BiNGO extension.
The dysregulated genes within the complex gene panel were linked to 422 GO terms, consisting of 333 biological process terms, 23 molecular function terms, and 66 cell component terms, as identified by GO enrichment analysis. The top GO enrichment terms associated with DEGs by p-values are shown in Table 5. The key molecular biological processes identified among these genes are those involved in regulating the immune system and the organism’s immune response. Numerous genes have been implicated in protein binding. DEGs were predominantly linked to the extracellular region and the extracellular space.

Table 5.
Gene ontology enrichment analysis performed in Cytoscape using the BiNGO extension. The full set of dysregulated genes/proteins was considered in the analysis. The most enriched gene ontology terms based on the respective p-values are depicted.
A total of 918 GO terms were obtained from the analysis of seventeen hub genes. Of these GO terms, 893 were related to biological processes, 22 were associated with molecular function, and 23 were linked to cell component terms. Protein phosphorylation of amino acids constitutes a central molecular biological process. While protein binding was a common association among all hub genes, the top-ranked molecular function was cytokine receptor binding. DEGs were predominantly located in the extracellular space and region, as indicated in Table 6.

Table 6.
Gene ontology enrichment analysis in Cytoscape using the BiNGO extension. A set of seventeen hub-dysregulated genes/proteins was considered in the analysis. The most enriched gene ontology terms based on the respective p-values are depicted.
3.4. Multiomics Networks in MRONJ
To investigate the fundamental mechanisms of MRONJ regulation, OmicsNet tools to visualize multi-layered networks with a 3D-based layered layout were used. We detected a complex intrinsic network that was eventually reduced to a minimally connected network consisting of 1300 nodes (1289 genes/proteins and 11 miRNAs) and 7816 edges after merging the initial set of 22 miRNAs, 550 genes, and 292 proteins (see Figure 4).
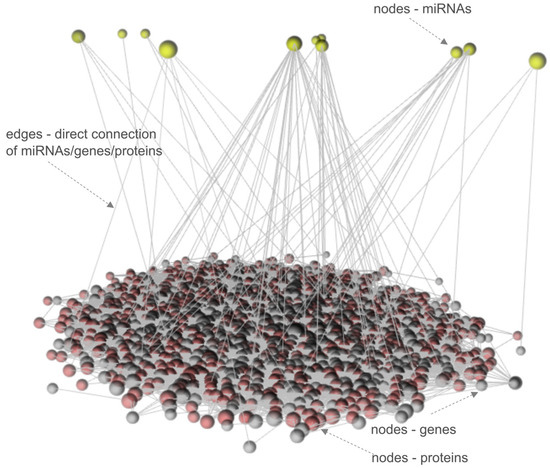
Figure 4.
The multi-omics 3D layered network of MRONJ.
Next, we integrated the 17 genes shared between the MCODE cluster and cytoHubba analysis with the 22 miRNAs that were differentially expressed, ultimately producing a highly interconnected new network. This network produced an interactome of seventeen input genes, including ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA, and seven input miRNAs (hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424) with connector genes/miRNAs using 1693 edges (Figure 5).
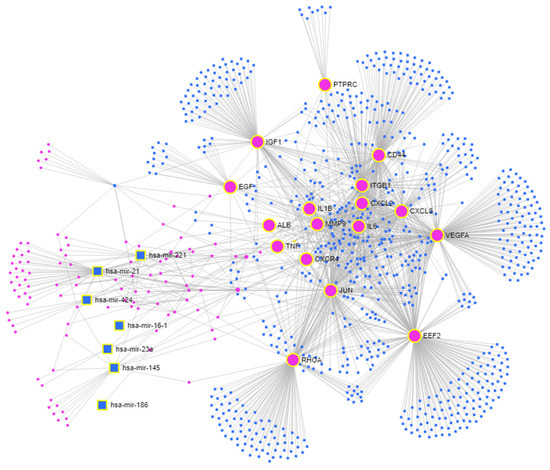
Figure 5.
The multi-omics network of MRONJ. Input genes—large pink circles; input miRNAs—large blue squares; connector genes—small pink circles; connector miRNAs—small blue squares.
3.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
To identify the pathways involved in medication-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw, we analyzed the associated genes/proteins of the complex panel of DEGs using the ReactomeFI tool within Cytoscape. Table 7 and Figure 6a indicate that DEGs were notably enriched in the top ten signaling pathways, specifically in the Innate immunity system pathways. These pathways form the nonspecific part of immunity and include functions such as Neutrophil degranulation (R-HSA-6798695) and regulation of the complement cascade (R-HSA-6803157). Similarly, pathway enrichment analysis was performed on the significantly dysregulated Reactome signaling pathways using the set of 17 hub genes/proteins identified in MRONJ (Table 8, Figure 6b).

Table 7.
Pathway enrichment analysis of the Reactome signaling pathways dysregulated in MRONJ ranked according to their p-values. The full set of dysregulated genes/proteins was considered in the analysis.
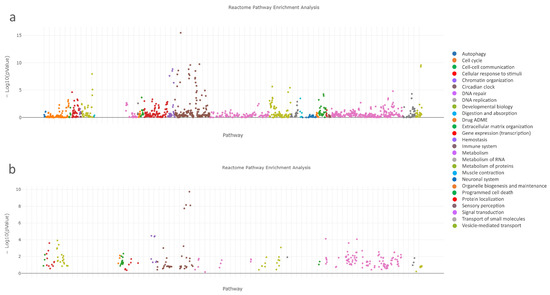
Figure 6.
Pathway enrichment analysis of significantly dysregulated Reactome signaling pathways ranked according to the p-values; (a) the full set of dysregulated genes/proteins, (b) the set of hub genes/proteins of MRONJ.

Table 8.
Pathway enrichment analysis of Reactome signaling pathways dysregulated in MRONJ ranked according to their p-values. The set of seventeen hub-dysregulated genes/proteins was considered in the analysis.
To map the signaling pathways of MRONJ and to identify potential Reactome molecular pathway targets of miRNAs, the associated miRNAs (hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424), obtained with the OmicsNet tools (Figure 5), underwent an in silico analysis with the DIANA Tools mirPath v.4 database. MiRNA-centric analysis of hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424 was carried out with the help of the TarBase v8.0 database and miTarBase2022 as a secondary target source, searching for the direct miRNA target genes. The union of Reactome pathways option was used in the analysis. The results of the analysis are shown in Table 9. The Reactome pathways Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 signaling (R-HSA-6785807) and signaling by interleukins (R-HSA-449147) show the most comprehensive association of miRNAs with gene targets consisting of IL1B, VEGFA, and CXCL8.

Table 9.
Pathway enrichment analysis of significantly dysregulated Reactome signaling pathways conducted on the set of seven miRNAs (hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424) of MRONJ based on the p-value. Direct target genes of the set of seventeen input genes (ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA) are displayed.
4. Discussion
To explore the pathological mechanisms of MRONJ, we utilized gene profiling datasets, proteins, and miRNAs. A variety of analytical strategies were employed to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying MRONJ, including PPI network analysis, GO enrichment, and Reactome pathway enrichment analysis.
Antiresorptive therapy, including bisphosphonates, denosumab, and angiogenesis inhibitors, may trigger MRONJ, which can affect both the maxilla and mandible [44,45]. Several hypotheses have been developed regarding the pathophysiology of MRONJ: (1) suppression of bone resorption; (2) inflammation and oral microbial infection; (3) inhibition of angiogenesis and anti-lymphangiogenesis; (4) dysfunction of innate or acquired immunity (T and B cells, macrophages, DCs, and natural killer cells); and (5) soft tissue toxicity are all potential adverse effects [46,47].
Pathway enrichment analysis is a valuable tool for gaining a mechanistic comprehension of the intricate gene, miRNA, and protein inventories resulting from omics experiments. It assists in the interpretation of biomedical data to reveal the molecular basis of disease [48]. Our analysis identified immune dysfunction-related pathways associated with MRONJ as the main reason for developing and progressing osteonecrosis. When analyzing the entire pool of genes and proteins, it is evident that the Reactome signaling pathways that are significantly dysregulated are primarily dominated by the Innate immune system and Neutrophil degranulation pathways, as indicated by the p-values. Reducing the set of hub genes to 17, which includes ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA, resulted in the dominance of cytokine signaling pathways in the immune system. Moreover, simultaneously analyzing hub genes with miRNAs (hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424) using network-based multiomics analysis revealed dysregulated pathways in the immune system’s cytokine signaling, specifically signaling by interleukins.
There is increasing evidence that inflammatory osteoimmunology is critical to the development of osteonecrosis [49]. Cytokines that regulate inflammatory responses contribute to the onset and progression of osteonecrosis [17,50,51]. In individuals with osteonecrosis, necrotic cells produce cytokines that attract inflammatory cells, triggering both local and systemic immune responses [17,52,53].
The function of immune cells and bone-forming cells, especially osteoblasts and osteoclasts, is regulated by cytokines, inflammatory chemokines, and growth factors [54]. Research confirms the involvement of cytokine networks in osteoclast differentiation and regulation. Cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukins 1, -6, -7, -8, -11, -15, -17, -23, and -34, facilitate the process of osteoclast differentiation. By contrast, anti-osteoclastogenic cytokines, namely interferons alpha, beta, and gamma and interleukins 3, -4, -10, -12, -27, and -33, suppress osteoclasts. [55].
The pathogenesis of inflammatory bone disease is significantly influenced by T cells and B cells [56]. There have been intense discussions regarding new roles for B cells and a potential role for peripheral blood γδ T cells [57,58]. Γδ T cells are innate lymphocytes with a crucial role in regulating immune homeostasis [59]. Kalyan et al. investigated the potential predictive role of peripheral blood γδ T cells in osteonecrosis of the jaw. The authors propose that the loss of γδ T cells caused by bisphosphonates may be involved in the development of osteonecrosis [57]. Moreover, the proliferation of macrophages and γδ T cells promotes inflammation in zoledronic acid-induced jaw necrosis, as the authors of the study [60] concluded.
The understanding of biological systems is facilitated by the objective study of PPIs. An effective approach to characterizing system-wide PPIs is the use of PPI networks. These networks are constructed from pairwise protein interactions and serve as an efficient tool for describing PPI landscapes [61]. To investigate protein functions and biological processes based on predicted PPIs and to gain new insights into diseases, the DEG PPI network was analyzed in this study. For osteonecrosis of the jaw, 17 hub genes with aberrant expression were selected. They included ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA.
Various signaling molecules, such as VEGFA, EGF, MMP9, and TNF, contribute to angiogenesis by stimulating the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells [62]. VEGFA is a highly potent pro-angiogenic factor that plays a critical role in the healing of microvascular wounds associated with bisphosphonate administration [63]. A statistically significant increase in VEGFA gene expression was also demonstrated in response to zoledronic acid [64]. The physiological processes of angiogenesis and vascular remodeling involve the regulation of non-coding RNAs, specifically miRNA-based regulation (as noted by reference [65]). Objective evaluation of these processes is necessary for accurate understanding.
MicroRNAs are small endogenous RNA molecules (∼22 nt) that were recently discovered. Disorders such as cancer or heart disease have demonstrated the diagnostic potential of circulating miRNAs [66,67]. MiRNA-mediated RNA interference, a unique mechanism that binds miRNAs to different direct targets, controls both post-transcriptional gene expression and protein expression [68].
Our OmicsNet network analysis generated an interactome of input genes including ALB, CD44, CXCL2, CXCL8, CXCR4, EEF2, EGF, IGF1, IL1B, IL6, ITGB1, JUN, MMP9, PTPRC, RHOA, TNF, and VEGFA with input miRNAs comprising hsa-mir-16-1, hsa-mir-21, hsa-mir-23a, hsa-mir-145, hsa-mir-186, hsa-mir-221, and hsa-mir-424. Further analysis focused on miRNA identified the most extensively linked miRNAs targeting IL1B, VEGFA, CXCL8, and CD44 directly (Table 9).
MiR-145 targets mainly the interleukins [38] and is also implicated in M2 macrophage polarization [69]. Silencing miR-145 leads to the advancement of femoral head regeneration by upregulating VEGFA [70].
The PPI network revealed that CXCL8 [71] is among the factors related to the progression of osteonecrosis of the jaw, and our analysis identified it as a direct target of miR-23a. Earlier studies reported a significant reduction of miR-23a-3p during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells of bone marrow origin [72]. Furthermore, inhibition of miR-23a in a rat model resulted in a lower incidence of osteonecrosis [73].
Serum microRNAs, including miR-21, miR-23a, and miR-145, were observed to be dysregulated in BRONJ rats [37]. Furthermore, candidate microRNA expressions were confirmed in human samples. During the progression of BRONJ, there was an upregulation of circulating miR-21, which corresponds to the alteration of miR-21 in pro-osteoclastogenesis [37].
5. Conclusions
The emergence of high-throughput platforms for the comprehensive analysis of genes, proteins, and other biological molecules has afforded an exceptional capability for the recognition of novel, valid signatures of disease-related processes.
In conclusion, our systematic review study indicates specific alterations in proteins, genes, and microRNAs and thus unravels novel insights into the molecular mechanism behind the MRONJ disease. The identified dysregulated genes in MRONJ are mostly linked to the regulation of immune system processes and the immune response of the organism. These dysregulated genes significantly enrich pathways related to the Innate immunity system, a crucial component of the nonspecific part of immunity. Particularly important are the 17 hub genes, which exert dominance in the cytokine signaling pathways within the immune system. Additionally, the interaction network between these hub genes and dysregulated miRNAs uncovered pathways associated with the cytokine signaling in the immune system, particularly the signaling by interleukins pathway. Subsequent miRNA analysis showed a set of highly connected miRNAs with direct targeting of multiple genes such as IL1B, VEGFA, CXCL8, and CD44.
This study has potential limitations that should be noted. There was considerable heterogeneity observed between studies, which may impact the interpretation of the results. Factors such as patient selection variability, differences in the origins and causes of MRONJ, and variations in the material and methodology used could contribute to this heterogeneity. To ensure more reliable results, it would be beneficial to establish strict inclusion/exclusion criteria based on the disease state and MRONJ treatment in future studies. Additionally, our objective was to present a comprehensive overview of the pathophysiological processes of MRONJ in humans using multi-omics techniques. Expanding the research to encompass other types of non-coding RNAs could prove helpful in filling this gap. Furthermore, there is a shortage of data for analysis due to the limited amount of metabolomics research.
Despite the limitations of this study, the panel of proteins, genes, and microRNAs presented, along with their associated pathways, constitutes a significant advancement toward comprehending the intricate cause of MRONJ.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L., I.T. and V.S.; formal analysis, G.L. and I.T.; funding acquisition, I.T.; investigation, G.L., I.T. and V.S.; methodology, G.L. and I.T.; project administration, G.L.; supervision, G.L.; visualization, G.L.; writing—original draft, G.L.; writing—review and editing, G.L., I.T. and V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Slovak Research and Development Agency APVV-19-0476, the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Slovak Republic, and the Slovak Academy of Sciences VEGA 1/0405/24.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Hermes LabSystems s.r.o. for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Marx, R.E. Pamidronate (Aredia) and Zoledronate (Zometa) Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Jaws: A Growing Epidemic. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaloo, T.L.; Felsenfeld, A.L.; Tetradis, S. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in a Patient on Denosumab. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.H.; Middlefell, L.S.; Mizen, K.D. Osteonecrosis of the Jaws Induced by Anti-RANK Ligand Therapy. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 48, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibahara, T. Antiresorptive Agent-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (Aronj): A Twist of Fate in the Bone. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2019, 247, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, T.; Neirinckx, V.; Rogister, B.; Gilon, Y.; Wislet, S. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Cellular Therapeutic Approaches. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 8768162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw—2014 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosella, D.; Papi, P.; Giardino, R.; Cicalini, E.; Piccoli, L.; Pompa, G. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Clinical and Practical Guidelines. J. Int. Soc. Prevent. Communit. Dent. 2016, 6, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Brijs, K.; Miclotte, I.; Vermeire, S.; Darche, V.; Politis, C. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated with Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitors. Int. J. Oral. Max. Surg. 2020, 49, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, P.; López-Cedrún, J.L.; Arenaz, J.; Scully, C. Denosumab-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of Action and Role in Clinical Practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimolbutr, K.; Porter, S.; Fedele, S. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Associated with Antiangiogenics in Antiresorptive-Naïve Patient: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8071579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Mannion, C.J. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws and Quality of Life: Review and Structured Analysis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwech, N.; Nilsson, J.; Gabre, P. Incidence and Risk Factors for Medication-related Osteonecrosis after Tooth Extraction in Cancer Patients—A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2023, 9, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Mottes, M.; Valenti, M.T. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (Mronj): Are Antiresorptive Drugs the Main Culprits or Only Accomplices? The Triggering Role of Vitamin d Deficiency. Nutrients 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Aghaloo, T.; Carlson, E.R.; Ward, B.B.; Kademani, D. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws—2022 Update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 920–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Niu, Y. Pathogenesis and Multidisciplinary Management of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, L.; Ren, W.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, C.; Yang, S.; Zhi, K. The Role of the Immune Response in the Development of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 606043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Hakam, A.E.; McCauley, L.K. Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Bolland, M.J.; Grey, A.B. Is Bisphosphonate-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Caused by Soft Tissue Toxicity? Bone 2007, 41, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, A.; Khamaisi, M. Diabetes as a Risk Factor for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, G.; Bellizzi, M.G.; Fatuzzo, I.; Zoccali, F.; Cavalcanti, L.; Greco, A.; Vincentiis, M.D.; Ralli, M.; Fiore, M.; Petrella, C.; et al. Salivary Biomarkers in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Proteomic Overview. Proteomes 2022, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium; Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Britto, R.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; et al. Uniprot: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maere, S.; Heymans, K.; Kuiper, M. Bingo: A Cytoscape Plugin to Assess Overrepresentation of Gene Ontology Categories in Biological Networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3448–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape Stringapp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, H.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Ko, M.-T.; Lin, C.-Y. Cytohubba: Identifying Hub Objects and Sub-Networks from Complex Interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W. An Automated Method for Finding Molecular Complexes in Large Protein Interaction Networks. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Feng, X.; Stein, L. A Human Functional Protein Interaction Network and Its Application to Cancer Data Analysis. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Ewald, J.; Xia, J. OmicsNet 2.0: A Web-Based Platform for Multi-Omics Integration and Network Visual Analytics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W527–W533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xia, J. Microrna Regulatory Network Analysis Using Mirnet 2.0. In Transcription Factor Regulatory Networks; Song, Q., Tao, Z., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2594, pp. 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Raje, N.; Woo, S.-B.; Hande, K.; Yap, J.T.; Richardson, P.G.; Vallet, S.; Treister, N.; Hideshima, T.; Sheehy, N.; Chhetri, S.; et al. Clinical, Radiographic, and Biochemical Characterization of Multiple Myeloma Patients with Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrhan, F.; Hyckel, P.; Ries, J.; Stockmann, P.; Nkenke, E.; Schlegel, K.A.; Neukam, F.W.; Amann, K. Expression of Msx-1 Is Suppressed in Bisphosphonate Associated Osteonecrosis Related Jaw Tissue-Etiopathology Considerations Respecting Jaw Developmental Biology-Related Unique Features. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrhan, F.; Amann, K.; Möbius, P.; Weber, M.; Preidl, R.; Ries, J.; Stockmann, P. BRONJ-Related Jaw Bone Is Associated with Increased Dlx-5 and Suppressed Osteopontin—Implication in the Site-Specific Alteration of Angiogenesis and Bone Turnover by Bisphosphonates. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrhan, F.; Hyckel, P.; Amann, K.; Ries, J.; Stockmann, P.; Schlegel, K.; Neukam, F.; Nkenke, E. Msx-1 Is Suppressed in Bisphosphonate-Exposed Jaw Bone Analysis of Bone Turnover-Related Cell Signalling after Bisphosphonate Treatment: ONJ and Msx-1 Expression. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, Y.; Ghayor, C.; Lindhorst, D.; Essig, H.; Weber, F.; Rücker, M.; Schumann, P. Antimicrobial Peptide Gene Expression in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Tao, Y.; Wang, C.; Shuai, Y.; Jin, L. Circulating microRNA Panel as a Novel Biomarker to Diagnose Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, C.; Oteri, G.; Allegra, A.; Mania, M.; D’Ascola, A.; Avenoso, A.; Innao, V.; Allegra, A.G.; Campo, S. Altered microRNA Expression Profile in the Peripheral Lymphoid Compartment of Multiple Myeloma Patients with Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumbigere-Math, V.; Michalowicz, B.; Jong, E.; Griffin, T.; Basi, D.; Hughes, P.; Tsai, M.; Swenson, K.; Rockwell, L.; Gopalakrishnan, R. Salivary Proteomics in Bisphosphonate-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yeon, A.; Parker, S.J.; Shahid, M.; Thiombane, A.; Cho, E.; You, S.; Emam, H.; Kim, D.-G.; Kim, M. Alendronate-Induced Perturbation of the Bone Proteome and Microenvironmental Pathophysiology. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badros, A.Z.; Meddeb, M.; Weikel, D.; Philip, S.; Milliron, T.; Lapidus, R.; Hester, L.; Goloubeva, O.; Meiller, T.F.; Mongodin, E.F. Prospective Observational Study of Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Multiple Myeloma: Microbiota Profiling and Cytokine Expression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 704722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, E.; Eggers, B.; Heim, N.; Kramer, F.-J.; Nokhbehsaim, M.; Götz, W. Bevacizumab and Sunitinib Mediate Osteogenic and Pro-Inflammatory Molecular Changes in Primary Human Alveolar Osteoblasts in Vitro. Odontology 2022, 110, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Bravo, S.B.; Carballo, J.; Chantada-Vázquez, M.D.P.; Bagán, J.; Bagán, L.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.M.; Conde-Amboage, M.; López-López, R.; García-García, A.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics in Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Proof-of-concept Study. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferneini, E.M. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (Mronj). J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 1801–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, H. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: An Update. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaloo, T.; Hazboun, R.; Tetradis, S. Pathophysiology of Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. 2015, 27, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroshima, S.; Al-Omari, F.A.; Sasaki, M.; Sawase, T. Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Literature Review and Update. Genesis 2022, 60, e23500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimand, J.; Isserlin, R.; Voisin, V.; Kucera, M.; Tannus-Lopes, C.; Rostamianfar, A.; Wadi, L.; Meyer, M.; Wong, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Pathway Enrichment Analysis and Visualization of Omics Data Using: Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 482–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tan, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yue, C. Osteoimmunology and Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yao, Z.; Xue, L.; Wang, D.; Tan, Z. The Role of Immune Cells in Modulating Chronic Inflammation and Osteonecrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1064245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Pu, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, C. Porphyromonas, Treponema, and Mogibacterium Promote Il8/Ifnγ/Tnfα-Based pro-Inflammation in Patients with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 13, 1851112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M. Inflammation, Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Bone Regeneration. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, Y. Inflammasome Complexes: Crucial Mediators in Osteoimmunology and Bone Diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasekara, D.S.; Kim, S.; Rho, J. Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasekara, D.S.; Yun, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Rho, J. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzmann, M.N. T-Cells and B-Cells in Osteoporosis. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. Obes. 2014, 21, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyan, S.; Quabius, E.S.; Wiltfang, J.; Mönig, H.; Kabelitz, D. Can Peripheral Blood γδ T Cells Predict Osteonecrosis of the Jaw? An Immunological Perspective on the Adverse Drug Effects of Aminobisphosphonate Therapy. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzmann, M.N. Do Γδ T Cells Predict Osteonecrosis of the Jaw? J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribot, J.C.; Lopes, N.; Silva-Santos, B. Γδ T Cells in Tissue Physiology and Surveillance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Shan, L. Determination of the Molecular Mechanism by Which Macrophages and γδ-T Cells Contribute to ZOL-Induced ONJ. Aging 2020, 12, 20743–20752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, T.; Cai, Y. Protein-protein Interaction Networks as Miners of Biological Discovery. Proteomics 2022, 22, 2100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Dixit, M. Microrna Key to Angiogenesis Regulation: Mirna Biology and Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Tar. 2018, 18, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, P.; Patel, V.; Festy, F.; Hosny, N.; Cook, R.J. In-Vivo Imaging of the Microvasculature of the Soft Tissue Margins of Osteonecrotic Jaw Lesions. Brit. Dent. J. 2017, 223, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlrich, E.J.; Coates, D.E.; Cullinan, M.P.; Milne, T.J.; Zafar, S.; Zhao, Y.; Duncan, W.D.; Seymour, G.J. The Bisphosphonate Zoledronic Acid Regulates Key Angiogenesis-Related Genes in Primary Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2016, 63, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, B. Mechanisms of lncRNA/microRNA Interactions in Angiogenesis. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 116900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. Mirna-Based Biomarkers, Therapies, and Resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, G.K.; Khullar, N.; Sidhu, I.S.; Navik, U.S.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H.; Bhatti, J.S. Emerging Role of Non-coding RNA in Health and Disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiropoulou, G.; Pampalakis, G.; Lianidou, E.; Mourelatos, Z. Emerging Roles of microRNAs as Molecular Switches in the Integrated Circuit of the Cancer Cell. RNA 2009, 15, 1443–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Du, K.L.; Guo, P.Y.; Zhao, R.M.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, C.Q. IL-16 Regulates Macrophage Polarization as a Target Gene of Mir-145-3p. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, X.Z.; Qiao, G.Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z.L. MiR-145 Silencing Promotes Steroid-Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head Repair via Upregulating VEGF. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J. Differentially Expressed Genes Reveal the Biomarkers and Molecular Mechanism of Osteonecrosis. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8684137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Fan, J.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, R.C.; Weng, X. Microrna-23a Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Targeting Lrp5. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 2016, 72, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Ren, S.; Fan, J.; Weng, X. MicroRNA-23a-3p Inhibitor Decreases Osteonecrosis Incidence in a Rat Model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9331–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).