Abstract
The amino acid L-arginine serves as substrate for the nitric oxide synthase which is crucial in vascular function and disease. Derivatives of arginine, such as asymmetric (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), are regarded as markers of endothelial dysfunction and have been implicated in vascular disorders. While there is a variety of studies consolidating ADMA as biomarker of cerebrovascular risk, morbidity and mortality, SDMA is currently emerging as an interesting metabolite with distinct characteristics in ischemic stroke. In contrast to dimethylarginines, homoarginine is inversely associated with adverse events and mortality in cerebrovascular diseases and might constitute a modifiable protective risk factor. This review aims to provide an overview of the current evidence for the pathophysiological role of arginine derivatives in cerebrovascular ischemic diseases. We discuss the complex mechanisms of arginine metabolism in health and disease and its potential clinical implications in diverse aspects of ischemic stroke.
Keywords:
ADMA; atherosclerosis; arginine; atrial fibrillation; biomarker; endothelial dysfunction; ESUS; homoarginine; SDMA; stroke 1. Precision Stroke Medicine: on Search for Novel Biomarkers
Stroke is globally the second leading cause of death and morbidity [1]. While stroke-associated mortality decreased between 1990 and 2010, stroke prevalence, incidence as well as mortality rates again raised between 2010 and 2017 [2], despite optimized treatment options and intervention programs. Moreover, stroke burden is also increasing in young adults [3]. According to recent findings from the Global Burden of Disease study, the life-time risk to suffer stroke is about 25% starting at the age of 25 years [3]. Facing the challenges of this global cerebrovascular disease epidemic the need of biomarkers supporting individual stroke patient care in terms of precision medicine is becoming increasingly evident [4,5]. This holds true for estimating the individual risk for cerebrovascular diseases for primary preventive strategies but also for secondary prevention after the event. Stroke is a complex disease of diverse underlying risk factors and etiologies and current evidence underscores that a thorough individualized investigation of these conditions is needed for the purpose of an optimal treatment [4]. Thus, there are intense efforts in identifying appropriate imaging, genetic or blood biomarkers that are able to reflect the underlying pathophysiology and are useful for clinical decision making. L-arginine (Arg) derivatives may meet the conditions of such clinically interesting targets in cerebrovascular diseases. For this narrative review article, we conducted a comprehensive literature search through PubMed and selected original articles, reviews and meta-analyses on Arg and its derivatives in ischemic stroke, underlying risk factors and etiological diseases. We aim to provide an overview of the current evidence on how the Arg metabolism is involved in cerebrovascular pathophysiology and how Arg derivatives may constitute valuable biomarkers of risk, morbidity and mortality as well as etiology of ischemic stroke.
2. Metabolism of Arginine and its Derivatives
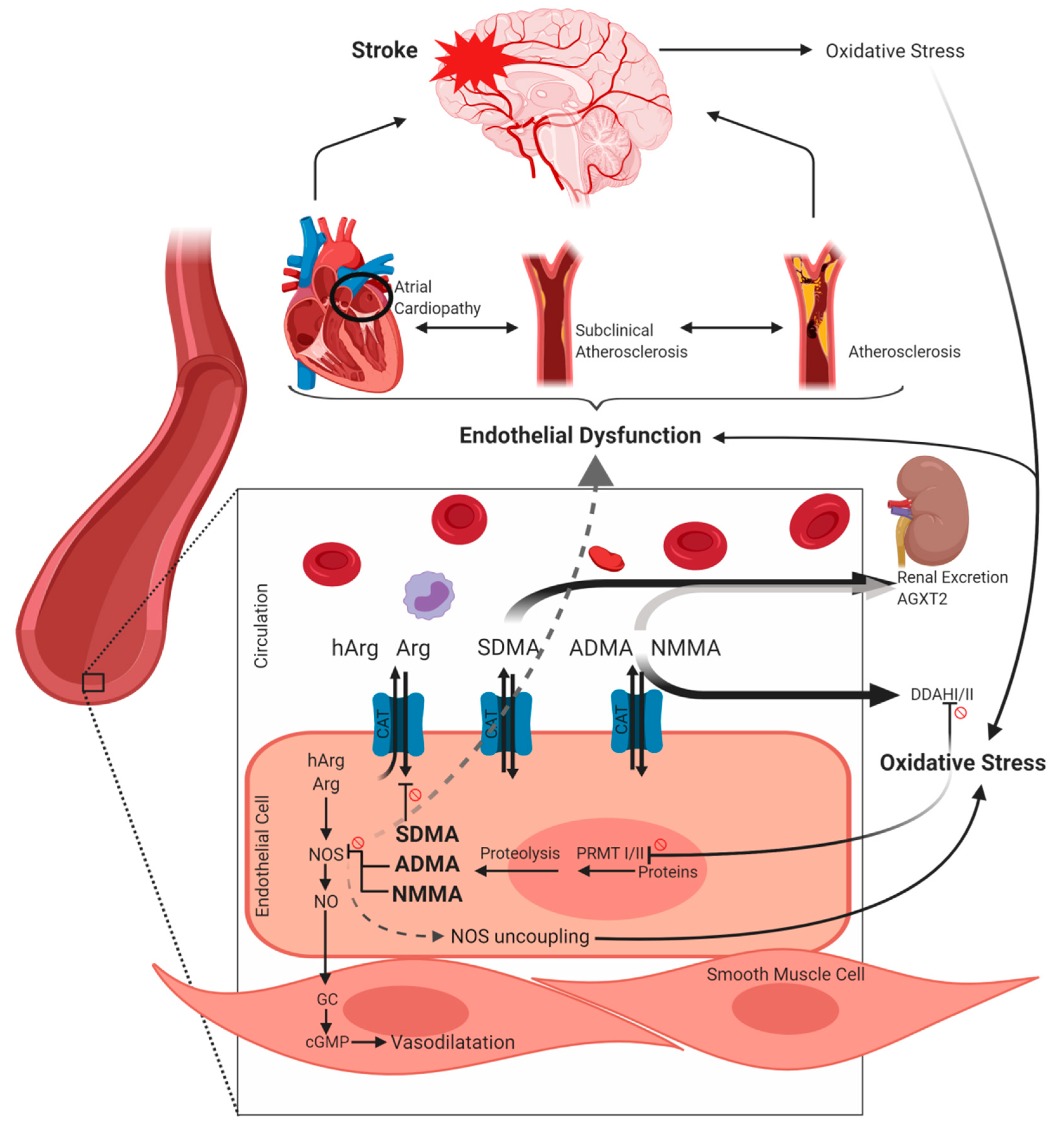
The amino acid Arg is synthesized in the kidney via the urea cycle. Cells which are not synthesizing Arg alone are able to take up Arg via cationic amino acid transporters (CAT). Arginine serves as substrate of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase which exists in three isoforms: the inducible NOS (iNOS), the neuronal NOS (nNOS) and the endothelial NOS (eNOS) [6]. Homoarginine (hArg), which is structurally similar to Arg, primarily originates from the catalytic activity of arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT) but probably urea cycle enzymes are also involved [6]. Homoarginine serves—although with low affinity—as a substrate of NOS and, moreover, may lead to an increased bioavailability of Arg by inhibiting the enzyme arginase. Further endogenous derivatives of Arg are symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and monomethylarginine (NMMA). At first, proteins are methylated by protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMT) I or II. While PRMT I catalyzes methyl groups asymmetrically, PRMT II leads to a symmetric arrangement [7]. Subsequently, methylarginine residues are released during proteolysis of proteins with methylated arginine residues. ADMA and NMMA are endogenous NOS inhibitors competing with Arg and hArg. In contrast, SDMA was identified as inhibitor of cellular Arg uptake via CAT. As a result, methylarginines lead to a deprivation of the bioavailability of NO which is a key endogenous regulator of vascular tone, angiogenesis, inhibition of platelet activation as well as leukocyte adhesion [8,9]. Nitric oxide moreover leads to a decreased endothelial expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) [10] and further leukocyte adhesion molecules [11]—a mechanism which is therefore regarded as protective in early stages of atherosclerosis [8]. Proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and thus formation of fibrous plaque which is a hallmark of further established atherosclerotic lesions is also inhibited by NO [8,12]. Abnormal neuronal NO signalling has been implicated in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease and also in neurodegeneration following stroke [13].
Furthermore, when the bioavailability of Arg is reduced, a shift of the enzymatic activity of NOS may occur, resulting in the production of superoxide anions (radical oxygen species, ROS)—often referred as “NOS uncoupling” [14]. Further NO inactivation may be caused by its reaction with the superoxide anion resulting in formation of peroxynitrite which is a potent oxidant causing damage of proteins, lipids and DNA [8]. Generation of vascular superoxide was correlated with ADMA in patients with coronary heart disease [15]. Feliers et al. [16] reported that also SDMA may cause eNOS uncoupling in glomerular endothelial cells. Thus, both dimethylarginines are not only associated with decreased bioavailability of NO but may also contribute to increased ROS-production [15,16]. Reactive oxygen species are crucial in the progression of atherosclerosis [17]. Vice versa, states of oxidative stress like inflammation or cellular damage, as for example induced by stroke, themselves lead to augmentation of dimethylarginine production via supporting PRMT activity and inhibiting the dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH) [18] (see paragraph 4). DDAH is the enzyme degrading ADMA and NMMA, existing in two isoforms, being expressed constitutively [19]. An alternative minor elimination route is the mitochondrial alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase 2 (AGXT2) which is primarily located in the kidney and metabolizes not only ADMA but also to some extend SDMA [20]. Both, ADMA and in particular SDMA, are excreted via the kidney unmetabolized, explaining high correlations with renal function [21]. However, the pathological relevance of free ADMA and SDMA remains controversial given the fact that the free forms of dimethylarginines comprise only weak inhibitory potency towards NOS [22]; nevertheless, there is mounting evidence of Arg derivatives as promising targets in cerebrovascular diseases which will be discussed below (Figure 1).
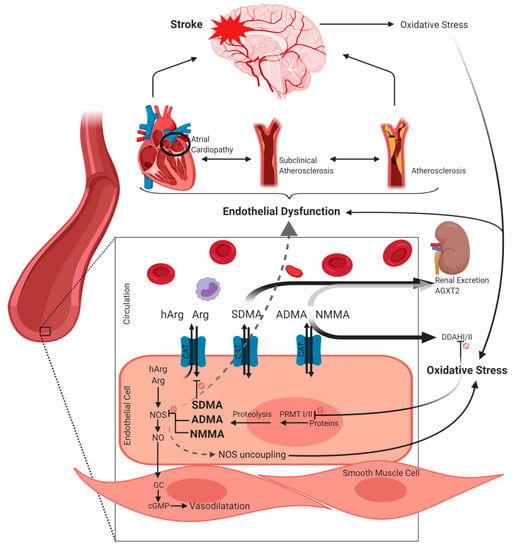
Figure 1.
Overview on metabolism of arginine (Arg), homoarginine (hArg), asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) and monomethylarginine (NMMA) as well as putative links to cerebrovascular risk and disease. Prohibition signs besides lines refer to an inhibitory relation. For further explanation see Section 2. The figure was created using BioRender.
3. Arginine Derivatives as Markers of Cerebrovascular Risk and Mortality
3.1. The Relation of ADMA and SDMA to Atherosclerotic Disease
As discussed above, dimethylarginines are associated with reduced bioavailability of NO, either via competing with Arg at the catalytic active side of NOS (ADMA) or via inhibition of the cellular Arg uptake by SDMA. Dimethylarginines are therefore regarded as markers of endothelial dysfunction which is an early step in the initiation of atherosclerosis [23]. The first evidence for ADMA as a risk marker in stroke patients came from Korean researchers investigating plasma ADMA concentrations in elderly patients [24]. Plasma ADMA was determined with high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection (HPLC-FL) and found to be doubled in 52 stroke patients as compared with 35 age and sex-matched controls. More importantly, the odds ratio (OR) for recurrent stroke for the upper median ADMA level of total subjects was even seven-fold increased. A few years later, increased concentrations of ADMA were reported for hemorrhagic and cardio-embolic stroke as well as transient ischemic attack (TIA) patients in the Swedish population of Kalmar [25].
The functional relevance of ADMA has been proven by Kielstein et al. showing that infusion of ADMA in healthy adults does not only lead to higher arterial resistance and blood pressure [26] but also to decreased cerebral perfusion [27] which underscores the role of ADMA as active mediator rather than a mere biomarker of endothelial dysfunction. In accordance, Baum et al. [28] reported significant associations between Arg derivatives with measure of vascular function in 5.000 individuals. The pathophysiological impact of Arg derivatives in atherosclerosis is furthermore supported by experimental work showing that ADMA is associated with foam cell formation [29] as well as with migration [30] and apoptosis [31] of vascular smooth muscle cells [30]. Interestingly, ADMA suppresses endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) in patients with coronary heart disease [32]. EPC play an important role in the regeneration of injured endothelium [32].
Progression and vulnerability of atherosclerotic lesions is driven by inflammatory mechanisms [33]. ADMA may be increased by systemic inflammation and subsequently lead to endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary heart disease or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [34]. The link of ADMA and inflammation in RA patients is meanwhile confirmed by different studies and meta-analyses [35,36,37] suggesting that ADMA may constitute as vascular risk marker in this vulnerable patient collective. This is further supported by a study in RA patients demonstrating an association of ADMA with homocysteine and with a methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) polymorphism which are implicated in atherosclerosis [38].
Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT) is a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis and regarded as predictor of vascular diseases [39]. While one study described an inverse relation of ADMA with CIMT [40], there are meanwhile numerous studies proving a positive correlation between circulating ADMA and/or SDMA concentrations with CIMT in patients with diverse demographics and different underlying diseases [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56], however, with ethnical differences [57]. In a long-term follow-up study over six years, Furuki et al. [47] showed that ADMA was an independent predictor of CIMT progression. Interestingly, in an analysis of the Framingham offspring cohort, an independent association of ADMA with CIMT in the internal carotid artery (ICA) was confirmed but not with that in the common carotid artery (CCA), implying a site-specific role of ADMA in atherosclerotic disease [52]. Of note, CIMT at the ICA might be the superior measure of cardiovascular risk compared with CIMT at the CCA [39]. In a study including patients with recent ischemic stroke or TIA an association between hArg/ADMA ratio and the aortic intima media thickness has been reported [58].
The relevance of dimethylarginines in stroke due to large artery atherosclerosis will be discussed in paragraph 5.1.
3.2. ADMA and SDMA in Relation to Vascular Risk Factors
Hypertension is the most important stroke risk factor [59]. Nitric oxide deficiency as well as oxidative stress play an important role in arterial hypertension. Likewise, numerous investigations have shown a link between ADMA levels and the occurrence and development of hypertension [60,61,62]. Controversially, there are also studies in the general population which could not prove this association [63]. Of note, chronic SDMA infusion in otherwise healthy mice did not lead to an alteration of blood pressure, concluding that SDMA is unlikely to be a causal pathophysiological factor [64].
ADMA was found to be highly elevated in young patients with hypercholesterolaemia [65]. A potential mechanistic link might be based on the upregulation of ADMA synthesis through LDL cholesterol [66]. Vice versa, in a preclinical hypercholesterolemia model the reduction of ADMA levels was related to less atherosclerotic lesions [67]. Interestingly, in a study including 3.310 patients undergoing coronary angiography, SDMA was identified as marker of high density lipoprotein (HDL) dysfunction, markedly in patients with renal insufficiency which may implicate another pathophysiologic link between renal disease, SDMA and premature vascular disorders [68]. In the original study by Yoo et al. [24] ADMA was moreover found to be positively correlated with homocyst(e)ine.
Importantly, in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS) who often reveal only few vascular risk factors [69] a strong correlation between the CHA2DS2VASC and both dimethylarginines, especially with SDMA, was found [46]. CHA2DS2VASC has been previously shown to be a reliable instrument predicting recurrent cerebral ischemia and death in ESUS patients [70]. An association between CHA2DS2VASC and both dimethylarginines as well as hArg/dimethylarginine ratios has been recently proven in three independent cohorts of patients with cerebrovascular diseases [71].
Nitric oxide released from endothelial cells strongly inhibits platelet activation and vascular adhesion [72,73]. In patients undergoing percutaneous angioplasty ADMA was shown to be associated with platelet activation. In accordance, in hypertensive patients higher ADMA levels may lead to increased platelet aggregation via cGMP signalling [74,75]. Thus, Arg derivatives may potentially play a role also in platelet activation during stroke.
3.3. Dimethylarginines Predict Morbidity and Mortality of Cerebrovascular Diseases
In a meta-analysis by Willeit et al. [76] including 19,842 individuals, those with ADMA levels in the highest tertile compared with those in the lowest tertile showed significantly higher risk for cardiovascular diseases (hazard ratio, HR 1.42 (1.29–1.56)), coronary heart disease (HR 1.39 (1.19–1.62)) and especially for stroke (HR 1.60 (1.33–1.91)). However, in the same data set, SDMA levels did not show a significant association with these vascular outcome measures (HR for stroke: 1.31 (0.83–2.07)) [76]. As described above, the relevance of SDMA as risk factor for vascular endpoints might be higher in patients who suffer from renal insufficiency [77,78]. In a sub-study of the ARISTOTLE trial, Horowitz et al. [79] investigated ADMA and SDMA in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). While ADMA concentrations were weakly related to thromboembolic events, the authors found an association of SDMA with bleeding events and of both dimethylarginines with increased mortality [79].
In total, there are far less studies focussing on SDMA compared with ADMA [18,80]. As described above, SDMA is an excellent marker of renal function which itself is related with vascular diseases [81]. Though, there is evidence that SDMA reflects vascular risk and disease independent from the extent of renal insufficiency [82]. Interestingly, Emrich et al. [77] demonstrated in a study of 528 patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) that SDMA was superior to other Arg derivatives in predicting CKD progression as well as vascular events including stroke. Two independent prospective studies showed that SDMA predicts short- and long-term outcome following ischemic stroke [83,84]: Lüneburg and colleagues showed in 137 acute ischemic stroke patients who were admitted to the emergency unit that plasma SDMA was associated with composite detrimental outcome as comprised as death, recurrent stroke, myocardial infarction and re-hospitalization in the first 30 days after the event—an association which was mediated by the link of SDMA and renal function [84]. In the other study, survival was independently related to lower SDMA during a median time of follow-up of 7.4 years in 394 patients with ischemic stroke while ADMA barely missed significance [83]. Thus, SDMA is currently emerging as an interesting target in cerebrovascular diseases. Table 1 and Table 2 provide an overview on the discussed clinical studies investigating ADMA and SDMA in cerebrovascular diseases.

Table 1.
Overview on selected clinical studies and meta-analyses evaluating ADMA in cerebrovascular diseases.

Table 2.
Overview on selected clinical studies and meta-analyses evaluating SDMA in cerebrovascular diseases.
3.4. Homoarginine as Marker and Target in Cerebrovascular Diseases
A decade ago, hArg was studied in regard to cardiovascular and all-cause mortality [89]. In contrast to dimethylarginine derivatives, hArg levels were inversely associated with adverse events and mortality [90]. Most consistently, low hArg levels are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, which was shown in subjects referred for coronary angiography, in hemodialysis patients with diabetes mellitus, in stroke patients, but also population-based cohorts [89,91,92,93,94]. A recent meta-analysis confirmed the inverse association of hArg with all-cause mortality (HR 0.64 [0.57–0.73]) [95]. More specifically, low hArg levels were strongly associated with fatal strokes and revealed a trend to increase stroke risk [96,97]. In prospective studies of stroke patients, low hArg levels were independently associated with increased long-term all-cause mortality and short-term adverse events, respectively (Table 3) [91]. In addition to cerebrovascular patients, increased hArg levels (i.e., 1-SD log plasma hArg) were also associated with a risk reduction for major adverse cardiovascular events including stroke [93]. See Table 3 for an overview on clinical studies evaluating hArg as biomarker in cerebrovascular diseases.

Table 3.
Overview on selected clinical studies evaluating hArg in cerebrovascular diseases.
Homoarginine has been implicated to play a role in vascular function [90,99,100,101]. Correspondingly, epidemiological studies revealed an inverse association of hArg with aortic wall thickness and aortic plaque burden [93], an inverse correlation of hArg/ADMA ratio with aortic intima-media thickness [58] and a link between hArg/SDMA ratio with internal carotid artery stenosis and unfavorable outcome after stroke [71,98].
Most importantly, hArg supplementation confers indeed beneficial effects in vascular disease models. First, AGAT-deficient mice are devoid of hArg and revealed increased infarct sizes and an impaired cardiac contractibility, which were normalized upon hArg supplementation [91,102]. Furthermore, hArg supplementation attenuated detrimental effects of diabetic kidney damage, preserved systolic function in a model of coronary artery disease, reduced neointimal hyperplasia in balloon-injured rat carotids and attenuated post-myocardial infarction heart failure [91,103,104,105,106].
Although mouse studies revealed a causal link between hArg and vascular disease, the direct protective effect in humans remains to be established [107]. In a recent clinical trial, pharmacokinetic and -dynamic parameters were studied in healthy volunteers orally supplemented with 125mg hArg or placebo daily for 4 weeks using a cross-over design [108]. Supplementation was well tolerated and increased hArg levels by 7 fold without any alteration of vascular or neurological parameters [108,109]. Currently, a randomized placebo-controlled trial studies the administration of oral hArg in acute stroke patients with low hArg levels (https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; unique identifier: NCT03692234). Future studies will answer the question, if hArg deficiency is a modifiable protective cerebrovascular risk factor.
4. Acute Response of Arginine Derivatives after Ischemic Stroke
After the acute onset of stroke, the local reaction to the ischemic tissue based on cellular damage, proteolysis and oxidative stress consecutively induces a secondary systemic reaction. In this setting, an increase in expression of PRMTs and for ADMA a decreased activity of DDAH elevates systemic levels of dimethylarginines. More extended acute brain damage in larger cerebral infarction accelerates cellular damage and proteolysis resulting in further increase of dimethylarginines. In patients with acute ischemic stroke several studies demonstrated the increase of dimethylarginines; while studies including ADMA are numerous, those including SDMA are sparse.
Brouns and colleagues [85] reported dimethylarginine concentrations in 88 acute ischemic stroke and TIA patients within 24 hours of onset. This study is remarkable in several aspects. Firstly, ADMA as well as SDMA levels increased with increased severity as assessed by the National Institutes of Health stroke scale (NIHSS). Secondly, significant correlations between outcome, evaluated by the modified Rankin scale (mRS) at three months after stroke, and both dimethylarginine derivatives existed and third, ADMA and SDMA were measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within 24 hours of stroke onset. This indicates that elevated ADMA and SDMA in the hyperacute phase of stroke originate from cerebral cellular damage and proteolysis.
The kinetics during the acute phase of stroke seem to be different between Arg, SDMA and ADMA. ADMA seems to peak rather early within hours after admission to the hospital while SDMA increases and L-arginine decreases during the first days after admission [86,88,110]. Both, the time courses of ADMA and SDMA relate to the clinical outcome assessed by mRS, while SDMA and in particular Arg, moreover, independently predict post-stroke infections [86,110]. The kinetics observed in stroke patients are similar to those seen in septic patients, and also these Arg derivatives may help distinguish between patients with favorable from unfavorable outcome [111,112].
Higher ADMA levels were also detected in 40 Chinese TIA patients compared to controls [113]. In contrast to this, in a Spanish study there was no difference in ADMA levels in 238 ischemic stroke patients and controls [87]. However, stroke etiology or time of blood withdrawal was not indicated in this study. The authors suggested genetic, socio-economic or nutritional factors explaining differences to other stroke patient cohorts. In 52 Turkish patients with acute ischemic stroke ADMA levels were higher than in controls, while NO levels measured in stroke patients were lower than in controls [114]. One might wonder if ADMA increase is directly linked to the extent of acute brain injury. This remains unclear, since no correlation of ADMA and S100B concentrations has been found in 58 ischemic stroke patients [115] but a weak correlation of ADMA, SDMA and S100B has been shown in another study in 55 ischemic stroke patients [88].
There is less data about SDMA after ischemic stroke, since initially greater importance for stroke pathophysiology was attributed to ADMA due to its role as endogenous NOS inhibitor. Meanwhile also SDMA levels have been repeatedly measured, showing that these are also elevated after the acute event of stroke. In 55 acute ischemic stroke patients, SDMA levels at 6 hours were associated with neurological worsening [110]. In another study, 67 acute ischemic stroke patients with unfavorable outcome showed an elevation as early as 6 hours until 3 days after the event of stroke [86]. Brouns et al. [85] demonstrated increased SDMA levels in CSF, while this increase was pronounced in more severe stroke patients, possibly via PRMTs due to increased proteolysis. There was no association of SDMA increase with stroke etiology in these two studies [85,86]. Controversially, in 363 ischemic stroke patients there was an increase in SDMA levels in patients with cardioembolic strokes but not in other stroke subtypes [25]. In concordance, in a cohort of 231 acute ischemic stroke patients SDMA levels were also elevated, when AF was detected in these patients [83]. Thus, it is noticeable that SDMA increase mostly occurs in the etiology of cardioembolic infarctions suggesting endothelial preconditions that provide levels in a certain dimension or even potentiate these levels in the event of stroke. However, cardioembolic strokes represent the most severe subtype, while the amount of destruction might further elevate SDMA levels. Interestingly, in a patient cohort of 88 ischemic stroke patients we found lower SDMA and higher ratios of Arg/ADMA, Arg/SDMA and ADMA/SDMA in patients with ESUS compared to patients with diagnosed AF as cardioembolic stroke etiology. SDMA and ADMA were determined at 7 days after stroke [46]. Most importantly, at follow-up of these patients at least one year after index stroke, SDMA values were almost stable over time (p < 0.001; r = 0.788) and still remained significantly higher in AF compared with ESUS-patients [116]. These results might indicate that indeed SDMA is rather related to the cardioembolic etiology than driven by the acute ischemic response (also see Section 5).
Potential Mechanisms of Dimethylarginine Response after Ischemic Stroke
Obviously in ischemic stroke the acute and massive reduction of cerebral blood flow is to be made accountable for the immediate damage of neurons. It needs to be discussed that in the early stages of stroke pathology ADMA contributes to poor cerebral perfusion.
ADMA assumingly limits the cerebral perfusion in physiological conditions and in case of cerebrovascular injury by affecting the vascular tone and compliance. Nitric oxide synthase and NO represent the most important endogenous regulators of vasodilation in cerebral arterioles [117]. In an animal model in rats, administration of its endogenous inhibitor ADMA reduced the diameter of the basilar artery, while in rabbits the diameter of cerebral arterioles was reduced. Administration of Arg reversed this effect [118]. In mice administration of ADMA reduced response of cerebral arterioles to acetylcholine as vascular tone relaxation was restricted to 70%, whereas in transgenic mice with DDAH-1 overexpression relaxation of cerebral vessels as response to acetylcholine was not impaired [119]. In human middle cerebral arteries obtained from 26 autopsies administration of ADMA and L-NMMA impaired acetylcholine induced endothelial relaxation [120]. Additional administration of Arg revised this effect. Kielstein and colleagues administered ADMA in 20 healthy individuals over 40 minutes. In these individuals cerebral blood flow was detected to be significantly impaired, while systemic blood pressure was not altered [27]. These data suggest, that increased ADMA levels after the acute event of stroke might further reduce cerebral perfusion and thereby causes loss of penumbral tissue. One could even suggest that there is a link between increased ADMA levels and successful recanalization therapy, which had been investigated in acute stroke patient cohorts. Here, recanalization as reached by administration of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rtPA) and mechanical recanalization as performed by endovascular catheter therapy were investigated in separate clinical studies. In 41 acute ischemic stroke patients with large cerebral vessel occlusion undergoing mechanical recanalization, pretreatment levels of ADMA in patients with non-successful recanalization were higher than in successful therapy. However, in multivariate analysis there was no significant association between ADMA levels and the grade of recanalization [121].
Further evidence for a role of ADMA in acute medical recanalization treatment comes from 90 ischemic stroke patients of the German Multicenter EPO Stroke Trial. Patients had different treatment regimen, since they either received erythropoietin (EPO), placebo, rtPA + placebo or EPO + rtPA. Serum ADMA levels were observed from day 1 (pretreatment) until day 7 [122]. While ADMA levels increased in general, there was a significant reduction in the rtPA + placebo group compared with the placebo group. ADMA levels were correlated with outcome, although it remains unclear whether lower ADMA levels could contribute to favorable outcome. One might again suggest better reperfusion due to increasing NO levels after lack of endogenous inhibition by ADMA. Remarkably, rtPA is administered in a solution of rtPA and as carrier substance for stabilization of Arg. One could suggest, that early supplement of Arg in ischemic stroke might improve cerebral blood flow, while late supplement might lead to massive NO production ending in neurotoxic effects as caused by uncoupling and reactive oxygen species [123,124]. However, in 43 acute ischemic stroke patients with intravenous thrombolytic treatment using recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator, pretreatment levels of ADMA were not associated with outcome [125]. In summary, so far, an independent influence of ADMA in recanalization treatment has been confirmed neither in mechanical nor in medical recanalization approaches.
During the acute stages of stroke, ADMA levels are increased by oxidative stress resulting in activation of PRMTs and inhibition of DDAH activity [126,127]. Here, ADMA might be a further generator of oxidative stress via uncoupling of eNOS and iNOS, which leads to synthesis of superoxides [126,128,129]. So far, studies are missing that show ADMA induced uncoupling of NOS in the cerebral circulation. After ischemic stroke, NO as synthesized by iNOS and nNOS is significantly increased. Extended NO levels possess neurotoxic properties since NO levels react with oxygen radicals to form the toxic compound peroxynitrite [130,131,132,133]. After ischemic stroke, expression of NOS isoforms differs in regard to temporal and spatial aspects. Mouse studies suggest that inhibition of iNOS and nNOS overexpression is neuroprotective, while inhibition of eNOS impairs cerebral blood flow and thereby could be detrimental for the penumbral tissue [134]. Herewith, effects of ADMA as assumingly non-selective NOS inhibitor might be protective and detrimental all at once. We suggest dose-dependent effects which might essentially be controlled by timing and the amount of NO produced. In macrophages NO-synthesis can be regulated by ADMA derived from endothelial cells [135]. However, it remains unclear if endothelial ADMA also regulates NO synthesis in neurons.
Analysis of isoform specific inhibition of DDAH might clarify the diverse NO–DDAH–ADMA pathway after acute ischemic stroke, which would be urgently needed to identify any potential treatment targets. Recently, the importance of ADMA for NO-synthesis in human circulation has been challenged. While ADMA has been shown to effectively inhibit nNOS, the inhibitory potential of ADMA in regard to eNOS seems to be by far weaker [22,136]. This might at least indicate a lack of sufficient knowledge regarding the role of ADMA in patients. By influencing the inflammatory cascade after the acute event of stroke, ADMA might well enhance secondary brain injury, leading to worse patient outcome. A single therapeutic approach for lowering ADMA levels in an animal model was negative. In this transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model in mice infarction size did not differ in transgenic mice with DDAH-1 overexpression compared to wild-type animals [137]. However, neither ADMA levels nor DDAH-1 activity differed in these animals [137]. Recently, in a DDAH-1 knock-out rat model of MCAO, ADMA levels were increased while NO was reduced [138]. Administration of Arg in the knock-out group reduced neurological damage and increased levels of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1alpha) [138].
In different cell culture models, ADMA triggers production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [139,140]. In monocytes ADMA elevates the synthesis of TNF-alpha in a ROS/NF-kappaB dependent pathway [139]. In endothelial cells ADMA increases activation of NF-kappaB and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated kinases as well as levels of TNF-alpha and ICAM-1 [140]. ADMA enhances adhesion of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) on endothelial cells and triggers their degranulation [141].
In 58 ischemic stroke patients Chen and colleagues investigated the association of ADMA with mediators of inflammation [115]. The distinct temporal dynamics of ADMA levels after the event with peak values at time points when IL-6 levels already decreased may indicate that ADMA is unlikely to induce the inflammatory response. However, ADMA levels were associated with levels of IL-6 and CRP at several time points after stroke [115]. Molnar and colleagues detected an association of early ADMA and MCP-1 levels in 55 ischemic stroke patients [110]. Interestingly, in other conditions of acute inflammation, ADMA might rather be decreased in the acute setting, while levels elevate again when other inflammation markers decline [142].
Compared to ADMA data about the role of SDMA after acute stroke again are sparse. Experimental data point to a potential pathophysiological role of SDMA in acute stroke via modulation of NO levels, ROS and inflammatory processes. In experimental conditions concentrations of 1-10 mmol/L SDMA indirectly limits NO-synthesis by reduction of intracellular Arg uptake and renal tubular Arg absorption [143,144]. SDMA concentrations between 2-100µmol/L dose dependently enhanced ROS production in endothelial cells [82]. SDMA has been shown to be a weak nNOS inhibitor, while any data showing efficacy of SDMA for inhibition of other NOS isoforms are missing (for a review see Reference [136]). In monocytes SDMA increased ROS production by modulation of store-operated calcium channels [145]. Another study from the same group demonstrated that in monocytes SDMA increases activation of NF-kappaB and expression of TNF-alpha and IL-6 [146]. Certainly, these experimental conditions do not reflect those in stroke patients.
In ischemic stroke patients, SDMA was significantly correlated with serum concentrations of the proinflammatory mediators MCP-1 and IL-6 [115]. Of note, SDMA and MCP-1 were correlated already at the early stage only hours after the acute event, while there were further correlations days after stroke between SDMA, MCP-1 and IL-6. Interestingly, Molnar and colleagues confirmed the early correlation of SDMA and MCP-1 [110]. SDMA and CRP were only correlated at later time points at 3 days after stroke [88]. In 43 ischemic stroke patients receiving IVT using rtPA, SDMA differed at each time point during the first week after stroke including pretreatment levels depending on clinical outcome [125]. However, multivariate analysis could not confirm an independent association between SDMA pretreatment levels and outcome in IVT. In summary, further studies are warranted to investigate if SDMA contributes in particular to secondary brain injury.
5. Arginine Derivatives as Markers of Stroke Etiology
5.1. Large Artery Atherosclerosis
The pathophysiologic link of Arg derivatives with atherosclerosis was discussed above. Cordts et al. [71] recently reported that ratios of hArg/ADMA and hArg/SDMA are associated with strokes due to AF or large artery atherosclerosis and are moreover predictive for prevalent stenosis of the internal carotid artery in three independent cohorts. Scherbakov and colleagues reported elevated ADMA levels in cardioembolic or large artery stroke [147]. In 262 ischemic stroke patients with intracranial atherosclerotic stroke, ADMA levels were increased compared to controls without stroke [148]. Interestingly, hArg/SDMA ratio showed a stronger relation with atherosclerotic burden compared with hArg/ADMA [71]. The degree of re-stenosis after carotid endarterectomy (CEA) has been found to be related to ADMA levels [149]. These results are clearly in line with the described relevance of Arg derivatives in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic disease.
5.2. Small Vessel Disease
Tsuda et al. [150] reported an association of ADMA levels with occurrence of small vessel disease which was independent from classical cardiovascular risk factors. Moreover, ADMA correlated with the extent of cerebral leukoaraiosis. This finding was recently confirmed in a study investigating persons with asymptomatic white matter hyperintensities in whom inflammatory or coagulation disorders have been excluded [151]. Besides the association of ADMA to imaging measures of small vessel disease, a relation of ADMA levels with progression of cognitive impairment has been reported [152]. Furthermore, a role of ADMA has been implicated in rare microangiopathic diseases like Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) [153]. Interestingly, dimethylarginines were shown to be positively correlated with Hachinsky Ischemic Score (HIS) and might therefore indicate vascular cognitive impairment [154]. In the study by Cordts et al. [71] hArg/ADMA and hArg/SDMA ratios enabled to discriminate lacunar from territorial strokes—an effect that was predominantly explained by higher hArg values in patients with small vessel disease compared with patients with other stroke etiologies.
5.3. Cardioembolic Stroke and Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source
The identification of the distinct etiology of ischemic stroke is crucial for its secondary prevention. Despite extensive diagnostic workup including cerebral, vascular und cardiac imaging as well as rhythm analyses a significant proportion of ischemic stroke remains unexplained. In 2015 Hart et al. [155] introduced the concept of the so called „embolic stroke of undetermined source“ (ESUS) which accounts for cryptogenic strokes with an embolic pattern in cranial imaging. ESUS accounts for approximately 16% of all ischemic strokes [156]. It is presumed that a significant part of ESUS will be due to subclinical paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF). As a result, two multicenter clinical trials (RE-SPECT ESUS [157] and NAVIGATE ESUS [158]) have been performed to test the hypothesis that ESUS patients might benefit from oral anticoagulation rather than platelet inhibition. However, both studies failed to prove this approach [157,158], indicating that proper workup for investigation of the individual stroke mechanism is still crucial for choosing the appropriate secondary preventive therapy. The same applies for concurrent stroke etiologies, like e.g. AF and high-grade carotid stenosis. In conclusion, novel biomarkers that support the diagnostics of stroke etiology would be advantageous for determining the appropriate individual therapy and consequently reduce the burden of recurrent strokes.
Current data indicate that a diseased left atrium—recently referred as so called “atrial cardiopathy” [159]—might lead to enhanced thrombembolic risk independently of AF which is regarded as a mere symptom of the disease process [160,161]. Endothelial dysfunction mechanisms and subclinical atherosclerosis are closely related to the development of atrial cardiopathy in terms of a systemic disorder [162,163,164,165,166]. Hypothetically, endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness contribute to a higher cardiac afterload and consecutively to myocardial remodelling processes in the atrium [167,168]. Moreover, experimental and clinical studies implicate an important role of NOS signalling in AF [166]. As a result, Arg derivatives have been previously investigated as potential markers of AF.
Schulze et al. [83] demonstrated that SDMA levels as well as the ratios between Arg/ADMA, Arg/SDMA and Arg/NMMA were significantly different in stroke patients with AF compared to those with sinus rhythm in a univariate analysis. Stamboul et al. [169] reported higher ADMA levels in patients who developed AF after myocardial infarction. A stepwise increase of ADMA concentrations has been shown in controls, in patients with lone AF and in patients with AF and other comorbidities [170]. This notion fostered further investigation relating ADMA and SDMA to permanent rather than paroxysmal AF in acute ischemic stroke [171]. Of note, AF patients exhibit a high proportion of cardiovascular risk factors. In an analysis of the Framingham cohort, Schnabel et al. [172] reported that Arg derivatives were not independently altered in AF patients after accounting for vascular risk factors. However, in another population-based study—the Gutenberg Health Study—we found a probable association of Arg derivatives with occurrence of AF, and moreover, independent correlations with electrocardiography and echocardiography-based measures of atrial disease [173]. Interestingly, SDMA, but not ADMA, was associated with left atrial dimension and P-wave duration in this analysis [173]. Cordts et al. [71] demonstrated a relation of hArg/ADMA and hArg/SDMA-ratios with cardioembolic stroke and stroke due to large artery disease.
In another study of patients with ischemic stroke SDMA and Arg/dimethylarginine ratios were significantly different between ESUS and AF in total as well as newly diagnosed AF [46], indicating a potential application in clinical practice. Furthermore, SDMA concentrations were shown to be associated with subsequently diagnosed AF after ESUS and correlate with left atrial volume index in ESUS patients and might therefore support identification of atrial cardiopathy in this stroke entity as recently reported by Ziegler et al. [116].
Interestingly, successful occlusion of the left atrial appendage led to a significant reduction of SDMA levels, while no changes concerning ADMA were observed [174]. Moreover, a polymorphism in the gene coding for AGXT2 which metabolizes ADMA and SDMA is associated with AF [175]. AGXT2 variants have been previously associated with circulating SDMA [176,177], heart rate variability [177] and stroke subtypes (lacunar vs. territorial infarctions) [176]. These data may indicate a pathogenic causal role of Arg derivatives and especially of SDMA in the development of AF. Of note, SDMA blood concentrations are largely dependent on renal function by which this marker is increasingly considered as potential measure for this purpose [178]. Conversely, renal insufficiency is a long-acknowledged factor in vascular diseases and AF [179]. Keeping in mind that AGXT2 is highly expressed in kidney cells [180], the SDMA metabolism is of high interest for future studies investigating the pathogenic link between this metabolite and renal and vascular disease. Of note, ADMA and SDMA might also be useful for risk prediction in anticoagulated AF-patients [79,181], as already discussed above.
Taken together, there are diverse and recent data underscoring the potential role of Arg derivatives as markers for identifying the underlying mechanism of ischemic stroke. Larger and prospective studies are needed to validate these findings.
6. Conclusions
Due to its physiological influence on vascular function, the Arg metabolism is of high interest in cerebrovascular diseases. ADMA is meanwhile confirmed as a biomarker of vascular risk, morbidity and mortality in a variety of large studies and meta-analyses. Although less studies are focussing on SDMA, this Arg derivative is currently emerging as another target and indeed might constitute characteristics divergent from ADMA, such as an association with cardioembolic stroke etiology. Besides the relation of Arg derivatives for risk and occurrence of ischemic stroke there is also a response of these metabolites after cerebral ischemia which further might contribute to secondary brain injury. In contrast, hArg is inversely associated with adverse events and mortality in cerebrovascular diseases and might constitute a modifiable protective risk factor. Taken together, Arg derivatives are promising diagnostic and therapeutic targets in diverse settings of cerebrovascular diseases. Future clinical studies are needed to validate the findings discussed in order to enable a translation into clinical practice.
Funding
This work was supported by PRACTIS—Clinician Scientist Program of Hannover Medical School, funded by the German Research Foundation (grant number: DFG, ME 3696/3-1) (G.M.G.) and by an Else Kröner-Exzellenzstipendium from the Else Kröner Fresenius Stiftung (grant number: 2018_EKES.04) (C.U.C.). The APC was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Open Access Publication Fund of Hannover Medical School.
Conflicts of Interest
C.U.C. received a lecture fee from Pfizer. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AE | adverse event |
| AGAT | arginine:glycine amidinotransferase |
| ADMA | asymmetric dimethylarginine |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| Arg | Arginine |
| CADASIL | Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy |
| CAT | cationic amino acid transporters |
| CES | cardioembolic stroke |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| CIMT | carotid intima media thickness |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| DDAH | dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| EPC | endothelial progenitor cells |
| ESUS | embolic stroke of undetermined source |
| hArg | Homoarginine |
| HC | healthy controls |
| HIF | hypoxia inducible factor |
| HIS | Hachinsky Ischemic Score |
| HPLC-FL | high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| ICA | internal carotid artery |
| IL | interleukin |
| IS | ischemic stroke |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LAA | large artery atherosclerosis |
| MACE | major cardiovascular outcome event |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MTHFR | methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
| mRS | modified Rankin scale |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health stroke scale |
| NMMA | monomethylarginine |
| nNOS | neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| NR | not reported |
| n.s. | not significant |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PRMT | protein arginine methyltransferases |
| ROS | radical oxygen species |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| rtPA | recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SDMA | symmetric dimethylarginine |
| SVD | small vessel disease |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Ikeda, T.; Feigin, V.L. Global, Regional and Country-Specific Burden of Ischaemic Stroke, Intracerebral Haemorrhage and Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.B. Introduction for Focused Updates in Cerebrovascular Disease. Stroke 2020, STROKEAHA119024159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke Collaborators; Feigin, V.L.; Nguyen, G.; Cercy, K.; Johnson, C.O.; Alam, T.; Parmar, P.G.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Global, Regional, and Country-Specific Lifetime Risks of Stroke, 1990 and 2016. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, J.D.; Rost, N.S.; Leung, T.W.; Montaner, J.; Muir, K.W.; Brown, S.; Arenillas, J.F.; Feldmann, E.; Liebeskind, D.S. Principles of Precision Medicine in Stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, A.N.; Janowski, M.; Oz, H.S.; Roberts, J.; Bix, G.; Dore, S.; Stowe, A.M. Biomarker Application for Precision Medicine in Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitz, K.; Lacy, M.; Atzler, D. Amino Acids and their Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, M.D.; Brown, T.; Zheng, Y.G. The Biological Axis of Protein Arginine Methylation and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric Oxide Synthases: Regulation and Function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzebska, N.; Mangoni, A.A.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Rodionov, R.N. The Second Life of Methylarginines as Cardiovascular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiher, A.M.; Fissthaler, B.; Schray-Utz, B.; Busse, R. Nitric Oxide Modulates the Expression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, P.; Suzuki, M.; Granger, D.N. Nitric Oxide: An Endogenous Modulator of Leukocyte Adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4651–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaki, T.; Nakayama, M.; Kato, R. Inhibition by Nitric Oxide and Nitric Oxide-Producing Vasodilators of DNA Synthesis in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 189, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, J.R.; Chernova, T.; Forsythe, I.D. Nitric Oxide Signaling in Brain Function, Dysfunction, and Dementia. Neuroscientist 2010, 16, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.U.; Lewerenz, J.; Gerloff, C.; Magnus, T.; Donzelli, S. Nitroxyl in the Central Nervous System. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 14, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniades, C.; Shirodaria, C.; Leeson, P.; Antonopoulos, A.; Warrick, N.; Van-Assche, T.; Cunnington, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pillai, R.; Ratnatunga, C.; et al. Association of Plasma Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine (ADMA) with Elevated Vascular Superoxide Production and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling: Implications for Endothelial Function in Human Atherosclerosis. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliers, D.; Lee, D.; Gorin, Y.; Kasinath, B.S. Symmetric Dimethylarginine Alters Endothelial Nitric Oxide Activity in Glomerular Endothelial Cells. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Palagiri, D.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, N.; Deb-Chatterji, M.; Dong, Q.; Kielstein, J.T.; Weissenborn, K.; Worthmann, H. Asymmetric Dimethyarginine as Marker and Mediator in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15983–16004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Kimoto, M.; Sasaoka, K. Purification and Properties of a New Enzyme, NG,NG-Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase, from Rat Kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Kimoto, M.; Watanabe, H.; Sasaoka, K. Metabolism of NG,NG- and NG,NG-Dimethylarginine in Rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 252, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Böger, R.H. The Role of Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginines in Renal Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D.D. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA), Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA) and Homoarginine (hArg): The ADMA, SDMA and hArg Paradoxes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davignon, J.; Ganz, P. Role of Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109, III27–III32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, S. Elevated Levels of Plasma Homocyst(E)Ine and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Elderly Patients with Stroke. Atherosclerosis 2001, 158, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanby, P.; Teerlink, T.; Brudin, L.; Brattstrom, L.; Nilsson, I.; Palmqvist, P.; Carlsson, M. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) as a Risk Marker for Stroke and TIA in a Swedish Population. Atherosclerosis 2006, 185, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Impraim, B.; Simmel, S.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Tsikas, D.; Frolich, J.C.; Hoeper, M.M.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Cardiovascular Effects of Systemic Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition with Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine in Humans. Circulation 2004, 109, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Donnerstag, F.; Gasper, S.; Menne, J.; Kielstein, A.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Scalera, F.; Cooke, J.P.; Fliser, D.; Bode-Böger, S.M. ADMA Increases Arterial Stiffness and Decreases Cerebral Blood Flow in Humans. Stroke 2006, 37, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, C.; Johannsen, S.S.; Zeller, T.; Atzler, D.; Ojeda, F.M.; Wild, P.S.; Sinning, C.R.; Lackner, K.J.; Gori, T.; Schwedhelm, E.; et al. ADMA and Arginine Derivatives in Relation to Non-Invasive Vascular Function in the General Population. Atherosclerosis 2016, 244, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, I.V.; Kajstura, M.; Sawamura, T.; Goligorsky, M.S. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Upregulates LOX-1 in Activated Macrophages: Role in Foam Cell Formation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, T.; Yu, X.; Xin, W.; Lan, X.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Du, G. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Confers the Communication between Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells and Leads to VSMC Migration through p38 and ERK1/2 Signaling Cascade. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Jiang, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Xin, H.; Deng, H.; Li, Y. Role of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Homocysteine-Induced Apoptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thum, T.; Tsikas, D.; Stein, S.; Schultheiss, M.; Eigenthaler, M.; Anker, S.D.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Ertl, G.; Bauersachs, J. Suppression of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Human Coronary Artery Disease by the Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor Asymmetric Dimethylarginine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geovanini, G.R.; Libby, P. Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Overview and Updates. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2018, 132, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniades, C.; Demosthenous, M.; Tousoulis, D.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Toutouza, M.; Marinou, K.; Bakogiannis, C.; Mavragani, K.; Lazaros, G.; et al. Role of Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine in Inflammation-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Human Atherosclerosis. Hypertension 2011, 58, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoo, A.; Dimitroulas, T.; Hodson, J.; Smith, J.P.; Douglas, K.M.; Kitas, G.D. Cumulative Inflammation Associates with Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A 6 Year Follow-Up Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2015, 54, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafari, P.; Zarifian, A.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Taghadosi, M.; Rafiei, A.; Samimi, Z.; Niksolat, F. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginine Concentration as an Indicator of Cardiovascular Diseases in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Sandoo, A.; Kitas, G.D. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine as a Surrogate Marker of Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12315–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Sandoo, A.; Hodson, J.; Smith, J.; Douglas, K.M.; Kitas, G.D. Associations between Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Homocysteine, and the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) C677T Polymorphism (rs1801133) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, T.Z.; Lee, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Plaque in Cardiovascular Risk Assessment. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging 2014, 7, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsuga, J.; Török, J.; Magyar, M.T.; Valikovics, A.; Gesztelyi, R.; Kéki, S.; Csiba, L.; Zsuga, M.; Bereczki, D. Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Negatively Correlates with Intima-Media Thickness in Early-Onset Atherosclerosis. CED 2007, 23, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Sun, L.; Du, L.; Zhang, T.; Xin, W.; Lan, X.; Du, G. Association of Circulating Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: Evidence from 6168 Participants. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xiong, R.; Feng, S.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Association of Circulating Levels of ADMA with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozalper, V.; Kara, M.; Tanoglu, A.; Cetındaglı, I.; Ozturker, C.; Hancerlı, Y.; Hıra, S.; Kara, K.; Beyazıt, Y.; Yazgan, Y. Evaluation of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Familial Mediterranean Fever: The Relationship between the Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Endocan with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilisson, J.; Zagura, M.; Zilmer, K.; Salum, E.; Heilman, K.; Piir, A.; Tillmann, V.; Kals, J.; Zilmer, M.; Pruunsild, C. Increased Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness and Myeloperoxidase Level in Children with Newly Diagnosed Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mels, C.M.C.; Schutte, A.E.; Huisman, H.W.; Smith, W.; Kruger, R.; van Rooyen, J.M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Atzler, D.; Böger, R.H.; Malan, N.T.; et al. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Symmetric Dimethylarginine Prospectively Relates to Carotid Wall Thickening in Black Men: The SABPA Study. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, G.M.; Biber, S.; Sieweke, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Gabriel, M.M.; Putzer, A.S.; Hasse, I.; van Gemmeren, T.; Schuppner, R.; Worthmann, H.; et al. Plasma Dimethylarginine Levels and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness are Related to Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Embolic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuki, K.; Adachi, H.; Enomoto, M.; Otsuka, M.; Fukami, A.; Kumagae, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Nanjo, Y.; Kakuma, T.; Imaizumi, T. Plasma Level of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) as a Predictor of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression: Six-Year Prospective Study using Carotid Ultrasonography. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuki, K.; Adachi, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Enomoto, M.; Satoh, A.; Hino, A.; Hirai, Y.; Imaizumi, T. Plasma Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) are Related to Intima-Media Thickness of the Carotid Artery: An Epidemiological Study. Atherosclerosis 2007, 191, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Hodson, J.; Sandoo, A.; Smith, J.; Kitas, G.D. Endothelial Injury in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Crosstalk between Dimethylarginines and Systemic Inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccioni, G.; Scotti, L.; D’Orazio, N.; Gallina, S.; Speziale, G.; Speranza, L.; Bucciarelli, T. ADMA/SDMA in Elderly Subjects with Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis: Values and Site-Specific Association. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6391–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine is Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2015, 37, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, R.; Xanthakis, V.; Polak, J.F.; Schwedhelm, E.; Sullivan, L.M.; Benndorf, R.; Schulze, F.; Vasan, R.S.; Wolf, P.A.; Böger, R.H.; et al. Association of the Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor ADMA with Carotid Artery Intimal Media Thickness in the Framingham Heart Study Offspring Cohort. Stroke 2009, 40, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notsu, Y.; Yano, S.; Shibata, H.; Nagai, A.; Nabika, T. Plasma Arginine/ADMA Ratio as a Sensitive Risk Marker for Atherosclerosis: Shimane CoHRE Study. Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimirova-Kitova, L.; Terzieva, D.; Marinov, B. Intima-Media Thickness and Flow-Mediated Vasodilation in Asymptomatic Subjects with Newly Detected Severe Hypercholesterolemia. Echocardiography 2009, 26, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimirova-Kitova, L.; Deneva, T.; Marinov, B. Predictors of the Intima-Media Thickness of Carotid Artery in Asymptomatic Newly Detected Severe Hypercholesterolemic Patients. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2010, 30, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahls, M.; Friedrich, N.; Atzler, D.; Felix, S.B.; Nauck, M.A.; Böger, R.H.; Volzke, H.; Schwedhelm, E.; Dorr, M. L-Arginine and SDMA Serum Concentrations are Associated with Subclinical Atherosclerosis in the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mels, C.M.; Loots, I.; Schwedhelm, E.; Atzler, D.; Böger, R.H.; Schutte, A.E. Nitric oxide synthesis capacity, ambulatory blood pressure and end organ damage in a black and white population: the SABPA study. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Yanchev, G.R.; Kayacelebi, A.A.; Hanff, E.; Bledau, N.; Widera, C.; Sonnenschein, K.; Haghikia, A.; Weissenborn, K.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. The Role of L-Arginine/L-Homoarginine/Nitric Oxide Pathway for Aortic Distensibility and Intima-Media Thickness in Stroke Patients. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, A.K.; Esenwa, C.; Elkind, M.S.V. Stroke Risk Factors, Genetics, and Prevention. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.; Huang, L. Restoration of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine–Nitric Oxide Balance to Prevent the Development of Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11773–11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, B.; Ates, I.; Ozkayar, N.; Kundi, H.; Topcuoglu, C.; Dede, F.; Sennaroglu, E. Are Increased Oxidative Stress and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Levels Associated with Masked Hypertension? Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2016, 38, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taner, A.; Unlu, A.; Kayrak, M.; Tekinalp, M.; Ayhan, S.S.; Arıbaş, A.; Erdem, S.S. The Value of Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Levels for the Determination of Masked Hypertension in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwan, L.v.d.; Davids, M.; Scheffer, P.; Dekker, J.; Stehouwer, C.; Teerlink, T. L-Homoarginine and L-Arginine are Antagonistically Related to Blood Pressure in an Elderly Population: The Hoorn Study. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldink, H.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Park, J.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Bode-Böger, S.; Schuett, H.; Haghikia, A.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Kielstein, J.T. Effects of Chronic SDMA Infusion on Glomerular Filtration Rate, Blood Pressure, Myocardial Function and Renal Histology in C57BL6/J Mice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Szuba, A.; Tsao, P.S.; Chan, J.R.; Tangphao, O.; Blaschke, T.F.; Cooke, J.P. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA): A Novel Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction: Its Role in Hypercholesterolemia. Circulation 1998, 98, 1842–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böger, R.; Sydow, K.; Borlak, J.; Thum, T.; Lenzen, H.; Schubert, B.; Tsikas, D.; Bode-Böger, S. LDL Cholesterol Upregulates Synthesis of Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine in Human Endothelial Cells: Involvement of S-Adenosylmethionine–Dependent Methyltransferases. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, S.J.; Worner, E.A.; Buijs, N.; Richir, M.; Cynober, L.; van Leeuwen, P.A.; Couderc, R. The Arginine/ADMA Ratio is Related to the Prevention of Atherosclerotic Plaques in Hypercholesterolemic Rabbits when Giving a Combined Therapy with Atorvastatine and Arginine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12230–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewinger, S.; Kleber, M.E.; Rohrer, L.; Lehmann, M.; Triem, S.; Jennings, R.T.; Petrakis, I.; Dressel, A.; Lepper, P.M.; Scharnagl, H.; et al. Symmetric Dimethylarginine, High-Density Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasner, S.E.; Lavados, P.; Sharma, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Davalos, A.; Shamalov, N.; Cunha, L.; Lindgren, A.; Mikulik, R.; et al. Characterization of Patients with Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source in the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaios, G.; Vemmos, K.; Lip, G.Y.; Koroboki, E.; Manios, E.; Vemmou, A.; Rodriguez-Campello, A.; Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Giralt-Steinhauer, E.; Arnao, V.; et al. Risk Stratification for Recurrence and Mortality in Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. Stroke 2016, 47, 2278–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, K.; Grzybowski, R.; Lezius, S.; Luneburg, N.; Atzler, D.; Neu, A.; Hornig, S.; Böger, R.H.; Gerloff, C.; Magnus, T.; et al. Guanidino Compound Ratios are Associated with Stroke Etiology, Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis and CHA2DS2-VASc Score in Three Cross-Sectional Studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 397, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, R.; Lückhoff, A.; Bassenge, E. Endothelium-Derived Relaxant Factor Inhibits Platelet Activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1987, 336, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alheid, U.; Frölich, J.C.; Förstermann, U. Endothelium-Derived Relaxing Factor from Cultured Human Endothelial Cells Inhibits Aggregation of Human Platelets. Thromb. Res. 1987, 47, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meirelles, L.R.; Mendes-Ribeiro, A.C.; Santoro, M.M.; Mendes, M.A.; Da Silva, M.N.; Mann, G.E.; Brunini, T.M. Inhibitory Effects of Endogenous L-Arginine Analogues on Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Platelets: Role in Platelet Hyperaggregability in Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunini, T.T. Inhibition of L-Arginine Transport in Platelets by Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and N-Monomethyl-L-Arginine: Effects of Arterial Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 31, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, P.; Freitag, D.F.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Gobin, R.; Mayr, M.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Chowdhury, R. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Cardiovascular Risk: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 22 Prospective Studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrich, I.E.; Zawada, A.M.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Fliser, D.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Heine, G.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA) Outperforms Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Other Methylarginines as Predictor of Renal and Cardiovascular Outcome in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2018, 107, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, E.H.; von Scholten, B.J.; Reinhard, H.; Persson, F.; Teerlink, T.; Hansen, T.W.; Parving, H.H.; Jacobsen, P.K.; Rossing, P. Symmetric and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine as Risk Markers of Cardiovascular Disease, all-Cause Mortality and Deterioration in Kidney Function in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J.D.; De Caterina, R.; Heresztyn, T.; Alexander, J.H.; Andersson, U.; Lopes, R.D.; Steg, P.G.; Hylek, E.M.; Mohan, P.; Hanna, M.; et al. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginine Predict Outcomes in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: An ARISTOTLE Substudy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, S.; Sonntag, S.R.; Lieb, W.; Maas, R. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginine as Risk Markers for Total Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, R.W.; Cheng, M.R.I.; Grant, R.A.; Shantikumar, S.; Xu, G.; Oozeerally, I.; Brunskill, N.J.; Gray, L.J. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode-Böger, S.M.; Scalera, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Breithardt, G.; Fobker, M.; Reinecke, H. Symmetrical Dimethylarginine: A New Combined Parameter for Renal Function and Extent of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, F.; Carter, A.M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Ajjan, R.; Maas, R.; von Holten, R.A.; Atzler, D.; Grant, P.J.; Böger, R.H. Symmetric Dimethylarginine Predicts all-Cause Mortality Following Ischemic Stroke. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luneburg, N.; von Holten, R.A.; Topper, R.F.; Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Böger, R.H. Symmetric Dimethylarginine is a Marker of Detrimental Outcome in the Acute Phase After Ischaemic Stroke: Role of Renal Function. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2012, 122, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouns, R.; Marescau, B.; Possemiers, I.; Sheorajpanday, R.; De Deyn, P.P. Dimethylarginine Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Hyperacute Ischemic Stroke Patients are Associated with Stroke Severity. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthmann, H.; Chen, S.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Li, N.; Deb, M.; Tryc, A.B.; Goldbecker, A.; Dong, Q.; Kielstein, J.T.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; et al. High Plasma Dimethylarginine Levels are Associated with Adverse Clinical Outcome After Stroke. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Clausen, C.F.; Córdoba-Porras, A.; Bedoya, G.; Silva, F.A.; Zarruk, J.G.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Villa, L.A. Increased Plasma Levels of Total Homocysteine but Not Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Hispanic Subjects with Ischemic Stroke FREC-VI Sub-Study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, T.; Pusch, G.; Papp, V.; Feher, G.; Szapary, L.; Biri, B.; Nagy, L.; Keki, S.; Illes, Z. The L-Arginine Pathway in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Severe Carotid Stenosis: Temporal Profiles and Association with Biomarkers and Outcome. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marz, W.; Meinitzer, A.; Drechsler, C.; Pilz, S.; Krane, V.; Kleber, M.E.; Fischer, J.; Winkelmann, B.R.; Bohm, B.O.; Ritz, E.; et al. Homoarginine, Cardiovascular Risk, and Mortality. Circulation 2010, 122, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzler, D.; Schwedhelm, E.; Choe, C.U. L-Homoarginine and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Atzler, D.; Wild, P.S.; Carter, A.M.; Böger, R.H.; Ojeda, F.; Simova, O.; Stockebrand, M.; Lackner, K.; Nabuurs, C.; et al. Homoarginine Levels are Regulated by L-Arginine:Glycine Amidinotransferase and Affect Stroke Outcome: Results from Human and Murine Studies. Circulation 2013, 128, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilz, S.; Teerlink, T.; Scheffer, P.G.; Meinitzer, A.; Rutters, F.; Tomaschitz, A.; Drechsler, C.; Kienreich, K.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; et al. Homoarginine and Mortality in an Older Population: The Hoorn Study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 44, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzler, D.; Gore, M.O.; Ayers, C.R.; Choe, C.U.; Böger, R.H.; de Lemos, J.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Schwedhelm, E. Homoarginine and Cardiovascular Outcome in the Population-Based Dallas Heart Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Paynter, N.P.; Giulianini, F.; Manson, J.E.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.C.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Albert, C.A.; Clish, C.; Rexrode, K.M. Metabolomic Profiles Associated with all-Cause Mortality in the Women’s Health Initiative. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Carru, C.; Mangoni, A.A. Homoarginine and all-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, C.; Meinitzer, A.; Pilz, S.; Krane, V.; Tomaschitz, A.; Ritz, E.; März, W.; Wanner, C. Homoarginine, Heart Failure, and Sudden Cardiac Death in Haemodialysis Patients. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Tomaschitz, A.; Meinitzer, A.; Drechsler, C.; Ritz, E.; Krane, V.; Wanner, C.; Bohm, B.O.; Marz, W. Low Serum Homoarginine is a Novel Risk Factor for Fatal Strokes in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. Stroke 2011, 42, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Lezius, S.; Cordts, K.; Gerloff, C.; Böger, R.H.; Schwedhelm, E.; Grant, P.J. Low Homoarginine/SDMA Ratio is Associated with Poor Short- and Long-Term Outcome After Stroke in Two Prospective Studies. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, R.N.; Oppici, E.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Jarzebska, N.; Brilloff, S.; Burdin, D.; Demyanov, A.; Kolouschek, A.; Leiper, J.; Maas, R.; et al. A Novel Pathway for Metabolism of the Cardiovascular Risk Factor Homoarginine by Alanine:Glyoxylate Aminotransferase 2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabák, A.; Bajor, T.; Temesi, A. Comparison of Substrate and Inhibitor Specificity of Arginase and Nitric Oxide (NO) Synthase for Arginine Analogues and Related Compounds in Murine and Rat Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 198, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, S.; Elliot, D.J.; Da Boit, M.; Gray, S.R.; Lewis, B.C.; Mangoni, A.A. Homoarginine and Inhibition of Human Arginase Activity: Kinetic Characterization and Biological Relevance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faller, K.M.E.; Atzler, D.; McAndrew, D.J.; Zervou, S.; Whittington, H.J.; Simon, J.N.; Aksentijevic, D.; Ten Hove, M.; Choe, C.U.; Isbrandt, D.; et al. Impaired Cardiac Contractile Function in Arginine:Glycine Amidinotransferase Knockout Mice Devoid of Creatine is Rescued by Homoarginine but Not Creatine. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, M.D.; Gao, T.; Venkatachalam, M.; Morris, S.M.; Awad, A.S. L-Homoarginine Supplementation Prevents Diabetic Kidney Damage. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, R.N.; Begmatov, H.; Jarzebska, N.; Patel, K.; Mills, M.T.; Ghani, Z.; Khakshour, D.; Tamboli, P.; Patel, M.N.; Abdalla, M.; et al. Homoarginine Supplementation Prevents Left Ventricular Dilatation and Preserves Systolic Function in a Model of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellera, F.; Ganzetti, G.S.; Froio, A.; Manzini, S.; Busnelli, M.; Meinitzer, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Chiesa, G.; Parolini, C. L-Homoarginine Administration Reduces Neointimal Hyperplasia in Balloon-Injured Rat Carotids. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzler, D.; McAndrew, D.J.; Cordts, K.; Schneider, J.E.; Zervou, S.; Schwedhelm, E.; Neubauer, S.; Lygate, C.A. Dietary Supplementation with Homoarginine Preserves Cardiac Function in a Murine Model of Post-Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure. Circulation 2017, 135, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karetnikova, E.S.; Jarzebska, N.; Markov, A.G.; Weiss, N.; Lentz, S.R.; Rodionov, R.N. Is Homoarginine a Protective Cardiovascular Risk Factor? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzler, D.; Schonhoff, M.; Cordts, K.; Ortland, I.; Hoppe, J.; Hummel, F.C.; Gerloff, C.; Jaehde, U.; Jagodzinski, A.; Böger, R.H.; et al. Oral Supplementation with L-Homoarginine in Young Volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonhoff, M.; Weineck, G.; Hoppe, J.; Hornig, S.; Cordts, K.; Atzler, D.; Gerloff, C.; Böger, R.; Neu, A.; Schwedhelm, E.; et al. Cognitive Performance of 20 Healthy Humans Supplemented with L-Homoarginine for 4weeks. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 50, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, T.; Pusch, G.; Nagy, L.; Keki, S.; Berki, T.; Illes, Z. Correlation of the L-Arginine Pathway with Thrombo-Inflammation may Contribute to the Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iapichino, G.; Umbrello, M.; Albicini, M.; Spanu, P.; Bellani, G.; Polli, F.; Pavlovic, R.; Cugno, M.; Fermo, I.; Paroni, R. Time Course of Endogenous Nitric Oxide Inhibitors in Severe Sepsis in Humans. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010, 76, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.S.; Nierhaus, A.; Rosler, G.; Lezius, S.; Harlandt, O.; Schwedhelm, E.; Böger, R.H.; Kluge, S. Symmetrical (SDMA) and Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine (ADMA) in Sepsis: High Plasma Levels as Combined Risk Markers for Sepsis Survival. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, N. The Relationship between Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and ABCD2 Score in Transient Ischemic Attack Patients. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2014, 53, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ercan, M.; Mungan, S.; Guzel, I.; Celik, H.T.; Bal, C.; Abusoglu, S.; Akbulut, D.; Oguz, E.F.; Yilmaz, F.M. Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Nitric Oxide Levels in Turkish Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Weissenborn, K.; Kielstein, J.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Deb, M.; Li, N.; Tryc, A.; Goldbecker, A.; Dong, Q.; et al. Association of Dimethylarginines and Mediators of Inflammation After Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, N.L.; Sieweke, J.T.; Biber, S.; Gabriel, M.M.; Schuppner, R.; Worthmann, H.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Bavendiek, U.; et al. Markers of Endothelial Pathology to Support Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19424–19429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Pelligrino, D.A.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Lassen, N.A. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition and Cerebrovascular Regulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, F.M.; Brian, J.E.; Heistad, D.D. Response of Cerebral Blood Vessels to an Endogenous Inhibitor of Nitric Oxide Synthase. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, H1522–H1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayoub, H.; Rodionov, R.N.; Lynch, C.; Cooke, J.P.; Arning, E.; Bottiglieri, T.; Lentz, S.R.; Faraci, F.M. Overexpression of Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase Inhibits Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in the Cerebral Circulation. Stroke 2008, 39, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segarra, G.; Medina, P.; Ballester, R.M.; Lluch, P.; Aldasoro, M.; Vila, J.M.; Lluch, S.; Pelligrino, D.A. Effects of some Guanidino Compounds on Human Cerebral Arteries. Stroke 1999, 30, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppner, R.; Dirks, M.; Grosse, G.M.; Bockmann, M.; Goetz, F.; Pasedag, T.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Budde, U.; Lanfermann, H.; et al. ADAMTS-13 Activity Predicts Outcome in Acute Ischaemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Worthmann, H.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Joumaah, M.; Li, N.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Hecker, H.; Kielstein, J.T.; Ehrenreich, H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Weissenborn, K. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Response to Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator and Erythropoietin in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 2128–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Willmot, M.; Gray, L.; Gibson, C.; Murphy, S.; Bath, P.M. A Systematic Review of Nitric Oxide Donors and L-Arginine in Experimental Stroke; Effects on Infarct Size and Cerebral Blood Flow. Nitric Oxide 2005, 12, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harston, G.W.; Sutherland, B.A.; Kennedy, J.; Buchan, A.M. The Contribution of L-Arginine to the Neurotoxicity of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator Following Cerebral Ischemia: A Review of rtPA Neurotoxicity. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzer, A.S.; Worthmann, H.; Grosse, G.M.; Goetz, F.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Dirks, M.; Kielstein, J.T.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Budde, U.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; et al. ADAMTS13 Activity is Associated with Early Neurological Improvement in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydow, K.; Munzel, T. ADMA and Oxidative Stress. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2003, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Teyssier, C.; Strahl, B.D.; Stallcup, M.R. Role of Protein Methylation in Regulation of Transcription. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, S.M.; Holian, A. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Induces Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Murine Lung Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Xia, N.; Steven, S.; Oelze, M.; Hanf, A.; Kroller-Schon, S.; Munzel, T.; Li, H. New Therapeutic Implications of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Function/Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, P.A.; Whitehurst, A.; Lawson, N.; Bath, P.M. Plasma Nitric Oxide (Nitrate/Nitrite) Levels in Acute Stroke and their Relationship with Severity and Outcome. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 12, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, P.L.; Panahian, N.; Dalkara, T.; Fishman, M.C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Effects of Cerebral Ischemia in Mice Deficient in Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase. Science 1994, 265, 1883–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Haensel, C.; Araki, E.; Ross, M.E.; Iadecola, C. Gene-Dosing Effect and Persistence of Reduction in Ischemic Brain Injury in Mice Lacking Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. Brain Res. 2000, 872, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samdani, A.F.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Nitric Oxide Synthase in Models of Focal Ischemia. Stroke 1997, 28, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Gibson, C.L. Nitric Oxide, Ischaemia and Brain Inflammation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickling, S.A.; Holden, D.P.; Cartwright, J.E.; Nussey, S.S.; Vallance, P.; Whitley, G.S. Regulation of Macrophage Nitric Oxide Synthesis by Endothelial Cells: A Role for NG,NG-Dimethylarginine. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1999, 167, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Does the Inhibitory Action of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) on the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity Explain its Importance in the Cardiovascular System? the ADMA Paradox. J. Controvers. Biomed. Res. 2017, 3, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leypoldt, F.; Choe, C.U.; Gelderblom, M.; von Leitner, E.C.; Atzler, D.; Schwedhelm, E.; Gerloff, C.; Sydow, K.; Böger, R.H.; Magnus, T. Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase-1 Transgenic Mice are Not Protected from Ischemic Stroke. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X. DDAH-1 Via HIF-1 Target Genes Improves Cerebral Ischemic Tolerance After Hypoxic Preconditioning and Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion-Reperfusion. Nitric Oxide 2020, 95, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Bai, Y.P.; Chen, M.F.; Shi, R.Z.; Jiang, D.J.; Fu, Q.M.; Tan, G.S.; Li, Y.J. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Induces TNF-Alpha Production Via ROS/NF-kappaB Dependent Pathway in Human Monocytic Cells and the Inhibitory Effect of Reinioside C. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L.; Wang, S.; Li, N.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Deng, H.W.; Li, Y.J. The Inhibitory Effect of Simvastatin on the ADMA-Induced Inflammatory Reaction is Mediated by MAPK Pathways in Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Leitner, E.C.; Klinke, A.; Atzler, D.; Slocum, J.L.; Lund, N.; Kielstein, J.T.; Maas, R.; Schmidt-Haupt, R.; Pekarova, M.; Hellwinkel, O.; et al. Pathogenic Cycle between the Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine and the Leukocyte-Derived Hemoprotein Myeloperoxidase. Circulation 2011, 124, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Maas, R.; Cutrupi, S.; Pizzini, P.; Finocchiaro, P.; Cambareri, F.; Panuccio, V.; Martorano, C.; Schulze, F.; Enia, G.; et al. Asymmetric Dimethyl-Arginine (ADMA) Response to Inflammation in Acute Infections. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closs, E.I.; Basha, F.Z.; Habermeier, A.; Forstermann, U. Interference of L-Arginine Analogues with L-Arginine Transport Mediated by the Y+ Carrier hCAT-2B. Nitric Oxide 1997, 1, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojo, A.; Welch, W.J.; Bremer, V.; Kimoto, M.; Kimura, K.; Omata, M.; Ogawa, T.; Vallance, P.; Wilcox, C.S. Colocalization of Demethylating Enzymes and NOS and Functional Effects of Methylarginines in Rat Kidney. Kidney Int. 1997, 52, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Dhondt, A.; Leybaert, L.; Vanholder, R. Role of Symmetric Dimethylarginine in Vascular Damage by Increasing ROS Via Store-Operated Calcium Influx in Monocytes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, E.; Barreto, D.; Liabeuf, S.; Glorieux, G.; Eloot, S.; Barreto, F.; Massy, Z.; Vanholder, R. Symmetric Dimethylarginine as a Proinflammatory Agent in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherbakov, N.; Sandek, A.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Kung, T.; Turhan, G.; Liman, T.; Ebinger, M.; von Haehling, S.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Endres, M.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction of the Peripheral Vascular Bed in the Acute Phase After Ischemic Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 33, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Oh, M.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Moon, G.J.; Kim, G.M.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, K.H.; Bang, O.Y. Distinct Roles of Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stroke. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 77, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.A. Carotid Restenosis is Associated with Plasma ADMA Concentrations in Carotid Endarterectomy Patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Hypertension in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2007, 38, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, F.; Cifù, A.; Pessa, M.E.; Domenis, R.; Gigli, G.L.; Sanvilli, N.; Nilo, A.; Garbo, R.; Curcio, F.; Giacomello, R.; et al. ADMA as a Possible Marker of Endothelial Damage. A Study in Young Asymptomatic Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Fan, Y.; Mu, L.; Ma, L.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y. S100B and ADMA in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Cognitive Dysfunction. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 354, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufa, A.; Blardi, P.; De Lalla, A.; Cevenini, G.; De Stefano, N.; Zicari, E.; Auteri, A.; Federico, A.; Dotti, M.T. Plasma Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarct and Leukoencephalopathy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 26, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleszar, M.G.; Wiśniewski, J.; Zboch, M.; Diakowska, D.; Gamian, A.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Targeted Metabolomic Analysis of Nitric Oxide/L-Arginine Pathway Metabolites in Dementia: Association with Pathology, Severity, and Structural Brain Changes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, R.G.; Diener, H.C.; Coutts, S.B.; Easton, J.D.; Granger, C.B.; O’Donnell, M.J.; Sacco, R.L.; Connolly, S.J. Cryptogenic Stroke/ESUS International Working Group. Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source: The Case for a New Clinical Construct. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.S.; Vanassche, T.; Bosch, J.; Giruparajah, M.; Swaminathan, B.; Mattina, K.R.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Arauz, A.; O’Donnell, M.J.; Ameriso, S.F.; et al. Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source: Prevalence and Patient Features in the ESUS Global Registry. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 11, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.C.; Sacco, R.L.; Easton, J.D.; Granger, C.B.; Bernstein, R.A.; Uchiyama, S.; Kreuzer, J.; Cronin, L.; Cotton, D.; Grauer, C.; et al. Dabigatran for Prevention of Stroke After Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.G.; Sharma, M.; Mundl, H.; Shoamanesh, A.; Kasner, S.E.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Pare, G.; Kirsch, B.; Pogue, J.; Pater, C.; et al. Rivaroxaban for Secondary Stroke Prevention in Patients with Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source: Design of the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Trial. Eur. Stroke J. 2016, 3, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkind, M.S.V. Atrial Cardiopathy and Stroke Prevention. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Kamel, H.; Elkind, M.S.V. Atrial Cardiopathy: A Mechanism of Cryptogenic Stroke. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2017, 15, 591–599. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, H.; Bartz, T.M.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Okin, P.M.; Thacker, E.L.; Patton, K.K.; Stein, P.K.; deFilippi, C.R.; Gottesman, R.F.; Heckbert, S.R.; et al. Atrial Cardiopathy and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study). Stroke 2018, 49, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Li, Z.; Goette, A.; Mera, F.; Honeycutt, C.; Feterik, K.; Wilcox, J.N.; Dudley, S.C., Jr.; Harrison, D.G.; Langberg, J. Downregulation of Endocardial Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression and Nitric Oxide Production in Atrial Fibrillation: Potential Mechanisms for Atrial Thrombosis and Stroke. Circulation 2002, 2854–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guazzi, M.; Belletti, S.; Lenatti, L.; Bianco, E.; Guazzi, M.D. Effects of Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation on Endothelial Function in Hypertension Or Diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesurendra, R.S.; Casadei, B. Atrial Fibrillation: Effects Beyond the Atrium? Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 105, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeringa, J.; Kuip, D.; Hofman, A.; Kors, J.; Rooij, F.; Lip, G.; Witteman, J. Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: The Rotterdam Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, I.M.; Sridhar, A.; Györke, S.; Cardounel, A.J.; Carnes, C.A. Nitric Oxide Synthases and Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, K.; Kiechl, S. Atherosclerosis and Atrial Fibrillation---Two Closely Intertwined Diseases. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Choisy, S.C.; Barman, P.; Zhang, H.; Hancox, J.C.; Jones, S.A.; James, A.F. Atrial Remodeling and the Substrate for Atrial Fibrillation in Rat Hearts with Elevated Afterload. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamboul, K.; Lorin, J.; Lorgis, L.; Guenancia, C.; Beer, J.; Touzery, C.; Rochette, L.; Vergely, C.; Cottin, Y.; Zeller, M. Atrial Fibrillation is Associated with a Marker of Endothelial Function and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Willoughby, S.R.; Schultz, C.; Alasady, M.; Rangnekar, G.; Dang, J.; Gan, C.; Lau, D.H.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Young, G.D.; et al. Thrombogenic Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Importance of Comorbid Conditions and Intracardiac Changes. JACC. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csecsei, P.; Varnai, R.; Nagy, L.; Keki, S.; Molnar, T.; Illes, Z.; Farkas, N.; Szapary, L. L-Arginine Pathway Metabolites can Discriminate Paroxysmal from Permanent Atrial Fibrillation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Ideggyogy Sz. 2019, 72, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Maas, R.; Wang, N.; Yin, X.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Ellinor, P.T.; Lubitz, S.A.; McManus, D.D.; Magnani, J.W.; et al. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Related Arginine Derivatives, and Incident Atrial Fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 2016, 176, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramuschkat, M.; Appelbaum, S.; Atzler, D.; Zeller, T.; Bauer, C.; Ojeda, F.M.; Sinning, C.R.; Hoffmann, B.; Lackner, K.J.; Böger, R.H.; et al. ADMA, Subclinical Changes and Atrial Fibrillation in the General Population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, K.; Behnes, M.; Barth, C.; Wenke, A.; Sartorius, B.; El-Battrawy, I.; Mashayekhi, K.; Kuschyk, J.; Hoffmann, U.; Papavasiliu, T.; et al. Occlusion of Left Atrial Appendage Affects Metabolomic Profile: Focus on Glycolysis, Tricarboxylic Acid and Urea Metabolism. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppala, I.; Kleber, M.E.; Bevan, S.; Lyytikainen, L.P.; Oksala, N.; Hernesniemi, J.A.; Makela, K.M.; Rothwell, P.M.; Sudlow, C.; Dichgans, M.; et al. Associations of Functional Alanine-Glyoxylate Aminotransferase 2 Gene Variants with Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Stroke. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüneburg, N.; Lieb, W.; Zeller, T.; Chen, M.; Maas, R.; Carter, A.M.; Xanthakis, V.; Glazer, N.L.; Schwedhelm, E.; Seshadri, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of L-Arginine and Dimethylarginines Reveals Novel Metabolic Pathway for Symmetric Dimethylarginine. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, I.; Kleber, M.E.; Lyytikäinen, L.; Hernesniemi, J.A.; Mäkelä, K.; Oksala, N.; Laaksonen, R.; Pilz, S.; Tomaschitz, A.; Silbernagel, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study on Dimethylarginines Reveals Novel AGXT2 Variants Associated with Heart Rate Variability but Not with overall Mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Damaso, E.; Oliva-Damaso, N.; Rodriguez-Esparragon, F.; Payan, J.; Baamonde-Laborda, E.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, F.; Santana-Estupiñan, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.C. Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.C.; Proietti, M.; Guiducci, E.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolism in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplin, B.; Wang, Z.; Slaviero, A.; Tomlinson, J.; Dowsett, L.; Delahaye, M.; Salama, A.; Wheeler, D.C.; Leiper, J. Alanine-Glyoxylate Aminotransferase-2 Metabolizes Endogenous Methylarginines, Regulates NO, and Controls Blood Pressure. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.P.; Sukhovershin, R.A. Novel Markers for Adverse Events in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).