Abstract
The activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is a main driver of cell growth, proliferation, survival, and chemoresistance of cancer cells, and, for this reason, represents an attractive target for developing targeted anti-cancer drugs. There are plenty of preclinical data sustaining the anti-tumor activity of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors as single agents and in combination in lymphomas. Clinical responses, including complete remissions (especially in follicular lymphoma patients), are also observed in the very few clinical studies performed in patients that are affected by relapsed/refractory lymphomas or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. In this review, we summarize the literature on dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors focusing on the lymphoma setting, presenting both the three compounds still in clinical development and those with a clinical program stopped or put on hold.
1. Introduction
The activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/v-akt murine lymphoma viral oncogene homolog (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is a main driver of cell growth, proliferation, survival, and chemoresistance of cancer cells [1,2,3,4,5]. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway has already represented an attractive target for developing targeted anti-cancer drugs for many years, and, indeed, many isoform-specific, pan-inhibitors, or dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors have already entered the clinical evaluation and also undergone approval by regulatory agencies [1,2,3,4]. The pathway is also important for lymphoma cells and its pharmacological inhibition has shown clinical benefit for patients that are affected by different lymphoproliferative neoplasms [1,2,6].
The present review will focus on dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors in clinical and pre-clinical development for patients that are affected by hematological malignancies after providing an overview of the pathway in relation with cancer.
2. The PI3K Signaling Pathway
Human cells express three classes of PI3Ks proteins, according to primary sequence homology, regulation, and in vitro substrate specificity [1,3,4,7,8]. PI3Ks are composed by a catalytic isoform complexed with a regulatory subunit, which regulates the activity, localization, and binding of the dimer. In mammals, class I PI3Ks are divided into IA and IB subclasses that are based on their regulation criteria. Class IA PI3Ks includes heterodimers of p110 catalytic subunit and p85 regulatory subunit. The class IA catalytic subunit isoforms are encoded by the genes PIK3CA, PIK3CB, and PIK3CD (p110α, p110β, and p110δ, respectively). These isoforms can associate with any of five regulatory isoforms, p85α and its splicing variants p55α and p50α (PIK3R1), p85β (PIK3R2), and p55γ (PIK3R3), generally called p85 type regulatory subunits [7]. Class IB PI3Ks are heterodimers of a p110γ catalytic subunit (PIK3CG) with regulatory isoforms p101 (PIK3R5) or p87 (PIK3R6). The catalytic isoforms p110α and p110β are ubiquitously expressed, while p110δ and p110γ are mainly expressed in leukocytes, but also in other tissues, such as heart, pancreas, liver, and skeletal muscle [8]. Class IA are activated by receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), while G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) activate class IB PI3Ks. The phosphotyrosines in the RTK consensus YxxM sequence can physically interact with the regulatory subunit or indirectly through adaptor proteins, such as IRS1 (insulin receptor substrate) and IRS2, leading to the autophosphorylation of tyrosines by RTK homodimerization and the recruitment of PI3K to the plasma membrane [7]. Ras (Rat sarcoma) can activate class I PI3Ks by direct binding to the p110 catalytic isoform [3]. Class II PI3Ks solely consist of the catalytic subunit, which has three isoforms PI3K-C2α, PI3K-C2β, PI3K-C2γ (encoded by PIK3C2A, PIK3C2B, PIK3C2G), while using phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI(4)P) as substrate [8]. Class II PI3Ks regulate angiogenesis, cellular growth and survival, but they are less characterized than class I PI3Ks [8]. Class III PI3Ks is composed by a single PIK3C3 gene, translated in the VPS34 (vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 34) protein, which forms a heterodimer with VPS15 (encoded by PIK3R4) and produces phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate (PI(3)P) [9]. The VPS34-VPS15 dimer is implicated in intracellular trafficking and autophagy [10].
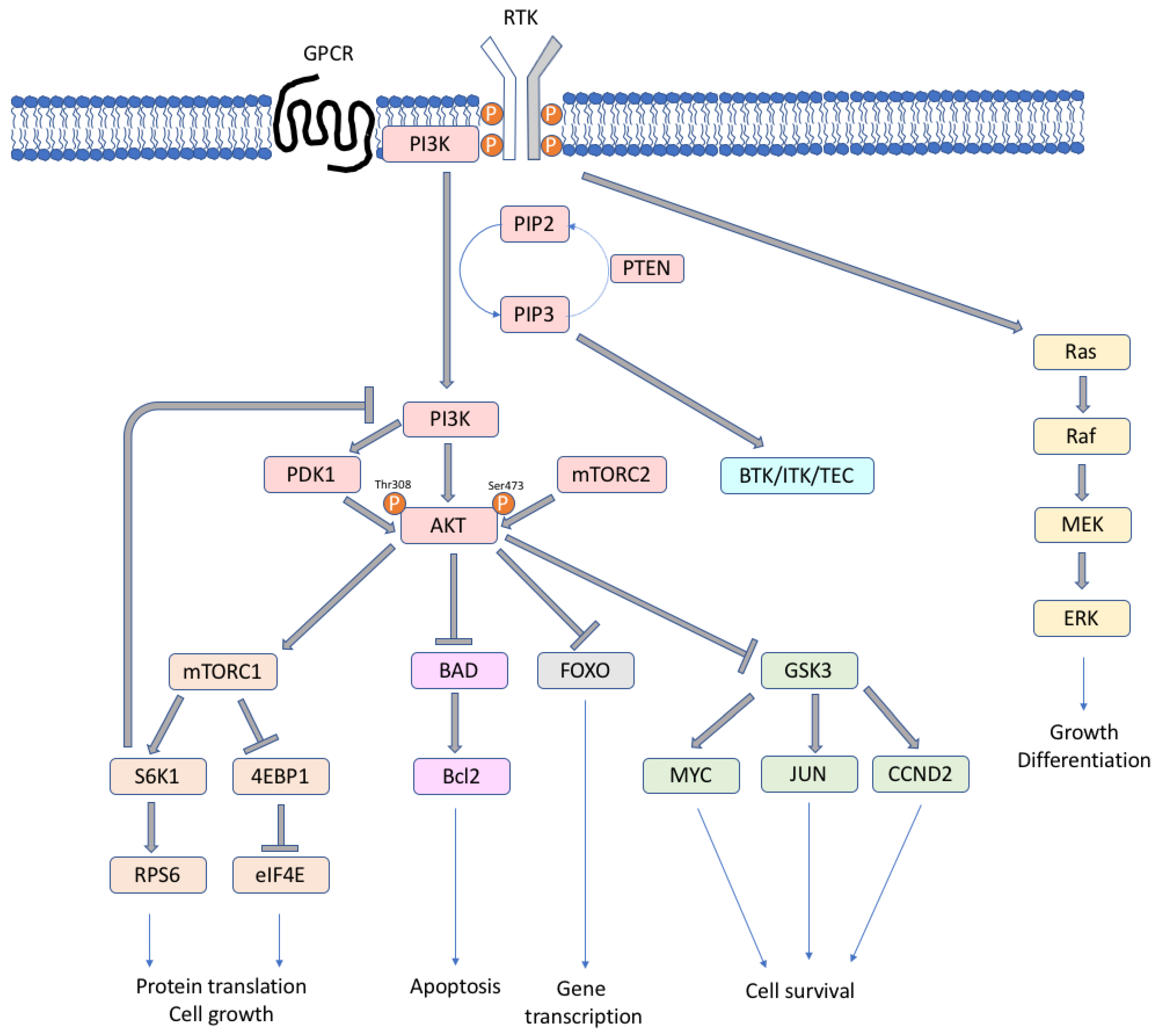
The various forms of PI3K play different roles, among them memory storage and retrieval [11,12], metabolism and insulin signaling [13], and immunity [14]. The activated form of the lipid kinases PI3Ks phosphorylates the 3′-hydroxyl group of plasma membrane phosphoinositides (PtdIns), producing three types of second messengers: phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate (PI(3)P), phosphatidylinositol 3,4-biphosphate (PI(3,4)P2), and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PI(3,4,5)P3/PIP3) [7]. The PIP3 levels are regulated by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog), which is an important tumor suppressor, with phosphatase activity that is able to convert PIP3 to PI(3,4)P2. When the second messenger PIP3 is formed, downstream PI3K targets, such as AKT and mTOR, are activated (Figure 1). PIP3 binds and phosphorylates AKT at Ser473 by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (TORC2) and at Thr308 by phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) [7]. The activation of AKT is maximal when both sites are phosphorylated, and it leads to the phosphorylation of large spectra of proteins that are involved in cell growth, survival and progression, protein synthesis, and metabolism [7,8,15]. AKT can activate TORC1 complex, which regulates ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1, or p70S6K), eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1), two key regulators of protein synthesis [16], RAS/ERK, forkhead/winged helix box class O (FOXO) family, and other pathways. AKT inhibits the apoptotic pathway by negatively regulating the pro-apoptotic Bcl2 family proteins and mediating p53 degradation. In lymphocytes, the TEC family tyrosine-kinase proteins BTK (bruton tyrosine kinase), ITK (IL2 inducible T-cell kinase), and TEC are PI3K effectors that are activated by PIP3, with potential anti-tumor therapeutic implications. TORC1 or S6K1 are involved in a negative feedback regulation loop; their activation leads to the deactivation of the PI3K, AKT, and ERK pathway [17,18].
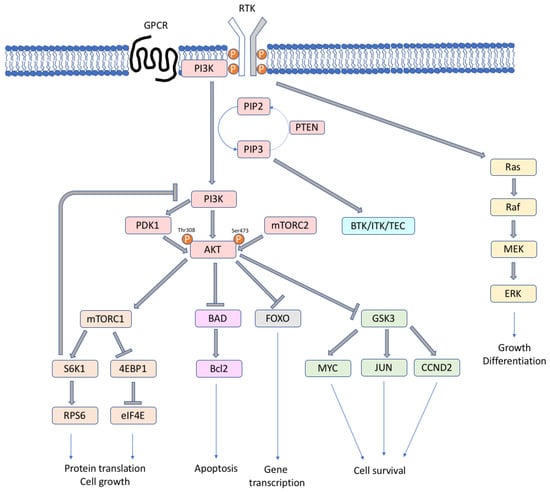
Figure 1.
Simplified scheme of the PI3K/mTOR signaling cascade.
3. PI3K Pathway and Metabolism
PI3K signaling is activated upon grow factor stimulation and grow factor receptors activation, including insulin receptor (INSR), which regulates metabolic homeostasis. Conformational changes of the activated receptors allow autophosphorylation and the activation of INSR, which recruits IRS proteins, which are phosphorylated by INSR and finally create the binding motif for p85 [3,19]. The early insulin-driven PI3K signaling leads to enhanced glucose transporters (GLUT) translocation in the membrane [20] and augmented transcription and translation of genes coding for these transporters [21], increasing the glucose uptake in muscle and fat cells. The isoform p110α mediates glucose homeostasis in muscle, liver, and fat [22]. The regulatory subunit p85 could act both as a positive and negative regulator of insulin signaling. In fact, p85 could also block IRS signaling [23], which causes the inhibition of insulin signaling and formation of insulin resistance. Based on its normal biologic functions, it is obvious that pharmacological targeting the of PI3K/mTOR pathway as cancer treatment is unlikely to be devoid of on-target metabolism-related toxicities. Indeed, drugs that target p110α induce acute insulin resistance, which causes severe hyperglycemia, leading to hyperinsulinemia [3].
4. Deregulation of the Signaling in Cancer
As already mentioned, a constitutive activation and deregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is almost a hallmark of cancers cells [1,2,4,24,25]. Somatic mutations in the genes encoding for the catalytic PI3K isoforms (i.e., PIK3CA) or regulatory isoforms (i.e., PIK3R1) are frequent [24,26,27]. Mutations targeting catalytic class I PI3K isoforms are only associated to PIK3CA catalytic isoform, while in the other class I catalytic isoforms PIK3CB, PIK3CD, and PIK3CG tumor associated mutations are very rare [28,29]. Mutations in the PIK3CA are associated with augmented kinase activity and cluster in two ‘hotspots’, one in the exon 9 (E542K and E545K, in the helical domain), the other in exon 20 (H1047R, in the kinase domain) [28,30,31]. The E542K and E545K mutations disrupt the inhibitory interface with the regulatory subunit p85, while H1047R mutation enhance the interaction of the kinase domain with cell membranes. Nevertheless, proteins p100β, p100δ, and p100γ are also capable of inducing oncogenic transformation in their wild-type form [32], in line with the fact that PIK3CB, PIK3CD, and PIK3CG are generally amplified or overexpressed, but not mutated, in cancer. Genes encoding AKT isoforms, mTOR, and PTEN are targeted by somatic mutations deregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mutations in the RTK or RAS genes, RTK receptor overexpression/amplification, autocrine loops involving RTKs, and the ligands are also recurrent events [6].
The regulatory isoforms p85 are also involved in tumorigenesis. Specific PIK3R1 mutations in the region of the protein that interacts with p110 stabilize the p110 isoforms and abrogate the inhibitory action of p85 on p110 [33]. Mutations in other PI3K regulator subunits are rare.
The amplification of AKT1 and AKT2 and activating mutation of AKT1 (in E17K) increase AKT1 binding to the plasma membrane and its phosphorylation in solid tumors [34].
A study investigated the somatic alterations involving the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in pan-cancers, finding mutations or copy number alterations in PIK3CA (14% mutated, 6% amplified), PTEN (9% mutated, 7% deletion or two-hit loss), PIK3R1 (4% mutated), AKT1 (1% mutated, 3% amplified), and MTOR (4% amplified) [24]. In 5% of cases, genomic rearrangements in PTEN and PIK3R1 have been found. Mutations in AKT1, MTOR, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, and PTEN with predicted functional effects have higher phospho-AKT levels when compared to tumors with no alteration, and the PTEN copy losses were associated with AKT activation. They also found an association between STK11 mutation, STK11 copy loss, PTEN copy loss, PIK3CA amplification, higher phospho-4EBP1 expression, and worst patient outcome. Interestingly, mutations that were related to RTK signaling were not associated with PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation.
5. Deregulation of the Signaling in Lymphoma
The PI3K pathway is activated by a large number of mechanisms across B-cell malignancies. In patients, PIK3CA mutations or amplification were found, respectively, in 8% of DLBCL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), mainly in the catalytic domain, [35,36], and in 68% of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) [37,38]. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients rarely have PIK3CA mutations [39] and amplification of PIK3CA has been reported in 5.6% of the cases [40]. PTEN loss was observed in 15% of MCL patients [37,38], in 37–55% of DLBCL patients [35,41,42], and in 21% of follicular lymphoma (FL) [43]. Low levels of PTEN were observed also in CLL patients [44]. Among DLBCL, the loss of PTEN expression was found in 55% of GCB (germinal center B-cell type) DLBCL patients, and only in 14% of non-GCB DLBCL cases [41]. In GCB DLBCL cell lines and primary patient samples, PTEN status was inversely correlated with the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, suggesting that activation of this pathway could give an oncogenic addiction for this subtype of DLBCL. In fact, in GCB DLBCL, deletions of PTEN, and amplification of the MIR17HG (microRNA-17-92 cluster) sustain cell proliferation [45]. Similar deregulation of PTEN and MIR17HG is also in place in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) cells, in which the constitute activation of the MYC oncogene that is due to chromosomal translocation also directly activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR [46,47,48,49].
PI3K pathway activation can also be mediated by B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. The phosphorylation of CD19 by BCR leads to the binding of the regulatory subunit p85, and the recruitment of the p110 catalytic subunit [50]. BTK, which is a downstream protein of BCR, is activated by PI3K (by PIP3) in B cells.
Recurrent mutations in PIK3CD, PIK3R1, and MTOR occur in DLBCL primary tumors [51]. Three cases were characterized by single point mutation T → G in the catalytic domain of PIK3CD, converting Asp (uncharged side chains) in Lys (charged side chains). The mutations in PIK3CD, PIK3R1, and MTOR did not all cluster in a single hot spot of the gene, but they were spread across it. PIK3CD mutations were localized in the catalytic domain (N948K, E1021K), PIK3R1 mutations occurred in the RhoGAP-p85 domain (V172M, A210D), and in the COG4942 domain (Y470D, D560G), MTOR mutations were in the HEAT domain (A835T), close to the FAT and rapamycin binding domains (N1765D, A37T, T182K), and to the FATC domain (V619I). The cell lines with MTOR mutations showed a higher sensitivity to PI3K inhibitor than those that did not harbor MTOR mutations, which suggests that sensitivity to PI3K inhibitors correlates with MTOR mutations.
In GCB DLBCL cell lines, a tonic (antigen-independent) BCR signaling activates AKT, regulates proliferation and size with different magnitudes, and AKT knockout resulted in toxicity [52].
Chronic active BCR signaling is typical of ABC (activated B cell) DLBCL, the subgroup of DLBCL with constitutive activation of NFκB (nuclear factor κB), also regulated by PI3K [53].
The phosphorylation of AKT was detected in 52% of DLBCL [54], and the sensitivity to AKT inhibition correlated to the efficacy of the inhibitor to block phosphorylation of S6K1 and RPS6 [55]. Cell lines expressing AKT-independent S6K1, as activated by upregulation of PIM2 (Pim-2 Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase) or activation of BCR, are resistant to AKT inhibitors. Combining AKT inhibitor with BTK, PIM2, or S6K1 inhibitors could overcome resistance to AKT inhibition in this subtype of lymphoma.
Finally, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling also plays an important role in the different non-neoplastic cells that are present in the tumor microenvironment, for example regulating the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, the M1/M2 polarization of macrophages, and the activation and/or differentiation of T cells [56,57,58,59,60,61,62].
6. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors in Lymphoma
We can recognize different classes of compounds targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: pan-PI3K inhibitors, isoform specific inhibitors (i.e., idelalisib), dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors, AKT inhibitors, allosteric mTOR inhibitors (rapalogs) inhibitors, and mTOR kinase inhibitors [1,2,4,14,63,64,65,66,67,68,69]. An interesting strategy is to target several PI3K isoforms as well as mTOR instead of a single PI3K isoform or only mTOR. In fact, the catalytic isoform of the p110 subunit and mTOR have structural similarities, and targeting two crucial points of the same pathway could lead to higher efficacy, could overcome feedback inhibition coming from mTOR inhibition [70], and the risk of drug resistance that should easily come out in the case of treatment with compounds targeting a single p110 isoform [71,72,73]. Indeed, the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors have shown, at least in the preclinical setting, an improved than what achieved targeting individually single PI3K isoforms, all PI3K isoforms or mTOR [74,75,76,77]. Table 1 shows an exhaustive list of the dual class I PI3K and mTOR inhibitors. Table 2 summarizes the clinical data available for patients that are affected by lymphoma enrolled in phase I/II studies with such a class of compounds. The chemical structures, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) names, and molecular weights for all of the compounds are shown in Table 3 or Table S1, depending on their current clinical development stage. Indeed, there are only three dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors that are still in clinical development for humans: bimiralisib, GDC-0084, and gedatolisib.

Table 1.
List of dual Pi3K/mTOR inhibitors sorted by their official name, if assigned, or by their common/alternative name.

Table 2.
Clinical trials evaluating dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors as single agents that have enrolled lymphoma patients *.

Table 3.
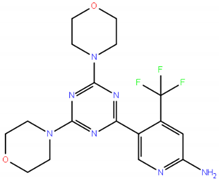
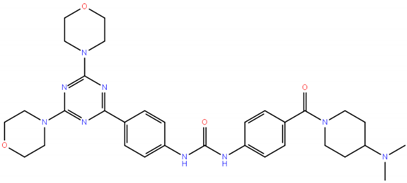
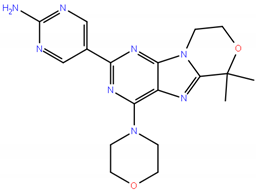
Chemical structures of the three dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors still in clinical development. Data collected from https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/ [83], http://zinc.docking.org/substances/home/ [84], https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ [85], https://www.drugbank.ca/ [86], https://fdasis.nlm.nih.gov/srs/. MW, molecular weight. IUPAC, International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Additional dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors are presented in Table S1.
GDC-0084 (RG 7666) is orally given and it passes the blood brain barrier (BBB) and it has been specifically developed for patients with brain tumors or with brain metastases from solid tumors [87,88,89]. Gedatolisib (PF05212384/PKI-587) is an intravenous inhibitor of PI3Ks (preferentially of p110α, also acting on the mutant forms) and TORC1/TORC2 with preclinical activity in different solid tumor models [90,91]. There are no data in lymphoma models, while the compound has been extensively tested in lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia models [92,93,94,95]. No lymphoma patient was treated in the phase I study [96].
Bimiralisib (PQR309) inhibits all of the PI3Ks (p110α, first, followed by p110δ, p110β, and p110γ) and TORC1/TORC2 [97]. It is an oral compound and it is capable of crossing the BBB [97]. When comparing the published data [97,98], bimiralisib has an overlapping inhibition of p110α with voxtalisib, a reduced inhibition of p110δ, p110β, and p110γ, a higher activity on mTOR, and a reduced activity on the off-target DNA-PK [97]. Bimiralisib has in vitro and in vivo anti-lymphoma activity in models that were derived from B and T cell lymphomas [75], and also from canine DLBCL [99]. The pattern of activity is highly correlated to what was achieved by apitolisib, another dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor (see below), but bimiralisib shows higher IC50 values [75]. Bimiralisib also shows in vitro activity in lymphoma cell lines with primary or secondary resistance to the PI3Kδ inhibitor idelalisib [75]. Analysis of transcriptome and phospho-proteomics of DLBCL cells that were exposed to bimiralisib demonstrates that the compound modulates transcripts and proteins that are involved in fundamental pathways and signaling cascades: BCR signaling, NFκB pathway, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, mRNA processing, apoptosis, cell cycle, MAPK/RAS signaling, Myc pathway, and glycolysis [75]. Moreover, the modulation of these pathways occurs via changes at both the RNA and protein phosphorylation levels. However, while the mTOR pathway and mRNA metabolism are more regulated at the protein level, cell cycle and BCR signaling changes are more driven by expression level changes [75]. Interestingly, the early changes at the RNA level seen after bimiralisib exposure are largely overlapping with what was observed after exposing the same DLBCL cell lines to the p100δ inhibitor idelalisib, the p100δ/ p100γ inhibitor duvelisib, or the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib [75], in accordance with studies that were performed in normal B cells after BTK and PI3K genetic silencing [100]. Importantly, an adaptive mechanism with an early upregulation of genes coding members of the BCR signaling is induced by bimiralisib, idelalisib, duvelisib and ibrutinib, partially explaining the benefit of targeting the BCR signaling with compounds targeting multiple of its members [75]. Bimiralisib as well as other BCR signaling inhibitors, up-regulates CXCR4, which is a possible marker of adaptive resistance [75,101].
Following the completion of a phase 1 study in patients with advanced solid tumors [102], bimiralisib has entered the clinical setting for patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoma (phase I/II: II NCT02249429, NCT03127020), and for patients with relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphomas (NCT02669511). Unfortunately, the only data publicly available refer to the first 15 patients that were enrolled in the phase I (NCT02249429). Reported severe (G3/G4) side effects include hyperglycemia, rhabdomyolysis, anorexia, neutropenia, sepsis, pneumonitis, and fatigue. Clinical responses were seen in 27% of 11 evaluable patients with one complete response (CR) in a FL patient and partial responses (PR) in two patients (DLBCL, MZL) (Table 2), and stable diseases (SD) in FL (3/4 patients), MCL (1/2 patients), and T-cell lymphoma (1/1 patients) [78]. The pattern of activity, with most of the responses in FL, is similar to what was reported with another dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor voxtalisib (see below) [79,80].
All of the other dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors have not reached the clinical development stage or the latter has been permanently or temporarily stopped. Among these, here we will only discuss the two agents with available clinical data, whilst we refer to the Supplementary Material for the other compounds.
Voxtalisib (XL765/SAR245409) preferentially targets p110γ, followed by p110α, p110δ, p110β, and TORC1/TORC2 with activity in a variety of solid tumor models [98]. It is an oral compound and passes the BBB [98]. Voxtalisib also has preclinical anti-tumor activity in models of lymphoma and CLL [103]. The positive laboratory data have led to different clinical trials as single agent and also in combination in patients with hematological cancers [79,80,104].
Sixteen patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma (MCL, FL, DLBCL, others) received voxtalisib in an expansion cohort [79] of the phase I study for patients with solid tumors (NCT00485719) [105] (Table 2). The toxicity profile included fatigue, gastrointestinal and cutaneous adverse events, liver enzyme abnormalities, and cytopenia [79]. Three patients achieved a clinical response with one CR in a FL patients and two PR in patients (DLBCL, MCL, one patient each) [79]. Although not reaching the definition of PR, two FL experienced tumor regression and six patients had SD, with one MCL and one FL receiving treatment for four months or longer [79]. Reductions in PI3K/mTOR and ERK pathway activity were seen in the serial tumor biopsies done, which were only successfully performed in one patient (MCL with PR) [79]. There was no evident modulation of chemokine or cytokine levels by drug exposure. Only two of 12 patients that underwent serial measurements presented changes [79]. Although they were both cases with clinical responses (CR and PR), the observed changes were not concordant with no overlapping changes and with the IL16 (interleukin 16) levels behaving in the opposite way [79]. Based on these results, a phase II study with voxtalisib (NCT01403636) enrolled 167 patients with relapsed or refractory disease (FL, MCL, DLBCL, CLL) [80] (Table 2). Clinical responses were seen in all of the subtypes, but especially in FL (41%), followed by MCL and CLL (12 and 11%, respectively) [80]. Only two of the 42 (5%) DLBCL patients responded [80]. Complete responses were observed in FL (11%, 5/47) and MCL (7%, 3/42) [80]. SD was seen in 33% (14/42) of MCL patients, 30% (14/46) of FL, 10% (4/41) of DLBCL, and 66% (23/35) of CLL [80]. The median progression-free survival was 58 weeks for FL patients, 24 for CLL, nine for MCL, and seven for DLBCL [80].
No useful information came from genetic studies done on tumor samples before treatment or from the measurement of cytokines and chemokines in plasma samples in both the phase I [79] and in the phase II [80] voxtalisib studies. In the phase I study, only two of 12 patients that underwent serial measurements presented changes [79]. Although they were both cases with clinical responses (CR and PR), the observed changes were not concordant and the IL16 levels modulated in the opposite way [79].
The combination has also been studied in a phase I clinical trial study (NCT01410513), evaluating voxtalisib in combination with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab plus or minus the chemotherapy agent bendamustine in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies [104]. The study enrolled 37 patients, 16 in the rituximab arm (CLL, n. = 11; MCL, n. = 3; FL, n. = 2) and 21 in the triple combination arm (CLL, n. = 12; MCL, n. = 6; FL, n. = 3) [104]. The safety profile (characterized by nausea, fatigue, and vomiting) was acceptable, with no interactions among drugs at the pharmacokinetic level [104]. There was clinical activity: one CR in FL patient and five PRs in the voxtalisib/rituximab; three CRs (one patient with MCL, two with CLL) and eight PRs in the voxtalisib/rituximab/bendamustine arm [104].
The clinical development of voxtalisib has been stopped [106] due to limited clinical anti-tumor activity observed in two phase I studies enrolling 83 (NCT00485719) [105] and 49 (NCT01596270) [106] patients with advanced solid tumors.
The LY294002/SF1101 derivative SF1126 is a multikinase inhibitor, which targets the PI3K isoforms and TORC1/TORC2, but also DNA-PK and the BET Bromodomain proteins [107,108,109]. SF1126 has preclinical anti-tumor activity in B and T cell lymphoma models [110], as well from multiple myeloma [111]. None of the five patients with B cell lymphoid neoplasm that were enrolled in the phase I study (NCT00907205) achieved a CR or PR [81] (Table 2). Two CLL patients (one with no prior therapy) achieved a SD [81].
7. Future Perspective for Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors
As evident from what summarized for each individual compound, dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors that have entered the clinical evaluation have not achieved as good results as expected. The main reason could be the frequent occurrence of dose-limiting toxicities that do not allow for reaching potentially active doses [1,2,3,4,112]. This does not come as a surprise since dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors target multiple proteins that play fundamental roles in a variety of normal tissues. The main toxicities include diarrhea [80,81,102,113,114,115,116,117], vomiting [102,114,116,117,118], nausea [80,102,114,117,118,119], rash [96,102,106,113,114,118,119,120,121], fatigue [80,102,105,106,113,114,117,118,121,122], decreased appetite [80,105,117,118,119], hyperglycemia [96,102,114,115,119,120,122,123], mucositis [89,96,114,115,118,122], increase in liver enzymes [96,102,105,124], and thrombocytopenia [114,122,124]. The additional dose limiting toxicities reported in individual trials, which does mean they are specific to a single compound, include allergic reactions [124], bradycardia and myocardial ischemia [89], dysgeusia [118], hypertension [102], pneumonitis [115], uveitis [114], and suicide attempt [102].
Different dosing schedules could improve the toxicity profile and provide the best therapeutic window. For example, apitolisib given once weekly [123] has shown better tolerability than once daily [120]. Other approaches include intermittent dosing, dose reductions, and interruptions that are based on side effects [1,2,3].
Alternative modalities to decrease the side effects that have been explored are the delivery of the compounds preferentially to cancer cells (sparse preclinical data with BEZ235 in CaCO(3) nanocrystals [125] or in liposomes [126]) or lowering the doses of the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors in the context of combination therapies can help to overcome the toxicity issue. Combinations would also be important for two additional reasons. First, the addition of a second compound can overcome the primary or acquired resistance to the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors [3,4,5]. Indeed, resistance to both PI3K and mTOR inhibitors is due to genetic events that maintain the same pathway active or via activation of alternative signaling cascades [3,4,64]. Second, the activation of PI3K/mTOR signaling is a frequent mechanism of resistance to other targeted agents [3,4]. Studies conducted mainly in the solid tumor setting suggest that combinations with other agents can be feasible [104,113,114,127,128], although toxicities can still be an issue [106,127,129,130,131,132,133].
Preclinical data that were obtained in different lymphoma models indicate that dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors synergize with both targeted and chemotherapy agents, as presented in Table 4. For few combinations, synergism has been observed in different laboratories and/or obtained with different dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors, underlying the robustness of the data.

Table 4.
Combinations based on dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors with available preclinical data in lymphomas.
While also considering the toxicity profile and its already established role in CLL and lymphomas [151], the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax appears as an interesting drug to be combined with dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Bimiralisib, dactolisib, and omipalisib have all shown synergism when combined with venetoclax [75,139,140,141]. Combining dactolisib with venetoclax induces the accumulation of pro-apoptotic BAD and BIM and down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic MCL1 [139,140], with the ability to revert secondary resistance to venetoclax [139]. The combination of bimiralisib with venetoclax is much more active than the single agents in GCB and ABC DLBCL xenograft models, as well as causing an increase in cell death in CLL primary cells [75].
Another combination that is sustained by multiple data is with histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Dactolisib, bimiralisib, and omipalisib have been successfully combined with panobinostat [75,145] or Vorinostat [141]. In ABC, GCB and double hit DLBCL, and MCL cell lines, dactolisib had major effect when combined with HDAC inhibitor panobinostat, AKT inactivation, MCL1 downregulation, and BIM upregulation contribute to the effect of the combination of dactolisib with panobinostat [145,147,152].
Combination with the FDA approved BTK inhibitor ibrutinib appears to be another interesting combination, as shown using apitolisib, bimiralisib [75], and dactolisib [143] in ABC DLBCL and MCL models [75,143].
Bimiralisib and other BCR signaling inhibitors induce the increased expression of both PIM1 and PIM2, kinases that are involved in lymphomagenesis and potential therapeutic targets. The combination of bimiralisib with the PIM inhibitor AZD1208 [153] is largely synergistic in both GCB and ABC DLBCL cells with an increased G0/G1 cell cycle arrest [75]. The addition of the PIM inhibitor SGI-1776 to dactolisib is associated with MCL1 downregulation and increased cell death in the ABC DLBCL cell lines [76].
Bimiralisib [75] and PF04691502 [136] have been beneficially combined with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in the DLBCL and MCL cell lines. The addition of rituximab to a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors with rituximab is the only combination that has been clinically evaluated. Indeed, we have already mentioned the voxtalisib phase I trial that has reported some clinical activity [104].
Similar results have been obtained with three dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors (dactolisib, bimiralisib, and omipalisib) added to proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib or marizomib) [75,141,144,149]. In particular, the addition of dactolisib reverts the resistance to proteasome inhibitors in a bortezomib-resistant MCL cell line decreasing AKT and mTOR signaling [144].
Finally, the effect of this class of agents on the tumor microenvironment and how this indirect activity can be exploited, especially in combination with immuno-oncology drugs, such as the bispecific antibodies, is an open issue [154,155].
8. Conclusions
Based on the importance of the p110α in different solid tumors, a bigger relevance to this isoform has been given in the design of compounds and in the population of patients that are enrolled in the clinical studies. However, there are plenty of preclinical data sustaining the anti-tumor activity of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors as single agents and in combination in lymphomas. Additionally, clinical responses, including CR (especially in the FL setting), are clearly observed in the very few clinical studies that were performed in patients affected by relapsed/refractory lymphomas or CLL. Unfortunately, the vast majority of clinical trials that were performed in patients with solid tumors have been disappointing due to unacceptable toxicity profile and/or to a lack of meaningful clinical activity. Based on these clinical results, the clinical development of all but three dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors has been stopped, although they could be beneficial for some patients that were affected by lymphoid neoplasms. Different schedules of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors given as single agents in specific patients’ populations (for example, high risk or relapsed/refractory FL patients) or combination regimens (for example, with venetoclax) appear still worthy of further clinical investigations. The use of tools to identify the responders at an early time-point, possibly paired with still-to-be defined robust biomarkers, will help in optimizing the use of dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors, avoiding both toxicities to patients that are unlikely to benefit and costs to the health care system.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/3/1060/s1.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, C.T., F.B.; data curation, A.L.; visualization, C.T.; writing—review and editing, C.T. and F.B.; supervision, A.S. and F.B.; project administration, F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
A.L.: part-time employee of Net4Science. A.S.: institutional research funds from: Bayer, ImmunoGen, Merck, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche; travel grant from AbbVie. F.B.: institutional research funds from Acerta, ADC Therapeutics, Bayer AG, Cellestia, CTI Life Sciences, EMD Serono, Helsinn, ImmunoGen, Menarini Ricerche, NEOMED Therapeutics 1, Oncology Therapeutic Development, PIQUR Therapeutics AG; consultancy fee from Helsinn, Menarini; expert statements provided to HTG; travel grants from Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Janssen-Cilag AG, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, PIQUR Therapeutics AG. The other co-authors do not report any conflict of interest.
References
- Janku, F. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway inhibitors in solid tumors: From laboratory to patients. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 59, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: Are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brana, I.; De Dosso, S.; Dienstmann, R.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J.; Markman, B. Recent Developments in Anticancer Agents Targeting PI3K, AKT and mTORC1/2. Top. Anti-Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 95–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcaro, A. Development of drugs targeting the PI3K signalling pathway in leukemias and lymphomas. EMJ 2015, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Yuzugullu, H.; Zhao, J.J. PI3K in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Dhand, R.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; MacDougall, L.K.; Stein, R.; Zvelebil, M.J.; Domin, J.; Panaretou, C.; Waterfield, M.D. A human phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex related to the yeast Vps34p-Vps15p protein sorting system. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 3339–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohda, C.; Nakanishi, R.; Kadowaki, M. Hyperactivity, memory deficit and anxiety-related behaviors in mice lacking the p85α subunit of phosphoinositide-3 kinase. Br. Dev. 2009, 31, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouzkey, I.; Rosenblum, K.; Maroun, M. Memory of Conditioned Taste Aversion Is Erased by Inhibition of PI3K in the Insular Cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dann, S.G.; Selvaraj, A.; Thomas, G. mTOR Complex1-S6K1 signaling: At the crossroads of obesity, diabetes and cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.G.; Blunt, M.D.; Carter, E.; Ward, S.G. Inhibition of PI3K signaling spurs new therapeutic opportunities in inflammatory/autoimmune diseases and hematological malignancies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 1027–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, K.D.; Corcoran, R.B.; Engelman, J.A. The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, A.; Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Rojo, F.; Salmena, L.; Alimonti, A.; Egia, A.; Sasaki, A.T.; Thomas, G.; Kozma, S.C.; et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantley, L.C.; Songyang, Z. Specificity in recognition of phosphopeptides by src-homology 2 domains. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 1994 (Suppl. 18), 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Czech, M.P. The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, E.C.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Cantley, L.C. Metabolic Reprogramming by the PI3K-Akt-mTOR Pathway in Cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016, 207, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foukas, L.C.; Bilanges, B.; Bettedi, L.; Pearce, W.; Ali, K.; Sancho, S.; Withers, D.J.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. Long-term p110α PI3K inactivation exerts a beneficial effect on metabolism. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Sobkiw, C.L.; Hirshman, M.F.; Logsdon, M.N.; Li, T.Q.; Goodyear, L.J.; Cantley, L.C. Loss of class IA PI3K signaling in muscle leads to impaired muscle growth, insulin response, and hyperlipidemia. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwok-Shing Ng, P.; Kucherlapati, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Tsang, Y.H.; de Velasco, G.; Jeong, K.J.; Akbani, R.; Hadjipanayis, A.; et al. A Pan-Cancer Proteogenomic Atlas of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Alterations. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 820–832 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Hu, Z.; Mahal, B.A.; Zhao, S.D.; Kensler, K.H.; Pi, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Genetic Ancestry and Genomic Alterations across Cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 549–560 e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millis, S.Z.; Ikeda, S.; Reddy, S.; Gatalica, Z.; Kurzrock, R. Landscape of Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Pathway Alterations Across 19784 Diverse Solid Tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bardelli, A.; Silliman, N.; Ptak, J.; Szabo, S.; Yan, H.; Gazdar, A.; Powell, S.M.; Riggins, G.J.; et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 2004, 304, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.L.; Kuehn, H.S.; Zhao, F.; Niemela, J.E.; Deenick, E.K.; Palendira, U.; Avery, D.T.; Moens, L.; Cannons, J.L.; Biancalana, M.; et al. Dominant-activating germline mutations in the gene encoding the PI(3)K catalytic subunit p110delta result in T cell senescence and human immunodeficiency. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, A.G.; Kang, S.; Vogt, P.K. Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Bader, A.G.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mutations identified in human cancer are oncogenic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Denley, A.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Vogt, P.K. Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110β, -γ, and -δ isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Hillmann, P.; Hofmann, B.T.; Hart, J.R.; Vogt, P.K. Cancer-derived mutations in the regulatory subunit p85α of phosphoinositide 3-kinase function through the catalytic subunit p110α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15547–15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpten, J.D.; Faber, A.L.; Horn, C.; Donoho, G.P.; Briggs, S.L.; Robbins, C.M.; Hostetter, G.; Boguslawski, S.; Moses, T.Y.; Savage, S.; et al. A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, J.; Bavi, P.P.; Al-Harbi, S.; Siraj, A.K.; Al-Dayel, F.; Uddin, S.; Al-Kuraya, K. PIK3CA mutations are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2368–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Qin, T.; Shi, D. Mutations of the PIK3CA gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar, S.; Clear, A.; Bodor, C.; Maharaj, L.; Lee, A.; Calaminici, M.; Matthews, J.; Iqbal, S.; Auer, R.; Gribben, J.; et al. P110alpha-mediated constitutive PI3K signaling limits the efficacy of p110delta-selective inhibition in mantle cell lymphoma, particularly with multiple relapse. Blood 2013, 121, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyrri, A.; Papageorgiou, S.; Liakata, E.; Scorilas, A.; Rontogianni, D.; Kontos, C.K.; Argyriou, P.; Pectasides, D.; Harhalakis, N.; Pappa, V.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase catalytic subunit alpha gene amplification contributes to the pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5724–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincevic, M.; Tobin, G.; Rosenquist, R. Infrequent occurrence of PIK3CA mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Hanna, M.; Tesar, B.; Werner, L.; Pochet, N.; Asara, J.M.; Wang, Y.E.; Dal Cin, P.; Fernandes, S.M.; Thompson, C.; et al. Integrative genomic analysis implicates gain of PIK3CA at 3q26 and MYC at 8q24 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3791–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, M.; Grau, M.; Lenze, D.; Wenzel, S.S.; Wolf, A.; Wollert-Wulf, B.; Dietze, K.; Nogai, H.; Storek, B.; Madle, H.; et al. PTEN loss defines a PI3K/AKT pathway-dependent germinal center subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12420–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Yao, S.N.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Z.H.; Ma, J.; Xia, Q.X.; Fu, K.; Yang, S.J. PTEN tumor suppressor plays less prognostic role than P53 tumor suppressor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2010, 51, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiaoui, O.I.; Nunes, J.A.; Castanier, C.; Devillier, R.; Broussais, F.; Fabre, A.J.; Naimi, D.; Bouabdallah, R.; Olive, D.; Xerri, L. Constitutive AKT activation in follicular lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.J.; Zhang, R.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Fang, C.; Zhang, L.N.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Xu, W. Low expression level of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten predicts poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.W.; Emre, N.C.; Kohlhammer, H.; Dave, S.S.; Davis, R.E.; Carty, S.; Lam, L.T.; Shaffer, A.L.; Xiao, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arise by distinct genetic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13520–13525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.; Sun, Z.; Jima, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Miles, R.; Richards, K.L.; Dunphy, C.H.; Choi, W.W.; Srivastava, G.; et al. The genetic landscape of mutations in Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, B.M.; Gerhard, D.S.; Jiang, A.; Griner, N.B.; Abramson, J.S.; Alexander, T.B.; Allen, H.; Ayers, L.W.; Bethony, J.M.; Bhatia, K.; et al. Genome-wide discovery of somatic coding and noncoding mutations in pediatric endemic and sporadic Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Young, R.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Shaffer, A.L.; Hodson, D.J.; Buras, E.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics. Nature 2012, 490, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea, R.I.; Love, C.L.; Shingleton, J.R.; Reddy, A.; Bailey, J.A.; Moormann, A.M.; Otieno, J.A.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Oduor, C.I.; Schroeder, K.M.S.; et al. The whole-genome landscape of Burkitt lymphoma subtypes. Blood 2019, 134, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Kipps, T.J. Inhibitors of B-cell receptor signaling for patients with B-cell malignancies. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Grubor, V.; Love, C.L.; Banerjee, A.; Richards, K.L.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Dunphy, C.; Choi, W.; Au, W.Y.; Srivastava, G.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havranek, O.; Xu, J.; Kohrer, S.; Wang, Z.; Becker, L.; Comer, J.M.; Henderson, J.; Ma, W.; Man Chun Ma, J.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tonic B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romashkova, J.A.; Makarov, S.S. NF-kappaB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature 1999, 401, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Hussain, A.R.; Siraj, A.K.; Manogaran, P.S.; Al-Jomah, N.A.; Moorji, A.; Atizado, V.; Al-Dayel, F.; Belgaumi, A.; El-Solh, H.; et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood 2006, 108, 4178–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezell, S.A.; Wang, S.; Bihani, T.; Lai, Z.; Grosskurth, S.E.; Tepsuporn, S.; Davies, B.R.; Huszar, D.; Byth, K.F. Differential regulation of mTOR signaling determines sensitivity to AKT inhibition in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9163–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brenner, A.K.; Andersson Tvedt, T.H.; Bruserud, Ø. The Complexity of Targeting PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signalling in Human Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: The Importance of Leukemic Cell Heterogeneity, Neighbouring Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Immunocompetent Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Falcone, I.; Pilotto, S.; Bria, E.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M.; Ciuffreda, L. Role of mTOR Signaling in Tumor Microenvironment: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beielstein, A.C.; Pallasch, C.P. Tumor Metabolism as a Regulator of Tumor-Host Interactions in the B-Cell Lymphoma Microenvironment-Fueling Progression and Novel Brakes for Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guri, Y.; Nordmann, T.M.; Roszik, J. mTOR at the Transmitting and Receiving Ends in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, W.; Wang, M. PI3K in cancer: Its structure, activation modes and role in shaping tumor microenvironment. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Massi, D.; Teng, M.W.L.; Mandala, M. PI3K-AKT-mTOR inhibition in cancer immunotherapy, redux. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 48, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Graupera, M.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Impact on Tumor Cells, Their Protective Stroma, Angiogenesis, and Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1090–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, E.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Tabernero, J. Pushing the Envelope in the mTOR Pathway: The Second Generation of Inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Franklin, R.A.; Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; Libra, M.; Candido, S.; Malaponte, G.; et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascade inhibitors: How mutations can result in therapy resistance and how to overcome resistance. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1068–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Brattain, M.G.; Zhong, H. Dual inhibitors of PI3K/mTOR or mTOR-selective inhibitors: Which way shall we go? Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 5528–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.S.; Wang, L.Z.; Dai, X.; Tseng, S.H.; Loo, S.J.; Sethi, G. Judicious Toggling of mTOR Activity to Combat Insulin Resistance and Cancer: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Hu, Y. Small molecules targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinases. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, A.M.; Chiarini, F.; Evangelisti, C.; Cappellini, A.; Buontempo, F.; Bressanin, D.; Fini, M.; McCubrey, J.A. Two hits are better than one: Targeting both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin as a therapeutic strategy for acute leukemia treatment. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymann, M.P.; Schultz, C. The chemical biology of phosphoinositide 3-kinases. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 2022–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.E.; Rojo, F.; She, Q.B.; Solit, D.; Mills, G.B.; Smith, D.; Lane, H.; Hofmann, F.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ludwig, D.L.; et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.; Amante, R.J.; Bentires-Alj, M. Anticipating mechanisms of resistance to PI3K inhibition in breast cancer: A challenge in the era of precision medicine. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Markman, B.; Scaltriti, M.; Eichhorn, P.J.; Valero, V.; Guzman, M.; Botero, M.L.; Llonch, E.; Atzori, F.; Di Cosimo, S.; et al. NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, prevents PI3K signaling and inhibits the growth of cancer cells with activating PI3K mutations. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8022–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3Kdelta inhibitors in cancer: Rationale and serendipity merge in the clinic. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; McKinney, M.S.; Love, C.; Liu, Q.; Fan, A.; Patel, A.; Smith, J.; Beaven, A.; Jima, D.D.; Dave, S.S. PAK1 mediates resistance to PI3K inhibition in lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantelli, C.; Gaudio, E.; Arribas, A.J.; Kwee, I.; Hillmann, P.; Rinaldi, A.; Cascione, L.; Spriano, F.; Bernasconi, E.; Guidetti, F.; et al. PQR309 Is a Novel Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor with Preclinical Antitumor Activity in Lymphomas as a Single Agent and in Combination Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Eucker, J.; Liu, H.; Muller, A.; Possinger, K.; Scholz, C.W. Concurrent inhibition of PI3-kinase and mTOR induces cell death in diffuse large B cell lymphomas, a mechanism involving down regulation of Mcl-1. Cancer Lett. 2013, 339, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, J.J.; Edgar, K.A.; Guan, J.; Berry, M.; Prior, W.W.; Lee, L.; Lesnick, J.D.; Lewis, C.; Nonomiya, J.; Pang, J.; et al. GDC-0980 is a novel class I PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor with robust activity in cancer models driven by the PI3K pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.P.; Popat, R.; Stathis, A.; Krasniqi, F.; Eyre, T.A.; Ng, C.H.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Schmidt, C.; Wicki, A.; Ivanova, E.; et al. A Dose-Escalation (DE) Study with Expansion Evaluating Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of the Novel, Balanced PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PQR309 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; Egile, C.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Jiang, J.; Shi, W.; Bentzien, F.; Rasco, D.; Abrisqueta, P.; Vose, J.M.; Tabernero, J. Efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of SAR245409 (voxtalisib, XL765), an orally administered phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor: A phase 1 expansion cohort in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Hamadani, M.; Hayslip, J.; Janssens, A.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Ottmann, O.; Arnason, J.; Tilly, H.; Millenson, M.; Offner, F.; et al. Voxtalisib (XL765) in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e170–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, D.; Chiorean, E.G.; Harris, W.B.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Stejskal-Barnett, A.; Qi, W.; Anthony, S.P.; Younger, A.E.; Rensvold, D.M.; Cordova, F.; et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the pan-PI3K/mTORC vascular targeted pro-drug SF1126 in patients with advanced solid tumours and B-cell malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, D.; Qi, W.; Stejskal, A.; Cooke, L.; Garlich, J.R. SF1126, a Pan-PI3K Inhibitor Has Superior Preclinical Activity to CAL-101 a PI3K Delta-Specific Inhibitor in Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrian-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.; Irwin, J.J. ZINC 15--Ligand Discovery for Everyone. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippen, F.M.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Kuter, B.M.; Fink, A.L.; Bihun, I.V.; Lastrapes, M.; Penson, T.; Schmidt, S.P.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Ning, J.; et al. The Dual PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor GDC-0084 Achieves Antitumor Activity in PIK3CA-Mutant Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3374–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, T.P.; Ndubaku, C.O.; Salphati, L.; Alicke, B.; Cheong, J.; Drobnick, J.; Edgar, K.; Gould, S.E.; Lee, L.B.; Lesnick, J.D.; et al. Discovery of Clinical Development Candidate GDC-0084, a Brain Penetrant Inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Olivero, A.; Lu, X.; Mueller, L.; Fernandez Coimbra, A.; Gerstner, E.R.; Rodon Ahnert, J. A first-in-human phase 1 study to evaluate the brain-penetrant PI3K/mTOR inhibitor GDC-0084 in patients with progressive or recurrent high-grade glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. 15), 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.M.; Dehnhardt, C.M.; Delos Santos, E.; Chen, Z.; Dos Santos, O.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Khafizova, G.; Brooijmans, N.; Mallon, R.; Hollander, I.; et al. Bis(morpholino-1,3,5-triazine) derivatives: Potent adenosine 5’-triphosphate competitive phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: Discovery of compound 26 (PKI-587), a highly efficacious dual inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallon, R.; Feldberg, L.R.; Lucas, J.; Chaudhary, I.; Dehnhardt, C.; Santos, E.D.; Chen, Z.; dos Santos, O.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Venkatesan, A.; et al. Antitumor efficacy of PKI-587, a highly potent dual PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazi, M.; Moharram, S.A.; Marhall, A.; Kazi, J.U. The dual specificity PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PKI-587 displays efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Cancer Lett. 2017, 392, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasian, S.K.; Teachey, D.T.; Li, Y.; Shen, F.; Harvey, R.C.; Chen, I.M.; Ryan, T.; Vincent, T.L.; Willman, C.L.; Perl, A.E.; et al. Potent efficacy of combined PI3K/mTOR and JAK or ABL inhibition in murine xenograft models of Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblad, O.; Cordero, E.; Puissant, A.; Macaulay, L.; Ramos, A.; Kabir, N.N.; Sun, J.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Haraldsson, K.; Hemann, M.T.; et al. Aberrant activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway promotes resistance to sorafenib in AML. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5119–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Moharram, S.A.; Kazi, J.U. Acute leukemia cells resistant to PI3K/mTOR inhibition display upregulation of P2RY14 expression. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Molina, J.R.; Bendell, J.; Spicer, J.; Kwak, E.L.; Pandya, S.S.; Millham, R.; Borzillo, G.; Pierce, K.J.; et al. First-in-Human Study of PF-05212384 (PKI-587), a Small-Molecule, Intravenous, Dual Inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaufils, F.; Cmiljanovic, N.; Cmiljanovic, V.; Bohnacker, T.; Melone, A.; Marone, R.; Jackson, E.; Zhang, X.; Sele, A.; Borsari, C.; et al. 5-(4,6-Dimorpholino-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine (PQR309), a Potent, Brain-Penetrant, Orally Bioavailable, Pan-Class I PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor as Clinical Candidate in Oncology. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7524–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Laird, A.D.; Du, X.; Wu, J.; Won, K.A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hsu, P.P.; Qian, F.; Jaeger, C.T.; Zhang, W.; et al. Characterization of the activity of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor XL765 (SAR245409) in tumor models with diverse genetic alterations affecting the PI3K pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresu, L.; Ferraresso, S.; Marconato, L.; Cascione, L.; Napoli, S.; Gaudio, E.; Kwee, I.; Tarantelli, C.; Testa, A.; Maniaci, C.; et al. New molecular and therapeutic insights into canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma elucidates the role of the dog as a model for human disease. Haematologica 2019, 104, e256–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Ferl, G.Z.; An, S.S.; Donahue, A.C.; Satterthwaite, A.B.; Witte, O.N. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase regulate overlapping sets of genes in B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ouyang, J.; Wienand, K.; Bojarczuk, K.; Hao, Y.; Chapuy, B.; Neuberg, D.; Juszczynski, P.; Lawton, L.N.; Rodig, S.J.; et al. CXCR4 upregulation is an indicator of sensitivity to B-cell receptor/PI3K blockade and a potential resistance mechanism in B-cell receptor-dependent diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Haematologica 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicki, A.; Brown, N.; Xyrafas, A.; Bize, V.; Hawle, H.; Berardi, S.; Cmiljanovic, N.; Cmiljanovic, V.; Stumm, M.; Dimitrijevic, S.; et al. First-in human, phase 1, dose-escalation pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral dual PI3K and mTORC1/2 inhibitor PQR309 in patients with advanced solid tumors (SAKK 67/13). Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 96, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijssen, R.; Ter Burg, J.; van Bochove, G.G.; de Rooij, M.F.; Kuil, A.; Jansen, M.H.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Baars, J.W.; Virone-Oddos, A.; Spaargaren, M.; et al. The pan phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor SAR245409 (voxtalisib/XL765) blocks survival, adhesion and proliferation of primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2016, 30, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, F.T.; Gore, L.; Gao, L.; Sharma, J.; Lager, J.; Costa, L.J. Phase Ib trial of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor voxtalisib (SAR245409) in combination with chemoimmunotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; Tabernero, J.; Markman, B.; Patnaik, A.; Tolcher, A.W.; Baselga, J.; Shi, W.; Egile, C.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Laird, A.D.; et al. Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of SAR245409 (XL765), a novel, orally administered PI3K/mTOR inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehnert, J.M.; Edelman, G.; Stein, M.; Camisa, H.; Lager, J.; Dedieu, J.F.; Ghuysen, A.F.; Sharma, J.; Liu, L.; LoRusso, P.M. A phase I dose-escalation study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of a tablet formulation of voxtalisib, a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlich, J.R.; De, P.; Dey, N.; Su, J.D.; Peng, X.; Miller, A.; Murali, R.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Kundra, V.; et al. A vascular targeted pan phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor prodrug, SF1126, with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, G.A.; Garlich, J.R.; Su, J.; Peng, X.; Newblom, J.; Weber, K.; Durden, D.L. Synthesis and cancer stem cell-based activity of substituted 5-morpholino-7H-thieno[3,2-b]pyran-7-ones designed as next generation PI3K inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1922–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, A.; Werner, T.; Chung, C.W.; Savitski, M.M.; Falth Savitski, M.; Grandi, P.; Hopf, C.; Lindon, M.; Neubauer, G.; Prinjha, R.K.; et al. The commonly used PI3-kinase probe LY294002 is an inhibitor of BET bromodomains. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Stejskal, A.; Morales, C.; Cooke, L.C.; Garlich, J.R.; Mahadevan, D. SF1126, a Pan-PI3K Inhibitor has Potent Pre-Clinical Activity in Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2012, 4, 2017–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Dey, N.; Terakedis, B.; Bersagel, L.; Li, Z.H.; Mahadevan, D.; Garlich, J.R.; Trudel, S.; Makale, M.T.; Durden, D.L. An integrin-targeted, pan-isoform, phosphoinositide-3 kinase inhibitor, SF1126, has activity against multiple myeloma in vivo. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broggini, M.; Caiola, E. ESMO E-Learning: PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Available online: https://oncologypro.esmo.org/Education-Library/ESMO-E-Learning-and-V-Learning/PI3K-Akt-mTOR-Pathway (accessed on 24 May 2015).
- Munster, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Hong, D.; Schellens, J.H.; van der Noll, R.; Specht, J.; Witteveen, P.O.; Werner, T.L.; Dees, E.C.; Bergsland, E.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of GSK2126458, an Oral Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodon, J.; Perez-Fidalgo, A.; Krop, I.E.; Burris, H.; Guerrero-Zotano, A.; Britten, C.D.; Becerra, C.; Schellens, J.; Richards, D.A.; Schuler, M.; et al. Phase 1/1b dose escalation and expansion study of BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors including patients with advanced breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo, J.M.; Birrer, M.; Davis, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Gollerkeri, A.; Gore, M.; Houk, B.; Lau, S.; Poveda, A.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; et al. A randomized phase II non-comparative study of PF-04691502 and gedatolisib (PF-05212384) in patients with recurrent endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 142, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markman, B.; Tabernero, J.; Krop, I.; Shapiro, G.I.; Siu, L.; Chen, L.C.; Mita, M.; Melendez Cuero, M.; Stutvoet, S.; Birle, D.; et al. Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of the oral phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and mTOR inhibitor BGT226 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Muro, K.; Sato, M.; Moriya, A. Phase I study of BGT226, a pan-PI3K and mTOR inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid cancers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, M.I.; Molina, A.M.; Lakhman, Y.; Patil, S.; Woo, K.; DeLuca, J.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, J.J.; Feldman, D.R.; Motzer, R.J.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of BEZ235, a Dual Inhibitor of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K) and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR), in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncologist 2016, 21, 787–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Tsushima, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Watanabe, J.; Endo, M.; Hirashima, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Murakami, H.; Naito, T.; Taira, T.; et al. 460PPHASE I CLINICAL TRIAL OF DS-7423, AN ORAL PI3K/MTOR DUAL INHIBITOR, IN JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH ADVANCED SOLID TUMORS. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25 (Suppl. 4), iv153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dolly, S.O.; Wagner, A.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Krug, L.M.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Zauderer, M.G.; Lolkema, M.P.; Apt, D.; Yeh, R.F.; et al. Phase I Study of Apitolisib (GDC-0980), Dual Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, C.D.; Adjei, A.A.; Millham, R.; Houk, B.E.; Borzillo, G.; Pierce, K.; Wainberg, Z.A.; LoRusso, P.M. Phase I study of PF-04691502, a small-molecule, oral, dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR, in patients with advanced cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.C.; Kurkjian, C.; Infante, J.R.; Bauer, T.M.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Greco, F.A.; Shih, K.C.; Thompson, D.S.; Lane, C.M.; Finney, L.H.; et al. A phase 1 study of the sachet formulation of the oral dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 given twice daily (BID) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollebecque, A.; Clamp, A.; Horsley, L.; Morgan, J.A.; Bahleda, R.; George, S.; Shaw, D.; Lauchle, J.O.; Ware, J.; Desai, R.; et al. Abstract B153: A phase I study evaluating the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) activity of the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor GDC-0980 administered once weekly (QW). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10 (Suppl. 11), B153. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, M.; Watanabe, K.; Amagasaki, T.; Natsume, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Quadt, C.; Shirao, K.; Minami, H. A phase I study of single-agent BEZ235 special delivery system sachet in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, V.; Civallero, M.; Citti, C.; Cosenza, M.; Baldassarre, F.; Cannazza, G.; Pozzi, S.; Sacchi, S.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Ciccarella, G. Cell-Penetrating CaCO(3) Nanocrystals for Improved Transport of NVP-BEZ235 across Membrane Barrier in T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Qiao, Y.; Lee, P.; Wang, L.; Chang, A.; Ravi, S.; Rogers, T.A.; Lu, L.; Singhana, B.; Zhao, J.; et al. Antitumor efficacy of liposome-encapsulated NVP-BEZ 235 in combination with irreversible electroporation. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Alsina, M.; Soares, H.P.; Brana, I.; Britten, C.D.; Del Conte, G.; Ezeh, P.; Houk, B.; Kern, K.A.; Leong, S.; et al. A Multi-Arm Phase I Study of the PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors PF-04691502 and Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) plus Irinotecan or the MEK Inhibitor PD-0325901 in Advanced Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, K.; Burris, H.; Gomez, P.; Lynn Henry, N.; Isakoff, S.; Campana, F.; Gao, L.; Jiang, J.; Mace, S.; Tolaney, S.M. Phase I/II dose-escalation study of PI3K inhibitors pilaralisib or voxtalisib in combination with letrozole in patients with hormone-receptor-positive and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer refractory to a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Br. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 154, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, C.; Chi, K.N.; Castellano, D.; de Bono, J.; Gravis, G.; Dirix, L.; Machiels, J.P.; Mita, A.; Mellado, B.; Turri, S.; et al. Phase Ib dose-finding study of abiraterone acetate plus buparlisib (BKM120) or dactolisib (BEZ235) in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 76, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise-Draper, T.M.; Moorthy, G.; Salkeni, M.A.; Karim, N.A.; Thomas, H.E.; Mercer, C.A.; Beg, M.S.; O’Gara, S.; Olowokure, O.; Fathallah, H.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of the Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor Dactolisib (BEZ235) Combined with Everolimus in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Hsieh, A.C.; Kim, W.; Friedlander, T.; Lin, A.M.; Louttit, M.; Ryan, C.J. A Phase I Study of Abiraterone Acetate Combined with BEZ235, a Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, in Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Oncologist 2017, 22, 503-e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilley-Olson, J.E.; Bedard, P.L.; Fasolo, A.; Cornfeld, M.; Cartee, L.; Razak, A.R.; Stayner, L.A.; Wu, Y.; Greenwood, R.; Singh, R.; et al. A phase Ib dose-escalation study of the MEK inhibitor trametinib in combination with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor GSK2126458 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Cohen, R.B.; Laird, A.D.; Mace, S.; Engelman, J.A.; Ruiz-Soto, R.; Rockich, K.; Xu, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Martinez, P.; et al. Phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor SAR245409 (XL765) in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civallero, M.; Cosenza, M.; Marcheselli, L.; Pozzi, S.; Sacchi, S. NVP-BEZ235 alone and in combination in mantle cell lymphoma: An effective therapeutic strategy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, K.; Jin, Z.; Fu, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. Synergistic effect of oridonin and a PI3K/mTOR inhibitor on the non-germinal center B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.Q. PF-04691502, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor has potent pre-clinical activity by inducing apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest in aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ju, W.; Zhang, M.; Wilson, K.M.; Petrus, M.N.; Bamford, R.N.; Zhang, X.; Guha, R.; Ferrer, M.; Thomas, C.J.; Waldmann, T.A. Augmented efficacy of brentuximab vedotin combined with ruxolitinib and/or Navitoclax in a murine model of human Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civallero, M.; Cosenza, M.; Pozzi, S.; Bari, A.; Ferri, P.; Sacchi, S. Activity of BKM120 and BEZ235 against Lymphoma Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 870918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, G.S.; Al-Harbi, S.; Mazumder, S.; Hill, B.T.; Smith, M.R.; Bodo, J.; Hsi, E.D.; Almasan, A. MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies. Cell. Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Tang, S.S.; Ortiz, V.; Vo, T.T.; Fruman, D.A. MCL-1-independent mechanisms of synergy between dual PI3K/mTOR and BCL-2 inhibition in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35202–35217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Gaughan, D.C.; He, L.; Shen, W.; Mavis, C.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J. GSK458 Is a Novel Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor with Preclinical Antitumor Activity in T Cell Lymphomas as a Single Agent and in Combination Therapy. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Sementino, E.; Pei, J.; Kadariya, Y.; Ito, T.K.; Testa, J.R. Co-targeting of Akt and Myc inhibits viability of lymphoma cells from Lck-Dlx5 mice. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews Griner, L.A.; Guha, R.; Shinn, P.; Young, R.M.; Keller, J.M.; Liu, D.; Goldlust, I.S.; Yasgar, A.; McKnight, C.; Boxer, M.B.; et al. High-throughput combinatorial screening identifies drugs that cooperate with ibrutinib to kill activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Park, S.; Lee, J.E.; Jang, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, S.S. The dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 exhibits anti-proliferative activity and overcomes bortezomib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma cells. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Aust, M.M.; Benson, E.C.; Wallace, L.; Friedberg, J.; Grant, S. PI3K/mTOR inhibition markedly potentiates HDAC inhibitor activity in NHL cells through BIM- and MCL-1-dependent mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4849–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Qing, K.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. Low dose of lenalidmide and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor trigger synergistic cytoxicity in activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2016, 35, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buglio, D.; Lemoine, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Vega, F.; Berry, D.; Younes, A. NVP-BEZ235, A Dual Inhibitor of Phosphoinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K) and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR), Is a Potent Inhibitor of Lymphoma Cell Growth and Survival. Blood 2011, 118, 4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, P.; Bhende, P.M.; Foote, M.; Dittmer, D.P.; Park, S.I.; Damania, B. Dual inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin and mitogen activated protein kinase pathways in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhende, P.M.; Park, S.I.; Lim, M.S.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, NVP-BEZ235, is efficacious against follicular lymphoma. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, T.; Tang, G.; Mavis, C.; Gu, J.J.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.J.; Barth, M.J. Omipalisib (GSK458), a Novel Pan-PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, Exhibits In Vitro Anti-Lymphoma Activity in Chemotherapy-Sensitive and -Resistant Models of Burkitt Lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalniz, F.F.; Wierda, W.G. Targeting BCL2 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Other Hematologic Malignancies. Drugs 2019, 79, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, M.; Wallace, L.; Grant, S. Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR by BEZ235 Dramatically Potentiates Panobinostat-Induced Lethality in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Through Multiple Mechanisms. Blood 2013, 122, 817. [Google Scholar]
- Keeton, E.K.; McEachern, K.; Dillman, K.S.; Palakurthi, S.; Cao, Y.; Grondine, M.R.; Kaur, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, A.; et al. AZD1208, a potent and selective pan-Pim kinase inhibitor, demonstrates efficacy in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bartlett, N.L.; Assouline, S.; Yoon, S.-S.; Bosch, F.; Sehn, L.H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Shadman, M.; Gregory, G.P.; Ku, M.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Induces Complete Remissions in Poor Prognosis Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients, Including Those Who Are Resistant to or Relapsing After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapies, and Is Active in Treatment through Multiple Lines. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 6. [Google Scholar]
- Viardot, A.; Bargou, R. Bispecific antibodies in haematological malignancies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 65, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).