Quinoline and its derivatives have been widely used as metal ion chelating agents, metal extracting agents,
corrosive inhibitors and they often show biological activity. They can be used as building blocks in
medicine synthesis when the compounds possess other functional group. The chloromethylation of
8-hydroxyquinoline was reported [1]. Here we report the chloromethylation of 2-methyl-
8-hydroxyquinoline.
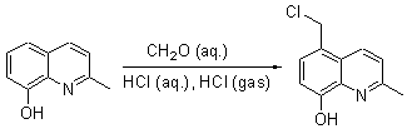
2-Methyl-8-hydroxyquinoline (12 g, 75 mmol) was dissolved in 12 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid
and 12 ml (75 mmol) of 36% formaldehyde was added to the solution. The mixture was cooled in ice
water bath with stirring and was treated with hydrogen chloride gas for 3 h at 0-5°C. After reaction
finished, the yellow mixture was poured on ice and the solution neutralized with NaHCO3 solution. The
product was collected by filtration and recrystallized from ethanol-water to get 10.2 g (65%) of the title
product as a pale yellow solid.
M. p. (ethanol-water): 128-130°C.
1H NMR (200MHz, CDCl3): 2.7 (s, 3H, Me), 4.9 (s, 2H, CH2Cl), 7.0 (d, JHH=7.2Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 8.4 (d,
JHH= 7.2Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.6 (m, 2H, Ar-H).
IR (KBr): 3500-2500 (br), 1608, 1573, 1518, 1387, 1363, 1332, 1274, 1163, 1081, 1007, 828, 716.
Anal. Calc. for C11H10ClNO (207.67): C 63.62, H 4.86, N 6.75. Found: C 63.45, H 4.91, N 6.66.
References
- Burckhalter, J. H.; Leib, R. I. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 26, 4078.
Sample Availability: available from the authors and MDPI. |
© 2001 MDPI. All rights reserved. Molecules website www.mdpi.org/molecules/.