The authors wish to make the following changes to the paper [1]:
In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figure 6 as published. Human error may have occurred during assembly of the subfigures; therefore another representative picture has been chosen for panel D. The corrected Figure 6 appears below. The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. The original publication has also been updated.
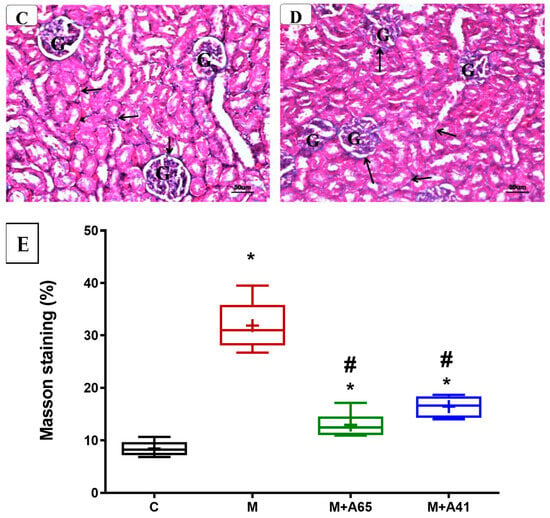
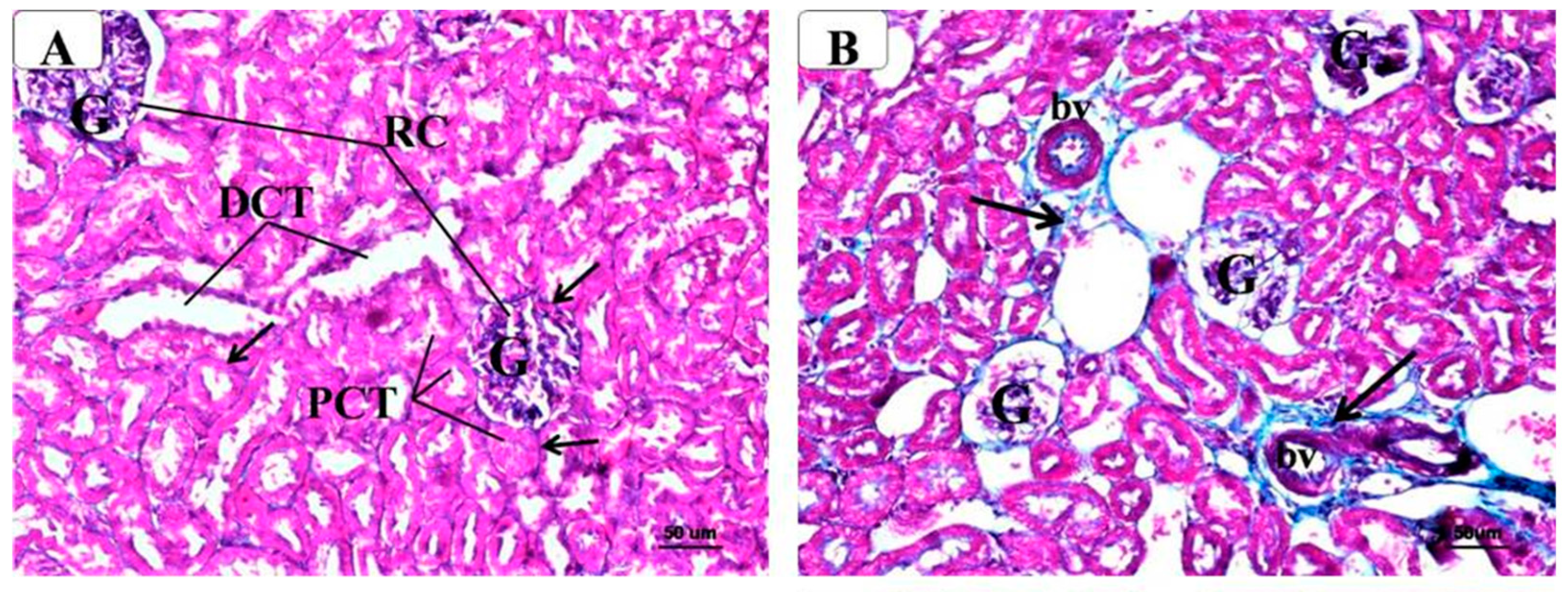
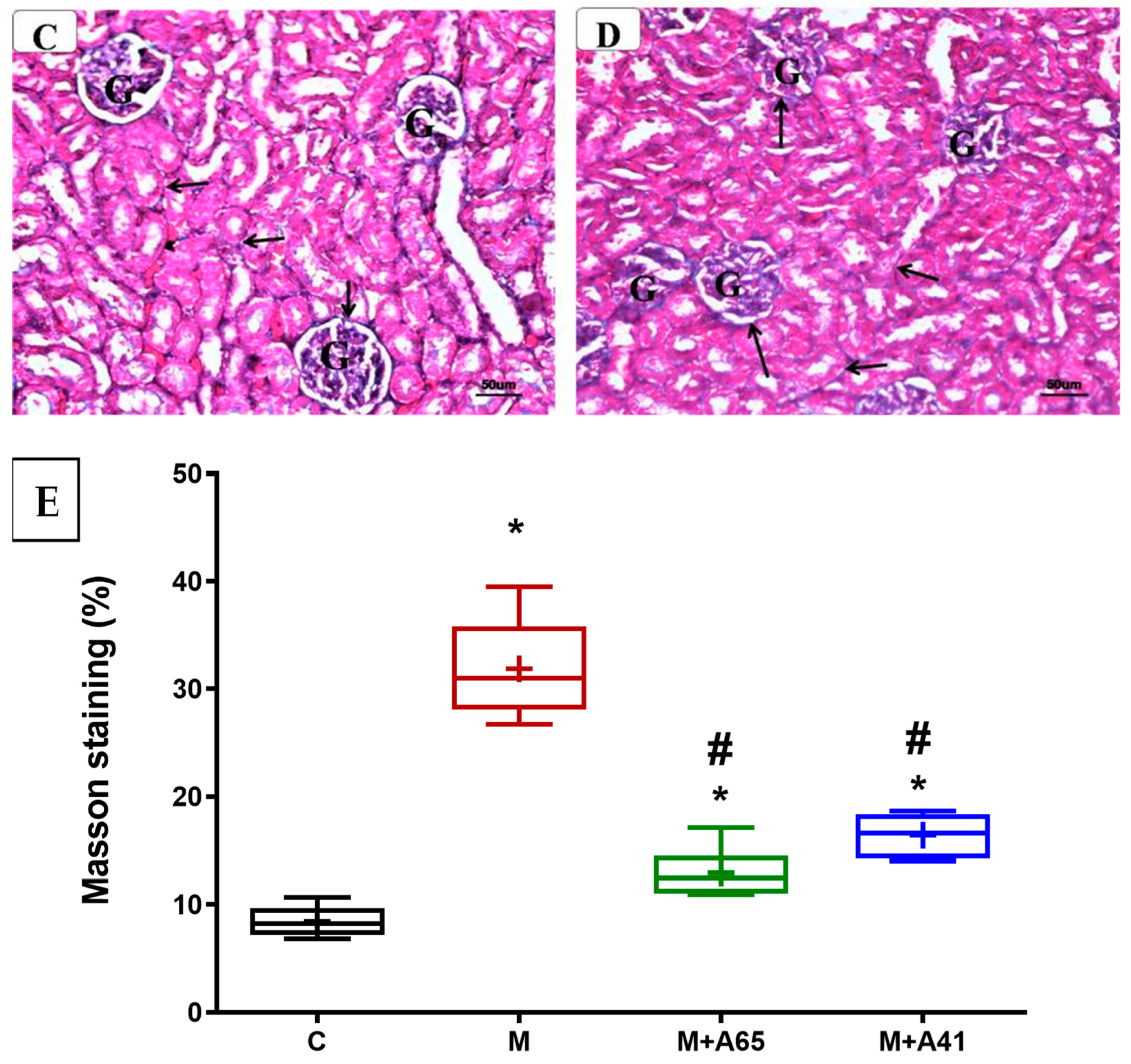
Figure 6.
Representative photomicrographs of the renal cortex of different groups stained with Masson’s Trichrome. Note the marked increase in collagenous fibers (↑) in the kidney of metabolic syndrome (B) around the glomeruli (G) and tubules (PCT, DCT) as compared with the control (A). In contrast, AM6545-treated metabolic syndrome (C) and AM4113-treated metabolic syndrome (D) showed noticeable reductions in collagenous fibers. (Masson’s Trichrome, A, B, C, and D × 200). (E) The quantification of Masson’s Trichrome staining expressed as a percentage. The results are shown as box plots; the means are shown as (+) (n = 8). * Significantly different from “C” at p < 0.05, # Significantly different from “M” at p < 0.05.
Reference
- Eid, B.G.; Neamatallah, T.; Hanafy, A.; El-Bassossy, H.M.; Binmahfouz, L.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Hasan, A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.; Vemuri, K.; Makriyannis, A. Interference with TGFβ1-Mediated Inflammation and Fibrosis Underlies Reno-Protective Effects of the CB1 Receptor Neutral Antagonists AM6545 and AM4113 in a Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome. Molecules 2021, 26, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).