Enhancing Sulfidization and Flotation of Smithsonite Using Eco-Friendly Triethanolamine: Insights from Experimental and Simulation Studies
Abstract
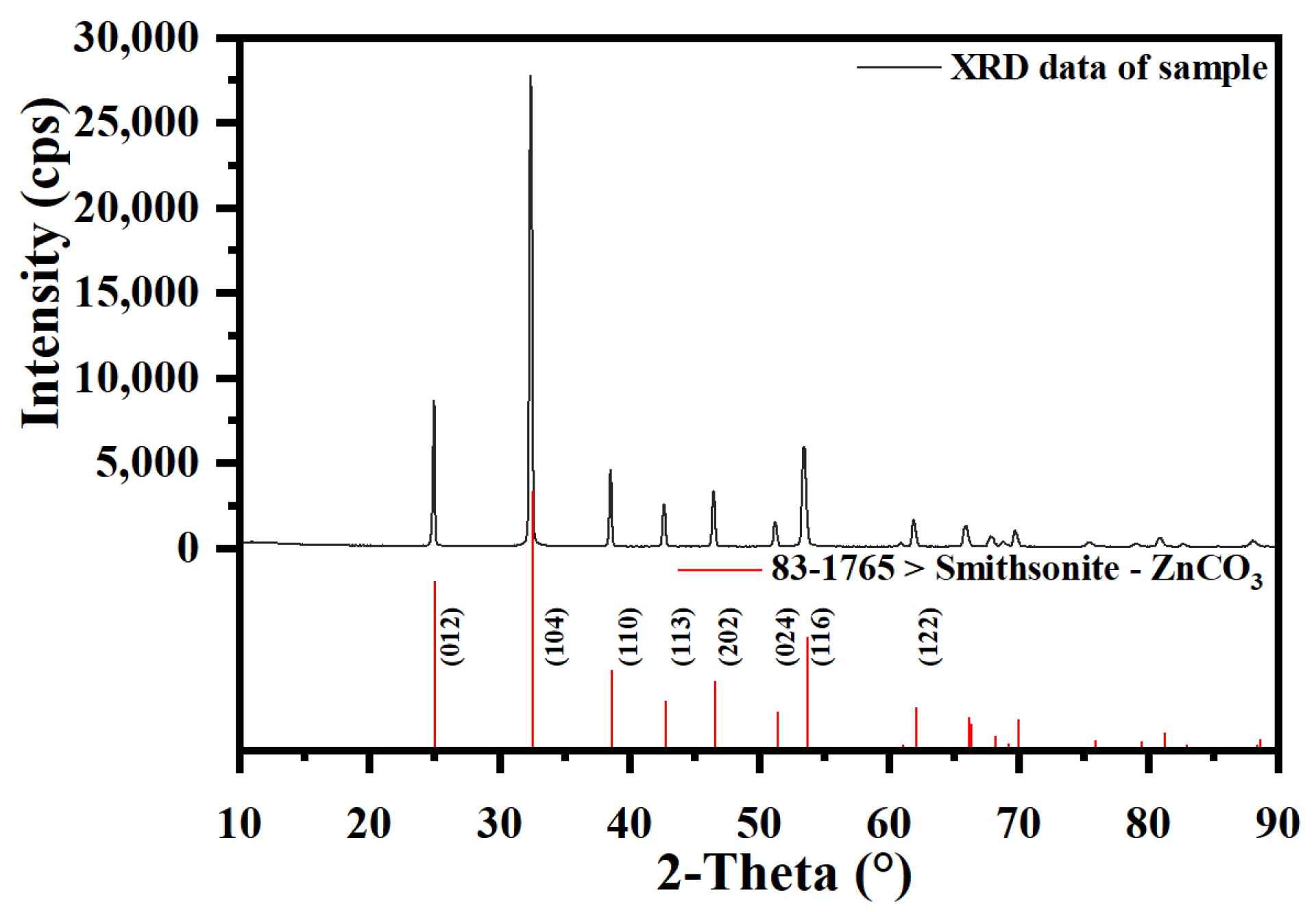
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
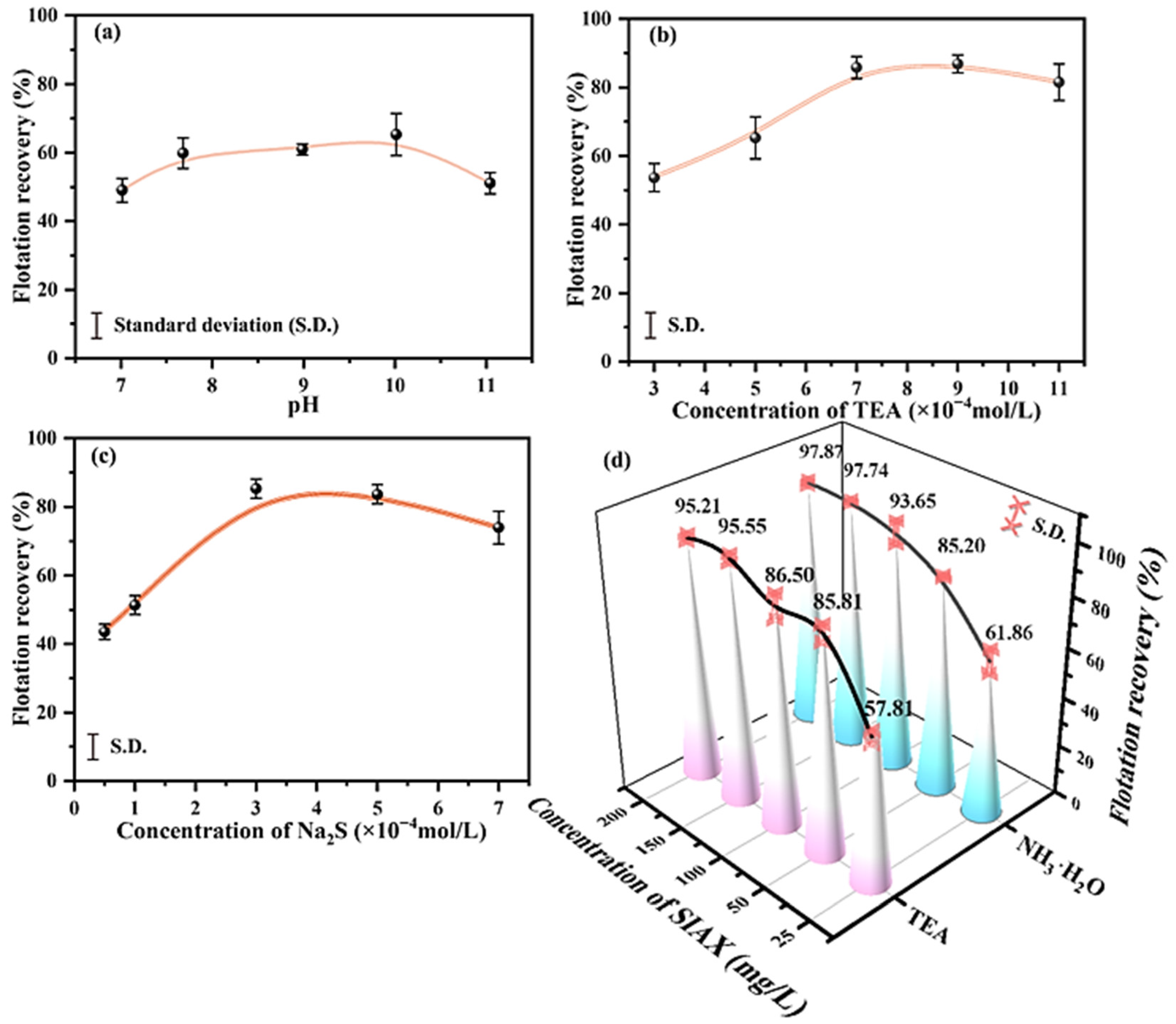
2.1. TEA Improves the Flotation Behavior of Smithsonite
2.2. Contribution of TEA Modification to the Chemical State of Sulfidization Production
2.2.1. Chemical State Characterization of Superficial Sulfidization Production
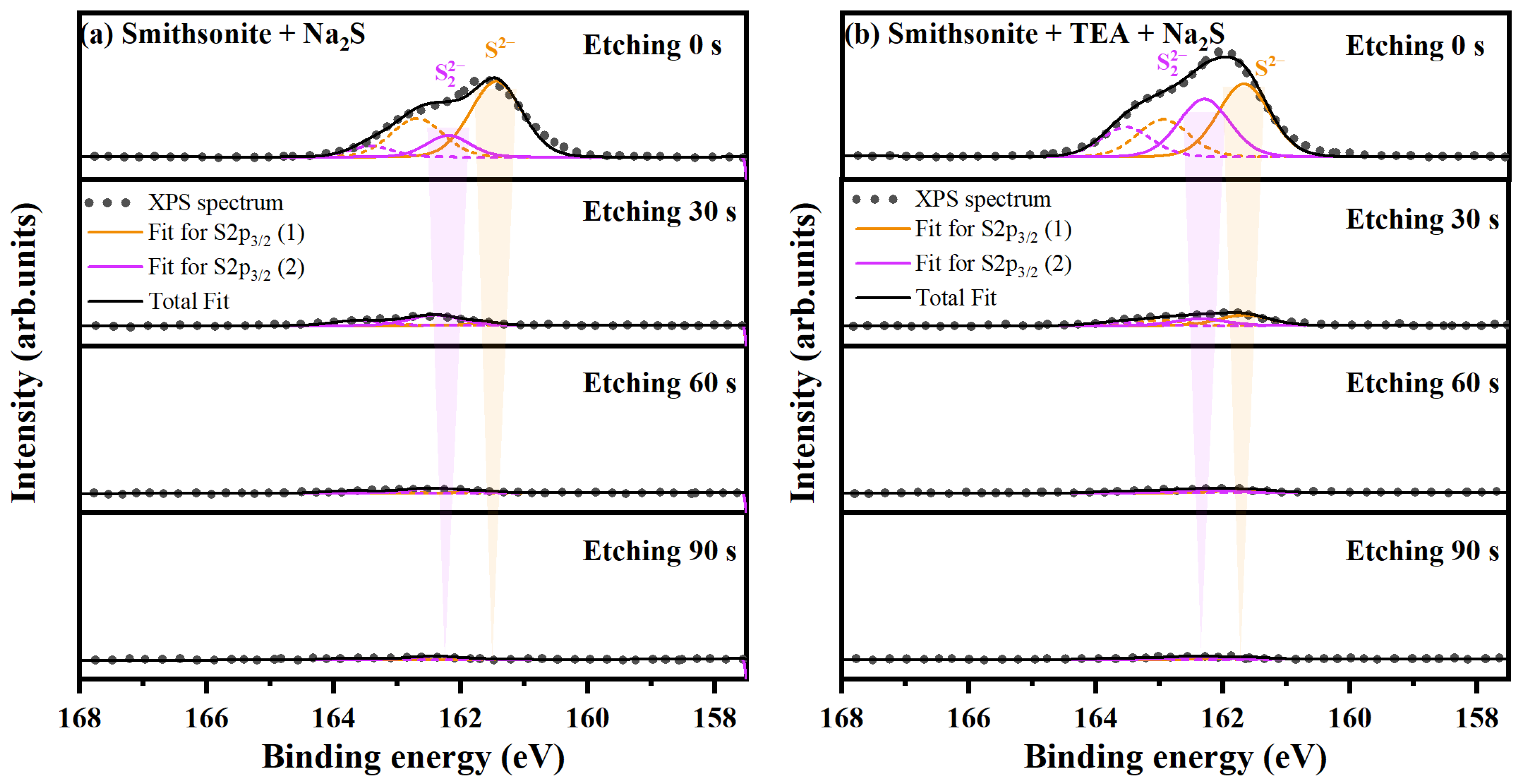
2.2.2. In-Depth Analysis of Sulfidization Production Chemical State
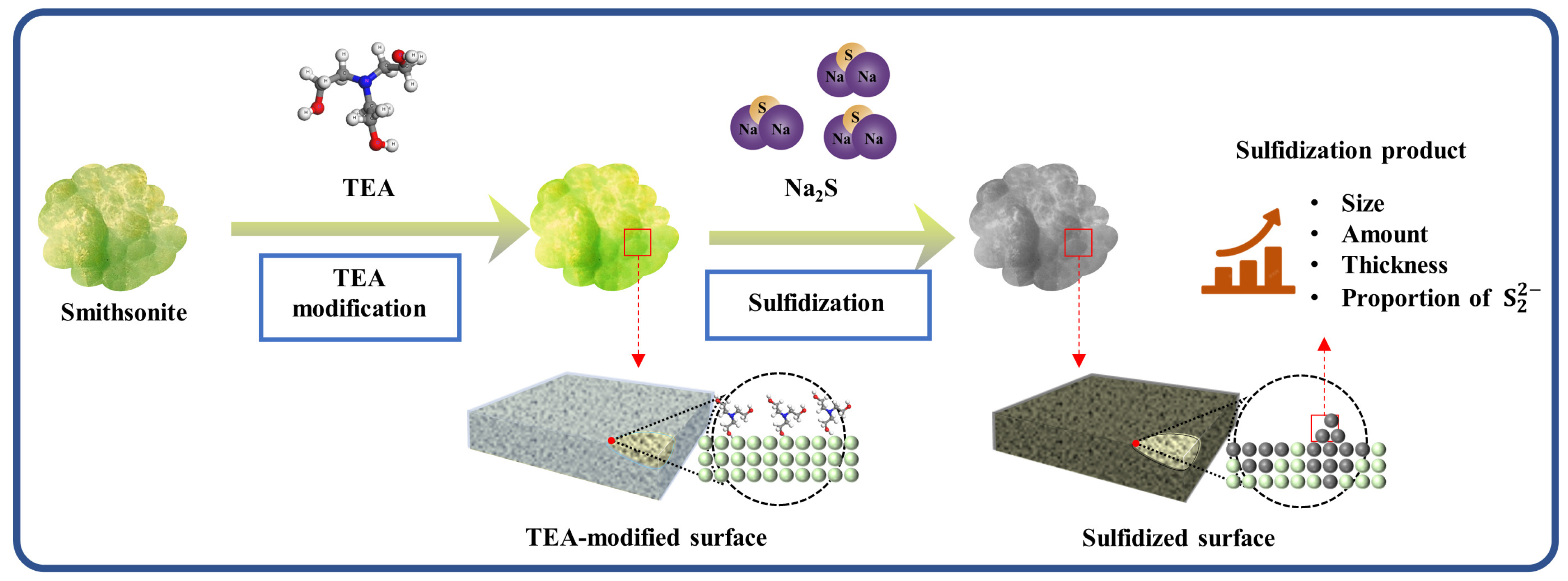
2.3. Contribution of TEA Modification to the Distribution and Morphology of Sulfidization Production
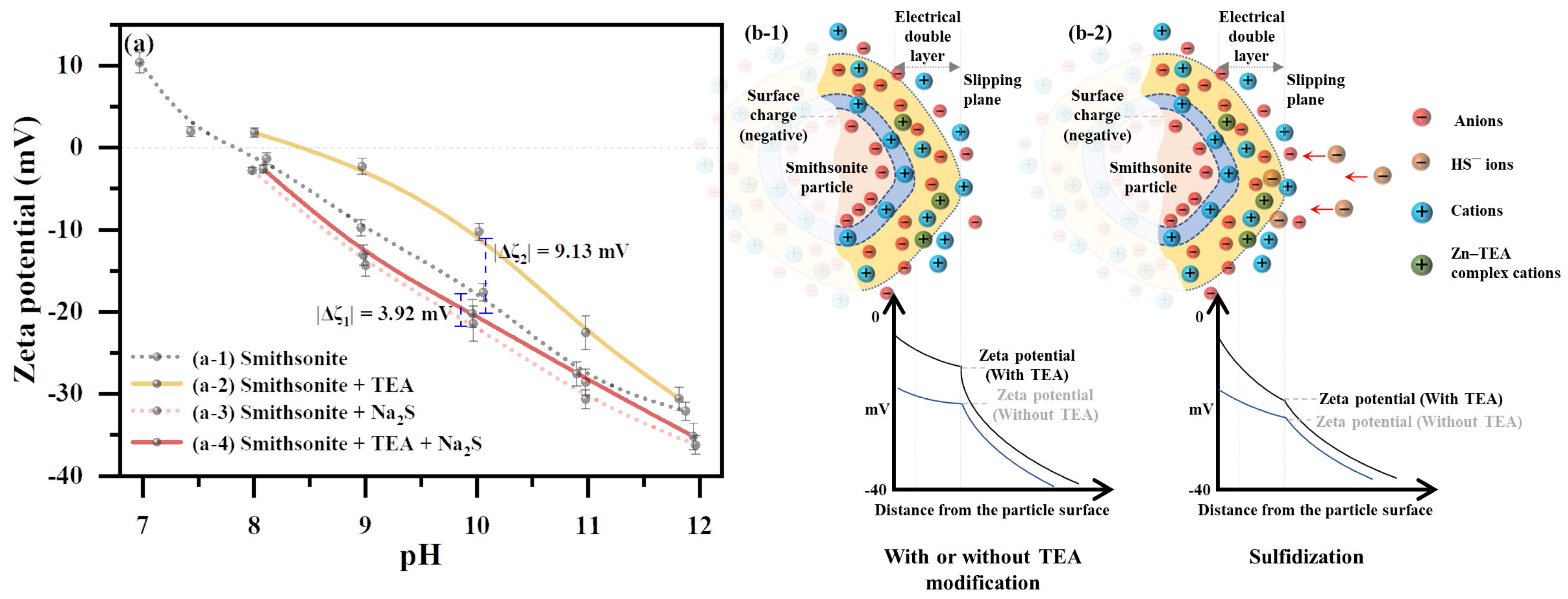
2.4. Effect of TEA Modification on the Smithsonite Surface Potential
2.5. Mechanism of TEA Modification Enhancing Surface Sulfidization
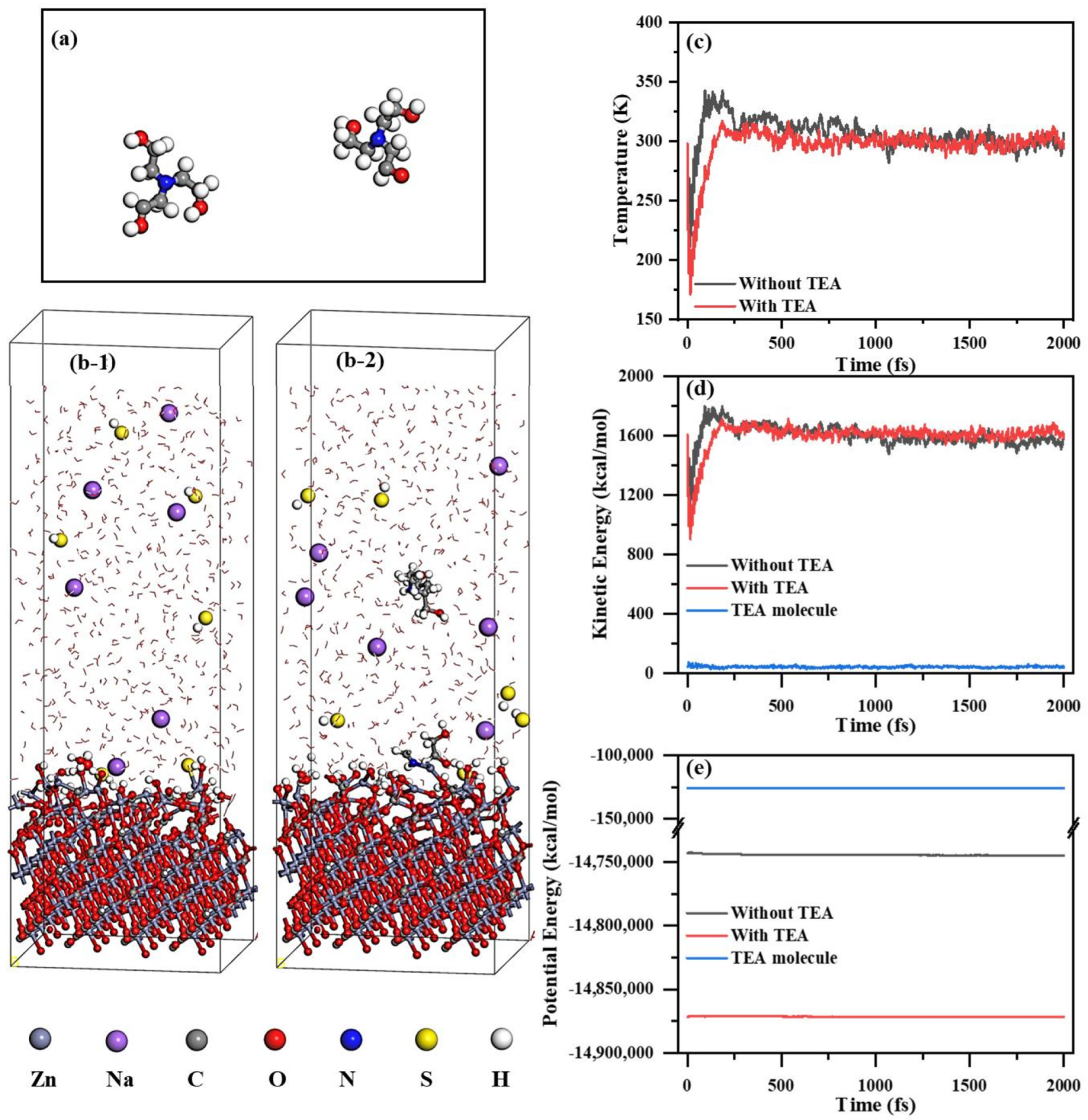
2.5.1. AIMD Analysis of TEA Contribution to Energy Change in Sulfidization Process
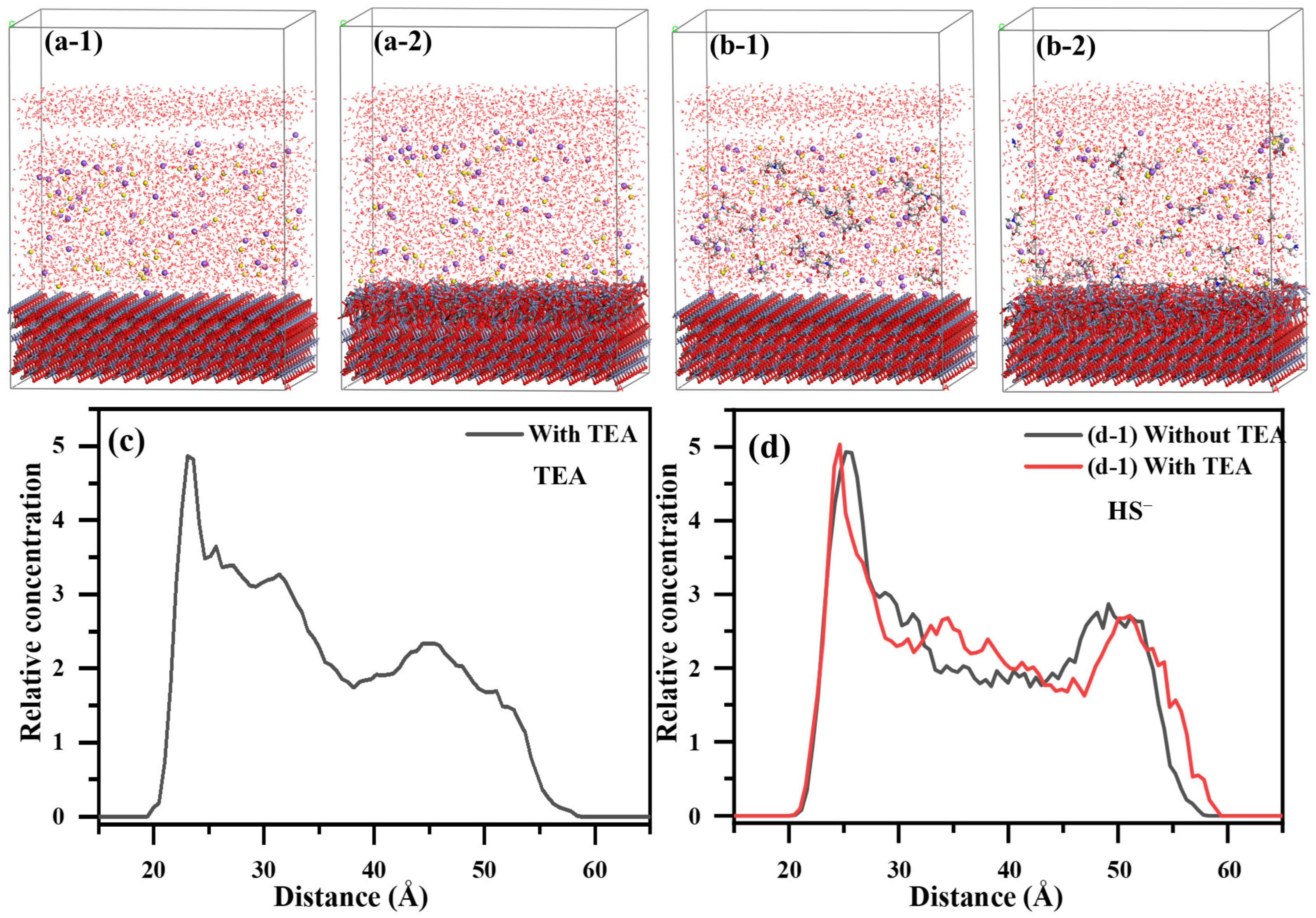
2.5.2. MD Characterization of TEA Impact on the Adsorption Structure of Sulfide Layer
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Experimental Methods
3.2.1. Single Mineral Flotation
3.2.2. Characterization of Surface State and Morphology
3.2.3. Zeta Potential Measurement
3.2.4. AIMD and MD Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subramani, T.; Lilova, K.; Householder, M.; Yang, S.; Lyons, J.; Navrotsky, A. Surface energetics of wurtzite and sphalerite polymorphs of zinc sulfide and implications for their formation in nature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 340, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, S.; Giurco, D.; Retamal, M.; Mason, L.; Mudd, G. Global projection of lead-zinc supply from known resources. Resources 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Feng, Q.-M.; Zhang, G.-F.; Shi, Q.; Luo, Y.-J.; Li, C.-B. Improved hemimorphite flotation using xanthate as a collector with S(II) and Pb(II) activation. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2018, 25, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanqun, Z.; Yuan, L.; Schvartz, C.; Langlade, L.; Fan, L. Accumulation of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in plants and hyperaccumulator choice in Lanping lead–zinc mine area, China. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitzman, M.W.; Reynolds, N.A.; Sangster, D.F.; Allen, C.R.; Carman, C.E. Classification, genesis, and exploration guides for nonsulfide zinc deposits. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 685–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsang, S.; Louvel, M.; Rosa, A.D.; Amboage, M.; Anzellini, S.; Widmer, R.N.; Redfern, S.A. Effect of salinity, pressure and temperature on the solubility of smithsonite (ZnCO3) and Zn complexation in crustal and upper mantle hydrothermal fluids. Chem. Geol. 2021, 578, 120320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, S.; Xian, Y.; Zhao, L.; Feng, Q.; Bai, S.; Han, G.; Lang, J. Lead ion modification and its enhancement for xanthate adsorption on smithsonite surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 498, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M. A review of zinc oxide mineral beneficiation using flotation method. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, O.O.; Bodede, O.R.; Popoola, T.P. Froth Flotation Beneficiation A Sure Way to Value Addition to Arufu (Nigeria) Zinc Ore towards Smelting Grade Concentrate Production. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2020, 5, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Wen, S.; Bai, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Q. Co-adsorption mechanism of isoamyl potassium xanthate and ammonium dibutyl dithiophosphate on sulfidized smithsonite in dodecylamine flotation system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Ye, G. The surface dissolution process of smithsonite and its effect on flotation behaviour. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 676, 132118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Deng, J.; Wen, S. Application of ToF-SIMS and PCA to study interaction mechanism of dodecylamine and smithsonite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 496, 143698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Fang, P.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Y. Design and selection of flotation collectors for zinc oxide minerals based on bond valence model. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, M.; Gui, X.; Cao, Y.; Babel, B.; Rudolph, M.; Weber, S.; Kappl, M.; Butt, H.-J. The application of atomic force microscopy in mineral flotation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, S. Characterization of zinc sulfide species on smithsonite surfaces during sulfidation processing: Effect of ammonia liquor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 61, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S. Formation of zinc sulfide species on smithsonite surfaces and its response to flotation performance. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 709, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wen, S.; Deng, J.; Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Study on the sulfidation behavior of smithsonite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Lin, L.B.; Xie, H.X.; Tong, X.T. Study on separation of low-grade zinc oxide ore with sulfurization-amination flotation, Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ou, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, B.; Xia, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. The effect of surface vacancy on adsorption of HS on smithsonite (101) surface: A DFT study. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 624, 126713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-X.; Lv, J.-F.; Wang, H.; Wen, S.-M.; Pang, J. Formation of zinc sulfide species during roasting of ZnO with pyrite and its contribution on flotation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, W.; Han, G. Enhanced adsorption of sulfide and xanthate on smithsonite surfaces by lead activation and implications for flotation intensification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, S.; Xian, Y.; Liang, G.; Li, M. Pb ion Pre-Modification enhances the sulfidization and floatability of smithsonite. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y. Study on sulfide layer attenuation behavior of smithsonite during sulfidization flotation. Front. Mater. 2020, 6, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Ding, Z.; Wen, S. Promoting sulfidation of smithsonite by zinc sulfide species increase with addition of ammonium chloride and its effect on flotation performance. Miner. Eng. 2018, 125, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Bai, X.; Chang, W.; Cui, C.; Zhao, W. Surface modification of smithsonite with ammonia to enhance the formation of sulfidization products and its response to flotation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ma, W.; Wen, S.; Bai, S.; Deng, J.; Yin, Q. Contribution of ammonium ions to sulfidation-flotation of smithsonite. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, G.; Xian, Y. Determination of Pb sulfide formation on smithsonite surface in NH3-Pb-S aqueous solution system. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 649, 129445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, M.; Yang, B.; Feng, Q.; Liu, D. Enhanced sulfidization flotation mechanism of smithsonite in the synergistic activation system of copper–ammonium species. Miner. Eng. 2022, 187, 107796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Liu, Q.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Lai, H. Determining the lead-sulfur species formed on smithsonite surfaces during lead-ion enhanced sulfidation processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.S.; Eric, F. XPS & FTIR Study of Adsorption Characteristics Using Cationic and Anionic Collectors on Smithsonite. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2006, 05, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ji, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, B. The role of S(II) and Pb(II) in xanthate flotation of smithsonite: Surface properties and mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 442, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, B.; Yi, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, D. Synergistic activation of smithsonite with copper-ammonium species for enhancing surface reactivity and xanthate adsorption. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Babasafari, Z. Effectiveness of triethanolamine on grindability and properties of portland cement in laboratory ball and vibrating disk mills. Ceram. Silik. 2014, 58, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, C.; Bozzini, B.; Calderón, J.A. Electrodeposition of copper from triethanolamine as a complexing agent in alkaline solution. Electrochimica Acta 2022, 425, 140654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Wen, S.; Liu, J.; Bai, S.; Feng, Q. Synergetic adsorption of dodecylamine and octyl hydroxamic acid on sulfidized smithsonite: Insights from experiments and molecular dynamics simulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 329, 125106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ou, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G. Understanding the impact of ammonium salt on the sulfidization of smithsonite from coordination chemistry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 635, 157723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Su, J.-F.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.-H. Separation of sulfide lead-zinc-silver ore under low alkalinity condition. J. Central South Univ. 2012, 19, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xian, Y.; Wen, S.; Liang, G. Enhancement of xanthate adsorption on lead-modified and sulfurized smithsonite surface in the presence of ammonia. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantauzzi, M.; Atzei, D.; Elsener, B.; Lattanzi, P.; Rossi, A. XPS and XAES analysis of copper, arsenic and sulfur chemical state in enargites. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dake, L.S.; Baer, D.R.; Zachara, J.M. Auger parameter measurements of zinc compounds relevant to zinc transport in the environment. Surf. Interface Anal. 1989, 14, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.S.C.; Skinner, W.M.; Gerson, A.R. XPS of sulphide mineral surfaces: Metal-deficient, polysulphides, defects and elemental sulphur. Surf. Interface Anal. 1999, 28, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S. Surface modification of malachite with ethanediamine and its effect on sulfidization flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, N.; Ström, M.; Shipway, P.; Rudd, C. Corrosion resistance of zinc–magnesium coated steel. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 3669–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchida, S.; Kawachi, M.; Koshikawa, H. Kinetic investigation of galvanic dissolution of ZnS and PbS with FeS2 from hydrothermal sulfides in seawater. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 129, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürbeth, W.; Stratmann, M. The delamination of polymeric coatings from electrogalvanised steel—A mechanistic approach: Part 1: Delamination from a defect with intact zinc layer. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmiz, O.; Stupavska, M.; Wulff, H.; Kersten, H.; Brablec, A.; Cernak, M. Deposition of Zn-containing films using atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. A metal-organic framework host for highly reversible dendrite-free zinc metal anodes. Joule 2019, 3, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.; Woods, R.; Wouterlood, H. An XPS investigation of the surface of natural sphalerites under flotation-related conditions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1989, 26, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartio, I.J.; Basilio, C.I.; Yoon, R.-H. An XPS study of sphalerite activation by copper. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5274–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. Towards reliable X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Sputter-damage effects in transition metal borides, carbides, nitrides, and oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 542, 148599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Wu, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Shuming, W.; Huang, L.; Chen, H. Surface modification of hemimorphite via double-complexation by ammonium fluoride and copper ion to promote sulfidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 612, 155797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wen, S.; Liang, G.; Xian, Y.; Chen, L. Ammonia pretreatment for enhancement of Pb ions adsorption on smithsonite surface and its flotation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 153069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Upadhyay, S.; De, S. A facile method to estimate the effective membrane pore charge density through surface zeta potential measurement. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Ming, H. Surface electrochemical properties of red mud (bauxite residue): Zeta potential and surface charge density. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratenko, Y.; Fundamensky, V.; Ignatyev, I.; Zolotarev, A.; Kochina, T.; Ugolkov, V. Synthesis and crystal structure of two zinc-containing complexes of triethanolamine. Polyhedron 2017, 130, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Duay, J.; Lambert, T.N.; Aidun, R. Impact of triethanolamine as an additive for rechargeable alkaline Zn/MnO2Batteries under limited depth of discharge conditions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.A.; Andrés, J.; Li, M.S.; Sambrano, J.R.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. Zinc blende versus wurtzite ZnS nanoparticles: Control of the phase and optical properties by tetrabutylammonium hydroxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20127–20137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, A.; Abbas, Z.; Hashim, M.; Fahad, A. Effect of Sintering Temperature on Co0. 5 Zn0. 5 Fe2 O4 Nano-Particles Evolution and Particle Size Distribution. Adv. Nanopart. 2015, 4, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühne, T.D.; Iannuzzi, M.; Del Ben, M.; Rybkin, V.V.; Seewald, P.; Stein, F.; Laino, T.; Khaliullin, R.Z.; Schütt, O.; Schiffmann, F.; et al. CP2K: An electronic structure and molecular dynamics software package—Quickstep: Efficient and accurate electronic structure calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 194103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Feng, J.; Shang, H.; Wu, J. Graphdiyne-porphyrin composite materials GDY/Por and Por@GDY for lithium ion battery anodes. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

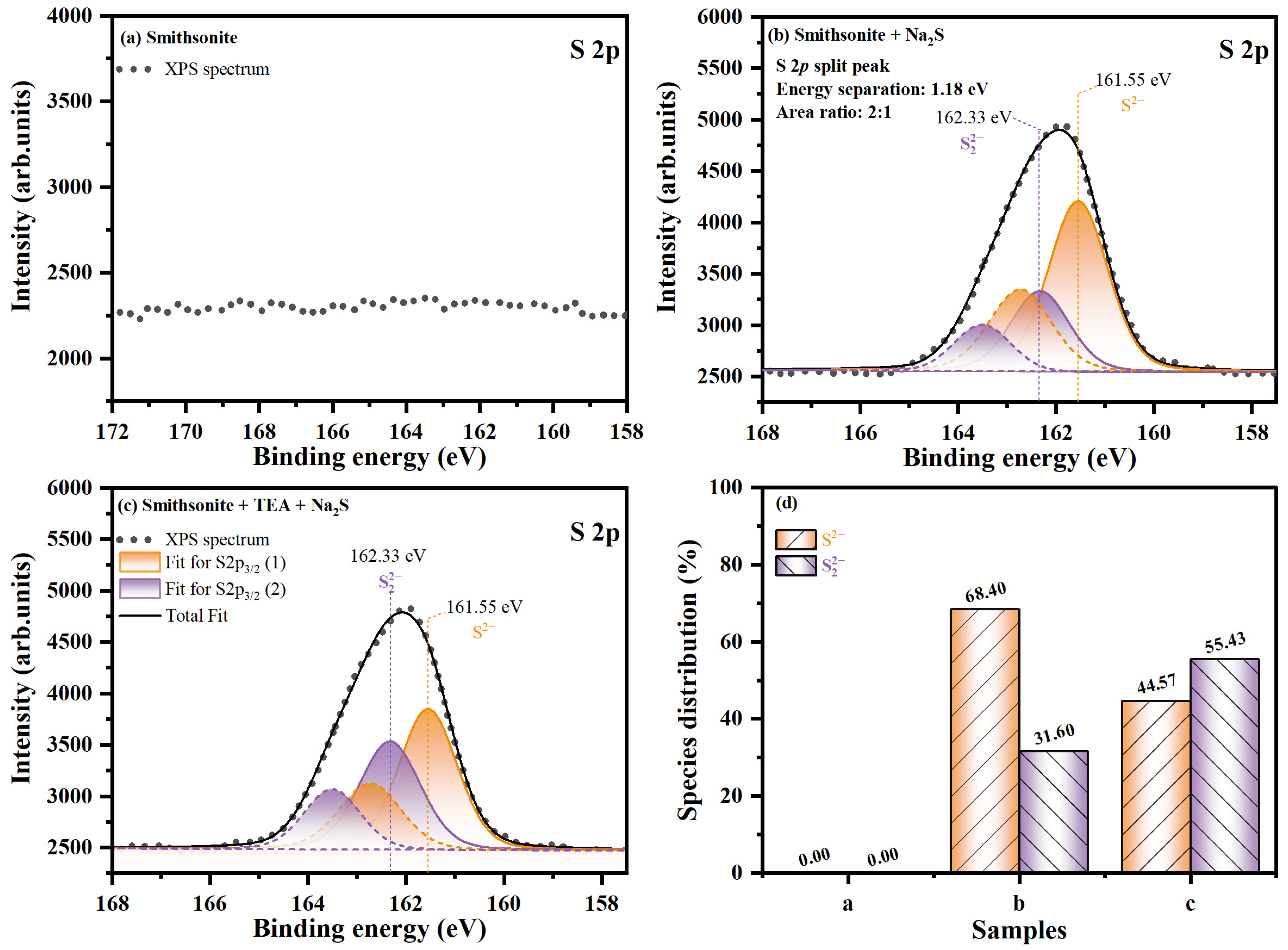
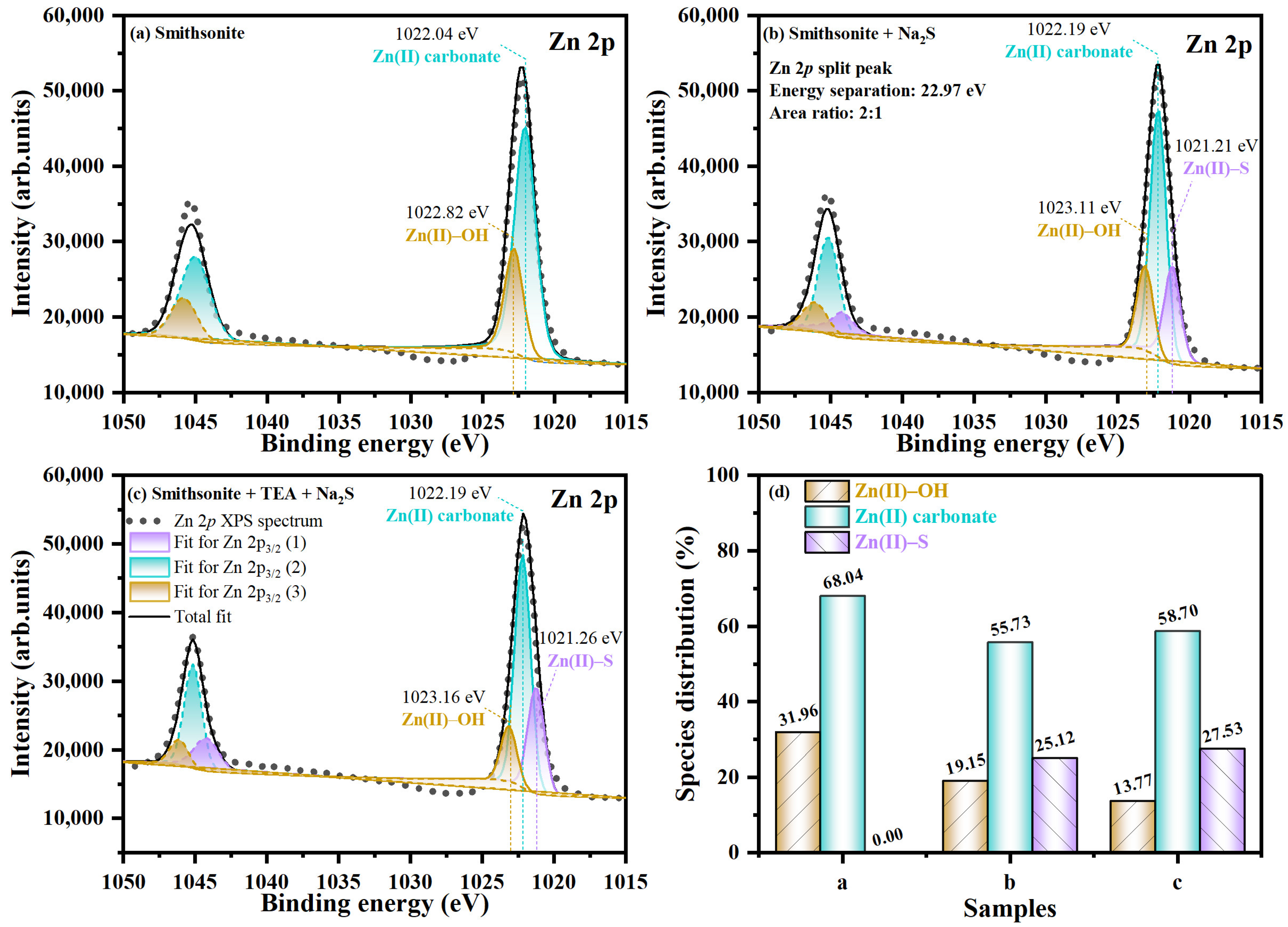

| Elements | Samples | Core Peaks | BE./eV | FW. (I)/eV | At (II)/% | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | a | / | / | / | / | / |
| b | S 2p3/2 (1) | 161.55 | 1.41 | 5.27 | S2− | |
| S 2p3/2 (2) | 162.33 | 1.38 | 2.43 | S22− | ||
| c | S 2p3/2 (1) | 161.55 | 1.38 | 4.27 | S2− | |
| S2p3/2 (2) | 162.33 | 1.45 | 3.44 | S22− | ||
| Zn | a | Zn 2p3/2 (1) | 1022.04 | 1.75 | 15.56 | ZnCO3 |
| Zn 2p3/2 (2) | 1022.82 | 1.52 | 6.09 | Zn–OH | ||
| b | Zn 2p3/2 (1) | 1021.21 | 1.33 | 7.05 | Zn–S | |
| Zn 2p3/2 (2) | 1022.19 | 1.32 | 15.64 | ZnCO3 | ||
| Zn 2p3/2 (3) | 1023.11 | 1.33 | 5.37 | Zn–OH | ||
| c | Zn 2p3/2 (1) | 1021.26 | 1.35 | 7.68 | Zn–S | |
| Zn 2p3/2 (2) | 1022.19 | 1.31 | 16.38 | ZnCO3 | ||
| Zn 2p3/2 (3) | 1023.16 | 1.29 | 3.84 | Zn–OH |
| Etching Time/s | Sample | Smithsonite + Na2S | Smithsonite + TEA + Na2S | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2− | S22− | S2− | S22− | ||
| 0 | BE./eV | 161.44 | 162.20 | 161.68 | 162.30 |
| FW./eV | 0.96 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 0.94 | |
| At/% | 11.04 | 2.66 | 10.97 | 8.53 | |
| 30 | BE./eV | 161.61 | 162.40 | 161.66 | 162.36 |
| FW./eV | 0.60 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | |
| At/% | 0.13 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.61 | |
| 60 | BE./eV | 161.60 | 162.40 | 161.59 | 162.32 |
| FW./eV | 0.61 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | |
| At/% | 0.07 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.26 | |
| BE./eV | 161.40 | 162.40 | 161.60 | 162.40 | |
| FW./eV | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | |
| At/% | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.21 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Liang, G.; Xian, Y.; Wen, S. Enhancing Sulfidization and Flotation of Smithsonite Using Eco-Friendly Triethanolamine: Insights from Experimental and Simulation Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143433
Zhang S, Liang G, Xian Y, Wen S. Enhancing Sulfidization and Flotation of Smithsonite Using Eco-Friendly Triethanolamine: Insights from Experimental and Simulation Studies. Molecules. 2024; 29(14):3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143433
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Song, Guanyu Liang, Yongjun Xian, and Shuming Wen. 2024. "Enhancing Sulfidization and Flotation of Smithsonite Using Eco-Friendly Triethanolamine: Insights from Experimental and Simulation Studies" Molecules 29, no. 14: 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143433
APA StyleZhang, S., Liang, G., Xian, Y., & Wen, S. (2024). Enhancing Sulfidization and Flotation of Smithsonite Using Eco-Friendly Triethanolamine: Insights from Experimental and Simulation Studies. Molecules, 29(14), 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143433








