Abstract
Chalcones have shown a broad spectrum of biological activities with clinical potential against various diseases. The biological activities are mainly attributed to the presence in the chalcones of the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl system, perceived as a potential Michael acceptor. Chalcones could activate the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway through a Michael addition reaction with the cysteines of Keap1, which acts as a redox sensor and negative regulator of Nrf2. This modification allows the dissociation of Nrf2 from the cytoplasmic complex with Keap1 and its nuclear translocation. At this level, Nrf2 binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) and activates the expression of several detoxification, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes as well as genes involved in the clearance of damaged proteins. In this regard, the Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway is a new potential pharmacological target for the treatment of many chronic diseases. In this review we summarize the current progress in the study of Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway activation by natural and synthetic chalcones and their potential pharmacological applications. Among the pharmacological activities highlighted, anti-inflammatory activity was more evident than others, suggesting a multi-target Michael acceptor mechanism for the chalcones involving key regulators of the Nrf2 and nuclear factor- κB (NF-κB) pathways.
1. Introduction
Chalcone or 1,3-diaryl-2-propen-1-one is a common chemical scaffold found in several natural and synthetic chalcone derivates, that exists as either a trans (E) or cis (Z) isomer (Figure 1a), of which the trans isomer is thermodynamically more stable [1]. Chalcone derivatives have exerted a broad spectrum of biological effects such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiprotozoal, antiulcer, antihistaminic, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and also neuroprotective activities [2,3,4]. These biological activities are mainly attributed to the presence in the chalcones of the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl system, perceived as a potential Michael acceptor [5,6]. This moiety can readily form covalent bonds with nucleophiles such as the sulfhydryl of cysteine residues present in cellular peptides or proteins to obtain the Michael adduct (Figure 1b), which may play an important role in their biological activities [2].
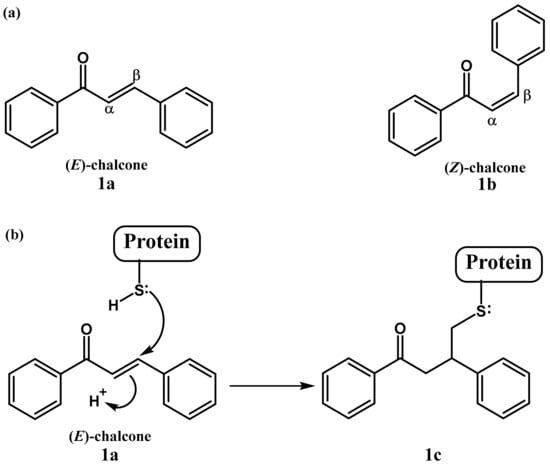
Figure 1.
Chalcone structure (a) and its Michael addition with cysteine (b).
Chalcones and other Michael acceptors could activate the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway (Figure 2) through covalent bonds with the cysteines of Keap1, which contains at least 27 cysteine residues with different levels of reactivity and acts as a redox sensor and negative regulator of Nrf2 [6,7,8]. This modification reduces the ability of Keap1 to induce ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 as well as allowing the dissociation of Nrf2 from the cytoplasmic complex with Keap1 and its translocation into the nucleus [9].
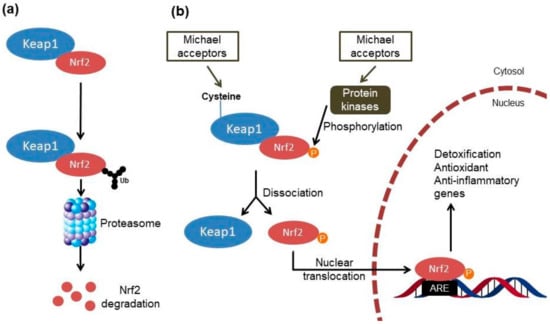
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of Nrf2–ARE pathway activation by Michael acceptors. (a) Under baseline conditions, Nrf2 forms a complex with Keap1 in the cytosol, which facilitates the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 by the proteasome. (b) The dissociation of the Nrf2–Keap1 complex is an essential prerequisite for Nrf2/ARE activation by Michael acceptors that happens through two mechanisms: (i) by modification of the cysteines in Keap1, which leads to conformational changes in this protein and the subsequent release of Nrf2; (ii) by activation of kinases that phosphorylate Nrf2 and thereby free it from Keap1-mediated complex. After nuclear translocation, Nrf2 binds to ARE in the promoter regions of various detoxification, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes. Nrf2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; ARE, antioxidant response element; Ub, ubiquitin; P, phosphate.
At a nuclear level, Nrf2 binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE) or the electrophile responsive element and activates the expression of several detoxification, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes as well as genes involved in the clearance of damaged proteins [9,10]. These genes also encode enzymes that generate the major intracellular antioxidant, glutathione (GSH). Recent studies also reported Keap1-independent mechanisms of Nrf2 regulation (Figure 2), such as the activation of protein kinase signaling cascades by molecules that modify the cellular redox status [11]. In particular, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway can activate the Nrf2 signaling through the inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3β) [12]. Furthermore, the p38-mitogen activated protein kinase (p38-MAPK) pathway can phosphorylate Nrf2 and stabilize the association between Nrf2 and Keap1 proteins, promoting its breakdown [11]. Recent studies also showed functional cross-talk between Nrf2 and the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); these nuclear factors regulate cellular responses to oxidative stress and inflammation, respectively [13]. Under normal conditions, NF-κB is taken in the cytosol through the interaction with the nuclear κ-B inhibitor (IκBα). The IκB kinase (IKK) activation evoked by tissue damage or infection allows the degradation of IκBα and subsequently the nuclear translocation and activation of NF-κB [14]. Therefore, the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway can exert anti-inflammatory effects through indirect mechanisms by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and consequently NF-κB activity, and through direct mechanisms by modulating the transcription of anti- and pro-inflammatory genes, and inhibiting IKK activity through the interaction with Keap1 [13]. In this regard, the chalcones also demonstrate the ability to control inflammation through the inhibition of IKK activity and the DNA binding of NF-κB via a Michael acceptor-related mechanism [15,16,17,18].
The Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway involved in oxidative stress and inflammation is a new potential pharmacological target for the treatment of many diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, airway disorders, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis [14,19]. In drug discovery, several natural and synthetic compounds have demonstrated the ability to modulate the Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway, most of which are activators [20]. Based on the interaction mechanism, Nrf2 activators are classified into electrophilic activators, which act through the modification of Keap1 cysteine residues, and non-electrophilic activators that target the protein–protein interaction interface of Keap1/Nrf2 [20,21]. Recently, some researchers started to identify Nrf2 inhibitors for the treatment of cancers that express a constitutive activation of the Nrf2 function, which contributes to undesired protection of the cancer cells against oxidative stress and xenobiotics. However, further studies are necessary to explain the biological significance of Nrf2 activation in cancer [20].
Among the electrophilic activators of Nrf2, chalcones are mainly soft electrophiles and attract soft nucleophiles like thiols, rather than hard nucleophiles like amino and hydroxyl groups [6]. These highlights suggest that chalcones could be less prone to adverse off-target effects than other electrophilic activators of Nrf2. In this context, compounds with a very high reactivity against Nrf2 may not be the best choice for the design of an ideal Nrf2 activator [22].
Previous reviews have described a broad spectrum of biological activities for chalcones, suggesting a potentially promiscuous target profile [1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, a knowledge of the different mechanisms of chalcones and direct molecular targets is important for the future clinical development of chalcone compounds. Among the potential molecular targets, the Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway is characteristic for its complexity and cross-talks with multifunctional proteins [14], yet has not been systematically reviewed for chalcones. In this review, we will summarize the experimental evidence of direct interactions of natural (Table 1) and synthetic (Table 2) chalcones with the Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway and the pharmacological relevance of these interactions. We will not consider the few chalcones that show an ability to inhibit or modulate the Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway in cancer prevention and therapy.

Table 1.
Natural chalcones as Nrf2 inducers.

Table 2.
Synthetic chalcones as Nrf2 inducers.
2. Targeting the Nrf2 Pathway by Natural Chalcones
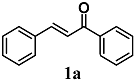
Liu et al. evaluated the anti-inflammatory properties of trans-chalcone (1a), an α,β-unsaturated flavonoid present in several plants and a major precursor of other flavonoids, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interleukin (IL)-6-treated bovine aortic endothelial cells (ECs) [23]. In particular, they recorded the ability of 1a to reduce the adhesion of monocyte THP-1 cells, to stimulate the overexpression of the adhesion molecule ICAM-1, an early event of the inflammatory process, and to inhibit the activation of STAT3 and NF-κB in IL-6- and LPS-treated ECs. Moreover, 1a showed a higher activity than other flavonoids which lack the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group, suggesting that this functional group was crucial for the anti-inflammatory activity recorded. In this regard, the authors also highlighted that the anti-inflammatory response elicited by 1a could be ascribed to its ability to transiently deplete intracellular GSH levels, emphasizing that the thiol-dependent redox state may influence the activity of this chalcone. Further, they determined that 1a upregulated nuclear Nrf2 levels, ARE-luciferase, thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) activities, probably in response to the electrophilic stress generated. Taken together, these results support the contribution of the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety of 1a to its anti-inflammatory properties at endothelial level. Martinez et al. also evaluated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of 1a in a model of ultraviolet B radiation skin damage in hairless mice [24]. They reported that topical administration of 1a reduced several parameters of skin inflammation and oxidative stress, such as skin edema, myeloperoxidase (MPO), lactoperoxidase (LPO) and matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) activities, as well as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression. Nrf2, HO-1, GSH peroxidase 1 (GPX1) and GSH reductase (GR) expressions, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) activity and GSH levels were also enhanced at skin level by treatment with 1a. On the basis of these findings, the authors suggest further studies to confirm a therapeutic approach with 1a for the treatment of UVB radiation skin damage.
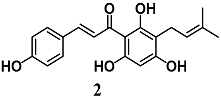
Lee et al. investigated the anti-inflammatory activity of xanthohumol (2), a polyphenol chalcone from hops (Humulus lupulus L.), in microglial BV2 cells [25]. Chalcone 2 reduced the release of pro-inflammatory mediators including nitric oxide (NO), IL-1β, and TNF-α, as well as the activation of the NF-κB pathway in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells. Moreover, 2 triggered the activation of the Nrf2–ARE pathway, the transcription of NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) and HO-1 and the increase of GSH levels. Yao et al. also demonstrated that 2 activated the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 to confer neuroprotection against oxidative damage in neuronal PC12 cells [26]. Treatment of PC12 cells with 2 upregulated several cytoprotective genes, as well as the corresponding proteins, including GSH, HO-1, NQO1, thioredoxin 1 (Trx1), and TrxR1. This strengthening of the intracellular antioxidant defense system was associated with prevention of ROS accumulation and neuronal death induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in PC12 cells. Interestingly, the authors recorded that both the hydrogenation of 2 and Nrf2-knockdown in PC12 cells abolished its neuroprotective effect, indicating that the α,β-unsaturated ketone structure in 2 and the activation of Nrf2 are key determinants for the neuroprotection of 2. More recently, Brodziak-Jarosz et al. confirmed the ability of 2 to form a covalent bond with the sensor protein Keap1, an event that triggers Nrf2 activation, using a click chemistry approach and AREc32 cells [27]. They showed a weaker electrophilicity for 2, suggesting its more selective interaction with the most nucleophilic thiols. Further, they did not disregard the fact that some noncovalent protein interactions can contribute to target selectivity of 2. Taken together, these findings at microglial and neuronal level suggested the potential use of 2 to prevent inflammatory and oxidative damage in the brain.
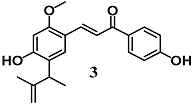
Kim et al. evaluated the ability of Licochalcone E (3), a retrochalcone derivative identified in Glycyrrhiza-inflata, to activate the Nrf2/ARE pathway in several in vitro and in vivo models of gliosis and neurodegeneration [28]. Chalchone 3 decreased the LPS-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 cells, and also protected neuronal SH-SY5Y cells from 6-OHDA cytotoxicity. In similar experimental conditions, 3 was shown to activate the Nrf2–ARE system and up-regulate NQO1 and HO-1 downstream. Both the cytoprotective activity and the up-regulation of HO-1 and NQO1 by 3 were also established in an in vivo 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) animal model. The contribution of Nrf2 to the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective activities of 3 was confirmed using siRNA-mediated Nrf2-silencing cells as well as in the presence of a specific inhibitor of HO-1 or NQO1.
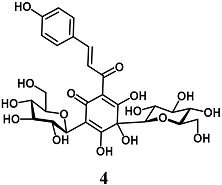
Liu et al. evaluated the cytoprotective effects of Hydroxysafflor yellow A (4), a chalcone glycoside isolated from Carthamus tinctorius, against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells [29]. In this regard, chalcone glycoside 4 raised the HO-1 activity, Akt phosphorylation and Nrf2 nuclear translocation, and, most importantly, reduced the H9c2 cardiomyocyte death evoked by I/R. In these experimental conditions, the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway partially abolished the results obtained on HO-1, Nrf2 and cardiomyocyte death, suggesting that the cardioprotective effect recorded with 4 depends on different mechanisms, including the activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Subsequently, Hu et al. and Chen et al. corroborated the ability of 4 to protect H9c2 cells under different ischemic-like conditions, through Nrf2 pathway activation [30,31]. They confirmed these findings on ischemia-reperfusion and isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats, respectively. Interestingly, in the same in vivo models, 4 also showed synergistic cardioprotective effects with Danshensu and acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid on the Nrf2 pathway. Taken together, these highlights suggest that 4 may improve the prognosis of myocardial infarction after post-ischemia reperfusion.
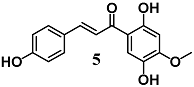
Lee et al. showed the ability of 4,2′,5′-trihydroxy-4′-methoxychalcone (5), a chalcone isolated from the heartwood of D. odorifera, to inhibit the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway as well as several parameters of inflammation, including NO production, COX-2 and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, and TNF-α and IL-1β release in LPS-stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages [32]. These results indicate that 5 may be considered for further development for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory diseases.
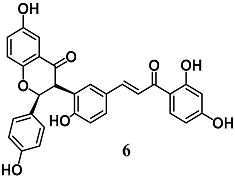
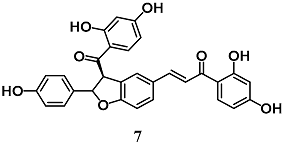
Ajiboye et al. investigated the capability of lophirones B (6) and C (7), chalcone dimers present in Lophira alata, to induce expressions and activities of cytoprotective enzymes at liver level [33]. Chalcone 6 and 7 administrations to rats increased and decreased the levels of nuclear Nrf2 and cytoplasmic Keap1, respectively, leading to the enhancement of several cytoprotective [GSH S-transferase (GST), NQO1, erythropoietin-producing human hepatocellular receptor (EPH) and UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A1 (UGT1A1)] and antioxidant [superoxide dismutase (SOD), CAT, GPX and GR] enzymes. These data indicate the detoxification potentials of 6 and 7 at liver level.
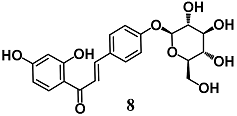
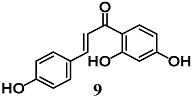
Wang et al. evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of various flavonoids derived from the roots of Glycyrrhizae uralensis in macrophage RAW264.7 cells stimulated by LPS [34]. Among these flavonoids, isoliquiritin (8) and isoliquiritigenin (9) showed a higher inhibition of the inflammatory responses mediated by RAW264.7 cells than liquiritigenin. A mechanistic approach also showed the ability of 8 and 9 to activate Nrf2 and induce UGT1A1 and NQO1 enzymes in RAW264.7 cells. The authors further found that both 8 and 9 induced HO-1 expression regardless of Nrf2 expression in hepatic HepG2-C8 cells. With regard to NF-κB signaling, they recorded an inhibition of IκBα degradation and phosphorylation only for 9. Zeng et al. investigated the ability of 9 to control NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways during intracerebral hemorrhage in rats [35]. Chalcone 9 suppressed NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome components and activated Nrf2-mediated antioxidant system. Moreover, 9 counteracted several parameters of neurological damage. Taken together, these findings suggest that 9 can modify several components of the inflammatory processes at different tissue and organ levels including brain.
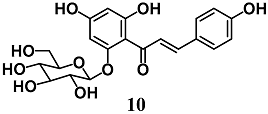
Han et al. showed that isosalipurposide (10), a chalcone isolated from Corylopsis coreana Uyeki, activates the Nrf2–ARE signaling pathway via the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 ERK1/2 and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in human hepatic HepG2 cells [36]. They also demonstrated that Nrf2 activation elicited by 10 indicated its ability to increase the protein levels of glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL) and HO-1, as well as intracellular GSH levels, resulting in increased resistance of HepG2 cells against tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage.
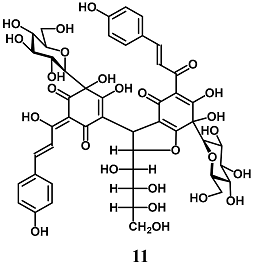
Ma et al. reported that among the components of Carthamus tinctorius, Safflower yellow B (11), a quinochalcone glycoside, protects HepG2 cells against the oxidative damage induced by H2O2 [37]. In particular, 11 reduced H2O2-dependent intracellular ROS production, malondialdehyde (MDA) formation and cell damage, and increased antioxidant enzyme activity, such as GPX and SOD. The authors also demonstrated that 11 induced the activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and GPX and SOD levels by triggering the Akt pathway.
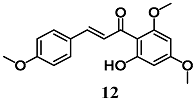
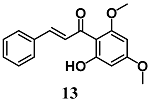
Pinner et al. compared the ability of flavokawains A (12) and B (13), methoxylated chalcones from Kava (Piper methysticum), to induce an adaptive cellular response in HepG2 cells [38]. Both methoxylated chalcones activated the transcription factors Nrf2, increasing the expression of antioxidant and heat shock (Hsp) response genes, in HepG2. In particular, 12 and 13 increase HO-1, glutamate-cysteine ligase complex (GCLC), heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 1A (HSPA1A) and Dnaj heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member A4 (DNAJA4) gene expression as well as intracellular total GSH levels. In addition, pre-treatment of HepG2 cells with 12 and 13 prevented cell death induced by subsequent treatment with H2O2; interestingly, 12 was more effective than 13. On the basis of the antioxidant, cytoprotective and toxic effects recorded with 12, the authors suggest its potential use as a chemopreventive agent.
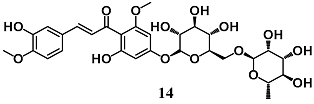
Martinez et al. investigated the potential dermatological use of hesperidin methyl chalcone (14), an antioxidant flavonoid, to prevent and/or reduce UVB irradiation-induced skin inflammation and oxidative stress in hairless mice [39]. The topical administration of 14 protected the skin from UVB damage, enhancing endogenous antioxidant systems, including CAT activity and GSH levels, as well as GPX1, GR, Nrf2 and HO-1 mRNA expression, and inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as TNF-α and IL-1β. These data suggest that 14 is a promising chalcone derivative for protecting the skin from the damage of UVB irradiation.
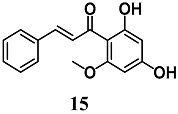
Peng et al. reported the capability of cardamonin (15), a chalcone isolated from Alpinia katsumadai, to reduce oxidative stress and cell death induced by H2O2 and 6-OHDA in neuronal PC12 cells [40]. Treatment of PC12 cells with 15 increased Nrf2 nuclear translocation, resulting in the enhancement of total GSH levels and HO-1, NQO1, Trx1, TrxR1, GCLC and glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier (GCLM) gene expression. The silencing of Nrf2 expression in PC12 cells abolished the neuroprotective effects of 15, indicating that its neuroprotection may be mediated by Nrf2 activation. Other authors evaluated the particular ability of 15 to also upregulate Nrf2-regulated selenoenzymes, such as GPX2 and TrxR1 in intestinal Caco-2 cells [41].
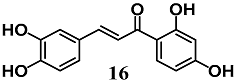
Wang et al. identified butein (16), a flavonoid chalcone found in Toxicodendron vernicifluum, as a novel inducer of HO-1 expression in adipocytes in vitro and in vivo [42]. Chalcone 16 increased HO-1 expression in adipocyte 3T3-L1 cells and promoted Keap1 degradation as well as Nrf2 nuclear translocation. These findings were reversed by a p38-MAPK inhibitor, suggesting its involvement in 16 activation of Nrf2 in adipocytes. In addition, the enhancement of HO-1 decreased ROS formation and the process of adipogenesis. The authors also recorded the ability of 16 to inhibit adipose hypertrophy and adipose tissue inflammation in C57BL/6 mice fed with a high-fat diet.
3. Targeting the Nrf2 Pathway by Synthetic Chalcones
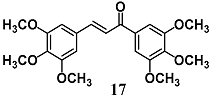
Alcaraz et al. evaluated the role of HO-1 and Nrf2 in the anti-inflammatory activity of 3′, 4′, 5′, 3, 4, 5-hexamethoxy-chalcone (17), a synthetic chalcone already characterized, at least in part, for its anti-inflammatory properties against NO production and iNOS induction [43]. In RAW264.7 cells stimulated with LPS, chalcone 17 inhibited NF-κB translocation into the nucleus, DNA binding and transcriptional activity, along with activation of Nrf2 and HO-1. In particular, the authors demonstrated that in the same experimental conditions 17 generated an increase of ROS without toxicity, responsible for Nrf2 and HO-1 activation, suggesting a different mechanism of action from antioxidant chalcones.
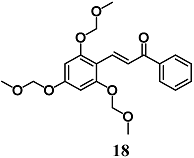
Lee et al. previously showed a potent anti-inflammatory effect of 2′,4′,6′-tris(methoxymethoxy) chalcone (18), a synthetic chalcone derivative, in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Subsequently, they also evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of 18 in a trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis model and the involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in the anti-inflammatory responses in intestinal HT-29 cells [44]. Treatment of mice with 18 reduced several markers of mucosal inflammation, such as IL-1β and TNF-α and mucosal ulceration induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Chalcone 18 also prevented TNF-α-induced inflammation in HT-29 cells through the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and a consequent increase of HO-1 expression. In particular, 18 inhibited TNF-α-induced NF-κB p65 translocation directly and indirectly by HO-1, without affecting IκBα degradation. Further, the authors demonstrated that upstream ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation induced by 18 was required to activate the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. These findings suggest a potential use of 18 in the treatment of intestinal inflammatory diseases.
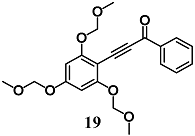
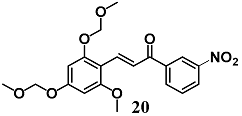
During development of optimal anti-inflammatory chalcones, Park et al. synthesized another two new chalcone derivatives (19 and 20) that showed an ability to inhibit LPS-stimulated NO and TNF-α production in RAW264.7 cells, a typical early inflammatory response [45,46]. In this regard, mechanistic studies demonstrated that both chalcones decreased NO production in RAW264.7 cells via simultaneous induction of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibition of the activator protein 1 (AP-1) activation.
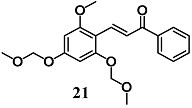
Jin et al. synthesized an additional synthetic 21 derivative and investigated its anti-inflammatory effects in RAW264.7 cells [47]. Chalcone 21 inhibited NO release and iNOS expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells via down-regulation of the inflammatory p38/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway as well as inhibition DNA binding of NF-κB. They also demonstrated the induction of the protective Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. In particular, the activation of this pathway required a transient depletion of GSH, suggesting that early impairment of the redox state is necessary to trigger Nrf2 activation. Based on these findings, the authors suggested the evaluation of the anti-inflammatory properties of 21 in an in vivo model. Taken together, the results support the suggestion that chalcone derivatives 19, 20 and 21 could be potential agents for the treatment of inflammation-associated diseases.
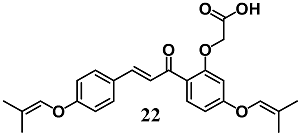
Shibuya et al. investigated the mechanisms that underlie the anti-ulcer activity of 20-carboxymethoxy-4,4-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyloxy)chalcone (22) in gastric epithelial RGM-1 cells [48]. In particular, the authors demonstrated that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induction by 22 treatment is associated with Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation in gastric cells. These results show that the angiogenetic action of 22, through VEGF production, can contribute to its ability to promote ulcer healing.
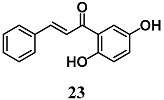
Kachadourian et al. assessed the mechanisms by which 2′,5′-dihydroxychalcone (23) increases cellular GSH levels using MCF-7/AREc32 cells, a cell line stably expressing a luciferase reporter gene driven by ARE [49]. In particular, they showed that an increase of Nrf2–ARE activity and GSH levels induced by 23 could be ascribed to a combination of ROS-dependent and -independent pathways using several inhibitors of ROS and MAPK pathways. These authors suggest other studies to evaluate the contribution of 23 on possible synergistic effects on the activation of the Nrf2–ARE transcriptional pathway.
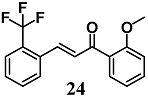
Kumar et al. evaluated the potency of a chalcone derivative series to activate the expression of Nrf2 as well as antioxidant genes including GCLM, NQO1 and HO-1 [50]. The structure–activity relationship analysis showed that chalcone derivatives with a trifluoromethyl substitution at ortho position on ring B were the most active compounds in human bronchial epithelial Beas-2B cells. Among these chalcones, 2-trifluoromethyl-2′-methoxychalone (24) showed the highest ability to increase all the antioxidant genes. Interestingly, a similar profile of gene induction was also recorded in the small intestine of mice treated by gavage with 24. Further, the authors reported that the activation of Nrf2 by 24 was independent of redox status changes, but they did not determine whether this phenomenon could be ascribed to its ability to directly modify the thiols of Keap1. In other studies [51], chalcone 24 reduced inflammation and airway hyper responsiveness in a mouse model of allergic asthma and prevented dermal fibrosis in fibroblasts of subjects with systemic sclerosis, and in a mouse model of fibrosis through the activation of Nrf2 [51,52].
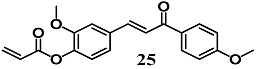
Wu et al. synthesized the chalcone 25 based on chalcone derivatives (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one with known anti-inflammatory properties [53]. Chalcone 25 increased the expression of Nrf2-dependent antioxidant genes, such as GCLC and HO-1, and their corresponding proteins, together with counteracting neuronal death induced by H2O2 in PC-12 cells. These preliminary data suggest that 25 could prevent oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative disease by activating the Nrf2–ARE pathway.
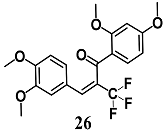
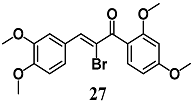
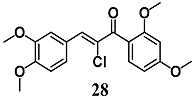
From a series of α-X-substituted 2′,3,4,4′-tetramethoxychalcones, Rucker et al. recorded the highest ability to activate the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and to inhibit NF-κB, with corresponding effects on their respective transcriptional gene products for α-X-substituted 26, 27, 28 (X = CF3, Br and Cl) in several in vitro models, including MCF-7/AREc32 cells, RAW264.7 cells, human macrophages and cervical HeLa cells [54]. The results emphasize that chemical-fine tuning of the Michael acceptor site is necessary to improve the anti-inflammatory activity of chalcones. More recently, Jobst et al. demonstrated the ability of 26 and 27 to inhibit the Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling in IL-3 dependent Ba/F3 and HeLa cells, suggesting that both chalcones can also interact with different kinases, expanding their pharmacological effect profile [55].
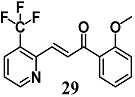
Lounsbury et al. synthesized other pyridyl chalcones, introducing pyridine nitrogen atoms into various positions of the two aromatic rings of 29 [56]. Pyridyl chalcone 29 enhanced HO-1 expression 3-fold higher than the non-heterocyclic chalcone 29 in bronchial epithelial Beas-2B cells. This antioxidant activity in bronchial cells was confirmed in vivo on lungs of mice treated orally with 29.
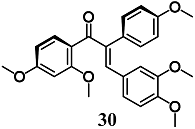
Kaufmann et al. demonstrated that among a series of α-X-substituted 2′,3,4,4′-tetramethoxychalcones (α-X-TMCs, X = H, F, Cl, Br, I, CN, Me, p-NO2-C6H4, Ph, p-OMe-C6H4, NO2, CF3, COOEt, COOH), able to activate the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibit NF-κB downstream target genes, only E-α-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2′,3,4,4′-tetramethoxychalcone (E-α-p-OMe-C6H4-TMC) (30) showed a significant cytoprotective effect against staurosporine-induced toxicity in RAW264.7 cells [57]. In this regard, the cytoprotective effect of 30 may be partly related to both the non-toxic activation and inhibition of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways, respectively. The authors also evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of 30 in RAW264.7 cells treated with LPS [58]. The results confirmed the ability of 30 to control several inflammatory parameters including the release of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), remarkably through the activation of Nrf2/HO-1.
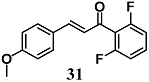
Zhong et al. previously found that a novel chalcone 31 was able to inhibit the inflammatory response in macrophages treated with LPS [59]. Subsequently, they also demonstrated the ability of 31 to decrease the cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis and apoptosis induced by high glucose and streptozocin (STZ) in H9c2 cells and mice, respectively. In both models, the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects of 31 were associated with NF-κB nucleus entry blockage and Nrf2 activation. The authors suggest that 31 can be a potential cardioprotective compound, targeting NF-κB and Nrf2 in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DMC).
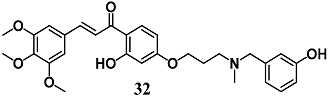
Rampa et al. demonstrated the ability of the leaving fragment (32) during ChEs’ carbamoylation by(E)-3-(((3-(3-hydroxy-4-(3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl)phenoxy)propyl)(methyl)amino)methyl)phenyl methylcarbamate to exert indirect antioxidant activity in terms of intracellular GSH increase as well as the ability to counteract the neurotoxicity elicited by amyloid oligomers in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells [60]. On the basis of the electrophilic trans-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl framework of 32, the authors hypothesize that this chalcone derivative could increase the antioxidant endogenous defense via the Keap1/Nrf2¬–ARE pathway.
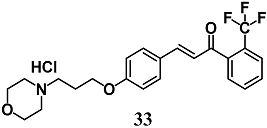
Lee et al. reported a novel morpholine-containing chalcone (33) that induces Nrf2 nuclear translocation and NQO1, HO-1, GCL expression, and protease activities of proteasome subunits PSMB5, PSMB7, PSMB8 and PSMA1, as well as lowering α-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic CATH.a cells [61]. In MPTP mice, chalcone 33 activated a similar Nrf2 pathway and prevented both impaired motor activity and nigrostriatal neurodegeneration. Therefore, they suggest a potential employment of 33 toward development of the therapy for Parkinson’s disease.
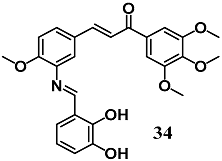
From a series of Aza resveratrol–chalcone derivatives, You et al. selected the chalcone 34 that previously showed the highest anti-inflammatory activity against the inflammation induced by LPS in macrophages, to evaluate its ability to control the oxidative stress and inflammation in in vitro and in vivo models of DCM [62,63]. Chalcone 34 reduced the fibrosis, hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by high glucose and STZ in H9c2 cells and mice, respectively. In both DCM models, the treatment with 34 was remarkably associated with NF-κB nucleus entry inhibition and Nrf2 activation, promoting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The results indicated that 34 can be a promising cardioprotective agent in the treatment of DCM by inhibiting inflammation and alleviating oxidative stress. This study showed that NF-κB and Nrf2 could be therapeutic targets of chalcones to control the pathogenesis of DCM.
4. Conclusions
The present review indicates that chalcones mainly exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, cardioprotective, neuroprotective and cytoprotective activities through Keap1/Nrf2–ARE pathway activation. Among these activities, anti-inflammatory activity was more evident than other pharmacological activities, suggesting a multi-target Michael acceptor mechanism for the chalcones, involving key regulators of the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways, such as Keap1, IKK, NF-κB, ERK1/2, JNK and p38-MAPK (Figure 3). The multi-target effects of the chalcones on cross-talk between the Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways can synergize in the overall anti-inflammatory effect. Considering that most chronic diseases are multifactorial and involve different etiological target, this multi-target approach may be useful for therapy [20]. However, the critical feature of chalcones is their potential promiscuity, or poor selectivity, leading to off-target interactions and hence undesirable side effects and compromised potency [4,64,65]. In this regard, many studies selected in this review recorded data of chalcones from phenotypic cell-based screenings combined with animal-based models, without employing biochemical studies to evaluate the selectivity of the chalcones against the cysteine residues on the protein target. In conclusion, a better understanding of the relationship between Nrf2 activation and the overall therapeutic effects as well as interaction manners and therapeutic relevance of such interaction should facilitate further development of chalcone-based therapeutic agents.
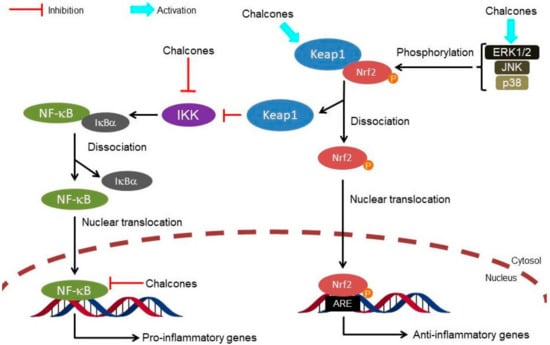
Figure 3.
Multi-target interaction of chalcones on cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways involved in inflammation. Nrf2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; ARE, antioxidant response element; P, phosphate; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; p38-MAPK, p38-mitogen activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IκBα, nuclear κ-B inhibitor; IKK, IκB kinase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T., C.V.J. and M.d.F.S.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, A.T., F.M. and M.d.F.S.; Writing-Review & Editing, F.S., G.S. and L.P.; Supervision, A.T. and C.V.J.
Funding
This work was supported by PRIN 2015 (project: 20152HKF3Z; project: 2015SKN9YT003).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gomes, M.N.; Muratov, E.N.; Pereira, M.; Peixoto, J.C.; Rosseto, L.P.; Cravo, P.V.L.; Andrade, C.H.; Neves, B.J. Chalcone derivatives: Promising starting points for drug design. Molecules 2017, 22, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, C.; Zhang, W.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Xing, C.; Miao, Z. Chalcone: A privileged structure in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7762–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Anand, A.; Kumar, V. Recent developments in biological activities of chalcones: A mini review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Xing, C. Diverse molecular targets for chalcones with varied bioactivities. Med. Chem. (Los. Angeles). 2015, 5, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maydt, D.; De Spirt, S.; Muschelknautz, C.; Stahl, W.; Müller, T.J.J. Chemical reactivity and biological activity of chalcones and other α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Xenobiotica 2013, 43, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Massiah, M.A.; Bozak, R.E.; Hicks, R.J.; Talalay, P. Potency of Michael reaction acceptors as inducers of enzymes that protect against carcinogenesis depends on their reactivity with sulfhydryl groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, X.M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The Keap1-Nrf2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.; Fishbein, J.C. Chemistry of the cysteine sensors in Kelch-Like ECH-Associated Protein 1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T.; Lipton, S. Recent advances in understanding NRF2 as a druggable target: Development of pro-electrophilic and non-covalent NRF2 activators to overcome systemic side effects of electrophilic drugs like dimethyl fumarate. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Kazantsev, A.G. Activation of Nrf2 signaling as a common treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2017, 7, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBean, G.J.; López, M.G.; Wallner, F.K. Redox-based therapeutics in neurodegenerative disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1750–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Velasco, D.; De Sagarra, R.M.; Cuadrado, A. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14841–14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardyn, J.; Ponsford, A.; Sanderson, C. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Manda, G.; Hassan, A.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Barbas, C.; Daiber, A.; Ghezzi, P.; León, R.; López, M.G.; Oliva, B.; et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 as a therapeutic target for chronic diseases: A systems medicine approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 348–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; Sandur, S.K.; Sung, B.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Butein, a tetrahydroxychalcone, inhibits nuclear factor (NF)-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene expression through direct inhibition of IκBα kinase β on cysteine 179 residue. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17340–17350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, P.; Alvarez, R.; Ortiz, M.A.; Alvarez, S.; Piedrafita, F.J.; de Lera, A.R. Inhibition of IκB kinase-β and anticancer activities of novel chalcone adamantyl arotinoids. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5431–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Tanabe, S.; Tago, K.; Itoh, H.; Mashino, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Kasahara, T. Licochalcone a potently inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Induced Nuclear Factor-κB activation through the direct inhibition of IκB Kinase complex activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.-H.; Chang, J.-K.; Hsu, Y.-L.; Kuo, P.-L. Chalcone arrests cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis through induction of mitochondrial pathway and inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B signalling in human bladder cancer cells. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 101, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-C.; Ji, J.-A.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; You, Q.-D. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: An update. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 924–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, J.; Lin, H.; Gu, K.; Feng, F. Recent progress in the development of small molecule Nrf2 modulators: A patent review (2012–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, D.A.; Goldstein, M.; Albanyan, H.; Jin, H.; Hu, L. Discovery of direct inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction as potential therapeutic and preventive agents. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.; Yamamoto, M. The rise of antioxidant signaling-The evolution and hormetic actions of Nrf2. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 244, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.W.; Wu, C.C.; Wung, B.S. Chalcone inhibits the activation of NF-κB and STAT3 in endothelial cells via endogenous electrophile. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Vale, D.L.; Steffen, V.S.; Vicentini, F.T.M.C.; Vignoli, J.A.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Casagrande, R. Trans-chalcone added in topical formulation inhibits skin inflammation and oxidative stress in a model of ultraviolet B radiation skin damage in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 171, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Lim, J.; Gal, J.; Kang, J.C.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.Y.; Choi, H.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of xanthohumol involves heme oxygenase-1 induction via NRF2-ARE signaling in microglial BV2 cells. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, B.; Ge, C.; Peng, S.; Fang, J. Xanthohumol, a polyphenol chalcone present in hops, activating nrf2 enzymes to confer protection against oxidative damage in pc12 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodziak-Jarosz, L.; Fujikawa, Y.; Pastor-Flores, D.; Kasikci, S.; Jirásek, P.; Pitzl, S.; Owen, R.W.; Klika, K.D.; Gerhäuser, C.; Amslinger, S.; et al. A click chemistry approach identifies target proteins of xanthohumol. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Lim, J.; Bang, Y.; Gal, J.; Lee, S.U.; Cho, Y.C.; Yoon, G.; Kang, B.Y.; Cheon, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Licochalcone E activates Nrf2/antioxidant response element signaling pathway in both neuronal and microglial cells: Therapeutic relevance to neurodegenerative disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, X.C.; Xiang, M.X.; Bian, C.; Chen, P. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression by hydroxysafflor yellow A conferring protection from anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 160, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Antioxidant effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A and acetyl-11-keto-boswellic acid in combination on isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Wei, G.; Xi, M.; Yan, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wen, A. Synergistic cardioprotective effects of Danshensu and hydroxysafflor yellow A against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury are mediated through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Li, B.; Im, N.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, G.S. 4,2′,5′-Trihydroxy-4′-methoxychalcone from dalbergia odorifera exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by inducing heme oxygenase-1 in murine macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Yakubu, M.T.; Oladiji, A.T. Electrophilic and reactive oxygen species detoxification potentials of chalcone dimers is mediated by redox transcription factor Nrf-2. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.Y.; Bai, L.P.; Pan, H.D.; Shu, L.M.; Kong, A.N.T.; Leung, E.L.H.; Liu, L.; Li, T. Flavonoids derived from liquorice suppress murine macrophage activation by up-regulating heme oxygenase-1 independent of Nrf2 activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, R.; Feng, L.; Fu, Z.; Yang, S.; Deng, X.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, S. Isoliquiritigenin alleviates early brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage via suppressing ROS- and/or NF-ΚB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. J. Neuroinfl. 2017, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.Y.; Cho, S.S.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Jang, C.H.; Park, D.E.; Bang, J.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Ki, S.H. The chalcone compound isosalipurposide (ISPP) exerts a cytoprotective effect against oxidative injury via Nrf2 activation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 287, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Li, C.; Qiao, Y.; Lu, C.; Li, J.; Song, W.; Sun, J.; Zhai, X.; Niu, J.; Ren, Q.; et al. Safflower yellow B suppresses HepG2 cell injury induced by oxidative stress through the AKT/Nrf2 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinner, K.D.; Wales, C.T.K.; Gristock, R.A.; Vo, H.T.; So, N.; Jacobs, A.T. Flavokawains A and B from kava (Piper methysticum) activate heat shock and antioxidant responses and protect against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in HepG2 hepatocytes. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Steffen, V.S.; Caviglione, C.V.; Pala, D.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Casagrande, R. Topical formulation containing hesperidin methyl chalcone inhibits skin oxidative stress and inflammation induced by ultraviolet B irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Spirt, S.; Eckers, A.; Wehrend, C.; Micoogullari, M.; Sies, H.; Stahl, W.; Steinbrenner, H. Interplay between the chalcone cardamonin and selenium in the biosynthesis of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant enzymes in intestinal Caco-2 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 91, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Hou, Y.; Yao, J.; Fang, J. Activation of Nrf2-driven antioxidant enzymes by cardamonin confers neuroprotection of PC12 cells against oxidative damage. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ka, S.O.; Lee, Y.; Park, B.H.; Bae, E.J. Butein induction of HO-1 by p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in adipocytes attenuates high-fat diet induced adipose hypertrophy in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 799, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaraz, M.J.; Vicente, A.M.; Araico, A.; Dominguez, J.N.; Terencio, M.C.; Ferrándiz, M.L. Role of nuclear factor-κB and heme oxygenase-1 in the mechanism of action of an anti-inflammatory chalcone derivative in RAW 264.7 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Sohn, D.H.; Jin, X.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, S.C.; Seo, G.S. 2′,4′,6′-Tris(methoxymethoxy) chalcone protects against trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis and blocks tumor necrosis factor-α-induced intestinal epithelial inflammation via heme oxygenase 1-dependent and independent pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jin, X.Y.; Jin, F.; Hur, J.; Ko, G.; Sohn, D.H. KB-34, a newly synthesized chalcone derivative, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages via heme oxygenase-1 induction and blockade of activator protein-1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 606, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.H.; Kim, H.S.; Hur, J.; Jin, X.Y.; Jin, Y.L.; Sohn, D.H. YL-I-108, a synthetic chalcone derivative, inhibits lipopolysaccharide- stimulated nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages: Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 induction and blockade of activator protein-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, P.H.; Hur, J.; Kim, S.A.; Kim, H.S.; Sohn, D.H. 2′-Methoxy-4′6′-Bis(Methoxymethoxy)chalcone inhibits nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 106, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, A.; Onda, K.; Kawahara, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Omi, T.; Nagaoka, M.; Matsui, H.; Hirano, T. Sofalcone, a gastric mucosa protective agent, increases vascular endothelial growth factor via the Nrf2-heme-oxygenase-1 dependent pathway in gastric epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachadourian, R.; Pugazhenthi, S.; Velmurugan, K.; Backos, D.S.; Franklin, C.C.; McCord, J.M.; Day, B.J. 2′,5′-Dihydroxychalcone-induced glutathione is mediated by oxidative stress and kinase signaling pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Hassan, M.; Wu, H.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Parmar, V.S.; Biswal, S.; Malhotra, S. V Novel chalcone derivatives as potent Nrf2 activators in mice and human lung epithelial cells. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4147–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussan, T.E.; Gajghate, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mandke, P.; McCormick, S.; Sudini, K.; Kumar, S.; Breysse, P.N.; Diette, G.B.; Sidhaye, V.K.; et al. Nrf2 reduces allergic asthma in mice through enhanced airway epithelial cytoprotective function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L27–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhu, H.; Lord, G.; Bhattachayya, M.; Jones, B.M.; Allaway, G.; Biswal, S.S.; Korman, B.; Marangoni, R.G.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; et al. Nrf2 exerts cell-autonomous antifibrotic effects: Compromised function in systemic sclerosis and therapeutic rescue with a novel heterocyclic chalcone derivative. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 71–86.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Z.; Cheng, C.C.; Shen, L.L.; Wang, Z.K.; Wu, S.B.; Li, W.L.; Chen, S.H.; Zhou, R.P.; Qiu, P.H. Synthetic chalcones with potent antioxidant ability on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18525–18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rücker, H.; Al-Rifai, N.; Rascle, A.; Gottfried, E.; Brodziak-Jarosz, L.; Gerhäuser, C.; Dick, T.P.; Amslinger, S. Enhancing the anti-inflammatory activity of chalcones by tuning the Michael acceptor site. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobst, B.; Weigl, J.; Michl, C.; Vivarelli, F.; Pinz, S.; Amslinger, S.; Rascle, A. Inhibition of interleukin-3- and interferon- α-induced JAK/STAT signaling by the synthetic α-X-2′,3,4,4′-tetramethoxychalcones α-Br-TMC and α-CF3-TMC. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 1187–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lounsbury, N.; Mateo, G.; Jones, B.; Papaiahgari, S.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Teijaro, C.; Gordon, J.; Korzekwa, K.; Ye, M.; Allaway, G.; et al. Heterocyclic chalcone activators of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) with improved in vivo efficacy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5352–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, K.B.; Al-Rifai, N.; Ulbrich, F.; Schallner, N.; Rücker, H.; Enzinger, M.; Petkes, H.; Pitzl, S.; Goebel, U.; Amslinger, S. The Cytoprotective Effects of E-α-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-2′,3,4,4′-Tetramethoxychalcone (E-α-p-OMe-C6H4-TMC)—A Novel and Non-Cytotoxic HO-1 Inducer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, K.B.; Gothwal, M.; Schallner, N.; Ulbrich, F.; Rücker, H.; Amslinger, S.; Goebel, U. The anti-inflammatory effects of E-α-(p-methoxyphenyl)-2′,3,4,4′-tetramethoxychalcone are mediated via HO-1 induction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 35, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.; Wu, L.; Qian, Y.; Fang, Q.; Liang, D.; Wang, J.; Zeng, C.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G. Blockage of ROS and NF-κB-mediated inflammation by a new chalcone L6H9 protects cardiomyocytes from hyperglycemia-induced injuries. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampa, A.; Montanari, S.; Pruccoli, L.; Bartolini, M.; Falchi, F.; Feoli, A.; Cavalli, A.; Belluti, F.; Gobbi, S.; Tarozzi, A.; et al. Chalcone-based carbamates for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.A.; Son, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, J.; Han, S.H.; Shin, N.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway and neuroprotection of nigral dopaminergic neurons by a novel synthetic compound KMS99220. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Qian, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Ye, S.; Chen, T.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Liang, G. An Aza resveratrol–chalcone derivative 6b protects mice against diabetic cardiomyopathy by alleviating inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ge, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pan, J.; Song, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, J.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of paralleled Aza resveratrol-chalcone compounds as potential anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment of acute lung injury. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihvola, V.; Levonen, A.L. Keap1 as the redox sensor of the antioxidant response. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, D.; Engel, C.K.; Glombik, H. The Keap1–Nrf2 protein–protein interaction: A suitable target for small molecules. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2017, 24, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).