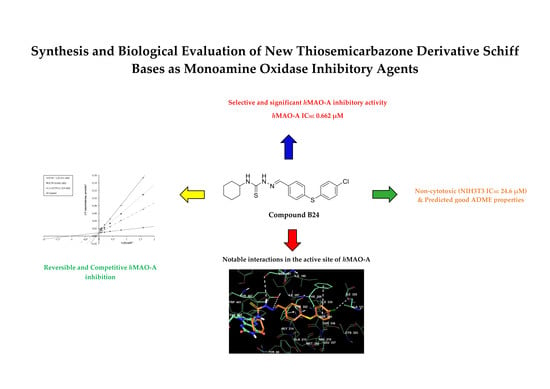
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Schiff Bases as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
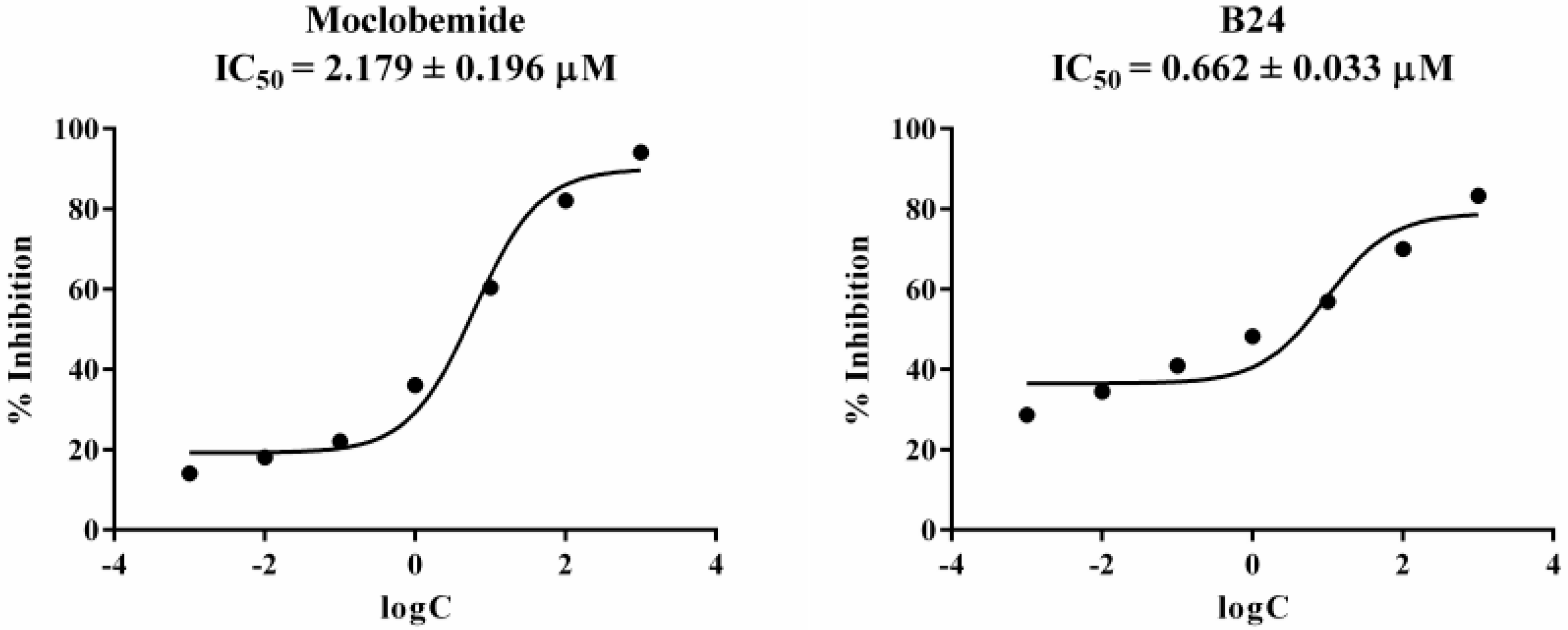
2.2. Monoamine oxidase Inhibition Assay
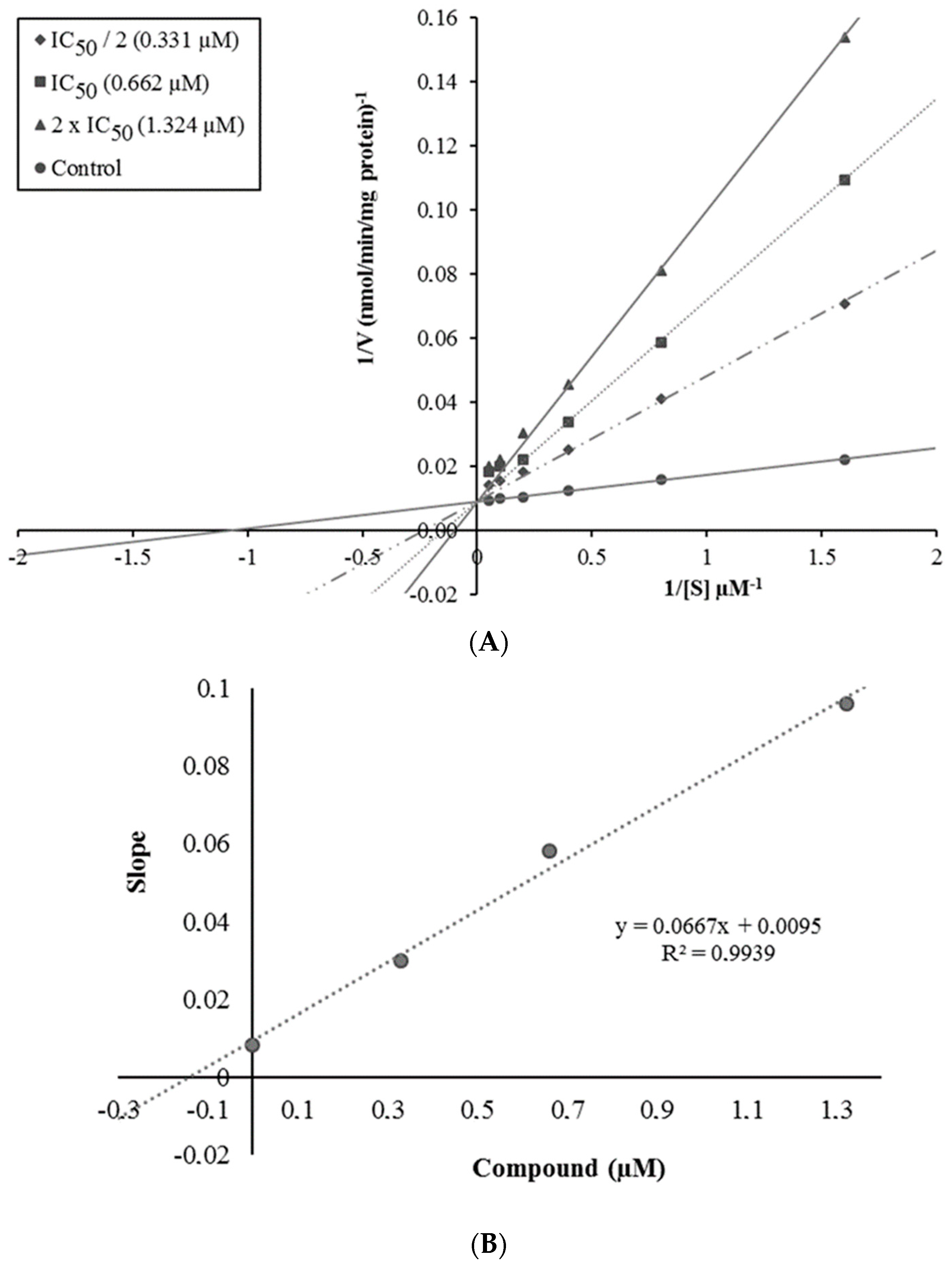
2.3. Enzyme Kinetic Studies
2.4. Cytotoxicity Test
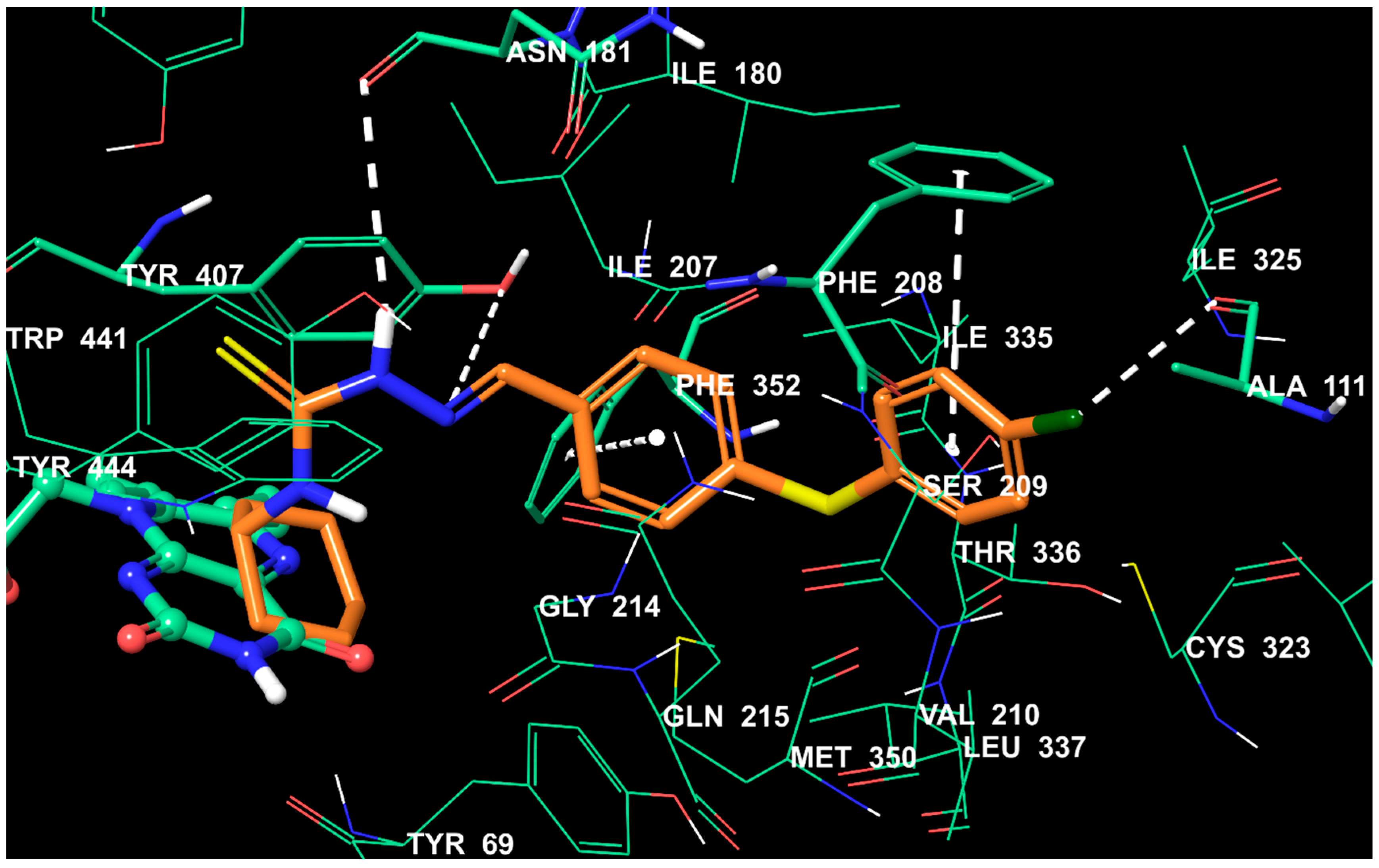
2.5. Molecular Docking Studies
2.6. Theoretical Determination of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Chemistry
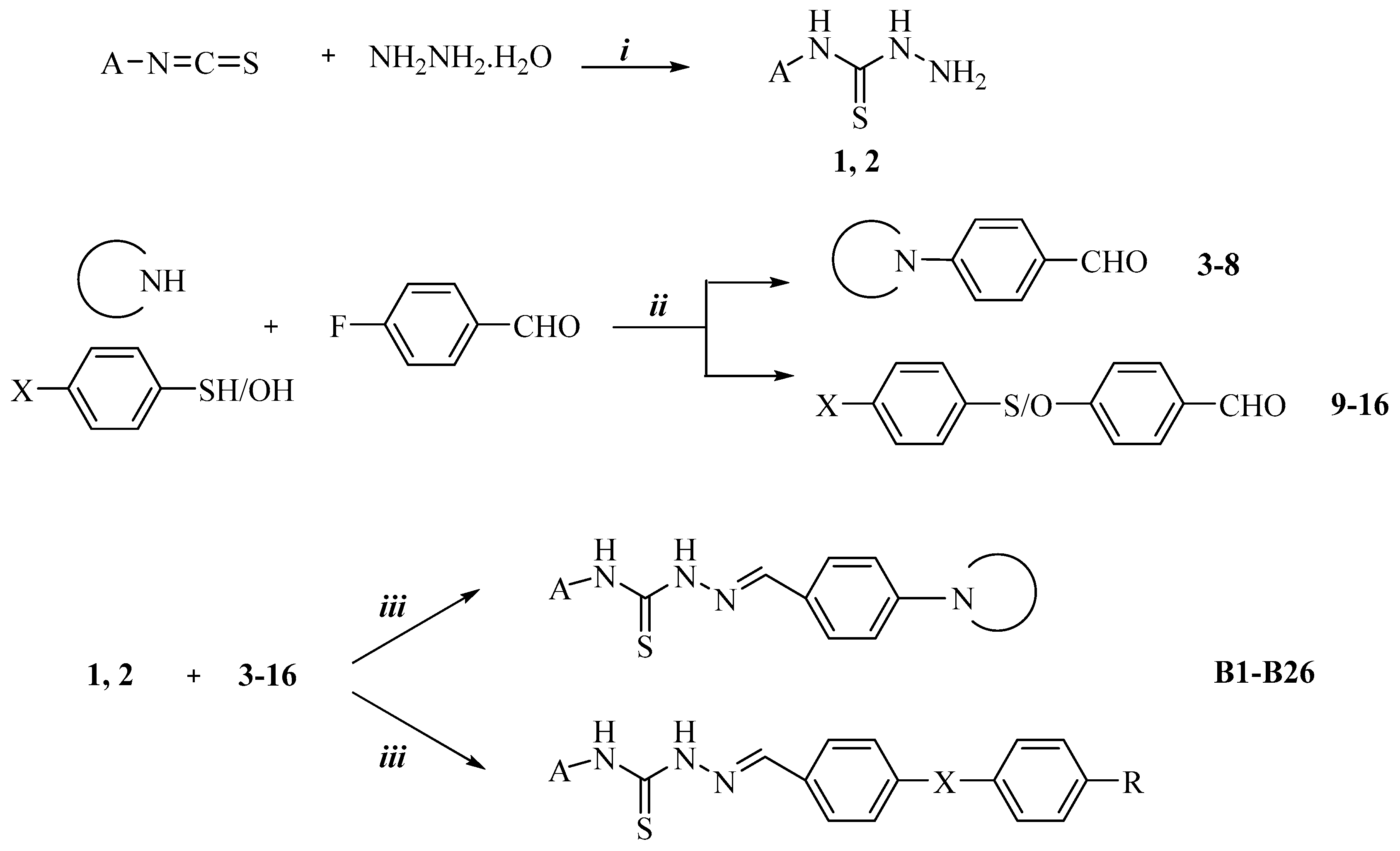
3.2.1. Synthesis of N-Phenyl/Cyclohexylhydrazinecarbothioamides 1,2
3.2.2. Synthesis of 4-Substituted Benzaldehyde Derivatives 3–16
3.2.3. Synthesis of 2-(4-Substituted Benzylidene)-N-phenyl/cyclohexylhydrazine-1-carbothioamide Derivatives B1–B26
3.3. MAO Inhibition Assay
3.4. Enzyme Kinetic Studies
3.5. Cytotoxicity Test
3.6. Molecular Docking Studies
3.7. Theoretical Determination of ADME Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evranos-Aksöz, B.; Yabanoğlu-Çiftçi, S.; Uçar, G.; Yelekçi, K.; Ertan, R. Synthesis of some novel hydrazone and 2-pyrazoline derivatives: Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities and docking studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3278–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Adeniyi, A.A.; Soliman, M.E.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Exploration of chlorinated thienyl chalcones: A new class of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Jang, B.K.; Cho, N.C.; Park, J.H.; Yeon, S.K.; Ju, E.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, G.; Pae, A.N.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Synthesis of a series of unsaturated ketone derivatives as selective and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6486–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Esteban, G.; Ojima, M.; Bautista-Aguilera, O.M.; Inokuchi, T.; Moraleda, I.; Iriepa, I.; Samadi, A.; Youdim, M.B.; Romero, A.; et al. Donepezil + propargylamine + 8-hydroxyquinoline hybrids as new multifunctional metal-chelators, ChE and MAO inhibitors for the potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.P. Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1968, 17, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, J.; Magyar, K. Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 1972, 5, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pare, C.M. Unwanted effects of long-term medication in schizophrenia and depression. Pharmakopsychiatr. Neuropsychopharmakol. 1976, 9, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.; Chen, K.; Ridd, M.J. Monoamine oxidase: From genes to behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Newton-Vinson, P.; Hubalek, F.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structure of human monoamine oxidase B, a drug target for the treatment of neurological disorders. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, B.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis of some novel 2-substituted benzothiazole derivatives containing benzylamine moiety as monoamine oxidase inhibitory agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldron, C.; Van der Auwera, I.; Deraeve, C.; Gornitzka, H.; Wera, S.; Pitié, M.; Van Leuven, F.; Meunier, B. Preparation of cyclo-phen-type ligands: Chelators of metal ions as potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1976–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayton, S.; Lei, P.; Bush, A.I. Metallostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvarapu, L.N.; Somala, A.R.; Koduru, J.R.; Baek, S.O.; Ammireddy, V.R. A critical review on analytical and biological applications of thio- and phenyl-thiosemicarbazones. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, B.S.; Jain, V.K. Analytical applications of thiosemicarbazones and semicarbazones. Microchem. J. 1988, 38, 144–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Rajendran, K.G.; West, D.X. The anti-inflammatory activity of metal complexes of heterocyclic thiosemicarbazones, 2-substituted pyridine N-oxides and 2-pyridylthioureas. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1996, 10, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandaivelu, U.; Padmini, V.G.; Suneetha, K.; Shireesha, B.; Vidyasagar, J.V.; Rao, T.R.; K N, J.; Basu, A.; Jayaprakash, V. Synthesis, antimicrobial and anticancer activity of new thiosemicarbazone derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2011, 344, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Mohamed, R.R.; Seoudi, R.S. Synthesis and characterization of some novel antimicrobial thiosemicarbazone O-carboxymethyl chitosan derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 63, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallari, J.P.; Guiguemde, W.A.; Guy, R.K. Antimalarial activity of thiosemicarbazones and purine derived nitriles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3546–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Bhat, P.; Thomas, A.; Srividya, M.; Sriram, D. Novel isatinyl hiosemicarbazones derivatives as potential molecule to combat HIV-TB coinfection. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Mishra, S.P.; Mishra, R. Synthesis and evaluation of biological activities of thiosemicarbazones derivatives. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2011, 3, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.B.; Nanda, R.K.; Kothapalli, L.P.; Hamane, S.C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of Schiff’s bases and 2-azetidinones of isonicotinyl hydrazone as potential antidepressant and nootropic agents. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.M.; Mohamed, Y.A.; El-Bayouki, K.A.M.; Basyouni, W.M.; Abbas, S.Y. Synthesis of some new 4(3H)-quinazolinone-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazones and their metal complexes and a study on their anticonvulsant, analgesic, cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities—Part-1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, S.; Ferino, G.; Quezada, E.; Santana, L.; Friedman, C. Predicting monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity through ligand-based models. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2258–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavan, N.V. Essentials of Medical Biochemistry: With Clinical Cases, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Sağlık, B.N.; Ilgın, S.; Özkay, Y. Synthesis of new donepezil analogues and investigation of their effects on cholinesterase enzymes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-Å resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reniers, J.; Robert, S.; Frederick, R.; Masereel, B.; Vincent, S.; Wouters, J. Synthesis and evaluation of β-carboline derivatives as potential monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C.; Mattevi, A. The FAD binding sites of human monoamine oxidases A and B. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, F.; Binda, C.; Khalil, A.; Li, M.; Mattevi, A.; Castagnoli, N.; Edmondson, D.E. Demonstration of isoleucine 199 as a structural determinant for the selective inhibition of human monoamine oxidase B by specific reversible inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15761–15766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Nakagawa, A.; Ito, A.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of rat monoamine oxidase A and its specific recognitions for substrates and inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, A.M.; Soldevila, M.; Navarro, A.; Kidd, K.K.; Oliva, B.; Bertranpetit, J. Positive selection in MAOA gene is human exclusive: Determination of the putative amino acid change selected in the human lineage. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 115, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- QikProp, version 4.8; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Duffy, E.M. Prediction of drug solubility from structure. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, Ö.D.; Osmaniye, D.; Demir Özkay, Ü.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Ilgın, S.; Baysal, M.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. MAO enzymes inhibitory activity of new benzimidazole derivatives including hydrazone and propargyl side chains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices-Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity ISO-10993-5, 3rd ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Gheewala, N.; Suthar, A.; Shah, A. In-vitro cytotoxicity activity of Solanum nigrum extract against Hela cell line and Vero cell line. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Maestro, version 10.6; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Schrödinger, version 2016-2; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- LigPrep, version 3.8; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Glide, version 7.1; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016.
- Toprakçí, M.; Yelekçi, K. Docking studies on monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Estimation of inhibition constants (Ki) of a series of experimentally tested compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4438–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds B1–B24 are available from the authors. |
| Compound | A | X | Secondary Amine | R | Compound | A | X | Secondary Amine | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | phenyl | - | piperidine | - | B14 | cyclohexyl | - | piperidine | - |
| B2 | phenyl | - | 2-metilpiperidine | - | B15 | cyclohexyl | - | 2-metilpiperidine | - |
| B3 | phenyl | - | 4-metilpiperidine | - | B16 | cyclohexyl | - | 4-metilpiperidine | - |
| B4 | phenyl | - | 4-phenylpiperazine | - | B17 | cyclohexyl | - | 4-phenylpiperazine | - |
| B5 | phenyl | - | (4-methoxyphenyl)piperazine | - | B18 | cyclohexyl | - | (4-methoxyphenyl)piperazine | - |
| B6 | phenyl | O | - | CH3 | B19 | cyclohexyl | O | - | CH3 |
| B7 | phenyl | S | - | CH3 | B20 | cyclohexyl | S | - | CH3 |
| B8 | phenyl | O | - | OCH3 | B21 | cyclohexyl | O | - | OCH3 |
| B9 | phenyl | S | - | OCH3 | B22 | cyclohexyl | S | - | OCH3 |
| B10 | phenyl | O | - | Cl | B23 | cyclohexyl | O | - | Cl |
| B11 | phenyl | S | - | Cl | B24 | cyclohexyl | S | - | >Cl |
| B12 | phenyl | O | - | F | B25 | cyclohexyl | O | - | F |
| B13 | phenyl | S | - | F | B26 | cyclohexyl | S | - | F |
| Compound | MAO-A Inhibition % | MAO-B Inhibition % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−3 M | 10−4 M | 10−3 M | 10−4 M | |
| B1 | 21.08 ± 0.34 | 13.77 ± 0.29 | 15.80 ± 0.30 | 10.21 ± 0.14 |
| B2 | 30.68 ± 0.85 | 16.28 ± 0.97 | 27.08 ± 0.46 | 18.83 ± 0.37 |
| B3 | 20.77 ± 0.55 | 15.51 ± 0.50 | 17.85 ± 0.28 | 11.41 ± 0.33 |
| B4 | 30.85 ± 1.07 | 26.77 ± 0.79 | 20.32 ± 0.67 | 16.10 ± 0.62 |
| B5 | 32.61 ± 1.03 | 16.63 ± 0.51 | 29.88 ± 0.88 | 14.43 ± 0.41 |
| B6 | 26.98 ± 0.77 | 11.79 ± 0.28 | 22.58 ± 0.62 | 16.77 ± 0.44 |
| B7 | 30.10 ± 1.20 | 24.08 ± 0.81 | 23.45 ± 0.16 | 18.79 ± 0.27 |
| B8 | 34.83 ± 0.79 | 19.76 ± 0.71 | 25.17 ± 0.82 | 20.25 ± 0.80 |
| B9 | 24.56 ± 0.89 | 18.80 ± 0.62 | 18.62 ± 0.40 | 14.11 ± 0.36 |
| B10 | 40.79 ± 1.23 | 32.88 ± 0.77 | 20.43 ± 0.58 | 16.02 ± 0.69 |
| B11 | 35.90 ± 0.22 | 30.01 ± 0.45 | 31.34 ± 0.74 | 27.85 ± 0.61 |
| B12 | 32.06 ± 0.68 | 26.33 ± 0.57 | 29.66 ± 1.02 | 16.88 ± 0.47 |
| B13 | 36.65 ± 1.13 | 27.19 ± 0.84 | 27.49 ± 0.66 | 20.66 ± 0.73 |
| B14 | 41.08 ± 1.26 | 27.09 ± 0.67 | 23.47 ± 0.48 | 18.65 ± 0.33 |
| B15 | 39.48 ± 1.05 | 20.06 ± 0.97 | 22.17 ± 0.88 | 14.20 ± 0.41 |
| B16 | 37.96 ± 1.00 | 29.88 ± 0.98 | 24.63 ± 0.48 | 21.74 ± 0.36 |
| B17 | 48.83 ± 1.02 | 39.77 ± 1.26 | 30.75 ± 0.78 | 17.49 ± 0.77 |
| B18 | 39.40 ± 0.62 | 31.28 ± 0.57 | 26.79 ± 0.49 | 22.62 ± 0.40 |
| B19 | 53.56 ± 1.08 | 40.57 ± 1.12 | 32.06 ± 0.81 | 27.05 ± 0.69 |
| B20 | 41.33 ± 0.39 | 35.66 ± 0.27 | 28.20 ± 0.66 | 21.63 ± 0.50 |
| B21 | 58.52 ± 1.36 | 35.75 ± 0.91 | 37.03 ± 0.40 | 30.49 ± 0.38 |
| B22 | 50.88 ± 1.09 | 38.29 ± 0.97 | 27.88 ± 0.45 | 20.22 ± 0.41 |
| B23 | 64.85 ± 1.04 | 46.10 ± 0.77 | 24.55 ± 0.68 | 19.62 ± 0.44 |
| B24 | 83.31 ± 1.08 | 70.07 ± 1.12 | 14.43 ± 0.26 | 11.79 ± 0.30 |
| B25 | 57.14 ± 1.17 | 32.38 ± 0.68 | 30.40 ± 0.60 | 24.61 ± 0.43 |
| B26 | 51.33 ± 0.38 | 36.09 ± 0.22 | 27.99 ± 0.19 | 19.89 ± 0.11 |
| Moclobemide | 91.42 ± 4.60 | 77.86 ± 3.71 | - | - |
| Selegiline | - | - | 97.69 ± 4.16 | 94.42 ± 3.89 |
| Compound | MW | DHB | AHB | PSA | logP | logS | PCaco | PM | PMDCK | logBB | CNS | VRF | VRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 338.470 | 2 | 5 | 49.573 | 4.334 | −6.156 | 2663.609 | 2 | 2461.245 | −0.222 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B2 | 352.496 | 2 | 5 | 49.147 | 4.574 | −6.362 | 2679.674 | 2 | 2477.294 | −0.212 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B3 | 352.496 | 2 | 5 | 49.575 | 4.660 | −6.598 | 2663.218 | 2 | 2460.854 | −0.231 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B4 | 415.555 | 2 | 6 | 55.441 | 5.471 | −7.686 | 2584.097 | 2 | 2381.928 | −0.281 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B5 | 445.581 | 2 | 6.75 | 63.922 | 5.519 | −7.822 | 2584.100 | 3 | 2381.931 | −0.352 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B6 | 361.461 | 2 | 4.5 | 52.430 | 4.937 | −6.253 | 2720.949 | 3 | 2518.564 | −0.333 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B7 | 377.521 | 2 | 4 | 44.334 | 5.540 | −7.067 | 2720.949 | 3 | 4269.676 | −0.249 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B8 | 377.460 | 2 | 5.25 | 60.912 | 4.696 | −5.858 | 2720.951 | 3 | 2518.566 | −0.388 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B9 | 393.521 | 2 | 4.75 | 52.815 | 5.296 | −6.666 | 2720.951 | 3 | 4269.729 | −0.304 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B10 | 381.879 | 2 | 4.5 | 52.431 | 5.129 | −6.434 | 2720.949 | 2 | 6213.625 | −0.154 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B11 | 397.939 | 2 | 4 | 44.334 | 5.730 | −7.247 | 2720.949 | 2 | 10,000 | −0.070 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B12 | 365.424 | 2 | 4.5 | 52.431 | 4.873 | −6.063 | 2720.949 | 2 | 4554.137 | −0.207 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B13 | 381.485 | 2 | 4 | 44.334 | 5.473 | -6.872 | 2720.949 | 2 | 7721.149 | −0.123 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B14 | 344.517 | 2 | 5 | 47.948 | 4.598 | −6.731 | 3310.935 | 0 | 3266.539 | −0.115 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B15 | 358.544 | 2 | 5 | 47.521 | 4.838 | −6.938 | 3331.393 | 0 | 3288.360 | −0.106 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B16 | 358.544 | 2 | 5 | 47.989 | 4.898 | −7.145 | 3204.223 | 0 | 3153.046 | −0.138 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B17 | 421.602 | 2 | 6 | 54.099 | 5.652 | −8.096 | 2974.126 | 0 | 2908.896 | −0.199 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B18 | 451.629 | 2 | 6.75 | 62.782 | 5.827 | −8.356 | 3504.952 | 1 | 3665.702 | −0.174 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B19 | 367.508 | 2 | 4.5 | 50.803 | 5.204 | −6.835 | 3382.919 | 1 | 3343.532 | −0.226 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B20 | 383.569 | 2 | 4 | 42.707 | 5.810 | −7.656 | 3382.919 | 1 | 5668.228 | −0.139 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B21 | 383.507 | 2 | 5.25 | 59.285 | 4.959 | −6.433 | 3382.922 | 1 | 3343.534 | −0.282 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| B22 | 399.568 | 2 | 4.75 | 51.188 | 5.562 | −7.249 | 3382.922 | 1 | 5668.299 | −0.194 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B23 | 387.926 | 2 | 4.5 | 50.804 | 5.395 | −7.015 | 3382.919 | 0 | 8248.927 | −0.048 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B24 | 403.987 | 2 | 4 | 42.707 | 6 | −7.835 | 3382.919 | 0 | 10,000 | -0.040 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| B25 | 371.472 | 2 | 4.5 | 50.804 | 5.138 | −6.642 | 3382.919 | 0 | 6045.866 | −0.102 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| B26 | 387.532 | 2 | 4 | 42.707 | 5.741 | −7.459 | 3382.919 | 0 | 10,000 | −0.015 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çavuşoğlu, B.K.; Sağlık, B.N.; Osmaniye, D.; Levent, S.; Acar Çevik, U.; Karaduman, A.B.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Schiff Bases as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010060
Çavuşoğlu BK, Sağlık BN, Osmaniye D, Levent S, Acar Çevik U, Karaduman AB, Özkay Y, Kaplancıklı ZA. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Schiff Bases as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇavuşoğlu, Betül Kaya, Begüm Nurpelin Sağlık, Derya Osmaniye, Serkan Levent, Ulviye Acar Çevik, Abdullah Burak Karaduman, Yusuf Özkay, and Zafer Asım Kaplancıklı. 2018. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Schiff Bases as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents" Molecules 23, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010060
APA StyleÇavuşoğlu, B. K., Sağlık, B. N., Osmaniye, D., Levent, S., Acar Çevik, U., Karaduman, A. B., Özkay, Y., & Kaplancıklı, Z. A. (2018). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Schiff Bases as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Agents. Molecules, 23(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010060