The authors wish to make the following correction to their paper [1]. In Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, the legend was incorrectly displayed. The corrected legends of Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 are as follows:
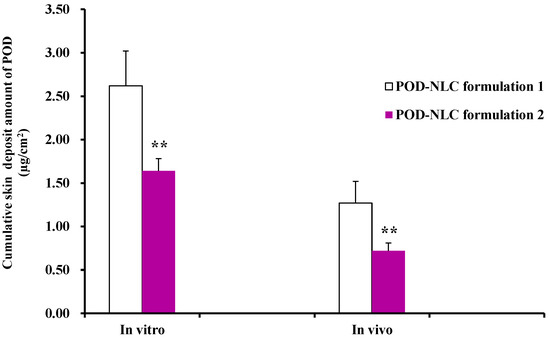
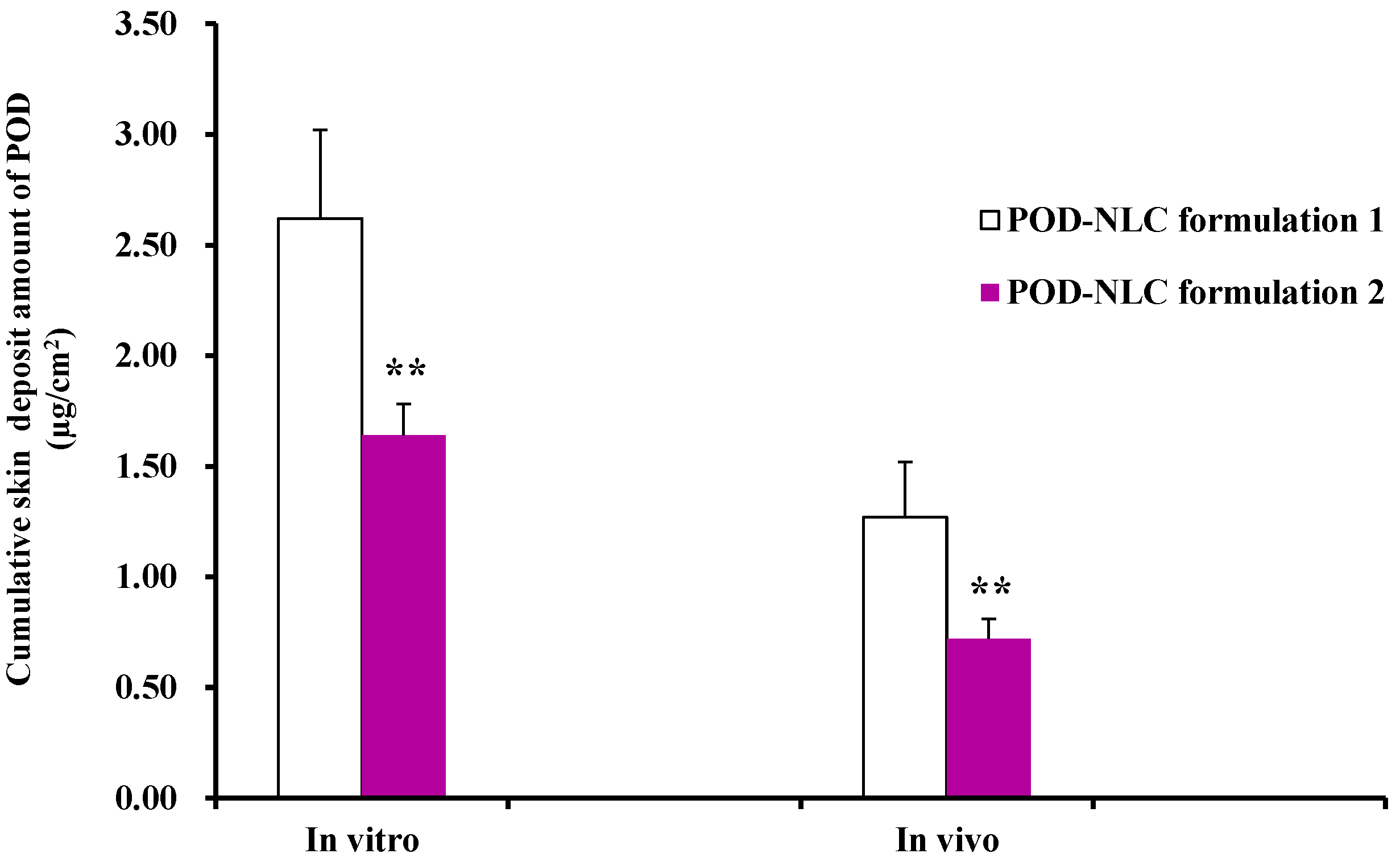
Figure 4.
In vitro and in vivo rat skin deposit amounts of POD at 8 h after the topical treatment of POD-NLC formulation 1 or POD-NLC formulation 2. Note: “**” represents p ˂ 0.01 compared with POD-NLC formulation 1.
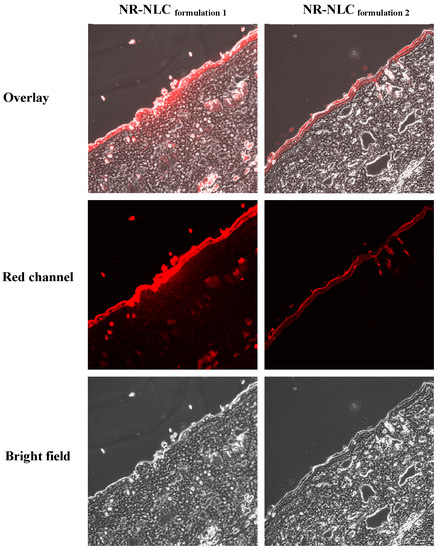
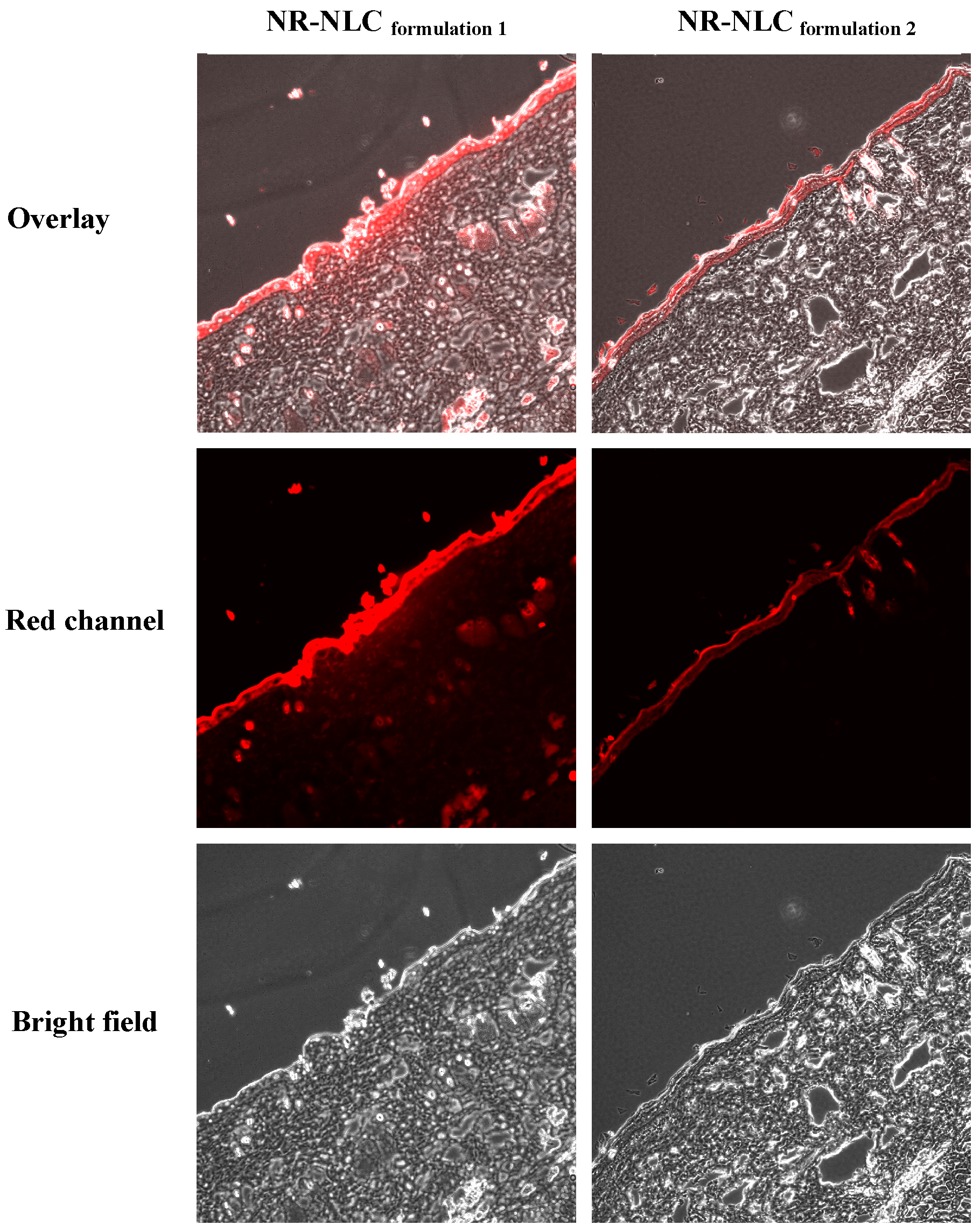
Figure 5.
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of vertical slices (10 μm) of rat skin, 4 h after the administration of Nile red-loaded NLC (NR-NLC) formulation 1 (109.7 nm) and NR-NLC formulation 2.
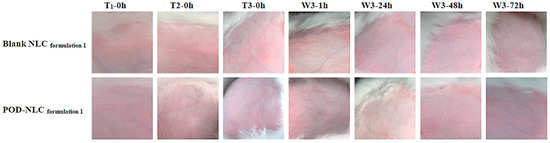
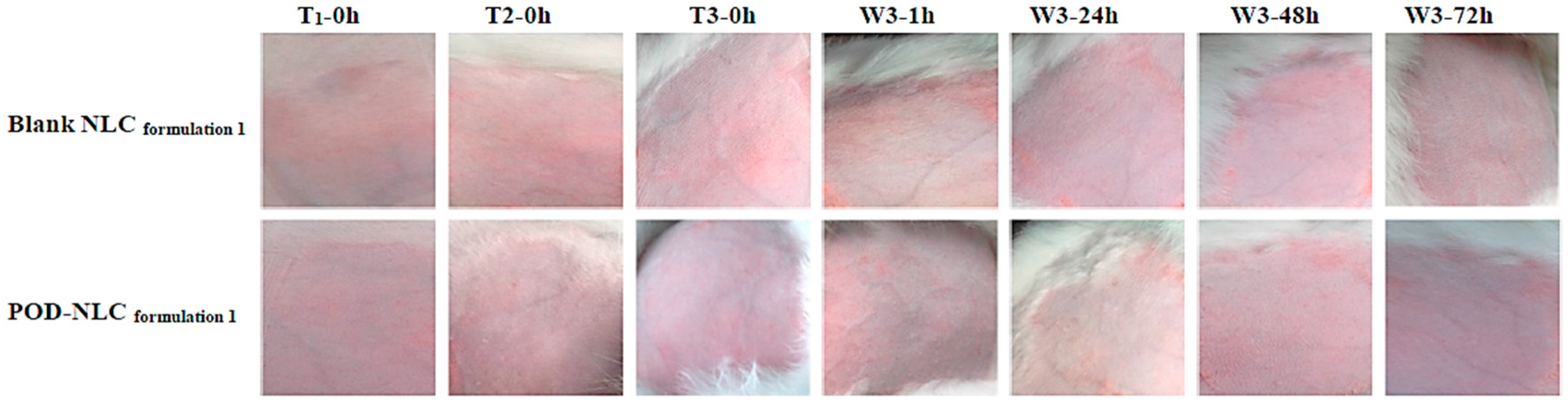
Figure 6.
Images of intact rabbit skin before and after three topical administrations of POD-NLC formulation 1 or blank NLC formulation 1. Notes: T1-0 h, T2-0 h and T3-0 h represent immediately before the first, second, and third times of administration; W3-1 h, W3-24 h, W3-48 h, and W3-72 h represent 1, 24, 48, and 72 h after washing off the residual remnants of the formulation following the last administration.
These changes do not affect the scientific results. The manuscript will be updated and the original will remain online on the article webpage. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused to readers by these changes.
Reference
- Zhao, J.; Piao, X.; Shi, X.; Si, A.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Podophyllotoxin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Skin Targeting: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2016, 21, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).