Abstract
Two pairs of diastereoisomeric acetylenic norlignan compounds with PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh skeleta: (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2), and (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D (3) and (1S, 2R)- crassifogenin D (4), were isolated from the ethanolic extract of rhizomes of Curculigo crassifolia. Compounds 3 and 4 are new and their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic evidence and comparisons with literature data.
Introduction
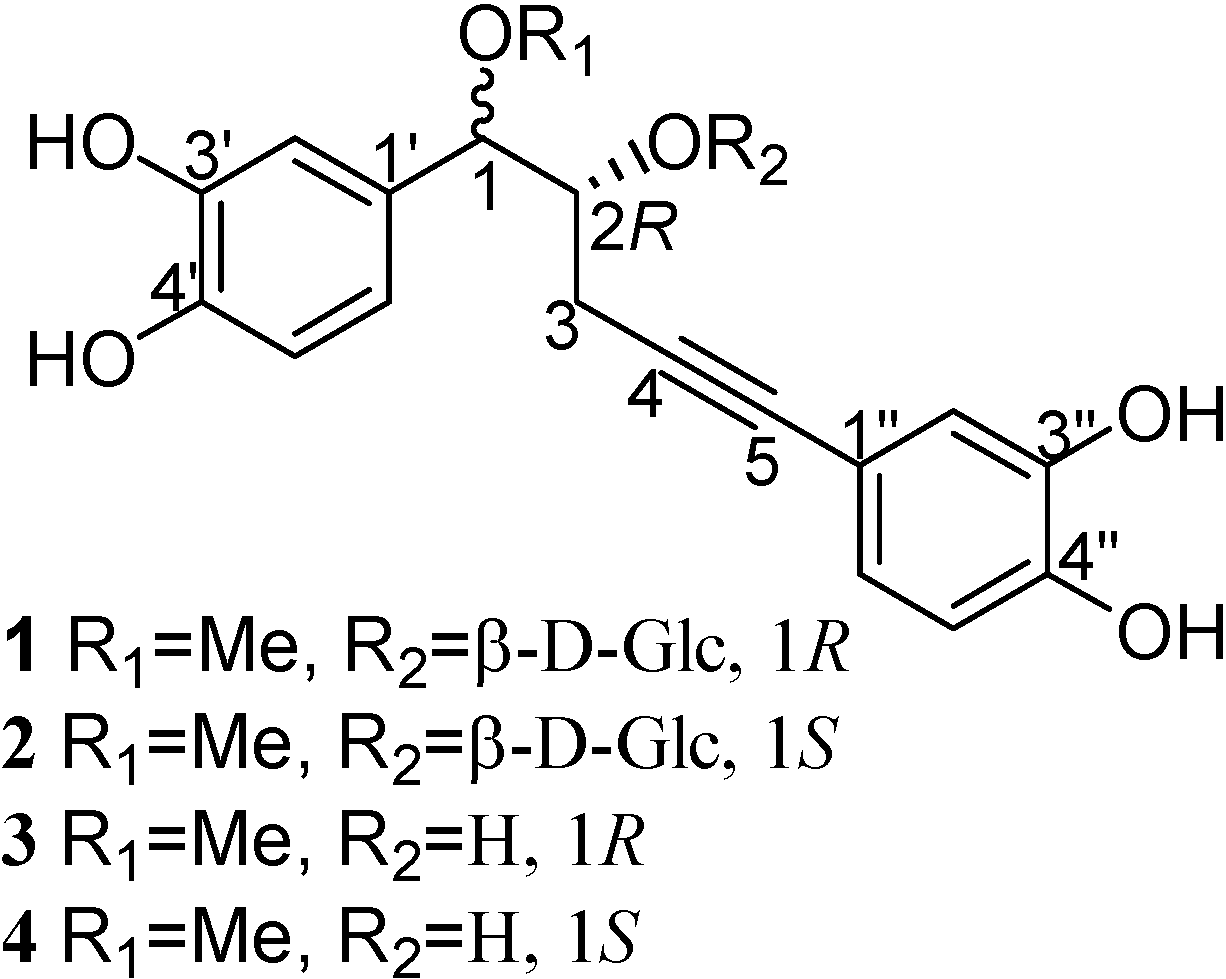
Curculigo crassifolia (Bak.) Hook. f. belongs to the Hypoxidaceae family and is found throughout the Western and Southern regions of China. Its rhizomes are used as a tonic and a folk medicine for treating child pneumonitis [1]. Despite the use of the rhizomes of this plant as a folk remedy, reports on the chemical constituents of this plant are scarce [2,3,4]. In continuation of our studies on the norlignan constituents of the rhizomes of C. crassifolia, we now report that this plant is rich in acetylenic norlignan compounds and we describe the isolation and structural elucidation of two pairs of acetylenic norlignans and their corresponding glucosides: (1R, 2R)-1-O-methyl- nyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2), and (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D (3) and (1S, 2R)-crassifogenin D (4), which contain PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh moieties (Figure 1).
Results and Discussion
The 95% EtOH extract of air-dried and powdered rhizomes of C. crassifolia was suspended in H2O and then passed through D101 resin column eluting with H2O and EtOH. Further repeated column chromatography of the EtOH eluted residue on silica gel and Sephadex LH-20 led to the isolation of two pairs of acetylenic norlignan compounds with PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh skeletons. Among them, the known compounds 1 and 2 were identified as (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside by comparing their physical and spectroscopic data with literature values [5,6].

Table 1.
1H-NMR (400 MHz, δ in ppm, J in Hz) data for compounds 1-4 in CD3OD.
| NO. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.38 d (6.28) | 4.47 d (3.76) | 4.08 d (8.20) | 4.09 d (3.40) |
| 2 | 4.14 m | 4.14 m | 3.82 m | 3.75 m |
| 3 | 2.70 dd (17.12, 4.76) | 2.56 dd (13.84, 5.28) | 2.46 dd (16.65, 4.30) | 2.46 dd (16.65, 4.30) |
| 2.30 dd (17.12, 5.20) | 2.30 dd (13.84, 4.56) | 2.20 dd (16.65, 5.95) | 2.20 dd (16.65, 5.95) | |
| 2' | 6.89 d (1.44) | 6.89 d (1.44) | 6.87 d (1.50) | 6.87 d (1.50) |
| 5' | 6.81 d (8.16) | 6.81 d (8.16) | 6.80 d (8.00) | 6.80 d (8.00) |
| 6' | 6.75 dd (8.16, 1.44) | 6.75 dd (8.16, 1.44) | 6.75 dd (8.00, 1.50) | 6.75 dd (8.00, 1.50) |
| 2'' | 6.87 d (1.58) | 6.87 d (1.58) | 6.82 d (2.00) | 6.82 d (2.00) |
| 5'' | 6.71 d (8.12) | 6.71 d (8.12) | 6.71 d (8.08) | 6.71 d (8.08) |
| 6'' | 6.80 dd (8.12, 1.58) | 6.80 dd (8.12, 1.58) | 6.78 dd (8.08, 2.00) | 6.78 dd (8.08, 2.00) |
| OMe | 3.25 s | 3.37 s | 3.18 s | 3.18 s |
| Glc. | ||||
| 1 | 4.63 d (7.56) | 4.60 d (7.80) | ||
| 2 | 3.30- 3.42 m | 3.30- 3.42 m | ||
| 3 | 3.30- 3.42 m | 3.30- 3.42 m | ||
| 4 | 3.30- 3.42 m | 3.30- 3.42 m | ||
| 5 | 3.30- 3.42 m | 3.30- 3.42 m | ||
| 6 | 3.89 dd (11.84, 2.00) | 3.89 dd (11.84, 2.00) | ||
| 3.70 dd (11.84, 5.32) | 3.70 dd (11.84, 5.32) |
Compound 1, 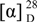 +26.50º (c 0.16, MeOH), was obtained as a white amorphous powder and assigned a molecular formula of C24H28O11 on the basis of the HRFAB-MS (-) (m/z 491.1565 [M-1]-, calcd. 491.1553). The IR absorption at 3441 cm-1 indicated the presence of hydroxyl groups. The 1H-NMR spectrum displayed signals for six aromatic protons in two ABX systems, and seven sugar protons, in addition to signals for four aliphatic protons at δ 4.38 (d, H-1), 4.14 (m, H-2), 2.30 (dd, H-3), and 2.70 (dd, H-3). Both sets of ABX systems, one at 6.89 (d, J = 1.44 Hz, H-2'), 6.81 (d, J = 8.16 Hz, H-5'), and 6.75 (dd, J = 8.16, 1.44 Hz, H-6') and the other at 6.87 (d, J = 1.58 Hz, H-2''), 6.71 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, H-5''), and 6.80 (dd, J = 8.12, 1.58 Hz, H-6''), were consistent with two catechol-like moieties, with the latter being conjugated with a acetylene function (δ 84.4, 83.7). Analysis of the signals of seven sugar protons suggested a β-D-glucosyl unit with the anomeric proton at δ 4.63 (d, J = 7.56 Hz). These assignments were made by analyzing the H-H COSY spectrum, incorporating HMQC data. The placement of 1-O-methyl and 2-O-β-D-Glc was made from the observation of the three-bond coupling of H-1 to C-1 of the methyl group, anomeric proton to C-2, and H-2 to the anomeric carbon in the HMBC spectrum. The two remaining quaternary carbon signals (δ 84.4, 83.7) belong to the acetylenic bond. The HMBC spectrum also revealed couplings of H-2 and H-3 to C-4, H-2' and H-6' to C-5. Taking all these chemical shifts and their coupling relationships into consideration, the structure sequence of PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh for 1 was arrived at, allowing the attachment of a methoxyl group at C-1 position and the β-D-Glc moiety at the C-2 position (Figure 1).
+26.50º (c 0.16, MeOH), was obtained as a white amorphous powder and assigned a molecular formula of C24H28O11 on the basis of the HRFAB-MS (-) (m/z 491.1565 [M-1]-, calcd. 491.1553). The IR absorption at 3441 cm-1 indicated the presence of hydroxyl groups. The 1H-NMR spectrum displayed signals for six aromatic protons in two ABX systems, and seven sugar protons, in addition to signals for four aliphatic protons at δ 4.38 (d, H-1), 4.14 (m, H-2), 2.30 (dd, H-3), and 2.70 (dd, H-3). Both sets of ABX systems, one at 6.89 (d, J = 1.44 Hz, H-2'), 6.81 (d, J = 8.16 Hz, H-5'), and 6.75 (dd, J = 8.16, 1.44 Hz, H-6') and the other at 6.87 (d, J = 1.58 Hz, H-2''), 6.71 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, H-5''), and 6.80 (dd, J = 8.12, 1.58 Hz, H-6''), were consistent with two catechol-like moieties, with the latter being conjugated with a acetylene function (δ 84.4, 83.7). Analysis of the signals of seven sugar protons suggested a β-D-glucosyl unit with the anomeric proton at δ 4.63 (d, J = 7.56 Hz). These assignments were made by analyzing the H-H COSY spectrum, incorporating HMQC data. The placement of 1-O-methyl and 2-O-β-D-Glc was made from the observation of the three-bond coupling of H-1 to C-1 of the methyl group, anomeric proton to C-2, and H-2 to the anomeric carbon in the HMBC spectrum. The two remaining quaternary carbon signals (δ 84.4, 83.7) belong to the acetylenic bond. The HMBC spectrum also revealed couplings of H-2 and H-3 to C-4, H-2' and H-6' to C-5. Taking all these chemical shifts and their coupling relationships into consideration, the structure sequence of PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh for 1 was arrived at, allowing the attachment of a methoxyl group at C-1 position and the β-D-Glc moiety at the C-2 position (Figure 1).
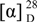 +26.50º (c 0.16, MeOH), was obtained as a white amorphous powder and assigned a molecular formula of C24H28O11 on the basis of the HRFAB-MS (-) (m/z 491.1565 [M-1]-, calcd. 491.1553). The IR absorption at 3441 cm-1 indicated the presence of hydroxyl groups. The 1H-NMR spectrum displayed signals for six aromatic protons in two ABX systems, and seven sugar protons, in addition to signals for four aliphatic protons at δ 4.38 (d, H-1), 4.14 (m, H-2), 2.30 (dd, H-3), and 2.70 (dd, H-3). Both sets of ABX systems, one at 6.89 (d, J = 1.44 Hz, H-2'), 6.81 (d, J = 8.16 Hz, H-5'), and 6.75 (dd, J = 8.16, 1.44 Hz, H-6') and the other at 6.87 (d, J = 1.58 Hz, H-2''), 6.71 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, H-5''), and 6.80 (dd, J = 8.12, 1.58 Hz, H-6''), were consistent with two catechol-like moieties, with the latter being conjugated with a acetylene function (δ 84.4, 83.7). Analysis of the signals of seven sugar protons suggested a β-D-glucosyl unit with the anomeric proton at δ 4.63 (d, J = 7.56 Hz). These assignments were made by analyzing the H-H COSY spectrum, incorporating HMQC data. The placement of 1-O-methyl and 2-O-β-D-Glc was made from the observation of the three-bond coupling of H-1 to C-1 of the methyl group, anomeric proton to C-2, and H-2 to the anomeric carbon in the HMBC spectrum. The two remaining quaternary carbon signals (δ 84.4, 83.7) belong to the acetylenic bond. The HMBC spectrum also revealed couplings of H-2 and H-3 to C-4, H-2' and H-6' to C-5. Taking all these chemical shifts and their coupling relationships into consideration, the structure sequence of PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh for 1 was arrived at, allowing the attachment of a methoxyl group at C-1 position and the β-D-Glc moiety at the C-2 position (Figure 1).
+26.50º (c 0.16, MeOH), was obtained as a white amorphous powder and assigned a molecular formula of C24H28O11 on the basis of the HRFAB-MS (-) (m/z 491.1565 [M-1]-, calcd. 491.1553). The IR absorption at 3441 cm-1 indicated the presence of hydroxyl groups. The 1H-NMR spectrum displayed signals for six aromatic protons in two ABX systems, and seven sugar protons, in addition to signals for four aliphatic protons at δ 4.38 (d, H-1), 4.14 (m, H-2), 2.30 (dd, H-3), and 2.70 (dd, H-3). Both sets of ABX systems, one at 6.89 (d, J = 1.44 Hz, H-2'), 6.81 (d, J = 8.16 Hz, H-5'), and 6.75 (dd, J = 8.16, 1.44 Hz, H-6') and the other at 6.87 (d, J = 1.58 Hz, H-2''), 6.71 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, H-5''), and 6.80 (dd, J = 8.12, 1.58 Hz, H-6''), were consistent with two catechol-like moieties, with the latter being conjugated with a acetylene function (δ 84.4, 83.7). Analysis of the signals of seven sugar protons suggested a β-D-glucosyl unit with the anomeric proton at δ 4.63 (d, J = 7.56 Hz). These assignments were made by analyzing the H-H COSY spectrum, incorporating HMQC data. The placement of 1-O-methyl and 2-O-β-D-Glc was made from the observation of the three-bond coupling of H-1 to C-1 of the methyl group, anomeric proton to C-2, and H-2 to the anomeric carbon in the HMBC spectrum. The two remaining quaternary carbon signals (δ 84.4, 83.7) belong to the acetylenic bond. The HMBC spectrum also revealed couplings of H-2 and H-3 to C-4, H-2' and H-6' to C-5. Taking all these chemical shifts and their coupling relationships into consideration, the structure sequence of PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh for 1 was arrived at, allowing the attachment of a methoxyl group at C-1 position and the β-D-Glc moiety at the C-2 position (Figure 1).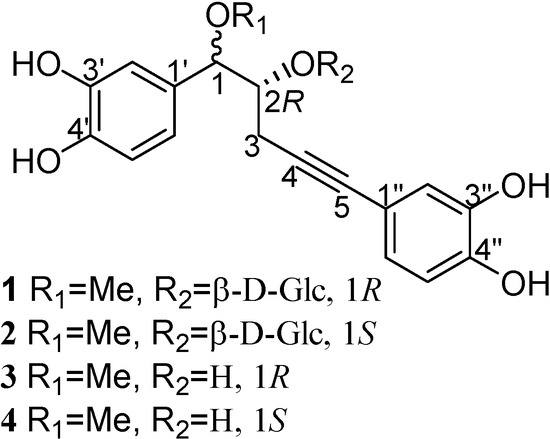
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1-4.
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1-4.
Since compound 1 is a nyasicoside-type norlignan from the Curculigo genus, from a biogenetic point of view, the C-2 stereochemistry in 1 should possess a 2R configuration [6]. Further comparison of the coupling constant between H-1 and H-2 (6.28 Hz) and the optical rotation (+26.50º) with literature values [5,6], suggest 1R and 2R stereochemistry in 1. Hence, 1 is (1R, 2R)-1-O-methyl- nyasicoside.
Compound 2 was obtained as a white amorphous powder and assigned a molecular formula of C24H28O11 from its negative HRFAB-MS data. The 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra showed that 2 was obtained in a ratio of 1:5 with compound 1. Most of the NMR signals of the mixture were in pairs. The 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra of 2 are closely similar to that of 1, except for this difference of the coupling constant between H-1 and H-2 (δ 4.38, d, J = 6.28 Hz in 1 and δ 4.47, d, J = 3.76 Hz in 2) (Table 1 and Table 2). For instance, 2 displayed signals for two ABX systems belonging to the aromatic protons, protons of a β-D-glucosyl moiety (δ 4.60, d, J = 7.80 Hz, H-1; δ 3.30-3.42, m, H-2-H-5; δ 3.89, dd, J = 2.00, 11.84 Hz, H-6a; δ 3.70, dd, J = 5.32, 11.84 Hz, H-6b), and four aliphatic protons at δ 4.47 (d, H-1), 4.14 (m, H-2), 2.30 (dd, H-3), and 2.56 (dd, H-3). These assignments were made by analyzing the H-H COSY spectrum, incorporating HMQC data. The placement of 1-O-methyl and 2-O-β-Glc was made from the observation of the three-bond coupling of H-1 to methoxy carbon, anomeric proton to C-2, and H-2 to the anomeric carbon in the HMBC spectrum. The two remaining carbon signals (δ 84.7, 83.6) belong to the acetylenic bond. These data suggested that 2 and 1 possessed the same norlignan PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh sequence. From a biogenetic point of view, the configuration of C-2 in 2 should be 2R [6]. Further comparing the coupling constant between H-1 and H-2 (3.76 Hz) with literature values [6], this would require 1S and 2R stereochemistry in 2. Hence, 2 is (1S, 2R)-1-O- methylnyasicoside.

Table 2.
13C-NMR (100 MHz, δ in ppm) data for compounds 1-4 in CD3ODa.
| NO. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85.8 d | 85.6 d | 86.4 d | 87.0 d |
| 2 | 79.5 d | 79.4 d | 73.9 d | 74.5 d |
| 3 | 22.4 t | 22.3 t | 24.9 t | 24.5 t |
| 4 | 84.4 s | 84.7 s | 85.6 s | 85.2 s |
| 5 | 83.7 s | 83.6 s | 82.7 s | 82.8 s |
| 1' | 130.4 s | 130.2 s | 131.3 s | 131.3 s |
| 2' | 116.0 d | 116.0 d | 115.8 da | 115.8 da |
| 3' | 145.8 s | 145.8 s | 145.6 s | 145.6 s |
| 4' | 146.3 s | 146.3 s | 145.9 s | 145.9 s |
| 5' | 116.0 d | 116.0 d | 115.9 da | 115.9 da |
| 6' | 120.8 d | 120.6 d | 120.7 d | 120.2 d |
| 1'' | 116.2 s | 116.2 s | 116.3 s | 116.3 s |
| 2'' | 119.4 d | 119.4 d | 119.2 d | 119.2 d |
| 3'' | 146.1 s | 146.1 s | 145.8 s | 145.8 s |
| 4'' | 146.7 s | 146.7 s | 146.3 s | 146.3 s |
| 5'' | 116.2 d | 116.2 d | 116.1 d | 116.1 d |
| 6'' | 124.9 d | 124.9 d | 124.6 d | 124.6 d |
| OMe | 57.1 q | 57.3 q | 56.8 q | 56.8 q |
| Glc. | ||||
| 1 | 102.4 d | 102.7 d | ||
| 2 | 74.7 d | 74.7 d | ||
| 3 | 77.6 d | 77.6 d | ||
| 4 | 71.3 d | 71.3 d | ||
| 5 | 77.8 d | 77.8 d | ||
| 6 | 62.6 t | 62.6 t |
a These values may be interchangeable in the same column.
Although compound 1 was successfully purified, attempts to purify compound 2 failed. Reasons for this could be the small amount present and small differences in the interactions between this pair of diastereoisomers, and the column material used for their separation. Compounds 3 and 4 were assigned to (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D (3) and (1S, 2R)-crassifogenin D (4); they had the same molecular formula of C18H18O6 on the basis of the HRFAB-MS (-) (m/z 329.1037 [M-1]-, calcd 329.1025). They were obtained as a 1:1 mixture, unresolvable by TLC and HPLC on account of the small amount obtained (only 4 mg, see Experimental). Most of the NMR signals of the mixture were in pairs. The 1H-NMR spectrum showed the presence of two 3,4-disubstituted aromatic rings. According to a selective 1H-decoupling experiment, incorporating HMQC and HMBC spectra, compounds 3 and 4 possessed the same norlignan PhCH(OR1)CH(OR2)CH2C≡CPh sequence as compounds 1 and 2. 1D and 2D NMR spectra showed that compounds 3 and 4 were aglycones of compounds 1 and 2, respectively. The δ values at C-2 in 3 and 4 were shifted upfield 5 - 6 compared to those of 1 and 2, while the δ values at C-1 and C-3 in 3 and 4 were downfield shifted, due to the absence of a β-D-glucose unit at C-2. The δ values of remaining carbons in 3 and 4 were similar to the corresponding positions of 1 and 2 (Table 2). The correlation peak between C-1 and protons of OCH3 in the HMBC spectra of 3 and 4 confirmed that OCH3 was linked at C-1. Compounds 3 and 4 are also nyasicoside-type norlignans, so from a biogenetic point of view, the C-2 stereochemistry in 3 and 4 should possess 2R configuration [6]. Further comparing the coupling constant between H-1 and H-2 (8.20 Hz in 3, and 3.40 Hz in 4), this would require 1R and 2R stereochemistry in 3, and 1S and 2R stereochemistry in 4. From the above results and comparison to those of compounds 1 and 2, the structures of (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D (3) and (1S, 2R)-crassifogenin D (4) were established as aglycones of compounds 1 and 2. Compounds 3 and 4 were detected by RP-8 TLC in the EtOH extract, which showed 3 and 4 were not artifacts of 1 and 2 produced by the isolation procedure. Since compounds 3 and 4 were obtained as a 1:1 mixture of (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D and (1S, 2R)-crassifogenin D, the (+)-(1R, 2R) optical rotation in 3 and the (-)-(1S, 2R) one in 4 cancel each other out, and a zero optical rotation was observed for the mixture of 3 and 4. On the other hand, the mixture of 1 and 2 was obtained in a ratio of 5:1, so the (+)-(1R, 2R) configuration in 1 was predominant compared to the (-)-(1S, 2R) one of the minor component 2, so an optical rotation of +12.37º was observed for the mixture of 1 and 2.
Experimental
General
The optical rotations were obtained on a JASCO-370 polarimeter. The UV spectra were recorded in MeOH on a UV-2401PC Spectrometer. The IR spectra were recorded on a Bio-Rad FTS-35 spectrometer using KBr pellets. The MS data were obtained on an Autospec-3000 spectrometer operating in negative ion mode. 1D and 2D NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker AM-400 or a Bruker DRX-500 spectrometer with TMS as an internal standard. Column chromatography was performed on Sephadex LH-20 (25-100 µm, Pharmacia Fine Chemical Co. Ltd.) and silica gel (200-300 mesh, Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co.). TLC was carried on silica gel G precoated plates (Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co.) and spots were detected by 5% sulfuric acid reagents followed by heating.
Plant material
The plant material was collected in Eshan Prefecture, Yunnan Province, China, in October 2002 and identified as Curculigo crassifolia by Prof. Ping-hua Yu, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Science, where a voucher specimen (No. 20021018) was deposited.
Extraction and isolation
The air-dried and powered rhizomes of C. crassifolia (10 kg) were extracted with 95% EtOH (3×50 L) at room temperature, then the combined extracts were evaporated in vacuo to afford a residue (562 g). The residue was suspended in H2O and then passed through D101 resin column eluting with H2O and EtOH. The EtOH eluent was concentrated in vacuo to give a residue (500 g), which was fractionated by CC (silica gel, 3000 g, 200-300 mesh; with CHCl3-MeOH, 9:1) to afford 5 fractions (1-5). Fraction 2 (13 g) was refractionated on a silica gel column (220 g, CHCl3-MeOH, 9.5:0.5, 1600 mL) to provide 8 fractions (2-1 to 2-8). Fraction 2-4 (210 mg) was purified by repeated Sephadex LH-20 chromatography (EtOH) to afford a mixture of (1R, 2R)-crassifogenin D (3) and (1S, 2R)-crassifogenin D (4) (4 mg): white amorphous powder. 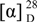 = 0º (c 0.12, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.56), 256 (4.08), 289 (3.77) nm; IR νmax: 3441, 2924, 1629, 1517, 1443, 1283, 1179, 1111, 815, 583cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1, 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 329 [M-H]-; HR-FAB- MS m/z: [M-H]-329.1037 (calcd. for C18H17O6, 329.1025). Fraction 5 (210 g) was refractionated by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 2000 mL each eluent) to yield 12 crude fractions (5-1 to 5-12). Fraction 5-7 (4.34 g) was purified by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 700 ml each eluent) to yield 6 fractions (5-7-1 to 5-7-6). Fraction 5-7-4 (612 mg) was repeatedly purified on Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH) to afford a mixture of (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2) (212 mg) and pure 1 (18 mg). White amorphous powder;
= 0º (c 0.12, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.56), 256 (4.08), 289 (3.77) nm; IR νmax: 3441, 2924, 1629, 1517, 1443, 1283, 1179, 1111, 815, 583cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1, 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 329 [M-H]-; HR-FAB- MS m/z: [M-H]-329.1037 (calcd. for C18H17O6, 329.1025). Fraction 5 (210 g) was refractionated by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 2000 mL each eluent) to yield 12 crude fractions (5-1 to 5-12). Fraction 5-7 (4.34 g) was purified by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 700 ml each eluent) to yield 6 fractions (5-7-1 to 5-7-6). Fraction 5-7-4 (612 mg) was repeatedly purified on Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH) to afford a mixture of (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2) (212 mg) and pure 1 (18 mg). White amorphous powder; 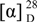 : +12.37º (c 0.18, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.34), 255 (3.96), 289 (3.65) nm. IR νmax: 3441, 2926, 2045, 1546, 1473, 1179cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1; 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 491 [M-H]-; HR-FAB-MS m/z: [M-H]- 491.1565 (calcd. for C24H27O11, 491.1553).
: +12.37º (c 0.18, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.34), 255 (3.96), 289 (3.65) nm. IR νmax: 3441, 2926, 2045, 1546, 1473, 1179cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1; 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 491 [M-H]-; HR-FAB-MS m/z: [M-H]- 491.1565 (calcd. for C24H27O11, 491.1553).
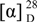 = 0º (c 0.12, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.56), 256 (4.08), 289 (3.77) nm; IR νmax: 3441, 2924, 1629, 1517, 1443, 1283, 1179, 1111, 815, 583cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1, 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 329 [M-H]-; HR-FAB- MS m/z: [M-H]-329.1037 (calcd. for C18H17O6, 329.1025). Fraction 5 (210 g) was refractionated by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 2000 mL each eluent) to yield 12 crude fractions (5-1 to 5-12). Fraction 5-7 (4.34 g) was purified by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 700 ml each eluent) to yield 6 fractions (5-7-1 to 5-7-6). Fraction 5-7-4 (612 mg) was repeatedly purified on Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH) to afford a mixture of (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2) (212 mg) and pure 1 (18 mg). White amorphous powder;
= 0º (c 0.12, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.56), 256 (4.08), 289 (3.77) nm; IR νmax: 3441, 2924, 1629, 1517, 1443, 1283, 1179, 1111, 815, 583cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1, 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 329 [M-H]-; HR-FAB- MS m/z: [M-H]-329.1037 (calcd. for C18H17O6, 329.1025). Fraction 5 (210 g) was refractionated by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 2000 mL each eluent) to yield 12 crude fractions (5-1 to 5-12). Fraction 5-7 (4.34 g) was purified by Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH-H2O, 0:1-1:0; 700 ml each eluent) to yield 6 fractions (5-7-1 to 5-7-6). Fraction 5-7-4 (612 mg) was repeatedly purified on Sephadex LH-20 (EtOH) to afford a mixture of (1R, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (1) and (1S, 2R)-1-O-methylnyasicoside (2) (212 mg) and pure 1 (18 mg). White amorphous powder; 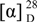 : +12.37º (c 0.18, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.34), 255 (3.96), 289 (3.65) nm. IR νmax: 3441, 2926, 2045, 1546, 1473, 1179cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1; 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 491 [M-H]-; HR-FAB-MS m/z: [M-H]- 491.1565 (calcd. for C24H27O11, 491.1553).
: +12.37º (c 0.18, MeOH); UV (MeOH): λmax (lg ε): 205 (4.34), 255 (3.96), 289 (3.65) nm. IR νmax: 3441, 2926, 2045, 1546, 1473, 1179cm-1; 1H-NMR see Table 1; 13C-NMR see Table 2; FAB-MS m/z: 491 [M-H]-; HR-FAB-MS m/z: [M-H]- 491.1565 (calcd. for C24H27O11, 491.1553).Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30670217), International Foundation for Science (F/4340-1), the Science and Technology Foundation of Distinguished Young Scholars of Anhui Province (08040106812) and the Innovative Research Team of 211 Project in Anhui University (02203104/04).
References
- Institutum Botanicum Kunmingense, Academiae Sinicae. In Flora Yunnanica; Wu, C.Y. (Ed.) Science Press: Beijing; Vol. 6, p. 819. (in Chinese)
- Li, N.; Wang, K.J.; Chen, J.J.; Zhou, J. Two novel glucosyl-fused compounds from Curculigo crassifolia (Hypoxidaceae). Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6445–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, J.J.; Zhou, J. Two New Phenolic Glycosides from Rhizomes of Curculigo crassifolia. Z. Naturforsch. B. 2006, 61b, 611–614. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.J.; Li, N. Antioxidant Phenolic Compounds from Rhizomes of Curculigo crassifolia. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.; Su, M.J.; Lee, S.S. Bioactive norlignan glucosides from Curculigo capitulata. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.L.; Chen, C.H.; Lee, S.S. Three novel constituents from Curculigo capitulata and revision of C-2 stereochemistry in nyasicoside. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Available from authors.
© 2008 by the authors. Licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
