Abstract
Black tea was extracted for 2, 8 and 18 h with absolute acetone, N,N-dimethyl-formamide (DMF), ethanol and methanol and their 50% aqueous solutions. The extracts were screened for total polyphenol contents, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. The polyphenol content of the extracts was found to be in the range of 0.44-114.01 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g dry weight tea, depending on the solvent used and the length of the extraction process. In general, aqueous acetone or DMF extracts displayed the highest polyphenol contents and antioxidant activity, while absolute acetone was the least efficient solvent. Antioxidant activities of tea extracts tested using the reducing power and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl (DPPH) radical methods ranged from 0.09 to 1.18 and from 2.60 to 95.42 %, respectively, depending on the extraction conditions and the antioxidant activities correlated well with the polyphenol concentrations. Aqueous solvent black tea extracts also possessed antibacterial activity, depending on the solvent used and bacterial species tested. Staphylococcus aureus was found to be the most sensitive to all tea extracts, except for the methanol extract. Tea extracts were not effective against Y. enterocolitica, L. monocytogenes and E. coli O157:H7.
Introduction
Tea is a widely consumed beverage throughout the world. The growing interest in the potential health benefits of tea, together with its popularity as a beverage, have prompted numerous investigations on the chemical constituents of tea and their biological properties [1], such as antimutagenic [2], anticarcinogenic and antioxidant [3,4], antibacterial [5,6] and antiallergic activities [7]. These therapeutic effects of tea, mainly green tea and its catechins, have been extensively examined in microbial and mammalian cell systems. It was also suggested that tea phenolics may suppress formation of mutagenic and carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in cooked foods [8]. The polyphenols, the most dominant constituents in tea, have been considered to be a major dietary factor responsible for health effects. The antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols are mostly due to their powerful scavenging and antioxidant activity, which inactivates direct carcinogens and inhibits the activation of indirect carcinogens extracellularly [9]. The antioxidant action of polyphenol compounds depends on their free radical scavenging capacity and iron reducing ability [10]. The total polyphenol amounts determined from the same plant and their corresponding antioxidant and antimicrobial activities may vary widely, depending on extraction conditions applied. Water and DMF showed the highest efficiency for extraction of quercetin and its glycoside from some foods among the various solvents used [11]. Similarly, Brenes et al. [12] reported that use of DMF as an extraction solvent resulted in a complete extraction of phenols from olive oils, compared to methanol. On the other hand, methanol extracts showed the highest antioxidant and antimicrobial activities in seabuckthorn seeds which were extracted with chloroform, ethyl acetate, acetone and methanol [13]. It was reported that aqueous ethanol and methanol extracts of red and black currant contained more polyphenols than water extracts and that their contents increased with the duration of the extraction process [14]. Recently, we compared various solvent systems including water and neat DMF, acetone, and methanol or ethanol and various concentrations of these organic solvents in water (50 and 80 %) for the polyphenol content in the resulting extracts and the antioxidant activity of teas. A 50% concentration of each solvent was found to be the most efficient for these parameters in comparison to the other concentrations and water alone was considerably less efficient than all aqueous solvent mixtures used [15]. Different solvent extraction systems showed a wide range in the concentrations of individual phenolic compounds in Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) leaf and the effect of different extraction times (2, 4 and 8 h) on their antioxidant activity depended on solvents used [16]. Although there have been some reports on the antioxidant activity of black tea [15,17,18] little or no information is available on its antimicrobial activity and the effect of extraction conditions on these properties. Therefore, the aims of this study were (1) to determine antioxidant activities of black tea extracts and their antibacterial activities against different food-borne pathogens which have undesirable effects on quality, safety and shelf life of foods, and (2), to identify the effects of different extraction solvents of varying polarities and the extraction times on these two properties and the polyphenol contents of tea. In the present study, the antioxidant activity of tea extracts was determined using two methods based on different mechanisms. One was the DPPH radical scavenging assay most widely used for studying polyphenols from plants, including tea, and the other is reducing power (RP) which was chosen due to the fact that iron-polyphenol complex was demonstrated to cause the inhibition of formation of oxygen radicals associated with many pathological conditions [10] and also probably growth of some pathogen microorganisms [5].
Results and Discussion
Polyphenol content
The polyphenol contents of tea extracts were examined and the results are presented in Table 1. All of the different solvent extraction systems used showed a wide range of polyphenol concentrations, from 0.4 to 114 (GAE)/g dry weight tea, depending on the solvent used and the extraction times.

Table 1.
Effect of different solvents and extraction times on total polyphenol content (mg GAE/g dw tea) and antioxidant activity of black tea a
| Parameter | Extr. Time (h) | Extraction solvent | |||
| Acetone | DMF | ||||
| 50% | >99% | 50% | >99% | ||
| Total polyphenols | 2 | 114.01±1.13c G | 0.44±0.04a A | 95.60±0.42a F | 18.57±0.08a C |
| 8 | 92.76±0.97a F | 1.43±0.04b A | 104.96±1.43b G | 44.14±0.93b C | |
| 18 | 98.19±1.10b F | 1.62±0.04c A | 109.36±0.71c G | 49.10±1.97c C | |
| Ethanol | Methanol | ||||
| 50% | >99% | 50% | >99% | ||
| 2 | 74.35±0.16a E | 0.48±0.06a A | 58.38±1.42a D | 8.58±0.62a B | |
| 8 | 85.37±0.64b E | 1.87±0.15b A | 62.87±1.87a D | 22.82±1.10b B | |
| 18 | 86.31±3.50b E | 2.13±0.13b A | 68.69±1.34b D | 23.14±0.70b B | |
| Antioxidant activity | Acetone | DMF | |||
| 50% | >99% | 50% | >99% | ||
| PR | 2 | 1.16±0.06a F | 0.09±0.00a A | 1.11±0.01a F | 0.34±0.00a C |
| 8 | 1.08±0.01a G | 0.11±0.00b A | 1.16±0.01b H | 0.59±0.00b D | |
| 18 | 1.04±0.02a F | 0.11±0.00b A | 1.18±0.00c G | 0.62±0.00c C | |
| % Inhibition | 2 | 95.42±0.33c G | 2.60±0.18a A | 93.73±0.46b F | 46.72±0.63a D |
| 8 | 93.75±0.06a G | 3.05±0.20a A | 92.06±0.16a F | 78.30±0.25b D | |
| 18 | 94.67±0.13b E | 2.65±0.15a A | 94.60±0.24b E | 83.20±1.76c D | |
| Antioxidant activity | Ethanol | Methanol | |||
| 50% | >99% | 50% | >99% | ||
| PR | 2 | 0.87±0.00a E | 0.10±000a A | 0.67±0.01a D | 0.22±0.00a B |
| 8 | 0.94±0.00c F | 0.13±0.00c B | 0.76±0.00c E | 0.39±0.01b C | |
| 18 | 0.89±0.00b E | 0.12±0.00b A | 0.74±0.00b D | 0.38±0.00b B | |
| % Inhibition | 2 | 94.36±0.22b FG | 4.99±0.13a B | 85.81±0.63a E | 25.04±0.75a C |
| 8 | 93.24±0.11a G | 5.86±0.07b B | 90.99±0.68b E | 52.28±0.51b C | |
| 18 | 94.87±0.13b E | 6.31±0.12c B | 92.85±0.07c E | 54.20±0.30b C | |
a Data are expressed as means ± SE of triplicate experiments. Means in a column (a-c across extraction times) not having a common letter are different (p<0.05). Means in a row (A-G across solvent types) not having a common letter are different (p<0.05).
All the 50% solvent extracts contained higher amounts of polyphenols, compared to their corresponding neat ones, after 2, 8 and 18 h of extraction (p<0.05). Among the solvents tested the highest levels of polyphenols after 2 h of extraction were achieved using 50% acetone, followed by 50% DMF > 50 % ethanol > 50 % methanol > DMF > methanol > ethanol ≈ acetone, respectively. The orders of polyphenol contents in tea extracts at 8 and 18 h were almost the same as that observed at 2 h. The only difference was that in these cases 50% DMF gave the highest polyphenol content, followed by 50% acetone. From the statistical test using two-way ANOVA it could be concluded that the total polyphenol content was influenced significantly by solvent and extraction time (Table 2), as was reported previously for almond hulls and pine sawdust [19] and for plant by-products [14].

Table 2.
Variance analysis results on the effect of solvent type, extraction time and their interactions on total polyphenol and antioxidant activity of black tea determined by two different methods.
| Source of variance | DFa | Total polyphenol | Antioxidant activity | ||||||
| % Inhibition | PR | ||||||||
| MSb | F value | MS | F value | MS | F value | ||||
| Solvent | 7 | 16218.98 | 3927.44* | 14046.14 | 18770.82* | 1.56 | 2973.97* | ||
| Time | 2 | 452.39 | 109.55* | 592.01 | 791.15* | 0.04 | 77.58* | ||
| Solvent x Time | 14 | 184.30 | 44.63* | 204.70 | 273.55* | 0.01 | 23.20* | ||
| Error | 48 | 4.13 | 0.748 | 0.00 | |||||
a Degree of freedom; b Mean squares; * Significant at p< 0.05
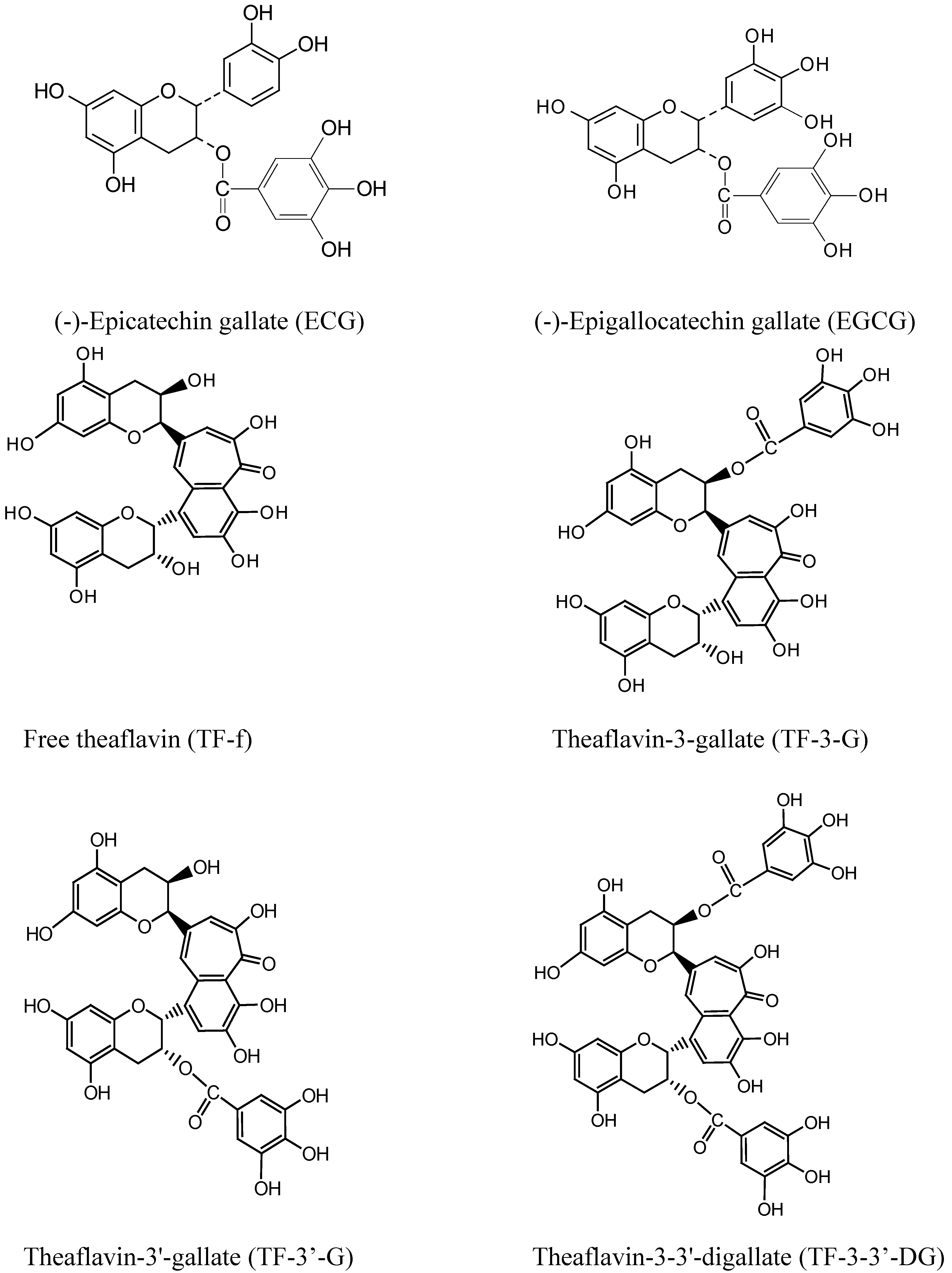
This was also consistent with HPLC results obtained from our unpublished work carried out with different black tea, where the effect of extraction conditions on the individual phenolics of black tea was studied. For example, absolute methanol extracted 7.8-8.5 fold more epigallocatechin gallate, epicatechin gallate and four individual theaflavins (free theaflavin, theaflavin-3-gallate, theaflavin-3’-gallate, theaflavin-3,3’-digallate; Figure 1) which were the main phenolics detected in all tea extracts, compared to absolute ethanol.
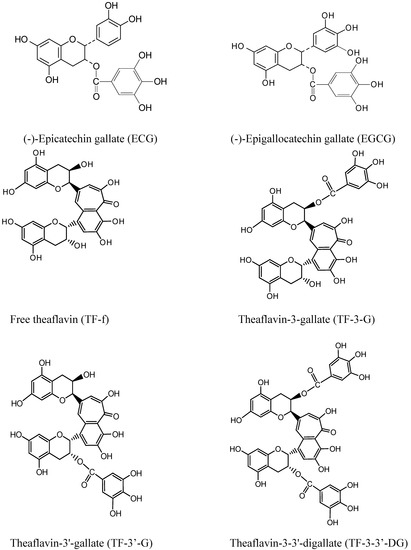
Figure 1.
Phenolics in tea extracts.
Figure 1.
Phenolics in tea extracts.
The results from this study show that variations in the polyphenol content of various extracts varied widely, depending on the polarities of solvent used and that aqueous solvents were more efficient in extracting total phenolics, compared to their corresponding absolute ones, indicating that the black tea polyphenols were highly polar compounds. Similar observations were reported in previous studies [16,20]. Thus, in the study carried out by Wang et al. [21], various concentrations of ethanol ranging from 15% to 96% were investigated for the extraction of phenolic compounds such as rosmarinic and caffeic acids from some herbs and ethanol concentrations between 30% and 60% were found to give the highest extraction yields for both compounds. This result is in accordance with Nepote et al. [22], who found that 50% ethanol gave maximum total phenolics from peanut skin over the range of 20-96% ethanol tested. According to Chavan et al. [23], aqueous acetone extracts from different peas had higher polyphenol contents than acetone ones, which support our results. While increases in the extraction time from 2 h to 8 h significantly increased polyphenol content of tea extracts, except for 50% acetone extracts (p<0.05) (Table 1), upon further increases from 8 h to 18 h, the polyphenol contents increased only slightly, but the difference was found to be significant (p<0.05) in 50% acetone, acetone, 50% DMF, DMF and 50% methanol extracts. The results showed that the variation in polyphenol content with increasing extraction time varied depending on solvent used, which was reported previously for Orthosiphon stamineus plants [16].
Antioxidant activity
The reducing power (RP) of black tea extracts, using solvents of different polarities at different extraction times was found to range between 0.1-1.2 (Table 1). Aqueous solvents (50%) gave higher RP values than the corresponding absolute solvents. At 2 h of extraction, RP values of tea extracts were significantly affected by the extraction solvents with the following order from high to low: 50% acetone ≥ 50% DMF > 50% ethanol > 50% methanol > DMF > methanol > ethanol ≈ acetone. On the other hand, at 8 h and 18 h the highest RP of the extracts was obtained with 50% DMF, followed by 50% acetone > 50% ethanol > 50% methanol > DMF > methanol > ethanol ≥ acetone. It is clear that polar aqueous solvents dissolve more polar plant polyphenols with higher RP at all different extraction times. This conclusion is in agreement with the results of Negi et al. [13], who reported that methanol extract of seabuckthorn seed had higher RP than extracts using low polarity chloroform. It was also noted that iron binding by tea phenolics depended on their molecular structure. For example, a large number of OH groups enhanced Fe-binding efficiency [24]. Based on this evidence, higher reducing powers of aqueous tea extracts can be attributed to their containing more hydrophilic phenolics. Increasing extraction time from 2 h up to 18 h caused a variation in the reducing powers of the extracts, depending on solvent used (Table 1). Reducing powers of all tea extracts except for 50% aqueous acetone increased significantly as extraction times increased from 2 to 8h (p<0.05). On the other hand, extended times (from 8 to 18 h) caused a significant increase (p<0.05) in the RP of 50% DMF and DMF extracts, but did not affect that of other solvent extracts. Black tea contains complex catechins and theaflavins generated by the oxidative processes used in tea production [4,17,25]. Theaflavins may be considered to be the main contributors to RP of the extracts, due to their ability to bind iron [26]. Reducing powers and total polyphenols of tea extracts at 2, 8 and 18 h of extraction correlated significantly (R2 = 0.98, 0.99 and 0.99, respectively). Satoh et al. [27] also observed that there was a strong correlation between the RP and total phenolic content of different tea extracts including black tea. However, Psarra, et al. [28] found a poor correlation (R2=0.60) between RP and total polyphenol of wines and also a high correlation (R2=0.81) for radical scavenging activity. The differences may be due to the different polyphenol composition of materials investigated.
The results of the free radical scavenging activity of tea extracts at the different extraction times are shown in Table 1. The activities obtained for black tea extracts were found to vary from 2.6 to 95.4%. 50% aqueous solvent extracts exhibited higher and more significant inhibitory activity against DPPH radical in comparison with their corresponding absolute solvent ones for all extraction times and this trend was similar to that observed for polyphenol content and reducing power measurements. This can be attributed to higher concentration of polyphenol present in these extracts. The effect of the extracting solvent on DPPH scavenging activity has also been reported by previous studies [13,29,30]. For both 2 and 8h of extraction the order of radical scavenging activity of the extracts was: 50% acetone ≥ 50% ethanol ≥ 50% DMF > 50% methanol > DMF > methanol > ethanol > acetone, respectively. However, after 18 h of extraction there was no significance difference (p<0.05) in the radical scavenging activity values among all four aqueous solvents. However, among the four absolute solvents DMF exhibited the greatest scavenging activity, followed by methanol, ethanol and acetone, respectively. Increases in extraction time (2-18 h) resulted in variations in the scavenging activity of the extracts, depending on solvent used (Table 1). Activities of 50% methanol, DMF, ethanol and methanol extracts increased significantly with the increase of extraction time (p<0.05). However, those of other solvent extracts were not affected. This trend was different from that observed with RP. It may be attributed to the fact that different methods to measure antioxidant activity with various mechanisms may lead to different observations [31]. With the DPPH method, antioxidant activity and total phenolics of black tea extracts correlated significantly at 2, 8 and 18 h of extraction (R2=0.89, 0.85 and 0.84, respectively). Contrary to the results of Psarra et al. [28] on wines, this study showed that correlation of RP with total polyphenols is stronger than that of radical scavenging activity, which can be attributed to different reactivity of polyphenols in black tea in different antioxidant assays.
Antibacterial activity
In this study, only aqueous solvent black tea extracts at 2, 8 and 18 h were screened for antibacterial activity against six different bacterial species because our preliminary experiments (not shown here) showed that absolute solvent extracts did not display significant activity against test bacteria. The inhibitory effect of aqueous solvent extracts of teas on the growth of test bacteria is presented in Table 3. Extraction solvents used as controls had no inhibitory effects on the six bacteria tested. All black tea extracts except for the 50 % methanol one showed varying antibacterial activity against S. aureus, H. alvei and B. cereus, depending on the solvent used, but no activity was shown against the other bacteria. It is clear that Gram-positive bacteria were more sensitive to tea extracts than Gram-negative ones. Higher resistance of Gram-negative bacteria is attributed to the presence of lipopolysaccharides in their outer membranes [32,33]. In general, increasing the extraction time from 2 to 18 h significantly increased the antibacterial activity of the extracts depending on the bacterium tested and the solvent used (Table 3). With respect to the solvent used, the differences between antibacterial activity of tea extracts was significant (p<0.05), depending on the test species and extraction time. There is no data on the same materials in literature. However, differences in antibacterial activity of various solvent extracts have been reported in previous studies with seabuckthorn seed [13] and grape seed [33]. There was no correlation (R2=0.00) between amounts of polyphenol and antibacterial activity of tea extracts. Similar results were reported by the study of Yildirim et al. [34] where ether, ethanol and hot water extracts of Polygonum cognatum were tested against five different microorganisms. While the polyphenol contents of ethanol (0.50 µg/mL) and water extracts (0.48 µg/mL) were similar and higher than an ether one (0.01 µg/mL), the water extract only did not show antimicrobial activity against the studied microorganisms. Furthermore, ether extraction was more efficient than the ethanol one. Additionally, Negi et al. [13] reported that an acetone extract of seabuckthorn seed had higher antibacterial activities than an ethyl acetate extract which had the higher phenolic contents than the acetone one. However, antibacterial activity of plant extracts is attributed to individual phenolic compounds by the previous studies [6,35,36]. On the other hand, an additional research on phenolic composition of each aqueous solvent extract is required for comprehensive assessment of individual compounds exhibiting antibacterial activity.

Table 3.
Antibacterial activity of black tea aqueous extracts.
| Bacterium | Extr. time (h) | Diameter of inhibited zone (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetone | DMF | Ethanol | Methanol | ||
| S. aureus | 2 | 12.00±0.00 | 13.00±0.00a | 8.00±0.00a | nz |
| 8 | 13.00±0.00B | 14.00±0.00bC | 8.67±0.17bA | nz | |
| 18 | 13.00±0.00B | 14.33±0.33bC | 9.00±0.00cA | nz | |
| H. alvei | 2 | 8.00±0.00a | nz | nz | nz |
| 8 | 8.17±0.17a | nz | nz | nz | |
| 18 | 9.00±0.00b | nz | nz | nz | |
| Y. enterocolitica | 2 | nz | nz | nz | nz |
| 8 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
| 18 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
| L. monocytogenes | 2 | nz | nz | nz | nz |
| 8 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
| 18 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
| B. cereus | 2 | 8.00±0.00C | 7.00±0.00aA | 7.67±0.17aB | nz |
| 8 | 11.00±0.00 | 8.00±0.00b | 8.00±0.00a | nz | |
| 18 | 12.00±0.00B | 8.33±0.33bA | 8.00±0.00aA | nz | |
| E. coli O157:H7 | 2 | nz | nz | nz | nz |
| 8 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
| 18 | nz | nz | nz | nz | |
a Data are expressed as means ± SE of triplicate experiments. Means in a column (a-c across extraction times) not having a common letter are different (p<0.05). Means in a row (A-C across solvent types) not having a common letter are different (p<0.05). nz: No inhibition zone detected.
Conclusions
In the present study, 50% aqueous solvent extracts from black tea at 2, 8 and 18 h gave markedly higher amounts of total polyphenol and antioxidant activity as compared to absolute ones. In general, among aqueous solvents acetone or DMF was the most efficient solvent with respect to the three parameters measured. In the case of absolute solvent extracts, DMF and methanol were much more efficient than ethanol and acetone. For each parameter, with increasing extraction time different trends were observed, depending on the solvent used. Total polyphenol content of tea extracts had a considerable contribution to their antioxidant activity determined by two different methods. Aqueous solvent extracts from black tea were also observed to possess antibacterial activity depending on the solvent used and bacterium tested.
Experimental
Plant materials and chemicals
Black tea (Camellia sinensis L) was purchased from a local market in Ankara-Turkey. Tea samples were ground to pass a 710µm screen and stored at + 4°C before experiments. DMF, ethanol and methanol were either analytical or HPLC grade from Fluka (BioChemica-Fluka Chemie GmbH, Buchs-Switzerland). Acetone was from Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Folin-Ciocalteu’s reagent was from Merck (Darmstadt-Germany). DPPH and TCA (trichloroacetic acid) were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). All other chemicals were analytical grade and from Merck.
Extraction of tea polyphenols
Black tea extracts were prepared using methanol, ethanol, DMF, acetone and their 50% water diluted solutions as solvents. The ground tea samples (0.2 g) were extracted on a horizontal shaker with the appropriate solvent (10 mL) at 23±2 °C for different times (2, 8 and 18 h). The samples were filtered through Whatman No.1 filter paper to remove rough particles and then centrifuged (10 min, 10,000 × g). The supernatant was stored at –18 °C until analyzed. Each solvent extraction was carried out in triplicate.
Determination of total polyphenols
The amount of total polyphenol was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu method [37]. A gallic acid calibration curve ranging from 0.005 to 0.05 mg/mL was prepared and the results determined from the regression equation of the calibration curve (y= 62.94x-0.67, R2=0.99) were expressed as mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g tea on dry weight basis. Tea extract (1 mL) diluted 10-75 times with de-ionized water (to obtain an absorbance in the range of the prepared calibration curve) was mixed with 3-fold-diluted Folin-Ciocalteu phenol reagent (1 mL). Sodium carbonate solution (2 mL, 35%) was added to the mixture, which was shaken thoroughly and diluted to 6 mL by adding water (2 mL). The mixture is allowed to stand for 30 min and the blue color formed was measured at 700 nm using a double beam spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-VIS 1601).
Antioxidant activity determination by reducing power
The reducing power (PR) of tea extracts was determined according to the Yuan et al. [30] with slight modifications. Tea extract (0.5 mL) was mixed with phosphate buffer (1.25 mL, 0.2 M, pH 6.6) and potassium ferricyanide (1.25 mL, 1%) and the mixture was incubated at 50 °C in a water bath for 20 min. The sample was then cooled and mixed with 10% TCA (1.25 mL). Afterwards, a sample aliquot (1.25 mL) was mixed with distilled water (1.25 mL) and 0.1% ferric chloride (0.25 mL) and then left to react at room temperature for 10 min. Sample absorbance was read at 700 nm. An increase in the absorbance (A) of the reaction mixture indicated an increase in the reducing power.
Antioxidant activity determination by DPPH radical scavenging assay
The antioxidant activity of tea samples was measured by using the DPPH assay [38,39] with some minor modifications. Tea extract (80 μL) diluted 15-fold with distilled water was mixed with an aliquot of 6x10-5 M DPPH radical in methanol (1185 μL). Distilled water was used as a control instead of extract. The reaction mixture was vortex-mixed and let to stand at 25 °C in the dark for 60 min. Absorbance at 517 nm was measured using a spectrophotometer using methanol as blank. Antioxidant activity was expressed as percentage inhibition (% I) of the DPPH radical and was determined by the following equation [40]:

Antibacterial activity
To determine antibacterial activity, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes (ATCC 7644, Oxoid, UK), Escherichia coli O157:H7, Hafnia alvei, Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and Bacillus cereus were used as test bacteria. Y. enterocolitica 0:3 was grown in Tyriptic Soy Broth (Merck, Germany) at 30 ºC for 18-24 h. The other bacteria were grown in the same medium at 37 ºC for 18-24 h. Test microorganisms were obtained from the culture collections of Ankara University, Department of Food Engineering, Ankara, Turkey. Antibacterial activity was determined by the disc diffusion method [41]. A sterilized 6 mm diameter antibacterial susceptibility blank disc (Oxoid, Basinstoke, UK) was loaded with 200 µL (4 mg) of each extract of black tea (20 mg/mL) and left to dry in an open sterile Petri dish in a laminar air flow hood (Forma Scientific, Turkey). The test bacterium was transferred onto a 9 cm diameter Petri dish containing Nutrient Agar (Merck, Germany) using a sterile cotton swab and spread over the whole surface of the medium as a thin film. The inhibition of bacterial growth was evaluated by measuring the diameter of the transparent inhibition zone around each disc. Control disc was loaded with the same solvent and dried using the same method as the treated disc.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS for Windows (ver.10.1) and experimental results were expressed as means ± standard errors of triplicate measurements. Analyses of variance were performed by one-way and two-way ANOVA procedures. Significant differences between means were determined by Duncan’s multiple range test. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05. Correlations between variables were established by regression analysis [42].
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by Research Grant No. 2005-0745-004-HPD from the Scientific Research Projects (BAP) of Ankara University, Turkey.
References
- Gupta, S.; Saha, B.; Giri, A.K. Comparative antimutagenic and anticlastogenic effects of green tea and black tea: a review. Mutat. Res. 2002, 512, 37–65. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, B.; Pramanick, S.; Mukhopadhyoy, S.; Giri, A.K. Inhibition of benzo[a]pyrene induced mutagenicity and genotoxicity multiple test systems. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C. Screening of anticarcinogenic ingredients in tea polyphenols. Cancer Lett. 1997, 114, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Bhaduri, A. Black tea is a powerful chemopreventor of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: comparison with its individual catechin constituents and green tea. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Comm. 2001, 284, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.T.; Lu, Z.; Chou, M.W. Mechanism of inhibition of tannic acid and related compounds on the growth of intestinal bacteria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1998, 36, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Sakanaka, S.; Juneja, L.R.; Taniguchi, M. Antimicrobial effects of green tea polyphenols on thermophilic spore-forming bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 90, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Nagai, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Ema, K.; Kanda, E.; Mitsuda, H. Changes in O-methylated catechins and chemical component contents of “Benifuuki” green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) beverage under various extraction conditions. Food Sci. Technol Res. 2005, 11, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Oguri, A.; Suda, M.; Totsuka, Y.; Sugimura, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Inhibitory effects of antioxidants on formation of heterocyclic amines. Mutat. Res. 1998, 402, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, Y.; Hora, Y. Antimutagenic and anticarcinogenic activity of tea polyphenols. Mutat. Res. 1999, 436, 69–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino, M.; Murakami, K. Interaction of iron with polyphenolic compounds: application to antioxidant characterization. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 257, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wach, A.; Pyrzyńska, K.; Biesaga, M. Quercetin content in some food and herbal samples. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Brenes, M.; Garcia, A.; Garcia, P.; Garrido, A. Rapid and complete extraction of phenols from olive oil and determination by means of a coulometric electrode array system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5178–83. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, P.S.; Chauhan, A.S.; Sadia, G.A.; Rohinishree, Y.S.; Ramteke, R.S. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of various seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed extracts. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapornik, B.; Prosĕk, M.; Wondra, A.G. Comparison of extracts prepared from plant by-products using different solvents and extraction time. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 214–222. [Google Scholar]
- Turkmen, N.; Sari, F.; Velioglu, Y.S. Effects of extraction solvents on concentration and antioxidant activity of black and black mate tea polyphenols determined by ferrous tartrate and Folin-Ciocalteu methods. Food Chem. 2005, 99, 835–841. [Google Scholar]
- Akowuah, G.A.; Ismail, Z.; Norhayati, I.; Sadikun, A. The effects of different extraction solvents of varying polarities on polyphenols of Orthosiphon stamineus and evaluation of the free radical- scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Langley-Evans, S.C. Antioxidant potential of green and black tea determined using the ferric reducing power (FRAP) assay. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 51, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, L.D.; Alves, A.A.; Macedo, D.V.; Kubota, L.T. Peroxidase-based biosensor as a tool for a fast evaluation of antioxidant capacity of tea. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Pinelo, M.; Rubilar, M.; Sineiro, J.; Nunez, M.J. Extraction of antioxidant phenolics from almond hulls (Prunus amygdalus) and pine sawdust (Pinus pinaster). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.M.; Doval, M.M.; Sturla, M.A.; Judis, M.A. Antioxidant properties of polyphenol-containing extract from soybean fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004, 106, 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Provan, G.J.; Helliwell, K. Determination of rosmarinic acid and caffeic acid in aromatic herbs by HPLC. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nepote, V.; Grosso, N.R.; Guzman, C.A. Optimization of extraction of phenolic antioxidants from peanut skins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, U.D.; Shahidi, F.; Naczk, M. Extraction of condensed tannins from beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L.) as affected by different solvents. Food Chem. 2001, 75, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, S.; Apenten, R.K.O. Iron binding characteristics of phenolic compounds: some tentative structure-activity relations. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, A.J.; Mullen, W.; Crozier, A. On-line high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of the antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in green and black tea. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, N.J.; Castelluccio, C.; Tijburg, L.; Rice-Evans, C. The antioxidant properties of the theaflavins and their gallate esters- radical scavengers or metal chelators? FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, E.; Tohyama, N.; Nishimura, M. Comparison of the antioxidant activity of roasted tea with green, oolong, and black teas. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Psarra, E.; Makris, D.P.; Kallithraka, S.; Kefalas, P. Evaluation of the antiradical and reducing properties of selected Greek white wines: correlation with polyphenolic composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadanovic-Brunet, J.M.; Djilas, S.M.; Cetkovic, G.S. Free-radical scavenging activity of wormwood (Artemisia absinthium) extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.V.; Bone, D. E.; Carrington, M.F. Antioxidant activity of dulse (Palmira palmata) extract evaluated in vitro. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 485–494. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Ho, C. Antioxidant activities of buckwheat extracts. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 743–749. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoreky, N.S.; Nakahara, K. Antibacterial activity of extracts from some edible plants commonly consumed in Asia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 80, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Baydar, N.G.; Ozkan, G.; Sagdic, O. Total phenolic contents and antibacterial activities of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) extracts. Food Control 2004, 15, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Polyganum cognatum Meissn extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Selvi, T.; Sakariah, K.K. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of grape (Vitis vinifera) seed extracts. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, G.; Sagdic, O.; Baydar, N.G.; Karamahmutoglu, Z. Antibacterial activities and total phenolic contents of grape pomace extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 807–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Obanda, M.; Owuor, P.O. Flavanol composition and caffeine content of green leaf as quality potential indicators of Kenyan black teas. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Katalinic, V.; Milos, M.; Modun, D.; Music, I.; Boban, M. Antioxidant effectiveness of selected wines in comparison with (+)-catechin. Food Chem. 2004, 80, 593–600. [Google Scholar]
- Atoui, A.K.; Mansouri, A.; Boskou, G.; Kefalas, P. Tea and herbal infusions: their antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, G.C.; Duh, P.D. Scavenging effect of methanolic extracts of peanut hulls on free-radical and active oxygen species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherries, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
