Simple Summary
Retinoblastoma (RB) proteins and E2F transcription factors partner together to regulate the cell cycle in many eukaryotic organisms. In organisms that lack one or both of these proteins, other proteins have taken on the essential function of cell cycle regulation. RB and E2F also have important functions outside of the cell cycle, including DNA repair. This review summarizes the non-canonical functions of RB and E2F in maintaining genome integrity and raises the question of whether such functions have always been present or have evolved more recently.
Abstract
Members of the E2F transcription factor family regulate the expression of genes important for DNA replication and mitotic cell division in most eukaryotes. Homologs of the retinoblastoma (RB) tumor suppressor inhibit the activity of E2F factors, thus controlling cell cycle progression. Organisms such as budding and fission yeast have lost genes encoding E2F and RB, but have gained genes encoding other proteins that take on E2F and RB cell cycle-related functions. In addition to regulating cell proliferation, E2F and RB homologs have non-canonical functions outside the mitotic cell cycle in a variety of eukaryotes. For example, in both mammals and plants, E2F and RB homologs localize to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and directly promote repair by homologous recombination (HR). Here, we discuss the parallels between mammalian E2F1 and RB and their Arabidopsis homologs, E2FA and RB-related (RBR), with respect to their recruitment to sites of DNA damage and how they help recruit repair factors important for DNA end resection. We also explore the question of whether this role in DNA repair is a conserved ancient function of the E2F and RB homologs in the last eukaryotic common ancestor or whether this function evolved independently in mammals and plants.
1. Introduction
The RB tumor suppressor gene (RB1) was originally isolated through positional cloning of a chromosomal segment frequently deleted in the childhood cancer retinoblastoma [1]. RB1 is also commonly mutated in several other cancers, including sarcomas, lung cancers, and triple-negative breast cancers [2]. In many cancers, the RB protein is maintained in an hyperphosphorylated, inactive state by genetic or epigenetic alterations resulting in increased and inappropriate cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity. Overall, RB function is disrupted in most, if not all tumors, and its disruption is considered a hallmark of cancer [3].
An important advance in understanding the molecular function of RB was the discovery that it is a component of complexes containing E2F family members [4]. E2F, a cellular transcription factor, was first characterized as a regulator of the adenovirus E2 gene [5]. Subsequently, E2F1 was isolated as an RB-binding protein capable of activating the expression of both the adenovirus E2 gene and endogenous cellular genes involved in DNA replication and cell cycle progression [5,6,7]. Additional RB and E2F family members were later identified by their sequence similarity in humans, other animals, and plants [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. RB family members are identified by a conserved pocket domain, which binds to E2F proteins. E2F family members are identified by their DNA binding domains, which recognize similar DNA consensus binding sites in the promoters of cell cycle-regulated genes [13,15,16,17]. These E2F target genes encode proteins important for DNA replication and mitosis and are actively repressed when RB is bound to E2F.
In addition to regulating cell proliferation, both animal and plant E2F and RB homologs have important functions outside the mitotic cell cycle, including transcription-independent functions that maintain genome integrity and promote DNA repair. The role of these non-canonical functions of E2F and RB in suppressing tumor development and how the loss of these functions might be therapeutically exploited have been discussed in several recent review articles [18,19,20,21]. This review focuses on another open question in the RB/E2F field: Which shared cell cycle-independent functions form the original core functions of E2F and RB and which functions independently evolved later in multicellular animals and plants?
2. Evolutionary History of E2F and RB Homologs in Eukaryotes
Genomic sequence comparisons have revealed homologs of E2F and RB in all major groups of eukaryotes, indicating that these two genes were components of the original cell cycle network that existed in the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA) approximately 1.6 to 2 billion years ago [22,23,24,25]. The LECA likely had at least three E2F genes: One typical E2F gene, one atypical E2F gene, and one DP (dimerization partner) gene, each with related DNA binding domains [22,24,25]. Typical E2F proteins, such as human E2F1-E2F5, are dynamically regulated through interactions with RB pocket proteins and require dimerization with a DP subunit to efficiently bind DNA (Figure 1A). Atypical E2F family members, such as human E2F7 and E2F8, have two DNA binding domains, do not interact with RB homologs, and do not dimerize with DP proteins. Typical E2F family members generally repress transcription when associated with RB and activate transcription when free from RB. Atypical E2Fs repress the transcription of target genes by mechanisms independent of RB [9,26].
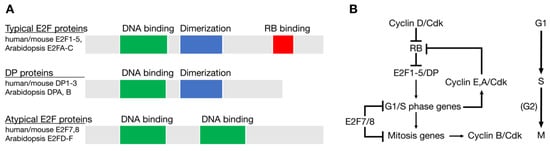
Figure 1.
Conservation of E2F and RB in the Last Common Eukaryotic Ancestor (LECA). (A) Structure of the three types of E2F family member proteins. (B) The cell cycle regulatory network of the LECA based on genomic sequence comparisons across eukaryotic groups.
The LECA cell cycle network also likely included at least one CDK and multiple cyclins that regulated events in different phases of the cell cycle (Figure 1B). Studies from a variety of eukaryotes have demonstrated how RB and E2F homologs link the activity of CDKs with the periodic expression of genes important for cell cycle progression and cell division [13,17,27]. Phosphorylation of RB by D-type cyclin-CDKs initially allows the induction of genes important for the G1/S phase transition, including G1/S phase cyclins, like human CCNE (cyclin E) and CCNA (cyclin A). The accumulation of these cyclins further increases CDK activity in the cell, maintains RB in a hyperphosphorylated state, and allows for the E2F-dependent activation of genes important for DNA replication and mitosis (Figure 1).
Based on the genomic sequences of S. pombe and S. cerevisiae, it was originally thought that all fungi lacked homologs of E2F and RB [22,23]. In these yeasts, functions analogous to those of E2F-RB in regulating the periodic expression of genes important for cell proliferation have been taken on by the SBF/MBF family of transcription factors [23]. Further, just as E2F binding to RB prevents it from activating its target genes, SBF binding to partners such as Whi5 also blocks SBF from activating transcription, and just as RB is targeted by CDKs, Whi5 is also targeted for inactivation by CDKs [28,29]. E2F and SBF/MBF transcription factors also recognize similar DNA sequence motifs in the promoters of cell cycle-regulated genes [24]. Yet, despite recognizing similar motifs, the DNA binding domains of E2F and SBF/MBF transcription factors are unrelated and bind to DNA through different mechanisms [30,31,32]. The DNA binding domains of fungal SBF/MBF factors are most closely related to the KilA-N domain-containing proteins found in a family of DNA viruses that infect both eukaryotes and bacteria [24,33].
Although absent in S. pombe and S. cerevisiae, some fungi have E2F and RB homologs. Zoosporic fungi, which include the flagellated chytrids, have a hybrid cell cycle network in which both E2F-RB and SBF-Whi5 factors regulate the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation [24]. In other types of fungi, such as common bread molds, RB homologs are absent but E2F homologs are present. This suggests a model in which the ancestral fungal progenitor bore homologs of E2F and RB that were lost in specific linages as SBF-Whi5 replaced E2F-RB in the fungal cell cycle network (Figure 2A). This model is supported by phylogenic analyses demonstrating that plants, which have a full complement of E2F and RB genes, diverged from other eukaryotes before fungi diverged from metazoans [23,24].
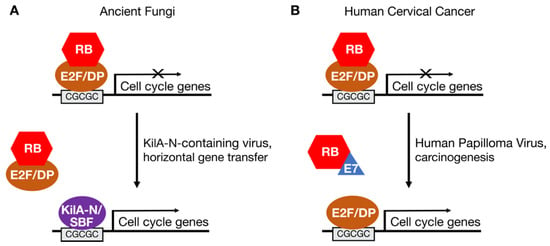
Figure 2.
Hijacking of the RB-E2F pathway by viral proteins in the fungal ancestor and in cervical cancers. (A) SBF transcription factors in fungi may have arisen through a horizontal gene transfer event involving a virus encoding a KilA-N-related protein. (B) Human papilloma virus (HPV) encodes the E7 oncoprotein, which inhibits RB and activates endogenous E2F transcription factors to drive expression of cellular genes needed for viral replication. E7 is one of the viral genes that is integrated into the genome of most cervical cancer cells.
The similarity of yeast SBF/MBF proteins to viral KilA-N proteins has led to the hypothesis that SBF/MBF was introduced into the fungal lineage by virus-mediated horizontal gene transfer [24,33]. This gene transfer event, in which a virus-derived KilA-N/SBF gene became integrated into the genome of the fungal ancestor, may have played a role in the divergence of fungi from metazoans. The functions of viral KilA-N proteins are poorly understood. However, given that SBF/MBF and E2F transcription factors bind similar DNA motifs [24], some viral KilA-N proteins may also bind E2F DNA motifs and activate the expression of E2F target genes in infected cells (Figure 2A). By activating genes important for DNA replication, KilA-N proteins might help create a cellular environment favorable to viral replication in the host [24].
This proposed hijacking of the E2F-RB pathway by a virus-derived SBF-like gene in the fungal ancestor is similar to the mechanism by which the human papilloma virus (HPV) E7 protein hijacks the canonical E2F-RB pathway to cause cervical cancer (Figure 2B). The E7 protein is expressed early after infection and targets RB family members for inactivation [34]. The interaction of E7 with RB releases transcriptionally active E2F to induce the expression of cellular genes important for DNA replication. That is, E7 creates a permissive environment in infected cells allowing HPV to replicate its small, circular genome. On rare occasions, a part of the HPV genome that encodes E7 and another viral oncoprotein, E6, integrates into a host cell genome causing deregulated proliferation and carcinogenesis.
RB homologs in animals and plants actively repress transcription by interacting with and recruiting chromatin modifying enzymes to the promoters of E2F target genes [13,17,27,35,36]. Several of these chromatin modifying enzymes contain a LxCxE amino acid motif that binds to a conserved cleft in the RB pocket domain and allows RB to bind both the chromatin modifiers and E2F factors simultaneously [37]. Cyclin D homologs in animals and plants also have LxCxE motifs that are used to bind and target RB for CDK-mediated phosphorylation. Moreover, the HPV E7 protein, and many other proteins from viruses that infect both animals and plants, also contain LxCxE motifs that are used to disrupt RB-E2F complexes [5,8,38]. Apparently, a number of unrelated DNA viruses have independently evolved LxCxE motif-containing proteins to target RB-E2F complexes as a common strategy for virus replication in both animals and plants [17,39].
4. Homologs of E2F and RB in Mammals and Plants Directly Regulate DNA Double-Strand Break Repair
Another shared function of RB and E2F in mammals and plants is a direct role in promoting DNA DSB repair at sites of damage. E2F1 and RB (in mammals) and E2FA and RBR (in plants) each form foci that overlap with markers of DNA DSBs, such as γH2AX and BRCA1 [90,91,92,93,94,95]. Localization of mammalian E2F1 and RB to DSBs requires phosphorylation of E2F1 by the ATM kinase and phospho-specific binding to a BRCT domain in the TopBP1 protein [91,94,95]. RB participates in this process by stabilizing the interaction between phosphorylated E2F1 and TopBP1 at sites of damage (Figure 3). ATM kinase activity is also required for plant E2FA and RBR to localize to DSBs, but whether E2FA phosphorylation or binding to TopBP1 is involved has not been tested [92,93].
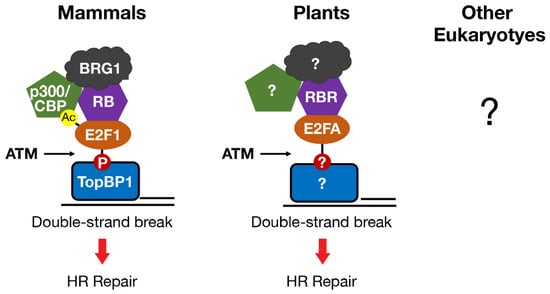
Figure 3.
E2F and RB homologs in mammals and plants localize to DNA double-strand breaks in an ATM-dependent manner to directly promote repair by homologous recombination. In mammals, E2F1 post-translational modifications regulate protein–protein interactions that localize E2F1-RB to double-strand breaks and recruit the chromatin modifying enzymes p300/CBP and BRG1. Whether E2F and RB homologs directly regulate DNA repair by similar mechanisms in other eukaryotes is unknown.
In both mammals and plants, the localization of E2F and RB homologs to DSBs is associated with the promotion of repair by HR and the maintenance of genome integrity [90,91,92,95,96,97,98,99,100]. Some early events in the DNA damage response, such as γH2AX foci formation, are unaffected by the absence of RB or E2F homologs. On the other hand, recruitment of the RAD51 DNA recombinase to sites of damage is significantly impaired in the absence of either RB/RBR or E2F1/E2FA [90,91,92,95]. In mammals, loading of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex at DNA breaks is also compromised when RB or E2F1 are depleted or when E2F1 is mutated [91,99]. Others have shown that RB is also important for the recruitment of CtIP, a protein that works with MRN in the DNA end resection step of DSB repair [98]. Whether RBR and E2FA promote the recruitment of Arabidopsis MRN or CtIP to sites of damage has not been examined, but it would be consistent with impaired RAD51 foci formation in RBR mutant cells [90,92]. This direct role for mammalian and plant homologs of E2F and RB in HR repair extends to meiotic recombination [95,101].
In mammals, the regulation of DNA repair by E2F1 and RB involves remodeling chromatin structure at DNA breaks to enhance access to the repair machinery and to facilitate DNA end processing [95,99]. The mechanism by which E2F1 and RB remodel chromatin at DNA breaks shares similarities with how they regulate gene transcription. In fact, E2F1 and RB recruit some of the same chromatin modifying enzymes, e.g., the histone acetyltransferases p300 and CBP, and the chromatin remodeler BRG1, to both DSBs and gene promoters [60,61,95,99,102,103,104,105,106,107]. Recruitment of p300 and CBP to DSBs involves an interaction between the bromodomains of p300 and CBP and a motif on E2F1 that is acetylated in response to DNA damage (Figure 3) [99]. Recruitment of p300/CBP to DSBs by E2F1 and RB leads to the acetylation of histone H3 at lysines 18 (H3K18ac) and 56 (H3K56ac) in chromatin flanking DSBs. These findings establish a link between E2F1 acetylation and histone acetylation at DSBs and reveal a novel E2F1 reader function for the bromodomains of p300 and CBP.
BRG1 recruitment to DSBs also involves an association with the TopBP1-E2F1-RB complex, likely through the well-established interaction between BRG1 and RB [102,106]. The histone H3 acetylation marks deposited by p300/CBP may also act as docking sites for the bromodomain of BRG1 to facilitate its recruitment and/or function at DSBs. Recent reviews have highlighted how histone acetyltransferases and nucleosome remodeling complexes cooperate to modify chromatin structure at sites of DNA damage to facilitate repair [108,109,110]. In particular, p300/CBP-mediated histone acetylation at sites of damage cooperates with BRG1 to reduce nucleosome density and allow efficient DNA end resection [95,99]. E2F1 and RB also indirectly promote the recruitment of the Tip60 acetyltransferase to induce histone H4 acetylation, another histone mark associated with efficient DSB repair [99,111]. Although it has been proposed that Arabidopsis E2FA and RBR also promote HR repair by remodeling chromatin structure at sites of damage, direct regulation of chromatin structure flanking DSBs by plant E2F and RB homologs has not yet been reported [112].
Recruitment of mammalian E2F1 to DSBs is independent of its DNA binding and transcriptional activation domains, as an N-terminal 83 amino acid fragment of E2F1 is sufficient to localize a fused GFP reporter to DSB foci [94]. In contrast, mutating the E2F1 ATM/ATR-mediated phosphorylation site (serine 31 in humans and serine 29 in mice) abolishes binding to TopBP1 in response to DNA damage and blocks the recruitment of E2F1 to DSBs [94,95]. A mouse knock-in model was developed in which this site of phosphorylation was mutated to alanine (S29A) [113]. Like E2f1-/- knockout mice, E2f1S29A/S29A knock-in mice are viable and appear normal. The expression of E2F target genes, including those involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and DNA repair, are largely unaltered in cells and tissues from E2f1S29A/S29A mice [95,113]. However, the E2F1 S29A mutation prevents recruitment of E2F1, RB, BRG1, and p300/CBP to DSB sites and also impairs the recruitment of repair proteins like NBS1, Mre11, and Rad51 [95,99]. Thus, the E2f1S29A/S29A knock-in mouse model provides an experimental tool that specifically impairs the functions of E2F1, RB, BRG1, and p300/CBP at sites of DNA damage but not their functions in regulating cell cycle progression and other processes. It is notable that E2f1S29A/S29A knock-in mice are not significantly prone to developing spontaneous tumors but they are more prone to ultraviolet radiation-induced skin carcinogenesis [113]. E2f1S29A/S29A mice are also hypersensitive to ionizing radiation (IR) and have reduced fertility, phenotypes often associated with defective HR. Interestingly, loss of E2FA and RBR function in Arabidopsis also causes hypersensitivity to DNA damage and infertility [90,92,93,101].
Another E2f1 knock-in allele, termed 3KR, was developed to prevent acetylation of E2F1 and the interaction between E2F1 and the bromodomains of p300 and CBP [99]. In cells from E2f13KR/3KR mice, E2F1 and RB are still recruited to DSB sites, but p300, CBP and BRG1 are not. Further, E2f13KR/3KR cells display DNA repair defects like those observed in other E2f1 mutant cells [99]. Finally, like E2f1−/− knockout and E2f1S29A/S29A knock-in mice, E2f13KR/3KR knock-in mice are also hypersensitive to IR, indicating that the recruitment of chromatin modifying enzymes to sites of DSBs is a critical function of E2F1 and RB [99].
Given the similarities between mammalian and plant E2F and RB homologs in their abilities to localize to sites of DSBs and to directly promote efficient HR repair, it is possible that this transcription-independent function of E2F and RB was present in the LECA, before the divergence of plants and animals. Nonetheless, RB and E2F homologs have been demonstrated to localize to DNA damage foci only in humans, mice, Arabidopsis, and tobacco [90,91,92,93,94,95]. The N-terminal motif in E2F1 that is phosphorylated by ATM and is critical for E2F1 and RB recruitment to DSBs (SSQ), is conserved in other placental mammals but not in marsupials, monotremes, other vertebrates, or model invertebrates (Figure 4). This suggests that either E2F and RB homologs are not recruited to DSBs in animals outside the placental mammals or that E2F and RB homologs are recruited to DSBs in other eukaryotes through a different mechanism.

Figure 4.
The E2F1 protein N-terminal motif phosphorylated by ATM and required for E2F1 and RB location to DNA damage is not conserved beyond placental mammals.
Interestingly, E2FA in Arabidopsis, like E2F1 in placental animals, contains an “SSQ” motif in its N-terminus. However, whether this motif is phosphorylated by ATM or is involved in the recruitment of E2FA and RBR to sites of DNA damage in Arabidopsis is unknown. Regardless, the lack of conservation of this phosphorylation motif in other eukaryotes suggests that the ability of E2F and RB homologs to localize to sites of DNA damage in placental mammals and plants evolved independently. If so, then this independently acquired trait allowing E2F and RB to directly promote DSB repair is an example of convergent evolution at the molecular level.
5. Conclusions
RB and E2F are fundamental components of the cell cycle machinery in most eukaryotes. In both animals and plants, RB and E2F homologs have evolved additional, non-canonical functions beyond cell cycle regulation. Dysregulation of the RB-E2F axis is a hallmark of human cancer and occurs through multiple mechanisms. In some cancers, the RB1 gene is deleted or mutated such that both the canonical and non-canonical functions of RB are lost. These functions include a direct role for RB, in partnership with E2F1, in repairing DNA DSBs in the context of chromatin. Further research is needed to understand how loss of this repair function and other non-canonical functions contribute to the progression of cancers that have lost RB. Yet, despite these gaps in understanding, the finding that RB is important for HR repair reveals a potential vulnerability: Tumors lacking RB might be exploited therapeutically by treatments similar to those used for other cancers with impaired HR repair (e.g., PARP inhibitors) [95,98,114]. For cancers lacking RB1 mutations, although the canonical functions of RB might still be disrupted through abnormal CDK activity or association with viral oncoproteins, intact non-canonical functions of RB in DNA repair might foster resistance to conventional cancer therapies. For example, RB is recruited to DSB sites and contributes to efficient DNA repair in the human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS, which expresses a normal RB protein but lacks the p16 CDK inhibitor [95,99]. Consequently, exploiting this repair mechanism by inhibiting the function of RB in HR repair might sensitize RB-positive tumors to DNA DSB-inducing therapies. Indeed, blocking E2F1 and RB recruitment to DNA breaks may contribute to the efficacy of ATM inhibitors currently being investigated in the clinic [95,115]. Another possible approach for disrupting RB function in DSB repair would be to prevent the E2F1- and RB-dependent recruitment of p300 and CBP to sites of damage, using inhibitors of the bromodomains of p300 and CBP [99]. Continuing to refine our understanding of the non-canonical functions of RB and E2F family members may reveal additional approaches for the treatment of both RB positive and negative cancers. Given that many of these non-canonical functions of RB and E2F are present across Eukarya, studies in appropriate model organisms should play an important role in these investigative efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G.J., investigation, S.M. writing—original draft preparation, B.K.D. and D.G.J. writing—review and editing, S.M., B.K.D. and D.G.J., funding acquisition, D.G.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research described herein was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute (CA214723 to D.G.J. and Cancer Center Support Grant CA016672).
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Rebecca Deen for help with manuscript preparation and Joi Holcomb for research graphics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Friend, S.H.; Bernards, R.; Rogelj, S.; Weinberg, R.A.; Rapaport, J.M.; Albert, D.M.; Dryja, T.P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature 1986, 323, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, D.L.; Sage, J. Cellular mechanisms of tumour suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellappan, S.P.; Hiebert, S.; Mudryj, M.; Horowitz, J.M.; Nevins, J.R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell 1991, 65, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, J.R. E2F: A link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science 1992, 258, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helin, K.; Lees, J.A.; Vidal, M.; Dyson, N.; Harlow, E.; Fattaey, A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell 1992, 70, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelin, W.G., Jr.; Krek, W.; Sellers, W.R.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Ajchenbaum, F.; Fuchs, C.S.; Chittenden, T.; Li, Y.; Farnham, P.J.; Blanar, M.A.; et al. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell 1992, 70, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafi, G.; Burnett, R.J.; Helentjaris, T.; Larkins, B.A.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Sellers, W.R.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. A maize cDNA encoding a member of the retinoblastoma protein family: Involvement in endoreduplication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8962–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammens, T.; Li, J.; Leone, G.; De Veylder, L. Atypical E2Fs: New players in the E2F transcription factor family. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariconti, L.; Pellegrini, B.; Cantoni, R.; Stevens, R.; Bergounioux, C.; Cella, R.; Albani, D. The E2F family of transcription factors from Arabidopsis thaliana. Novel and conserved components of the retinoblastoma/E2F pathway in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9911–9919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, M.; Ito, M.; Uemukai, K.; Maeda, Y.; Nakagami, H.; Shinmyo, A. Isolation and characterization of the E2F-like gene in plants. FEBS Lett. 1999, 460, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, J.M.; Lees, J.A. Sibling rivalry in the E2F family. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Heuvel, S.; Dyson, N.J. Conserved functions of the pRB and E2F families. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Vidal, M.; Xie, J.E.; Dyson, N. RBF, a novel RB-related gene that regulates E2F activity and interacts with cyclin E in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jager, S.M.; Menges, M.; Bauer, U.M.; Murra, J.A. Arabidopsis E2F1 binds a sequence present in the promoter of S-phase-regulated gene AtCDC6 and is a member of a multigene family with differential activities. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 47, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.S.; Liu, J.; Xie, Z.; O’Neill, D.; Dotson, S. Arabidopsis E2Fa plays a bimodal role in regulating cell division and cell growth. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zluhan-Martinez, E.; Perez-Koldenkova, V.; Ponce-Castaneda, M.V.; Sanchez, M.P.; Garcia-Ponce, B.; Miguel-Hernandez, S.; Alvarez-Buylla, E.R.; Garay-Arroyo, A. Beyond What Your Retina Can See: Similarities of Retinoblastoma Function between Plants and Animals, from Developmental Processes to Epigenetic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, L.N.; Leone, G. The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Pruitt, S.C.; Hershberger, P.A.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Goodrich, D.W. Cell Cycle and Beyond: Exploiting New RB1 Controlled Mechanisms for Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez-Cruz, R.; Johnson, D.G. The Retinoblastoma (RB) Tumor Suppressor: Pushing Back against Genome Instability on Multiple Fronts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, F.A.; Goodrich, D.W.; Sage, J.; Dyson, N.J. Non-canonical functions of the RB protein in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Peng, B.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, K.; Yang, X.; Yu, L. The ancient function of RB-E2F pathway: Insights from its evolutionary history. Biol. Direct 2010, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, F.R.; Buchler, N.E.; Skotheim, J.M. Evolution of networks and sequences in eukaryotic cell cycle control. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 3532–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, E.M.; Turner, J.J.; Gordan, R.; Skotheim, J.M.; Buchler, N.E. Punctuated evolution and transitional hybrid network in an ancestral cell cycle of fungi. eLife 2016, 5, e09492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauber, R.; Cabreira, C.; de Freitas, L.B.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C.; Margis-Pinheiro, M. The evolutionary history of the E2F and DEL genes in Viridiplantae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 99, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ran, C.; Li, E.; Gordon, F.; Comstock, G.; Siddiqui, H.; Cleghorn, W.; Chen, H.Z.; Kornacker, K.; Liu, C.G.; et al. Synergistic function of E2F7 and E2F8 is essential for cell survival and embryonic development. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvoyes, B.; Gutierrez, C. Roles of plant retinoblastoma protein: Cell cycle and beyond. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Nishikawa, J.L.; Tang, X.; Millman, J.S.; Schub, O.; Breitkreuz, K.; Dewar, D.; Rupes, I.; Andrews, B.; Tyers, M. CDK activity antagonizes Whi5, an inhibitor of G1/S transcription in yeast. Cell 2004, 117, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, R.A.; McDonald, W.H.; Kalashnikova, T.I.; Yates, J., 3rd; Wittenberg, C. Cln3 activates G1-specific transcription via phosphorylation of the SBF bound repressor Whi5. Cell 2004, 117, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, I.A.; Treiber, M.K.; Olivi, L.; Smerdon, S.J. The X-ray structure of the DNA-binding domain from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell-cycle transcription factor Mbp1 at 2.1 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.M.; Koch, C.; Liu, Y.; Horton, J.R.; Knapp, D.; Nasmyth, K.; Cheng, X. Crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of Mbp1, a transcription factor important in cell-cycle control of DNA synthesis. Structure 1997, 5, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Fraenkel, E.; Pabo, C.O.; Pavletich, N.P. Structural basis of DNA recognition by the heterodimeric cell cycle transcription factor E2F-DP. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, L.M.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. Extensive domain shuffling in transcription regulators of DNA viruses and implications for the origin of fungal APSES transcription factors. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, RESEARCH0012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, K.; Howley, P.M. Human papillomavirus immortalization and transformation functions. Virus Res. 2002, 89, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, F.; Fazeli, Y.; Khuu, M.; Salcido, K.; Singh, S.; Benavente, C.A. Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein roles in epigenetic regulation. Cancers 2020, 12, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, A.; Gruissem, W. Arabidopsis RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED and Polycomb group proteins: Cooperation during plant cell differentiation and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.J.; Dyson, N.J. Retinoblastoma protein partners. Adv. Cancer Res. 2001, 82, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ach, R.A.; Durfee, T.; Miller, A.B.; Taranto, P.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L.; Zambryski, P.C.; Gruissem, W. RRB1 and RRB2 encode maize retinoblastoma-related proteins that interact with a plant D-type cyclin and geminivirus replication protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevins, J.R. Cell cycle targets of the DNA tumor viruses. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1994, 4, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.O.; Davidson, J.M.; Duronio, R.J. Endoreplication: Polyploidy with purpose. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2461–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Z.; Ouseph, M.M.; Li, J.; Pecot, T.; Chokshi, V.; Kent, L.; Bae, S.; Byrne, M.; Duran, C.; Comstock, G.; et al. Canonical and atypical E2Fs regulate the mammalian endocycle. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, M.J.; Bronson, R.T.; Harlow, E.; Dyson, N.J.; Yamasaki, L. Dp1 is required for extra-embryonic development. Development 2003, 130, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magyar, Z.; Horvath, B.; Khan, S.; Mohammed, B.; Henriques, R.; De Veylder, L.; Bako, L.; Scheres, B.; Bogre, L. Arabidopsis E2FA stimulates proliferation and endocycle separately through RBR-bound and RBR-free complexes. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, J.; Roy, R. The lin-35/Rb and RNAi pathways cooperate to regulate a key cell cycle transition in C. elegans. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.A.; Ahn, J.W.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, W.T.; Pai, H.S. Retinoblastoma protein regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and endoreduplication in plants. Plant J. 2005, 42, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabelli, P.A.; Liu, Y.; Dante, R.A.; Lizarraga, L.E.; Nguyen, H.N.; Brown, S.W.; Klingler, J.P.; Yu, J.; LaBrant, E.; Layton, T.M.; et al. Control of cell proliferation, endoreduplication, cell size, and cell death by the retinoblastoma-related pathway in maize endosperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1827–E1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J.; Du, W. Critical role of active repression by E2F and Rb proteins in endoreplication during Drosophila development. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3865–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvoyes, B.; de Mendoza, A.; Ruiz-Trillo, I.; Gutierrez, C. Novel roles of plant RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED (RBR) protein in cell proliferation and asymmetric cell division. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlander, J.; Chen, X.B.; Bosco, G. The N-terminal domain of the Drosophila retinoblastoma protein Rbf1 interacts with ORC and associates with chromatin in an E2F independent manner. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, G.; Du, W.; Orr-Weaver, T.L. DNA replication control through interaction of E2F-RB and the origin recognition complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, L.M.; Vandenbosch, R.; Pakenham, C.A.; Andrusiak, M.G.; Nguyen, A.P.; McClellan, K.A.; Svoboda, D.S.; Lagace, D.C.; Park, D.S.; Leone, G.; et al. Opposing regulation of Sox2 by cell-cycle effectors E2f3a and E2f3b in neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareta, M.S.; Gorges, L.L.; Hafeez, S.; Benayoun, B.A.; Marro, S.; Zmoos, A.F.; Cecchini, M.J.; Spacek, D.; Batista, L.F.; O’Brien, M.; et al. Inhibition of pluripotency networks by the Rb tumor suppressor restricts reprogramming and tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildwater, M.; Campilho, A.; Perez-Perez, J.M.; Heidstra, R.; Blilou, I.; Korthout, H.; Chatterjee, J.; Mariconti, L.; Gruissem, W.; Scheres, B. The RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED gene regulates stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis roots. Cell 2005, 123, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzat, R.; Borghi, L.; Gruissem, W. Emerging roles of RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED proteins in evolution and plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, P.L.; Wu, L.; de Bruin, A.; Chong, J.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Dureska, G.; Sites, E.; Pan, T.; Sharma, A.; Huang, K. Rb is critical in a mammalian tissue stem cell population. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Tsai, S.Y.; Leone, G. Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classon, M.; Dyson, N. p107 and p130: Versatile proteins with interesting pockets. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 264, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calo, E.; Quintero-Estades, J.A.; Danielian, P.S.; Nedelcu, S.; Berman, S.D.; Lees, J.A. Rb regulates fate choice and lineage commitment in vivo. Nature 2010, 466, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.R.; Maandag, E.R.; van Roon, M.; van der Lugt, N.M.; van der Valk, M.; Hooper, M.L.; Berns, A.; te Riele, H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature 1992, 359, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, S.; Beck, G.R., Jr.; Moran, E. Transcriptional activation by pRB and its coordination with SWI/SNF recruitment. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8282–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, S.; Xu, F.; Moran, E. Cooperative activation of tissue-specific genes by pRB and E2F1. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goupille, O.; Penglong, T.; Kadri, Z.; Granger-Locatelli, M.; Denis, R.; Luquet, S.; Badoual, C.; Fucharoen, S.; Maouche-Chretien, L.; Leboulch, P.; et al. The LXCXE Retinoblastoma Protein-Binding Motif of FOG-2 Regulates Adipogenesis. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3524–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, T.; Fazeli, A.; Schmitt, E.M.; Bronson, R.T.; Goodell, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature 1992, 359, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, Y.C.; Lai, C.C.; Herrup, K.; Lee, W.H.; Bradley, A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature 1992, 359, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Pakenham, C.A.; Dugal-Tessier, D.; Ruzhynsky, V.; Bae, S.; Tsai, S.Y.; Leone, G.; Slack, R.S.; Blais, A. Tissue-specific targeting of cell fate regulatory genes by E2f factors. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leviczky, T.; Molnar, E.; Papdi, C.; Oszi, E.; Horvath, G.V.; Vizler, C.; Nagy, V.; Pauk, J.; Bogre, L.; Magyar, Z. E2FA and E2FB transcription factors coordinate cell proliferation with seed maturation. Development 2019, 146, dev179333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, Z.; Shimizu, R.; Ohneda, O.; Maouche-Chretien, L.; Gisselbrecht, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Romeo, P.H.; Leboulch, P.; Chretien, S. Direct binding of pRb/E2F-2 to GATA-1 regulates maturation and terminal cell division during erythropoiesis. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilli, S.; Perez-Perez, J.M.; Di Mambro, R.; Llavata Peris, C.; Diaz-Trivino, S.; Del Bianco, M.; Pierdonati, E.; Moubayidin, L.; Cruz-Ramirez, A.; Costantino, P.; et al. RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED protein stimulates cell differentiation in the Arabidopsis root meristem by interacting with cytokinin signaling. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4469–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, D.; Heese, M.; Chen, P.; Harashima, H.; Roudier, F.; Gruttner, C.; Schnittger, A. Genome-wide identification of RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED 1 binding sites in Arabidopsis reveals novel DNA damage regulators. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, C.A.; Marshall, A.E.; Passos, D.T.; White, C.R.; Kim, S.J.; Cecchini, M.J.; Ferwati, S.; MacDonald, W.A.; Howlett, C.J.; Welch, I.D.; et al. An RB-EZH2 Complex Mediates Silencing of Repetitive DNA Sequences. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, M.J.; Dick, F.A. The biochemical basis of CDK phosphorylation-independent regulation of E2F1 by the retinoblastoma protein. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, F.A.; Dyson, N. pRB contains an E2F1-specific binding domain that allows E2F1-induced apoptosis to be regulated separately from other E2F activities. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Durango, D.E.; Ramos, K.A.; Bojang, P.; Ruiz, L.; Ramos, I.N.; Ramos, K.S. LINE-1 silencing by retinoblastoma proteins is effected through the nucleosomal and remodeling deacetylase multiprotein complex. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henaff, E.; Vives, C.; Desvoyes, B.; Chaurasia, A.; Payet, J.; Gutierrez, C.; Casacuberta, J.M. Extensive amplification of the E2F transcription factor binding sites by transposons during evolution of Brassica species. Plant J. 2014, 77, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Jiang, D.; Yang, W.; Jacob, Y.; Michaels, S.D.; He, Y. Arabidopsis homologs of retinoblastoma-associated protein 46/48 associate with a histone deacetylase to act redundantly in chromatin silencing. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Pritham, E.J. DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.N.; Feschotte, C. A Field Guide to Eukaryotic Transposable Elements. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladden, A.B.; Diehl, J.A. The cyclin D1-dependent kinase associates with the pre-replication complex and modulates RB.MCM7 binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9754–9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Maldonado, R.; Paolinelli, R.; Galbiati, L.; Giadrossi, S.; Giacca, M. Interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with Orc1 and its recruitment to human origins of DNA replication. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Winter, S.L.; Alexandrow, M.G. Cell cycle arrest by transforming growth factor beta1 near G1/S is mediated by acute abrogation of prereplication complex activation involving an Rb-MCM interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, D.; Yang, H.; Martelli, F.; Hofmann, F.; ElShamy, W.M.; Ganesan, S.; Scully, R.; Livingston, D.M. Active localization of the retinoblastoma protein in chromatin and its response to S phase DNA damage. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgendorf, K.I.; Leshchiner, E.S.; Nedelcu, S.; Maynard, M.A.; Calo, E.; Ianari, A.; Walensky, L.D.; Lees, J.A. The retinoblastoma protein induces apoptosis directly at the mitochondria. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coschi, C.H.; Ishak, C.A.; Gallo, D.; Marshall, A.; Talluri, S.; Wang, J.; Cecchini, M.J.; Martens, A.L.; Percy, V.; Welch, I.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of an RB-E2F1-Condensin II complex leads to aberrant replication and aneuploidy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longworth, M.S.; Herr, A.; Ji, J.Y.; Dyson, N.J. RBF1 promotes chromatin condensation through a conserved interaction with the Condensin II protein dCAP-D3. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, A.L.; Longworth, M.S.; Dyson, N.J. Loss of pRB causes centromere dysfunction and chromosomal instability. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, C.A.; Coschi, C.H.; Roes, M.V.; Dick, F.A. Disruption of CDK-resistant chromatin association by pRB causes DNA damage, mitotic errors, and reduces Condensin II recruitment. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonzalo, S.; Garcia-Cao, M.; Fraga, M.F.; Schotta, G.; Peters, A.H.; Cotter, S.E.; Eguia, R.; Dean, D.C.; Esteller, M.; Jenuwein, T.; et al. Role of the RB1 family in stabilizing histone methylation at constitutive heterochromatin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Fox, S.R.; Gunawardena, R.W.; Knudsen, E.S. Loss of RB compromises specific heterochromatin modifications and modulates HP1alpha dynamics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, C.E.; Francis, S.M.; Martens, A.L.; Julian, L.M.; Seifried, L.A.; Erdmann, N.; Binne, U.K.; Harrington, L.; Sicinski, P.; Berube, N.G.; et al. The retinoblastoma protein regulates pericentric heterochromatin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3659–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, S.; Harashima, H.; Chen, P.; Heese, M.; Bouyer, D.; Sofroni, K.; Schnittger, A. The retinoblastoma homolog RBR1 mediates localization of the repair protein RAD51 to DNA lesions in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1279–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, F.; Weaks, R.L.; Biswas, A.K.; Guo, R.; Li, Y.; Johnson, D.G. E2F1 promotes the recruitment of DNA repair factors to sites of DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, B.M.; Kourova, H.; Nagy, S.; Nemeth, E.; Magyar, Z.; Papdi, C.; Ahmad, Z.; Sanchez-Perez, G.F.; Perilli, S.; Blilou, I.; et al. Arabidopsis RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED directly regulates DNA damage responses through functions beyond cell cycle control. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Smetana, O.; Sanchez-Calderon, L.; Lincker, F.; Genestier, J.; Schmit, A.C.; Houlne, G.; Chaboute, M.E. Plant gammaH2AX foci are required for proper DNA DSB repair responses and colocalize with E2F factors. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lin, F.T.; Ruppert, J.M.; Lin, W.C. Regulation of E2F1 by BRCT domain-containing protein TopBP1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 3287–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez-Cruz, R.; Manickavinayaham, S.; Biswas, A.K.; Clary, R.W.; Premkumar, T.; Cole, F.; Johnson, D.G. RB localizes to DNA double-strand breaks and promotes DNA end resection and homologous recombination through the recruitment of BRG1. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2500–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.H.; Kim, K.P. E2F1 facilitates DNA break repair by localizing to break sites and enhancing the expression of homologous recombination factors. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentric, N.; Masoud, K.; Journot, R.P.; Cognat, V.; Chaboute, M.E.; Noir, S.; Genschik, P. The F-Box-Like Protein FBL17 Is a Regulator of DNA-Damage Response and Colocalizes with RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED1 at DNA Lesion Sites. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yam, J.C.; Tham, C.C.; Pang, C.P.; Chu, W.K. RB Regulates DNA Double Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice by Mediating CtIP Dependent End Resection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickavinayaham, S.; Velez-Cruz, R.; Biswas, A.K.; Bedford, E.; Klein, B.J.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Liu, B.; Bedford, M.T.; Johnson, D.G. E2F1 acetylation directs p300/CBP-mediated histone acetylation at DNA double-strand breaks to facilitate repair. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Goodrich, D.W. The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein is required for efficient processing and repair of trapped topoisomerase II-DNA-cleavable complexes. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8105–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Higgins, J.D.; Hui, J.T.; Li, J.; Franklin, F.C.; Berger, F. Retinoblastoma protein is essential for early meiotic events in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunaief, J.L.; Strober, B.E.; Guha, S.; Khavari, P.A.; Alin, K.; Luban, J.; Begemann, M.; Crabtree, G.R.; Goff, S.P. The retinoblastoma protein and BRG1 form a complex and cooperate to induce cell cycle arrest. Cell 1994, 79, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, C.J.; Pearson, A.; Malinowski, E.; Bartley, S.M.; Greenblatt, J.; Farnham, P.J. Activation of the murine dihydrofolate reductase promoter by E2F1. A requirement for CBP recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15883–15891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, H.; Kohno, T. CBP and p300 histone acetyltransferases contribute to homologous recombination by transcriptionally activating the BRCA1 and RAD51 genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, J.; Ploszaj, T.; Pulaski, L.; Robaszkiewicz, A. EP300-HDAC1-SWI/SNF functional unit defines transcription of some DNA repair enzymes during differentiation of human macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobeck, M.W.; Knudsen, K.E.; Fribourg, A.F.; DeCristofaro, M.F.; Weissman, B.E.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Knudsen, E.S. BRG-1 is required for RB-mediated cell cycle arrest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7748–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouche, D.; Cook, A.; Kouzarides, T. The CBP co-activator stimulates E2F1/DP1 activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 4139–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, L.Y.; Gong, F.; Miller, K.M. Bromodomain proteins: Repairing DNA damage within chromatin. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrod, A.; Lane, K.A.; Downs, J.A. The role of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex in the response to DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair 2020, 93, 102919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Miller, K.M. Preserving genome integrity and function: The DNA damage response and histone modifications. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 54, 208–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, R.; Loizou, J.I.; Yang, Y.G.; Cuenin, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Herceg, Z. Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H. Chromatin Remodeling and Epigenetic Regulation in Plant DNA Damage Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.K.; Mitchell, D.L.; Johnson, D.G. E2F1 Responds to Ultraviolet Radiation by Directly Stimulating DNA Repair and Suppressing Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3369–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.E.; Roes, M.V.; Passos, D.T.; DeWeerd, M.C.; Chaikovsky, A.C.; Sage, J.; Howlett, C.J.; Dick, F.A. RB1 deletion in retinoblastoma protein pathway-disrupted cells results in DNA damage and cancer progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00105-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavin, M.F.; Yeo, A.J. Clinical potential of ATM inhibitors. Mutat. Res. 2020, 821, 111695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).