Abstract
Correct in vivo diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) helps to avoid administration of disease-modifying treatments in non-AD patients, and allows the possible use of such treatments in clinically atypical AD patients. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers offer a tool for AD diagnosis. A reduction in CSF β-amyloid (marker of amyloid plaque burden), although compatible with Alzheimer’s pathological change, may also be observed in other dementing disorders, including vascular cognitive disorders due to subcortical small-vessel disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Thus, for the diagnosis of AD, an abnormal result of CSF β-amyloid may not be sufficient, and an increase in phospho-tau (marker of tangle pathology) is also required in order to confirm AD diagnosis in patients with a typical amnestic presentation and reveal underlying AD in patients with atypical or mixed and diagnostically confusing clinical presentations.
1. Introduction
Besides atrophy and neuronal as well as synaptic loss, there are two pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD): extracellular accumulation of amyloid beta peptide in the form of amyloid plaques and hyperphosphorylation of tau protein which polymerizes in the form of paired helical filaments, the key component of intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles []. From the clinical point of view, AD has long been considered as synonymous with amnestic dementia of the hippocampal type [], and in such typical cases, the accuracy of clinical diagnosis in specialized centers may approach or exceed 90% []. However, with time it became evident that AD may present with non-amnestic phenotypes [], including the frontal type of dementia [], posterior cortical atrophy [], primary progressive aphasia [] and even corticobasal syndrome []. Cases of AD mixed with cerebrovascular disease [], Lewy body pathology [] and normal-pressure hydrocephalus [] are not uncommon, and these additional pathologies may affect the clinical presentation. Furthermore, some patients with AD may present at the pre-dementia stage of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) []. In such atypical or mixed cases, in early disease, in the community and in the presence of comorbidities, diagnostic accuracy decreases []. In ~1/3 of patients clinically diagnosed with AD, the final diagnosis may be different [], whilst when a demented patient is considered not to suffer with AD, there is still a 39% chance of (co)occurrence of AD in an autopsy []. However, a correct diagnosis is needed in order to inform patients and relatives for the prognosis and for making the correct therapeutic decisions [].
On June 2021, the anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody aducanumab [] was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the USA [] for the treatment of MCI or mild dementia due to AD []. The approval was based on the ability of the antibody to effectively remove brain amyloid, according to the initial PRIME study [] (surrogate endpoint). From the clinical point of view, statistically significant cognitive benefits were observed in the high-dose branch of one study (EMERGE), while in a second study (ENGAGE) the results were not significant []. However, in a post hoc analysis of the latter study, data from patients receiving a high-dose treatment supported the positive findings of EMERGE []. Overall, the rate of cognitive decline seems to be reduced by ~23% [], but questions concerning the drug’s efficacy and safety have been raised [,]. Recognizing this residual uncertainty, the FDA approved aducanumab under the accelerated approval pathway [], in order to introduce a new treatment for such a devastating disease after more than 20 years. However, despite the discussion and the debates triggered [], current recommendations suggest that if such a disease-modifying treatment is to be administered, the diagnosis of AD should not be based solely on clinical criteria, but a more objective tool, including the “signature pattern” or “profile” of AD, which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarker testing should confirm [].
2. The CSF Alzheimer’s Disease Profile
During the last two decades, various CSF biomarkers have been developed for the (differential) diagnosis of AD [,]. With sensitivities and specificities approaching or exceeding 90%, they have been incorporated into various guidelines and diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease [,,]. They include amyloid beta peptide with 42 amino acids (Aβ42), which is a marker of amyloid pathology, inversely correlated with the amyloid plaque burden [], phospho-tau, mainly phosphorylated at a threonine residue at position 181 (τP-181), which is a marker of tau protein hyperphosphorylation as well as tangle formation [] and total tau protein (τT), which is considered as a non-specific marker of neuronal/axonal degeneration []. Amyloid beta peptide with 40 amino acids (Aβ40) can also be measured in the CSF, and it is useful in the form of the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, which seems to perform diagnostically better than Aβ42 alone []. These biomarkers may be helpful in the recognition and/or differential diagnosis of AD in patients with a typical amnestic presentation as well as in cases with atypical or mixed presentations [,,,,,].
Initially it was suggested that the AD CSF biomarker profile is characterized by low Aβ42 (or low Aβ42/Aβ40) and an increase in either τP-181 or τT []. Since typically in AD both τP-181 and τT are increased, this “either” usually does not create diagnostic confusion. However, in the occasional patient with low Aβ42 (indicating the presence of amyloid plaque load) and increased τT (indicating neuronal/axonal damage of any cause), but normal τP-181 (suggestive of absence of tangle formation), diagnostic doubt arises. Thus, it has been suggested that in addition to low Aβ42 both τP-181 and τT should be increased in order to fulfill the AD profile [].
More recently, the so-called AT(N) system (A for amyloid load, T for tau accumulation and N for neurodegeneration) [] has been proposed by the National Institute of Aging and Alzheimer’s Association (NIA–AA) Research Framework group, in which AD is viewed as a biological process, irrespective of the type (amnestic vs non-amnestic presentations), severity (MCI vs dementia) or even absence of symptoms (pre-clinical stage) at a certain time point []. In this context, the presence of reduced Aβ42 (or Aβ42/Aβ40) and increased τP-181 is considered as compatible with an AD diagnosis, since this profile indicates the presence of both amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, whilst τT may be either increased or normal. The presence of atrophy in magnetic resonance imaging may also serve as a marker of nonspecific neurodegeneration, replacing τΤ. Thus, a profile of A+T+(N+) or A+T+(N−) (+ for positive/abnormal test, − for negative/normal test) is compatible with AD [] (Figure 1).
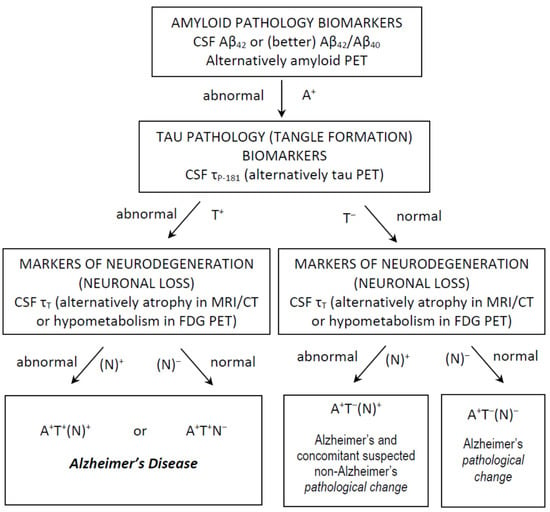
Figure 1.
Use of CSF classical biomarkers and the AT(N) classification system in everyday clinical practice, for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and Alzheimer’s pathological change. Other profiles are not compatible with Alzheimer’s continuum and are not shown.
3. Other Profiles
In cases without amyloidosis in the CSF, presenting the A−T+(N*) profile (* for either + or −), the AD diagnosis is not confirmed and this profile is usually compatible with one of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration pathologies (especially that of tau) []. On the other hand, the A+T−(N*) profile has extended differential diagnosis.
In Alzheimer’s disease, CSF biomarker changes may become evident 10‒20 years prior to the symptomatic stage [,,]. Usually (but not always), the first biomarker to become abnormal is Aβ42, which is reduced early in the asymptomatic stage, followed by an increase in τP-181, and it seems that most (but not all) AD patients enter the stage of MCI with both of the above biomarkers having become abnormal (although τP-181 may not have reached the maximally abnormal level yet) [,]. Thus, in AD, A+T−(N−) is usually observed in the asymptomatic stage []. However, the biochemical/pathological and clinical progression of AD is gradual and sometimes overlapping, and some patients with the A+T−(N−) profile may experience subtle cognitive symptoms or even MCI []. This profile is considered extremely rare in the mild dementia stage of AD []. Thus, in AD the A+T−(N−) profile is practically always observed in the pre-dementia and, usually, at the preclinical stages; since neurodegenerative changes remain limited, atrophy and increased τΤ are usually not evident yet. The above profile in the AT(N) system belongs to the so-called pathological change in Alzheimer’s, and is considered as a part of the Alzheimer’s continuum, but not synonymous to AD [].
On the other hand, the A+T−(N+) profile points to significant neurodegeneration and, since there is no indication of tangle formation, another (non-AD) pathology is suspected to be present together with amyloid pathology. A typical neurodegenerative disorder with this profile may be dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) []. However, is the A+T−N* profile always indicative of pathological change in Alzheimer’s (amyloid plaques)? In subcortical small-vessel disease (SSVD), CSF amyloid reduction is not uncommon [,,], and the same holds true for some patients with normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) [,] and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease [], whilst amyloid pathology may be present in a small percentage of patients with corticobasal degeneration []. One could argue that a concomitant AD-type pathology is not uncommon in SSVD [] and NPH []; however, low Aβ42 has also been observed in cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL), where the co-occurrence of AD pathology is extremely rare []. Thus, the A+T−N* profile may not always be synonymous with amyloid pathology.
4. Limitations
There are some limitations in classical CSF biomarker determinations. Test results are affected by preanalytical factors, including CSF sampling and storage in addition to internationally accepted guidelines have been formulated for this reason []. In addition, international quality control programs have been organized in order to optimize analytical performance [], and international projects have been launched with the aim of, among others, identifying and controlling for confounding factors, improving the methodologies used and harmonizing the levels of biomarkers []. Experience gained from such projects and strict adherence to guidelines may decrease measurement error []. However, there is still a significant intra- and inter-laboratory variability [,] and each laboratory should have its own cut-off values []. Diagnostically gray zones also exist and, if added to the possible measurement error, may lead to a variability of ±25%, especially important for the cut-off values [].
Discordant biomarker results have been observed in different reference laboratories, especially for Aβ42, and various factors may be responsible, including the APOE ε4 allele []. The Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, which performs better than Aβ42 alone [,] may reduce discordance to some extent [], but there is still some concern about inconsistent results, especially in the AT(N) system [].
Classical CSF biomarkers can identify the presence of AD in patients with mixed conditions, such as cerebrovascular disease (evident in neuroimaging) or DLB (fulfilling clinical criteria) with a concomitant AD pathology [,,,,], but they cannot identify other neurodegenerative pathologies in the presence of AD, i.e., the A+T+(N)+ profile is simply compatible with the presence of AD, but gives no information for a possible additional synucleinopathy or, rarely, one of the frontotemporal pathologies. Furthermore, normal levels of all three CSF classical biomarkers may be observed not only in normal aging, but also in psychiatric disorders which may present with cognitive complaints [,] and in some of the frontotemporal pathologies [], which may enter in the differential diagnosis of psychiatric disorders. Assessment of α-synuclein may be of value in the presence of Lewy body pathology [], but results are conflicting [,]. Another emerging biomarker is TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP43), which may prove helpful in identifying TDP43-related frontotemporal pathologies, especially when combined with the classical biomarkers []; much work still has to be done. The AT(N) system is flexible and may evolve into an ATX(N) system, incorporating new and emerging biomarkers of additional non-AD pathologies [].
Finally, one must keep in mind that CSF biomarkers are not stand-alone tools. As in most (if not all) areas of medicine, biochemical tests should be interpreted along with clinical, imaging and other laboratory data (and sometimes follow-up data) in order to reach the final diagnosis.
5. Concluding Remarks
According to the FDA approval, aducanumab targets parenchymal amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease and not in any condition with amyloid plaque burden (e.g., synucleinopathy with concomitant amyloid pathology). For CSF confirmation of an AD diagnosis, reduction in Aβ42 alone is not sufficient, since it may be compatible with pathological change in Alzheimer’s []; it may also be observed in other conditions such as DLB [] or vascular cognitive impairment [,], which in some patients may present with oligosymptomatic phenotypes (especially early in the disease progress) and enter into the differential diagnosis of AD. Neuropathological diagnosis of AD requires both amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles [] and thus, for the in vivo diagnosis of AD by CSF biomarkers, both reduced Aβ42 (or Aβ42/Aβ40) and increased τP-181 should be present []. Even if the AT(N) classification system [], other guidelines/criteria [,] or scoring systems such as the “Erlangen score” [] are not followed, it has been suggested that the τP-181/Aβ42 ratio may provide good diagnostic accuracy for the differential diagnosis of AD from other disorders [].
Keeping the above limitations in mind, biomarkers are not useful only in research, but also in clinical practice, showing both added and prognostic value [,]. They are not only able to confirm the presence of AD in typical cases, but they are able to identify AD in cases with atypical presentations such as primary progressive aphasia, corticobasal syndrome and posterior cortical atrophy [,,,]. Correct recognition of Alzheimer’s disease (not just amyloid pathology) helps to avoid administration of aducanumab (or any other anti-amyloid antibody) in non-AD patients, and makes possible the use of such disease-modifying treatments in clinically atypical AD patients.
The question arises as to whether amyloid PET alone is sufficient for the diagnosis of AD (especially in atypical presentations) and whether an additional tau PET would be required, with concerns regarding cost-effectiveness. CSF biomarkers are of much lower cost, but require a lumbar puncture which, being relatively invasive, is a source of concern in many patients and/or caregivers. Blood-based biomarkers, including Aβ42 and various forms of phospho-tau, might replace CSF and PET biomarkers in the future, since they are easily obtained, not only for initial diagnosis but also for repeated follow-up []; however, sensitivity and specificity to effectively discriminate AD from other dementias still has to be established [].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, critical review of the literature, original draft preparation, manuscript review and editing: G.P.P. and E.K. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
G.P.P. receives fees from Biogen International as a consultant of advisory board. E.K. has none.
References
- Jellinger, K.A.; Bancher, C. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease: A critical update. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1998, 54, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, O.L.; Becker, J.T.; Klunk, W.; Saxton, J.; Hamilton, R.L.; Kaufer, D.I.; Sweet, R.A.; Cidis Meltzer, C.; Wisniewski, S.; Kamboh, M.I.; et al. Research evaluation and diagnosis of probable Alzheimer’s disease over the last two decades: I. Neurology 2000, 55, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantzali, I.; Paraskevas, P.G.; Paraskevas, S.G.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Paraskevas, G.P. Atypical presentations of Alzheimer’s disease: Beyond amnestic dementia. Clin. Exp. Investig. 2020, 1, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.F.; Joshi, A.; Tassniyom, K.; Teng, E.; Shapira, J.S. Clinicopathologic differences among patients with behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 2013, 80, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutch, S.J.; Lehmann, M.; Schott, J.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C. Posterior cortical atrophy. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M. Primary progressive aphasia: Clinicopathological correlations. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Paraskevas, P.G.; Stefanis, L.; Kapaki, E. Corticobasal degeneration and corticobasal syndrome: A review. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, A.; Nordlund, A.; Jonsson, M.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Öhrfelt, A.; Stålhammar, J.; Eckerström, M.; Carlsson, M.; Olsson, E.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease–subcortical vascular disease spectrum in a hospital-based setting: Overview of results from the Gothenburg MCI and dementia studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peavy, G.M.; Edland, S.D.; Toole, B.M.; Hansen, L.A.; Galasko, D.R.; Mayo, A.M. Phenotypic differences based on staging of Alzheimer’s neuropathology in autopsy-confirmed dementia with Lewy bodies. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Schmitz, K.; Krasavina-Loka, N.; Yardimci, T.; Lipka, T.; Kolman, A.G.J.; Robbers, S.; Menge, T.; Kujovic, M.; Seitz, R.J. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.; Mastri, A.R.; Sung, J.H.; Frey, W.H. Clinically diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease: Neuropathologic findings in 650 cases. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1992, 6, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovici, G.D.; Gatsonis, C.; Apgar, C.; Chaudhary, K.; Gareen, I.; Hanna, L.; Hendrix, J.; Hillner, B.E.; Olson, C.; Lesman-Segev, O.H.; et al. Association of Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography With Subsequent Change in Clinical Management Among Medicare Beneficiaries With Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia. JAMA 2019, 321, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasko, D.; Hansen, L.A.; Katzman, R.; Wiederholt, W.; Masliah, E.; Terry, R.; Hill, L.R.; Lessin, P.; Thal, L.J. Clinical-neuropathological correlations in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Arch. Neurol. 1994, 51, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnell, K.; Religa, D.; Eriksdotter, M. Differences in drug therapy between dementia disorders in the Swedish dementia registry: A nationwide study of over 7,000 patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA’s Decision to Approve New Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fdas-decision-approve-new-treatment-alzheimers-disease (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Aducanumab Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/761178s003lbl.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Biogen. EMERGE and ENGAGE Topline Results: Two Phase 3 Studies to Evaluate Aducanumab in Patients with Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://investors.biogen.com/static-files/ddd45672-9c7e-4c99-8a06-3b557697c06f (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Alexander, G.C.; Emerson, S.; Kesselheim, A.S. Evaluation of aducanumab for Alzheimer disease: Scientific evidence and regulatory review involving efficacy, safety, and futility. JAMA 2021, 325, 1717–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopman, D.S.; Jones, D.T.; Greicius, M.D. Failure to demonstrate efficacy of aducanumab: An analysis of the EMERGE and ENGAGE trials as reported by Biogen, December 2019. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliavini, F.; Tiraboschi, P.; Federico, A. Alzheimer’s disease: The controversial approval of Aducanumab. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 3069–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.; Salloway, S. Aducanumab: Appropriate use recommendations. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrowder, D.A.; Miller, F.; Vaz, K.; Nwokocha, C.; Wilson-Clarke, C.; Anderson-Cross, M.; Brown, J.; Anderson-Jackson, L.; Williams, L.; Latore, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, G.P. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for cognitive disorders. An introductory overview. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Hampel, H.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K.; DeKosky, S.T.; Gauthier, S.; Selkoe, D.; Bateman, R.; et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: The IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, M.; Minthon, L.; Davidsson, P.; Granérus, A.K.; Clarberg, A.; Vanderstichele, H.; Vanmechelen, E.; Wallin, A.; Blennow, K. CSF levels of tau, beta-amyloid(1-42) and GAP-43 in frontotemporal dementia, other types of dementia and normal aging. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanderstichele, H.; De Vreese, K.; Blennow, K.; Andreasen, N.; Sindic, C.; Ivanoiu, A.; Hampel, H.; Bürger, K.; Parnetti, L.; Lanari, A.; et al. Analytical performance and clinical utility of the INNOTEST PHOSPHO-TAU181P assay for discrimination between Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2006, 44, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K.; Wallin, A.; Agren, H.; Spenger, C.; Siegfried, J.; Vanmechelen, E. Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid: A biochemical marker for axonal degeneration in Alzheimer disease? Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1995, 26, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewczuk, P.; Lelental, N.; Spitzer, P.; Maler, J.M.; Kornhuber, J. Amyloid-β 42/40 CSF concentration ratio in the diagnostics of Alzheimer’s disease: Validation of two novel assays. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 43, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.; Constantinides, V.C.; Pyrgelis, E.-S.; Paraskevas, P.G.; Papatriantafyllou, J.D.; Paraskevas, G.P. Biomarker-based diagnosis of cognitive disorders in a case series. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Kasselimis, D.; Kourtidou, E.; Constantinides, V.; Bougea, A.; Potagas, C.; Evdokimidis, I.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers as a Diagnostic Tool of the Underlying Pathology of Primary Progressive Aphasia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 55, 1453–31461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Boufidou, F.; Bourbouli, M.; Stefanis, L.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker profiling in corticobasal degeneration: Application of the AT(N) and other classification systems. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 82, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Kalfakis, N.; Andreadou, E.; Zalonis, I.; Vassilopoulos, D. CSF biomarker profile and diagnostic value in vascular dementia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, A.; Kapaki, E.; Boban, M.; Engelborghs, S.; Hermann, D.M.; Huisa, B.; Jonsson, M.; Kramberger, M.G.; Lossi, L.; Malojcic, B.; et al. Biochemical markers in vascular cognitive impairment associated with subcortical small vessel disease—A consensus report. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Bougea, A.; Constantinides, V.C.; Bourbouli, M.; Petropoulou, O.; Kapaki, E. In vivo Prevalence of Alzheimer Biomarkers in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2019, 47, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.H.; Herukka, S.K.; Andreasen, N.; Baldeiras, I.; Bjerke, M.; Blennow, K.; Engelborghs, S.; Frisoni, G.B.; Gabryelewicz, T.; Galluzzi, S.; et al. Recommendations for CSF AD biomarkers in the diagnostic evaluation of dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Feldman, H.H.; Frisoni, G.B.; Hampel, H.; Jagust, W.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. A/T/N: An unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology 2016, 87, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, A.M.; Xiong, C.; Jasielec, M.S.; Bateman, R.J.; Goate, A.M.; Benzinger, T.L.; Ghetti, B.; Martins, R.N.; Masters, C.L.; Mayeux, R.; et al. Longitudinal change in CSF biomarkers in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 226ra30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.J.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Knol, D.L.; Tijms, B.M.; Scheltens, P.; Verhey, F.R.; Visser, P.J.; Aalten, P.; Aarsland, D.; Alcolea, D.; et al. Prevalence of cerebral amyloid pathology in persons without dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.J.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Tijms, B.M.; Fagan, A.M.; Hansson, O.; Klunk, W.E.; van der Flier, W.M.; Villemagne, V.L.; Frisoni, G.B.; Fleisher, A.S.; et al. Association of Cerebral Amyloid-β Aggregation With Cognitive Functioning in Persons Without Dementia. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Holtzman, D.M. Biomarker modeling of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2013, 80, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhave, P.; Minthon, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Wallin, A.K.; Blennow, K.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of β-amyloid 1-42, but not of tau, are fully changed already 5 to 10 years before the onset of Alzheimer dementia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipi, E.; Salvadori, N.; Farotti, L.; Parnetti, L. Biomarker-Based Signature of Alzheimer’s Disease in Pre-MCI Individuals. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Constantinides, V.C.; Pyrgelis, E.S.; Kapaki, E. Mixed Small Vessel Disease in a Patient with Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapaki, E.N.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Tzerakis, N.G.; Sfagos, C.; Seretis, A.; Kararizou, E.; Vassilopoulos, D. Cerebrospinal fluid tau, phospho-tau181 and beta-amyloid1-42 in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A discrimination from Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Guo, J.; Yang, J. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.; Kilidireas, K.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Michalopoulou, M.; Patsouris, E. Highly increased CSF tau protein and decreased beta-amyloid (1–42) in sporadic CJD: A discrimination from Alzheimer’s disease? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Bak, T.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Borroni, B.; Boxer, A.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Grossman, M.; Hallett, M.; et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration. Neurology 2013, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, A.; Román, G.C.; Esiri, M.; Kettunen, P.; Svensson, J.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E. Update on Vascular Cognitive Impairment Associated with Subcortical Small-Vessel Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 1417–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, J.; Wisoff, J.; Miller, D.C.; Boksay, I.; Kluger, A.; Weiner, H.; Salton, J.; Graves, W. Alzheimer’s disease comorbidity in normal pressure hydrocephalus: Prevalence and shunt response. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formichi, P.; Parnetti, L.; Radi, E.; Cevenini, G.; Dotti, M.T.; Federico, A. CSF Biomarkers Profile in CADASIL-A Model of Pure Vascular Dementia: Usefulness in Differential Diagnosis in the Dementia Disorder. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 2010, 959257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- del Campo, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Bertolotto, A.; Engelborghs, S.; Hampel, H.; Simonsen, A.H.; Kapaki, E.; Kruse, N.; Le Bastard, N.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Recommendations to standardize preanalytical confounding factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers: An update. Biomark. Med. 2012, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Persson, S.; Arai, H.; Batish, S.D.; Bernardini, S.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Carrillo, M.C.; Chalbot, S.; et al. The Alzheimer’s Association external quality control program for cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EU Joint Programme—Neurodegenerative Disease Research. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease (BIOMARKAPD). Available online: https://www.neurodegenerationresearch.eu/fileadmin/Project_Fact_Sheets/PDFs/Biomarkers/BIOMARKAPD_Fact_Sheet_Template.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Bourbouli, M.; Kapaki, E.; Petropoulou, O.; Paraskevas, G.P. Improved Performance of CSF dementia biomarker measurements over time: The effect of quality control and harmonization programs. Biomarks Appl. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Persson, S.; Carrillo, M.C.; Collins, S.; Chalbot, S.; Cutler, N.; Dufour-Rainfray, D.; Fagan, A.M.; Heegaard, N.H.; et al. CSF biomarker variability in the Alzheimer’s Association quality control program. Alzheimers Dement. 2013, 9, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemantsverdriet, E.; Goossens, J.; Struyfs, H.; Martin, J.J.; Goeman, J.; De Deyn, P.P.; Vanderstichele, H.; Engelborghs, S. Diagnostic Impact of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker (Pre-)Analytical Variability in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 51, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewczuk, P.; Riederer, P.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Verbeek, M.M.; Dubois, B.; Visser, P.J.; Jellinger, K.A.; Engelborghs, S.; Ramirez, A.; Parnetti, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers for neurodegenerative dementias: An update of the Consensus of the Task Force on Biological Markers in Psychiatry of the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 19, 244–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelgsang, J.; Vukovich, R.; Wedekind, D.; Wiltfang, J. Higher Level of Mismatch in APOEε4 Carriers for Amyloid-Beta Peptide Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid. ASN Neuro 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemantsverdriet, E.; Ottoy, J.; Somers, C.; De Roeck, E.; Struyfs, H.; Soetewey, F.; Verhaeghe, J.; Van den Bossche, T.; Van Mossevelde, S.; Goeman, J.; et al. The Cerebrospinal Fluid Aβ1-42/Aβ1-40 Ratio Improves Concordance with Amyloid-PET for Diagnosing Alzheimer’s Disease in a Clinical Setting. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 60, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouilly, D.; Tisserand, C.; Nogueira, L.; Saint-Lary, L.; Rousseau, V.; Benaiteau, M.; Rafiq, M.; Carlier, J.; Milongo-Rigal, E.; Pagès, J.C.; et al. Taking the A Train? Limited Consistency of Aβ42 and the Aβ42/40 Ratio in the AT(N) Classification. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E.; Liappas, I.; Theotoka, I.; Mamali, I.; Zournas, C.; Lykouras, L. The diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid tau protein in dementing and nondementing neuropsychiatric disorders. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2005, 18, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.; Liappas, I.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Theotoka, I.; Rabavilas, A. The diagnostic value of tau protein, beta-amyloid (1–42) and their ratio for the discrimination of alcohol-related cognitive disorders from Alzheimer’s disease in the early stages. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 20, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Bonakis, A.; Kalfakis, N.; Zalonis, I.; Vassilopoulos, D. Diagnostic value of CSF biomarker profile in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2008, 22, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Vekrellis, K. The diagnostic value of CSF α-synuclein in the differential diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies vs. normal subjects and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Marcus, K.; Trenkwalder, C.; Schlossmacher, M.G. Quantification of α-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid as a biomarker candidate: Review of the literature and considerations for future studies. Biomarkers Med. 2010, 4, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Majbour, N.K.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Abdi, I.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Stefanis, L.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein Species in Cognitive and Movements Disorders. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbouli, M.; Rentzos, M.; Bougea, A.; Zouvelou, V.; Constantinides, V.C.; Zaganas, I.; Evdokimidis, I.; Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P. Cerebrospinal Fluid TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43 Combined with Tau Proteins as a Candidate Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia Spectrum Disorders. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2017, 44, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Cummings, J.; Blennow, K.; Gao, P.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Vergallo, A. Developing the ATX(N) classification for use across the Alzheimer disease continuum. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, B.T.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewczuk, P.; Zimmermann, R.; Wiltfang, J.; Kornhuber, J. Neurochemical dementia diagnostics: A simple algorithm for interpretation of the CSF biomarkers. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeburger, J.L.; Holder, D.J.; Combrinck, M.; Joachim, C.; Laterza, O.; Tanen, M.; Dallob, A.; Chappell, D.; Snyder, K.; Flynn, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers distinguish postmortem-confirmed Alzheimer’s disease from other dementias and healthy controls in the OPTIMA cohort. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 44, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, I.; Diez-Fairen, M.; Aguilar, M.; González, J.M.; Ysamat, M.; Tartari, J.P.; Carcel, M.; Alonso, A.; Brix, B.; Arendt, P.; et al. Added value of cerebrospinal fluid multimarker analysis in diagnosis and progression of dementia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmotte, K.; Schaeverbeke, J.; Poesen, K.; Vandenberghe, R. Prognostic value of amyloid/tau/neurodegeneration (ATN) classification based on diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid samples for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Petropoulou, O.; Bougea, A.; Vekrellis, K.; Evdokimidis, I.; Stamboulis, E.; Kapaki, E. CSF biomarkers β-amyloid, tau proteins and a-synuclein in the differential diagnosis of Parkinson-plus syndromes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 382, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Kodaira, S.; Kasahara, H.; Takai, E.; Nagashima, K.; Fujita, Y.; Makioka, K.; Hirayanagi, K.; Furuta, N.; Furuta, M.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Neuroimaging Markers in Clinical Subtypes of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 543866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Leuzy, A.; Karikari, T.K.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Dodich, A.; Boccardi, M.; Corre, J.; Drzezga, A.; Nordberg, A.; Ossenkoppele, R.; et al. The validation status of blood biomarkers of amyloid and phospho-tau assessed with the 5-phase development framework for AD biomarkers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntymenou, S.; Tsantzali, I.; Kalamatianos, T.; Voumvourakis, K.I.; Kapaki, E.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Stranjalis, G.; Paraskevas, G.P. Blood Biomarkers in Frontotemporal Dementia: Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).