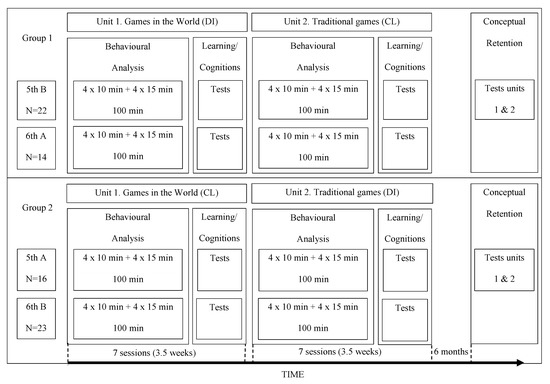
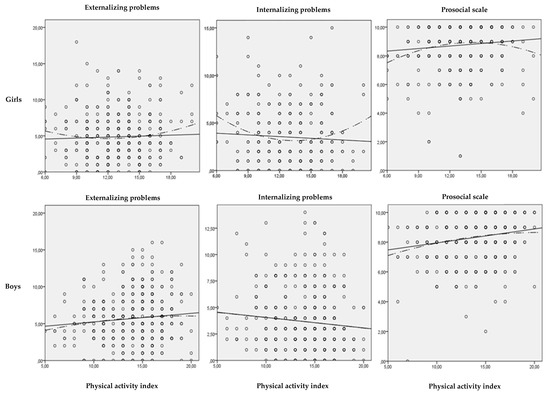
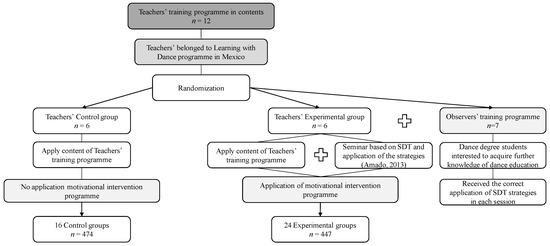
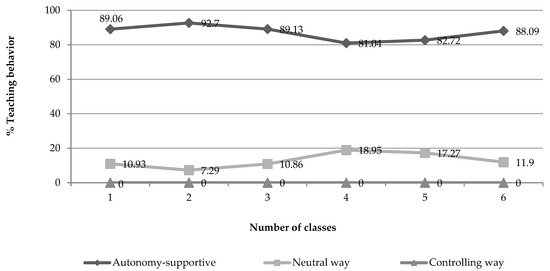
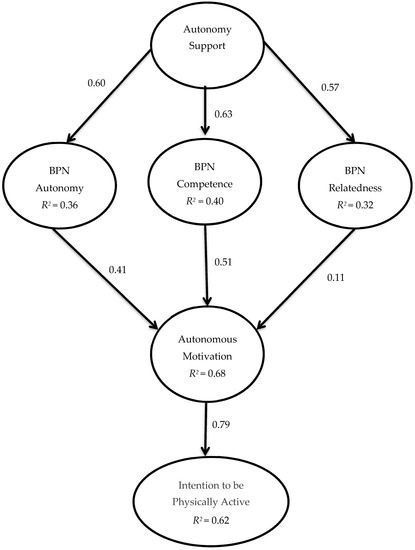
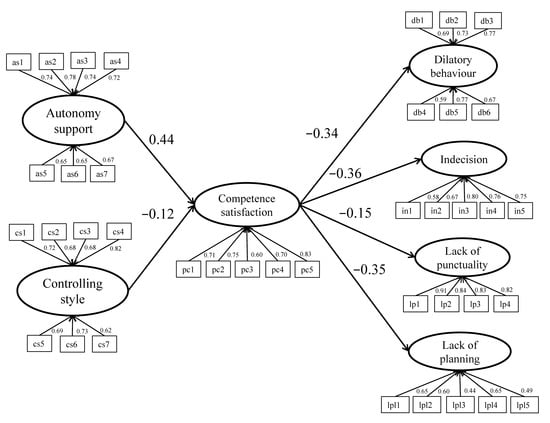
Sustainability, Motivation and the Teaching-Learning Process in Physical Education and Sport
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Education and Approaches".
Viewed by 89403Editors
Interests: motivation; psychosocial factors; healthy lifestyles; physical education; physical activity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: physical activity; sport; motivation; healthy lifestyles; psychological variables
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The aim of any learning process must include the sustainability of the learning outcomes over time. When considering these learning outcomes, motivation is a crucial influential factor in the subject’s behavior and, together with the application of different teaching methods, will determine the success (adherence) or failure (drop out) of the practice of physical activity and sport.
The purpose of this Special Issue of Sustainability is to gather the scientific progress on the importance of the application of different teaching methodologies as well as the development of motivational processes in the educational context (primary, secondary, and higher education) and in the extracurricular sports context. To consider these issues, the academic performance of students in the classroom could be analyzed alongside the social, emotional, cognitive, and biological aspects that determine the commitment to physical exercise and sports.
To do this, cross-sectional, longitudinal,l and intervention studies that analyze motivation and teaching methodologies in the context of physical education, physical activity, and sports for different ages can be presented. Likewise, validations of measurement instruments linked to the object of study of the current Special Issue are of interest.
Physical education, physical exercise, and sport professionals need to include both motivational strategies and innovative pedagogical practices that favor the increase in sports practice in order to sustain improved performance in the classroom and/or training sessions, as well as physical condition, group cohesion, and practitioner health. These studies are the basis of the sustainability that will produce quality in the educational process and in the sports context.
Prof. Dr. Ruth Jiménez Castuera
Prof. Dr. Marta Leyton Román
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Motivational process
- Teaching-learning process
- New teaching methodologies
- Physical Education
- Physical Activity and Sport
- Adherence
- Academic performance.
- Physical condition and Health
- Sustainability