Intelligent Wireless Networks
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Internet of Things".
Viewed by 61089Editors
Interests: grid and cloud computing; energy effectivenes and secure awareness in large scale distributed systems; data intensive computing; cybersecurity in ICT
Interests: large-scale distributed systems (design and performance); grid computing and cloud computing; peer-to-peer systems; big data management; data aggregation; information retrieval and ranking techniques; bio-inspired optimization methods
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: machine tearning, text mining, social network analysis (content analysis and group analysis of connections), web intelligence: decision support systems: recommendation systems, emotion analysis, data mining, e-health application, sensors based medical decisional system
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
In the context of the new global pandemic, many technical issues have come to life, people from all industries being forced to discover a way to continue their lives and work from their homes. In online classes and online gatherings where sensitive topics are discussed, people worry about their privacy being broken. First, the IT industry had to create the means to accommodate all the remote-working and then, as the learning curve adjusted, the privacy issues became increasingly stringent.
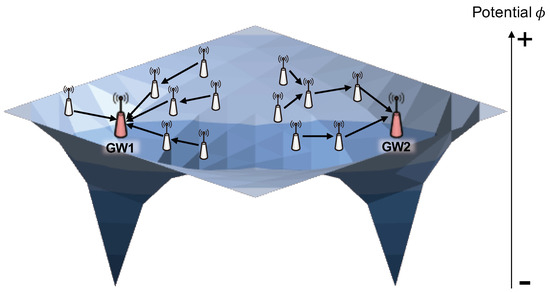
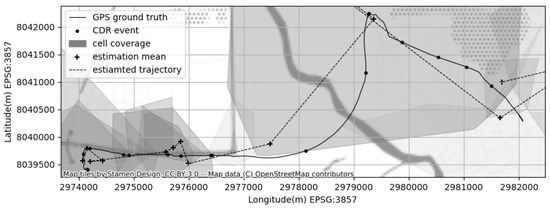
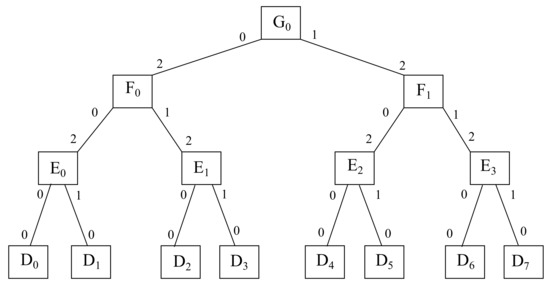
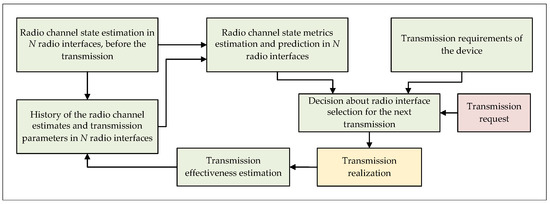
Several important aspects in the case of intelligent wireless networks refer to different types of systems that benefit from wireless networks—especially adaptive systems like fog/edge systems, IoT, and AAL. The architecture and communications models face with increasingly open issues related to resources and data management. These issues have increased the scientific research in the security of mobile networks, confirming the need to add an extra layer of security. That said, extra layers can be represented by trust and reputation, keeping in mind the network’s requirements of low latency, without significantly increasing the network’s offload.
The goal of this Topical Collection is to publish the most recent results in the development of intelligent wireless networks and their emerging applications. Researchers and practitioners working in this area are expected to take this opportunity to discuss and express their views on the current trends, challenges, and state-of-the-art solutions addressing various issues in intelligent wireless networks, ranging from architecture and communication models to specific algorithms and security aspects. Additionally, original review papers on this topic are also welcome.
We invite submissions on a wide range of research topics, spanning both theoretical and practical new solutions. The topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
- Edge/fog computing and architectures;
- Sensor networks and ad-hoc communication;
- Wireless real-time computing;
- High-speed communication systems;
- Embedded systems;
- Cyber-physical systems;
- Machine learning for wireless networks;
- Decision-making for wireless networks;
- Data mining in wireless networks;
- Trust and reputation in wireless networks;
- Security aspects in wireless networks;
- Emerging applications: IoT, smart cities, smart agriculture, ambient assisted living, Big Data analytics;
- Applications in medicine (wireless body area networks) and situation awareness (evacuation systems, indoor monitoring).
Prof. Dr. Joanna Kolodziej
Prof. Dr. Florin Pop
Prof. Dr. Katarzyna Węgrzyn-Wolska
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.