Journal Description
Powders
Powders
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on particle/powder science and technology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 29 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 13.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Photosensitization of TiO2 with Copper for the Photodegradation of Organic Contaminants in Water
Powders 2026, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010006 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Photocatalysis is a process in which a material utilizes light energy to degrade contaminants through oxidation reactions that decompose impurities upon contact with its surface. Titanium dioxide is one of the most widely used semiconductor materials due to its abundance, chemical stability, and
[...] Read more.
Photocatalysis is a process in which a material utilizes light energy to degrade contaminants through oxidation reactions that decompose impurities upon contact with its surface. Titanium dioxide is one of the most widely used semiconductor materials due to its abundance, chemical stability, and non-toxicity. However, its relatively wide bandgap restricts its photocatalytic activity to the ultraviolet region of the solar spectrum, limiting its overall efficiency under natural sunlight. The incorporation of copper nanoparticles into the TiO2 matrix enhances light absorption by extending its activity into the visible range, thereby improving its energy conversion efficiency. In this study, undoped and Cu-doped TiO2 powders were synthesized using the mechanochemical method. The characteristics of the prepared photocatalyst material were determined by XRD, SEM, absorbance, and chemical analysis. XRD analysis showed the formation of TiO2 in its anatase and rutile phases. Sphere-like shapes with a size of 100 nm were inferred from SEM images. The photocatalytic tests revealed that the Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles exhibited high photocatalytic activity in degrading contaminated water. This enhancement can be attributed to the formation of oxygen vacancies, which promote the photodegradation of organic compounds.
Full article
Open AccessReview
The Equation of Motion of Particles in Fluids—An Historical Perspective
by
Efstathios E. Michaelides
Powders 2026, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010005 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
This is a review article that covers the history of the development of the equation of motion for solid particles in fluids, starting with the early work, before the Navier–Stokes equations were developed. Particular emphasis is placed on the development of the transient
[...] Read more.
This is a review article that covers the history of the development of the equation of motion for solid particles in fluids, starting with the early work, before the Navier–Stokes equations were developed. Particular emphasis is placed on the development of the transient equation of motion, which features the history (or memory) term and the added mass (virtual mass) term. The salient features of the equation and the methods of their derivation are pointed out. Creeping, non-inertia flows as well as advective flows are surveyed, with particular emphasis on their effects on the functional form of the history term. Modifications to the hydrodynamic force due to possible interface slip are also examined. The review also deals with the inclusion of the weaker lateral (lift) forces and the inclusion of the effects of Brownian movement, which gives rise to thermophoresis—an important source of nanoparticle movement and surface deposition. The drag on irregularly shaped particles—another important feature of nanoparticles—is also examined. The review concludes with a short section on significant unknown issues and work that may be carried out in the near future for the theoretical and computational development of the subject.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Flow Behavior of Co-Processed Excipients Using Lactose and Microcrystalline Cellulose as Bulk Fillers
by
Paulo J. Salústio, Daniel Cingel, Telmo Nunes, José Catita, José P. Sousa e Silva and Paulo J. Costa
Powders 2026, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010004 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Powder flow is a constant concern in the production of solid dosage forms. Its concise and reliable determination and improvement are challenges for the pharmaceutical industry. Lactose (Lac) and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) are both widely used pharmaceutical fillers either alone or mixed. In
[...] Read more.
Powder flow is a constant concern in the production of solid dosage forms. Its concise and reliable determination and improvement are challenges for the pharmaceutical industry. Lactose (Lac) and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) are both widely used pharmaceutical fillers either alone or mixed. In this study, flow determination was performed through methods described on the European Pharmacopoeia. The results obtained showed poor flow and cohesive behavior for Lac and MCC powders and their mixtures (co-processed excipients). The 50% Lac_MCC mixture, with colloidal silicon dioxide (CSD) as the glidant in different proportions, showed relevant improvements in flow. In addition, the effective angle of wall friction (φx), the effective angle of internal friction (φe), arching, and ratholing were also determined, demonstrating the flow behavior in the discharge equipment. Outlet diameters that prevent blockages or insufficient powder flow were also determined. With this study, it was concluded that it was possible to prepare a co-processed excipient with optimal flow behavior composed of Lac_MCC and CSD as a glidant.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Ammonium Paratungstate Production from Scheelite Ore: Process Study, Morphology and Thermal Stability
by
Maria José Lima, Fernando E. S. Silva, Cleber da Silva Lourenço, Ariadne Silva, Jussier Vitoriano, Kivia Araujo, Matheus Silva, Marco Morales and Uílame Gomes
Powders 2026, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010003 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ammonium paratungstate (APT) was synthesized from scheelite ore concentrates from the Brejuí Mine in Currais Novos, Rio Grande do Norte, Northeast Brazil. The process involved acid leaching to obtain tungstic acid (H2WO4), followed by its conversion to APT. A
[...] Read more.
Ammonium paratungstate (APT) was synthesized from scheelite ore concentrates from the Brejuí Mine in Currais Novos, Rio Grande do Norte, Northeast Brazil. The process involved acid leaching to obtain tungstic acid (H2WO4), followed by its conversion to APT. A 23 factorial design evaluated the influence of temperature, HCl concentration, and reaction time on the leaching efficiency, revealing temperature and acid concentration as significant variables. Tungsten extraction reached 98.6% under moderate time and temperature conditions. The resulting H2WO4 phase exhibited a lamellar and porous morphology, facilitating its rapid dissolution and crystallization into APT at 60 °C. The produced nanometric APT exhibited high purity, a mixed rod-like/cubic morphology, and thermal stability above 600 °C. This work adds value to the Brazilian tungsten deposits by supporting more efficient and sustainable extraction routes for obtaining APT.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Brazilian Type F Fly Ash: Influence of Chemical Composition and Particle Size on Alkali-Activated Materials Properties
by
Adriano G. S. Azevedo
Powders 2026, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010002 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study assesses two Brazilian Type F fly ash samples (FA-A and FA-B), collected from the same thermoelectric complex in different years, to investigate their influence on the production of alkali-activated materials (AAMs). FA-A exhibited a slightly higher SiO2/Al2O
[...] Read more.
This study assesses two Brazilian Type F fly ash samples (FA-A and FA-B), collected from the same thermoelectric complex in different years, to investigate their influence on the production of alkali-activated materials (AAMs). FA-A exhibited a slightly higher SiO2/Al2O3 ratio (3.52 vs. 3.34) and a finer average particle size (D50 = 19.7 μm vs. 30.8 μm) than FA-B. X-ray diffraction revealed that FA-A presented a broad amorphous halo between 15° and 35° (2θ), indicative of phases with low atomic ordering, which are more susceptible to dissolution and capable of supplying Si- and Al-rich species for the formation of alkali activation products. These differences directly affected reactivity and mechanical performance. After 1 day of curing, FA-A-based matrices achieved 88.5 MPa in compressive strength—approximately 100% higher than FA-B (44.2 MPa). However, FA-A suffered a 19.6% strength reduction after 28 days of curing, whereas FA-B showed only a 3.8% decrease over the same period, reflecting better long-term stability. FTIR confirmed Na2CO3 formation in FA-A, associated with excess sodium (Na/Al = 2.07 after 28 days), while SEM revealed unreacted spheres persisting in FA-B, consistent with its lower dissolution rate. Water absorption was also significantly different, with FA-B matrices reaching values up to 52% lower than FA-A after 7 days of curing. These results demonstrate that even slight variations in chemical composition and atomic ordering, even for ashes from the same plant, strongly influence the reactivity, microstructure, and mechanical performance of alkali-activated binders.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Zeolite Synthesis from Spodumene Leach Residue and Its Application to Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solutions
by
Sofi Buzukashvili, Justin Paris, Helmi F. Kalahari, Sidney Omelon and Kristian E. Waters
Powders 2026, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders5010001 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents an approach to synthesizing LTA-type zeolite from spodumene residue generated during a lithium extraction process. A residue was obtained after leaching β-spodumene with 2 mol/L phosphoric acid. After solid–liquid separation, the delithiated residue was first treated with 2 mol/L sodium
[...] Read more.
This study presents an approach to synthesizing LTA-type zeolite from spodumene residue generated during a lithium extraction process. A residue was obtained after leaching β-spodumene with 2 mol/L phosphoric acid. After solid–liquid separation, the delithiated residue was first treated with 2 mol/L sodium hydroxide and then subjected to hydrothermal synthesis using sodium aluminate as an additional aluminum source. The resulting material was characterized by XRD, SEM-EDS, XPS, and FTIR, which collectively confirmed the formation of a crystalline material exhibiting the structural features, elemental composition, and morphological characteristics consistent with LTA-type zeolite. Additional analyses, including BET surface area, particle size distribution, and zeta potential measurements, were performed to further evaluate the physicochemical properties of the synthesized zeolite. The spodumene leach residue (SLR)-derived zeolite was further tested for its adsorption performance in heavy metal ions removal from a mixed ion solution containing Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, and Ni2+ ions. The zeolite demonstrated a high selectivity for Pb2+, followed by moderate uptake of Cu2+, while Zn2+ and Ni2+ adsorption was minimal. These findings demonstrate that spodumene residue, a waste by-product of lithium processing, can be effectively upcycled into LTA zeolite suitable for heavy metal remediation in water treatment applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mechanical Properties and Powder Rheology of Conventional and Innovative Excipients for Food Supplements in Solid Form
by
Giovanni Tafuro, Marta Faggian, Paola Soppelsa, Silvia Baracchini, Elena Casanova, Stefano Francescato, Giovanni Baratto, Stefano Dall’Acqua, Andrea Claudio Santomaso and Alessandra Semenzato
Powders 2025, 4(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040032 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The growing regulatory scrutiny and the emerging trends towards natural products and clean labels have led to a particular focus on food supplements’ composition, including excipients. The objective of this study is to establish a methodological approach combining conventional techniques, i.e., tapped density
[...] Read more.
The growing regulatory scrutiny and the emerging trends towards natural products and clean labels have led to a particular focus on food supplements’ composition, including excipients. The objective of this study is to establish a methodological approach combining conventional techniques, i.e., tapped density and flowability testers, with more objective and quantitative ones to identify alternative powder excipients that can replace conventional ones in the development of solid-dose formulations without affecting their processing, workability, and mechanical properties. In the first phase, the alternative powder excipients were characterized in terms of cohesiveness, compressibility, and flow function coefficient. We then evaluated the possibility of using selected excipient combinations to totally and/or partially replace the conventional excipients within three nutraceutical formulations. Glyceryl behenate at 1–3% w/w could be considered as a viable alternative lubricant to magnesium stearate without compromising the rheological properties of the mixtures. Fructo-oligosaccharides showed a free-flowing behavior comparable to calcium phosphate and microcrystalline cellulose, improving the flowability and compressibility of the formulations. The study of powder rheology could be advantageous to formulate new products or reformulate existing ones in a time- and money-saving way, leading to high-quality products that can appeal to consumers in terms of health-functional effectiveness.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Use of Chicken Eggshell Waste for Synthesizing Nano-Sized Calcium Aluminate Powder by Combining High-Energy Milling and Calcination
by
Fernanda Santos Maia Luna, Andrey Escala Alves and José Nilson França Holanda
Powders 2025, 4(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040031 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In recent years, sustainable recycling approaches for chicken eggshell waste have increased significantly worldwide due to environmental and circular economy benefits. This work aimed to synthesize and characterize a new calcium aluminate powder using chicken eggshell waste as an alternative source of calcium
[...] Read more.
In recent years, sustainable recycling approaches for chicken eggshell waste have increased significantly worldwide due to environmental and circular economy benefits. This work aimed to synthesize and characterize a new calcium aluminate powder using chicken eggshell waste as an alternative source of calcium carbonate through mechanical activation and subsequent calcination. The starting formulation consisting of the eggshell waste (CaCO3):Al2O3 (1:1) ratio was subjected to a high-energy milling process for 0 h, 15 h and 30 h and subsequent calcination at 1200 °C for 4 h. The resulting calcium aluminate powders have been investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential thermal analysis (DTA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and photoluminescence techniques. After calcination, a calcium aluminate-based composite powder with an average crystallite size between 46.45 nm and 52.27 nm and a predominance of the CaAl2O4 phase was found. The calcium aluminate powders produced (milled for 15 h and 30 h and calcined at 1200 °C) showed a luminescent behavior, emitting characteristic violet light with a wavelength between 380 and 418 nm. Our findings may provide a novel technical pathway for recycling chicken eggshell waste into calcium aluminate powder with luminescent properties.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Green Synthesis of Magnetic ZnO Nanocomposites and Potential Applications—A Systematic Literature Review
by
Lays da Silva Sá Gomes, Maryane Pipino Beraldo Almeida, Alex Ramos da Silva, Lucas Henrique Pereira Silva, Aroldo Geraldo Magdalena, Oswaldo Baffa and Angela Kinoshita
Powders 2025, 4(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040030 - 27 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Environmental contamination is a significant challenge, and nanotechnology shows promise in restoring ecosystems impacted by human activity. Magnetic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are notable for their antimicrobial and photocatalytic properties, making them valuable for various environmental and medical applications. Their ability to be
[...] Read more.
Environmental contamination is a significant challenge, and nanotechnology shows promise in restoring ecosystems impacted by human activity. Magnetic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are notable for their antimicrobial and photocatalytic properties, making them valuable for various environmental and medical applications. Their ability to be recovered and reused in the presence of a magnetic field enhances process sustainability. Furthermore, green synthesis using low-toxicity biological agents such as plant extracts and microorganisms offers a safer and more eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods. This systematic review examines the green synthesis of magnetic ZnO nanocomposites, highlighting advanced production techniques, methods, and potential applications. Four of the eleven studies analyzed specifically address the photocatalytic activity of green-synthesized ZnO nanocomposites, emphasizing their promise in environmental domains.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Are Drag Models Adequate? A Comprehensive Analysis of Drag Modelling for Regular and Irregular Particles
by
Sadaf Maramizonouz and Sadegh Nadimi
Powders 2025, 4(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040029 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Particles travelling within and interacting with any fluid media are found in both natural phenomena and industrial processes. Through these interactions, the particles experience a drag force, heavily influenced by their morphology, and significantly affecting their dynamics. This study examines the relationship between
[...] Read more.
Particles travelling within and interacting with any fluid media are found in both natural phenomena and industrial processes. Through these interactions, the particles experience a drag force, heavily influenced by their morphology, and significantly affecting their dynamics. This study examines the relationship between particle morphology and the drag force exerted on them, using both empirical models and computational simulations. The findings indicate that for regular and irregular particles of diverse morphologies, a combination of existing empirical models can predict the drag force within a 40% error margin. However, these models may fall short of meeting the accuracy demands in certain applications. To address this, the study provides clear guidelines for selecting the most suitable drag model based on particle morphology and flow regime.
Full article
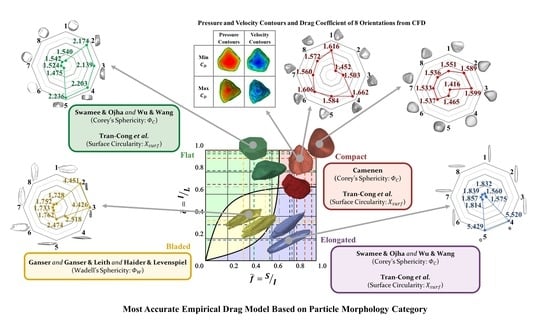
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks
by
Hongyu Liu, Yaqin Wang, Xicheng Wang, Rui Liu and Peng Zhang
Powders 2025, 4(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040028 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Titanium-containing nanoparticles have emerged as materials of significant technological importance due to their multifunctional properties and excellent performance. With their expanding applications, the amount of TiO2 nanoparticles (TNPs) being released into the soil environment has increased significantly. This review addresses the gap
[...] Read more.
Titanium-containing nanoparticles have emerged as materials of significant technological importance due to their multifunctional properties and excellent performance. With their expanding applications, the amount of TiO2 nanoparticles (TNPs) being released into the soil environment has increased significantly. This review addresses the gap in current research, which has predominantly focused on the environmental behavior of TNPs in aquatic systems while lacking systematic integration of the synergetic mechanism of adsorption–transformation–ecological effects in soil systems and its guiding value for practical applications. It deeply reveals the interaction mechanisms between TNPs and environmental pollutants. TNPs exhibit outstanding adsorption performance towards environmental pollutants such as heavy metals and organic compounds. Specifically, the maximum adsorption capacities of titanate nanowhiskers for the heavy metal ions Cu(II), Pb(II), and Cr(III) are 143.9 mg·g−1, 384.6 mg·g−1, and 190.8 mg·g−1, respectively. Additionally, 1-hydroxydinaphthoic acid surface-modified nano-TiO2 exhibits an adsorption rate of up to 98.6% for p-nitrophenol, with an enrichment factor of 50-fold. The transformation process of TNPs after pollutant adsorption profoundly affects their environmental fate, among which pH is a critical controlling factor: when the environmental pH is close to the point of zero charge (pHpzc = 5.88), TNPs exhibit significant aggregation behavior and macroscopic sedimentation. Meanwhile, factors such as soil solution chemistry, dissolved organic matter, and microbial activities collectively regulate the aggregation, aging, and chemical/biological transformation of TNPs. In the soil ecosystem, TNPs can exert both beneficial and detrimental impacts on various soil organisms, including bacteria, plants, nematodes, and earthworms. The beneficial effects include alleviating heavy metal stress, serving as a nano-fertilizer to supply titanium elements, and acting as a nano-pesticide to enhance plants’ antiviral capabilities. However, excessively high concentrations of TiO2 can stimulate plants, induce oxidative stress damage, and impair plant growth. This review also highlights promising research directions for future studies, including the development of safer-by-design TNPs, strategic surface modifications to enhance functionality and reduce risks, and a deeper understanding of TNP–soil microbiome interactions. These avenues are crucial for guiding the sustainable application of TNPs in soil environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Diagnosis and Solution of Pneumatic Conveying Bend Problems: Application of TRIZ-DEMATEL Coupling Technology
by
Jianming Su, Lidong Zhang, Xiaoyang Ma, Xinyu Xu, Yuhan Jia, Yuhao Pan, Lifeng Zhang, Changpeng Song and Tieliu Jiang
Powders 2025, 4(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040027 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mining, mineral processing, and power generation are just a few of the industries that have made extensive use of pneumatic conveying systems in recent years. The market for pneumatic conveying is anticipated to grow to a value of $30 billion by 2025. However,
[...] Read more.
Mining, mineral processing, and power generation are just a few of the industries that have made extensive use of pneumatic conveying systems in recent years. The market for pneumatic conveying is anticipated to grow to a value of $30 billion by 2025. However, problems with the pneumatic conveying process are common and include coal particle damage, pipe wall wear, and excessive system energy consumption. A new systematic framework for decision-making is created by combining the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) with the Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL). This methodology employs TRIZ-Ishikawa to determine the underlying causes of issues from six different perspectives. It then suggests remedies based on TRIZ technical contradictions and uses DEMATEL to examine how the solutions interact to determine the best course of action. This study confirms the viability of this approach in recognizing fundamental contradictions, producing workable solutions, and reaching scientific conclusions in challenging issues by using instances such as wear and tear, obstructions, and low conveying efficiency in pneumatic conveying system elbows. It offers particular references for real engineering projects and suggests practical solutions like employing quick-release flanges and installing multiple sets of airflow regulators.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characterising Ultrasint PP Nat 01 Polypropylene to Examine Its Feasibility in Powder Bed Fusion
by
Fredrick Mwania, Maina Maringa and Jacobus van der Walt
Powders 2025, 4(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030026 - 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The current study examines the feasibility of Ultrasint PP nat 01 polypropylene material in powder bed fusion through powder characterisation. The results obtained are also deemed to be pertinent when developing or validating analytical and numerical models of Polymer Laser Sintering, which were
[...] Read more.
The current study examines the feasibility of Ultrasint PP nat 01 polypropylene material in powder bed fusion through powder characterisation. The results obtained are also deemed to be pertinent when developing or validating analytical and numerical models of Polymer Laser Sintering, which were not within the scope of this paper. The following critical characteristics were examined: powder morphology, powder particle size distribution (PSD), bulk density, tapped density, melt flow index, thermal characteristics of the material, degree of crystallinity, and optical properties. Ultrasint PP nat 01 powder has a PSD in the range of 20–80 µm, which is within the recommended particle size distribution. The Hausner ratio, tapped density, and bulk density of the material were calculated and measured as 1.230 ± 0.05, 0.455 ± 0.02 g/cm3, and 0.370 ± 0.03 g/cm3, respectively. The melt flow index of Ultrasint PP nat 01 was measured as 15.8 g/10 min. The initial melting point of the material was determined to be 133.8 °C. The powder used had a relatively high sintering window of 30.7 °C, a degree of crystallinity of around 31.8%, and a high thermal stability of around 461.52 °C. The material was found to attain full fusion of particles at around 170 °C. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy indicated that Ultrasint PP nat 01 powder has poor radiation absorption, but high transmission properties.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Water-Based Spray Drying of WC-Co Powders: A Sustainable Route to Environmentally Safer Granulation Without Compromising Performance
by
Horea-Florin Chicinaș
Powders 2025, 4(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030025 - 17 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The spray drying of hard metal (WC-Co) powders is a critical step in the production of high-performance cutting and wear-resistant tools. Traditionally, organic solvents such as ethanol or acetone are employed in this process, despite posing substantial health, safety, and environmental risks. This
[...] Read more.
The spray drying of hard metal (WC-Co) powders is a critical step in the production of high-performance cutting and wear-resistant tools. Traditionally, organic solvents such as ethanol or acetone are employed in this process, despite posing substantial health, safety, and environmental risks. This study investigates a sustainable alternative by replacing organic solvents with water in the spray-drying process. We present a comparative analysis of granule morphology, flowability, and final mechanical properties between solvent-based and water-based routes. The water-based approach achieved a d50 of 99 µm, flow time of 27.8 s, and apparent density of 3.18 g/cm3, closely matching the solvent-based values (d50 = 93 µm, flow = 28.4 s, and ρ = 3.14 g/cm3). Hardness (HV30 ≈ 1650) and microstructure were equivalent across both routes, confirming that the substitution does not compromise performance. The water-based process also offers an estimated reduction of over 50% in CO2 emissions compared to traditional methods. These findings support the feasibility of water-based granulation as a viable, scalable, and safer route for WC-Co powder production, in alignment with dematerialization, circular material use, and the broader goals of sustainable development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microstructural Evolution of a Pre-Alloyed Duplex Stainless Steel 2205 with Boron Addition Prepared by Powder Metallurgy
by
Pedro Morita Terceiro and Juliano Soyama
Powders 2025, 4(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030024 - 22 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The addition of hard particles such as borides to a ductile stainless steel matrix can be very efficient for improving mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy represents a suitable route for developing these material modifications, combining high reproducibility and cost-effectiveness. The present research investigated the
[...] Read more.
The addition of hard particles such as borides to a ductile stainless steel matrix can be very efficient for improving mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy represents a suitable route for developing these material modifications, combining high reproducibility and cost-effectiveness. The present research investigated the effect of sintering time on an atomized, pre-alloyed 2205 stainless steel with 2.5 wt.% boron, using two different powder size distributions: fine (<45 µm) and coarse (250–500 µm). Cold uniaxial compaction was conducted using a cylindrical closed die. Sintering was carried out at 1200 °C with a dwell time of 2 and 4 h in argon atmosphere. Microstructural investigation showed that borides were formed in the powder’s atomization step and presented a small size with different morphologies. The borides significantly improved the hardness and compression strength. Compared to the reference 2205 stainless steel, specimens prepared with the fine powder size distribution achieved a twofold enhancement in yield stress, while hardness increased by 26%.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen
by
Raíssa Gabrielle Silva Araújo Andrade and Vádila Giovana Guerra
Powders 2025, 4(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030023 - 6 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are widely applied to reduce particle concentrations. However, the performance of ESPs is impaired in the nanosized diameter range due to the difficulty in electrically charging these particles. The present work evaluated the inclusion of a wire screen, perpendicular to
[...] Read more.
Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) are widely applied to reduce particle concentrations. However, the performance of ESPs is impaired in the nanosized diameter range due to the difficulty in electrically charging these particles. The present work evaluated the inclusion of a wire screen, perpendicular to the airflow, as an additional collecting electrode of a single-stage wire-plate ESP containing two collecting plates and a single discharge wire. ESP performance was evaluated in terms of voltage, air velocity and electrode positioning in relation to the beginning of the collecting plate (inlet spacings of 1.5, 10 and 23 cm). When compared to theoretical prediction, the penetration results presented a decay for larger particles not predicted by the diffusion battery model. It was observed that the inclusion of the wire screen increased the removal of ultrafine particles and that the overall collection efficiencies increased up to 70% in the operating conditions evaluated. Moreover, the central positioning of the electrodes (inlet spacing of 10 cm) achieved the highest collection efficiencies at high voltages, but the final positioning (inlet spacing of 23 cm) presented a better performance at higher air velocities. Therefore, the wire screen can be an alternative to enhance nanoparticle collection.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study of the Thermal Wick-Debinding Used in Low-Pressure Powder Injection Molding
by
Mohamed Amine Turki, Dorian Delbergue, Gabriel Marcil-St-Onge and Vincent Demers
Powders 2025, 4(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030022 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Thermal wick-debinding, commonly used in low-pressure injection molding, remains challenging due to complex interactions between binder transport, capillary forces, and thermal effects. This study presents a numerical simulation of binder removal kinetics by coupling Darcy’s law with the Phase Transport in Porous Media
[...] Read more.
Thermal wick-debinding, commonly used in low-pressure injection molding, remains challenging due to complex interactions between binder transport, capillary forces, and thermal effects. This study presents a numerical simulation of binder removal kinetics by coupling Darcy’s law with the Phase Transport in Porous Media interface in COMSOL Multiphysics. The model was validated and subsequently used to study the influence of key debinding parameters. Contrary to the Level Set method, which predicts isolated binder clusters, the Multiphase Flow in Porous Media method proposed in this work more accurately reflects the physical behavior of the process, capturing a continuous binder extraction throughout the green part and a uniform binder distribution within the wicking medium. The model successfully predicted the experimentally observed decrease in binder saturation with increasing debinding temperature or time, with deviation limited 3–10 vol. % (attributed to a mandatory brushing operation, which may underestimate the residual binder mass). The model was then used to optimize the debinding process: for a temperature of 100 °C and an inter-part gap distance of 5 mm, the debinding time was minimized to 7 h. These findings highlight the model’s practical utility for process design, offering a valuable tool for determining optimal debinding parameters and improving productivity.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Chemical Fingerprint of Smokeless Powders: Insights from Headspace Odor Volatiles
by
Miller N. Rangel, Andrea Celeste Medrano, Haylie Browning, Shawna F. Gallegos, Sarah A. Kane, Nathaniel J. Hall and Paola A. Prada-Tiedemann
Powders 2025, 4(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030021 - 29 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Smokeless powders are a commonly used low explosive within the ammunition industry. Their ease of purchase has allowed criminals to use these products to build improvised explosive devices. Canines have become a vital tool in locating such improvised devices. With differing fabrication processes,
[...] Read more.
Smokeless powders are a commonly used low explosive within the ammunition industry. Their ease of purchase has allowed criminals to use these products to build improvised explosive devices. Canines have become a vital tool in locating such improvised devices. With differing fabrication processes, one of the most difficult challenges for canine handlers is the optimal selection of training aids to choose as odor targets to allow for broad generalization. Several studies have been underway to understand the chemical odor characterization of smokeless powders, which can help provide canine teams with essential information to understand odor signatures from powder varieties. In this study, a SPME method optimization was conducted using unburned smokeless powders to provide a chemical odor profile assessment. Concurrently, statistical analysis using PCA and Spearman’s rank correlations was performed to explore whether odor volatile composition depicted associations between and within powder brands. The results showed that a longer extraction time (24 h) was optimal across all powders, as this yielded higher compound abundance and number of extracted odor volatiles. The optimal SPME fiber varied per powder, depicting the complexity of powder composition. There were 66 highly frequent compounds among the 18 powders, including 2-ethyl-1-hexanol, diphenylamine (DPA), and dibutyl phthalate. Principal component analysis (PCA) showed that while powders may be of the same type (single/double base), they can still portray clustering differences across and within brands. The Spearman’s rank correlation within powder type suggested that the double-base powders had a slightly higher similarity index when compared with the single-base powder types. Understanding the volatile odor profiles of various smokeless powders can enhance canine training by informing the selection of effective training aids and supporting odor generalization.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Deposition: A DPM and PBM Approach for Particles in a Two-Phase Turbulent Pipe Flow
by
Alkhatab Bani Saad, Edward Obianagha and Lande Liu
Powders 2025, 4(3), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030020 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Particle deposition is a phenomenon that occurs in many natural and industrial systems. Nevertheless, the modelling and understanding of such processes are still quite a big challenge. This study uses a discrete phase model (DPM) to determine the deposition constant for the particles
[...] Read more.
Particle deposition is a phenomenon that occurs in many natural and industrial systems. Nevertheless, the modelling and understanding of such processes are still quite a big challenge. This study uses a discrete phase model (DPM) to determine the deposition constant for the particles in a liquid phase flowing in a horizontal pipe. This study also develops a steady-state population balance equation (PBE) for the particles in the flow involving deposition and aggregation and an unsteady-state PBE for particles depositing on the wall. This establishes a mathematical relationship between the deposition constant and velocity. An industrial setting of a 1000 m long pipe of 0.5 m in diameter was used for the population balance modelling (PBM). Based on the extracted deposition constant from the DPM, it was found that the particle deposition velocity increases with the continuous flow velocity. However, the number and volume of the deposit particles on the wall reduce with the increase of the continuous flow velocity. The deposition was found mainly taking place in the inlet region and reduces significantly towards the pipe outlet. The deposition was also found driven by advection of particles. Calculated deposit thickness showed that increasing the continuous flow velocity from 1 m s−1 to 5 m s−1, the thickness at the inlet would reduce to nearly 1/40th. With a 10 m s−1 flow, this would be 1/80th.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Selective Separation of SiO2 and SnO2 Particles in the Submicron Range: Investigating Salt and Surfactant Adsorption Parameter
by
Claudia Heilmann, Lisa Ditscherlein, Martin Rudolph and Urs Alexander Peuker
Powders 2025, 4(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030019 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
The separation of particles smaller than 1 µm either by composition or by size is still a challenge. For the separation of SiO2 and SnO2, the creation of a selective separation feature and the specific adsorption of salts and surfactants
[...] Read more.
The separation of particles smaller than 1 µm either by composition or by size is still a challenge. For the separation of SiO2 and SnO2, the creation of a selective separation feature and the specific adsorption of salts and surfactants were investigated. The adsorption of various salts, e.g., AlCl3, ZnCl2, MnCl2 and MgCl2 were therefore analyzed, and the necessary concentration for the charge reversal of the material was determined. It was noticed that the investigated materials differ in their isoelectric point (IEP) and therefore in their adsorption behavior because only ZnCl2 and MgCl2 are suitable for a charge reversal of both metal oxides. The phase transfer of the pure material at different pH values with ZnCl2 or MgCl2 and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) revealed that the adsorption behavior of the particle has an influence on the phase transfer. As a result, the phase transfer of SiO2 is pH dependent, whereas the phase transfer of SnO2 operates over a wider pH range. This allowed the separation of SiO2 and SnO2 to be controlled by the salt and surfactant concentration as well as pH. The separation of SiO2 and SnO2 was investigated for various parameters such as salt and surfactant concentration, particle concentration and composition of the mixture. Also, pH 8, where a selective phase transfer for SiO2 occurs, and pH 6, where the greatest difference between the materials exists, were also investigated. By comparing the parameters, it was found that the combination of ZnCl2/SDS and MgCl2/SDS enables a selective separation of the materials. Furthermore, it was also found that the concentration of SDS has a significant effect on the separation, as the formation of a bilayer structure is important for the separation, and therefore, higher SDS concentrations are required at higher particle concentrations to increase the separation efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Multidimensional Particle Properties: Characterization, Description, Separation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Alloys, Applied Mechanics, Crystals, J. Compos. Sci., Powders, Nanomaterials
Multiscale Characterization, Mechanical Behavior and Computational Simulation of Bulk Materials, Metallic Powders and/or Nanoparticles
Topic Editors: Xiangnan Pan, Qing Peng, Hui Qi, Raj DasDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Sustainability, ChemEngineering, Processes, Separations, Gases, Powders
Carbon Capture, Storage and Utilisation Technologies (CCS/CCU)—3rd Edition
Topic Editors: Federica Raganati, Paola AmmendolaDeadline: 31 January 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Powders
Recent Progress on Powder Materials for Additive Manufacturing
Guest Editor: Yachao WangDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Powders
Powder Flow: Advancing Characterisation, Modelling, and Industrial Control
Guest Editors: Vivek Garg, Tong Deng, Michael BradleyDeadline: 30 November 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Powders
Multidimensional Particle Properties: Characterization, Description, Separation
Collection Editors: Urs Alexander Peuker, Alfred P. Weber, Einar Kruis, Doris Segets






