Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Experimental Unit
2.2. Wire Screen Characteristics
2.3. The Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
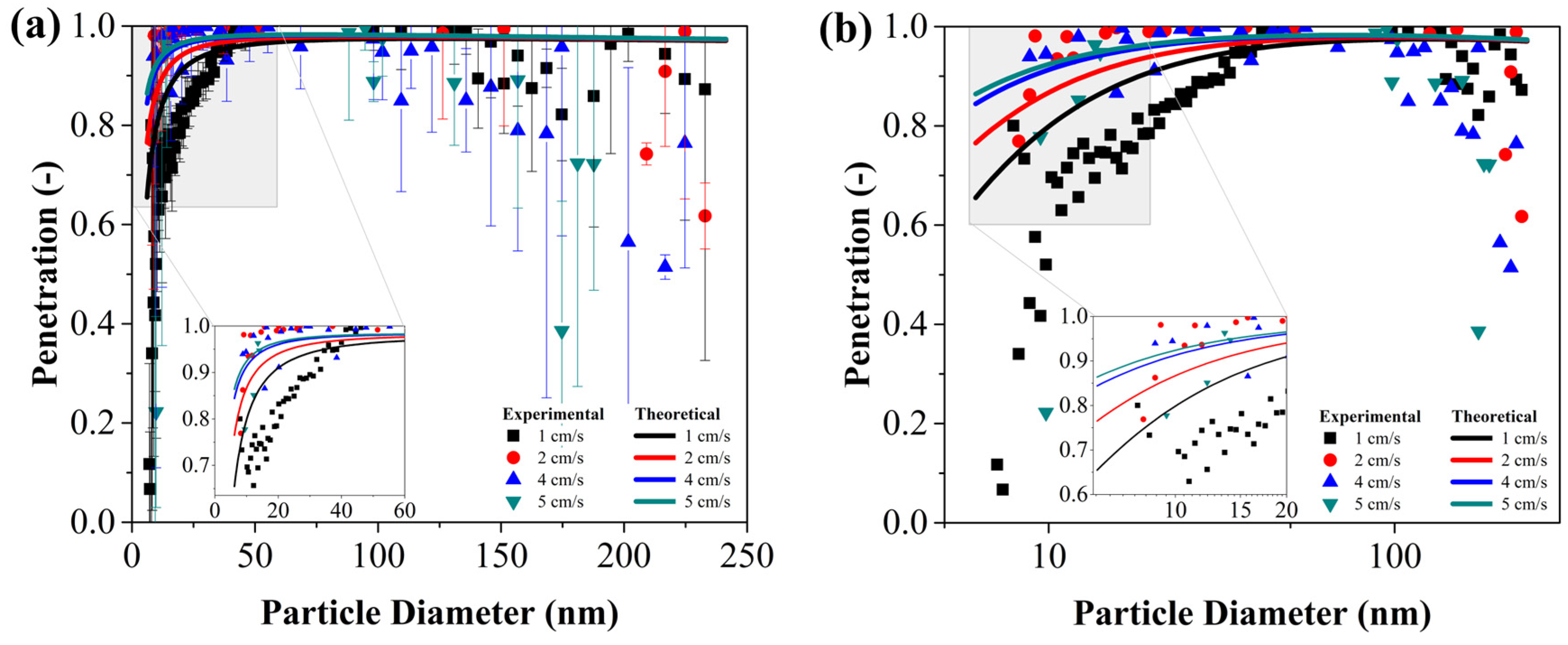
3.1. Penetration
3.2. Current–Voltage Curves
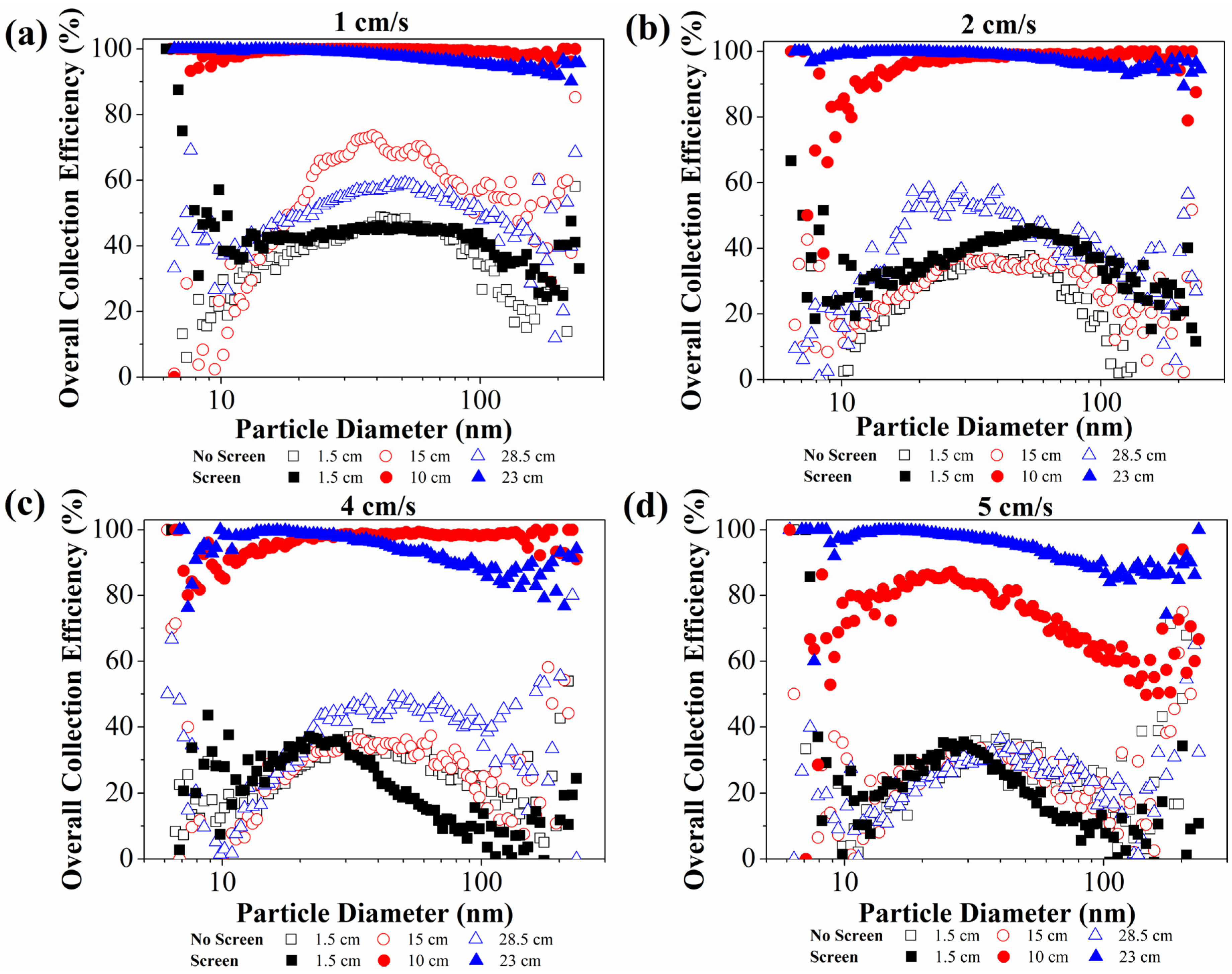
3.3. Effect of the Inclusion of the Wire Screen on the Fractional Collection Efficiency
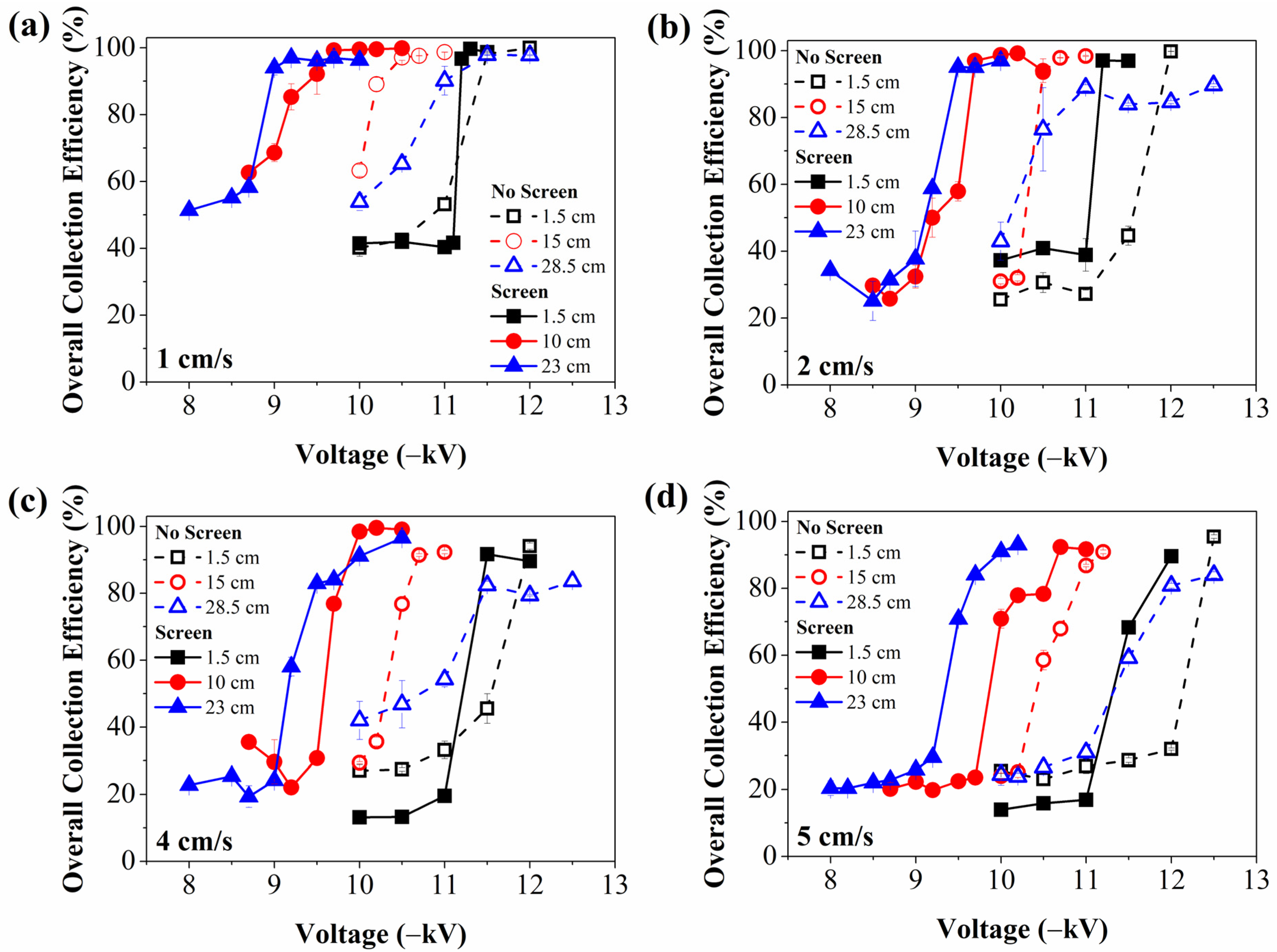
3.4. Effect of the Wire Screen Inclusion on ESP Performance in a Wider Voltage Range
4. Conclusions
- The experimental results of penetration agreed with the theoretical estimation for particles up to 60 nm, and then presented a decay not predicted by the equation used. On the other hand, the single fiber efficiency presented the expected behavior but with its minimum peak at a lower diameter range (70–122 nm) than previously reported in the literature.
- The enhancement of nanoparticle collection with the inclusion of the wire screen was confirmed for most of the operating conditions tested, with increases up to 70%, and achieving collection efficiencies higher than 90%.
- It was observed that the central positioning of the single discharge electrode and the wire screen (inlet spacing of 10 cm) achieved the lowest outlet concentrations (below 20 μg/m3) at voltages above 9 kV. However, the final positioning (inlet spacing of 23 cm) presented the best performance at the air velocities of 4 and 5 cm/s, with maximum collection efficiencies of 99% and 93%, respectively. The initial positioning (inlet spacing of 1.5 cm) presented the worst performance for most operating conditions.
- Furthermore, the wire screen improved the collection efficiency of ultrafine particles with diameters up to 30 nm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, X.; Lu, J. Numerical investigation of the sensible heat storage in novel electrostatic precipitators with liquid-filled collection electrodes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 255, 123993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.; Guo, C.; Laycock, A.; Cui, X.; Belinga-Desaunay-Nault, M.-F.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Leonard, M.; Smith, R. Aerosol exposure at air-liquid-interface (AE-ALI) in vitro toxicity system characterisation: Particle deposition and the importance of air control responses. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 100, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shangguan, W. Comprehensive control of PM 2.5 capture and ozone emission in two-stage electrostatic precipitators. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Yook, S.-J. Discharge electrode shape optimization for the performance improvement of electrostatic precipitator with six-branched spike discharge electrode and hexagonal collecting plate. Powder Technol. 2025, 453, 120662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Air Quality Guidelines Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-003422-8. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Andrews, A.J.; Hogan, C.J. Evaluation of particle mass transfer rates in electrostatic precipitators. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 307, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, G.N.; Diniș, C.M.; Iagăr, A. Investigations on Three-Section Plate-Type Electrostatic Precipitators Used in Thermoelectric Power Plants. Energies 2023, 16, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applied Electrostatic Precipitation; Parker, K.R., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 978-94-009-1553-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Nawale, P.; Sahu, M. Design, development and performance evaluation of a miniature electrostatic precipitator in an indoor environment. J. Electrost. 2025, 134, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.; Marchewicz, A.; Sobczyk, A.T.; Krupa, A.; Czech, T. Two-stage electrostatic precipitators for the reduction of PM2.5 particle emission. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 67, 206–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tao, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Yin, W.; Shangguan, W.; Bai, Z. Re-entrainment mechanism of submicron particles during electrostatic capture process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 308, 121417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Guan, Q.; Zeng, G.; Yang, L. Improving the electrostatic precipitation removal efficiency on fine particles by adding wetting agent during the chemical agglomeration process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 230, 107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W.; Shao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, C.; Hu, D.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Improving the removal of particles via electrostatic precipitator by optimizing the corona wire arrangement. Powder Technol. 2021, 388, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shao, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Enhancing fine particle removal by electrostatic precipitation from flue gas with a high PM concentration: Effect of various electrode configurations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, A.; Lehtoranta, K.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Karppanen, M.; Murtonen, T.; Martikainen, J.; Kuusisto, J.; Nyyssönen, S.; Koponen, P.; Piimäkorpi, P.; et al. Performance of a Wet Electrostatic Precipitator in Marine Applications. JMSE 2023, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badami, M.M.; Tohidi, R.; Aldekheel, M.; Farahani, V.J.; Verma, V.; Sioutas, C. Design, optimization, and evaluation of a wet electrostatic precipitator (ESP) for aerosol collection. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 308, 119858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.; Sobczyk, A.T.; Marchewicz, A.; Czech, T.; Krupa, A. Performances of two-stage electrostatic precipitator with different types of discharge electrodes of unipolar electrostatic agglomerator. Powder Technol. 2024, 448, 120269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aquino Lima, F.; Guerra, V.G. Collection of nanoparticles by electrostatic precipitation operating over a wide range of electric fields. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, J.; Li, L.; Ouyang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Olson, B.A.; Hogan, C.J. Characterization of the bidimensional size and charge distribution of sub- and supermicrometer particles in an electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2023, 425, 118578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.E.; Guerra, V.G. Effect of low gas velocity on the nanoparticle collection performance of an electrostatic precipitator. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, M. Enhanced size-dependent efficiency of removal of ultrafine particles: New solution of two-stage electrostatic precipitator with thermophoresis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, A.; Sobczyk, A.T.; Marchewicz, A.; Jaworek, A. Fly ash and sorbent particles agglomeration and removal in system of electrostatic agglomerator and electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2024, 431, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Zhai, X.; Xiao, L. Synergistic Humidification and Chemical Agglomeration to Improve Capturing the Fine Particulate Matter by Electrostatic Precipitator. Coatings 2024, 14, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, W.; Ke, Y.; Yan, K. Development and experimental investigation of the narrow-gap coated electrostatic precipitator with a shield pre-charger for indoor air cleaning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.G.S.A.; Guerra, V.G. Discharge electrode influence on electrostatic precipitation of nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2021, 379, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aquino Lima, F.; Guerra, V.G. Influence of wire spacing and plate spacing on electrostatic precipitation of nanoparticles: An approach involving electrostatic shielding and diffusion charging. Particuology 2023, 80, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gu, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T.; Cao, Z.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Bu, S.; et al. Experiment and numerical simulation investigation on wire-plate electrostatic precipitator with expanded-shrunk spoilers. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, A.; Mishra, N.K.; Das, R. Enhancement of collection efficiency for capturing submicron particles emitted from biomass burning: A novel design of semi-circular corrugated plate electrostatic precipitator. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 13, 17059–17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ha, M.Y.; Lee, D. A numerical study on particle collection for wavy dielectric plate in 2-stage wire-plate electrostatic precipitator. J. Mech. Sci. Technol 2023, 37, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, M.B.; Asipuela, A.; Iváncsy, T. The effect of the corona wire distribution with W-type of collecting plates on the characteristics of electrostatic precipitators. J. Electrost. 2023, 125, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Xia, S. Experimental investigation on the performance of hybrid electrostatic-fabric precipitators with different structures. Powder Technol. 2023, 421, 118404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Song, Q.; Yao, Q. Experimental and numerical study of particle deposition on perforated plates in a hybrid electrostatic filter precipitator. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Alguacil, F.J. Electrostatic Precipitation of Ultrafine Particles Enhanced by Simultaneous Diffusional Deposition on Wire Screens. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Mainelis, G. Design and development of an Electrostatic Screen Battery for Emission Control (ESBEC). J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 107, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.W. The diffusion battery method for aerosol particle size Determination. J. Colloid Sci. 1955, 10, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Yeh, H.C. Theory of a screen-type diffusion battery. J. Aerosol Sci. 1980, 11, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Yeh, H.C.; Brinsko, K.J. Use of Wire Screens as a Fan Model Filter. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1985, 4, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Keating, J.A.; Kanapilly, G.M. Theory and calibration of a screen-type diffusion battery. J. Aerosol Sci. 1980, 11, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.C.; Cheng, Y.S.; Orman, M.M. Evaluation of various types of wire screens as diffusion battery cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 86, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Kousaka, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Hashimoto, N. Penetration of Nanometer-Sized Aerosol Particles Through Wire Screen and Laminar Flow Tube. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1997, 27, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Alguacil, F.J.; Nomura, T. Turbulent deposition of aerosol nanoparticles on a wire screen. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, M.; Cen, J.; Wang, Q.; Yan, K. Numerical investigation of particle re-entrainment mechanism and its suppression strategy in the high-temperature electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2024, 437, 119538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.G.S.A.; Guerra, V.G. Impact of Discharge Electrode Positioning on Nanoparticle Collection in a Single-Stage Wire-Plate Electrostatic Precipitator. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 25467–25478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4783-1:1989; Industrial Wire Screens and Woven Wire Cloth—Guide to the Choice of Aperture Size and Wire Diameter Combinations—Part 1: Generalities. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989.
- ISO 4783-2:1989; Industrial Wire Screens and Woven Wire Cloth—Guide to the Choice of Aperture Size and Wire Diameter Combinations—Part 2: Preferred Combinations Fow Woven Wire Cloth. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989.
- Mermelstein, J.; Kim, S.; Sioutas, C. Electrostatically Enhanced Stainless Steel Filters: Effect of Filter Structure and Pore Size on Particle Removal. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, N.; Aitsaid, H.; Aissou, M.; Nouri, H.; Zeghloul, T. Experimental study of the collection efficiency of three configurations of blades-plates-type electrostatic precipitators. Part. Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Long, W.; Tao, K.; Vafai, K. Numerical simulation of the collection efficiency of welding fume particles in electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol. 2023, 415, 118173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherbouche, F.; Benmimoun, Y.; Tilmatine, A.; Zouaghi, A.; Zouzou, N. Study of a new electrostatic precipitator with asymmetrical wire-to-cylinder configuration for cement particles collection. J. Electrost. 2016, 83, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Duan, W.; Fan, S.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S. Experiment and numerical simulation on the fine particle migration behaviors for the collection efficiency enhancement of a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator in pig house. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symbol | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Opening (mm) | 0.425 | |
| Diameter of the wire fiber (mm) | 0.23 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.45 | |
| Open area fraction (-) | 0.42 | |
| Solid volume fraction (-) | 0.29 | |
| Screen parameter (-) | 1.019 |
| Wire Inlet Spacing (cm) | Screen Position (cm) | Velocity (cm/s) | Voltage (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 4.5 | 1/2/4/5 | 10–12 |
| 10.0 | 13.0 | 8.5–11 | |
| 23.0 | 26.0 | 8–10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva Araújo Andrade, R.G.; Guerra, V.G. Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen. Powders 2025, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030023
Silva Araújo Andrade RG, Guerra VG. Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen. Powders. 2025; 4(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva Araújo Andrade, Raíssa Gabrielle, and Vádila Giovana Guerra. 2025. "Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen" Powders 4, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030023
APA StyleSilva Araújo Andrade, R. G., & Guerra, V. G. (2025). Enhanced Nanoparticle Collection Using an Electrostatic Precipitator Integrated with a Wire Screen. Powders, 4(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4030023






