Selected Papers from "CNRS"
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Sylvain Caillol
Dr. Sylvain Caillol
 Dr. Sylvain Caillol
Dr. Sylvain Caillol
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Institut Charles Gerhardt Montpellier (ICGM), CNRS, ENSCM, University of Montpellier, 34095 Montpellier, France
Interests: green and sustainable chemistry; building-blocks from biomass; biobased monomers and polymers
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Present in all fields of science, the CNRS ranks among the world's leading research organizations for its excellent results in research and innovation. The CNRS is thus at the forefront of international rankings: second most visible research institution on the web, fourth in the Nature Index ranking, sixth patent applicant in France and eighth most innovative public research organization. The CNRS employs nearly 32,000 people in the service of research in more than 1100 laboratories for a budget of 3.4 billion euros.
This collection aims to highlight the cutting-edge studies of CNRS scientists in the fields of polymer science.
Dr. Sylvain Caillol
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- polymer colloids
- polymer nanostructure
- biobased polymers
- supramolecular polymers
- biomedical applications
Published Papers (4 papers)
Open AccessReview
Biocompatible Glues: Recent Progress and Emerging Frontiers in Surgical Adhesion
by
Marine Boursier, Yves Bayon, Claire Negrell, Julien Pinaud and Sylvain Caillol
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5282
Abstract
Surgical adhesives and glues have gained significant attention in the medical field due to their potential to replace traditional sutures and staples in various surgical applications. This review explores the evolution of biocompatible adhesives, focusing on their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility.
[...] Read more.
Surgical adhesives and glues have gained significant attention in the medical field due to their potential to replace traditional sutures and staples in various surgical applications. This review explores the evolution of biocompatible adhesives, focusing on their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility. We discuss the key challenges in developing these materials, including their adhesive strength, degradation rate, and tissue compatibility. The article also delves into regulatory frameworks governing their use in clinical settings and highlights the ongoing innovations aimed at enhancing their performance and safety. Finally, the review examines the current trends in the development of next-generation surgical adhesives, with an emphasis on environmentally friendly and bioresorbable options. The importance of multidisciplinary collaboration in advancing these materials for clinical use is also underscored.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis and Assessment of Novel Sustainable Antioxidants with Different Polymer Systems
by
Agathe Mouren, Eric Pollet and Luc Avérous
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4393
Abstract
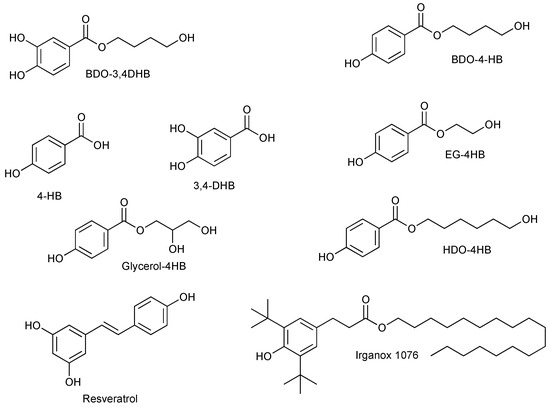
Antioxidants are essential to the polymer industry. The addition of antioxidants delays oxidation and material degradation during their processing and usage. Sustainable phenolic acids such as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid were selected. They were chemically modified by esterification to obtain various durable
[...] Read more.
Antioxidants are essential to the polymer industry. The addition of antioxidants delays oxidation and material degradation during their processing and usage. Sustainable phenolic acids such as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid were selected. They were chemically modified by esterification to obtain various durable molecules, which were tested and then compared to resveratrol, a biobased antioxidant, and Irganox 1076, a well-known and very efficient fossil-based antioxidant. Different sensitive matrices were used, such as a thermoplastic polyolefin (a blend of PP and PE) and a purposely synthesized thermoplastic polyurethane. Several formulations were then produced, with the different antioxidants in varying amounts. The potential of these different systems was analyzed using various techniques and processes. In addition to antioxidant efficiency, other parameters were also evaluated, such as the evolution of the sample color. Finally, an accelerated aging protocol was set up to evaluate variations in polymer properties and estimate the evolution of the potential of different antioxidants tested over time and with aging. In conclusion, these environmentally friendly antioxidants make it possible to obtain high-performance materials with an efficiency comparable to that of the conventional ones, with variations according to the type of matrix considered.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Thermal and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood-PLA Composites Processed by Additive Manufacturing for Building Insulation
by
Anis Bahar, Ameur El Amine Hamami, Ferhat Benmahiddine, Sofiane Belhabib, Rafik Belarbi and Sofiane Guessasma
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 4672
Abstract
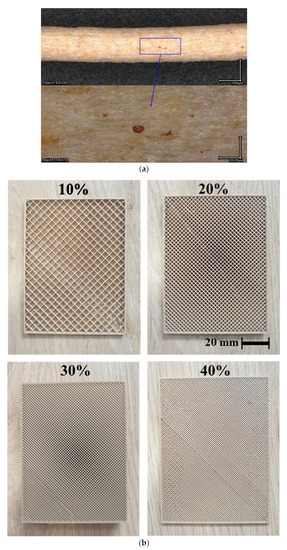
This study was aimed at considering the potential of wood-based composites processed using additive manufacturing as insulators in the building sector. A polylactic acid blend with 30% wood particles was used as a feedstock material in fused filament technology. Its thermal and mechanical
[...] Read more.
This study was aimed at considering the potential of wood-based composites processed using additive manufacturing as insulators in the building sector. A polylactic acid blend with 30% wood particles was used as a feedstock material in fused filament technology. Its thermal and mechanical properties were determined for various processing conditions, including printing temperature and infill rate. The results showed a minor contraction in its tensile performance as a result of the printing process. The printing temperature had a negligible effect on its stiffness and a limited influence on the other engineering constants, such as the tensile strength and ultimate stress. The thermal properties of printed structures have been found to significantly depend on the infill rate. Although the tested 3D printed wood-PLA material exhibited good thermal properties, which were tuneable using the printing conditions, its performance was still 38% to 57% lower compared to insulators such as the glass wool of the synthetic foams used in the building sector.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Phosphonate-Functionalized Polycarbonates Synthesis through Ring-Opening Polymerization and Alternative Approaches
by
Hien The Ho, Nam Hoai Nguyen, Marion Rollet, Trang N. T. Phan and Didier Gigmes
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3112
Abstract
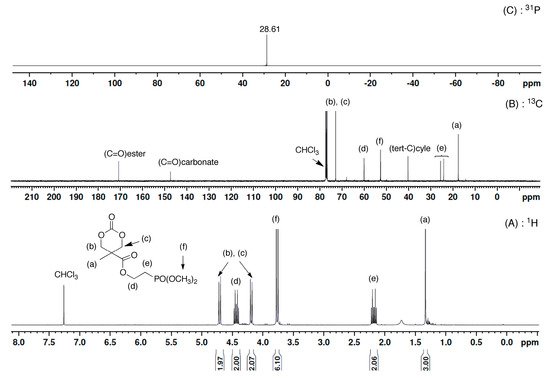
Well-defined phosphonate-functionalized polycarbonate with low dispersity (
Ð = 1.22) was synthesized using organocatalyzed ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of novel phosphonate-based cyclic monomers. Copolymerization was also performed to access different structures of phosphonate-containing polycarbonates (PC). Furthermore, phosphonate-functionalized PC was successfully synthesized using a combination
[...] Read more.
Well-defined phosphonate-functionalized polycarbonate with low dispersity (
Ð = 1.22) was synthesized using organocatalyzed ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of novel phosphonate-based cyclic monomers. Copolymerization was also performed to access different structures of phosphonate-containing polycarbonates (PC). Furthermore, phosphonate-functionalized PC was successfully synthesized using a combination of ROP and post-modification reaction.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures