Abstract
Metabolism is fundamental to many biological processes that govern the flow of energy and materials within organisms. Recently, several interspecific studies have suggested that ontogenetic phase shifts in the metabolism of teleost fish coincide with body mass increases during early development. The morphological and behavioral changes that accompany these metabolic shifts could explain differences in intraspecific size scaling metabolism, but it remains unclear whether these shifts are widespread in a variety of aquatic organisms, including non-teleost fish. Here, a metabolic study in sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus) was conducted to examine whether the ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism coincide with growth in a non-teleost fish. The results were also compared with previously published metabolic scaling data for the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to explore differences in intraspecific scaling patterns. The present study revealed that ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism do occur in sterlet sturgeon. These findings indicate that non-teleost fish likely undergo scaling mechanisms in metabolism similar to those of teleost fish.
1. Introduction
In many organisms, oxygen consumption is a reflection of metabolism, which is the fundamental process by which energy and material are exchanged within an organism. An organism’s metabolism allocates its available resources to growth, reproduction, and maintenance; therefore, metabolism should substantially influence its life history [1,2,3,4]. An organism’s metabolism () is expressed as a power function of body mass () according to the allometric equation , where a is the scaling coefficient (antilog of the intercept in a log–log plot) and b is the scaling exponent (slope in a log–log plot) [5,6]. is generally accepted to show negative allometry when scaled to body mass, as the scaling exponent is typically less than one. This indicates that the mass-specific metabolic rate (/) decreases with increasing body mass. In contrast, maximal metabolic rate (MMR) often scales with an exponent close to or even exceeding one, showing different scaling behavior depending on the level of activity (e.g., rest versus exercise). This phenomenon is recognized interspecifically (i.e., variation in metabolic scaling among different species) [7,8,9,10,11] and intraspecifically (i.e., variation in metabolic scaling within a single species across developmental stages) [8,10,12]; however, in many cases, a basic allometric equation cannot account for non-linear or curvilinear log–log metabolic scaling relationships [8,13,14,15,16]. Intraspecific differences in metabolism due to growth may be a complex process with several distinct phases [3,8,16,17,18,19]. Both the scaling constant (a) and the scaling exponent (b) of metabolic rate can be influenced not only by intrinsic factors such as growth, but also by extrinsic environmental conditions such as temperature [20,21]. Thus, the variation in the metabolic scaling exponent and scaling constant during ontogenesis must be understood.
Fish are ideal organisms for studying intraspecific metabolic differences because most fish develop from small eggs, then grow quickly [22,23], which enables researchers to accurately predict and test intraspecific metabolic changes. Among various teleost fish, the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) is a well-studied model species for investigating metabolic scaling during early development, owing to its clearly defined ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolic rate [16]. The entire ontogenetic mass range from larval to adult fish is roughly comparable to that between a mouse and an elephant [24]. This wide range is a key factor in analyzing mass–metabolism relationships, as changes in metabolic rate with size and growth stage are closely linked to morphological and behavioral changes [3,16,19,25,26,27]. Although several intraspecific analyses have revealed a metabolic scaling exponent range of approximately 0.4–1.3 in various fish species [25,27,28,29,30], the metabolic variation patterns of each species, particularly during the development of early life, have been controversial in ecophysiology [3,16]. For example, Oikawa et al. [31] and Post and Lee [32] suggested a biphasic relationship, where the scaling exponent changes from near isometry (i.e., close to unity) during the larval stage to negative allometry (i.e., less than unity) during the juvenile and/or later stages, indicating that the metabolic scaling exponent changes abruptly rather than gradually, at least during early life history. In contrast, Bochdansky and Leggette [33] have suggested a curvilinear relationship between mass and metabolism by performing a meta-analysis on many fish species. Although previous theories agree that both the metabolic scaling exponent and the metabolic constant can vary throughout ontogeny, the precise nature of metabolic scaling during early developmental stages in fish remains unclear. While several studies have reported both isometric and allometric scaling trajectories depending on species and experimental context [34,35,36,37], it is still uncertain whether ontogenetic isometric scaling occurs consistently across fish species. Therefore, further empirical investigation is needed to clarify the developmental dynamics of metabolic scaling during early ontogeny in teleost fish.
Recently, several studies have recently suggested that ontogenetic phase shifts in the metabolism of many organisms, including teleost fish, occur with an increase in body mass during the early development stages [3,8,16,17,18,19]. The Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), which weighs 0.00026–0.90000 g, has three interposing transitional phases at approximately 0.002, 0.010, and 0.200 g, with a constant scaling exponent in each phase [16]. Specifically, the intergroup scaling exponent (0.915 ± 0.0011, estimate ± S.E.M.) was significantly steeper than the intragroup scaling exponent (0.831 ± 0.0026) [16]. Furthermore, the intragroup scaling constant significantly increased with increased body mass [16]. This indicates that the isometric and/or near-isometric metabolic scaling during the early development stages could be influenced by a combined effect of the ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism. The transitional metabolism phases were accompanied by morphological and behavioral changes during the early development stages [16,19], making it an excellent indicator of development trajectory.
The sturgeon species are non-teleost fish that have gained the attention of several researchers due to their distinct appearance and life history (i.e., long-lived and late-maturing) [38]. Among them, the sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus (Linnaeus, 1758)) is one of the optimal species that can be used to explain the intraspecific metabolism of non-teleost fish. This species is an economically important aquaculture fish because of the excellent taste of its caviar, meat, oils, and isinglass, which is made from its swim bladders [39]. They exhibit relatively delayed sexual maturity, i.e., at approximately 4–5 years for males and 7–9 years for females, which is unique with regard to external appearance and traits in comparison with other non-teleost fish [40]. Moreover, they exhibit rapid growth during the protracted juvenile stage, but it slows down quickly [41,42]. Although this species has the smallest size among all sturgeon species, they are relatively large as compared with other non-teleost fish, with a maximum size of 125 cm and a weight of 20 kg [39]. This growth strategy is advantageous because it provides both the time and energy needed for the fish to reach their maximum size before first spawning, thereby increasing their potential life span [43]. In fact, they tend to have relatively long lives of up to 22–25 years [44]. These unique characteristics make this an ideal model fish for quantitative respirometry studies to better understand the various factors that influence intraspecific metabolism [44].
In this study, it was observed that sterlet sturgeon exhibit ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism as they grow since their specific metabolic demands (e.g., growth) are likely to be similar to the metabolic fluctuations that accompany the morphological and/or behavioral changes observed in teleost species, such as the Japanese flounder. The present study aimed to examine whether ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism occur in non-teleost species by performing quantitative respirometry studies on sterlet sturgeon of various sizes and weights.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and the ARRIVE Guidelines
All experimental processes were conducted and approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethical Committee on Animal Experimentation at the Tsukuba Research Institute, Fujikin Inc., Ltd., Tsukuba, Japan. Fish handling and sampling methods were conducted in accordance with the “Act on Welfare and Management of Animals” (Act No. 68, promulgated in 2005), the “Act on Welfare and Management of Animals” (Act No. 105, promulgated in 1973), and the “policy on the implementation of animal experiments, etc. at research institutions” (announced on 1 June 2006) (hereinafter referred to as “standard policy”) formulated by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of the Japanese government. The study followed the recommendations in the ARRIVE guidelines (https://arriveguidelines.org on 30 December 2022).
2.2. Fish Used
Resting metabolism rates were measured in 33 sterlets (Acipenser ruthenus), whose weights ranged from 0.0196 g (wet body mass, 3 days old) to 2.6368 g (64 days old). In this experiment, metabolism was measured using individuals obtained via artificial insemination from three females and one male. All fish were carefully bred in a 150 L polycarbonate cylinder tank with a steady supply of freshwater at approximately 19.0–21.0 °C. Food was dispensed based on an artificial diet supplemented with newly hatched live brine shrimp, Artemia sp., larvae enriched with eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), three times a day from 5 days old to 64 days old. Before measuring metabolic rates, the fish were transferred directly to a 30 L polycarbonate cylinder tank at 20.0 °C for 5–12 h in the case of fish that weighed in the range of 0.0196 (3 days old)–0.3919 g (29 days old), for 12–15 h in the case of fish in the 0.7646 g (37 days old)–1.2296 g (46 days old) range, and for more than 24 h in the case of fish that weighed >2.0000 g to allow them to adjust to the metabolic measuring temperature (i.e., 20.0 °C). Food was not supplied to the fish for 12–24 h to accurately measure their metabolism and body mass.
2.3. Metabolic Measurement
Oxygen consumption () was measured in fasted larvae and juveniles at 20 °C using a semi-closed method, following the approach of previous studies [3,31]. The metabolic rate recorded under these conditions reflects an intermediate metabolic state between strict resting and routine levels, characterized by minimal but spontaneous activity, as previously described in fish respirometry studies [45]. Since the prolarvae (or yolk-sac larvae) were very sensitive to physical stimuli, the following methods were used to minimize any damage caused by handling. First, the fish were carefully placed in 50 mL beakers, and then any dead or weak fish were removed with a pipette. The fish were then quickly transferred into a respiratory chamber and allowed to settle for an acclimatization period of about 2 h before measurement to eliminate any possible stress caused by the transfer. The respiration chambers used (62 to 361 mL) depended on body size (62 mL for 3–41-day-olds, 136 mL for 42–50-day-olds, and 361 mL for 57–64-day-olds). The detailed measurement conditions used in this study are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
A summary of the method used for measuring oxygen consumption.
Oxygen consumption was measured on a per-individual-fish basis using the Winkler titration method [31,46]. In brief, a blank chamber was installed to collect the water flowing from the respiration chamber containing the acclimated fish. The chambers were connected by silicone hoses that quickly removed partial air bubbles to avoid any failed oxygen concentration measurements. Once the air bubbles in the two chambers were completely removed, the water flow rate from the respiration chamber to the blank chamber was made constant using control valves. The oxygen concentration in the blank chamber was used as the control, because this concentration was equal to the initial oxygen concentration in water. When both chambers were sealed at the same time, the oxygen concentration in the respiration chamber was used as the treatment group, because this concentration could be decreased by the fish. By using the difference in oxygen concentration between the two groups, the background respiration was measured. Immediately after the oxygen concentration was calculated, fish body mass was determined. The metabolic measurement was performed with an illuminance of 80 lux at the surface of the water bath. A description of the respiration method is summarized in Table 1.
2.4. Data Analysis
Statistical models from previously published studies were used to determine the ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism [3]. Two statistical models were used to evaluate the multiple negative allometric relationships, omitting transitional phases. The first model for each incidence of negative allometry is expressed using the following equation:
where ‘’ is an intragroup scaling constant of the -th group and ‘’ is the scaling exponent of each group. The second model for the overall line constituting these allometries is expressed as follows:
where ‘α’ is an intergroup of one of the groups and ‘’ is the overall scaling exponent. Equations (1) and (2) can be rewritten as follows:
and
where ‘’ is , ‘’ is , and ‘’ and ‘’ reflect the random variation in the metabolism of the intra- and intergroups, respectively. Ordinary least-squares regression was used to estimate and to minimize the sum of the squares, which is the vertical distance of the group mean () from the overall (intergroup) line [47]. Given that can be represented as (), Equation (4) was reformulated as follows [48].
A one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to estimate statistical significance by computing the sums of squares, degrees of freedom, and mean squares attributable to each term of Equation (5). All data analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel for Office 365 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA).
3. Results
Oxygen consumption rates ( in µL fish−1 min−1) with an increase in body mass ( in g) and mass-specific metabolic rates ( in µL fish−1 min−1) are plotted in Figure 1. No clear allometric relationship was found between and in the early prolarval stage (0.0196–0.0238 g, from 4 days to 9 days old), as their intraspecific scaling exponents were almost in an isometric relationship during this stage (Figure 1).
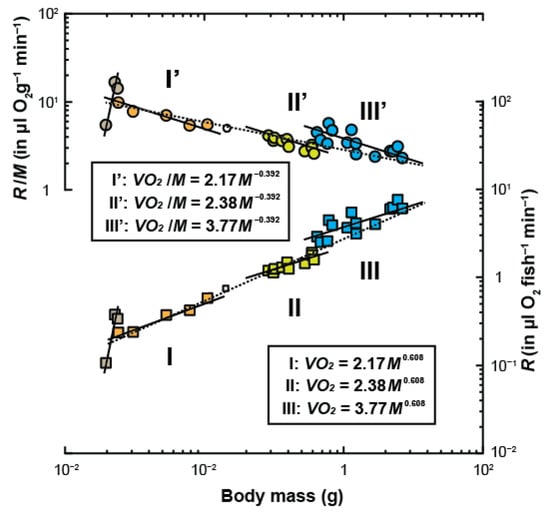
Figure 1.
Ontogenetic changes in oxygen consumption rates (, closed squares) and mass-specific rates of oxygen consumption (/, closed circles) with increasing body mass () of sterlet sturgeons during prolarval to early juvenile stages, which weighed 0.0196 g (wet body mass, 3 days old) up to 2.6368 g (64 days old) (n = 29). The vertical broken lines at around 0.0200 g represent and /, which increased daily from 3 days old to 9 days old, with no virtual increase in body mass. The ranges covered by three solid black lines for and / indicate intragroup phases of negative allometry. The small transparent symbols (ranges not covered by the solid lines, i.e., approximately 0.25 g) and/or intermediate phase shifting points (ranges covered by overlapping solid lines, i.e., approximately 0.65 g) represent values during the transitional phases. The broken lines on and / represent the intergroup lines excluding the transitional phases. Regression analysis of each line on is presented in Table 2, and ANCOVA is presented in Table 3. Text boxes explains that the intraspecific scaling exponent () at each stage represents the common slope of all three regression lines and that the scaling constant () represents the -value of the common slope.

Table 2.
Regression analysis of the mass–metabolism relationships in sterlet sturgeon at 20 °C. N, the number of determinations; p, the difference in the scaling exponent from unity, as determined by the two-tailed Student’s t-test; R2, the squared correlation coefficient between ( in µL fish−1 min−1) and ( in g). The results for the intra- and intergroups are shown in rows 1–3 and 4–6, respectively.
Table 2.
Regression analysis of the mass–metabolism relationships in sterlet sturgeon at 20 °C. N, the number of determinations; p, the difference in the scaling exponent from unity, as determined by the two-tailed Student’s t-test; R2, the squared correlation coefficient between ( in µL fish−1 min−1) and ( in g). The results for the intra- and intergroups are shown in rows 1–3 and 4–6, respectively.
| Group | N | Range of Body Mass (g) | Scaling Constant | Scaling Exponent (Mean ± S.E.M.) | p | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | 5 | 0.0241–0.1051 | 2.38 | 0.638 ± 0.077 | 1.85 × 10−2 | 0.958 |
| 2 a | 10 | 0.2884–0.6131 | 2.25 | 0.540 ± 0.096 | 1.35 × 10−3 | 0.799 |
| 3 a | 14 | 0.6438–2.6368 | 3.77 | 0.609 ± 0.106 | 3.04 × 10−3 | 0.735 |
| 1–3 b | 29 | 0.0241–2.6368 | α = 3.33 | = 0.791 ± 0.022 | 3.18 × 10−10 | 0.980 |
| 1–3 c | 29 | 0.0241–2.6368 | 3.27 | 0.768 ± 0.031 | 6.13 × 10−8 | 0.957 |
| Total | 30 | 0.0241–2.6368 | 3.23 | 0.763 ± 0.031 | 2.16 × 10−8 | 0.956 |
a Parameters were estimated to minimize the sum of squares of εij in each group. b Parameters were estimated to minimize the sum of squares of µi. c Parameters were estimated to minimize the sum of squares of Eij.

Table 3.
Summary statistics of the ontogenetic metabolic changes in sterlet sturgeon using one-way analysis of covariance (Equation (5)).
Table 3.
Summary statistics of the ontogenetic metabolic changes in sterlet sturgeon using one-way analysis of covariance (Equation (5)).
| Term | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | Mean Square Ratio | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| log α | 2.267 | 1 | 2.267 | 578 | 8.39 × 10−19 |
| µi | 0.0917 | 1 | 0.0917 | 23.4 | 5.68 × 10−5 |
| i | 0.0305 | 1 | 0.0305 | 7.78 | 9.95 × 10−3 |
| xij | 4.863 | 1 | 4.863 | 1240 | 7.92 × 10−23 |
| εij | 0.0980 | 25 | 0.00392 | ||
| Total (approximate mean) | 5.083 | 28 | |||
| Total (about zero) | 7.350 | 29 |
This indicates that the mass–metabolism relationship cannot be represented by the allometric relationship (i.e., ), despite the fact that a linear vertical relationship is shown as the log–log plot. This linear vertical relationship also suggests a rapid increase in the mass-specific metabolic rates during this stage (Figure 1). Therefore, this stage was not reflected in the regression analysis of mass–metabolism relationship.
The regression analysis of the mass–metabolism relationship is described in Table 1. The allometric relationships between and from the 12-day-old prolarvae (0.0241 g) to the 64-day-old juveniles (2.6368 g) interpose two stepwise increases of at approximately 0.25 and 0.65 g, with a scaling exponent maintained in each phase ( = 0.608). Each intraspecific scaling exponent was significantly less than that for all regression lines (p < 0.05, two-tailed t-test). The slopes of the intraspecific lines () in each group did not differ statistically (F2,23 = 0.11, p = 0.896; one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)). The intraspecific scaling exponent was estimated to be = 0.608 ± 0.061. The logarithms of the scaling constants in each group at = 0.608 were as follows: = 0.336 ± 0.084; = 0.377 ± 0.030; and = 0.576 ± 0.018. The scaling constants were as follows: = 2.17, = 2.38, and = 3.77. The interspecific scaling exponent was estimated to be = 0.791 ± 0.022. The detailed statistical results for all regression analyses are presented in Table 1.
One-way ANCOVA was conducted to assess the correctness of Equation (5) (Table 2). The values were not equal to zero (F1,25 = 23.40, p = 5.68 × 10−5; one-way ANCOVA), indicating that the group means did not lie on the overall line. Moreover, the intraspecific scaling exponent, = 0.608, was considerably different from the interspecific exponent, = 0.791 (F1,25 = 7.78, p = 9.95 × 10−3; one-way ANCOVA). As body mass increased, the intraspecific scaling constant ( increased exponentially from = 2.17 to = 3.77 (Figure 1). Thus, the ontogenetic phase shift in the metabolism of sterlet sturgeon can be given by because of the two stepwise increases in during their early life stages.
4. Discussion
4.1. Investigation of Ontogenetic Phase Shift in Metabolism
In this study, the relationship between resting routine metabolism and body mass from immediately after hatching until the juvenile stage in non-teleost fish was studied using the sterlet sturgeon. Notably, the relationship between the known oxygen consumption () and body mass (), a known metabolic measure of ontogenesis, was found to be , and it was confirmed that the scaling constant () had a tendency to rise sharply in stages. In other words, regression analysis of the relationship between resting routine metabolism and body mass in the non-teleost fish of early individual development showed that the scaling constant in each stage tended to increase rapidly twice; however, the scaling exponent remained at a certain level (i.e., = 0.608; Figure 1) This result suggests that the metabolic rate during early development does not simply indicate a non-linear or curvilinear log–log metabolic scaling relationship with the development of the organism (i.e., as body mass increases), but instead exhibits a rapid stepwise increase in the scaling constant (), resembling the pattern of climbing stairs, and the so-called ontogenetic phase shift in metabolism in the sterlet sturgeon, a non-teleost fish, may show a pattern similar to that of teleost fish (e.g., the tiger puffer and Japanese flounder). In other words, the stepwise increase in the scaling constant () from 2.17 to 3.77 of the sterlet sturgeon in early development was confirmed. Likewise, tendencies to show stepwise increase were confirmed from 2.75 to 7.25 in the tiger puffer and from 2.36 to 3.84 in the Japanese flounder. Furthermore, the overall scaling exponent exhibited a steeper tendency than the scaling exponents at each developmental stage in all species. Considering this point, it can be presumed that while the rate of energy metabolism per unit body mass decreases with increasing body mass in the early stages of individual development, the overall rate of energy metabolism is maintained at high levels by several increases in the scaling constant (). These results suggest that the scaling exponent of fish during early development may have been influenced by an ontogenetic phase shift in metabolism in which the scaling constant () exhibits a stepwise increase to explain the cause of the isometric or near-isometric phenomenon. This stepwise increase in the scaling constant () may reflect developmental transitions such as the maturation of gill structures, increased mitochondrial activity, and tissue composition changes, which enhance oxygen uptake efficiency and metabolic capacity as the fish grows [19]. Statistically, the results of ANCOVA confirmed that although the scaling exponent remained constant across groups (p = 0.896), the group means significantly differed (p = 5.68 × 10−5), validating the increase in the scaling constant () across developmental stages (Table 3).
Future studies will involve comparative transcriptomic analyses across transitional phases to investigate whether metabolic shifts are attributable to regulatory changes at the gene expression level.
4.2. Relationship Between Changes in Metabolic Scaling and Developmental Trajectory
Although the mechanism for the increased scaling constant () needs additional study, these shifts in metabolic scaling could be closely associated with its developmental trajectory [3]. In sterlet sturgeon, these milestones are typically defined as egg, prolarvae (9–17 mm in total length), larvae (17–50 mm), juvenile (50–450 mm), and adult (>450 mm) [41,42]. Interestingly, the ontogenetic milestones coincided precisely with the onset of the phase shifts in metabolism in sterlet sturgeon (Table 4). The transition from the prolarval stage to the larval stage was observed at ~0.25 g [41] (Table 4). During this transition, the development of respiratory organs (e.g., gills) was observed [49] (Table 4). As with other fish, the development of the gill lamellae and pseudobranch marks the transition from cutaneous to branchial respiration in sterlet sturgeon at this stage [49] (Table 4). Furthermore, the buccal cavity and gills that are developed induce a change in their feeding behavior, as the onset of exogenous feeding signals was also observed at this stage [41,49] (Table 4). The transition from the larval stage to the juvenile stage at ~0.65 g was marked by the formation of almost definitive adult gill structures [49] (Table 4). This implies that branchial respiration is functionally improved further because their gills become structurally more stable and have a much larger area similar to that of the adult gill structure [49] (Table 4). Similar to the gill structure, the embryonic finfold completely vanished and most of the fin apparatus was formed similar to the adult fin structure at this stage [41] (Table 4).

Table 4.
Changes in morphology and behavior associated with a phase shift in the scaling constant () during transitional phases.
These shifts in metabolic scaling are consistent with the findings for teleost fish. For example, the Japanese flounder had four distinct phases in which three stepwise increases in scaling constants at around 0.002, 0.01, and 0.2 g (~6, ~11, and ~28 mm in standard length) occurred during the transitional phases, which were accompanied by morphological and behavioral changes [16,19]. The rapid morphological change from isomorphoic three-dimensional growth to flat two-dimensional growth during the metamorphosis in Japanese flounder may be accompanied by a shift in metabolism because the transformation from larva to juvenile has been observed at ~0.01 g [16,19]. Previous studies have found that these shifts in metabolic scaling are related to body surface area because its scaling exponent corresponds to its metabolic scaling [19]. A change in their swimming behavior has also been reported to appear with the rapid metamorphosis. During the transformation from the larval to the juvenile stage, fish show a relatively sharp increase in maximum speed and swim much faster during metamorphosis than during either the larval or juvenile stages [54].
Taken together, these results indicate that the developmental stages during the early life of fish might be associated with their ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism. This association could likely universally explain the morphological and behavioral changes that occur during early life, even in non-teleost fish. Future studies should investigate whether these phenomena are similarly observed in other non-teleost fish to understand the relationship between shifts in metabolic scaling and development trajectory.
4.3. Relationship Between Changes in Metabolic Scaling and Eco-Physiological Traits
A recent study has suggested that the ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolic scaling are possibly related to the eco-physiological traits displayed by teleost fish during their early life stages [16,19]. For example, three stepwise increases in the scaling constant () at approximately 0.002, 0.01, and 0.1 g in tiger puffer fish (Takifugu rubripes) have been shown to facilitate their anti-predator adaptation because predator–prey interactions correspond to the three peaks in cannibalism during these early life stages [3]. Thus, it is possible that rapid-growing individuals are relatively quick to step up to the next phase of development with the increased scaling constant, which results in a higher metabolic rate and greater survival rate in comparison with slower-growing individuals under rearing conditions [3]. Although this study was carried out under artificial conditions, intracohort cannibalism in early life stages has been observed in various teleost fish, including the Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) [55,56] and the yellow tail (Seriola quinqueradiata) [57]. Interestingly, this explanation seems to be applicable to non-teleost fish as well. In fact, sterlet sturgeon leave the interstital spaces of rocky substrates and immediately disperse downstream near to the bottom because the prolarvae mostly lack the physical structure needed to escape predators and thus they move quickly to avoid attacks and capture prey [50,58,59].
At ~0.25 g, the larvae almost cease downstream migration and settle at the river bottom [50] (Table 4). This migration may be a mechanism for decreasing predation risk by avoiding threatened habitats. At ~0.65 g, the juveniles undergo rapid growth and feed primarily on benthic invertebrates, such as benthic crustaceans and mollusks [51,52,53] (Table 4). This strategy has evolutionary advantages because natural mortality is largely dependent on growth, i.e., settling in benthic habitats helps limit mortality since these habitats have a lower predation risk. Therefore, an increase in the scaling constant with growth implies that rapidly growing individuals have a higher chance of survival, whereas slow-growing individuals are more likely to suffer from predation. Although there was an experimental limitation regarding the results of this study due to the small number of individuals used, this finding could be an important step in understanding the eco-physiological traits of non-teleost fish. Future studies need to elucidate the mechanisms by which the scaling constant () increases with growth and how shifts in metabolic scaling influence eco-physiological traits, such as predator–prey interactions.
4.4. Metabolic Scaling of Fish During Early Developmental Stages
Previous studies reported that intraspecific metabolism tends to scale isometrically to body mass (i.e., b is equal or close to 1) in a variety of teleost fish during their larval and juvenile stages [3,16,24,25,27,30,31,32,60,61]. Similar tendencies have been observed in various invertebrates, birds, and mammals [8]. This is not a unique phenomenon, since isometric and/or near-isometric metabolic scaling during the early stages of development could be impacted by a stepwise increasing scaling constant (). In Japanese flounder, the scaling exponent was estimated to be isometric to the body mass (p = 0.052, two-tailed t-test) just after hatching (0.00026 g) and in 30-day-old larvae (0.0055 g) [16]. Similar to these findings for teleost fish, this study also shows sudden or progressive increases in the intraspecific scaling exponent throughout the early stages of development in sterlet sturgeon within a rather restricted size range. That is, the intraspecific scaling exponent was nearly isometric to body mass in 3-day-old to 9-day-old prolarvae (0.0196–0.0301 g) (p = 0.927, two-tailed t-test). Interestingly, when compared with the ratio of increasing body mass during this period, the Japanese flounder maintained isometric or near-isometric scaling until the body mass gain reached 21.15 times, whereas that of sterlet sturgeon was only 1.53 times. This means that the relatively isometric or near-isometric scaling period for sterlet sturgeon seems to be shorter than that for the Japanese flounder. Although, it is difficult to directly compare species-specific metabolic differences due to their varying initial and/or maximal sizes, the overall intraspecific scaling exponent (i.e., common slope) of the sterlet sturgeon ( = 0.608) was significantly lower than that of the Japanese flounder ( = 0.831, p = 0.035; two-tailed t-test). This tendency was also confirmed by the interspecific scaling exponent between the sterlet sturgeon ( = 0.915) (p < 0.01, two-tailed t-test). Taken together, these differences suggest that the relatively short isometric or near-isometric scaling period could cause the lower intraspecific scaling exponent. Overall, such isometric and/or near-isometric metabolic scaling during early development stages could be impacted by a hidden effect of ontogenetic phase shift on metabolism. These effects are thought to be valuable as empirical data (i.e., ontogenetic phase shift in metabolism) to explain the differences in scaling exponents in various fish species, including non-teleost fish.
4.5. Evaluation of the Metabolic Scaling Measuring Technique
In this study, the possibility of an ontogenetic phase shift in metabolism in the early developmental stages of the sterlet sturgeon, a non-teleost fish, was suggested. However, several technical limitations should be noted. First, although individuals derived from multiple families were used, family-specific metabolic variation and potential maternal effects may still influence the results, as shown in brown trout (Salmo trutta), where maternal effects caused differences in metabolic rate patterns among families [62]. Second, because metabolism was measured using the semi-closed method, distinguishing clearly between resting and routine metabolic rate was difficult, particularly since activity patterns change during ontogeny [32,63]. Third, the Winkler titration method used here, although reliable and economical, requires longer measurement times, which may reduce accuracy compared with modern oxygen sensor-based techniques [64].
To overcome these issues, future studies should consider approaches such as controlling or monitoring swimming activity [64], adopting oxygen sensor technology, and incorporating maternal effects into analytical frameworks. Moreover, comparisons across different populations and measurement techniques will be essential, and the integration of mixed-effects models could provide further advantages [37,65]. Such models are particularly effective at capturing individual-level variation in repeated or hierarchical sampling designs, thereby improving the robustness and interpretability of metabolic scaling analyses across fish species and developmental stages.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study provides evidence for ontogenetic phase shifts in the metabolism of non-teleost fish. Similar to the findings for teleost fish, the sterlet sturgeon exhibited three distinct negative allometric phases, characterized by two stepwise increases in the scaling constant during early growth at approximately 0.25 and 0.65 g, while maintaining a consistent scaling exponent in each phase ( = 0.608, i.e., common slope). These shifts were closely associated with developmental transitions, suggesting that ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism may serve as a more appropriate framework for explaining the morphological and behavioral changes observed during early life stages in fish. The outcomes of this study suggest the potential for stepwise changes in metabolic rate during early development in non-teleost fish. These findings contribute to a broader understanding of metabolic patterns during early ontogeny across diverse fish species. While further research is necessary, especially across different taxa and developmental conditions, the present results indicate that growth-related metabolic demands may lead to substantial changes in the scaling constant of metabolic rate, even in non-teleost fish.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Institutional Review Board and Ethical Committee on Animal Experimentation at the Tsukuba Research Institute, Fujikin Inc., Ltd., Tsukuba, Japan.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data generated in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Kiyoshi Hiraoka and his research group members at the Tsukuba Research Institute, Fujikin Inc., Ltd. (Tsukuba, Japan) for providing experimental animals and valuable suggestions while performing the experiments. I am grateful to Akane Ishida and Mikio Uchiba for their support and assistance throughout the experiment. I wish to thank the editors for editing the manuscript for English language and grammar. Finally, I sincerely thank the Editor and reviewers for their careful reading of the manuscript and their constructive comments and insightful suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Czarnołęski, M.; Kozłowski, J.; Stańczykowska, A.; Lewandowski, K. Optimal resource allocation explains growth curve diversity in zebra mussels. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2003, 5, 571–587. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Zuo, W.; Moses, M.E.; Woodruff, W.H.; Brown, J.H.; West, G.B. Energy uptake and allocation during ontogeny. Science 2008, 322, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Kanda, T.; Takeda, T.; Ishimatsu, A.; Oikawa, S. Ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism: Links to development and anti-predator adaptation. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, J.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Richards, J.; Allen, D. Relationship between growth and standard metabolic rate: Measurement artefacts and implications for habitat use and life-history adaptation in salmonids. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A. The Respiratory Exchange of Animals and Man; Longmans, Green: London, UK, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, M. Body size and metabolism. Hilgardia 1932, 6, 315–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, J.; Konarzewski, M.; Gawelczyk, A.T. Cell size as a link between noncoding DNA and metabolic rate scaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14080–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S. Beyond the ‘3/4-power law’: Variation in the intra-and interspecific scaling of metabolic rate in animals. Biol. Rev. 2005, 80, 611–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Phillips, N.F.; Seymour, R.S. The scaling and temperature dependence of vertebrate metabolism. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S. A unifying explanation for diverse metabolic scaling in animals and plants. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Frappell, P.B.; Chown, S.L. An information-theoretic approach to evaluating the size and temperature dependence of metabolic rate. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3616–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S. The 3/4-power law is not universal: Evolution of isometric, ontogenetic metabolic scaling in pelagic animals. Bioscience 2006, 56, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, G.C.; Birchard, G.F. Traditional allometric analysis fails to provide a valid predictive model for mammalian metabolic rates. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3581–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokotrones, T.; Savage, V.; Deeds, E.J.; Fontana, W. Curvature in metabolic scaling. Nature 2010, 464, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Yamaji, K.; Ishida, A.; Prokushkin, S.G.; Masyagina, O.V.; Hagihara, A.; Hoque, A.T.; Suwa, R.; Osawa, A.; Nishizono, T.; et al. Mixed-power scaling of whole-plant respiration from seedlings to giant trees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, M.; Oikawa, S. Ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism in a flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, W. A distribution must be made between the ontogeny and the phylogeny of metabolism in order to understand the mass exponent of energy metabolism. Respir. Physiol. 1984, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnoleski, M.; Kozlowski, J.; Dumiot, G.; Bonnet, J.C.; Mallard, J.; Dupont-Nivet, M. Scaling of metabolism in Helix aspersa snails: Changes through ontogeny and response to selection for increased size. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.I. Ontogeny of the respiratory area in relation to body mass with reference to resting metabolism in the Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1846). Fishes 2022, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, M.; Cozzoli, F.; Vignes, F.; Bertoli, M.; Pizzul, E.; Basset, A. Metabolic rate and climate change across latitudes: Evidence of mass-dependent responses in aquatic amphipods. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb244842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, M.; Cozzoli, F.; Basset, A. Metabolic rate and foraging behaviour: A mechanistic link across body size and temperature gradients. Oikos 2025, 2025, e10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, S.J.; Burggren, W.W.; Pelster, B.; Reiber, C.L.; Spicer, J. Comparative Developmental Physiology: Contributions, Tools, and Trends; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Killen, S.S.; Costa, I.; Brown, J.A.; Gamperl, A.K. Little left in the tank: Metabolic scaling in marine teleosts and its implications for aerobic scope. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.; Wells, R.M. Ontogenetic scaling of fish metabolism in the mouse-to-elephant mass magnitude range. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S. Metabolic scaling in complex living systems. Systems 2014, 2, 451–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.S.; Hirst, A.G.; Atkinson, D. Shape shifting predicts ontogenetic changes in metabolic scaling in diverse aquatic invertebrates. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Hirst, A.G.; Glazier, D.S.; Atkinson, D. Ecological pressures and the contrasting scaling of metabolism and body shape in coexisting taxa: Cephalopods versus teleost fish. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.; Johnston, N.M. Scaling of metabolic rate with body mass and temperature in teleost fish. J. Anim. Ecol. 1999, 68, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokma, F. Evidence against universal metabolic allometry. Funct. Ecol. 2004, 18, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killen, S.S.; Atkinson, D.; Glazier, D.S. The intraspecific scaling of metabolic rate with body mass in fishes depends on lifestyle and temperature. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, S.; Itazawa, Y.; Gotoh, M. Ontogenetic change in the relationship between metabolic rate and body mass in a sea bream Pagrus major (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Biol. 1991, 38, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.R.; Lee, J.A. Metabolic ontogeny of teleost fishes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochdansky, A.B.; Leggett, W.C. Winberg revisited: Convergence of routine metabolism in larval and juvenile fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; He, Y.; Du, B.; Li, X.; Jing, Y.; Luo, Y. Mass scaling of standard metabolic rate within and among individuals in Western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2025, 195, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Lu, L.; Jiang, M.; Jia, J.; Li, W.; Wu, H.; Liao, Y.; Li, J. Metabolic scaling: Individual versus intraspecific scaling of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2021, 191, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norin, T.; Malte, H.; Clark, T.D. Differential plasticity of metabolic rate phenotypes in a tropical fish facing environmental change. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norin, T.; Gamperl, A.K. Metabolic scaling of individuals vs. populations: Evidence for variation in scaling exponents at different hierarchical levels. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, R.; Lecointre, G. Biology and conservation of sturgeon and paddlefish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2000, 10, 355–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, A.; Ostaszewska, T.; Rożek, W. The ontogenetic development of the digestive tract and accessory glands of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus L.) larvae during endogenous feeding. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, L.S.; Bogdanov, A.S.; Kozhin, N.I.; Rass, T.S. Commercial Fishes of the USSR, Pshchepromizdat; VNIRO Atlas Tsvetnykhrisunkovryb: Mockva, Russia, 1949; p. 787. [Google Scholar]
- Rybnikár, J.; Prokeš, M.; Mareš, J.; Cileček, M. Early development and growth of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) in the Czech Republic. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2014, 59, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokeš, M.; Baruš, V.; Mareš, J.; Peňáz, M.; Baránek, V. Growth of sterlet Acipenser ruthenus under experimental and farm conditions of the Czech Republic, with remarks on other sturgeons. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2014, 59, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBreton, G.; Beamish, F.W. Growth, bioenergetics and age. In Sturgeons and Paddlefish of North America; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 195–216. [Google Scholar]
- Doroshov, S.I. Biology and culture of sturgeon Acipenseriformes. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Cech, J.J., Jr. Respirometry. In Methods in Fish Biology; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1990; pp. 335–362. [Google Scholar]
- Helm, I.; Jalukse, L.; Vilbaste, M.; Leito, I. Micro-Winkler titration method for dissolved oxygen concentration measurement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 648, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, K.A. Statistical Theory and Methodology in Science and Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, H.A.; McMahon, T.A. The 3/4 mass exponent for energy metabolism is not a statistical artifact. Respir. Physiol. 1983, 52, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, H.; Eagderi, S. Ontogeny of gill structure in Sterlet, Acipenser ruthenus (Linnaeus, 1758). Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2015, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmykov, V.A.; Ruban, G.I.; Pavlov, D.S. Migrations and resources of sterlet Acipenser ruthenus (Acipenseridae) from the lower reaches of the Volga River. J. Ichthyol. 2010, 50, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djikanovic, V.; Skoric, S.; Lenhardt, M.; Smederevac-Lalic, M.; Visnjic-Jeftic, Z.; Spasic, S.; Mickovic, B. Review of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus L. 1758) (Actinopterygii: Acipenseridae) feeding habits in the River Danube, 1694–1852 river km. J. Nat. Hist. 2015, 49, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strel’nikova, A.P. Feeding of juvenile sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus, Acipenseridae) in the Danube River midstream. J. Ichthyol. 2012, 52, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieszl, J.; Bogacka-Kapusta, E.; Kapusta, A.; Szymańska, U.; Martyniak, A. Feeding ecology of sterlet Acipenser ruthenus L. in the Hungarian section of the Danube River. Fish. Aquat. Life 2011, 19, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukuhara, O. Morphological and functional development of Japanese flounder in early life stage. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1986, 52, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillgruber, N.; Kloppmann, M.; Wahl, E.; Von Westernhagen, H. Feeding of larval blue whiting and Atlantic mackerel: A comparison of foraging strategies. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 51, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillgruber, N.; Kloppmann, M. Small-scale patterns in distribution and feeding of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus L.) larvae in the Celtic Sea with special regard to intra-cohort cannibalism. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2001, 55, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakura, Y.; Tsukamoto, K. Onset and development of cannibalistic behaviour in early life stages of yellowtail. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodorevskaya, R.P. Swimming Ability of Acipens erids at Early Stages of Ontogenesis. In Biological Bases of Development of Sturgeon Husbandry in Water Bodies of the USSR; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1979; pp. 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, D.S.; Nezdolii, V.K.; Khodorevskaya, R.P.; Ostrovskii, M.P.; Popova, I.K. Downstream Migration of Young Fish in the Volga and Ili Rivers; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Giguère, L.A.; Côté, B.; St-Pierre, J. Metabolic rates scale isometrically in larval fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 50, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.N.; Rønnestad, I.; van der Meeren, T.; Fyhn, H.J. Fuel and metabolic scaling during the early life stages of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Régnier, T.; Bolliet, V.; Labonne, J.; Gaudin, P. Assessing maternal effects on metabolic rate dynamics along early development in brown trout (Salmo trutta): An individual-based approach. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2010, 180, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, D.; Steffensen, J.F.; Farrell, A.P. The determination of standard metabolic rate in fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 81–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, M.A.; Moyano, M. Measuring respiration rates in marine fish larvae: Challenges and advances. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 173–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norin, T. Growth and mortality as causes of variation in metabolic scaling among taxa and taxonomic levels. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2022, 62, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).