Development and Modeling of Energy Storage Systems for Future Power Grids
A special issue of Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This special issue belongs to the section "D: Energy Storage and Application".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 July 2026 | Viewed by 1827
Special Issue Editors
Interests: hybrid energy storage systems; power quality; renewables; microgrids; battery state of health assessment
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
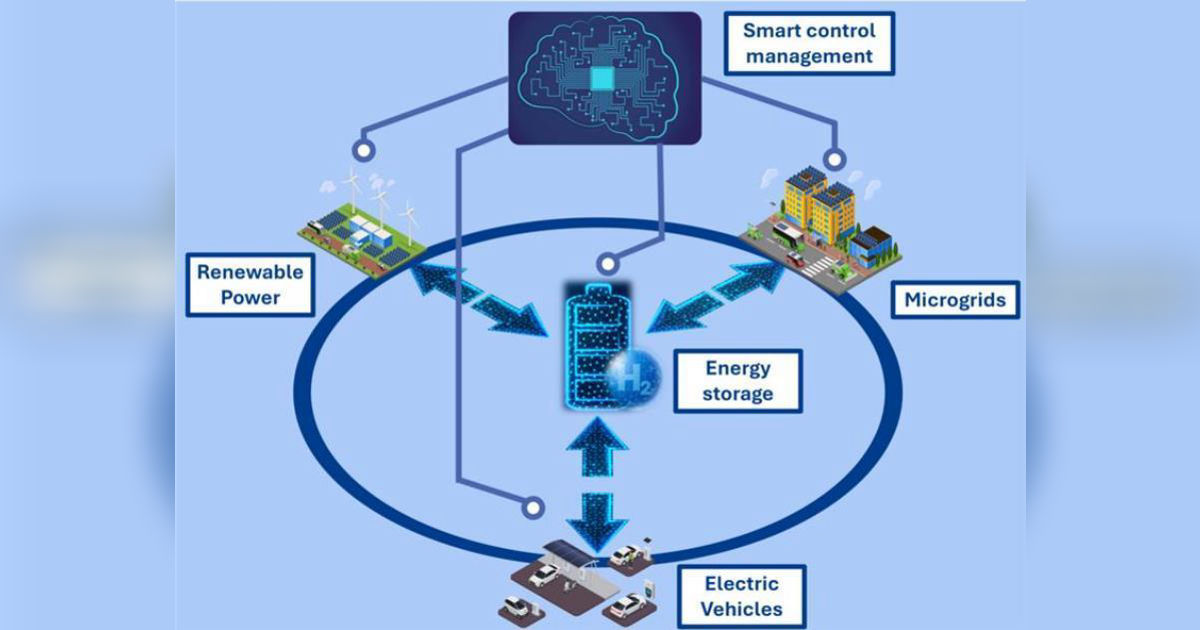
The transition from centralized fossil fuel-based to decentralized power production, including renewable energy sources, represents a critical step in addressing global environmental concerns. Nevertheless, renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, are inherently intermittent and non-programmable, so future power grids stability and reliability challenges need to be addressed. In this framework, the integration of energy storage systems into future power grids is vital for storing excess energy generated by renewable sources and enabling its use when demand exceeds supply.
This Special Issue focuses on the latest developments in energy storage technologies, emphasizing their integration into renewable-based grids. It highlights advances in the modelling, control, and application of energy storage systems that support renewable-based electric grids. Topics include, but are not limited to, innovative energy storage solutions for microgrids, advanced modelling approaches, transient stability analysis, and power smoothing techniques. A special focus is given to the implementation of energy storage systems for grid services. In particular, the study of battery electric vehicles performing vehicle-to-X (V2X) services, such as bidirectional vehicle-to-grid (V2G), vehicle-to-building (V2B) and vehicle-to-home (V2H), is undertaken. Additionally, this Special Issue covers crucial aspects such as energy storage control strategies, experimental testing, aging effects, state of health prediction and monitoring, and techno-economic analysis of these systems. Our goal is to foster research that supports the integration of energy storage systems into renewable-based power grids, providing more reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions. This Special Issue will advance our shared understanding of energy storage technologies, paving the way for their widespread adoption and contributing to the future of clean energy systems.
Dr. Dario Pelosi
Dr. Lorenzo Trombetti
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy storage systems
- renewables
- grid services
- power and energy management
- control strategies
- electric vehicles
- microgrids
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






