- 4.8Impact Factor
- 6.6CiteScore
- 20 daysTime to First Decision
Li-Ion Capacitors: Materials, Devices and Systems
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
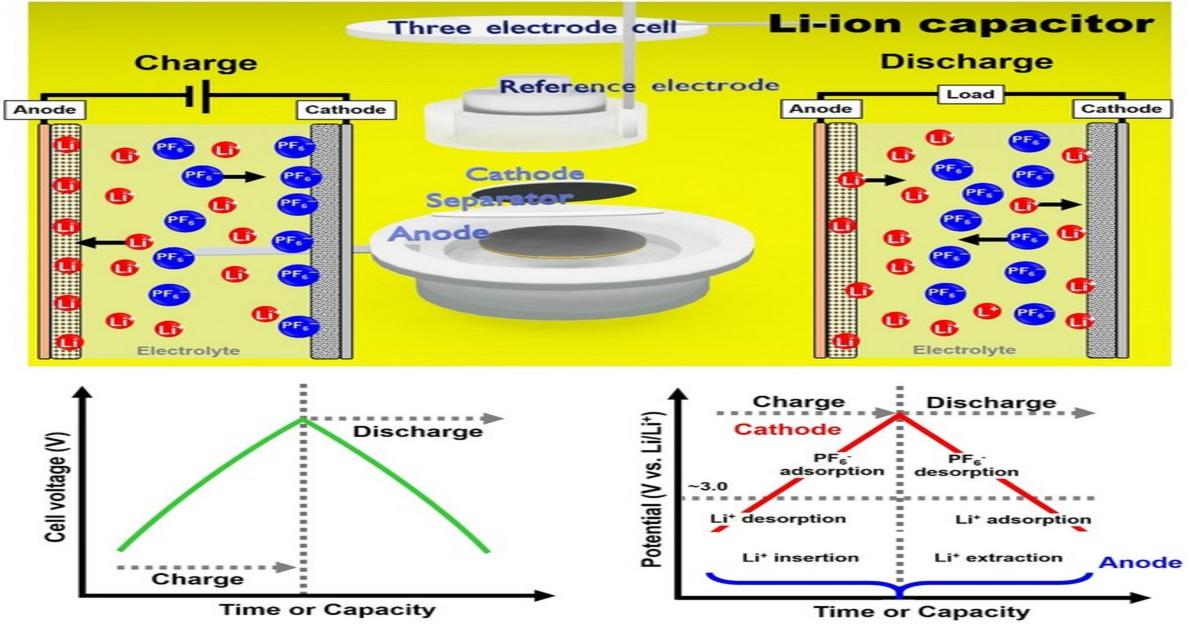
There is a strong need to enhance both the energy and power density of energy storage devices, especially in the fields of portable devices and transportation. Recently, Li-ion capacitors (LICs) have been attracting attention as energy storage devices which can compensate for the low power density and short cycle life of existing Li-ion batteries and for the low energy density of electric double-layer capacitors. LICs are categorized as hybrid capacitors, in which non-faradaic processes generating the electric double layer proceed on the cathode, and faradaic reactions occur within the anode through Li-ion insertion/extraction. Since the development of coin-type LICs by Kanebo in 1991 and the development of 1000 F-class high-capacitance LICs by Fuji Heavy Industries (now Subaru) in 2005, academia and industrial sectors have been intensively performing R&D. It is now an appropriate time to publish a Special Issue targeting recent developments and reviewing the technological trends and market penetration of LICs.
In addition to the wide variety in material selections of cathode and anode active materials, binders, electrolytes and separators, LICs have various device factors such as the mass ratio of cathode and anode active materials, anode pre-lithiation (pre-doping of Li ions) level and working cell voltage range that significantly influence their charge–discharge performances and lifetimes. Field experiences with LICs embedded in systems of the electronic device, transportation, robotics and machinery sectors are now highly needed to be published in order to share knowledge on their actual performances. The journal Batteries invites contributions to this Special Issue featuring recent technological developments in LICs from the aspect of materials, devices and systems. Review articles regarding LIC technology are also welcome.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Performance enhancement of LICs by using novel materials (cathode and anode active materials, conductive agents, binders, current collectors, electrolytes, separators, etc.) and by device optimization (electrode design, pre-lithiation strategy, cell assembly and packaging methodology, etc.);
- Material and electrochemical studies towards device components intended for use in LICs;
- Working mechanism studies of LICs in various working conditions (high and low temperatures, excessive charging and discharging, etc.);
- Aging behavior and modeling of LICs in various working conditions;
- Diagnosis or monitoring technology of LICs;
- Case studies of prototypes or commercial LICs used in industrial applications such as electronic devices and vehicles, and in special environments;
- Hybridization of LICs with other types of energy devices such as secondary batteries and fuel cells.
Prof. Dr. Seiji Kumagai
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Batteries is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- lithium-ion capacitors
- electrochemical capacitors
- hybrid capacitors
- electrode
- electrolyte
- pre-lithiation
- energy density
- power density
- lifetime
- aging
- diagnosis
- monitoring
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

