- Article
Survival Probabilities for Correlated Drifted Brownian Motions via Exit from Simplicial Cones
- Tristan Guillaume
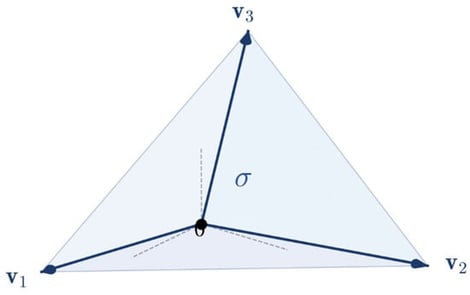
This paper investigates the finite-horizon survival probability for a system of correlated arithmetic Brownian motions with heterogeneous drifts and volatilities, focusing on the event in which one component remains strictly below all others. Using a whitening transformation of the covariance structure, we reduce the problem to the survival of a standard Brownian motion in a simplicial cone, characterized by its spherical cross-section. While explicit solutions are available in low dimensions, we address the computationally challenging tetrahedral angular case. We derive a semi-analytic formula for the survival probability via an eigenfunction expansion of the Dirichlet Laplace–Beltrami operator on this curved domain. For efficient implementation, we construct a diffeomorphism from the spherical tetrahedron to a fixed Euclidean tetrahedron, enabling the computation of angular eigenpairs through a stable finite-element scheme. For higher-dimensional regimes, we also introduce a covariance-based difficulty index and geometric bounds based on an inscribed spherical cap to assess spectral convergence and estimate long-time decay rates. Numerical experiments show that this offline–online approach achieves high accuracy and substantial speedups relative to Monte Carlo benchmarks.
10 March 2026