Abstract
Ceratophrys cranwelli, commonly known as the Cranwell’s horned frog or Pacman frog, is an amphibian species native to South America. This species has gained interest both as a pet among hobbyists and as a subject of scientific inquiry in veterinary medicine. A two-year-old pet male albino Ceratophrys cranwelli was presented exhibiting lethargy, weight loss, and anorexia, persisting for two months. Clinical examination revealed a fracture localized to the proximal third of the left femur accompanied by an osteolytic process. The patient was discharged with a treatment regimen for suspected secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism and an ulcerative skin lesion. Nevertheless, due to the progressive deterioration of the left thigh, amputation of the affected limb was proposed and performed at the coxofemoral joint. Histopathological analysis of the excised mass revealed an atypical mesenchymal mass consistent with a fibromyxochondroma. The surgical procedure was conducted under anesthesia induced by a combination of alfaxalone, ketamine, medetomidine, and butorphanol, with postoperative treatment consisting of enrofloxacin, meloxicam, and butorphanol. The patient showed good post-surgical recovery, exhibiting normal physiological and behavioral activities. This report highlights the management and the diagnostic challenges of a progressive limb lesion in a Ceratophrys cranwelli, offering insights into potential therapeutic approaches for similar cases in amphibians.
1. Introduction
The Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli), also commonly referred to as the Chacoan horned frog or Pacman frog, is a species of amphibian native to South America, with its habitat spanning Bolivia, Argentina, and Brazil [1]. Renowned for its distinctive appearance and fascinating behaviors, this species has not only captured the interest of hobbyists as a popular pet choice but has also become a subject of scientific inquiry in veterinary medicine. As amphibian populations face numerous threats globally, understanding the health dynamics of species like the Cranwell’s horned frog is crucial for developing effective management and conservation strategies. Consequently, there is a growing body of research dedicated to unraveling the complexities of diseases and health disorders affecting this species in both wild and captive settings [1,2,3,4]. Among the most prevalent disorders observed in captive Pacman frogs are nutritional imbalances (such as secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism, obesity, and corneal lipidosis), husbandry-related diseases, traumatic injuries, infectious and neoplastic diseases [5]. While some mesenchymal neoplasms have been documented in amphibians, including the Cranwell’s horned frog, there remains uncertainty regarding their nature, whether they represent true neoplasms, exuberant reparative responses to chronic inflammation, or formations analogous to bone fracture calluses [5,6,7].
2. Case Description
A two-year-old male albino Ceratophrys cranwelli was presented featuring a history of lethargy, reduced skin mucus production, weight loss, and anorexia persisting for the past 2 months. The terrarium housing arrangement included coconut fiber substrate supplemented with a 14-watt heating pad affixed to one of the lateral walls, maintaining a temperature range of 24–26 °C via a thermostat, with relative humidity levels between 60–80%. Cleaning procedures were conducted every 2 weeks, and the diet mostly consisted of live invertebrates (Blaptica dubia, Shelfordella lateralis, Acheta domesticus) provided twice a week. Calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation were added to the diet in powdered form, applied approximately twice weekly by dusting the live prey items.
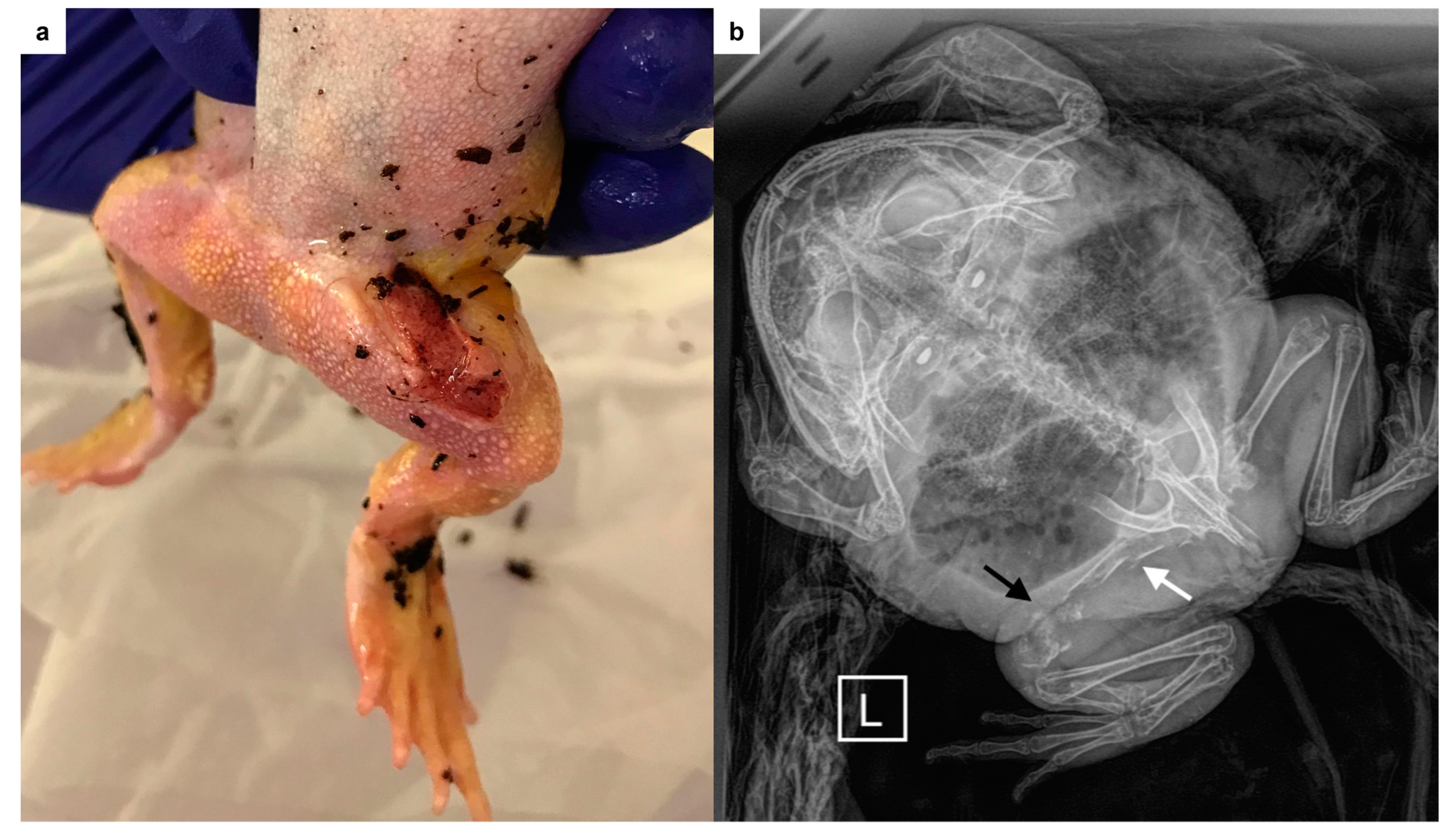
During the physical examination, the patient was alert but displayed a poor body condition and weighed 81 g. Bilateral moderate erythema was observed on the medial aspect of the thighs, accompanied by mild erythema on the skin covering the coelomic region. A 1.5 × 0.5 cm ulcerated skin lesion with irregular borders was identified on the cranial aspect of the left thigh (Figure 1a). Palpation revealed enlargement and firmness of the affected limb compared to the contralateral limb. The owner refused sedation for diagnostic imaging; radiographic imaging was therefore performed with the awake patient. Due to the uncooperative temperament of the animal, and aiming to avoid potential skin damage and stress related to manual restraint, a single radiograph was performed with the frog positioned in ventral recumbency in a plastic box. The radiographic findings revealed a fracture localized to the proximal third of the left femur, accompanied by an osteolytic process affecting its distal portion (Figure 1b).
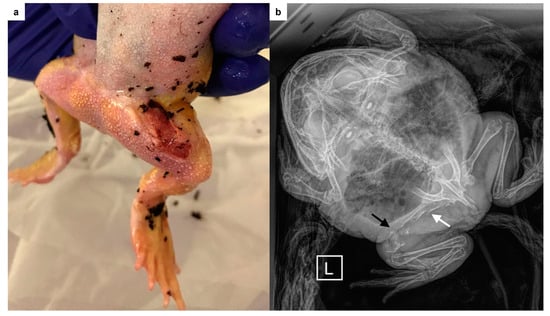
Figure 1.
(a) Enlarged and deformed left thigh of the Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli), with an ulcerated lesion noted on its cranial aspect. (b) Whole body radiograph of the Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratoprhys cranwelli) in ventral recumbency, showing a fracture of the proximal third of the femur (white arrow) and an osteolytic process in its distal part (black arrow).
As a traumatic event was not reported by the owner, a suspected secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism and subsequent metabolic bone disease was hypothesized, with development of a pathological fracture and a skin ulcerated lesion due to the altered ambulation and friction of the limb against the terrarium substrate. In this instance, although other differential diagnoses could have been considered, the decision to initiate treatment for presumed hyperparathyroidism was agreed upon with the owner, who preferred to pursue therapy prior to further diagnostic investigations. The treatment consisted of daily baths, utilizing a 2% calcium gluconate solution, along with daily exposure to UVB light for a duration of 6–8 h, supplemented by incorporating calcium carbonate into the diet. Additionally, for the management of the ulcerated lesion, topical administration of sulfadiazine/enrofloxacin drops (Baytril® Otic, Elanco Italia S.p.A., Sesto Fiorentino, Italy) was prescribed twice daily, alongside oral administration of meloxicam at a dosage of 0.5 mg/kg (Deflacam®, Fatro S.p.A., Ozzano dell’Emilia, Italy) once daily. Upon re-evaluation after seven days, while there was a slight reduction observed in the ulcerative lesion, the condition of the left thigh had deteriorated, exhibiting increased swelling and deformity. Considering the quick progressive worsening of the condition, amputation of the affected limb was proposed as a therapeutic intervention.
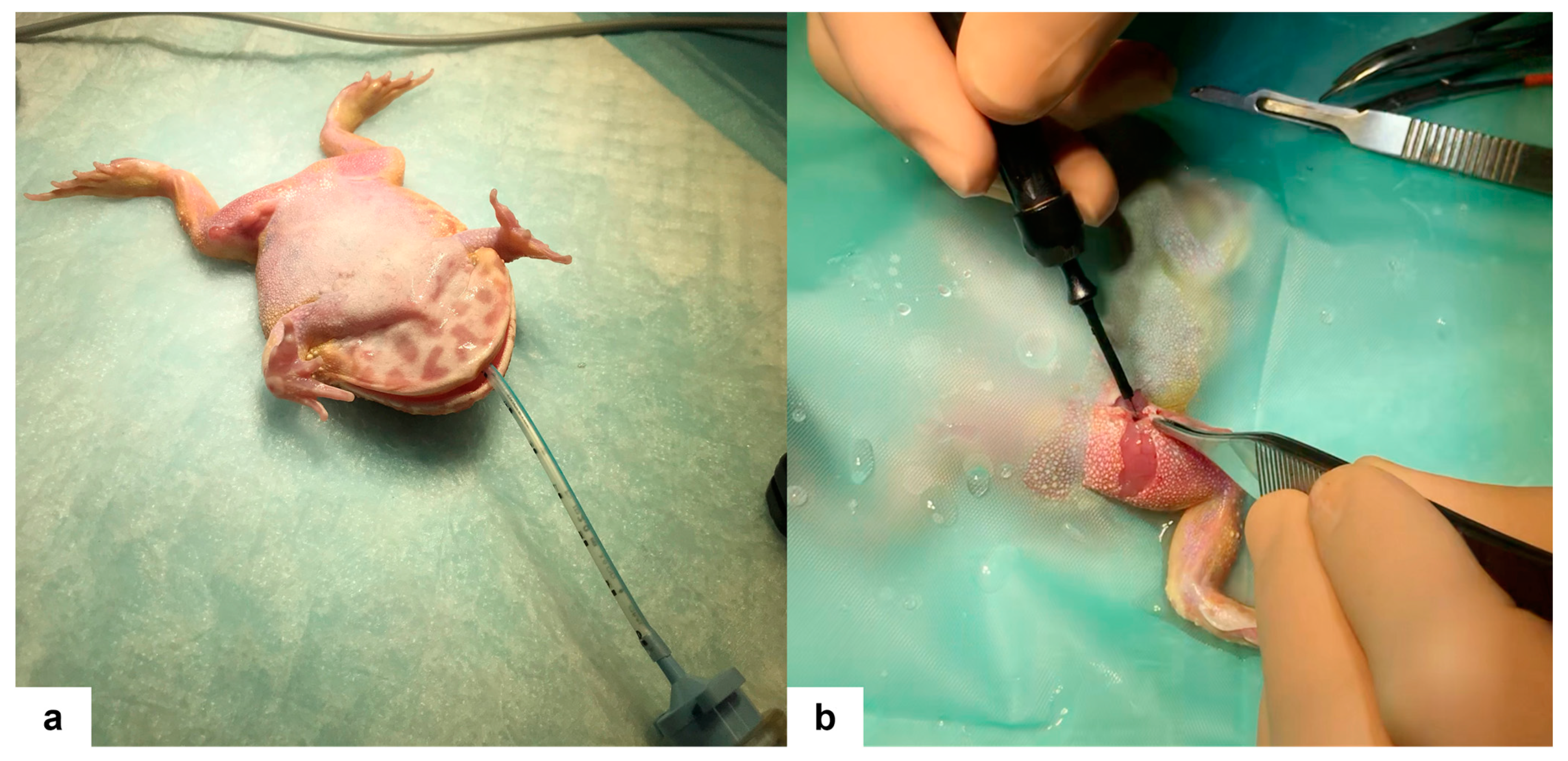
Anesthesia was induced utilizing a combination of drugs administered in the dorsal lymph sac, including 5.5 mg/kg alfaxalone (Alfaxan® Multidose, Jurox Pty Limited, Rutherford, Australia), 12 mg/kg ketamine (Lobotor®, Acme S.r.l., Corte Tegge, Italy), 0.5 mg/kg medetomidine (Dormisan, A.T.I. s.r.l., Ozzano dell’Emilia, Italy), and 1 mg/kg butorphanol (Nargesic®, Acme S.r.l., Corte Tegge, Italy). After 10 min, loss of righting reflex and loss of pedal and palpebral reflexes were obtained. Subsequently, a 2.0 mm uncuffed endotracheal tube was placed, and maintenance of anesthesia was performed with 1.5% isoflurane (IsoFlo, Zoetis Italia S.r.l, Rome, Italy) delivered in 100% O2 through a non-rebreathing respiratory system (Bain coaxial breathing system, Intersurgical, Wokingham, UK). Manual-assisted ventilation was provided at a rate of 10 breaths/min. The patient was positioned in dorsal recumbency on an adsorbent mat moistened with Lactated Ringer’s solution (Baxter S.p.A., Rome, Italy) with a heating pad placed underneath (Figure 2a). Intermittent monitoring of heart rate was conducted using an ultrasonic Doppler flow detector. Prior to surgical intervention, the skin was prepared by gentle rolling with sterile cotton swabs soaked in sterile Lactated Ringer’s solution while sterile plastic drapes were positioned.
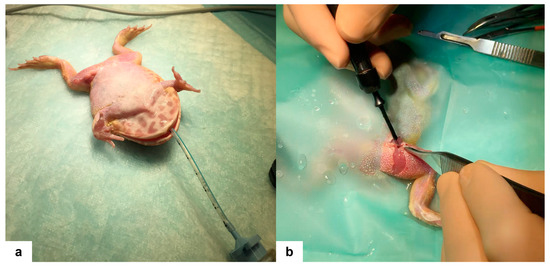
Figure 2.
(a) The Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli) in dorsal recumbency after intubation with a 2.0 mm endotracheal tube, prior to surgery. (b) Muscle dissection using a plasma scalpel after skin incision.
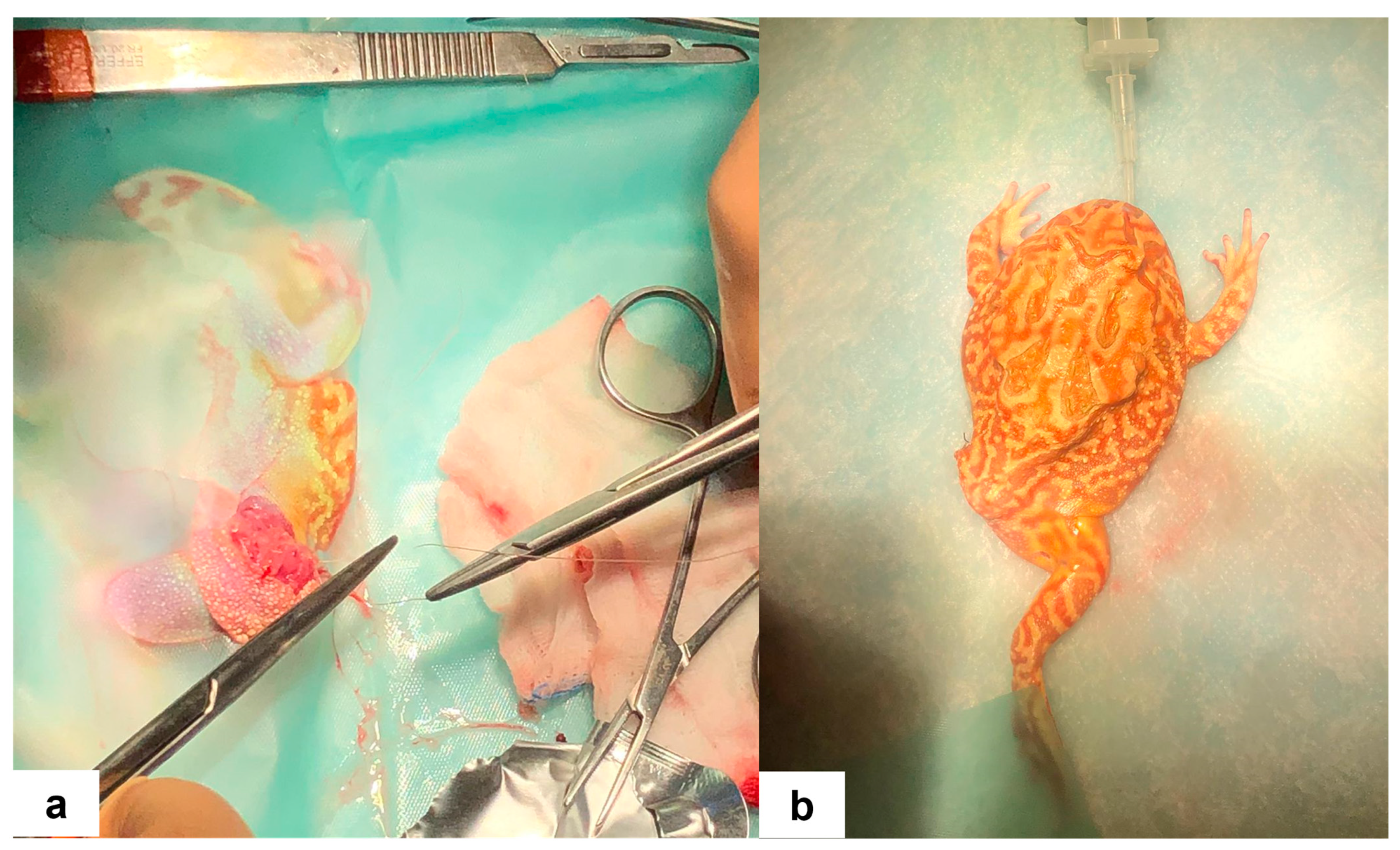
The amputation procedure of the left hind limb followed a technique analogous to that described for mammals [8], consisting of resection at the coxofemoral joint. The skin was incised proximally to the ulcerative lesion and distally to the coxofemoral joint to allow tension-free closure. Muscle dissection was performed using a plasma scalpel (Onemytis®, Otech Industry S.r.l., Alessandria, Italy) at their distal insertion to facilitate adequate coverage of the amputation site (Figure 2b). Major vessels were ligated using 5–0 monofilament absorbable sutures (Biosyn™, Covidien, Mansfield, MA, USA). The same suture type, employed in a horizontal mattress pattern, was used for skin closure (Figure 3a). Following the procedure, the excised hind limb was immersed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for subsequent histopathological analysis.
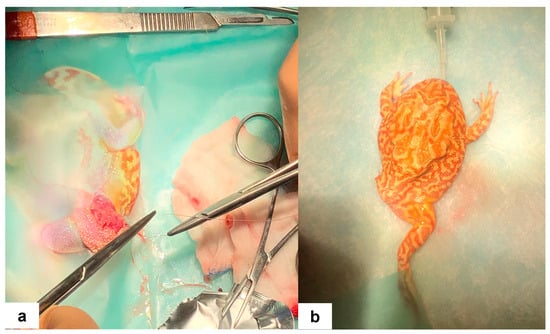
Figure 3.
(a) Skin suture after amputation of the left hind limb in the Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli). (b) The frog in ventral recumbency after the surgical procedure before recovery.
After completing the surgical procedures, the patient was positioned in ventral recumbency (Figure 3b), and 2.5 mg/kg of atipamezole (Sedastop®, Ecuphar Italia S.r.l., Milan, Italy) was administered in the dorsal lymph sac. Spontaneous breathing resumed within 10 min, while pedal and palpebral reflexes reoccurred within 25 min, accompanied by spontaneous movements. Subsequently, the patient was immersed in a bath containing a solution composed of equal parts Lactated Ringer’s solution and 5% Glucose (Baxter S.p.A., Roma, Italy) for a duration of 8 h.
Post-operative treatment consisted of 5 mg/kg enrofloxacin (Baytril® 25 mg/mL, Elanco Italia S.p.A., Sesto Fiorentino, Italy), 0.5 mg/kg meloxicam (Metacam® 2 mg/mL, Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health Italia S.p.A. Milan, Italy) injected subcutaneously once a day for 5 days, and 0.2 mg/kg butorphanol (Nargesic®, Acme S.r.l., Corte Tegge, Italy) injected subcutaneously once a day for 2 days. One day after surgery, the patient was ambulating despite the absence of a hind limb (Supplementary Materials, Video S1). Five days after the surgical procedure, the patient showed good general conditions and was discharged with oral enrofloxacin (Baytril® 2.5%, Elanco Italia S.p.A., Sesto Fiorentino, Italy) and meloxicam (Deflacam®, Fatro S.p.A., Ozzano dell’Emilia, Italy) to be given once a day until the tenth day from surgery at the same dosages already used. One week after the procedure, the owner reported resumption of normal physiological and behavioral activities, with spontaneous feeding (Supplementary Materials, Video S2) and absence of further pathological signs. The same conditions, with absence of clinical signs of recurrence, were reported until 16 months after the surgery, when the animal died. As the owner did not consent, necropsy was not performed.
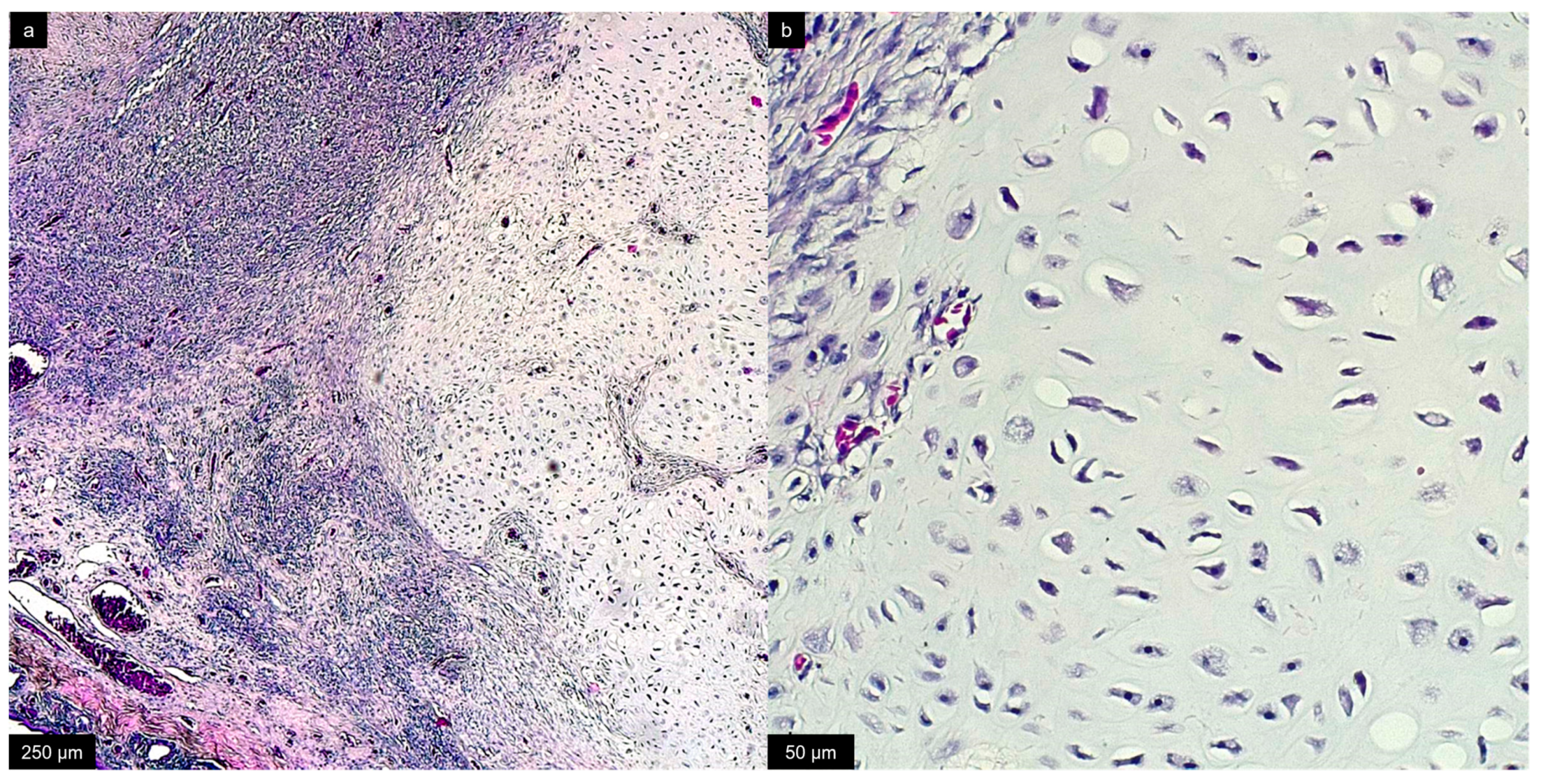
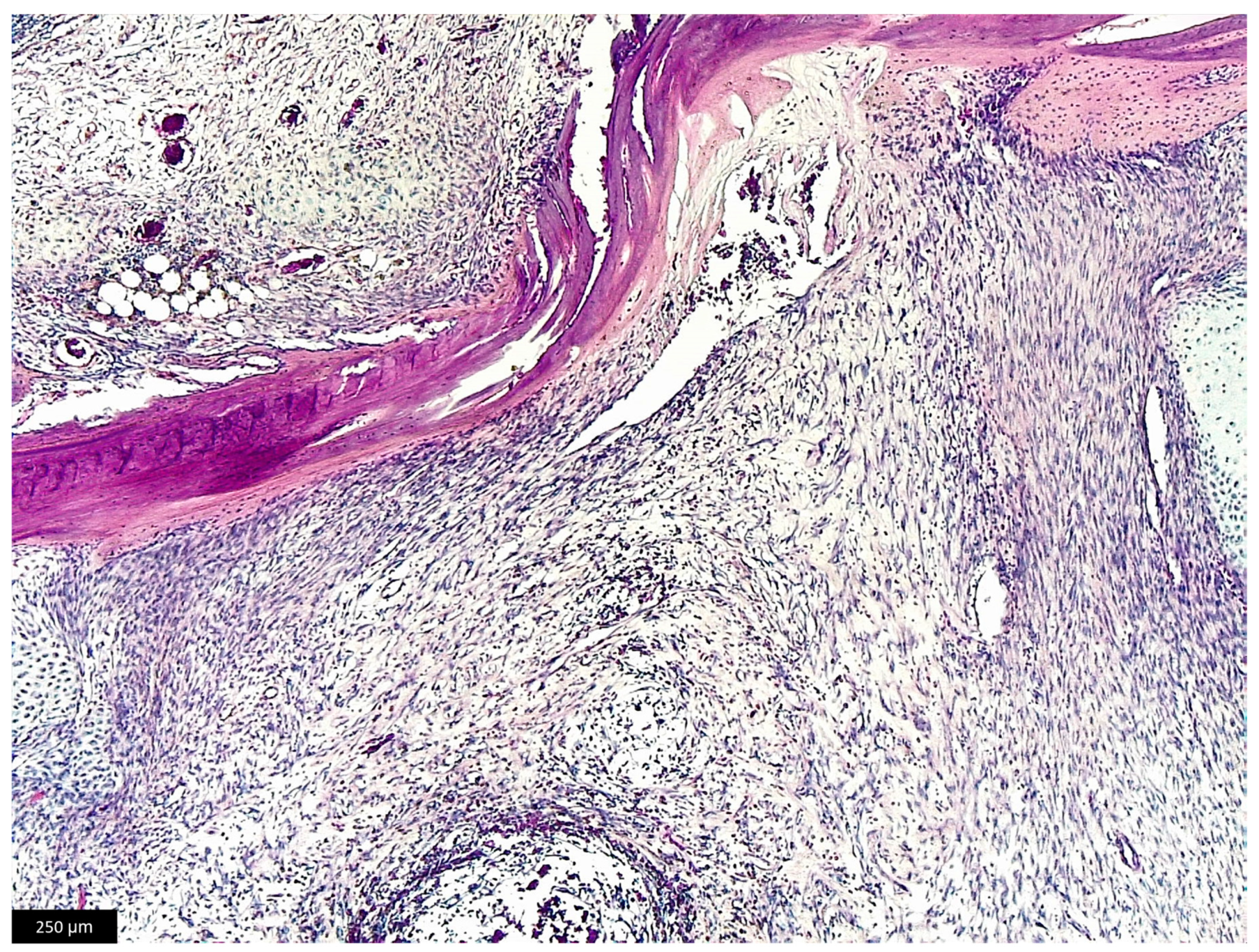
The excised mass was unencapsulated, not well-demarcated with infiltrative growth involving dermal, muscular, intraosseous, and periosteal tissues. Histological examination, performed on sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin, revealed a cellular population composed of spindle cells arranged in long interlacing bundles, areas of spindle to stellate cells admixed with myxoid extracellular matrix, and nodular areas of chondroid tissue (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Alcian Blue staining was positive in the myxoid extracellular matrix (Supplemental Materials, Figure S1). Overall, the cells showed minimal anisocytosis and anisokaryosis, and rare mitoses were present (mitotic count < 2). The final diagnosis was consistent with a fibromyxochondroma.
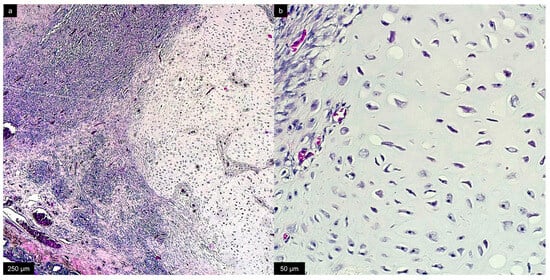
Figure 4.
Histological section of the excised mass. (a) Detail of neoplastic mass composed by areas of spindle cells and areas of chondroid metaplasia. Hematoxylin and eosin, bar = 250 µm. (b) Higher magnification of the area of chondroid metaplasia. Hematoxylin and eosin, bar = 50 µm.
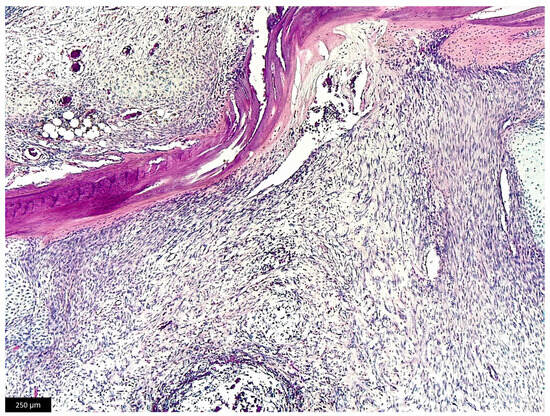
Figure 5.
Histological section showing the neoplastic mass, composed of spindle cells infiltrating bone tissue. Hematoxylin and eosin, bar = 250 µm.
3. Discussion
Myxomatous diseases have been documented in horned frogs, with reported cases including nodular facial myxomatous dermatitis [5] and oral myxoma [9]. However, to the authors’ knowledge, instances involving the limbs have not been previously reported. In other amphibian species, neoplasms such as fibromyxochondroma or chondromyxomas have been described, typically associated with skeletal structures of the head or limbs. These lesions often feature myxomatous cells at the periphery, gradually transitioning to fibrocyte-like and chondrocyte-like cells towards the center of the lesion [6,7]. Based on the current literature, the classification of tumors of this nature remains uncertain, with debate surrounding whether they represent true neoplasms or rather various manifestations of reactive processes such as chronic inflammation, hyperplasia, metaplasia, or callus formation secondary to a previous bone fracture, possibly exacerbated by secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism and subsequent metabolic bone disease [6,7]. In the present case, a potential secondary hyperparathyroidism, as initially hypothesized, would likely have led to the development of multiple pathologic fractures rather than a localized problem at the level of the femur and thus should potentially be ruled out. Regarding the possibility of an exuberant mesenchymal reparative lesion following trauma, the owner ruled out any traumatic event. Although the latter hypothesis cannot be totally excluded, the presence of a multinodular mass with infiltrative growth of bone and muscle tissue, together with the histologic finding, confirms the neoplastic nature of the lesion. The major differential diagnosis remains a form of soft tissue sarcoma with a low degree of malignancy, which in pet animals usually features local infiltrative growth and low metastatic potential [10]. The scarce knowledge of neoplastic lesions in this type of animal does not allow us to totally exclude a malignant form; however, given the low presence of cellular atypia and mitoses, a final diagnosis of fibromyxochondroma was made.
Hind-limb amputation, preferably performed at the coxofemoral joint, is considered appropriate for managing comminuted fractures of long bones in amphibians, and it is widely accepted as a palliative measure for neoplasms affecting the limbs, aimed at alleviating focal pain and enhancing overall quality of life [11,12]. In the clinical management of the present case, a straightforward surgical excision via hind limb amputation was pursued with a palliative intent. However, based on the available (albeit limited) literature, these lesions are typically locally invasive tumors that do not exhibit metastatic behavior, and complete surgical excision along with the elimination of predisposing factors are generally considered curative measures [7,13,14]. In the examined case, surgical margins were observed to be free of neoplastic cells but close to the mass, and, over the subsequent 16 months of clinical follow-up, no recurrence was observed.
Limb amputation necessitated the maintenance of stable anesthesia, which poses a challenge in amphibian patients due to their distinct physiological and anatomical characteristics, coupled with their small size [15,16,17]. Tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222), administered via immersion, stands as one of the most frequently employed anesthetic agents in amphibians [16,18]; however, dosages for various injectable agents, including dissociative drugs and α2-adrenergic receptor agonists, have also been documented [16,17,18,19]. In the present case, MS-222 was not readily available at the facility where the procedures were conducted, prompting the utilization of a combination of injectable anesthetic drugs. Ketamine, medetomidine, and butorphanol were combined with alfaxalone for their analgesic properties and to mitigate the dosage requirement of each individual agent. The dorsal lymph sac was selected as the site for injection, given its potential for rapid systemic drug absorption [19,20], thereby avoiding the necessity for intramuscular injection in a frog exhibiting a poor body condition.
Butorphanol and meloxicam were selected for perioperative analgesia. While the specific effects of these drugs have not been documented in the Cranwell’s horned frog, they have been used with positive results in other anuran and amphibian species [15,21,22,23,24,25], being selected for this reason in the present case. Despite the absence of a specific pain assessment for anurans performed in this case, the rapid resumption of ambulation and normal behavioral and feeding patterns suggest that pain management was effective in this patient with the mentioned drugs and dosages.
4. Conclusions
Overall, the employed anesthetic protocol, surgical equipment, and technique enabled hind-limb amputation to be performed without perioperative complications, and no clinical signs consistent with occurrence of metastatic lesions were noted until the animal’s death, 16 months after surgery. However, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations of this case report. Firstly, the absence of confirmation of the diagnosis prior to surgery and the inability to perform a necropsy upon the animal’s death limits the understanding of the underlying pathology and precludes definitive confirmation of the nature of the lesion and of the definitive cause of death. Furthermore, while the selected anesthetic and analgesic regimen was based on previous reports in other amphibian species, the lack of specific data on the efficacy and safety of these drugs in Cranwell’s horned frogs necessitates caution in extrapolating the findings in regard to this species. Additionally, the relatively short duration of post-surgical follow-up prevents a comprehensive assessment of long-term outcomes and the potential for recurrence or metastasis. The impossibility to perform a necropsy hindered a comprehensive understanding of the causes of death, leaving concurrent pathologies of various origins unable to be ruled out. Despite the exposed limitations, such an approach could be used to perform the described surgical procedure in this species, offering a palliative measure for progressive worsening lesions involving hind limbs in amphibians.
Based on a thorough literature search, this is the first published report of amputation as surgical treatment of such a type of mesenchymal mass involving a hind limb in a Cranwell’s horned frog.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the following: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pets1010003/s1, Video S1: Ambulation of the Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli) after amputation of the left hind limb; Video S2: Spontaneous feeding of the Cranwell’s horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli) after amputation of the left hind limb and discharge. Figure S1: Histological section (200× magnification). Detail of neoplastic cells infiltrating myofiber showing myxoid material in Alcian Blue staining.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. and C.O.; methodology, M.S., G.B. and C.O.; investigation, M.S., G.B., C.O. and L.M.; resources, M.M.v.D. and G.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S., G.B., C.O. and L.M.; supervision, M.M.v.D. and G.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were not necessary for this study, as a signed informed consent was considered adequate in the circumstance of a case report. A signed informed consent was obtained by the owner, allowing the abovementioned procedures to be performed and the use of data for scientific purposes.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the owner.
Data Availability Statement
Further information and data can be requested to the Authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Long, S.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Muhammad-Farooq, T.; Shen, Y. Reference intervals for hematology, plasma biochemistry, and bone mineral density in captive Ceratophrys cranwelli (Anura: Ceratophryidae). Anim. Dis. 2023, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappin, A.K.; Wilcox, S.C.; Moriarty, D.J.; Stoeppler, S.A.; Evans, S.E.; Jones, M.E. Bite force in the horned frog (Ceratophrys cranwelli) with implications for extinct giant frogs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langowski, J.K.A.; Singla, S.; Nyarko, A.; Schipper, H.; van den Berg, F.T.; Kaur, S.; Astley, H.C.; Gussekloo, S.W.S.; Dhinojwala, A.; van Leeuwen, J.L. Comparative and functional analysis of the digital mucus glands and secretions of tree frogs. Front. Zool. 2019, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goka, K.; Yokoyama, J.; Une, Y.; Kuroki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nakahara, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Inaba, S.; Mizutani, T.; Hyatt, A.D. Amphibian chytridiomycosis in Japan: Distribution, haplotypes and possible route of entry into Japan. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4757–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamukai, K.; Sugiyama, J.; Nagata, Y.; Tsutomu, O.; Katayama, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Kimura, M.; Une, Y. Epidemic nodular facial myxomatous dermatitis in juvenile Cranwell’s horned frogs Ceratophrys cranwelli. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 134, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.E.; Harshbarger, J.C. Spontaneous neoplasia in Amphibia. In Amphibian Medicine and Captive Husbandry, 1st ed.; Wright, K.M., Whitaker, B.R., Eds.; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 335–400. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, B.A.; Parker, J.M. Amphibian oncology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2004, 7, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, B.; Weigel, J.P. Amputation. In Veterinary Surgery Small Animal, 2nd ed.; Tobias, K.M., Johnson, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 1029–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Figueroa, O.; Mitchell, M.A.; Kim, D.Y.; Riggs, S.R. Oral myxoma in a South American horned frog (Ceratophrys ornata, Leptodactylidae). In Proceedings of the Association of Reptilian and Amphibian Veterinarians, Naples, FL, USA, 8–11 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, B.E.; Dernell, W.S. Tumor biology and pathology. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 13, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGeronimo, P.M.; Brandao, J. Orthopedics in reptiles and amphibians. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2019, 22, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffey, M.A. Principles and applications of surgical oncology in exotic animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2017, 20, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.F.; Justice, W.S.M.; Beckmann, K.M.; Denk, D.; Pocknell, A.M.; Stidworthy, M.F. Four cases of neoplasia in amphibians at two zoological institutions: Alpine newt Ichthyosaura alpestris, Red-eyed tree frog Agalychnis callidryas, Common frog Rana temporaria and Puerto Rican crested toad Peltophryne lemur. Int. Zoo Yearb. 2017, 51, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, E.; Harrison, S.H.; Posey, R.; Duke, E.G.; Troan, B.; Harrison, T. Analysis of published amphibian neoplasia case reports. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2020, 30, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailler, A.; Chai, N.; Huberdeau, P.; Sabatier, L.; Scotti, T.; Boister, R. Surgical management of a digestive tract hernia in a Wild marsh frog (Pelophylax ridibundus). J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2021, 31, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGeronimo, P.M.; Balko, J.A. Sedation and Anesthesia of Amphibians. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2022, 25, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sladakovic, I.; Divers, S.J. Amphibian anesthesia. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery, 3rd ed.; Divers, S.J., Stahl, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jayson, S. Amphibians. In Handbook of Exotic Pet Medicine, 1st ed.; Kubiak, M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 415–436. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, B.R.; Wright, K.M. Amphibian Medicine. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery, 3rd ed.; Divers, S.J., Stahl, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 992–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Hadfield, C.A.; Whitaker, B.R. Amphibian emergency medicine and care. J. Exot. Pet. Med. 2005, 14, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, C.; d’Ovidio, D.; Casoni, D. Alfaxalone–butorphanol versus alfaxalone–morphine combination for immersion anaesthesia in oriental fire-bellied toads (Bombina orientalis). Lab. Anim. 2016, 50, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, C.; Strobel, S.M.; Hagedorn, A.; Ott, S.; Kempf, H.; Waschulzik, B.; Gröger, M.; Kress, S.; Radermacher, P.; Potschka, H. A comparison of the analgesic effects of fentanyl and butorphanol in African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) under tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) anaesthesia. SOJ Anesthesiol. Pain Manag. 2018, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, D.J.; Taylor, D.K.; Mook, D.M. Analgesic effects of meloxicam, morphine sulfate, flunixin meglumine, and xylazine hydrochloride in African-clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koeller, C.A. Comparison of buprenorphine and butorphanol analgesia in the eastern red-spotted newt (Notophthalmus viridescens). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 48, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minter, L.J.; Clarke, E.O.; Gjeltema, J.L.; Archibald, K.E.; Posner, L.P.; Lewbart, G.A. Effects of intramuscular meloxicam administration on prostaglandin E2 synthesis in the North American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2011, 42, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).