Abstract
Background: External guide sequences (EGSs) are small RNA molecules capable of hybridizing to a target mRNA and rendering the target RNA susceptible to degradation by ribonuclease P (RNase P), a tRNA processing enzyme. Methods: In this study, natural tRNA-originated and engineered variant EGSs were constructed to target the mRNA encoding human CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5), an HIV co-receptor. Results: The EGS variant was about 100-fold more efficient in inducing RNase P-mediated cleavage of the CCR5 mRNA sequence in vitro than a natural tRNA-derived EGS. Furthermore, the expressed variant and natural tRNA-originated EGSs decreased CCR5 expression by 98% and 73–77% and reduced infection by the CCR5-tropic HIVBa-L strain in cells by more than 900- and 50-fold, respectively. By contrast, cells expressing these EGSs exhibited no change in the expression of CXCR4, another HIV co-receptor, and showed no reduction in infection by the CXCR4-tropic HIVIIIB strain, which uses CXCR4 instead of CCR5 as the co-receptor. Thus, the EGSs specifically targeted CCR5 but not CXCR4. Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that EGSs are effective and specific in diminishing HIV infection and represent a novel class of gene-targeting agents for anti-HIV therapy.
1. Introduction
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a zoonotic pathogen, is the causative agent of AIDS. Chemokine receptors serve as co-receptors for HIV-1 entry [1,2]. In particular, human CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) and CXCR4 serve as the primary co-receptors for macrophage tropic (M-tropic or R5) HIV strains (e.g., HIVBa-L) and T cell tropic (T-tropic or X4) HIV variants (e.g., HIVIIIB), respectively [3,4]. Studies have been performed to understand the normal physiological functions of CCR5 and suggested potential clinical benefits and pathological consequences due to its absence or reduced expression [5,6,7,8,9]. These results showed that CCR5 represents an excellent anti-HIV target because reduced CCR5 expression correlated with improved resistance to HIV infection and slowed HIV progression [10,11].
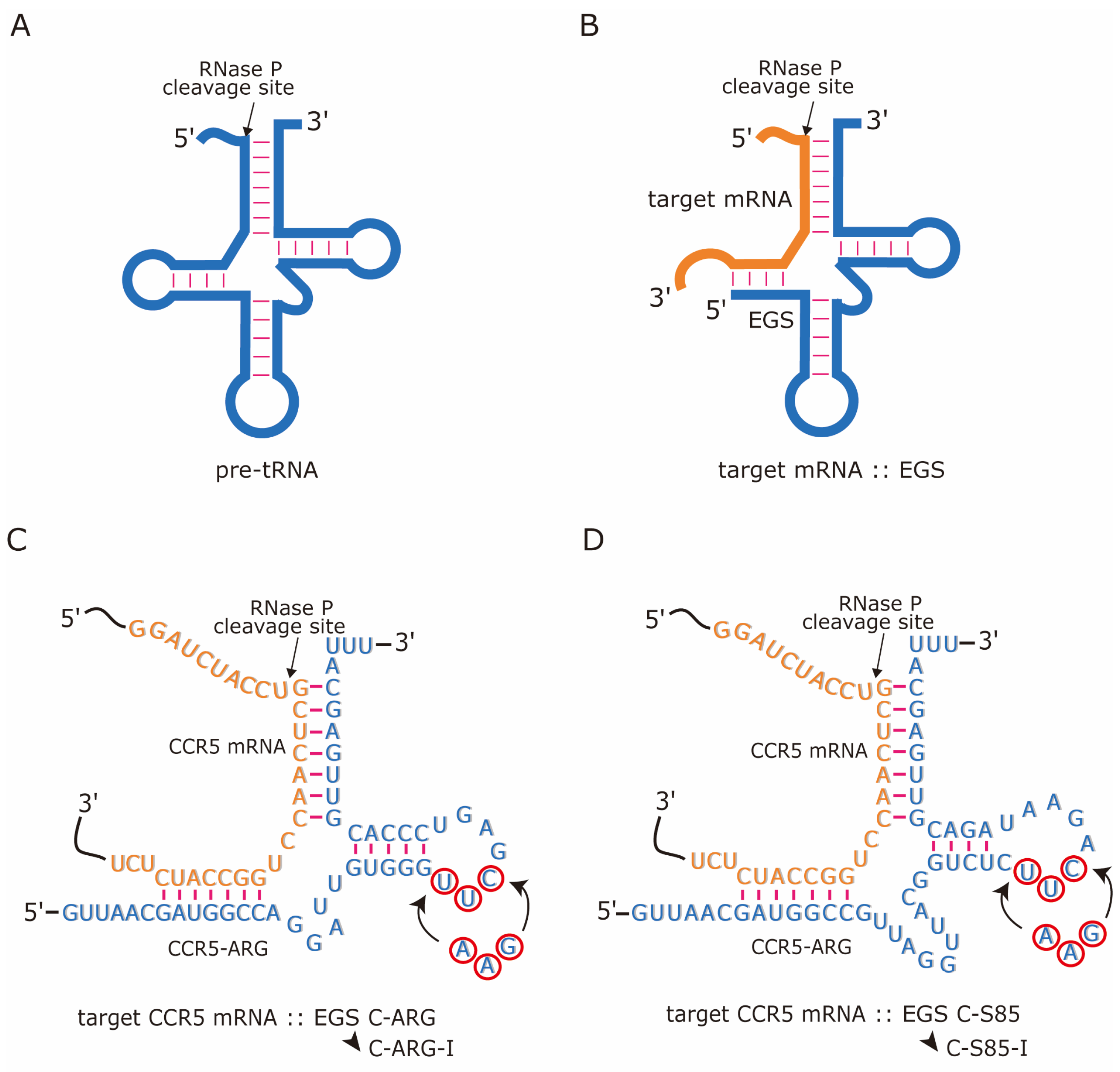
Nucleic acid gene interference and editing technologies, including ribozymes, antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and CRISP/Cas9 guide RNAs, have been explored as methods for studying and treating human diseases, such as HIV infection and AIDS [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Ribonuclease P (RNase P) catalyzes a hydrolysis reaction to generate 5′ mature termini of all tRNAs by cleaving a precursor tRNA leader sequence [16,19,20]. RNase P recognizes its diverse substrates primarily by their structures instead of their sequences (Figure 1A). Thus, this enzyme can cleave a target mRNA in the presence of a custom-designed RNA molecule called an external guide sequence (EGS) as long as the EGS binds to the mRNA in a complex resembling a pre-tRNA molecule (Figure 1A,B) [21,22]. EGS expression in human cells has been shown to reduce the gene expression and replication of HIV, herpes simplex virus (HSV-1), and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) by targeting their encoded mRNAs [23,24,25]. Moreover, EGS variants were generated using evolution in vitro procedures and exhibited better targeting activity in vitro than the EGS constructed from natural tRNA sequences [25]. However, whether these active EGS variants can be used to block HIV infection has not been investigated. Using CCR5 mRNA as the target, in this report, we investigated whether engineered EGS RNAs can effectively block CCR5 expression and shut down HIV infection in cultured cells.
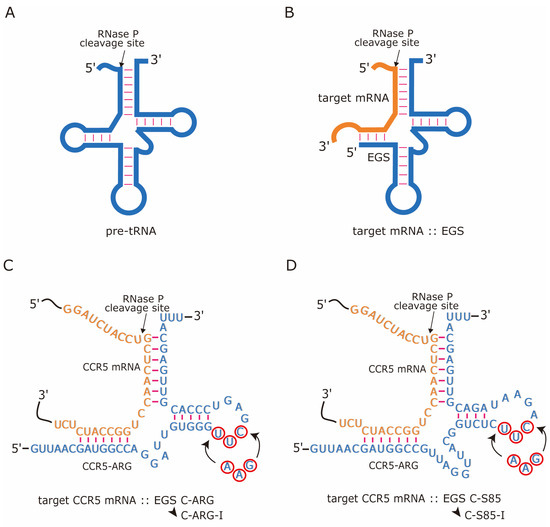
Figure 1.
Various RNase P substrates. (A) Pre-tRNA. (B) Complex of a target mRNA and an EGS resembling a pre-tRNA. (C) Complexes between the CCR5 mRNA sequence and active EGS C-ARG and inactive control EGS C-ARG-I, and (D) complexes between the CCR5 mRNA sequence and active EGS C-S85 and inactive control EGS C-S85-I. The C-ARG sequences equivalent to the T-stem, T-loop, and variable regions of a tRNA molecule were from tRNAarg [26]. The arrowhead indicates the RNase P cleavage site, which is 204 nucleotides downstream from the translation initiation site of CCR5 [27]. The three nucleotides marked in circles in C-ARG and C-S85 were mutated to generate control EGSs C-ARG-I and C-S85-I, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
HeLa cells, PA317 cells, human PM1 cells, HIV R5 strain Ba-L (HIVBa-L), and X4 strain IIIB (HIVIIIB) were obtained from Dr. Shibo Jiang and the NIH AIDS Research and Reference Reagents Program [28].
2.2. Construction of EGS RNAs and RNA Substrate
The DNA sequence that encodes substrate ccr5-s was constructed by PCR using pGEM3zf (+) as a template and oligonucleotides AF25 (5′-GGAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAG-3′) and CCR-s-3 (5′-GGTTCGGTCAGAGATGGCCAGGTTGAGCAGGTAGATCCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTA-3′) as the 5′ and 3′ primers, respectively. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to generate the DNA sequences of the EGSs with construct pTK112 DNA [23] as the template. To construct the DNA that encodes EGS C-ARG, the 5′ and 3′ primers were oligoARG5 (5′-GGAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAG GTTAACGATGGCCAGGATTGTGGG–3′) and oligoARG3 (5′-AAGCTTTAAACGCTCAACGTGGGACTCGAACCCACAATCCT-3′), respectively. To construct the DNA that encodes EGS C-ARG-I, the 5′ and 3′ primers were oligoARG5 and oligoARG-I3 (5′-AAGCTTTAAACGCTCAACGTGGGACTCCTTCCCACAATCCT-3′), respectively. To construct the DNA that encodes EGS C-S85, the 5′ and 3′ primers were oligoS855 (5′-GGAATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTTAACGATGGCCGUUAGGUUACGG-3′) and the oligoS853 (5′-AAGCTTTAAACGCTCAACGTCTATTCTGAAGAGACCGTAACCTAA-3′), respectively. To construct the DNA that encodes EGS C-S85-I, the 5′ and 3′ primers were oligoS855 and the oligoS85-I3 (5′-AAGCTTTAAACGCTCAACGTCTATTCTCTTGAGACCGTAACCTAA-3′), respectively.
2.3. Binding and Cleavage Assays In Vitro
Human RNase P (purified from HeLa cells) was allowed to react with [32P]-labeled ccr5-s in the presence of different EGSs at 37 °C in buffer A (100 mM NH4Cl, 50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, and 10 mM MgCl2) [22,25,29]. The cleavage reactions were analyzed by gel electrophoresis followed by use of a STORM 840 Phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics, Mountain View, CA, USA). The kinetic parameters were determined as described previously [25,29]. The equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) of the complexes of the EGSs and substrate ccr5-s were determined following the previously described protocol [25,29]. The values were the average of three experiments in duplicate.
2.4. Construction of the EGS-Expressing Cell Lines
The DNAs coding for the EGSs were subcloned into retroviral vector LXSN under the control of the U6 RNA promoter and transfected to PA317 cells [30,31]. At 48 h post transfection, the retrovirus-containing culture supernatants were used to infect human PM1 cells, and those cells containing EGSs were then selected and cloned in the presence of neomycin (800 µg/mL) (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Northern and western blot analyses were used to determine the mRNA and protein levels of actin, CXCR4, and CCR5, respectively, following the procedures described previously [23,32]. In northern blot analysis, total RNAs were harvested from culture cells, separated in formaldehyde gels, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, subjected to hybridization of [32P]-labeled DNA probes, and analyzed using a a STORM 840 Phosphorimager. The radiolabeled DNA probes to detect human H1 RNA, EGS RNAs, CXCR4 mRNA, and CCR5 mRNA were cloned from plasmid constructs pH1 RNA, ptRNAarg, pEGS-S85, pCXCR4, and pCCR5, respectively, and prepared as described previously [23,32].
2.5. Studies of HIV Gene Expression and Infection
PM1 cells that either expressed EGSs or did not express EGSs were infected with HIVBa-L or HIVIIIB (MOI of 0.05). Culture media were harvested at different times and HIV production was assessed by quantifying the p24 level with a p24 ELISA kit (Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA). To determine intracellular HIV RNA levels, RNA samples were isolated from infected cells collected at different times and quantified using a qRT-PCR assay that contained SYBR Green and amplified the tat sequence using actin mRNA as the internal control. The PCR reactions were run in a Bio-Rad iCycler with HIV primers 5-TA-5 (5′-CATCCAGGAAGTCAGCCT-3′) and 3-TA-3 (5′-TTCCTGCCATAGGAGATGC-3′) in PCR mix (1× titanium Taq PCR buffer, 1 mM dNTPs, SYBR Green (1:50,000), 10 nM fluorescein, 1× titanium Taq DNA polymerase (Bio-Rad)) [33]. The actin mRNA level was used as the control and quantified by qRT-PCR with 5′ primer Actin5 (5′-TGACGGGGTCACCCACACTGTGCCCATCTA-3′) and 3′ primer Actin3 (5′-CTAGAAGCATTGCGGTGGCAGATGGAGGG-3′) [34].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Experiments were carried out in duplicate and repeated three times. We assessed the data using GraphPad Prism software (version 10) and conducted statistical analyses with (one-way) analysis of variance (ANOVA). Differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Targeting CCR5 mRNA by RNase P-Associated EGSs In Vitro
We engineered EGSs (Figure 1C,D) to bind to a CCR5 mRNA sequence with no sequence homology with other members of the CC-chemokine receptor family [1,2]. The target CCR5 sequence in our study contained the RNase P cleavage site, which is 204 nucleotides downstream from the CCR5 translation initiation site [27]. The choice of this targeting sequence with no sequence homology with other CC-chemokine receptors would ensure no potential cross-targeting of other chemokine receptors by the anti-CCR5 EGSs. Additionally, the target CCR5 sequence may have lacked a secondary structure or protein binding and was likely accessible to EGS binding because our experiments showed that this CCR5 mRNA region was modified by dimethyl sulphate (DMS) in DMS-treated cells.
Using evolution in vitro procedures, we previously generated highly active EGS variants that induced RNase P degradation of the thymidine kinase (TK) mRNA sequence of HSV-1 [25]. In this study, we present the investigation of a newly identified and highly active EGS variant, V85, in directing RNase P cleavage of CCR5 mRNA (see below, Table 1). EGS C-S85 was derived from the EGS domain of V85, resembling the T-loop, T-stem, and variable regions of a tRNA (Figure 1D). EGS C-ARG was constructed from the human tRNAarg sequence [26] (Figure 1C). Control inactive EGSs C-S85-I and C-ARG-I were derived from C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively, and contained three point mutations (5′-UUC-3′ -> AAG) at the T-loop (Figure 1C,D). These three nucleotides are highly conserved [26,35] and critical for RNase P–EGS recognition [25,36,37].

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters in the cleavage reaction of the CCR5 mRNA substrate (ccr5-s) by RNase P in the presence of different EGSs. Experimental details are described in Materials and Methods.
Both EGS C-S85 and C-ARG efficiently induced human RNase P to cleave the 38 nucleotides long RNA substrate ccr5-s of the CCR5 mRNA sequence, with C-S85 being at least 100 times more active than C-ARG (Table 1). Moreover, C-S85 bound to ccr5-s about 150 times better than C-ARG (Table 1). These findings implied that the engineered EGS C-S85 may have formed additional interactions with ccr5-s and RNase P, leading to increased affinity to ccr5-s and enhanced targeting activity. On the contrary, control EGSs C-S85-I and C-ARG-I exhibited no targeting activity, consistent with previous observations that the T-loop mutations had no effect on EGS binding to mRNA but disrupted RNase P–EGS recognition and abolished the EGS-targeting activity [25,36,37]. Because C-S85-I (Kd = 0.017 ± 0.004 µM) and C-ARG-I (Kd = 2.7 ± 0.4 µM) shared identical antisense sequences (Figure 1C-D) and similar in vitro binding affinities to ccr5-s as C-S85 (Kd = 0.017 ± 0.004 µM) and C-ARG (Kd = 2.7 ± 0.4 µM), respectively (Table 1), we used C-S85-I and C-ARG-I as the controls for the antisense effects.
3.2. EGS Expression in Human Cells
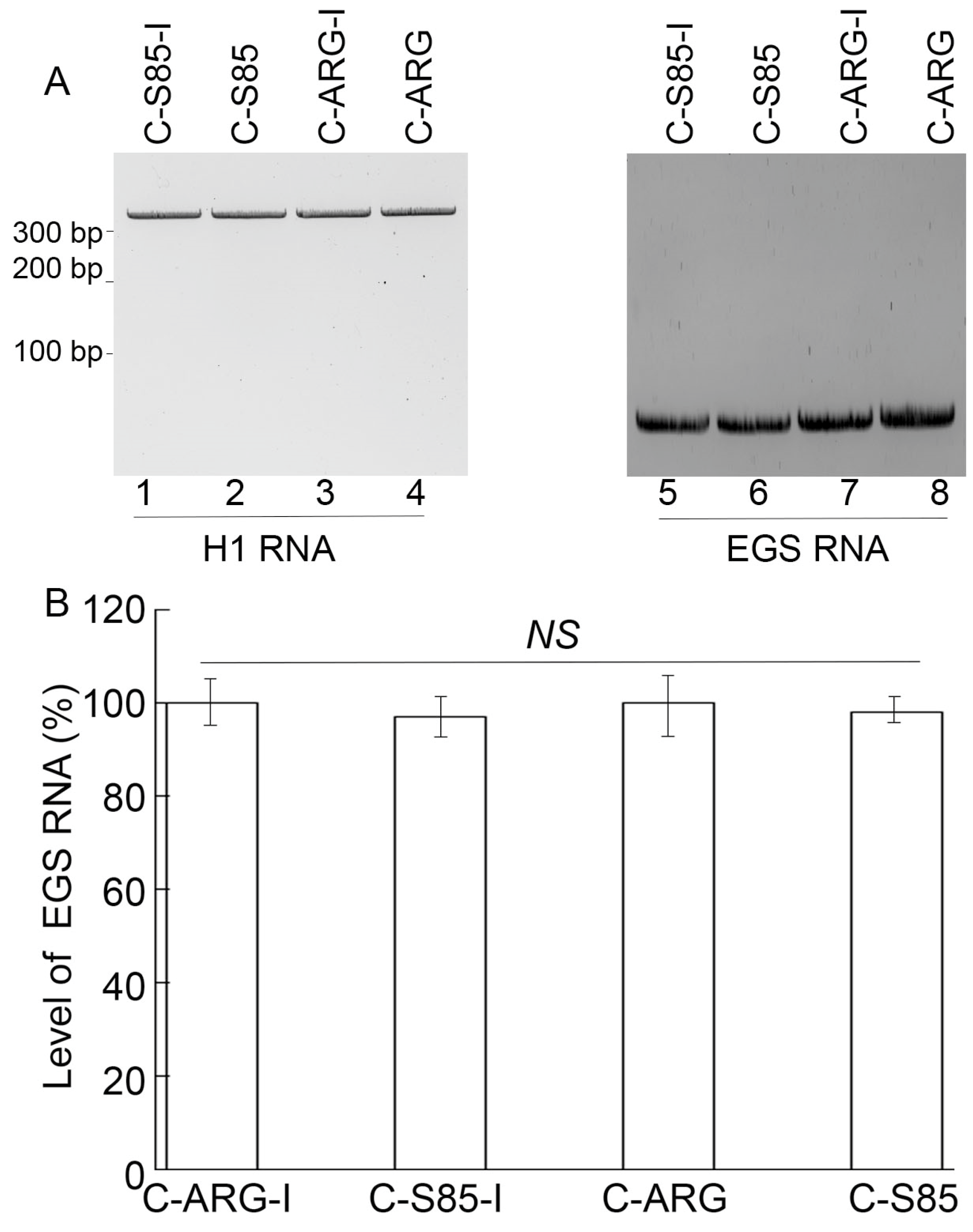
The EGS expression cassettes were inserted into retroviral vector LXSN and driven by the U6 RNA promoter [30,31,38]. Cell clones containing the EGS sequences were generated from PM1 cells, with similar levels of EGSs detected by northern blot analysis with H1 RNA expression as a loading control (Figure 2). The expression of the EGSs appeared to cause little cytotoxicity because the EGS-expressing cells and control cells transfected with the empty LXSN vector DNA alone showed no difference in viability and growth for 2.5 months.
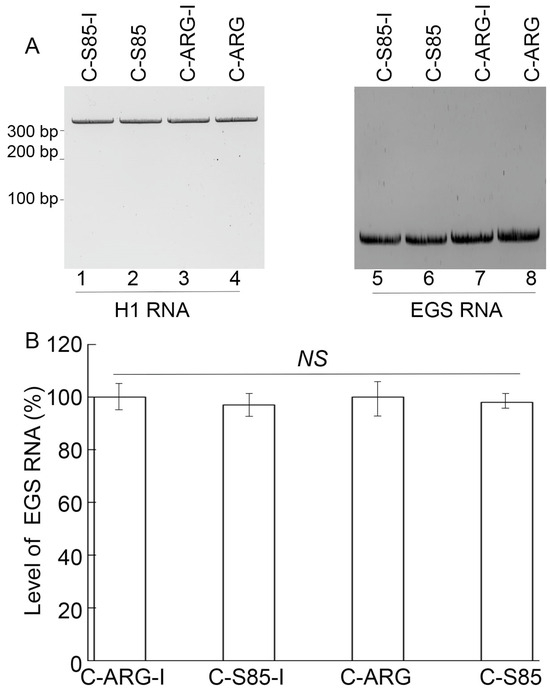
Figure 2.
EGS RNA (right panel) and H1 RNA (left panel) expression detected by northern blot analyses in cells with C-S85-I (lanes 1 and 5), C-S85 (lanes 2 and 6), C-ARG-I (lanes 3 and 7), and C-ARG (lanes 4 and 8) (A). (B) Levels of EGS RNAs shown in % in comparison to those in PM1 cells with C-ARG-I, indicated as the mean ± SD. NS, not significant. Experiments were conducted in duplicate and repeated three times.
3.3. CCR5 Expression Inhibition in EGS-Expressing Cells
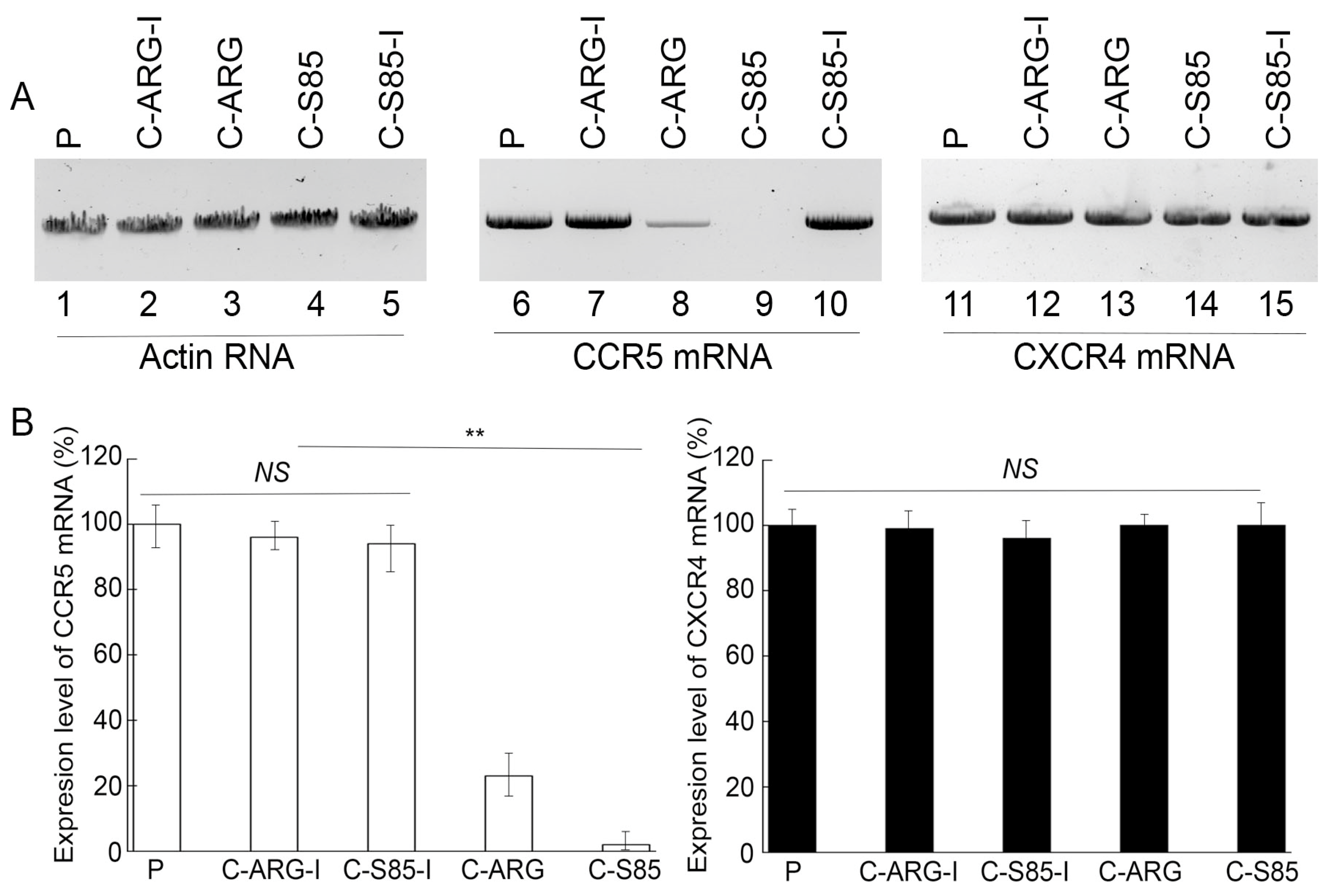
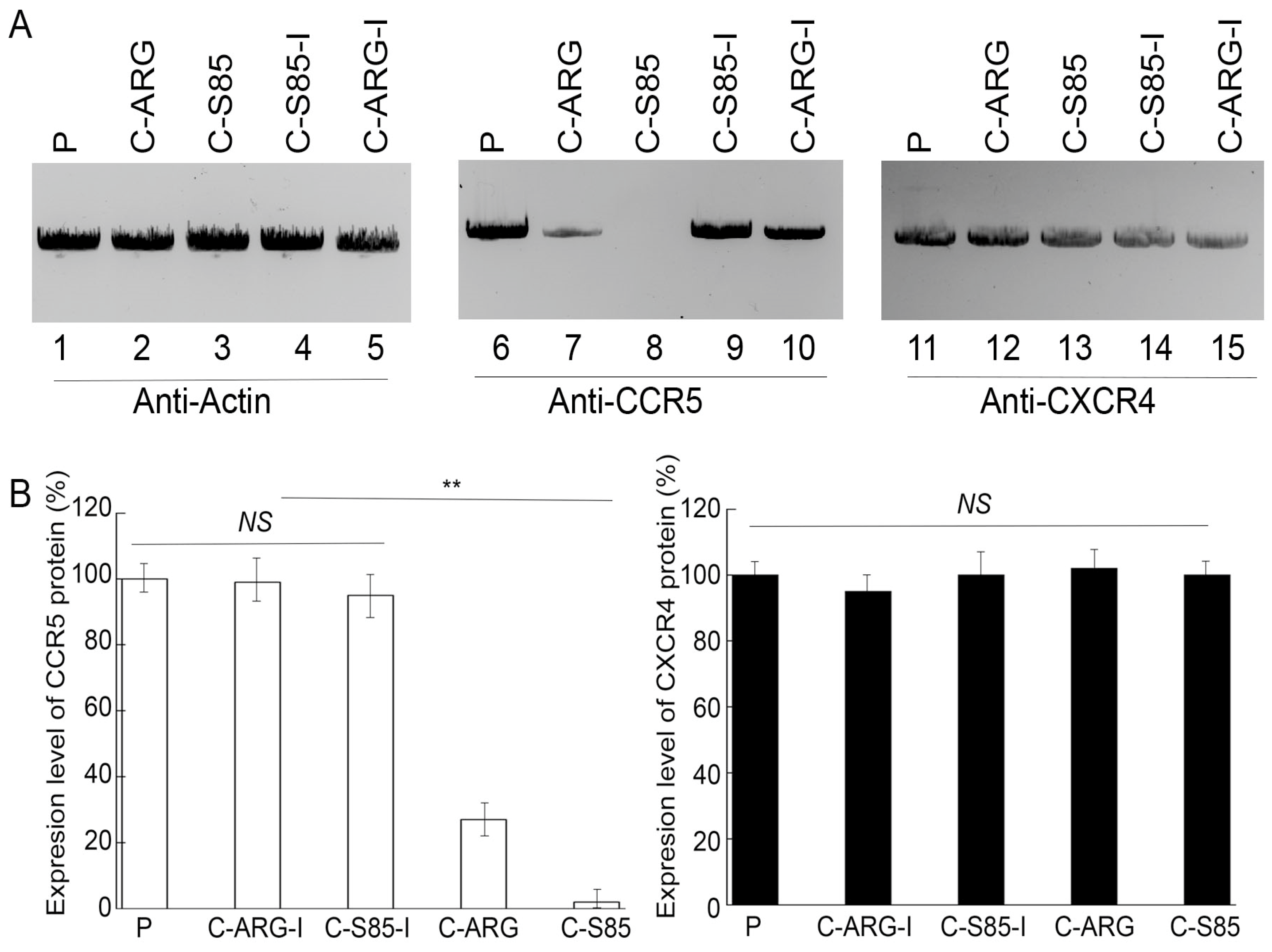
Northern blot analyses were used to assay the CCR5 and CXCR4 mRNA levels with actin mRNA as a loading control (Figure 3). Decreases of 98 ± 6% and 77 ± 5% in the CCR5 mRNA level were detected in cells with functional EGSs C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively, while reductions of less than 10% in the CCR5 mRNA level were found in cells with control EGSs C-S85-I and C-ARG-I (Figure 3). Western blot analyses with actin as a loading control showed reductions of 98 ± 6% and 73 ± 5% in the CCR5 protein level in cells with C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively, while reductions of less than 5% in the CCR5 protein level were found in cells with C-S85-I and C-ARG-I (Figure 4). No substantial changes were detected in the CXCR4 mRNA and protein levels among the cells (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Thus, the targeting activities of C-S85 and C-ARG to induce RNase P cleavage appeared to be (a) specific against CCR5 but not CXCR4 and (b) responsible for the substantial CCR5 expression decrease in cells.
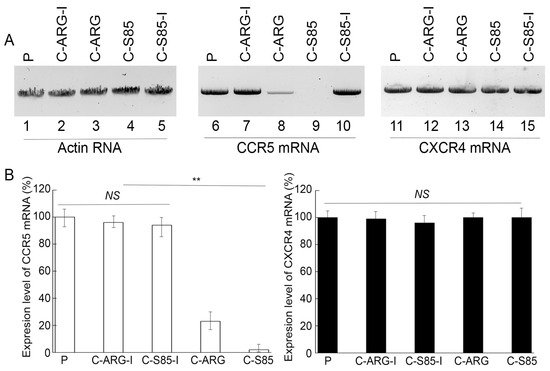
Figure 3.
Levels of CCR5 (~4.0 kb) (lanes 6–10) and CXCR4 (~1.7 kb) (lanes 11–15) mRNAs detected by northern blot analyses in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector (P, lanes 3, 8 and 13) and cell lines with C-ARG (lanes 1, 6, and 11), C-ARG-I (lanes 2, 7, and 12), C-S85-I (lanes 4, 9, and 14), and C-S85 (lanes 5, 10, and 15), with actin mRNA (~1.9 kb) as the loading control (lanes 1–5) (A). (B) CCR5 and CXCR4 mRNA levels shown in % in comparison to those in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector, indicated as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.05. NS, not significant.
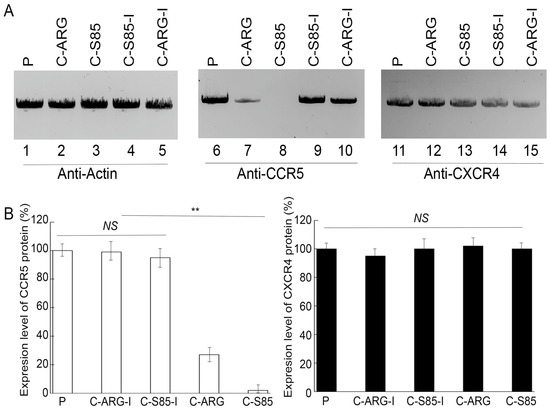
Figure 4.
Protein levels of CCR5 (~55 kD) (lanes 6–10) and CXCR4 (~45 kD) (lanes 11–15) detected by western blot analyses in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector (P, lanes 3, 8 and 13) and cell lines with C-ARG (lanes 1, 6, and 11), C-ARG-I (lanes 2, 7, and 12), C-S85-I (lanes 4, 9, and 14), and C-S85 (lanes 5, 10, and 15), with actin protein (~40 kD) as the loading control (lanes 1–5) (A). (B) CCR5 and CXCR4 protein levels shown in % in comparison to those in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector, indicated as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.05. NS, not significant.
3.4. HIV Infection Inhibition in the EGS-Expressing Cells
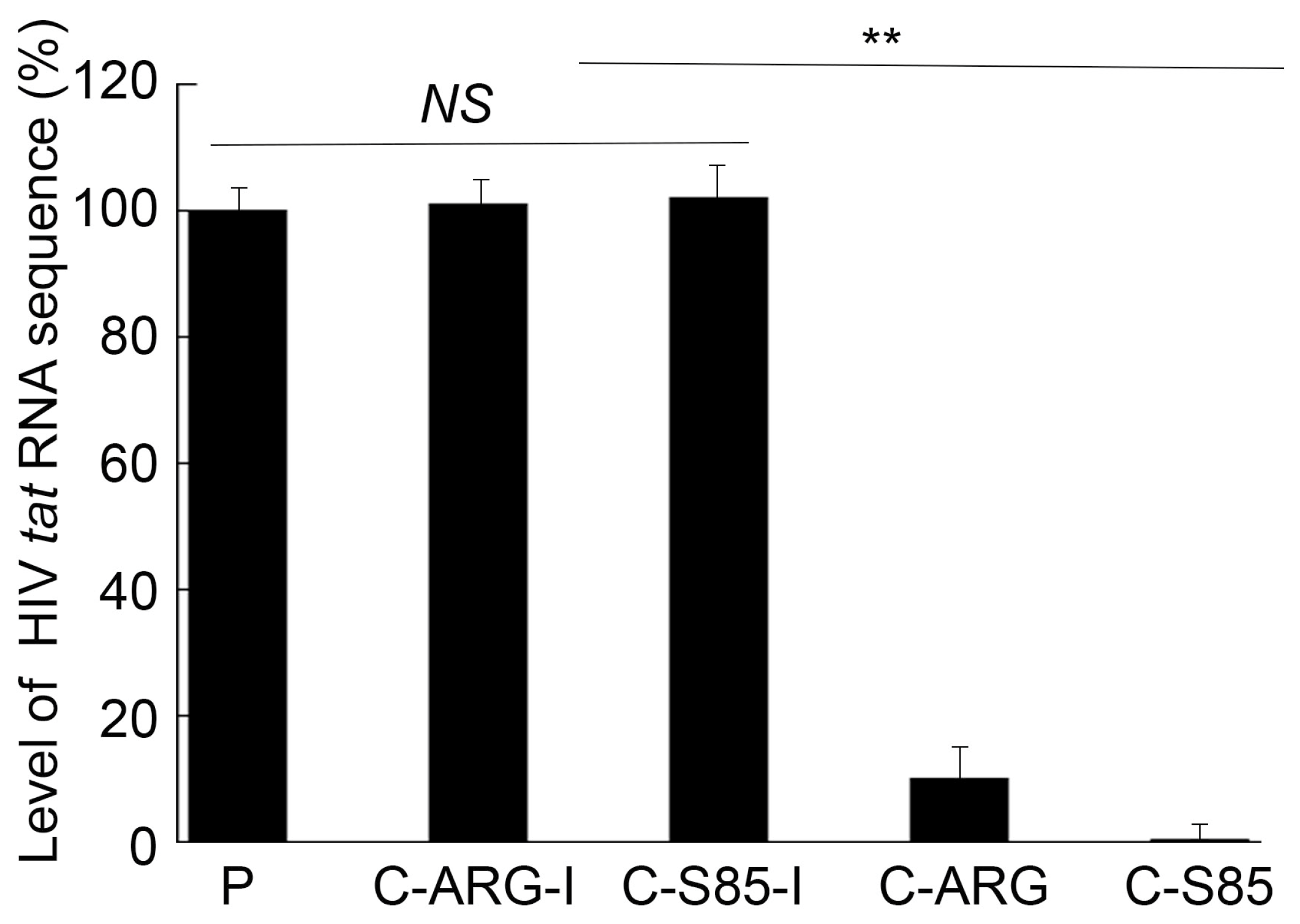
It is reasonable to suggest that a CCR5 expression decrease would inhibit infection by an M-tropic HIV strain (e.g., HIVBa-L) with CCR5 as the infection co-receptor [39,40]. Experiments were performed to study HIVBa-L infection of the EGS-expressing cells. The intracellular HIV RNA level, measured by qRT-PCR of the tat sequence using actin mRNA as the control, was reduced by 500- and 10-fold in cells with C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively (Figure 5). HIVBa-L replication in these cells was further assayed by measuring the level of viral p24 protein in the supernatant. The p24 level was reduced by more than 900- and 50-fold in cells with C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively, at 12 days post infection. By contrast, no changes in the intracellular HIV RNA and supernatant p24 levels were observed in cells with C-S85-I and C-ARG-I (Figure 6). Thus, HIV infection inhibition in cells with C-S85 and C-ARG appeared to be due to the RNase P cleavage of CCR5 mRNA induced by the EGSs.
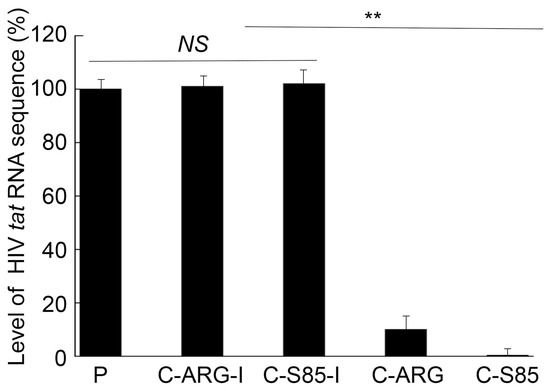
Figure 5.
Levels of intracellular HIV RNA quantified with qRT-PCR amplifying the tat sequence from PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector or cells with different EGSs. Results are shown in % in comparison to those in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector, indicated as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.05. NS, not significant.
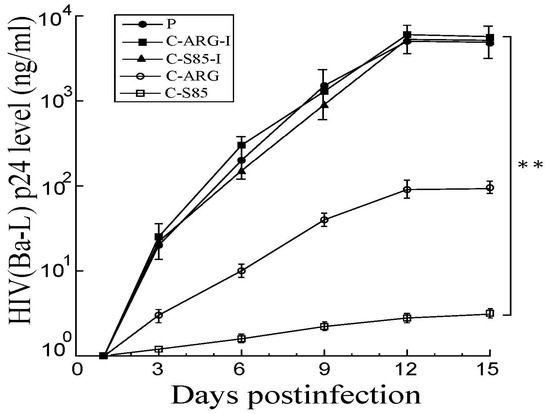
Figure 6.
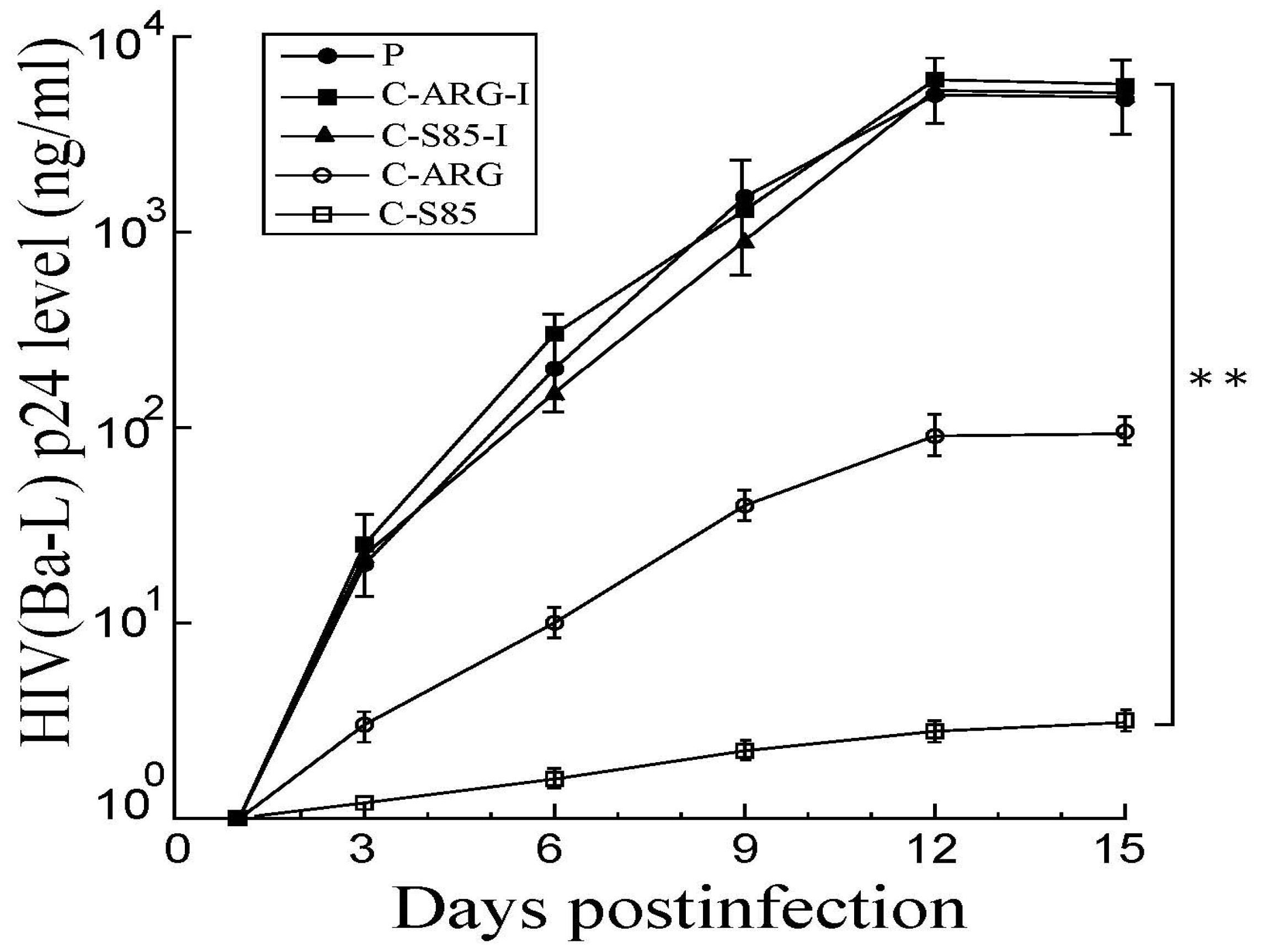
Growth of HIVBa-L in PM1 cells with empty LXSN vector and cells with different EGSs. Cells (5 × 105) were infected with HIVBa-L at a MOI of 0.05–0.1. Samples were collected at different times and viral production was monitored with the p24 antigen assay. Results are shown as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.05. Experiments were conducted in duplicate and repeated three times.
3.5. Specific EGS-Mediated Inhibition of M-Tropic but Not T-Tropic HIV Strains
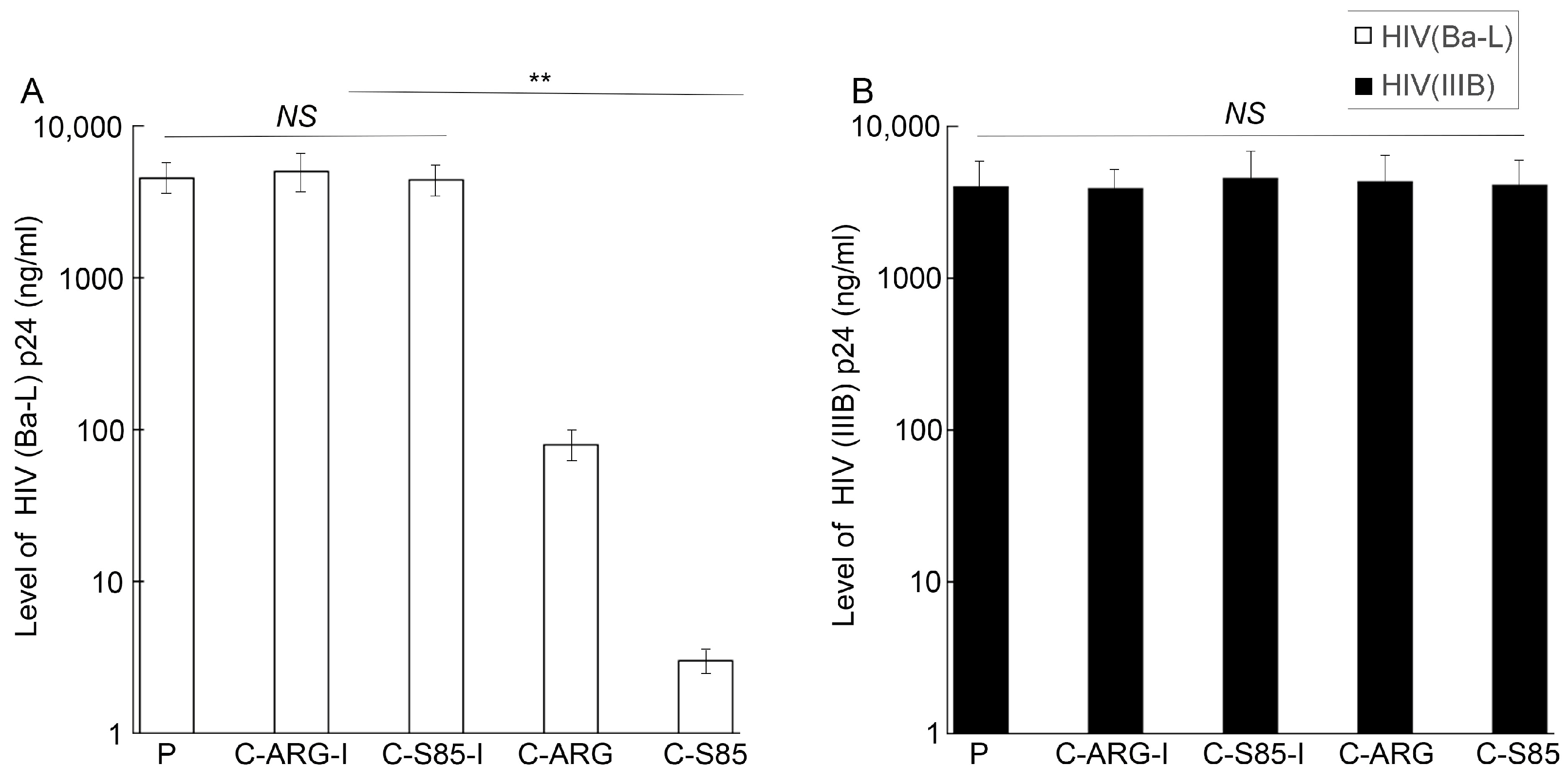
PM1 cells expressed both CCR5 and CXCR4, the co-receptors for the M-tropic (e.g., HIVBa-L) and T-tropic HIV strains (e.g., HIVIIIB), respectively [28,39]. Our results indicated that those cells expressing functional EGSs C-S85 and C-ARG exhibited reduced CCR5 expression but no change in CXCR4 expression (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Thus, it was reasonable to suggest that these cells should be resistant to infection by M-tropic viral strains but not T-tropic strains. To investigate this, we infected cells with X4 strain HIVIIIB and R5 strain HIVBa-L. At day 15 post infection, we assayed HIV infection and virion production by quantifying the viral p24 level in the culture supernatant. Cells with C-S85 and C-ARG were substantially resistant to HIVBa-L infection. Decreases of ~1000- and 60-fold in the p24 level were detected in strain Ba-L-infected cells with C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively (Figure 7). By contrast, these cells were susceptible to HIVIIIB infection as no change in the p24 level was detected in the strain IIIB-infected cells with no EGS or with C-S85, C1-ARG, C-S85-I, and C-ARG-I (Figure 7). These results implied that the inhibition of viral replication by C-S85 and C-ARG was specific because the same cells protected from CCR5-tropic HIVBa-L were still susceptible to CXCR4-tropic HIVIIIB. It was noted that cells with control inactive EGSs C-S85-I and C-ARG-I exhibited no resistance to infection by both HIVBa-L and HIVIIIB. These two EGSs exhibited similar affinity to the CCR5 mRNA sequence as C-S85 and C-ARG, respectively, but had little targeting activity. Thus, EGS-targeting activity to induce RNase P cleavage of the target CCR5 mRNA appeared to be responsible for reducing HIVBa-L replication.
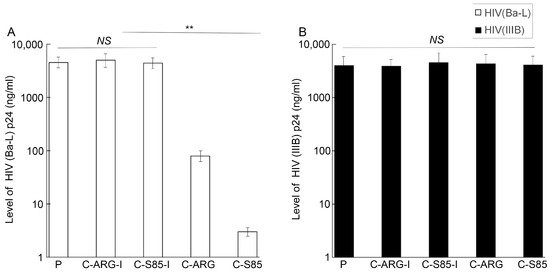
Figure 7.
Levels of supernatant HIV-1 p24 protein in cells infected with HIVBa-L (A) or HIVIIIB (B). Culture media were collected at 15 days post infection and the p24 level was quantified with a p24 ELISA kit. Results are shown as the mean ± SD. ** p < 0.05. Experiments were conducted in duplicate and repeated three times.
4. Discussion
Being responsible for processing all tRNAs in cells, RNase P is one of the most ubiquitous and active enzymes in nature [16,19,20]. Additionally, the EGS-induced RNase P cleavage of a target mRNA is specific. No irrelevant cleavage associated with RNase H-mediated cleavage directed by antisense phosphothioate molecules was detected during the EGS-induced RNase P cleavage [16,20,41]. Thus, EGSs represent excellent gene-targeting reagents for both basic research and clinical applications.
Several lines of evidence in our results imply that the anti-CCR5 EGS-targeting activity is specific. First, EGS expression demonstrated little cytotoxicity, as we detected no substantial differences in viability and growth between the parental cells and EGS-expressing cells for 2.5 months. Second, the antiviral effects of C-S85 and C-ARG (inhibiting HIV infection) appeared to result from the decrease in CCR5 expression. This is because CCR5 expression was reduced in cells with C-S85 and C-ARG but not with C-S85-I and C-ARG-I (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Third, C-S85 and C-ARG only decreased CCR5 expression but not the expression of other cellular genes, such as CXCR4 and actin (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Cells with C-S85 and C-ARG were resistant to M-tropic HIVBa-L but not T-tropic HIVIIIB, demonstrating that C-S85 and C-ARG specifically targeted CCR5 but not CXCR4.
EGSs with enhanced targeting activities can be generated by evolution in vitro procedures [42,43,44]. In this report, C-S85, which was derived from V85, a variant EGS selected in vitro [25], demonstrated improved targeting activity in vitro and in culture cells. Hence, our results reveal a feasible approach for developing active gene-targeting EGSs with in vitro selection procedures.
It is currently unknown how the C-S85 sequence accounts for its improved activity. C-S85 binds to ccr5-s about 150-fold better and is about 100-fold more active in guiding RNase P-mediated hydrolysis than C-ARG, the EGS constructed from natural tRNAarg. Perhaps additional tertiary interactions are present between C-S85 and ccr5-s, enhancing their binding and the formation of the ccr5-s–C-S85 complex. For example, the EGS sequences equivalent to the tRNA T-loop and variant domains (Figure 1) could possibly affect the folding of the mRNA–EGS complex and its binding to RNase P by increasing their interactions with the sequence resembling the D-loop [16,19,20,45]. In the ccr5-s–C-S85 complex, a part of C-S85 equivalent to the T-loop and variant domains may form additional interactions with RNase P and the 3′ region of ccr5-s, which resembles part of the D-loop (Figure 1D), leading to enhanced C-S85/ccr5-s binding and improved EGS targeting efficacy. Additional studies should elucidate the mechanism of how C-S85 increases the EGS targeting activity.
One of the potential approaches for gene therapy against HIV infection is to engineer anti-CCR5 and anti-CXCR4 EGS molecules and express them in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells prior to their differentiation into multi-lineage cells such as T cells and macrophages [10,11,15,17,46,47]. One limitation of our current study is that we only tested the effect of EGSs in human PM1 cells with laboratory-adapted HIV strains Ba-L and IIIB. It is important to test additional HIV strains, especially clinical isolates, in human primary cells, including the resting and activated CD4+ T cells that are known to be infected by HIV in vivo. We need to confirm whether EGSs are active in inducing RNase P cleavage of its target mRNA (i.e., CCR5 mRNA) and in shutting down CCR5 expression in these cells. These studies will reveal the potential of the RNase P-EGS approach against HIV infection in clinical settings.
We note that extensive studies have been conducted to understand the normal physiological functions of CCR5 and, more importantly, the potential clinical benefits and pathological consequences due to its absence or reduced expression [5,6,7,8,9]. These results indicated that CCR5 represents an excellent anti-HIV target because reduced CCR5 expression correlated with improved resistance to HIV infection and slowed HIV progression [10,11]. However, these studies also suggested that the absence of CCR5 or reduced CCR5 expression may have potential pathological consequences in vivo, such as increased risk for severe West Nile virus infection and its associated clinical complications [6,7]. Additional studies are needed to understand the CCR5 function in human physiology and the potential unwanted effects of the absence of CCR5 and reduced CCR5 expression. These studies will reduce the potential toxicity and side effects of CCR5 targeting and facilitate the development of new drugs targeting CCR5 for treating human diseases, including HIV [5,9].
While our current study showed that the constructed EGSs effectively inhibited HIV replication, the exact mechanism of how these EGSs block HIV infection and growth is currently not known. Detailed studies to investigate the effects of EGSs on each step of the HIV replication and infection cycle, such as viral entry, gene expression, and assembly, should reveal which step(s) of HIV infection and replication are blocked in EGS-expressing cells. For example, CCR5 is important for the entry of M-tropic HIV strains (e.g., HIVBa-L) [3,4]. It is likely that the cellular surface expression of CCR5 is also reduced due to the EGS-mediated inhibition of the overall expression of CCR5 in these cells. To investigate whether EGSs affect viral entry by downregulating CCR5 expression, it is important to determine whether the viral entry of these strains is inhibited and whether the level of inhibition correlates with the level of EGS-mediated reduction in the overall expression of CCR5 in these cells and the level of reduction in CCR5 expression on the surface of these cells. These studies will reveal the exact mechanism of how EGSs block HIV infection and replication and facilitate the development of these RNA molecules for anti-HIV application.
The EGS strategy against CCR5 targets a cellular gene at the HIV entry step and should minimize the emergence of HIV strains with drug-resistant mutations. Improved gene therapy against HIV can be further developed by combining other therapeutic strategies with EGS technology, including those based on ribozyme, RNAi, and CRISPR/gRNA methods [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Further studies on anti-CCR5 EGS antiviral activity, coupled with research on engineering EGSs with increased activity, will help to develop the RNase P-EGS technology for anti-HIV applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L., B.Y., and F.L.; methodology, Y.L., B.Y., and F.L.; validation, Y.L., B.Y., and F.L.; formal analysis, Y.L., B.Y., I.Z., and F.L.; investigation, Y.L., B.Y., I.Z., and F.L.; data curation, Y.L., B.Y., I.Z., and F.L.; writing, Y.L., B.Y., I.Z., and F.L.; supervision, F.L.; project administration, F.L.; funding acquisition, F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported by a Start-Up Fund at the University of California-Berkeley. I.Z. was supported by a block grant from the Graduate Division of the University of California-Berkeley.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Shibo Jiang for providing the HIV strains used in the study. Gratitude also goes to Phong Trang and Valeria Coria for advice and technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Deng, H.K.; Unutmaz, D.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Littman, D.R. Expression cloning of new receptors used by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature 1997, 388, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.; Lee, H.H.; Farber, J.M. Cloning of STRL22, a new human gene encoding a G-protein-coupled receptor related to chemokine receptors and located on chromosome 6q27. Genomics 1997, 40, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doranz, B.J.; Berson, J.F.; Rucker, J.; Doms, R.W. Chemokine receptors as fusion cofactors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Immunol. Res. 1997, 16, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.A. HIV entry and tropism: The chemokine receptor connection. Aids 1997, 11 (Suppl. A), S3–S16. [Google Scholar]
- Brelot, A.; Chakrabarti, L.A. CCR5 Revisited: How Mechanisms of HIV Entry Govern AIDS Pathogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2557–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Kaminski, V.L.; Chies, J.A.B. CCR5 gene editing—Revisiting pros and cons of CCR5 absence. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, W.G.; McDermott, D.H.; Lim, J.K.; Lekhong, S.; Yu, S.F.; Frank, W.A.; Pape, J.; Cheshier, R.C.; Murphy, P.M. CCR5 deficiency increases risk of symptomatic West Nile virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, G.; Nowak, D.; Mossner, M.; Ganepola, S.; Mussig, A.; Allers, K.; Schneider, T.; Hofmann, J.; Kucherer, C.; Blau, O.; et al. Long-term control of HIV by CCR5 Delta32/Delta32 stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangelista, L.; Vento, S. The Expanding Therapeutic Perspective of CCR5 Blockade. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Rossi, J.J.; Jung, U. Current progress and challenges in HIV gene therapy. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Current progress in the development of RNAi-based therapeutics for HIV-1. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, L.J.; Rossi, J.J. Approaches for the sequence-specific knockdown of mRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.W.; Joyce, G.F. A general purpose RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.A.; Cheng, Y.C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science 1993, 261, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong-Staal, F.; Poeschla, E.M.; Looney, D.J. A controlled, Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate the safety and effects in HIV-1 infected humans of autologous lymphocytes transduced with a ribozyme that cleaves HIV-1 RNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 2407–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrous, N.; Liu, F. Human RNase P: Overview of a ribonuclease of interrelated molecular networks and gene-targeting systems. RNA 2023, 29, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparmann, A.; Vogel, J. RNA-based medicine: From molecular mechanisms to therapy. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e114760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Doudna, J.A. CRISPR technology: A decade of genome editing is only the beginning. Science 2023, 379, eadd8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.; Marquez, S.M.; Pace, N.R. RNase P: Interface of the RNA and protein worlds. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, V.; Altman, S. RNase P:structure and catalysis. In The RNA World; Gesteland, R., Cech, T., Atkins, J., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 277, Chapter 6.1; Available online: http://rna.cshl.edu (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Forster, A.C.; Altman, S. External guide sequences for an RNA enzyme. Science 1990, 249, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Hwang, E.S.; Altman, S. Targeted cleavage of mRNA by human RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8006–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, B.; Sun, X.; Tang, W.; Trang, P.; Yang, Z.; Gong, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus major capsid protein expression and replication by ribonuclease P-associated external guide sequences. RNA 2019, 25, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, G.; Geffin, R.; Spruill, G.; Young, A.K.; Seivright, R.; Cardona, D.; Burzawa, J.; Hnatyszyn, H.J. Cross-clade inhibition of HIV-1 replication and cytopathology by using RNase P-associated external guide sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3406–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Kim, J.; Kilani, A.F.; Kim, K.; Dunn, W.; Jo, S.; Nepomuceno, E.; Liu, F. In vitro selection of external guide sequences for directing RNase P-mediated inhibition of viral gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30112–30120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogakos, T.; Brown, M.; Garzia, A.; Meyer, C.; Hafner, M.; Tuschl, T. Characterizing Expression and Processing of Precursor and Mature Human tRNAs by Hydro-tRNAseq and PAR-CLIP. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mummidi, S.; Ahuja, S.S.; McDaniel, B.L.; Ahuja, S.K. The human CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) gene. Multiple transcripts with 5′-end heterogeneity, dual promoter usage, and evidence for polymorphisms within the regulatory regions and noncoding exons. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30662–30671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusso, P.; Cocchi, F.; Balotta, C.; Markham, P.D.; Lioue, A.; Farci, P.; Pal, R.; Gallo, R.C.; Reitz, M.S. Growth of macrophage-tropic and primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) isolates in a unique CD4+ T-cell clone (PM1): Failure to downregulate CD4 and to interfere with cell-line-tropic HIV-1. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa, D.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, F. Inhibition of viral gene expression by human ribonuclease P. RNA 1998, 4, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.D.; Rosman, G.J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques 1989, 7, 980–982, 984–986, 989–990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Altman, S. Inhibition of viral gene expression by the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Genes. Dev. 1995, 9, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.C.; Vu, G.P.; Trang, P.; Zhang, C.Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, F. Effective inhibition of cytomegalovirus infection by external guide sequences in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13070–13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Vu, G.P.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Trang, P.; Lu, S.; Xiao, G.; Liu, F. RNase P-associated external guide sequence effectively reduces the expression of human CC-chemokine receptor 5 and inhibits the infection of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 509714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daftarian, P.M.; Kumar, A.; Kryworuchko, M.; Diaz-Mitoma, F. IL-10 production is enhanced in human T cells by IL-12 and IL-6 and in monocytes by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jühling, F.; Mörl, M.; Hartmann, R.K.; Sprinzl, M.; Stadler, P.F.; Pütz, J. tRNAdb 2009: Compilation of tRNA sequences and tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D159–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Altman, S. Selection of guide sequences that direct efficient cleavage of mRNA by human ribonuclease P. Science 1994, 263, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Trang, P.; Kim, K.; Zhou, T.; Deng, H.; Liu, F. Effective inhibition of Rta expression and lytic replication of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by human RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9073–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, E.; Castanotto, D.; Zhou, C.; Carbonnelle, C.; Lee, N.S.; Good, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Grange, T.; Pictet, R.; Kohn, D.; et al. The expression cassette determines the functional activity of ribozymes in mammalian cells by controlling their intracellular localization. RNA 1997, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.A.; Murphy, P.M.; Farber, J.M. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: Roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 657–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniasz, P.D.; Cullen, B.R. Chemokine receptors and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Front. Biosci. 1998, 3, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Benimetskaya, L.; Lebedeva, I.; Dignam, J.; Takle, G.; Stein, C.A. Intracellular mRNA cleavage induced through activation of RNase P by nuclease-resistant external guide sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, L.; Polisky, B.; Uhlenbeck, O.; Yarus, M. Diversity of oligonucleotide functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 763–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, J.W. In vitro genetics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, G.F. Directed molecular evolution. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin, M.C.; Engelke, D.R. Broadening the mission of an RNA enzyme. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 108, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkina, R.; Banerjea, A.; Bai, J.; Anderson, J.; Li, M.J.; Rossi, J. siRNAs, ribozymes and RNA decoys in modeling stem cell-based gene therapy for HIV/AIDS. Anticancer. Res. 2003, 23, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.S.; Akkina, R.; Bunnell, B.A.; Dropulic, B.; Planelles, V.; Pomerantz, R.J.; Rossi, J.J.; Zaia, J.A. Current status of gene therapy strategies to treat HIV/AIDS. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).