Abstract
Fine control of orofacial musculature is necessary to precisely accelerate and decelerate the articulators across exact distances for functional speech and coordinated swallows (Amerman & Parnell, 1990; Benjamin, 1997; Kent, Duffy, Slama, Kent, & Clift, 2001). Enhanced understanding of neural control for such movements could clarify the nature of and potential remediation for some dysarthrias and other orofacial myofunctional impairments. Numerous studies have measured orolingual force and accuracy during speech and nonspeech tasks, but have focused on young adults, maximum linguapalatal pressures, and upright positioning (O’Day, Frank, Montgomery, Nichols, & McDade, 2005; Solomon & Munson, 2004; Somodi, Robin, & Luschei, 1995; Youmans, Youmans, & Stierwalt, 2009). Patients’ medical conditions or testing procedures such as concurrent neuroimaging may preclude fully upright positioning during oral motor assessments in some cases. Since judgments about lingual strength and coordination can influence clinical decisions regarding the functionality of swallowing and speech, it is imperative to understand any effects of body positioning differences. In addition, sex differences in the control of such tasks are not well defined. Therefore, this study evaluated whether pressures exerted during tongue movements differ in upright vs. supine body position in healthy middle-aged men and women. Twenty healthy middle-aged adults compressed small air-filled plastic bulbs in the oral cavity at predetermined fractions of task-specific peak pressure in a randomized block design. Tasks including phoneme repetitions and nonspeech isometric contractions were executed in upright and supine positions. Participants received continuous visual feedback regarding targets and actual exerted pressures. Analyses compared average pressure values for each subject, task, position, and effort level. Speech-like and nonspeech tongue pressures did not differ significantly across body position or sex groups. Pressure matching was significantly less accurate at higher percentages of maximum pressure for both tasks. These results provide preliminary comparative data for the clinical assessment of individuals with orofacial myofunctional and neurological disorders.
INTRODUCTION
Behavioral correlates of tongue strength and control have been studied mostly in the upright seated position in healthy young adults, with limited attention to sex differences (Crow & Ship, 1996; Robin, Goel, Somodi, & Luschei, 1992; Trawitzki, Borges, Giglio, & Silva, 2011). A number of factors, however, may necessitate alternative positioning in clinical or research settings. Individuals with neuromuscular impairments may be unable to tolerate upright positioning during assessment of oral mechanism function. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) enables non-invasive examination of neural mechanisms underlying normal speech and swallowing movements but requires subjects to lie supine inside the scanner.
Position-associated alterations in resting position and movement kinematics have been substantiated for several oropharyngeal structures, with impacts on some functional behaviors. For example, participants tend to exhibit decreased superior-posterior pharyngeal space in supine as compared to upright positions (Moon & Canady, 1995; Perry & Kuehn, 2009; Van Holsbeke et al., 2013).
This is thought to be due to shifts in lingual and velopharyngeal position and shape. Position-related displacement of articulators and changes in muscle activity have been shown to vary within and across subjects (Perry, 2011; Stone et al., 2007; Stone, Sutton, Parthasarathy et al., 2002; Van Holsbeke et al., 2013). This suggests that the neuromuscular system implements a range of strategies to compensate for shifts in the orientation of gravitational pull on orolingual anatomy. These position-related perturbations may also contribute to the increased variability exhibited during speech movements in supine positioning, especially for anterior sounds (Perry, 2011; Pracharktam, Hans, Strohl, & Redline, 1994; Stone et al., 2007; Stone, Sutton, Parthasarathy, et al., 2002). Sustained vowels exhibited some differences across acoustic speech measures in supine (Shiller, Ostry, & Gribble, 1999; Stone et al., 2007). Positional deglutition studies revealed a more posterior hyoid position while supine, and a longer pharyngeal stage swallow for males in a reclined position (Barkmeier, Bielamowicz, Takeda, & Ludlow, 2002; Perry, Bae, & Kuehn, 2011). Given this evidence of differences in lingual position, movement patterns, and functional orolingual behaviors while supine, it is reasonable to question whether body position changes affect maximum tongue pressures and accuracy of pressure matching.
Previous studies of tongue strength, endurance, and movement accuracy have not consistently assessed for sex differences, and a recent meta-analysis involving 816 adults from 17 studies revealed significantly greater maximum tongue-elevation strength in men (Adams, Mathisen, Baines, Lazarus, & Callister, 2013). Interestingly, sex differences in raw tongue protrusion pressures were negated when a body composition correction was applied (Mortimore, Fiddes, Stephens, & Douglas, 1999). Men had greater endurance during isometric tongue press tasks in one study (Neel & Palmer, 2012) but not in another (Trawitzki et al., 2011). During an effort level matching task with tongue bulb compression, men and women exhibited similarly high degrees of accuracy and low variability, and were most accurate at the extremes of their maximum lingual pressure (Pmax) range (Somodi et al., 1995). Equivocal findings in the existing body of literature leave unanswered questions regarding sex differences for tongue pressure generation in different body positions. If positional or sex factors result in true physiological differences in tongue behavior, they must be considered in the design and interpretation of data from future studies, particularly in patients with oral neuromuscular impairments.
The objective of the present study was to clarify whether maximum and scaled pressures produced by healthy middle-aged women and men during orolingual (phoneme repetition and nonspeech) tasks differed in upright versus supine positions. Such physiological variations in tongue behavior could reflect fundamental differences in neurological control that may confound the design and interpretation of fMRI studies involving speech and tongue movements. Based on patterns of functional compensation described above, we hypothesize that healthy men and women will demonstrate similar magnitudes of target production during tongue movements in upright and supine positions.
MATERIALS and METHODS
Participants
Twenty right-handed [Edinburgh Handedness Inventory (Oldfield, 1971), average score + 88.5] healthy adults between 40 and 60 years of age (10 females; mean age 52.1 years) were enrolled in this study. Participants were screened to ensure (i) functional hearing and English proficiency for conversational exchanges and (ii) normal speech and oral motor function (per self-report and investigator observation). A certified speech-language pathologist screened subjects to rule out speech or other oral-motor abnormalities. Potential subjects were excluded for: (i) prior surgery on the brain or vocal tract (other than routine dental procedures); (ii) central or peripheral nervous system disease or injury that might perturb speech or voice function; and (iii) implanted metals or claustrophobia that would contraindicate participation in concurrent MRI protocols. MRI data are being prepared for separate publication.
All subjects provided written informed consent to participate in the study after reviewing verbal and written details regarding the purpose, duration, and nature of the study. The study was approved by the Human Subjects Committee at the University of Kansas Medical Center.
Instrumentation
The Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI Medical, Washington), an air-filled polymer bulb that has been repeatedly and reliably used to measure tongue-to-palate pressures (Adams et al., 2013), was utilized per established procedures (Hewitt et al., 2008; Luschei, 2009; Potter & Short, 2009; Solomon, Drager, & Luschei, 2002; Solomon & Robin, 2005; Solomon, Robin, & Luschei, 2000). Specifically, the tongue bulb was placed lengthwise in midline on the anterior hard palate of the oral cavity extending over and posterior to the alveolar ridge, at the typical point of contact for the speech sound tested, /t/. The maxillary and mandibular incisors rested lightly on the attached tubing to stabilize the jaw. Sixty-five feet of 1.67 mm ID polyethylene tubing connected the bulb to a custom-designed pressure transducer located outside the MRI scanner field. To enable measurement of small pressure changes in this system, 3 cm3 of air were injected to create baseline pressures of approximately 6895 pascals. Pneumatic pressure values from the tongue bulb were input through the transducer to a software routine (LabVIEW 7.1; National Instruments, Texas) on a laboratory computer (Latitude E5500; Dell Incorporated, Texas), which recorded data at 10Hz and integrated pressure feedback into a graphic display viewed by the participant.
Procedures
Participants performed speech-like (repetition of the unvoiced phoneme /t/) and nonspeech (isometric press) tasks while seated upright in a chair and while reclined in a supine position. Maximum voluntary contractions were obtained for each task in both positions using previously established protocols (Luschei, 2009; Solomon & Robin, 2005; Solomon et al., 2000; Solomon, Robin, Mitchinson, VanDaele, & Luschei, 1996). For each task and position, the highest peak pressure (Pmax) produced over three trials was used as the Pmax for all subsequent stimuli within LabVIEW (Solomon & Robin, 2005; Solomon et al., 2000).
Next, pressure data were acquired within a multifactorial, repeated-measures design. Subjects performed 90 repetitions of each study task, randomized and blocked by target effort level (25%, 50%, and 75% of the task-specific Pmax) and position (upright and supine). In addition to verbal instructions at the beginning of each data acquisition run, subjects received continuous cues for start/stop timing, target percentage of pressure, and exerted pressure via the LabVIEW display. The visual cues provided to the subject included two horizontal bars representing pressure, and color-coded words to signal subjects to “Get Ready” (2 seconds), “Go” (5 seconds per repetition), and “Rest” (3 seconds between repetitions, with a 13 second pause after every fifth repetition). The target percentage of Pmax was marked on the lower horizontal bar, and the upper bar filled from left to right to provide immediate visual feedback regarding the amount of pressure being produced by the subject.
Data Processing & Analysis
Average pressure values were calculated for each subject, task, position, and effort level using an Awk script (Bell Labs, New Jersey). All other statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (IBM Corporation, New York). Assumptions of normal distribution and equal variances were confirmed, and one-way ANOVAs compared Pmax for body position and sex groups. Two sets of three-way repeated measures ANOVAs were calculated. The first compared actual pressures across effort levels (25%, 50%, 75%, and Pmax), positions (supine, upright), and sex for each task. The second set assessed target vs. actual pressures across effort levels (25%, 50%, 75%) and positions. Statistical significance was accepted as p < 0.05. Although absolute pressure values here are not comparable to those reported in other studies because of the extensive and pressurized tubing setup, these values were considered only in relation to each subject’s Pmax for that task using the same bulb-tubing-transducer closed loop, thus enabling such within-subject comparisons.
RESULTS
Figure 1 illustrates mean pressure values for phoneme repetition (/t/ production) and for isometric tongue press across body position, sex, and effort level. One-way ANOVAs identified no significant differences in Pmax between upright and supine positions [phoneme F(1,38) = 0.42, p = 0.519, isometric F(1,38) = 0.19, p = 0.663] or between men and women [phoneme F(1,38) = 1.42, p = 0.241, isometric F(1,38) = 0.89, p = 0.352].
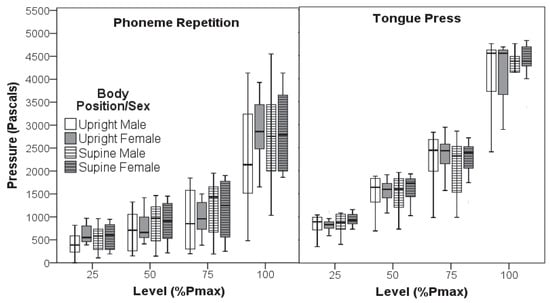
Figure 1.
Linguapalatal Pressures During Phoneme Repetition and Isometric Tongue Press. Linguapalatal pressures were obtained during speech (phoneme repetition, left panel) and nonspeech (isometric tongue press, right panel) tasks at 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of each participant’s task-specific peak pressure (Pmax) while middle-aged men and women were upright and supine. These absolute pressure values are not comparable to those reported in other studies because extensive tubing and injected air were required to locate the transducer outside the MRI field. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
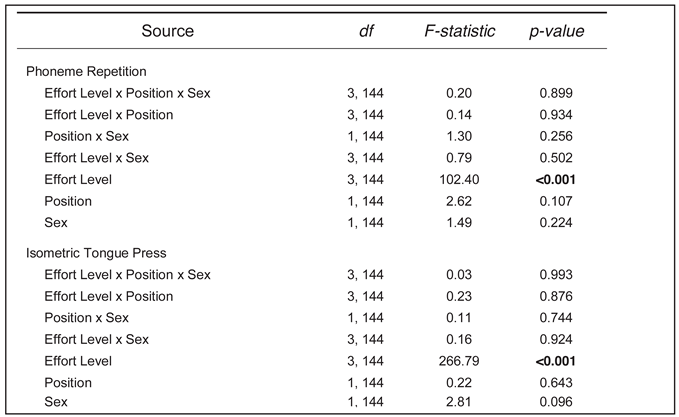
Detailed results of repeated measures ANOVAs for effort level, body position, and sex group are shown in Table 1. There were no significant two- or three-way interactions for either task (p ranged 0.256-0.934 for phoneme, 0.744-0.993 for isometric). Main effects were statistically significant for effort level [phoneme F(1,144) = 102.40, p < 0.001, isometric F(1,144) = 266.79, p < 0.001] as expected, but not for body position (phoneme p = 0.107, isometric p = 0.643) or sex group (phoneme p = 0.224, isometric p = 0.096).

Table 1.
Repeated Measures ANOVA for Phoneme Repetition and Isometric Tongue Press by Effort Level, Body Position, and Sex Group. Data for 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of Pmax were included in the calculations. (Statistically significant at p < 0.05 in bold.).
Since no sex differences were identified, data were collapsed across sex for analysis of pressure matching accuracy across position and effort level. These repeated measures ANOVAs (Table 2) identified significant two-way interactions between effort level and target vs. actual status for both tasks. Specifically, subjects were less accurate at pressure target matching at higher percentages of Pmax [phoneme F(1,228) = 14.83, p < 0.001, isometric F(1,228) = 13.65, p < 0.001]. Main effects confirmed that actual pressures were significantly lower than targets for both tasks [phoneme F(1,228) = 79.32, p < 0.001, isometric F(1,228) = 96.46, p < 0.001]. These trends are illustrated in Figure 2.

Table 2.
Repeated Measures ANOVA for Phoneme Repetition and Isometric Tongue Press by Effort Level, Body Position, and Target versus Actual Status. Data for 25%, 50%, and 75% of Pmax were included in the calculations and were collapsed across sex groups. (Statistically significant at p < 0.05).
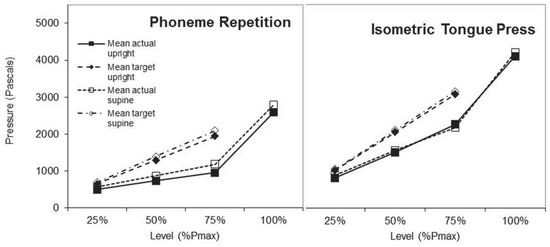
Figure 2.
Mean Actual and Target Linguapalatal Pressures During Phoneme Repetition and Isometric Tongue Press. In upright and supine positions, actual linguapalatal pressures during speech (phoneme repetition, left panel) and nonspeech (isometric tongue press, right panel) tasks differed from targets that were derived from participants’ task-specific peak pressures (Pmax). The absolute pressure values shown here are not comparable to those reported in other studies because extensive tubing and injected air were required to locate the transducer outside the MRI field.
DISCUSSION
The goal of the present study was to describe the impact of body position and sex group on the magnitude of pressure generation during tongue movements. Results supported the hypotheses that tongue pressures would not differ significantly between men and women or between upright and supine positioning for phoneme repetition and isometric tongue press tasks. Participants’ ability to match a target pressure accurately differed according to effort level. These findings have important implications for patient positioning during clinical assessment and subject/task selection during research design.
Maximum and scaled pressures generated by the tongue did not differ significantly by body position. These results expand the body of literature regarding position and function of orolingual structures across different body positions, although the results of previous investigations have been contradictory at times.
Some studies have documented body-position effects in supine orientation for relevant parameters, including tongue rotation (Parthasarathy, Stone, & Prince, 2005; Stone et al., 2007; Stone, Sutton, Parthasarathy et al., 2002; Tiede, Masaki, & Vatikiotis-Bateson, 2000; Wrench, Cleland, & Scobbie, 2011), hyoid position (Perry et al., 2011; Pracharktam et al., 1994), EMG activity of the palatoglossal and levator veli palatine muscles (Moon & Canady, 1995), posterior pharyngeal space (Pracharktam et al., 1994), and speech acoustics (Shiller et al., 1999). Other studies found that body position did not significantly affect velar shape (Perry, 2011; Perry et al., 2011), jaw position (Pracharktam et al., 1994; Shiller et al., 1999), or laryngeal EMG activity (Barkmeier et al., 2002). Variability within and across subjects suggest a range of compensations to changes in gravitational orientation (Moon & Canady, 1995; Perry et al., 2011; Pracharktam et al., 1994; Stone et al., 2007; Stone, Sutton, Parthasarathy, et al., 2002; Tiede et al., 2000; Wrench et al., 2011). Small sample sizes and differences in methodology may partially account for why the current findings differ from some previous data. In this sample, sex differences were negligible for maximum and scaled tongue pressures during phoneme repetition and isometric press. These findings are consistent with results of a number of other examinations of maximum tongue elevation pressure (Butler et al., 2011; Nicosia et al., 2000; Youmans, Stierwalt, & Clark, 2002; Youmans et al., 2009), although others have reported that men generated higher tongue pressures (Neel & Palmer, 2012; Stierwalt & Youmans, 2007; Trawitzki et al., 2011).
No reports regarding sex differences in tongue pressures during phoneme repetition are available, but women exhibit higher linguapalatal contact pressures during swallowing (Butler et al., 2011; Youmans et al., 2009). Stierwalt et al. (2007) speculated that the detection of sex differences might depend on study design factors such as adequately large sample size, subject age, and sex-balanced subject groups. While equal numbers of age-matched men and women were included in these data, a larger subject pool could reveal task-specific sex differences in future studies.
Pressure matching accuracy may reflect the ability of the motor plan to accommodate perturbations such as position changes or increased effort demands. In this study, pressure matching accuracy was not affected by body position for either task, but did vary by effort level. The lack of a body position effect on tongue pressure production is not overly surprising given that the resting position of the tongue has been shown to be similar across upright and supine positioning in several ultrasound studies (Stone, Parthasarathy et al., 2002; Stone, Sutton, & Crouse, 2002; Stone, Sutton, Parthasarathy et al., 2002). In other words, the starting point for the tongue’s movement trajectory does not appear to differ because of body positioning. Even though gravitational influences during actual tongue movements may be different, they apparently are not sufficient to perturb motor control plans or pressure generation capabilities for these tasks beyond the individual’s ability to compensate effectively. The interaction between pressure matching accuracy and effort level was significant in both tasks, with greater difficulty matching pressures at higher percentages of Pmax. Somodi et al. (1995) documented a similar effect; their subjects were less accurate in matching targeted pressure levels in the middle of the tongue’s physiological range (30 to approximately 70% of Pmax) as compared to the extremes of the range. This accuracy-effort interaction could suggest that increased effort levels strain the motor control plan beyond its stable range. This could be due to constraints in the degrees of freedom available to achieve such high pressures, or because the motor plan for these lingual tasks is not typically executed at such high effort levels and thus is insufficiently practiced to maintain accuracy. Individuals with motor control impairments, such as dysarthria or orofacial myofunctional disorders, may have even more difficulty adjusting to positional or effort-related demands than the healthy subjects assessed here.
Future studies could benefit from the use of a scaling formula to allow direct comparisons of tongue pressure values from the extended-tubing MR-compatible setup used in this study and a more typical short-tubed IOPI configuration. Analysis of changes in correlates of neural activation during these lingual tasks may enhance conceptualization of the neural networks involved in task performance and adaptation to positional and task effort demands. The present study of healthy middle-aged adults also provides comparative data for individuals with orofacial myofunctional and neurological impairments during similar testing paradigms, with the potential for expanding understanding of the neuropathophysiology underlying the relevant symptoms.
These preliminary results indicate that although the gravitational influences on tongue movements when upright versus supine are different, they do not appear to interfere significantly with pressure generation capabilities during speech and non-speech tasks in the healthy subjects included here. The data may inform the interpretation of tongue pressure measures in patients who are unable to tolerate upright positioning for medical reasons. This study provides normative data for an age range that is more comparable to that of individuals diagnosed with neuromuscular impairments than most previously reported data, although future studies should be expanded to consider the specific effects of body positioning and sex group on tongue pressures in relevant patient populations.
CONCLUSION
This study is the first to assess positional differences in modulated force production for isometric tongue press and phoneme repetition. Results from this sample of healthy older adults indicate that differences in maximum and scaled pressures during phoneme repetition and isometric tongue press do not differ from upright to supine positions to a statistically significant degree. Body position changes may interact with task effort demands to alter the accuracy of task performance at the extremes of the effort continuum. The absence of clear body-position differences in orolingual pressure generation offers reassurance that subjects in future studies that require supine body position can produce orolingual behaviors in a manner that is comparable to the upright position. Sex differences were insignificant, suggesting that sex is not an essential consideration in subject recruitment for similar studies. These results offer normative data regarding tongue strength and accuracy from healthy, middle-aged controls in upright and supine positions, and inform future assessment of lingual control in similar aged individuals with orofacial myofunctional and neurological disorders.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part by a grant from the American Speech-Language-Hearing Foundation and by the generosity of the Hoglund Brain Imaging Center. This project would not have been possible without the input and expertise of these contributors: Ali Bani-Ahmed; William Brooks, PhD; Kevin Dodd; Allan Schmitt; John Stanford, PhD; Nancy Pearl Solomon, PhD., CCC-SLP.
References
- Adams, V., B. Mathisen, S. Baines, C. Lazarus, and R. Callister. 2013. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 28, 3: 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerman, J. D., and M. M. Parnell. 1990. Auditory impressions of the speech of normal elderly adults. British Journal of Disorders of Communication 25, 1: 35–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barkmeier, J. M., S. Bielamowicz, N. Takeda, and C. L. Ludlow. 2002. Laryngeal activity during upright vs. supine swallowing. Journal of Applied Physiology 93, 2: 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, B. J. 1997. Speech production of normally aging adults. Seminars in Speech and Language 18, 2: 135–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butler, S. G., A. Stuart, X. Leng, E. Wilhelm, C. Rees, J. Williamson, and S. B. Kritchevsky. 2011. The relationship of aspiration status with tongue and handgrip strength in healthy older adults. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 66, 4: 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, H. C., and J. A. Ship. 1996. Tongue strength and endurance in different aged individuals. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 51, 5: 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, A., J. Hind, S. Kays, M. Nicosia, J. Doyle, W. Tompkins, R. Gangnon, and J. Robbins. 2008. Standardized instrument for lingual pressure measurement. Dysphagia 23, 1: 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R. D., J. R. Duffy, A. Slama, J. F. Kent, and A. Clift. 2001. Clinicoanatomical studies in dysarthria: Reviw, critique, and directions for research. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 44, 3: 535–551. [Google Scholar]
- Luschei, E. S. 2009. IOPI user's manual: Iowa oral performance instrument model 2.1. Carnation, WA: IOPI™ Northwest Co., LLC. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J. B., and J. W. Canady. 1995. Effects of gravity on velopharyngeal muscle activity during speech. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal 32, 5: 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimore, I. L., P. Fiddes, S. Stephens, and N. J. Douglas. 1999. Tongue protrusion force and fatiguability in male and female subjects. European Respiratory Journal 14, 1: 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Neel, A. T., and P. M. Palmer. 2012. Is tongue strength an important influence on rate of articulation in diadochokinetic and reading tasks? Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 55, 1: 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia, M. A., J. A. Hind, E. B. Roecker, M. Carnes, J. Doyle, G. A. Dengel, and J. Robbins. 2000. Age effects on the temporal evolution of isometric and swallowing pressure. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 55, 11: M634–M640. [Google Scholar]
- O’Day, C., E. Frank, A. Mongtomery, M. Nichols, and H. McDade. 2005. Repeated tongue and hand strength measurements in normal adults andindividuals with Parkinson’s disease. International Journal of Orofacial Myology 31: 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield, R. C. 1971. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9, 1: 97–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, V., M. Stone, and J. L. Prince. 2005. Spatiotemporal visualization of the tongue surface using ultrasound and kriging. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics 19, 6: 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J. L. 2011. Variations in velopharyngeal structures between upright and supine positions using upright magnetic resonance imaging. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal 48, 2: 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J. L., Y. Bae, and D. P. Kuehn. 2011. Effect of posture on deglutitive biomechanics in healthy individuals. Dysphagia 27, 1: 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J. L., and D. P. Kuehn. 2009. Magnetic resonance imaging and computer reconstruction of the velopharyngeal mechanism. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 20 Suppl. 2: 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, N. L., and R. Short. 2009. Maximal tongue strength in typically developing children and adolescents. Dysphagia 24, 4: 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracharktam, N., M. G. Hans, K. P. Strohl, and S. Redline. 1994. Upright and supine cephalometric evaluation of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and snoring subjects. Angle Orthodontist 64, 1: 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, D. A., A. Goel, L. B. Somodi, and E. S. Luschei. 1992. Tongue strength and endurance: Relation to highly skilled movements. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 35, 6: 1239–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Shiller, D. M., D. J. Ostry, and P. L. Gribble. 1999. Effects of gravitational load on jaw movements in speech. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 20: 9073–9080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solomon, N. P., K. D. Drager, and E. S. Luschei. 2002. Sustaining a constant effort by the tongue and hand: Effects of acute fatigue. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 45, 4: 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, N. P., and B. Munson. 2004. The effect of jaw position on measures of tongue strength and endurance. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 47, 3: 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, N. P., and D. A. Robin. 2005. Perceptions of effort during handgrip and tongue elevation in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 11, 6: 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, N. P., D. A. Robin, and E. S. Luschei. 2000. Strength, endurance, and stability of the tongue and hand in Parkinson disease. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 43, 1: 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, N. P., D. A. Robin, S. I. Mitchinson, D. J. VanDaele, and E. S. Luschei. 1996. Sense of effort and the effects of fatigue in the tongue and hand. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 39, 1: 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Somodi, L. B., D. A. Robin, and E. S. Luschei. 1995. A model of "sense of effort" during maximal and submaximal contractions of the tongue. Brain and Language 51, 3: 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierwalt, J. A., and S. R. Youmans. 2007. Tongue measures in individuals with normal and impaired swallowing. American Journal of Speech Language Pathology 16, 2: 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M., V. Parthasarathy, M. Li, J. Prince, C. Kambhamettu, M. Sutton, and M. Epstein. 2002. The effect of upright and supine positon on speech and pause. Working Papers and Technical Reports, No. 2002-02, Vocal Tract Visualization Laboratory. Baltimore, MD: University of Maryland Dental School. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M., G. Stock, K. Bunin, K. Kumar, M. Epstein, C. Kambhamettu, M. Li, V. Parthasarathy, and J. Prince. 2007. Comparison of speech production in upright and supine position. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 122, 1: 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M., M. Sutton, and U. Crouse. 2002. Exploring the effects of gravity on tongue motion using ultrasonic image sequences. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 111, 5: 2476A. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M., M. Sutton, V. Parthasarathy, J. Prince, M. Li, C. Kambhamettu, and M. Epstein. 2002. Effects of upright and supine orientation on tongue position during silence. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 112, 5: 2417A. [Google Scholar]
- Tiede, M. K., S. Masaki, and E. Vatikiotis-Bateson. 2000. Contrasts in speech articulation observed in sitting and supine conditions. Paper presented at the 5th Seminar on Speech Production, Kloster Seeon, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Trawitzki, L. V., C. G. Borges, L. D. Giglio, and J. B. Silva. 2011. Tongue strength of healthy young adults. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 38, 7: 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holsbeke, C. S., S. L. Verhulst, W. G. Vos, J. W. De Backer, S. C. Vinchurkar, P. R. Verdonck, J. W. van Doorn, N. Nadjmi, and W. A. De Backer. 2013. Change in upper airway geometry between upright and supine position during tidal nasal breathing. Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrench, A., J. Cleland, and J. M. Scobbie. 2011. An ultrasound protocol for comparing tongue countours: Upright vs supine. Paper presented at the 17th International Congress on Phonetic Sciences, Hong Kong. [Google Scholar]
- Youmans, S. R., J. A. Stierwalt, and H. M. Clark. 2002. Measures of tongue function in healthy adults. Paper presented at the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Atlanta, GA. [Google Scholar]
- Youmans, S. R., G. L. Youmans, and J. A. Stierwalt. 2009. Differences in tongue strength across age and gender: Is there a diminished strength reserve? Dysphagia 24, 1: 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors. 2013 Angela M. Dietsch, Carmen M. Cirstea, Ed T. Auer, Jr., Jeff P. Searl.