Abstract
Due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacity and, by inference, its involvement in the myelin stealth attainment, oral nutrient supplementation (ONS) with saffron has recently been investigated as a complementary treatment in multiple sclerosis (MS). The purpose of the present study was to systematically review the literature for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing saffron supplementation to placebo, or other interventions, in patients with an MS diagnosis. PubMed, CENTRAL, and clinicaltrials.gov were searched for relevant completed or ongoing RCTs. The Cochrane’s RoB tool 2.0 was used, and a qualitative synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) was performed. In total, five parallel, double-, or triple-blind RCTs were identified, fulfilling the study’s criteria, and were included in the SWiM. Intervention duration ranged from four weeks to a year. The summary RoB revealed some concerns, or even high risk for overall bias. The included RCTs failed to report particularities of their interventions (exact composition, active compound, safety assays, etc.) and adverse events. The SWiM revealed that according to the results of single trials, inflammation markers (TNF-a and IL-17) were reduced, and MS-specific biomarkers (MMP-9 and TIMP-1) and cognition were improved after saffron ONS, although definite conclusions regarding saffron efficacy with regard to these outcomes cannot be drawn. Two RCTs reported improvement in the redox status of patients receiving saffron, whereas, with regard to depression, the findings were conflicting. Overall, ONS with saffron compounds may prove beneficial in improving antioxidant defense and oxidative stress in patients with MS; however, the evidence appears scattered, heterogenous, and inadequate in terms of making any suggestions regarding the direction of effect of other outcomes. Trials of better design and MS-specific outcomes are required.
1. Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most typical non-traumatic, immune-mediated disease of the central nervous system (CNS) leading to disability, with an increasing global incidence and a high socioeconomic burden [1,2]. The progressive loss of myelin and inflammation of the white matter demyelinating lesions hampers the electrical signaling along the axons, propelling axonal damage and neurological dysfunctions [3]. Common symptoms in MS include sensory loss (numbness), visual disturbance, double vision and vision loss, muscle weakness and fatigue, ataxia, incoordination and impaired balance, chronic pain, cognitive impairment and brain atrophy, and bladder dysfunction, all of which gradually reduce the quality of life (QoL) of patients [4,5,6,7].
The development of MS is attributed to a synergy of environmental factors, genetic predisposition, and immune dysregulation, although the exact etiology remains unclear [8]. Established environmental factors associated with the development of MS include obesity [9], tobacco smoking [10], low vitamin D concentrations [11], viral exposure [12], and many more. Furthermore, accumulating evidence suggests that attaining redox balance is an important effector in the pathogenesis of MS pathogenesis and the development of symptoms [13]. The CNS in particular is very prone to oxidative damage for various reasons, including (i) the CNS has a limited ability to perform anaerobic respiration [14]; (ii) the fact that brain tissue works on oxidative metabolism; (iii) due to the low levels of antioxidant defense mechanisms, elevated Fe concentrations, and membrane elaborations, the oligodendrocyte population is predisposed to oxidative stress; and (iv) the high protein/lipid ratio constitutes myelin as a predisposing target for reactive oxygen species (ROS) [13,15]. As a result, the brains of patients with MS present elevated concentrations of oxidative stress markers [3], and the same is also apparent in serum samples [16]. This shift towards a pro-oxidant activity has been shown to have a direct effect on both central and peripheral aspects of MS, and thus ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) manipulation appears to be a viable pathway to improve disease progression [17].
As a result, specific dietary patterns with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, such as the Mediterranean diet [18,19], have been tested in patients with an MS diagnosis, although the sample sizes used were rather small to draw definite conclusions [20]. In parallel, patients with MS are often receiving alternative therapies as complementary treatments, with antioxidants being particularly popular [21]. In this manner, a variety of studies have evaluated oral nutrient supplementation (ONS) with individual nutrients and antioxidant compounds, aiming to slow the progression of the disease, reduce oxidative stress load, relieve symptoms, and improve anti-inflammatory response in MS [13,22,23,24].
Among the examined antioxidants, Crocus sativus L. (saffron) is a perennial belonging to the Iridaceae family [25], with several active ingredients, including safranal, crocin, crocetin, and picrocrocin [26]. A great body of evidence indicates that supplementation with saffron can yield antidepressant [26,27], cardioprotective [28], neuroprotective [29] and neurocognitive [30], and anxiolytic effects [26,31]. With regard to MS in particular, given the aforementioned properties of Crocus sativus L., it could prove to be a valuable complementary treatment for managing several symptoms of the disease. Findings from intervention trials lacking a comparator arm indicate that ONS with saffron can improve blood cholesterol concentrations [32] and reduce symptoms of fatigue [33]. Evidence of higher hierarchy, namely, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), have also evaluated saffron supplementation in MS; however, the exact effect has not been weighed using evidence synthesis methods.
Given the frequent use of antioxidant supplements from patients with MS, it is important to understand which ones are efficient and where further research is required. With this in mind, the aim of the present systematic review was to review and synthetize the evidence regarding saffron supplementation in patients with MS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review Protocol and PICO
The present review was designed and presented according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [34] with the Synthesis WIthout Meta-analysis (SWiM) extension [35]. The study’s protocol was published at the center for open science framework (OSF). The PICO of the study’s research question is detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
PICO components of the study’s research question.
2.2. Search Strategy, Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All studies related to the research question were identified in the PubMed and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) databases, the clinicaltrials.gov website, and gray literature searches, from inception until October 2021, by three independent reviewers. Any disagreement between reviewers was resolved by a senior researcher (D.P.B.). The search syntax used in each database is presented in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Search strings used in each database.
Rayyan [36] was used to scan and identify all retrieved items against the study’s criteria. Retrieved references were imported into Rayyan using a reference manager software (Mendeley), and duplicate entries were excluded.
Combinations of relevant keywords were used to identify relevant RCTs in the literature. The keywords used included (Crocus sativus), (saffron), (crocin), (crocetin), (safranal), and (multiple sclerosis).
The inclusion and exclusion criteria of the studies are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the studies included in the evidence synthesis.
Special caution was taken not to include RCTs investigating the effects of curcumin, which is also named as “Indian saffron” [25,37].
2.3. Outcomes of Interest
Outcomes of interest involved any specific index/score for MS, including fatigue, disability, inflammation markers, redox status, cognition, physical function, anxiety, depression, QoL, etc.
2.4. Risk of Bias
Eligible studies were assessed for bias with the use of the Cochrane’s revised Risk of Bias (RoB) tool 2.0 [38] by two authors, independently. Judgments were produced when there was low risk, some concerns or high RoB, regarding the randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcomes, selective reporting of the results, and the final assessment, regarding the overall bias of each RCT.
2.5. Data Extraction
Three independent researchers extracted data in predefined Excel spreadsheets. Recorded information involved sample particularities (size, age, % female, disease status), recruitment, funding, country of origin, study design and methodological characteristics (randomization particularities, masking, etc.), intervention and comparator arms, primary and secondary outcomes of interest, the number of drop-outs, adverse events (AEs), presented analyses, and general findings.
2.6. Data Synthesis
At least three RCTs examining the same outcome were deemed as necessary for an effective data synthesis. Since a meta-analysis was not feasible, vote counting was applied, according to the direction of effect (mean differences) for each outcome [39] (qualitative synthesis) in order to accompany the narrative synthesis [40]. The methodological characteristics of each study (sample size, RoB) were used to assess heterogeneity, on the basis of the Cochrane Handbook [40] and the SWiM guidelines [35].
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
Out of 139 studies screened in total, 5 distinct RCTs with an equal number of publications [41,42,43,44,45] fulfilled the protocol’s criteria and were included in the present systematic review. Figure 2 details the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram of the study selection process [34].
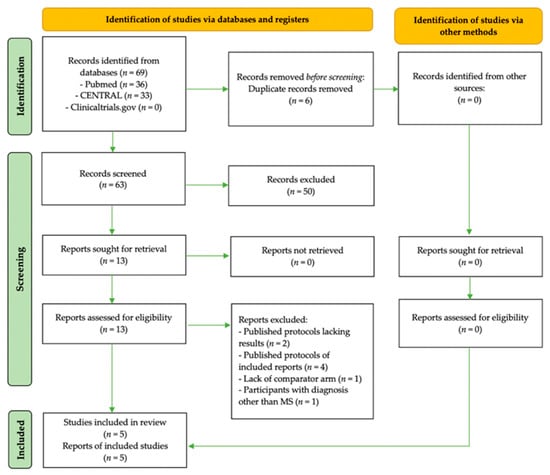
Figure 2.
PRISMA [34] flow diagram of the study selection process.
3.2. Characteristics of RCTs with Saffron Interventions in Patients with ΜS
Details of the RCTs fulfilling the study’s criteria, evaluating saffron interventions in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), are presented in Table 3. Five RCTs evaluated the effect of saffron supplementation in patients with an MS diagnosis [41,42,43,44,45].
3.2.1. Trial Design, Origin, and MS Diagnosis
All trials were conducted in Iran, in a parallel design manner, and were published between the years 2019–2020. Masking of the included RCTs were of either double [41,44,45], or triple blinding [42,43].
The McDonald et al. [46] criteria were applied for MS diagnosis by three trialist groups [41,42,44], with one also using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [41]. The trials conducted by Ahmadi [45] and Doosti [43] failed to report the applied MS diagnostic criteria.
3.2.2. Intervention and Comparator Particularities
The Ahmadi [45] and Ghiasian [41] trials administered daily doses of crocin equal to 30 mg. In the Ghasemi Sakha [42] trial, 1.5 g/day of saffron was prescribed, whereas in the trial conducted by Doosti et al. [43], the saffron dose was not reported. Finally, Adalat and associates [44] administered a traditional herbal syrup formulation (2 × 10 mL/day) containing C. sativus, H. perforatum, C. verum, and V. vinifera.
Intervention duration spanned between 4 weeks [41,44,45] and 12 months [42]. Doosti and associates [43] failed to report the duration of the intervention.
In all RCTs, placebos were used as comparators [41,42,43,44,45].
3.2.3. Sample Size
A rather small sample size was used in all RCTs, spanning from 40 [41,45] to 52 [44] patients in total per trial, prior to randomization. The pooled sample of patients of all RCTs consisted of 225 patients with an MS diagnosis. One trial, published in abstract format [43] only, failed to report the number of patients allocated in the intervention/comparator arms.

Table 3.
Characteristics of the parallel RCTs evaluating interventions with saffron in patients with MS, included in the qualitative synthesis.
Table 3.
Characteristics of the parallel RCTs evaluating interventions with saffron in patients with MS, included in the qualitative synthesis.
| First Author | Adalat [44] | Ahmadi [45] | Doosti [43] | Ghasemi Sakha [42] | Ghiasian [41] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication | Full-text | Full-text | Abstract | Full-text | Full-text |
| Journal | Galen. Med. J., 2019 | Biomedicine, 2020 | Mult. Scler J., 2019 | Iran J. Allergy Asthma Immunol., 2020 | J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol., 2019 |
| Origin | Iran | Iran | Iran | Iran | Iran |
| Registry | IRCT2016012916369N3 | IRCT2016122013194N3 | NR | IRCT138802091859N1 | IRCT2016092713194N2 |
| Design | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel |
| Funding | NR | NR | NR | NR | Neurophysiology Center |
| Masking | Double blind | Double blind | Triple blind | Triple blind | Double blind |
| Randomization | Blocked, PC-generated random numbers (1:1 ratio) | “Randomly” NOD | NR | “Randomly” NOD | PC-generated sequence |
| Recruitment | Sina Hospital, Tabriz | Farshchian Hospital, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences | NR | Sina Hospital, Emam Khomeni Hospital | Farshchian Hospital, Hamadan University |
| Study duration | NR | 2017 | NR | NR | NR |
| Participants | N = 52 adult patients with MS (EDDS ≤ 6) on SSRIs | N = 40 patients with RRMS and low disability (EDSS < 4) | N = 50 adult patients with RRMS (EDSS: 0–5.5) | N = 43 adult patients with RRMS (EDSS: 0–5.5) | N = 40 patients with RRMS |
| Participant age (years) | 20–50 R | 20–40 R | 18–50 R | 18–50 R | 29 ± 5 M (intervention); 31.5 ± 5.3 M (placebo) |
| Men/women (n) | 14/38 | 5/35 | NR | 4/39 | 5/35 |
| MS diagnostic criteria | McDonald et al. [46] criteria | NR | NR | McDonald et al. [46] | McDonald et al. [46] and MRI |
| Intervention | ONS with herbal syrup (2 × 10 mL/day) with C. sativus, V. vinifera, C. verum, H. perforatum (n = 26) | ONS with crocin (2 × 15 mg caps/day) (n = 20) | ONS with saffron NOD (n NR) | ONS with saffron (3 × 500 mg pill/day) (n = 21) | ONS with crocin (2 × 15 mg caps/day) (n = 20) |
| Comparator | Placebo syrup (n = 26) | Placebo (n = 20) | Placebo (n NR) | Placebo (n = 22) | Placebo (n = 20) |
| Intervention duration | 4 weeks | 4 weeks | NR | 12 months | 4 weeks |
| Standard therapy | SSRIs were only reported; MS medications were NR | NR | NR | Vitamin D3, vitamin B1, Ca, tolterodine, gabapentin, citalopram, amantadine | NR |
| Treatment adherence | By periodic phone follow-ups | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Ban of other antioxidants | Discontinuation at trial start (including herbal medicines) | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Main hypothesis | Δ in fatigue and sleep disorders (depression was presented instead) | Δ in oxidative stress | Δ in cognition and functional ability | Δ in proxy markers of disease severity | Δ in inflammation and oxidative and DNA damage |
| Outcomes | BDI | TAC, CAT, TTG, LPO from saliva and urine samples | EDSS, BDI, MACFIMS (PASAT, BWMT, DKEFS-ST, CO-WAT, CVLT, NAART), 9HPT | Serum levels of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 (its inhibitor) | LPO, TAC, TTG, IL-17, TNF-α, DNA damage |
| Assays | N/A | Absorbance (CAT), FRAP assay (TAC) | N/A | ELISA | Absorbance (TTG), FRAP (TAC), SP, ELISA (IL-17, TNF-a, DNA damage) |
| Dietary assessment | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| PE assessment | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| AEs | None | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Drop outs | Few relapsed (n = 2) or were dissatisfied (n = 4) (all on placebo) | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| n included in final analysis | n = 26 active arm n = 20 placebo | n = 20 active arm n = 20 placebo | NR | n = 21 active arm n = 22 placebo | n = 20 active arm n = 20 placebo |
| Analysis | PP | ITT | NR | ITT | ITT |
| Results | Those treated with the herbal extract demonstrated reduced BDI scores compared to participants in the placebo arm. | A difference in TTG, TAC, and LPO, except for CAT activity, was noted in the crocin arm. Crocin increased saliva TTG, TAC levels, and CAT, and lowered LPO. | Saffron improved MAC-FIMS subdomains (total learning-CVLT, PASAT, total and delay-BWMT, COWAT, DKEFS-ST, NAART). Dominant hand 9HPT differed between arms. | The level of MMP-9 was decreased, and that of TIMP-1 was increased in the saffron arm. | A decrease in the level of LPO, DNA damage, TNF-α, and IL-17, as well as an increase in the TAC of patients treated with crocin. |
Δ, change; AEs, adverse events; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory [47]; BVMT, Brief Visuospatial Memory Test [48]; CAT, catalase activity; COWAT, Controlled Oral Word Association Test [48]; CVLT, California Verbal Learning Test [48]; DKEFS-ST, Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System Sorting Test [48]; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale [49]; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FRAP, ferric reducing ability of plasma; ITT, intention-to-treat; LPO, lipid peroxidation; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MS, multiple sclerosis; NAART, North American Adult Reading Test [50]; N/A, not applicable; NOD, not other defined; NR, not reported; ONS, oral nutrient supplementation; PC, personal computer; PE, physical exercise; PP, per protocol; RRMS, relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis; TAC, total antioxidant capacity; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; TTG, total thiol groups; MACFIMS, Minimal Assessment of Cognitive Function in MS [48]; 9HPT, Nine Hole Peg Test [48]; PASAT, Paced Auditory Serial Addiction Test [48]; SP, spectrophotometry; SSRIs, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. R range; M mean ± standard deviation. In the majority of RCTs, participants had relapsing–remitting MS (RRMS) [41,42,43,45], whereas one RCT [44] recruited patients with MS on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
3.3. Outcomes Assessed in the Included Interventions
The RCTs included outcomes related to disability, inflammation, antioxidant and redox status, depression, cognitive and functional ability, and the assessment of MS-specific biomarkers. Changes in the expanded disability status scale (EDSS) were evaluated in one trial, although the results were not presented [43]. Outcomes related to inflammation markers included DNA damage, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-17 (ΙL-17) concentrations.
Assessed antioxidant activity and oxidative stress markers included the malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration, total antioxidant capacity (TAC, via the ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) method), catalase activity (CAT, via absorbance), lipid peroxidation (LPO) levels, and total thiol groups (TTG, assessed via colorimetry).
Depression was evaluated using the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [47]. In one RCT [43], cognition and functional ability were evaluated using the minimal assessment of cognitive function in MS (MACFIMS) [48] and its subscales, including the Paced Auditory Serial Addiction Test (PASAT) [48], the Delis–Kaplan executive Function System Sorting Test (DKEFS-ST) [48], the controlled oral word association test (COWAT) [48], the Brief Visuospatial Memory Test (BVMT) [48], the North American Adult Reading Test (NAART) [50], and the California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT) [48]. Finally, with regard to physical function, only finger dexterity was assessed, using the nine hole peg test (9HPT) [48].
MS-specific markers were also assessed in the included RCTs. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used for the assay of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a group of proteolytic enzymes dissolving the extracellular matrix. In particular, the assessment involved the levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), which facilitates the migration of T cells to the central nervous system and has been associated with reduced MS activity [51]. In parallel, the concentration of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) was also assessed, since it consists of an inhibitor of the MMP-9 function [42].
3.4. Risk of Bias Summary
The summary of risk of bias for the RCTs included in the qualitative synthesis is presented in Figure 3. According to the RoB, some concerns for overall risk of bias were apparent in the majority of RCTs (60%). The remaining (40%) RCTs exhibited high risk for overall bias. Unclear bias mainly involved the domains of randomization and selective reporting of outcomes.
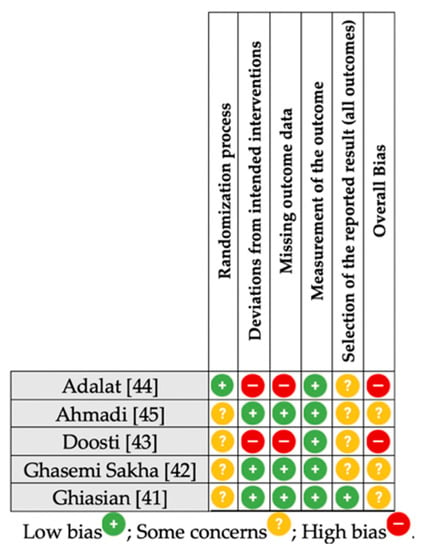
Figure 3.
Summary risk of bias [38] assessment for the included RCTs. RCT, randomized controlled trial.
3.5. AEs, Treament Adherence, and Other Biases
With regard to the AEs following saffron ONS, only one RCT [45] reported the lack of any adverse reactions. The rest of the trials failed to report any information related to Aes.
Treatment adherence was only assessed in one trial [44], with the remaining RCTs failing to control for this issue. The ban of antioxidant compounds at the beginning of the interventions was only performed by Adalat and associates [44], with the rest of the trials failing to control for this issue. Dietary intake was not recorded in any trial, despite the fact that it affects antioxidant intake and, by inference, redox status.
3.6. Synthesis without Meta-Analysis (SwiM)
Figure 4 details the effect direction plot of the outcomes assessed in the included synthesis. For the majority of outcomes, results were unanimous; however, great heterogeneity was apparent with regard to the outcomes and the number of trials assessing each outcome. For most outcomes, the total number of RCTs providing results were less than 3. Due to the clinical heterogeneity of the RCTs, a meta-analysis was not deemed as a safe option for the formulation of recommendations regarding saffron ONS.
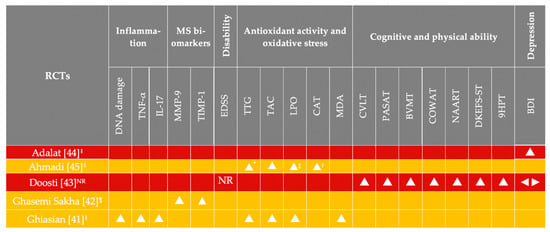
Figure 4.
Qualitative synthesis without meta-analysis of the outcomes in each RCT, favoring the saffron arms post-intervention. All RCTs had less than 50 participants in each arm. Background row colors denote study quality according to the RoB (red denotes high RoB; yellow denotes some concerns regarding RoB). BDI, Beck Depression Inventory [47]; BVMT, Brief Visuospatial Memory Test [48]; CAT, catalase activity; COWAT, Controlled Oral Word Association Test [48]; CVLT, California Verbal Learning Test [48]; DKEFS-ST, Delis–Kaplan Executive Function System Sorting Test [48]; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; LPO, lipid peroxidation; MDA, malondialdehyde; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MS, multiple sclerosis; NAART, North American Adult Reading Test [50]; NR, not reported; PASAT, Paced Auditory Serial Addiction Test [48]; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RoB, risk of bias; TAC, total antioxidant capacity; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; TTG, total thiol groups; 9HPT, Nine Hole Peg Test [48]; * saliva and urine samples; † saliva only; ‡ urine samples only; ‖ intervention duration < 3 months; ¶ intervention duration 12 months; ⯅ improved; ◄► no difference was recorded.
According to the results of one trial only [41], examined markers of inflammation (DNA damage, TNF-α, and IL-17) were reduced after the saffron intervention.
Indicators of antioxidant activity and oxidative damage were improved (TTG in two trials [41,45], CAT [45] and MDA [41] in one RCT each, LPO [41,45] and TAC [41,45] in all trials).
The only RCT [42] evaluating MS-specific markers reported a reduction in MMP-9 concentrations and a concomitant increase in TIMP-1.
With regard to disability status (EDSS), no results were presented, although the EDSS was a reported outcome in one trial [43].
As for depression, two trials indicated conflicting results, with Doosti et al. [43] suggesting lack of change after saffron supplementation and Adalat and associates [44] reporting an improvement in the BDI of participants receiving the herbal syrup containing Crocus sativus L.
Furthermore, ONS with saffron induced an improvement in all batteries of cognition in patients with MS, as indicated by a single RCT [43].
Collectively, it appears that ONS with active compounds of the Crocus sativus plant may improve circulating levels of TAC, TTG, and LPO, as indicated by two trials [41,45] with a similar direction of effects. For the remaining outcomes, the evidence is inadequate to make any suggestions regarding the direction of effect, as they were examined in one trial each.
4. Discussion
According to the available evidence evaluated. In the present SWiM, ONS with saffron appears to improve redox status in patients with MS. However, with regard to the other outcomes (inflammation, disability, depression, cognitive function, and MS-specific biomarkers), the evidence is yet inadequate to suggest post-supplementation improvements.
Saffron extracts include a variety of phenolic and flavonoid compounds, as well as crocins and crocetin, all of which consist of important antioxidant substances [52]. According to research, saffron intake can inhibit oxidative damage via a reduction in the concentrations of endogenously generated ROS, as well as a concomitant reduction in the production of pro-inflammatory biomarkers [25,53,54]. With regard to MDA and TAC levels in particular, it has been shown that ONS with saffron can induce significant improvements [55], as seen herein. In MS, the overproduction of ROS and oxidative stress biomarkers in activated microglia and macrophages, in conjunction to the inflammatory environment may affect the antioxidant defense system of the CNS, further propelling demyelination and neuronal loss [24,56,57]. Furthermore, the extracellular and intracellular redox milieu is also important for the generation, activation, and apoptosis of T cells [17]. Thus, although redox status is not included in the main outcomes for MS, it carries weight in guarding the integrity of myelin stealth and, thus, disease prognosis. Unfortunately, only one trial examined markers of inflammation [45], and thus we cannot conclude on the efficacy of saffron supplementation regarding this domain.
Anxiety disorders and depression consist of common issues among patients with chronic diseases, including MS, which can in turn have a negative impact on QoL [58,59,60]. Moreover, the anxiety-induced somatic symptoms are often attributed to the MS physical symptomatology [60]. Previous research has suggested that ONS with saffron compounds can improve symptoms of depression and anxiety [31,61,62] and are equally effective as synthetic antidepressants [63,64]. Conflicting results, however, were observed in the present synthesis [43,44], and this can be attributed to trial differences in the intervention duration, in the disease and comorbidity status of recruited participants, and in the exact composition of the intervention. Given that Adalat et al. [44] used a sample of patients with MS on concomitant SSRI therapy, it is highly likely that the provided saffron-containing syrup and the SSRIs acted synergistically in that trial, inducing more acute improvements in the BDI. One might also argue that the favorable results suggested in the trial might in fact be the residue of SSRI prescription alone, without any effect being initiated due to the intake of saffron. However, since both arms were on SSRI and the improvement was only noted in the saffron-receiving arm, it is safe to conclude that the concomitant intake of saffron and SSRIs was the driver of the induced improvement in the BDI of participants. Furthermore, it is unclear if the participants had primary-progressive MS (PPMS) or secondary-progressive MS (SPMS), where the treatment with disease-modifying drugs DMDs is less frequent and intake of the food-derived factor (FDF) is required [65]. Nevertheless, establishing FDFs for MS is not an easy task [65], and many studies are required to verify the findings.
In their majority, the included RCTs failed to provide information regarding the saffron active ingredients, and this might partly explain the heterogeneity observed regarding the outcome of depression. The active ingredients of saffron, including safranal, crocin, crocetin, and picrocrocin, exhibit different biological functions, medicinal properties, and antioxidant capacities [52]. Moreover, specific characteristics of the formula elaborations suggested by the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement for RCTs delivering herbal medicine interventions [25] were missing. Thus, the exact composition of each intervention, the dose of active saffron ingredients, the type and concentration of extract solvent used, purity tests, and many more characteristics are missing from the RCTs. This frequently non-standardized nature of the interventions involving herbal medicine can, in fact, multiply the probability for AEs, and for this, it is important to implement specific standards of safety and efficacy [66]. In a narrative review, Singletary [67] was the first to report the low and variable quality of trials administering saffron, and similar results have also been observed in other systematic reviews [25,28].
4.1. Heterogeneity in the Examined Outcome Measures
Interestingly, the included trials presented great heterogeneity in their reported outcomes. EDSS, the most used outcome in MS [68], providing a rapid assessment of the disability status of patients, was only applied in one trial [43], yet the results were not reported. According to empirical evidence [69], statistically significant outcomes are more likely to be reported, and thus we can assume that no effect was noted in the EDSS recorded by Doosti et al. [43]. Furthermore, as per the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) handbook for MS research [70], the selected outcomes in each MS trial must be relevant to health practitioners, decision makers, and patients. Herein, with regard to saffron, the trialists appear to select outcomes that are more sensitive to change (antioxidant status and oxidative stress, biomarkers, etc.), in an effort to understand the mechanisms driving Crocus Sativus L. possible efficacy.
In any case, the use of MS-specific standardized outcomes should be included in all future saffron trials, as detailed in the COMET handbook for MS research [70]. The use of standardized outcomes enables comparisons between interventions and the combination of data and results. On the other hand, the selection of non-standardized outcomes (as seen herein) may enable researchers to examine other results of particular interest for their research, but are more likely to produce positive findings and limit the ability to combine results and data [71]. Nevertheless, given that trial registries allow for the registration of any outcome, the fault is not solely on the part of the trialists. Moreover, these gaps in the use of standardized outcomes (core outcome set) has long been identified in the literature and appears to remain a challenge to this date [72].
4.2. RCTs in the Pipeline
Research on the effects of saffron in MS are still being investigated in two RCTs (Table 4). The main outcomes of these trials involve changes in the MACFIMS total score, depression (BDI) and QoL. Thus, it appears that publication of the results of these trials is expected to add evidence in the effect direction plots and guide recommendations with regard to these outcomes.

Table 4.
Parallel RCTs investigating ONS with saffron in patients with MS.
4.3. Limitations of the Present SWiM
Limitations of the present SR and SWiM include the relatively small number of RCTs with saffron interventions in MS and the heterogeneity in outcomes, not allowing for the formulation of recommendations. However, the synthesis performed herein allows us to understand gaps, bottlenecks, and limitations in the existing research and design better RCTs in the future. Heterogeneity in the selected outcomes consists of yet another issue for the present synthesis and the available evidence; however, the present findings can be used to for the design of better, future trials, using similar outcomes, thus enabling evidence synthesis. Another limitation involves the lack of AEs reporting in the trials, as per COMET instructions [70]. Other studies using saffron supplementation have reported a variety of AEs, including nausea, dizziness, headache, mouth dryness, poor appetite, fatigue, hypomania, agitation, and confusion [30,62].
4.4. Advice for Future Trials Administering Saffron in Patients with MS
The present systematic review revealed the low methodological quality and high bias of trials administering saffron in patients with MS. Future trialists working in MS should aim in selecting primary endpoints from the COMET handbook for MS research [70], supplemented by other outcomes that might be of particular interest to their research. Furthermore, the assessment/measurement of each outcome should follow the COSMIN (consensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement instruments) guidelines [73]. As far as interventions with complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) treatments are concerned, as already suggested [25], particularities regarding the intervention should clearly follow the CONSORT statement for RCTs delivering herbal medicine interventions [25] and include the exact composition of each intervention, the purification method, the dose of active ingredients, the type and concentration of extract solvent used, purity tests, etc. Last, but not least, AEs should be clearly reported according to the CONSORT harms checklist [74].
5. Conclusions
Although medical nutrition therapy, including nutrient supplementation, is not included in the clinical practice guidelines for the management of MS [75], it consists of a complementary treatment frequently selected by patients [76]. ONS with saffron compounds may prove beneficial in improving antioxidant defense and oxidative stress in patients with MS; however, the evidence is scattered and inadequate in terms of making any suggestions regarding the direction of effect of other outcomes. Trials of better design and MS-specific outcomes are required to aid decision making regarding the efficacy of supplementation with saffron in MS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.B., M.G.G., S.G.T. and E.D. (Efthimios Dardiotis); methodology, M.G.G., K.G. and S.G.T.; investigation, S.G.T., M.G.G. and E.D. (Efstratia Daskalou); quality assessment of studies, S.G.T., K.G., M.G.G. and D.P.B.; data extraction, M.G.G., S.G.T. and M.I.M.; formal analysis, M.G.G., S.G.T., D.P.B. and K.G.; resources, D.P.B. and E.D. (Efthimios Dardiotis); data curation, M.G.G., S.G.T., K.G. and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.G., S.G.T., K.G. and D.P.B.; writing—review and editing, M.G.G., S.G.T., K.G., A.G., E.D. (Efstratia Daskalou), M.I.M., E.D. (Efthimios Dardiotis) and D.P.B.; visualization, M.G.G. and S.G.T.; supervision, D.P.B. and E.D. (Efthimios Dardiotis); project administration, D.P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch-Henriksen, N.; Sørensen, P.S. The changing demographic pattern of multiple sclerosis epidemiology. Lancet. Neurol. 2010, 9, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Gui, L.N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Shi, S.; Cheng, Y. Oxidative Stress Marker Aberrations in Multiple Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis Study. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M. Multiple sclerosis: Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and clinical presentation. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 122, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X. Multiple sclerosis: Pathology, diagnosis and treatments. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboud, T.; Schuster, N.M. Pain Management in Multiple Sclerosis: A Review of Available Treatment Options. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2019, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andravizou, A.; Dardiotis, E.; Artemiadis, A.; Sokratous, M.; Siokas, V.; Tsouris, Z.; Aloizou, A.-M.; Nikolaidis, I.; Bakirtzis, C.; Tsivgoulis, G.; et al. Brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis: Mechanisms, clinical relevance and treatment options. Autoimmun. Highlights 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastain, E.M.L.; Miller, S.D. Molecular mimicry as an inducing trigger for CNS autoimmune demyelinating disease. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.G.; Genes, T.M. Obesity and Multiple Sclerosis—A Multifaceted Association. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehrinia, A.; Huang, J.; Hillert, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Olsson, T.; Kockum, I.; Constantinescu, C.S. Smoking Attributable Risk in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombash, S.E.; Lee, P.W.; Sawdai, E.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. Vitamin D as a Risk Factor for Multiple Sclerosis: Immunoregulatory or Neuroprotective? Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 796933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, C.; Baroni, L. Antioxidants for the Prevention and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: An Overview. In Bioactive Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements in Neurological and Brain Disease: Prevention and Therapy; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 341–353. ISBN 9780124115293. [Google Scholar]
- Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Doelman, C.J.A. Oxidants and antioxidants: State of the art. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongarzone, E.R.; Pasquini, J.M.; Soto, E.F. Oxidative damage to proteins and lipids of CNS myelin produced by in vitro generated reactive oxygen species. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 41, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armon-Omer, A.; Waldman, C.; Simaan, N.; Neuman, H.; Tamir, S.; Shahien, R. New Insights on the Nutrition Status and Antioxidant Capacity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, K.; Tenbrock, K.; Kipp, M. Oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis: Central and peripheral mode of action. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 277, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravejolahkami, A.R.; Paknahad, Z.; Chitsaz, A.; Hojjati Kermani, M.A.; Borzoo-Isfahani, M. Potential of modified Mediterranean diet to improve quality of life and fatigue severity in multiple sclerosis patients: A single-center randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, P.; Gioxari, A.; Daskalou, E.; Vasilopoulou, A.; Skouroliakou, M. Personalized Nutritional Intervention to Improve Mediterranean Diet Adherence in Female Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Dietetics 2022, 1, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz Sand, I. The Role of Diet in Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanistic Connections and Current Evidence. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, M.J.; Antonia Murcia, M.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.M.; Tur, J.A.; Mar Bibiloni, M.; Alonso, G.L.; Martínez-Tomé, M. Influence of Diet in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristotelous, P.; Stefanakis, M.; Pantzaris, M.; Pattichis, C.S.; Calder, P.C.; Patrikios, I.S.; Sakkas, G.K.; Giannaki, C.D. The Effects of Specific Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Antioxidant Vitamins on Gait and Functional Capacity Parameters in Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferorelli, P.; Antonelli, F.; Shevchenko, A.; Mischiati, C.; Doepp, M.; Lenzi, S.; Borromeo, I.; Feriotto, G.; Beninati, S. Reduction in Fatigue Symptoms Following the Administration of Nutritional Supplements in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, K.F.; Kirkland, A.E. Moving past antioxidant supplementation for the dietary treatment of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiogkas, S.G.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Gkiouras, K.; Zafiriou, E.; Papadopoulos, I.; Liaskos, C.; Dardiotis, E.; Sakkas, L.I.; Bogdanos, D.P. Effect of Crocus sativus (Saffron) Intake on Top of Standard Treatment, on Disease Outcomes and Comorbidities in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Synthesis without Meta-Analysis (SWiM) and Level of Adherence to the CONSORT Statement for Randomized Controlled Trials Delivering Herbal Medicine Interventions. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Saffron and its Active Components. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 43, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazadeh, V.; Zarezadeh, M.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Keramati, M.; Ghoreishi, Z.; Farnam, A. Saffron, as an adjunct therapy, contributes to relieve depression symptoms: An umbrella meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setayesh, L.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Clark, C.C.T.; Rezaei Kelishadi, M.; Khalili, P.; Bagheri, R.; Asbaghi, O.; Suzuki, K. The Effect of Saffron Supplementation on Blood Pressure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Lee, S.M.Y. Neuroprotective Potency of Saffron Against Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Other Brain Disorders: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 579052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Vrysis, C.; Chaitidis, N.; Kolotsiou, K.; Myserlis, P.G.; Kapogiannis, D. Effects of saffron (Crocus Sativus L.) on cognitive function. A systematic review of RCTs. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.A.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Pouchieu, C.; Dubreuil, S.; Gaudout, D.; Moras, B.; Pourtau, L.; Joffre, F.; Vaysse, C.; et al. Effects of Saffron Extract Supplementation on Mood, Well-Being, and Response to a Psychosocial Stressor in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel Group, Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, M.J.; Alonso Salinas, G.L.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.M.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Martínez-Tome., M.; Alonso, G.L. Effect of Daily Intake of a Saffron Infusion on Blood Cholesterol Levels. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, A.R.; Seied Amirhossein, L.; Jadidi, A.; Ghasami, K.; Khanmohamadi Hezave, A.; Aghae Pour, S.M.; Malekhosseni, S.; Kamalinejad, M.; Alimoradian, A.; Salehi, M. The effect of novel simple saffron syrup on fatigue reduction in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Sowden, A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Brennan, S.E.; Ellis, S.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Ryan, R.; Shepperd, S.; Thomas, J.; et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: Reporting guideline. BMJ 2020, 368, I6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the golden spice from Indian saffron, is a chemosensitizer and radiosensitizer for tumors and chemoprotector and radioprotector for normal organs. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.; Elbers, R.; Blencowe, N.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.; Eldridge, S.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Br. Med. J. 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, H.J.; Thomas, S. The effect direction plot: Visual display of non-standardised effects across multiple outcome domains. Res. Synth. Methods 2013, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, J.E.; Brennan, S.E. Synthesizing and presenting findings using other methods. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 321–347. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasian, M.; Khamisabadi, F.; Kheiripour, N.; Karami, M.; Haddadi, R.; Ghaleiha, A.; Taghvaei, B.; Oliaie, S.S.; Salehi, M.; Samadi, P.; et al. Effects of crocin in reducing DNA damage, inflammation, and oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis patients: A double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2019, 33, e22410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi Sakha, F.; Azimi Saeen, A.; Moazzeni, S.M.; Etesam, F.; Vaezi, A. Randomized, Triple-blind Placebo-controlled Trial to Determine the Effect of Saffron on the Serum Levels of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Iran. J. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2020, 19, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doosti, R.; Ghasemi-Sakha, F.; Saeedi, R.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Naser Moghadasi, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Madah Movahedi, M.; Toliyat, T.; Azimi, A.R. EP1592. A triple-blind, randomized controlled trial of Saffron in cognitive function of multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 884. [Google Scholar]
- Adalat, M.; Khalili, M.; Ayromlou, H.; Haririan, S.; Fazljou, S.M.B.; Rezaeizadeh, H.; Safari, A.A.; Zargaran, A. Antidepressant Effects of a Persian Medicine Remedy on Multiple Sclerosis Patients: A Double-Blinded Randomized Clinical Trial. Galen Med. J. 2019, 8, e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.A.; Kazemi, A.; Sabahi, M.; Razipour, S.; Salehipour, A.; Ghiasian, M.; Ghasemi, H.; Ranjbar, A. Probable antioxidant therapy of Saffron Crocin in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. Biomedicine 2020, 40, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, W.I.; Compston, A.; Edan, G.; Goodkin, D.; Hartung, H.-P.; Lublin, F.D.; McFarland, H.F.; Paty, D.W.; Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.; Steer, R.; Brown, G. Beck Depression Inventory, 2nd ed.; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, R.H.B.; Cookfair, D.; Gavett, R.; Gunther, M.; Munschauer, F.; Garg, N.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Validity of the minimal assessment of cognitive function in multiple sclerosis (MACFIMS). J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2006, 12, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttl, B. North American Adult Reading Test: Age norms, reliability, and validity. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2002, 24, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojano, M.; Avolio, C.; Liuzzi, G.M.; Ruggieri, M.; Defazio, G.; Liguori, M.; Santacroce, M.P.; Paolicelli, D.; Giuliani, F.; Riccio, P.; et al. Changes of serum sICAM-1 and MMP-9 induced by rIFNβ-1b treatment in relapsing-remitting MS. Neurology 1999, 53, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaiee, S.; Moini, S.; Hashemi, M.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of bioactive compounds and various extracts obtained from saffron (Crocus sativus L.): A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Sadeghi, O.; Rigi, S.; Tan, S.C.; Shokri, A.; Mousavi, S.M. Effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phyther. Res. 2021, 35, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thushara, R.M.; Hemshekhar, M.; Paul, M.; Shanmuga Sundaram, M.; Shankar, R.L.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Crocin prevents sesamol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human platelets. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2014, 38, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvaridzadeh, M.; Agah, S.; Estêvão, M.D.; Hosseini, A.S.; Heydari, H.; Toupchian, O.; Abdollahi, S.; Persad, E.; Abu-Zaid, A.; Rezamand, G.; et al. Effect of saffron supplementation on oxidative stress parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilgun-Sherki, Y.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: The need for effective antioxidant therapy. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, G.G.; Pacheco-Moisés, F.P.; Bitzer-Quintero, O.K.; Ramírez-Anguiano, A.C.; Flores-Alvarado, L.J.; Ramírez-Ramírez, V.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; Torres-Sánchez, E.D. Immunology and Oxidative Stress in Multiple Sclerosis: Clinical and Basic Approach. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeschoten, R.E.; Braamse, A.M.J.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Cuijpers, P.; van Oppen, P.; Dekker, J.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in Multiple Sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, A.; Maguire, R. Potentially modifiable associates of anxiety in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, S.A. Anxiety is more important than depression in MS—Yes. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Lane, M.; Rocks, T.; Ruusunen, A.; Loughman, A.; Lopresti, A.; Marshall, S.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F.; Dean, O.M. Effect of saffron supplementation on symptoms of depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ke, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, T.; Mentis, A.F.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Polissiou, M.G.; Tang, L.; et al. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and health outcomes: A meta-research review of meta-analyses and an evidence mapping study. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, W. Safety and Efficacy of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) for Treating Mild to Moderate Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2020, 208, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksarian, M.; Behzadifar, M.; Behzadifar, M.; Alipour, M.; Jahanpanah, F.; Re, T.S.; Firenzuoli, F.; Zerbetto, R.; Bragazzi, N.L. The efficacy of Crocus sativus (Saffron) versus placebo and Fluoxetine in treating depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2019, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanara, S.; Aprile, M.; Iacono, S.; Schirò, G.; Bianchi, A.; Brighina, F.; Dominguez, L.J.; Ragonese, P.; Salemi, G. The Role of Nutritional Lifestyle and Physical Activity in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis and Management: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Canter, P.H.; Ernst, E. A systematic review of randomised clinical trials of individualised herbal medicine in any indication. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singletary, K. Saffron: Potential Health Benefits. Nutr. Today 2020, 55, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inojosa, H.; Schriefer, D.; Ziemssen, T. Clinical outcome measures in multiple sclerosis: A review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwan, K.; Altman, D.G.; Arnaiz, J.A.; Bloom, J.; Chan, A.W.; Cronin, E.; Decullier, E.; Easterbrook, P.J.; Von Elm, E.; Gamble, C.; et al. Systematic review of the empirical evidence of study publication bias and outcome reporting bias. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, P.R.; Altman, D.G.; Bagley, H.; Barnes, K.L.; Blazeby, J.M.; Brookes, S.T.; Clarke, M.; Gargon, E.; Gorst, S.; Harman, N.; et al. The COMET Handbook: Version 1.0. Trials 2017, 18, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.; Williamson, P.R. Core outcome sets and systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargon, E.; Gurung, B.; Medley, N.; Altman, D.G.; Blazeby, J.M.; Clarke, M.; Williamson, P.R. Choosing important health outcomes for comparative effectiveness research: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsen, C.A.C.; Vohra, S.; Rose, M.R.; King-Jones, S.; Ishaque, S.; Bhaloo, Z.; Adams, D.; Terwee, C.B. Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) initiative: Protocol for an international Delphi study to achieve consensus on how to select outcome measurement instruments for outcomes included in a “core outcome set. ” Trials 2014, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Evans, S.J.W.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; O’Neill, R.T.; Altman, D.G.; Schulz, K.; Moher, D. Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: An extension of the CONSORT statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, P.; Rossano, R. Nutrition Facts in Multiple Sclerosis. ASN Neuro 2015, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiloudis, P.; Kesidou, E.; Bakirtzis, C.; Sintila, S.A.; Konstantinidou, N.; Boziki, M.; Grigoriadis, N. The Role of Diet and Interventions on Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).