Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the wide use of different disinfectants to reduce the spread of the virus in homes and public spaces. In particular, more chemical compounds are used in public places than they should be in order to control the epidemic in many parts of the world. However, with this practice, human health, biological diversity, and water resources can be adversely affected. Therefore, the possible effects of chemicals used for cleaning and hygiene purposes should be evaluated in an integrated manner. The chemicals effective in deactivating the virus and their possible environmental effects were explored in this article.
1. Introduction
One of the natural and unnatural disasters faced by the world is undoubtedly pandemics, and their effects have profoundly affected all societies for centuries [1]. The pandemics of the recent period are listed as SARS 2003, Influenza A H1N5 (bird flu) 2007, Influenza A H1N1 (swine flu) 2009, MERS 2012, Influenza A H7N9 2013, Ebola 2014, and Zika 2015. Pandemic is a general name given to epidemic diseases that spread in a wide area in more than one country or continent in the world and, according to the definition of the World Health Organization (WHO), there should be three criteria for a disease to be a pandemic. These are the fact that it is a mutated or new virus, can easily infect humans, and can be easily and continuously transmitted from person to person. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) first emerged as a new type of coronavirus in Wuhan, China at the end of December 2019 (Figure 1) [2]. Since there are no direct-acting drugs available for the treatment of COVID-19, it has so far spread to 210 countries around the world [3].
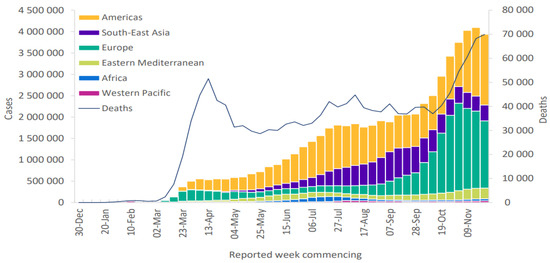
Figure 1.
Number of regional COVID-19 cases and total deaths by 29 November 2020 reported weekly adapted from WHO [2].
While the pressure of factors such as global warming and climate change, overpopulation growth, uncontrolled industrialization, and unplanned urbanization on environmental pollution is increasing, the relationship between humans and their environment has become more valuable than ever before due to the new type of COVID-19 pandemic surrounding the world. Due to the compulsory lockdown and social-economic activities caused by COVID-19, positive effects such as a decrease in water pollution, improvement in air quality (CO2, NO2, vehicle emission, etc.), and decrease in noise pollution have been observed in different parts of the world. In contrast, face masks, gloves, disinfectant products etc., by increased use, their haphazard disposal, and the generation of large amounts of hospital waste have had negative effects on the environment. Both positive and negative environmental effects of COVID-19 are presented in Figure 2 [4].
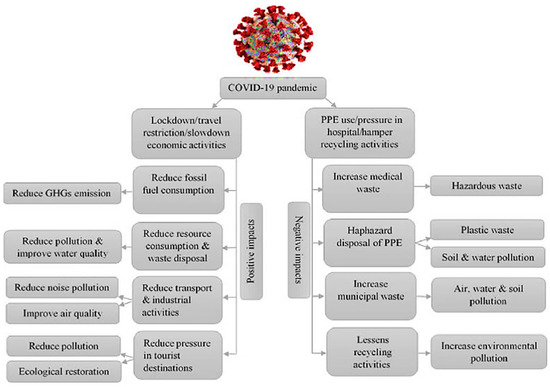
Figure 2.
Positive and negative environmental effects of the COVID-19 pandemic [4].
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the wide use of disinfectants (alcohol, soap, cologne, chlorinated compounds, antibacterial agents, etc.) to reduce the spread of the virus in homes and public spaces. However, human health, biological diversity, and water resources can be adversely affected by these chemicals that are used excessively. Within the scope of COVID-19 measures, chemicals are transported directly from soil to groundwater, from sewage systems to treatment facilities, from rainwater collection channels to rivers and seas by practices such as the use of chemicals for personal cleaning in homes, washing the main roads and streets in cities with chemicals, and spraying to open and closed areas. In addition, due to the lethal, toxic, and irritating properties of disinfecting chemicals used for cleaning and hygiene purposes, it has been determined that poisoning incidents due to disinfectants have increased during the COVID-19 pandemic [5,6].
According to the concept of “One Health”, it is linked to human health, environment, and animal health. Therefore, the possible effects of chemicals used for cleaning and hygiene purposes should be evaluated as a whole. In this article, chemicals used to inactivate viruses and their possible environmental effects were investigated. In particular, within the framework of this concept, human health comes to the fore. As the use of disinfectants has increased in both quarantine and other real applications with COVID-19, therefore, exposures to chemicals have increased compared to normal times. Zheng et al. [7] identified the formation of 19 different Quaternary ammonium compounds (QAC) in dust particles in indoor air before and during the COVID-19 outbreak. QACs at concentrations ranging from 1.95 to 531 μg/g were detected in >90% of samples collected during the pandemic. Generally, higher concentrations of QAC were found in homes that were disinfected more frequently. The findings suggest that indoor exposure to QACs is widespread and increasing during the pandemic. Exposure to QACs has been associated with several adverse health effects. QACs are recognized as asthmagens. Hence, the increased use of household disinfectants and other cleaning agents containing QACs during the COVID-19 pandemic is of significant concern [8,9].
Li et al. [10] tried to estimate human exposure to 22 disinfecting chemicals from contact with disinfected surfaces and hand washing. Due to the short hand-washing period, no health risks were observed from the use of disinfectant chemicals in hand washing. However, exposure from contact with disinfected surfaces may pose health risks for certain age groups.
Disinfection with the use of chemicals has been a common practice for years to remove pathogenic microorganisms. Disinfection is a method involving the use of a chemical agent to eliminate almost all recognized pathogenic microorganisms on inanimate surfaces. Today, it is a widely used practice to prevent COVID-19 infection in homes and public areas. In many parts of the world, high concentrations of disinfectant solutions are used by spraying in urban public areas to control the pandemic. In addition, many numbers and types of disinfectant products are applied to protect the health of individuals (hand, face, etc.) (See Figure 3).
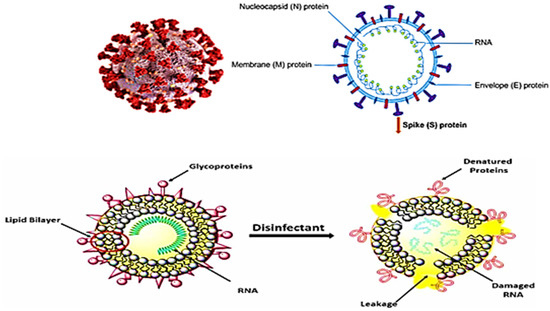
Figure 3.
Effect of disinfectants on its structural components [11].
The useability of existing disinfectants on most surfaces without the need for any mechanical equipment and cost-effectiveness increases the frequency of use. Numerous chemical disinfectants are used in the healthcare and home environment, including alcohol, chlorine and chlorine compounds (bleach), formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, standard and enhanced hydrogen peroxide, iodophors, peracetic acid, phenolics, and quaternary ammonium compounds. There are a wide variety of EPA approved disinfectants used for disinfection around the world [6,12]. The list of highly effective chemical disinfectants against coronavirus is summarized in Table 1 [6,13].

Table 1.
List of EPA-certificated disinfectant product ingredients against COVID-19 [13].
WHO recommends correct and consistent disinfection and environmental cleaning procedures. Surfaces should be thoroughly cleaned with water and disinfectant. The use of disinfectants such as sodium hypochlorite, which are preferred in hospitals, can be an effective method [14]. Disinfection and cleaning of frequently touched surfaces such as doors, toilets, tables, keys, and sinks should be done with domestic disinfectants. Different biocidal products such as alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, benzalkonium, or sodium hypochlorite are used worldwide for disinfection [15]. Disinfectants containing 62–71% ethanol or 0.1% sodium hypochlorite have proven to deactivate the presence of coronavirus on surfaces within one minute of exposure [16]. Cleaning should be done after disinfection for contaminated surfaces.
Generally, each disinfectant is intended for a specific purpose and should be used deliberatively. Therefore, descriptive information should be read carefully to ensure that the correct product is selected. In addition, care should be taken in the use of these products. Otherwise, different toxicities may be caused by misuse, improper storage, or excessive use. The active ingredients of most disinfectants used are harmful and corrosive chemical compounds, including chlorine releasing agents, oxidizing agents, and quaternary ammonium cations. Although some individuals can avoid contact with these chemicals with lockdown, other living groups are exposed to these chemicals directly or indirectly. During the lockdown period, some animals in the countryside may descend into the city and be exposed to these chemicals while exploring empty streets, parks, and waterways [17].
Disinfection in this temporary period can affect a large amount of biodiversity. For example, chlorinated disinfectants are acutely toxic to both terrestrial and aquatic organisms and can lead to respiratory and digestive lesions, and even death (Figure 4). Recently, hundreds of animals belonging to 17 different species are known to have died in Chongqing, China, due to the overuse of disinfectants [18]. As COVID-19 spreads around the world, the increased use of disinfectants can lead to global secondary disasters in human health and ecosystems. Scientific researchers have been conducted on exposure to the most commonly used disinfectant compounds (sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, etc.) previously [13,14,15,16]. All of these, when used regularly, increase the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and eye irritation on healthcare workers and individuals. Chemical residues remaining on a surface can be airborne and inhaled, thus contributing to poor indoor air quality, often with adverse effects for asthmatic, allergic, or sensitive persons. These residues may contain chemicals that can cause cancer, reproductive and respiratory disorders, and central nervous system impairment [17,18].

Figure 4.
Disinfection applications carried out in open areas within the scope of COVID-19.
Homes, quarantine centers, and hospitals have been generating large amounts of biomedical waste (BMW) worldwide since the COVID-19 pandemic. Personal protective equipment, test kits, surgical face masks, and nitrile gloves are the biggest contributors to waste volume. Described as COVID-19 waste, BMW is a major global concern for public health and environmental sustainability when discarded improperly. This waste must be disposed of after being disinfected with appropriate disinfection conditions.
The first step of strategies for the disinfection of COVID-19 waste is the classification of hospital waste. Classification of waste at its source is both efficient and the best practice to prevent the virus from spreading to other environments by waste. COVID-19 waste needs to be collected in separate bags, disinfected with specific solutions, and sealed. While it is possible to control these processes in hospitals, disinfection processes cannot be performed adequately because the control of COVID-19 waste in home quarantines is difficult [17]. Disinfection is an effective manner to remove pathogenic microorganisms that cause infectious diseases.
There are scientific norms for the selection and proper use of disinfectants in hospitals, laboratories, and homes that take into account their efficiency, suitability, and health risks. However, disinfectants used in outdoor environments to control infectious diseases such as COVID-19 do not have comparable guidelines or monitoring mechanisms. Considering the toxicological effects of disinfectants on both terrestrial and aquatic animals [19], this practice is likely to pose a serious threat to the urban environment, wildlife, and biodiversity in general. For example, the application of such high volumes of disinfectants can contaminate food and water supplies [20] or living spaces of free-living animals [21,22]. Therefore, it is important that disinfectants used to control COVID-19 in urban areas are selected and applied in a way that prevents unnecessary environmental pollution [2,19,23,24,25].
2. Conclusions
Since there is no legislation for the large-scale use of disinfectants in urban-areas settings, it is very important to develop strategies to minimize the environmental pollution caused by this practice. Several possible strategies can be proposed to respond to public health issues such as COVID-19 without harming the urban environment, individuals, and biodiversity.
- First, public health and environmental safety should be considered when deciding on when, where, and how disinfection should be carried out and which disinfectant to use. For example, rather than indiscriminate spraying of high volumes of disinfectants in biodiversity-rich areas such as urban parks, wetlands, and green spaces, it may be preferable to suspend human activities in such places.
- Second, as information on the ecological consequences of excessive application of disinfectants in cities is limited, further research on the potential threats of these practices to the environment and to biodiversity is urgently needed.
- Third, disinfectants should be developed as soon as possible which are low-risk, non-toxic, intervenable within a sudden and unexpected situation, and suitable for common application in open urban environments.
- Fourth, antibacterial products (soap, wipes, gels etc.) should not be preferred, especially in hand disinfectants. Because these products cause the death of beneficial bacteria in the human skin, the immune system of the individuals may be adversely affected.
To summarize, biological and environmental safety assessments and prevention systems need to be laid out, especially when managing future pandemic provisions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing-original draft preparation, writing-review and editing, visualization, H.Ç., T.B., İ.Ş. and Ş.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hui, D.S.; Azhar, E.I.; Madani, T.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Kock, R.; Dar, O.; Ippolito, G.; Mchugh, T.D.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health-The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Characterizes COVID-19 as a Pandemic. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Biswaranjan, P. Nurture to nature via COVID-19, a self-regenerating environmental strategy of environment in global context. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139088. [Google Scholar]
- Tanjena, R.S.M.; Didar-Ul, I. Environmental effects of COVID-19 pandemic and potential strategies of sustainability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04965. [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott, J.; Alexandridi, M.; Muscolini, M.; Tassone, E.; Palermo, E.; Soultsioti, M.; Zevini, A. The global impact of the coronavirus pandemic. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra Kumar, R.; Anushruti, A.; Butchi, R.A. Consequences of chemical impact of disinfectants: Safe preventive measures against COVID-19. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Filippelli, G.M.; Salamova, A. Increased indoor exposure to commonly used disinfectants during the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, O.; Varraso, R.; Boggs, K.M.; Quinot, C.; Zock, J.P.; Henneberger, P.K.; Speizer, F.E.; Le Moual, N.; Camargo, C.A. Association of occupational exposure to disinfectants with incidence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among US female nurses. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1913563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hora, P.I.; Pati, S.G.; McNamara, P.J.; Arnold, W.A. Increased use of quaternary ammonium compounds during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and beyond: Consideration of environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sangion, A.; Li, L. Evaluating consumer exposure to disinfecting chemicals against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and associated health risks. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Hussein, A.S. Chemical disinfectants of COVID-19: An overview. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 843–848. [Google Scholar]
- Kampf, G.; Todt, D.; Pfaender, S.; Steinmann, E. Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and its inactivation with biocidal agents. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 104, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EPA. List N: Disinfectants for Use against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). 2020. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-registration/list-n-disinfectants-useagainst-sars-cov-2-covid-19 (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Roy, A.; Parida, S.P.; Bhatia, V. Role of disinfection and hand hygiene: A COVID-19 perspective. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2020, 7, 2845–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qianyu, L.; Jason, Y.C.L.; Kun, X.; Pek, Y.M.Y.; Cally, O.; Pei, L.C.; Xian, J.L. Sanitizing agents for virus inactivation and disinfection. View 2020, 1, e16. [Google Scholar]
- Daeed, Y.; Hanns, M.; Ayda, F.A.; Alireza, M.J. Side effects of using disinfectants to fight coronavirus. Asian Pac. J. Environ. Cancer 2020, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sadia, I.; Tajiv, R.S.; Hyunjung, K. Disinfection technology and strategies for COVID-19 hospital and bio-medical waste management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141652. [Google Scholar]
- You, T. More than 100 Wild Animals Drop Dead near Coronavirus Epicentre in China after Workers ‘Sprayed Too Much Disinfectant’ to Prevent Coronavirus. 2020. Available online: https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-8029271/100-wild-animals-drop-dead-near-coronavirus-epicentre.html (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- El-Nahhal, I.; El-Nahhal, Y. Ecological consequences of COVID-19 outbreak. J. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Lin, M.; Deng, Q.; Ye, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Z. Analysis of the virus contamination and disinfection effect in isolation ward of patients with COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yin, W. Disinfection threatens aquatic ecosystems. Science 2020, 368, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sepp, T.; Ujvari, B.; Ewald, P.W.; Thomas, F.; Giraudeau, M. Urban environment and cancer in wildlife: Available evidence and future research avenues. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jane, L.J.J.; Thong, P.Y.; Rajendran, J.C.B.; Jason, R.M.; Nagendran, T.; Thiagarajan, M. Hand sanitizers: A review on formulation aspects, adverse effects, and regulations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3326. [Google Scholar]
- Hadis, F.; Parham, M.; Mansooreh, M.-H.; Sounkalo, D.; Sükran, K.; Khudaverdi, G.; Pasquale, P.; Silvano, E.; Hossein, S.K. Protection and disinfection policies against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Le Infez. Med. 2020, 2, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M. The one health approach-why is it so important? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).