Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Quality †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
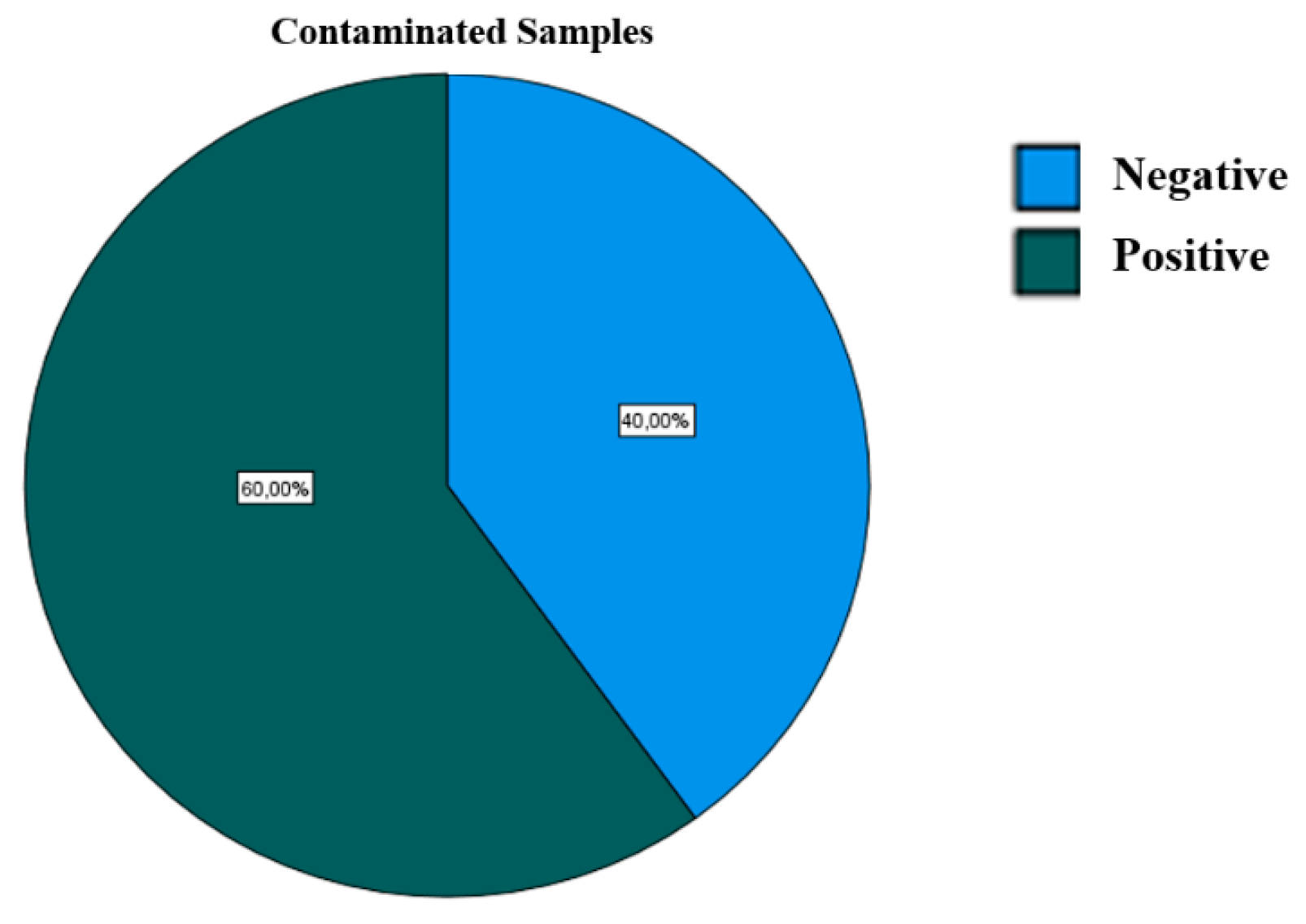
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souto, J.P.; Sarmento Lira, A.G.; Figueira, J.d.; Nascimento da Silva, A.; Silva, E.S. Poluição Fecal da Água: Microrganismos Indicadores. In Proceedings of the VI Congresso Brasileiro de Gestão Ambiental, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil, 23–26 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alves Cunha, M.C. Execução de Ensaios Microbiológicos nas Áreas Alimentar, Ambiental e Técnica em Contexto Empresarial. Master’s Dissertation, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, B.; Santos Oliveira, J. Qualidade da Água para Consumo Humano, 1st ed.; Lidel: Lisboa, Portugal, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Valente Bernardo, M.M. Comparação dos Métodos Aplicados na Deteção de Bactérias Coliformes, Escherichia coli e Enterococcus sp. em Águas para Fins Recriativos. Master’s Dissertation, Universidade do Algarve, Faro, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Quintela, S.D. Qualidade da Água para Consumo Humano: Riscos Associados à Presença de Biofilmes em Torneiras de Espaços Escolares. Master’s Dissertation, Escola Superior de Tecnologia da Saúde do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso, H.; Taveira, N.; Meliço-Silvestre, A. Microbiologia Médica; Lidel: Lisboa, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa Candeias, G.M. Qualidade Microbiológica do Gelo Usado em Estabelecimentos de Restauração e de Bebidas. Master’s Dissertation, Instituto Superior de Ciências da Saúde Egas Moniz, Almada, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Samples /Bacteria | Total Coliforms | Faecal Coliforms (E. coli) | Intestinal Enterococci | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Clostridium Sulfite-Reducing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO1 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO2 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO3 | 1 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO4 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 19 UFC/100 mL |
| SO5 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 1 UFC/100 mL |
| SO6 | 12 UFC/100 mL | 2 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO7 | >100 UFC/100 mL | 6 UFC/100 mL | 18 UFC/100 mL | 5 UFC/200mL | 1 UFC/100 mL |
| SO8 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO9 | >100 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 100 UFC/100 mL |
| SO10 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO11 | >100 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 40 UFC/100 mL |
| SO12 | >100 UFC/100 mL | 68 UFC/100 mL | 2 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | >100 UFC/mL |
| SO13 | 101 UFC/100 mL | 1 UFC/100 mL | 1 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 40 UFC/100 mL |
| SO14 | >100 UFC/100 mL | 15 UFC/100 mL | 13 UFC/100 mL | 104 UFC/200mL | 20 UFC/100 mL |
| SO15 | 30 UFC/100 mL | 1 UFC/100 mL | 1 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 15 UFC/100 mL |
| SO16 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | >15 UFC/mL |
| SO17 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO18 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO19 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| SO20 | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/100 mL | 0 UFC/200mL | 0 UFC/100 mL |
| Positive | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | Percentage | ||
| Bacterium | Total Coliforms | 9 | 28.1% |
| Faecal Coliforms/E. coli | 6 | 18.8% | |
| Enterococci | 5 | 15.6% | |
| Pseudomonas | 2 | 6.3% | |
| Sulphite Reducing Clostridium | 10 | 31.3% | |
| Total positive samples in the study | 32 | 100.0% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, C.; Costa, T.; Silva, N.; Valério, S.; Barroso, H.; Hilário, M.J.; Alves, S. Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Quality. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 22, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023022011
Silva C, Costa T, Silva N, Valério S, Barroso H, Hilário MJ, Alves S. Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Quality. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 22(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023022011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Catarina, Telma Costa, Nádia Silva, Sérgio Valério, Helena Barroso, Maria João Hilário, and Sara Alves. 2023. "Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Quality" Medical Sciences Forum 22, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023022011
APA StyleSilva, C., Costa, T., Silva, N., Valério, S., Barroso, H., Hilário, M. J., & Alves, S. (2023). Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Quality. Medical Sciences Forum, 22(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023022011





